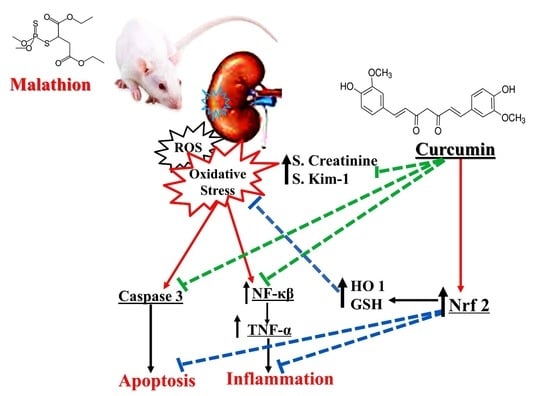
Curcumin Mitigates Malathion-Induced Renal Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis and Modulation of NF-κβ/TNF-α and Nrf2, and HO-1 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
- Group 1 (Control group): untreated and served as control;
- Group 3 (malathion group): received malathion by oral gavage at a dose of 100 mg/kg/day [17];
2.3. Creatinine Level Assessment
2.4. Assessment of Tubular Kidney Injury Molecule (Kim-1)
2.5. Assessment of Oxidant and Antioxidant State
2.5.1. Assessment of Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Antioxidant Enzymes (GSH)
2.5.2. Assessment of Total Oxidant Status (TOS)
2.5.3. Measurement of Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
2.5.4. Measurement of Oxidative Stress Index (OSI)
2.6. Histopathological Examination
2.7. Immunohistochemical Staining for Detection of NFκβ, TNF-α, Nrf2, Ho-1, and Caspase-3
- NFκβ: ABclonal Catalog No. A3108, Polyclonal Antibody in a dilution of 1/100;
- TNF-α: Servicebio Catalog No. GB11188, Polyclonal Antibody in a dilution of 1/1000;
- Caspase-3: Servicebio Catalog No. GB11532, Polyclonal Antibody in a dilution of 1/1000;
- Nrf2: Servicebio Catalog No. GB113808, Polyclonal Antibody in a dilution of 1/1000;
- Ho-1: ABclonal Catalog No. A19062, Polyclonal Antibody in a dilution of 1/100.
2.8. Measurement of the Area Percentage of Ho-1, TNF-α, Caspase-3, Nrf 2, and NFKB Positive Reactions in the Kidney
2.9. Statistical Analysis and Data Interpretation
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Curcumin on Serum Creatinine after Malathion Intoxication
3.2. Effects of Curcumin Administration on the Cellular Oxidative and Antioxidant Status
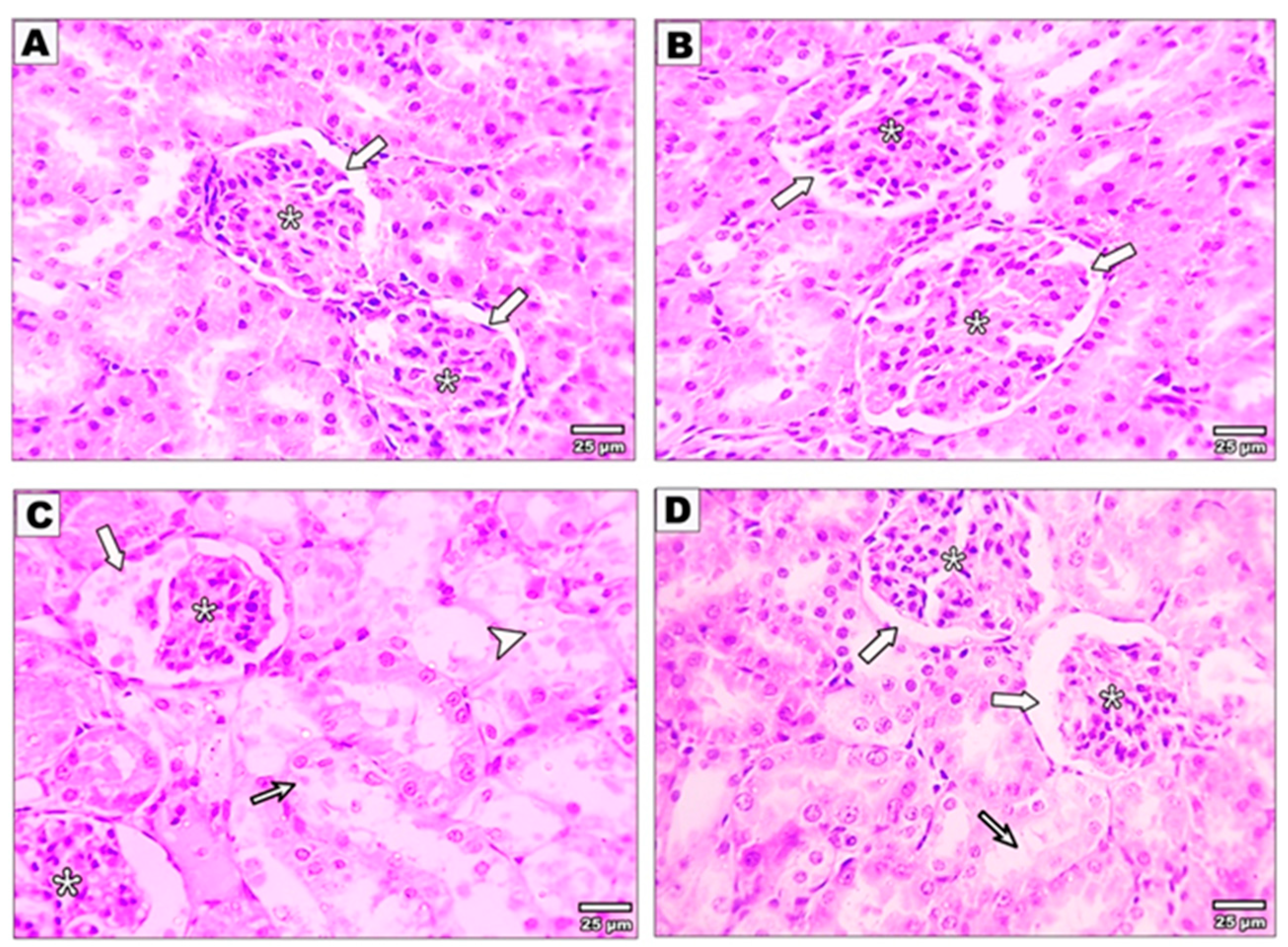
3.3. Effect of Curcumin on the Kidney Structure after Malathion Intoxication
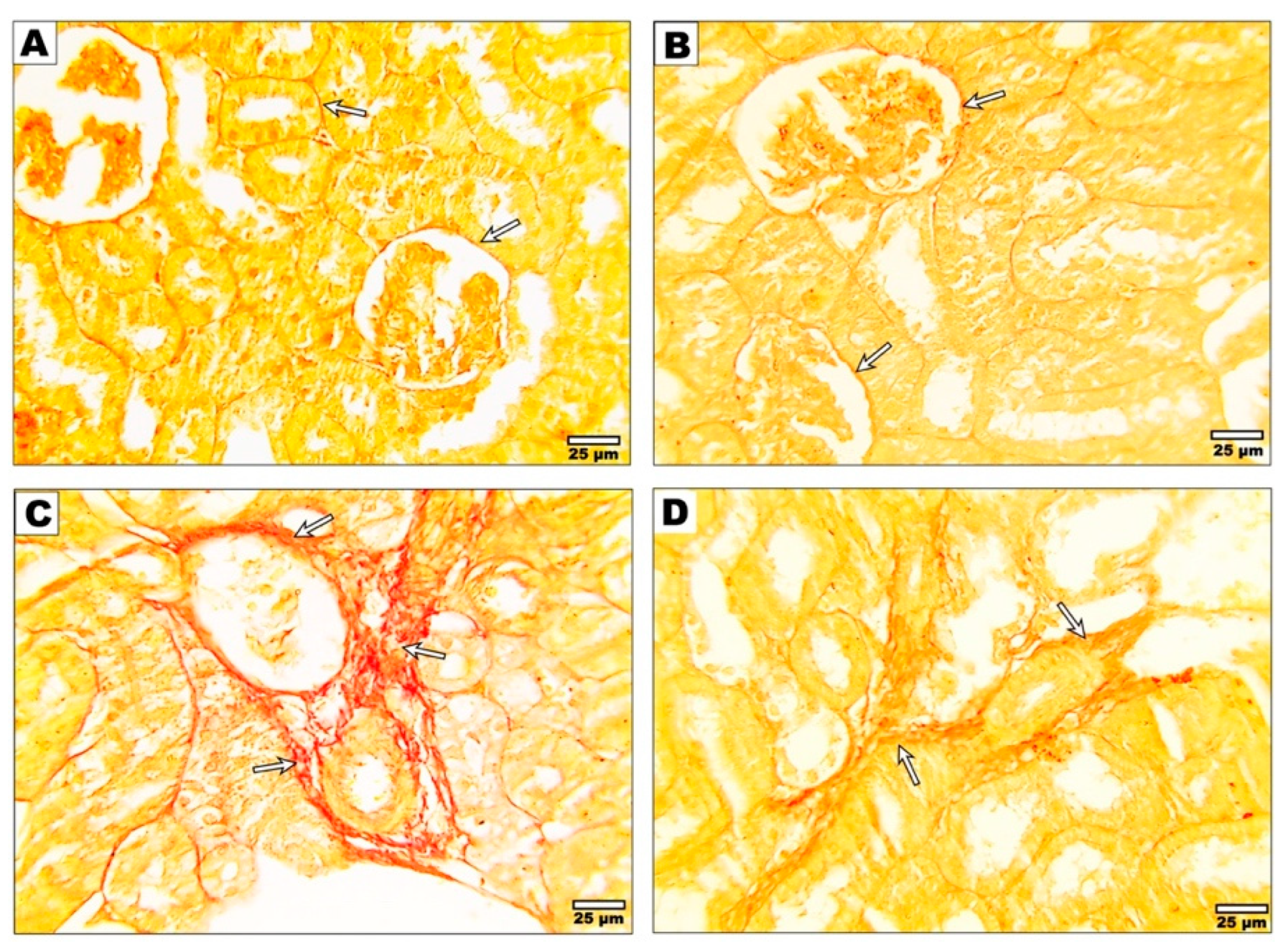
3.4. Effect of Curcumin on the Fibrotic Changes after Malathion Intoxication
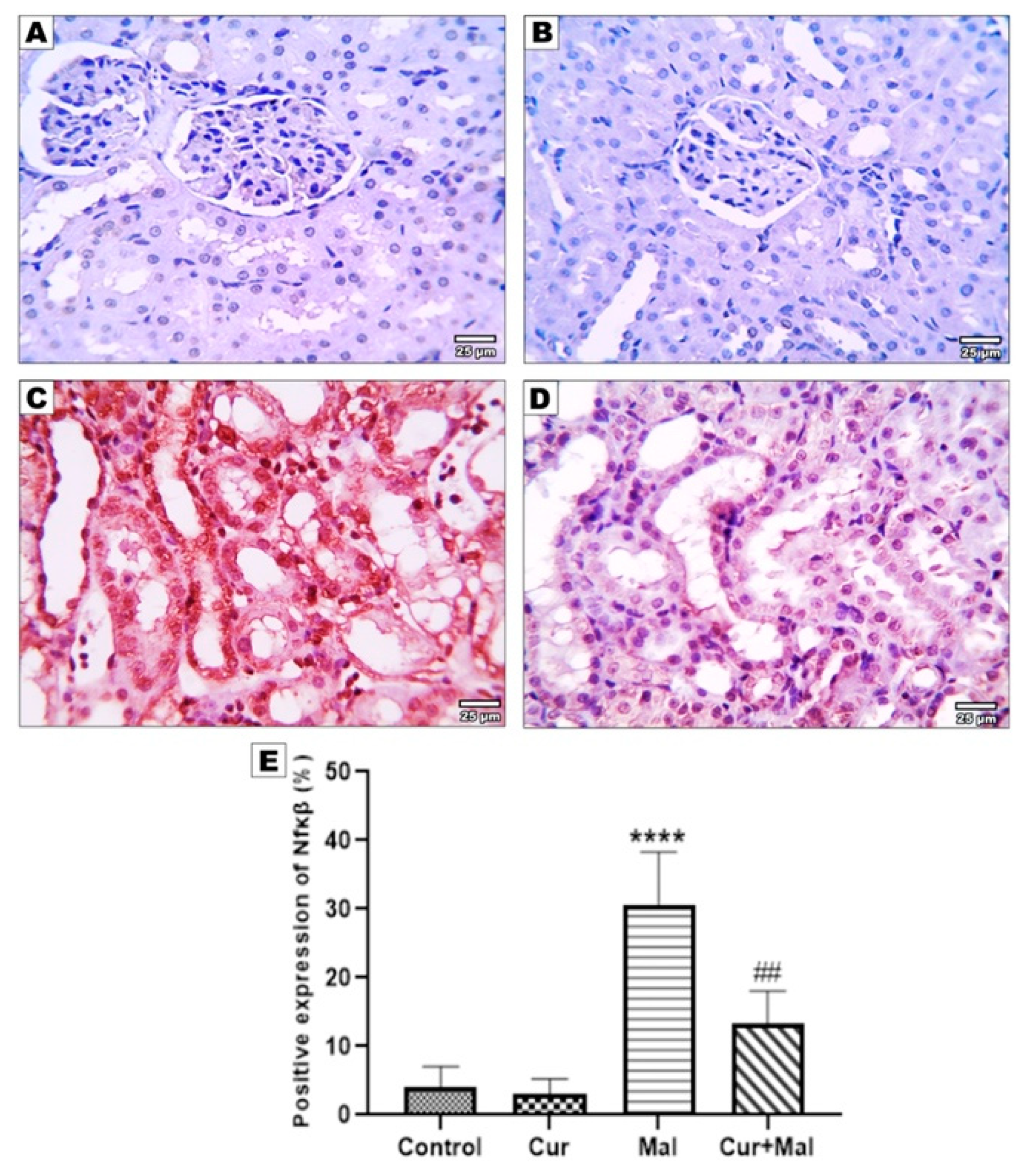
3.5. Morphometric Results of the Immunohistochemical Staining
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selmi, S.; Rtibi, K.; Grami, D.; Sebai, H.; Marzouki, L. Malathion, an organophosphate insecticide, provokes metabolic, histopathologic and molecular disorders in liver and kidney in prepubertal male mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, N.S.; Malik, J.; Rao, G.; Aggarwal, M.; Ranganathan, V. Effects of subchronic malathion exposure on the pharmacokinetic disposition of pefloxacin. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 22, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Patlolla, A.K.; Yedjou, C.G.; Moore, P.D. Environmental exposure and health effects associated with malathion toxicity. Toxic. Hazard Agrochem. 2015, 51, 2145–2149. [Google Scholar]
- Afshar, S.; Farshid, A.; Heidari, R.; Ilkhanipour, M. Histopathological changes in the liver and kidney tissues of Wistar albino rat exposed to fenitrothion. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2008, 24, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réus, G.Z.; Valvassori, S.S.; Nuernberg, H.; Comim, C.M.; Stringari, R.B.; Padilha, P.T.; Leffa, D.D.; Tavares, P.; Dagostim, G.; Paula, M.M.S.; et al. DNA Damage after Acute and Chronic Treatment with Malathion in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7560–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaoglu, O.T.; Sen, B.; Ekremoglu, M.; Severcan, C.; Pasaoglu, H. Effects of Acute Malathion Exposure on Renal Oxidant and Antioxidant Balance in Rats. Gazi Med. J. 2021, 32, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonar, S.M.; Yonar, M.E.; Ural, M. Antioxidant effect of curcumin against exposure to malathion in Cyprinus carpio. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2017, 63, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.M.; Al-Numair, K.S.; El-Desoky, G.E.; Yusuf, K.; Al Othman, Z.A.; Aboul-Soud, M.A.; Giesy, J.P. Protection of α-tocopherol and selenium against acute effects of malathion on liver and kidney of rats. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Wardyn, J.D.; Ponsford, A.H.; Sanderson, C.M. Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Wang, Q.M. The IKK NF-κB system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansanen, E.; Kuosmanen, S.M.; Leinonen, H.; Levonen, A.-L. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: Mechanisms of activation and dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sökmen, M.; Khan, M.A. The antioxidant activity of some curcuminoids and chalcones. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ak, T.; Gülçin, I. Antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of curcumin. Chem. Interact. 2008, 174, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabr, S.A.; Elsaed, W.M.; Eladl, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Asseri, S.M.; Eltahir, Y.A.M.; Elsherbiny, N.; Eldesoqui, M. Curcumin Modulates Oxidative Stress, Fibrosis, and Apoptosis in Drug-Resistant Cancer Cell Lines. Life 2022, 12, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Dai, X.; Xiao, N.; Wu, X.; Wei, Z.; Fang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Curcumin Ameliorates Memory Decline via Inhibiting BACE1 Expression and β-Amyloid Pathology in 5×FAD Transgenic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelani, H.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chang, D.; Nammi, S. Chronic treatment of curcumin improves hepatic lipid metabolism and alleviates the renal damage in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, C.; Kandemir, F.M. Molecular and biochemical investigation of the protective effects of rutin against liver and kidney toxicity caused by malathion administration in a rat model. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurulain, S.M.; Szegi, P.; Tekes, K.; Naqvi, S.N. Antioxidants in Organophosphorus Compounds Poisoning. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, M.A.; El-Deek, S.E.; Ghandour, N.M. Role of Melatonin and Curcumin in Amelioration of Malathion Toxicity in Rats Liver. Egypt. J. Nat. Toxins 2016, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Possamai, F.; Fortunato, J.; Feier, G.; Agostinho, F.; Quevedo, J.; Filho, D.W.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Oxidative stress after acute and sub-chronic malathion intoxication in Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 23, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, B.; Dakwar, S.; Said, O.; Abu-Hijleh, G.; Al Battah, F.; Kmeel, A.; Aziazeh, H. Evaluation of Medicinal Plant Hepatotoxicity in Co-cultures of Hepatocytes and Monocytes. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2006, 3, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M. The Study of Pentoxifylline Drug Effects on Renal Apoptosis and BCL-2 Gene Expression Changes Following Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in Rat. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kata, F.S. Short-time Effects of Malathion Pesticide on Functional and Histological Changes of Liver and Kidney in Female Mice. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 23, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasram, M.M.; Lamine, A.J.; Dhouib, I.B.; Bouzid, K.; Annabi, A.; Belhadjhmida, N.; Ben Ahmed, M.; El Fazaa, S.; Abdelmoula, J.; Gharbi, N. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of N-acetylcysteine against malathion-induced liver damages and immunotoxicity in rats. Life Sci. 2014, 107, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, A.; Afify, M.; Samy, N. Evaluation of adverse health effects of pesticides exposure [biochemical and hormonal] among Egyptian farmers. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 9, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar]
- Mooli, R.G.R.; Mukhi, D.; Ramakrishnan, S.K. Oxidative Stress and Redox Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2022, 12, 3167–3192. [Google Scholar]
- Aboubakr, H.M.; Elzohairy, E.A.; Ali, A.A.; Rashed, L.A.; Elkady, N.K.; Soliman, A.S. Therapeutic effects of N-acetylcysteine against malathion-induced hepatotoxicity. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, H.; Aytekin, I.; Hatipoglu, N.K.; Alp, A.; Ogun, M. Effects of sulforophane and curcumin on oxidative stress created by acute malathion toxicity in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16 (Suppl. S3), 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Selvi, N.M.K.; Sridhar, M.G.; Swaminathan, R.P.; Sripradha, R. Curcumin Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Activation of Redox-Sensitive Kinases in High Fructose- and High-Fat-Fed Male Wistar Rats. Sci. Pharm. 2015, 83, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attar, A.M. Physiological and Histopathological Investigations on the Effects of-Lipoic Acid in Rats Exposed to Malathion. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 203503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.A.A.; Rahman, A.; Belal, S.H.; Islam, M.A.; Sarker, M.E.H.; Arman, M.S.I.; Ekram, A.E.; Hoque, K.M.F. Histological study of the effect of malathion on liver and kidney tissues of mice model. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 6, 1043. [Google Scholar]
- Aslanturk, A.; Kalender, Y. Methomyl-induced nephrotoxicity and protective effect of curcumin in male rats. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, W. Curcumin Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting Local Fibroblast Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Deposition. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 126, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Li, Y.D. Effects of curcumin on the epithelial mesenchymal transition and TGF-beta/Smads signaling pathway in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2011, 31, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-S.; Gong, Z.-J.; Li, W.-H.; Wang, X.; Ling, T.-Y. Antifibrotic Effect of Curcumin in TGF-β1-Induced Myofibroblasts from Human Oral Mucosa. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Yi, C.O.; Jeon, B.T.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Kang, G.M.; Lee, J.E.; Roh, G.S.; Lee, J.D. Curcumin Attenuates Radiation-Induced Inflammation and Fibrosis in Rat Lungs. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 17, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetikno, V.; Sari, F.R.; Lakshmanan, A.P.; Arumugam, S.; Harima, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kawachi, H.; Watanabe, K. Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress, inflammation, and renal fibrosis in remnant kidney through the N rf2–keap1 pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, Z.Z.; Hsieh, C.W.; Chu, C.S.; Wung, B.S. Peanut arachidin-1 enhances Nrf2-mediated protective mechanisms against TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression and NF-κB activation in endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etewa, M.; El-Arab, S.E.-A.A.; Hamouda, M.H.; El Rahman, A.F.A.; Al Anany, M.G. The Effect of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors or Curcumin on Diet Induced Metabolic Syndrome with Cardiac Dysfunction in Rats. J. Recent Adv. Med. 2020, 2, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.M.; Salem, A.A.; Eassawy, M.M.T. Rutin protects against gamma-irradiation and malathion-induced oxidative stress and inflammation through regulation of mir-129-3p, mir-200C-3p, and mir-210 gene expressions in rats’ kidney. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 72930–72948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, S.; Arslan-Acaroz, D.; Demirel, H.H.; Varol, N.; Ozyurek, H.A.; Zemheri, F.; Kucukkurt, I. Taurine alleviates malathion induced lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, and proinflammatory cytokine gene expressions in rats. BioMedicine 2017, 96, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamry, H.I.; Aboushouk, A.A.; Soliman, M.M.; Albogami, S.M.; Tohamy, H.G.; Okle, O.S.E.; Althobaiti, S.A.; Rezk, S.; Farrag, F.; Helal, A.I.; et al. Ginseng® alleviates malathion-induced hepatorenal injury through modulation of the biochemical, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory markers in male rats. Life 2022, 12, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pober, J.S.; Min, W. Endothelial cell dysfunction, injury and death. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2006, 176 Pt 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar]
- Severcan, C.; Ekremoglu, M.; Sen, B.; Pasaoglu, O.; Akyurek, N.; Severcan, S.; Pasaoglu, H. Acute effects of different doses of malathion on the rat liver. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari-Zaer, A.; Marefati, N.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. The protective role of curcumin in myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelario-Jalil, E.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Gräf, S.; Bhatia, H.S.; Hüll, M.; Muñoz, E.; Fiebich, B.L. Resveratrol potently reduces prostaglandin E2production and free radical formation in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary rat microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2007, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, S.; Khan, M.A.; Bekhit, M.; Bai, H.; Cornish, T.; Mizuma, M.; Rudek, M.A.; Zhao, M.; Maitra, A.; Ray, B.; et al. A polymeric nanoparticle formulation of curcumin (NanoCurc™) ameliorates CCl4-induced hepatic injury and fibrosis through reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and stellate cell activation. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.C.; Zhang, D.D. The emerging role of the Nrf2–Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, M.; Raftari, M.; Cesário, R.; Salma, R.; Godoy, P.; Emami, S.N.; Haghdoost, S. Roles of Oxidative Stress and Nrf2 Signaling in Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Cells: A Possible General Mechanism of Resistance to Therapy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, J.; Park, S.-M.; Yang, S.-R. An Update on the Role of Nrf2 in Respiratory Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Qin, C.; Wei, P.; Luo, L.; Luo, L.; Huang, G.; Chen, A.; Liu, G. Anti-fibrosis activity of quercetin attenuates rabbit tracheal stenosis via the TGF-beta/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 250, 117552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.P.; Seldon, M.P.; Gregoire, I.P.; Vassilevskaia, T.; Berberat, P.O.; Yu, J.; Tsui, T.-Y.; Bach, F.H. Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulates the Expression of Adhesion Molecules Associated with Endothelial Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3553–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerra, V.G.; Negi, G.; Sharma, S.S.; Kumar, A. Potential therapeutic effects of the simultaneous targeting of the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways in diabetic neuropathy. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. Curcumin Activates the Nrf2 Pathway and Induces Cellular Protection Against Oxidative Injury. Curr. Mol. Med. 2020, 20, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varisli, B.; Caglayan, C.; Kandemir, F.; Gür, C.; Bayav, I.; Genc, A. The impact of Nrf2/HO-1, caspase-3/Bax/Bcl2 and ATF6/IRE1/PERK/GRP78 signaling pathways in the ameliorative effects of morin against methotrexate-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9641–9649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kızıl, H.E.; Caglayan, C.; Darendelioğlu, E.; Ayna, A.; Gür, C.; Kandemir, F.M.; Küçükler, S. Morin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity via targeting Nrf2/HO-1 and Bax/Bcl2/Caspase-3 signaling pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 3479–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogukan, A.; Sahin, N.; Tuzcu, M.; Juturu, V.; Orhan, C.; Onderci, M.; Komorowski, J.; Sahin, K. The Effects of Chromium Histidinate on Mineral Status of Serum and Tissue in Fat-Fed and Streptozotocin-Treated Type II Diabetic Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 131, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Liu, Y. Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2009, 1282, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.F.; Pereira-Wilson, C.; Rattan, S.I.S. Curcumin induces heme oxygenase-1 in normal human skin fibroblasts through redox signaling: Relevance for anti-aging intervention. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 55, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, M.; Akbarsha, M.A.; Oommen, O.V. In vivo protective effect of dietary curcumin in fish Anabas testudineus (Bloch). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 38, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, F.-M.; Kang, H.-C.; Lee, S.-T.; Chao, Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, L.-J.; Lin, W.-W. The anti-inflammatory actions of LCY-2-CHO, a carbazole analogue, in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.F.; Shen, X.Y.; Lio, C.K.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, C.S.; Liu, J.X.; Yao, Y.D.; Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Luo, P.; et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway by Nardochinoid C Inhibits Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. Front Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, S.W.G.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.-N.; Liu, X.-C.; Chen, X.-J.; Guan, G.-J.; Liu, G. Curcumin attenuates high glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis by regulating functional connections between caveolin-1 phosphorylation and ROS. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Shao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ng, J.C.; Peng, C. Malathion-induced testicular toxicity is associated with spermatogenic apoptosis and alterations in testicular enzymes and hormone levels in male Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hirahashi, J.; Cullere, X.; Mayadas, T.N. Elucidation of molecular events leading to neutrophil apoptosis following phagocytosis: Cross-talk between caspase 8, reactive oxygen species, and MAPK/ERK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28443–28454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu-Tarladacalisir, Y.; Sapmaz-Metin, M.; Karaca, T. Curcumin counteracts cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by preventing renal tubular cell apoptosis. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzer, F.; Kandemir, F.M.; Kucukler, S.; Comaklı, S.; Caglayan, C. Chemoprotective effects of curcumin on doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in wistar rats: By modulating inflammatory cytokines, apoptosis, oxidative stress and oxidative DNA damage. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonar, M.E. Chlorpyrifos-induced biochemical changes in Cyprinus carpio: Ameliorative effect of curcumin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzaei, M.; Tabrizian, K.; Alizadeh, Z.; Pasandideh, S.; Rezaee, R.; Mamoulakis, C.; Tsatsakis, A.; Skaperda, Z.; Kouretas, D.; Shahraki, J. Resveratrol, curcumin and gallic acid attenuate glyoxal-induced damage to rat renal cells. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Recent Developments in Delivery, Bioavailability, Absorption and Metabolism of Curcumin: The Golden Pigment from Golden Spice. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.I.; Ibrahim, M.A. Malathion induced testicular toxicity and oxidative damage in male mice: The protective effect of curcumin. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
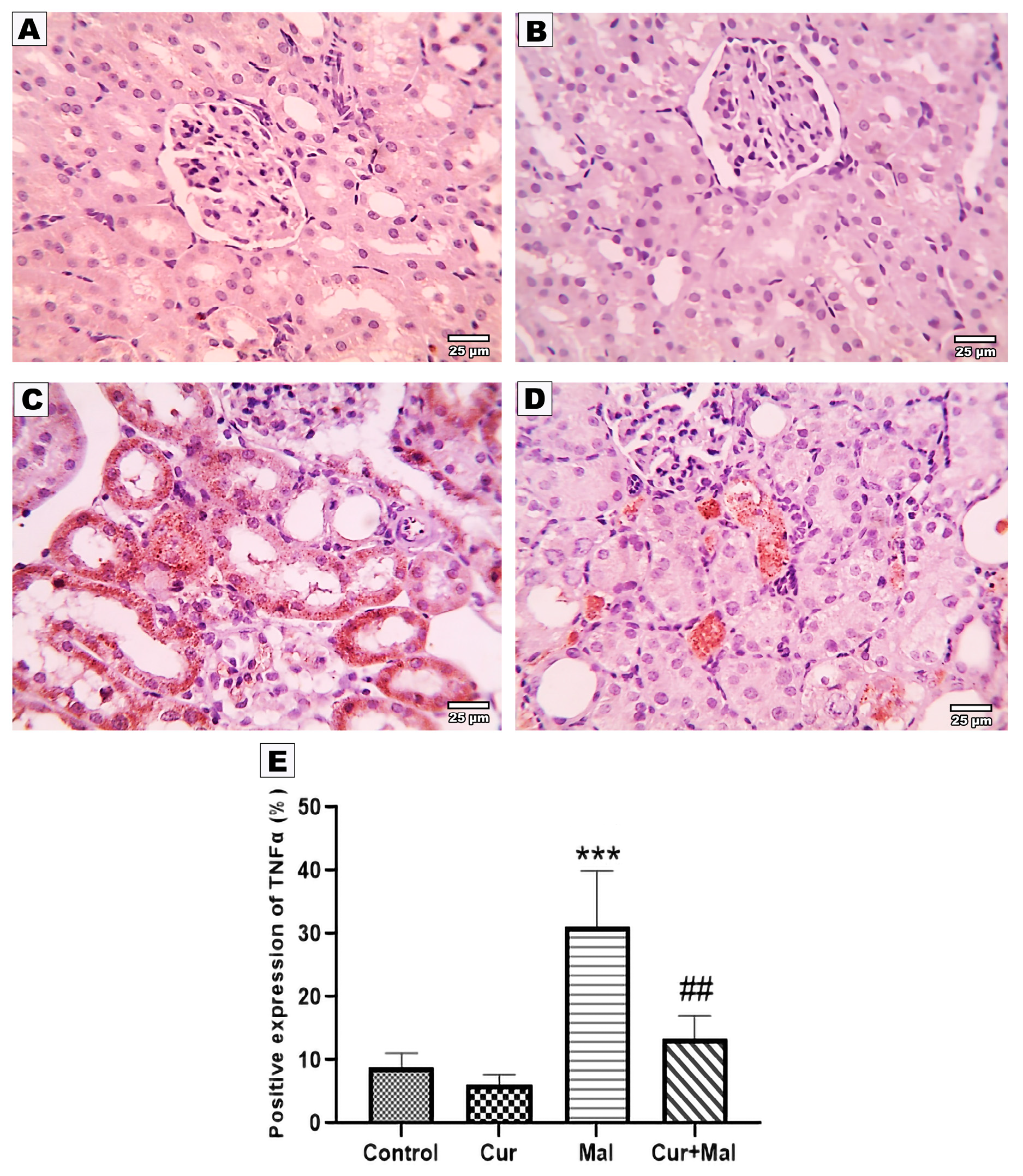
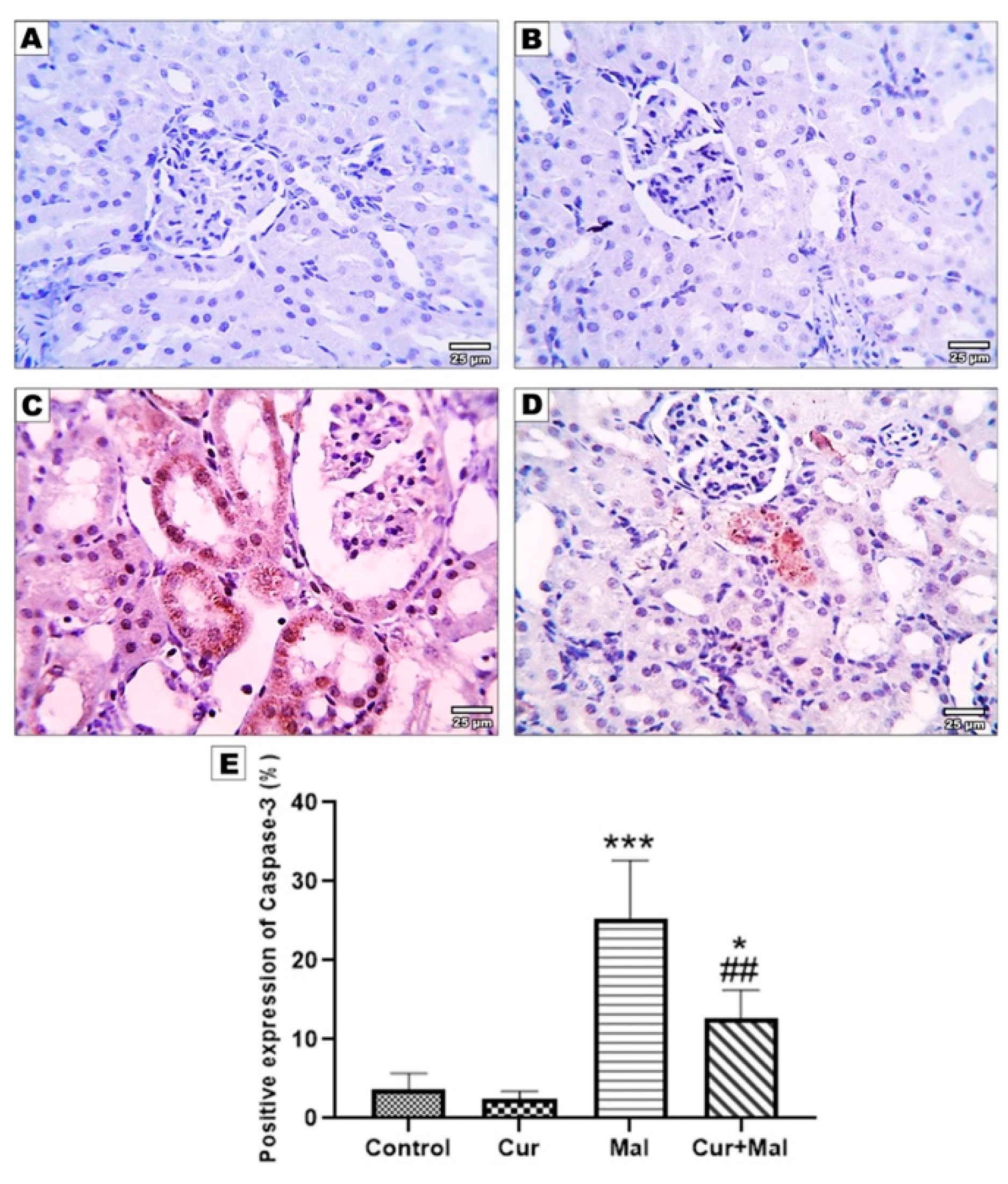
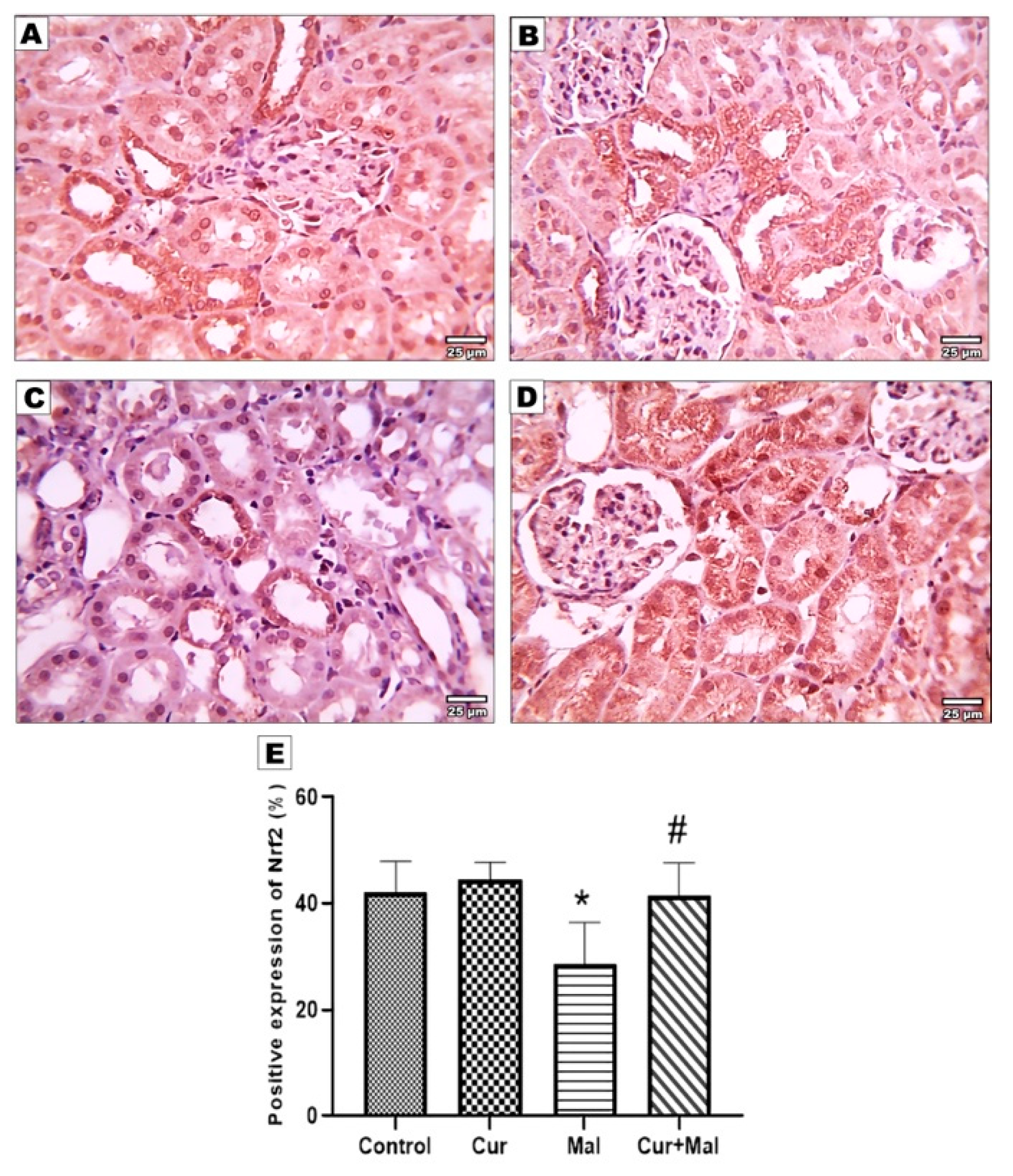
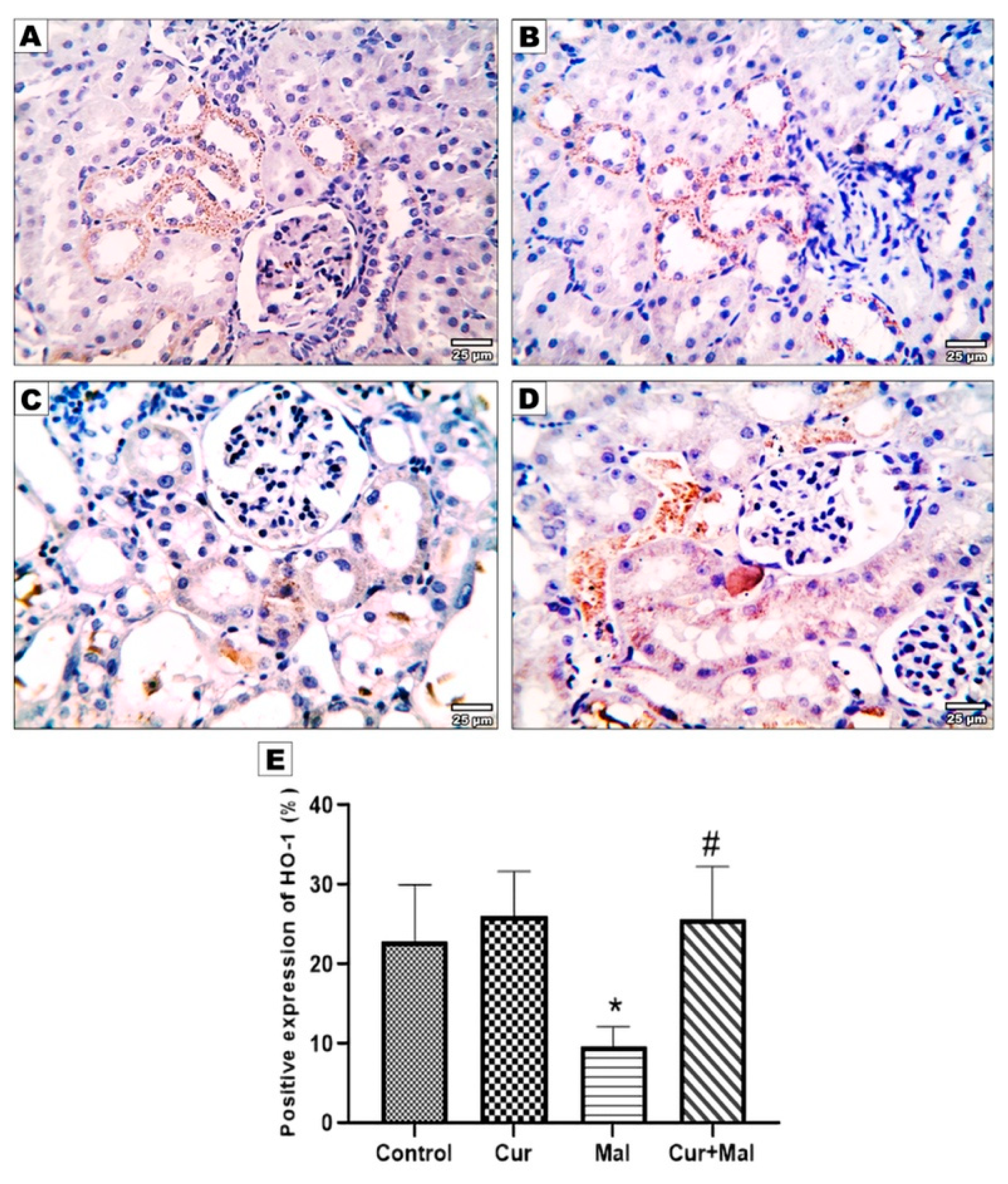
| Group 1 Controls | Group 2 Curcumin | Group 3 Malathion | Group 4 Curcumin + Malathion | Test of Significance between Groups | Test of Significance between Groups and Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 0.635 ± 0.017 | 0.51 ± 0.09 | 1.42 ± 0.34 | 0.973 ± 0.12 | p1 = 0.001 * p2 = 0.001 * p3 = 0.001 * | p4 = 0.262 p5 = 0.001 * p6 = 0.005 * |
| Serum KIM-1 pg/mL. | 653 ± 103.6 | 615 ± 96.7 | 2100 ± 258.2 | 1031 ± 173.1 | p1 = 0.0001 * p2 = 0.0218 * p3 = 0.0001 * | p4 = 0.988 p5 = 0.001 * p6 = 0.037 * |
| Tissue (Kidney) | Controls | Curcumin | Malathion | Curcumin + Malathion | Test of Significance between Groups | Test of Significance between Groups with Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA (nmol/g.tissue) | 5.61 ± 0.017 | 4.77 ± 0.43 | 11.05 ± 1.32 | 7.70 ± 1.29 | p1 < 0.001 * p2 < 0.001 * p3 < 0.001 * | p4 = 0.142 p5 < 0.001 * p6 = 0.001 * |
| GSH (mmol/g.tissue) | 2.10 ± 0.02 | 2.14 ± 0.19 | 0.603 ± 0.14 | 1.35 ± 0.22 | p1 < 0.001 * p2 < 0.001 * p3 < 0.001 * | p4 = 0.678 p5 < 0.001 * p6 < 0.001 * |
| TOS (μmolH2O2 Eq./L) | 22.5 ± 8.3 | 16.8 ± 10.8 | 52.7 ± 18.7 | 19.7 ±12.7 | p1 < 0.001 * p2 < 0.001 * p3 < 0.001 * | p4 = 0.01 p5 < 0.001 * p6 = 0.001 * |
| TAC (μmol Trolox Eq t/l) | 12.5 ± 3.7 | 17.9 ± 3.3 | 5.7 ± 2.9 | 18.2± 5.3 | p1 < 0.001 * p2 < 0.001 * p3 < 0.001 * | p4 = 0.001 p5 < 0.001 * p6 = 0.001 * |
| OSI (H2O2/Trolox) | 15.9 ± 5.3 | 11.3± 3.1 | 35.8 ± 7.3 | 21.9 ± 4.3 | p1 < 0.001 * p2 < 0.001 * p3 < 0.001 * | p4 = 0.01 p5 < 0.001 * p6 = 0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eldesoqui, M.; Ahmed, M.E.; Abdel-Kareem, M.A.; Badawy, M.M.; Dawood, A.F.; Mohamed, A.S.; Ibrahim, A.M.; El-Mansi, A.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Hendawy, M. Curcumin Mitigates Malathion-Induced Renal Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis and Modulation of NF-κβ/TNF-α and Nrf2, and HO-1 Signaling. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111117
Eldesoqui M, Ahmed ME, Abdel-Kareem MA, Badawy MM, Dawood AF, Mohamed AS, Ibrahim AM, El-Mansi AA, El-Sherbiny M, Hendawy M. Curcumin Mitigates Malathion-Induced Renal Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis and Modulation of NF-κβ/TNF-α and Nrf2, and HO-1 Signaling. Metabolites. 2023; 13(11):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111117
Chicago/Turabian StyleEldesoqui, Mamdouh, Magda E. Ahmed, Mona A. Abdel-Kareem, Mohamed Moharram Badawy, Amal Fahmy Dawood, Abdelaty Shawky Mohamed, Ateya Megahed Ibrahim, Ahmed A. El-Mansi, Mohamad El-Sherbiny, and Mahmoud Hendawy. 2023. "Curcumin Mitigates Malathion-Induced Renal Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis and Modulation of NF-κβ/TNF-α and Nrf2, and HO-1 Signaling" Metabolites 13, no. 11: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111117
APA StyleEldesoqui, M., Ahmed, M. E., Abdel-Kareem, M. A., Badawy, M. M., Dawood, A. F., Mohamed, A. S., Ibrahim, A. M., El-Mansi, A. A., El-Sherbiny, M., & Hendawy, M. (2023). Curcumin Mitigates Malathion-Induced Renal Injury: Suppression of Apoptosis and Modulation of NF-κβ/TNF-α and Nrf2, and HO-1 Signaling. Metabolites, 13(11), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13111117