Involvement of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Lipedema
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Tissue Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction and qPCR
2.4. Immunohistochemistry and Histology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
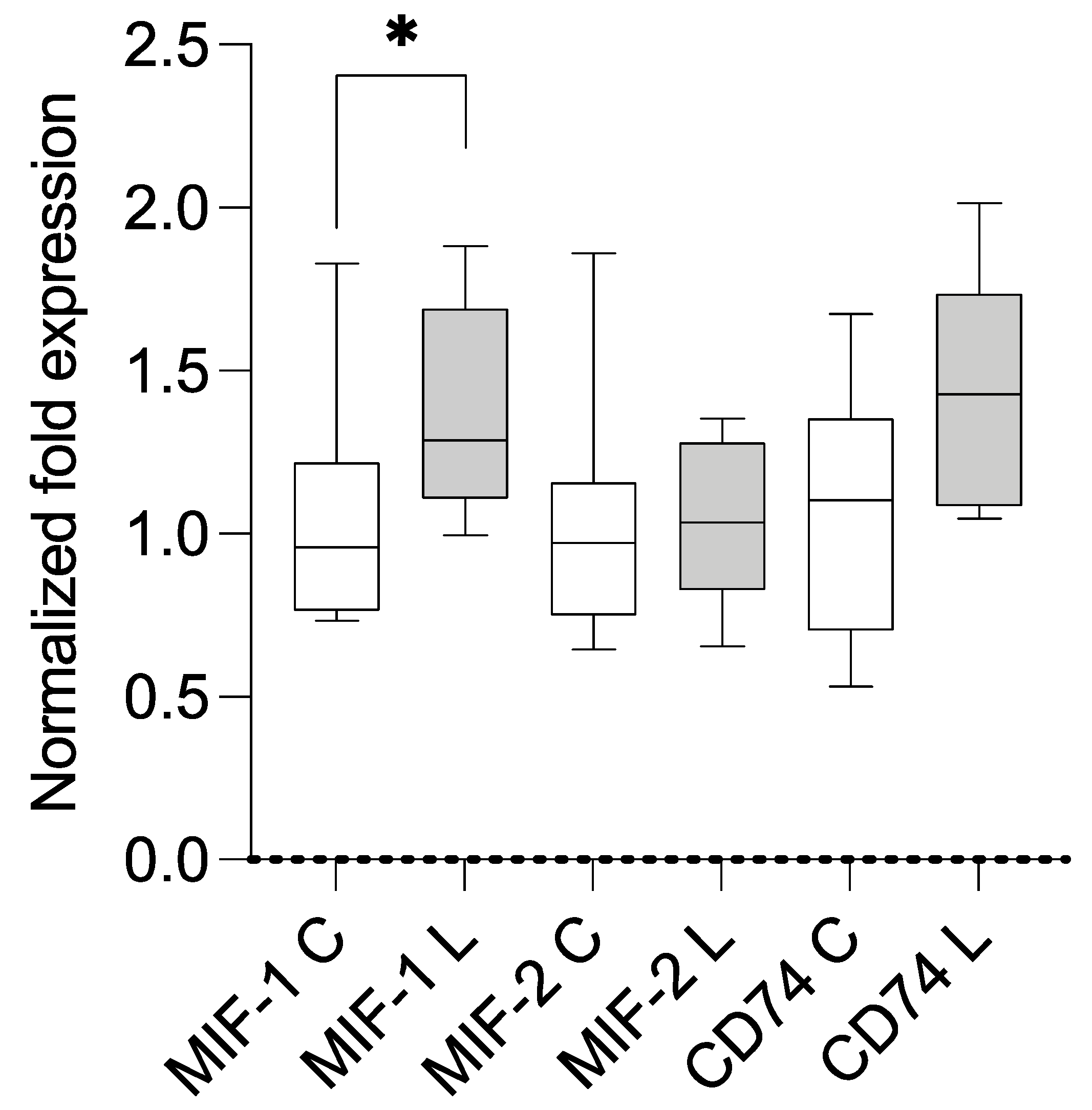
3.2. Expression Analysis Using qPCR and Correlation with BMI
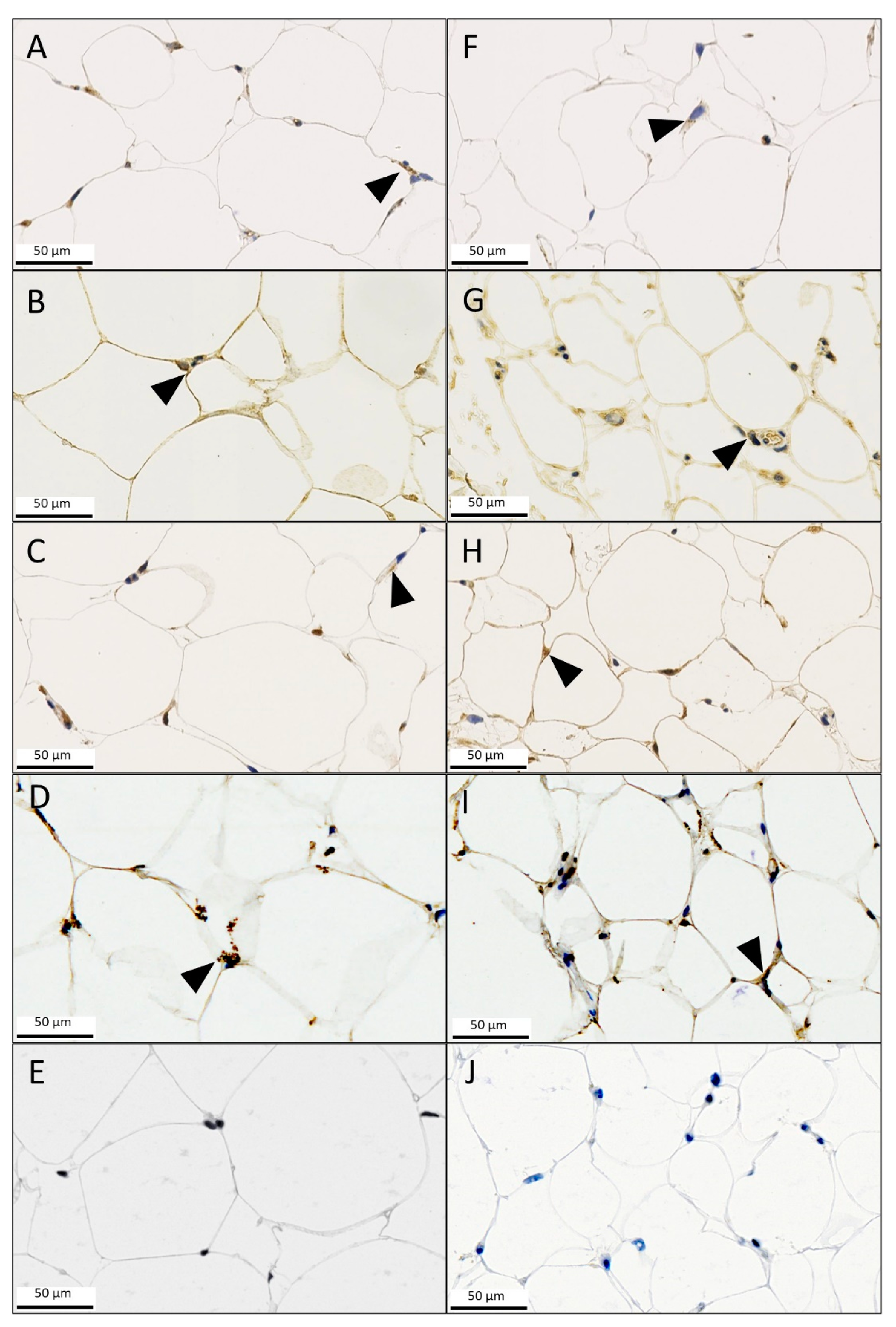
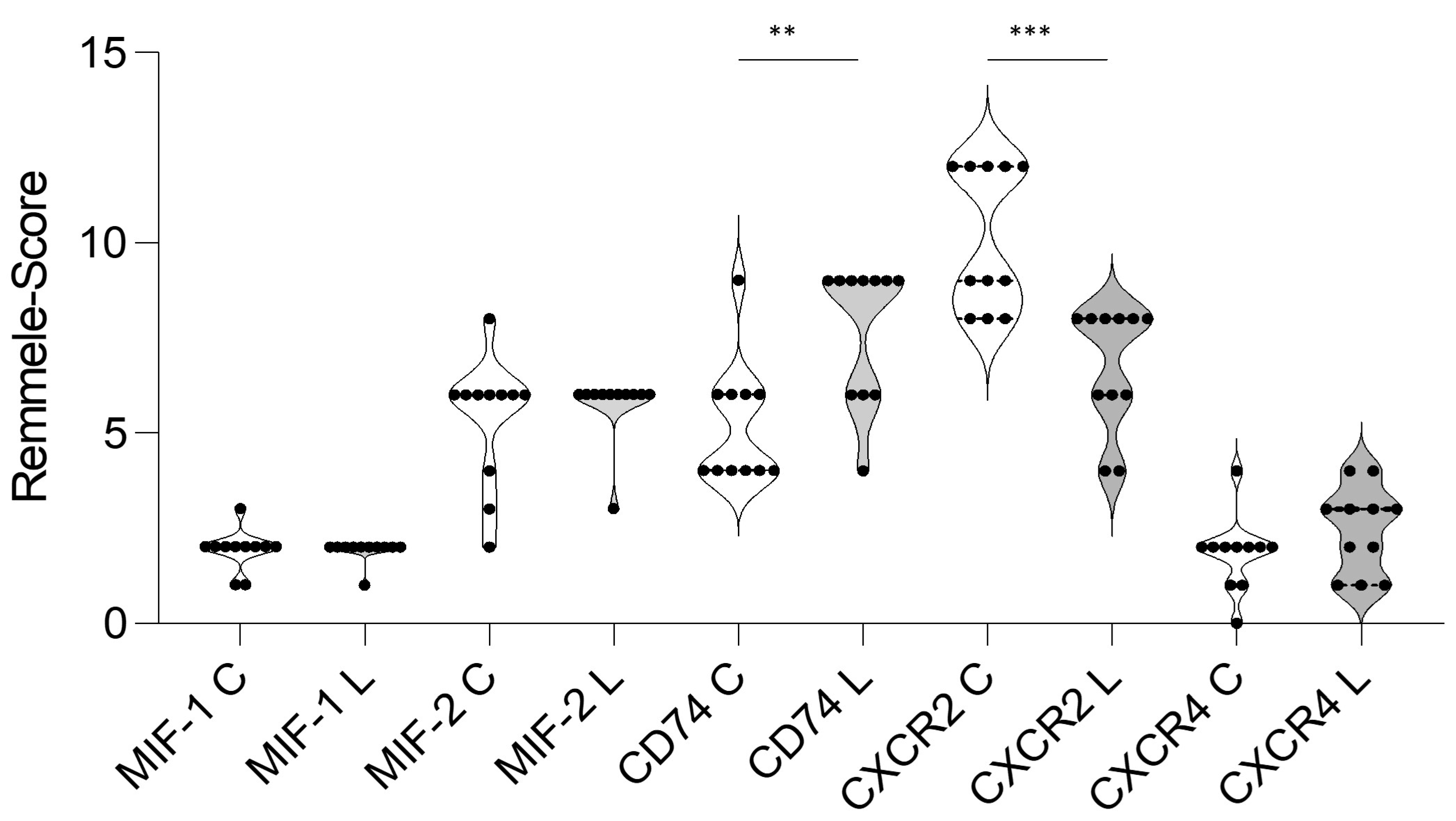
3.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruppa, P.; Georgiou, I.; Biermann, N.; Prantl, L.; Klein-Weigel, P.; Ghods, M. Lipedema-Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, D.W., II; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: A Relatively Common Disease with Extremely Common Misconceptions. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2016, 4, e1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Kurzrock, R.; Ebbinghaus, S.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Gordon, M.S.; Novotny, W.; Goldwasser, M.A.; Tohnya, T.M.; Lum, B.L.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, Y.S.; Wadeea, R.; Rosas, V.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: Friend and foe. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 33, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.-T.; von Lukowicz, D.; Lossagk, K.; Aitzetmueller, M.; Moog, P.; Cerny, M.; Erne, H.; Schmauss, D.; Duscher, D.; Machens, H.-G. New Insights on Lipedema: The Enigmatic Disease of the Peripheral Fat. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Cromer, W.; Allen, M.; Ussery, C.; Badowski, M.; Harris, D.; Herbst, K.L. Dilated Blood and Lymphatic Microvessels, Angiogenesis, Increased Macrophages, and Adipocyte Hypertrophy in Lipedema Thigh Skin and Fat Tissue. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 8747461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felmerer, G.; Stylianaki, A.; Hägerling, R.; Wang, A.; Ströbel, P.; Hollmén, M.; Lindenblatt, N.; Gousopoulos, E. Adipose Tissue Hypertrophy, An Aberrant Biochemical Profile and Distinct Gene Expression in Lipedema. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 253, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siems, W.; Grune, T.; Voss, P.; Brenke, R. Anti-fibrosclerotic effects of shock wave therapy in lipedema and cellulite. Biofactors 2005, 24, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felmerer, G.; Stylianaki, A.; Hollmén, M.; Ströbel, P.; Stepniewski, A.; Wang, A.; Frueh, F.S.; Kim, B.-S.; Giovanoli, P.; Lindenblatt, N.; et al. Increased levels of VEGF-C and macrophage infiltration in lipedema patients without changes in lymphatic vascular morphology. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, K.A.; Reynolds, C.M.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; Roche, H.M. Fats, inflammation and insulin resistance: Insights to the role of macrophage and T-cell accumulation in adipose tissue. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Pallua, N.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. The macrophage migration inhibitory factor protein superfamily in obesity and wound repair. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilstam, P.V.; Schulte, W.; Holowka, T.; Kim, B.-S.; Nouws, J.; Sauler, M.; Piecychna, M.; Pantouris, G.; Lolis, E.; Leng, L.; et al. MIF but not MIF-2 recruits inflammatory macrophages in an experimental polymicrobial sepsis model. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e127171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Tilstam, P.V.; Arnke, K.; Leng, L.; Ruhl, T.; Piecychna, M.; Schulte, W.; Sauler, M.; Frueh, F.S.; Storti, G.; et al. Differential regulation of macrophage activation by the MIF cytokine superfamily members MIF and MIF-2 in adipose tissue during endotoxemia. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4219–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Rongisch, R.; Hager, S.; Grieb, G.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Rennekampff, H.-O.; Bucala, R.; Bernhagen, J.; Pallua, N. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Acute Adipose Tissue Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, B.R.; Bennett, B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science 1966, 153, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Metz, C.N.; Fang, Y.; Xu, J.; Donnelly, S.; Baugh, J.; Delohery, T.; Chen, Y.; Mitchell, R.A.; Bucala, R. MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhagen, J.; Krohn, R.; Lue, H.; Gregory, J.L.; Zernecke, A.; Koenen, R.R.; Dewor, M.; Georgiev, I.; Schober, A.; Leng, L.; et al. MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstam, P.V.; Qi, D.; Leng, L.; Young, L.; Bucala, R. MIF family cytokines in cardiovascular diseases and prospects for precision-based therapeutics. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zernecke, A.; Bernhagen, J.; Weber, C. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2008, 117, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapurniotu, A.; Gokce, O.; Bernhagen, J. The Multitasking Potential of Alarmins and Atypical Chemokines. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Åman, P.; Grubb, A.; Panagopoulos, I.; Hindemith, A.; Rosengren, E.; Rorsman, H. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding rat D-dopachrome tautomerase. FEBS Lett. 1995, 373, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, M.; Zierow, S.; Leng, L.; Das, R.; Du, X.; Schulte, W.; Fan, J.; Lue, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, H.; et al. The D-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT) gene product is a cytokine and functional homolog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E577–E585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merk, M.; Mitchell, R.A.; Endres, S.; Bucala, R. D-dopachrome tautomerase (D-DT or MIF-2): Doubling the MIF cytokine family. Cytokine 2012, 59, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-S.; Tilstam, P.V.; Hwang, S.S.; Simons, D.; Schulte, W.; Leng, L.; Sauler, M.; Ganse, B.; Averdunk, L.; Kopp, R.; et al. D-dopachrome tautomerase in adipose tissue inflammation and wound repair. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhagen, J. Separating cytokine twins with a small molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18532–18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, L.E.; Hines, E.A.; Allen, E.V., Jr. Lipedema of the legs; a syndrome characterized by fat legs and edema. Ann. Intern. Med. 1951, 34, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Deuel, J.W.; Hollmén, M.; Felmerer, G.; Kim, B.-S.; Vasella, M.; Grünherz, L.; Giovanoli, P.; Lindenblatt, N.; Gousopoulos, E. A Distinct Cytokine Profile and Stromal Vascular Fraction Metabolic Status without Significant Changes in the Lipid Composition Characterizes Lipedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, F.; Grotzer, M.A.; Niggli, F.; Zimmermann, D.; Rushing, E.; Bode-Lesniewska, B. Ewing’s Sarcoma as a Second Malignancy in Long-Term Survivors of Childhood Hematologic Malignancies. Sarcoma 2016, 2016, 5043640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-J.; Xie, D.; Hu, P.-J.; Liao, Y.-J.; Deng, H.-X.; Kung, H.-F.; Zhu, S.-L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a potential prognostic factor in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 9916–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuren, L.; Kooistra, T.; Bernhagen, J.; Voshol, P.J.; Ouwens, D.M.; van Erk, M.; Weij, J.d.V.-V.d.; Leng, L.; van Bockel, J.H.; van Dijk, K.W.; et al. MIF deficiency reduces chronic inflammation in white adipose tissue and impairs the development of insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and associated atherosclerotic disease. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltabiano, R.; De Pasquale, R.; Piombino, E.; Campo, G.; Nicoletti, F.; Cavalli, E.; Mangano, K.; Fagone, P. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) and Its Homologue d-Dopachrome Tautomerase (DDT) Inversely Correlate with Inflammation in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. Molecules 2021, 26, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieb, G.; Simons, D.; Eckert, L.; Hemmrich, M.; Steffens, G.; Bernhagen, J.; Pallua, N. Levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and glucocorticoids in chronic wound patients and their potential interactions with impaired wound endothelial progenitor cell migration. Wound Repair. Regen. 2012, 20, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T.; Roger, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A regulator of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacher, M.; Meinhardt, A.; Lan, H.Y.; Mu, W.; Metz, C.N.; A Chesney, J.; Calandra, T.; Gemsa, D.; Donnelly, T.; Atkins, R.C.; et al. Migration inhibitory factor expression in experimentally induced endotoxemia. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Finucane, O.M.; Reynolds, C.M.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; Harford, K.A.; Morrison, M.; Baugh, J.; Roche, H.M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency ameliorates high-fat diet induced insulin resistance in mice with reduced adipose inflammation and hepatic steatosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.-C.; Wu, T.-N.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-H.; Wabitsch, M.; Tian, Y.-F.; Hsieh, P.-S. Targetted inhibition of CD74 attenuates adipose COX-2-MIF-mediated M1 macrophage polarization and retards obesity-related adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starlets, D.; Gore, Y.; Binsky, I.; Haran, M.; Harpaz, N.; Shvidel, L.; Becker-Herman, S.; Berrebi, A.; Shachar, I. Cell-surface CD74 initiates a signaling cascade leading to cell proliferation and survival. Blood 2006, 107, 4807–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhang, N.; Szweda, L.I.; Griffin, T.M.; Heuser-Baker, J.; Herlea-Pana, O.; Barlic-Dicen, J. Deficiency in adipocyte chemokine receptor CXCR4 exacerbates obesity and compromises thermoregulatory responses of brown adipose tissue in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4534–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopasov, A.E.; Blokhin, S.N.; Volkova, E.N.; Morozov, S.G. Chemokine Expression in Neutrophils and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Cells Obtained during Abdominoplasty from Patients with Obesity and Normal Body Weight. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 167, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D.; Yang, K.; Zang, S.; Lin, Z.; Chau, H.T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Lipocalin-2 mediates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by promoting neutrophil-macrophage crosstalk via the induction of CXCR2. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Qiao, L.; Yu, S.; Men, L.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Du, J. The antagonist of CXCR1 and CXCR2 protects db/db mice from metabolic diseases through modulating inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E1205–E1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, D.P.; Nebot, J.B.; Kelly, C.J.; Medina-Ruiz, L.; Schuette, F.; Graham, G.J. The chemokine receptor CXCR2 contributes to murine adipocyte development. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.P.; Pankhong, P.; Laddy, D.J.; Schoenly, K.A.; Yan, J.; Cisper, N.; Weiner, D.B. Comparative ability of IL-12 and IL-28B to regulate Treg populations and enhance adaptive cellular immunity. Blood 2009, 113, 5868–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Shu, T.; Wang, J. Cytokines and inflammation in adipogenesis: An updated review. Front. Med. 2019, 13, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priglinger, E.; Wurzer, C.; Steffenhagen, C.; Maier, J.; Hofer, V.; Peterbauer, A.; Nuernberger, S.; Redl, H.; Wolbank, S.; Sandhofer, M.T. The adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction cells from lipedema patients: Are they different? Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Rannikko, J.H.; Virtakoivu, R.; Cinelli, P.; Felmerer, G.; Burger, A.; Giovanoli, P.; Detmar, M.; Lindenblatt, N.; Hollmén, M.; et al. A distinct M2 macrophage infiltrate and transcriptomic profile decisively influence adipocyte differentiation in lipedema. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1004609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleemann, R.; Bucala, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: Critical role in obesity, insulin resistance, and associated comorbidities. Mediators Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 610479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, M.C.; Kleemann, R. Role of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Type 2 Diabetes, and Associated Hepatic Co-Morbidities: A Comprehensive Review of Human and Rodent Studies. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Leng, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Li, J.; McDonald, C.; Chen, Z.; Murphy, J.W.; Lolis, E.; et al. CD44 is the signaling component of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor-CD74 receptor complex. Immunity 2006, 25, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poojari, A.; Dev, K.; Rabiee, A. Lipedema: Insights into Morphology, Pathophysiology, and Challenges. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K. Endothelial nuclear factor kappaB in obesity and aging: Is endothelial nuclear factor kappaB a master regulator of inflammation and insulin resistance? Circulation 2012, 125, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, C.M.; Hovelmeyer, N.; Wunderlich, F.T. Mechanisms of chronic JAK-STAT3-SOCS3 signaling in obesity. Jak-stat 2013, 2, e23878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

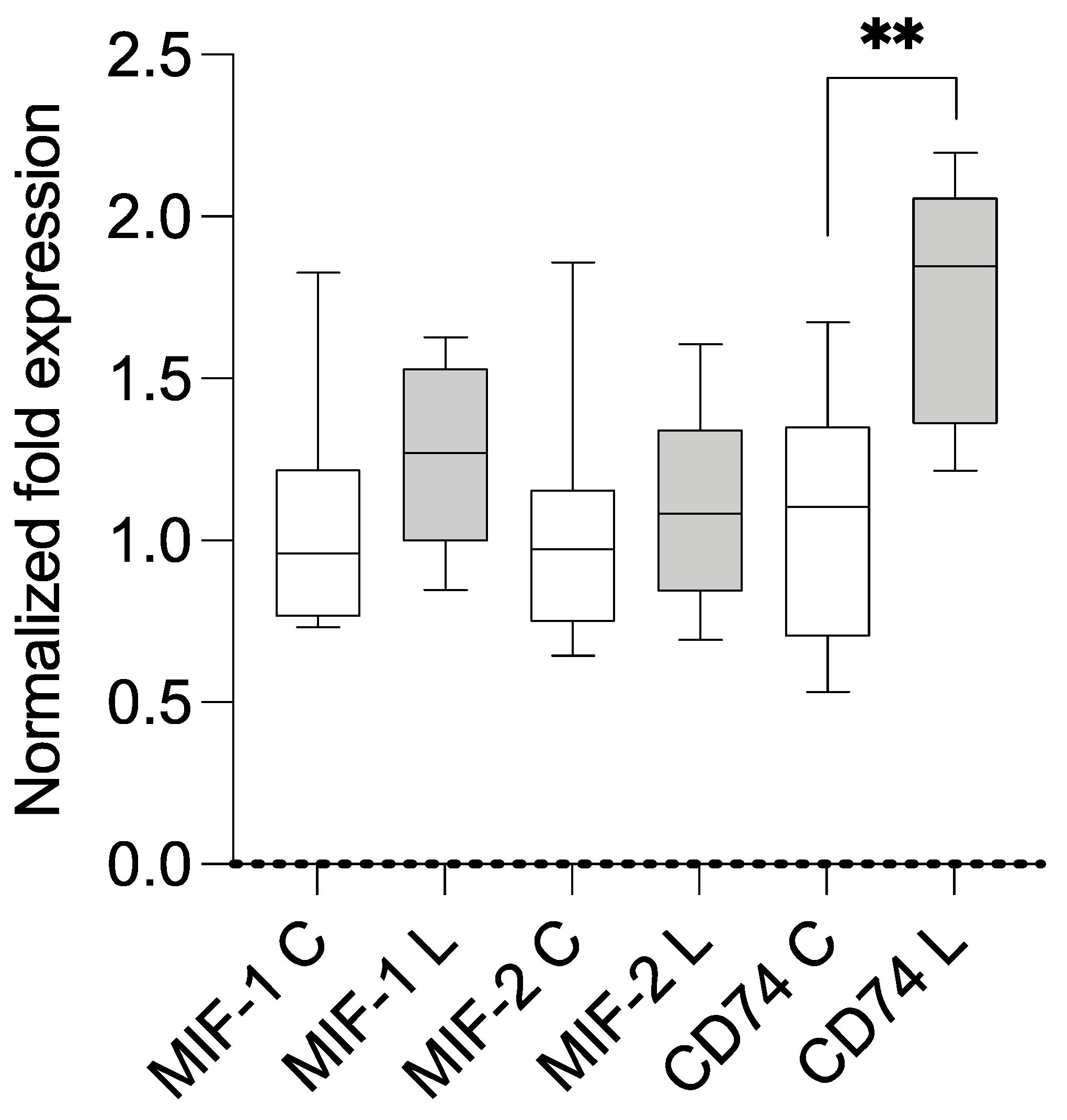
| Number of cases | 22 | p-value |
| Lipedema group | 11 | |
| Control group | 11 | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 22 | |
| Male | 0 | |
| Mean age (years) | 0.9824 | |
| Lipedema group | 47.18, 95%CI: 41.20–53.35 | |
| Control group | 47.27, 95%CI: 40.43–53.93 | |
| Mean weight (kg) | 0.4603 | |
| Lipedema group | 78.00, 95%CI: 70.26–95.30 | |
| Control group | 82.88, 95%CI: 70.96–85.04 | |
| Mean BMI (kg/m2) | 0.7530 | |
| Lipedema group | 27.98, 95%CI: 25.12–32.21 | |
| Control group | 28.61, 95%CI: 26.15–30.05 | |
| Lipedema stage | ||
| Stage I | 0 | |
| Stage II | 5 | |
| Stage III | 6 | |
| Stage IV | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasella, M.; Wolf, S.; Francis, E.C.; Grieb, G.; Pfister, P.; Reid, G.; Bernhagen, J.; Lindenblatt, N.; Gousopoulos, E.; Kim, B.-S. Involvement of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Lipedema. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101105
Vasella M, Wolf S, Francis EC, Grieb G, Pfister P, Reid G, Bernhagen J, Lindenblatt N, Gousopoulos E, Kim B-S. Involvement of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Lipedema. Metabolites. 2023; 13(10):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101105
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasella, Mauro, Stefan Wolf, Eamon C. Francis, Gerrit Grieb, Pablo Pfister, Gregory Reid, Jürgen Bernhagen, Nicole Lindenblatt, Epameinondas Gousopoulos, and Bong-Sung Kim. 2023. "Involvement of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Lipedema" Metabolites 13, no. 10: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101105
APA StyleVasella, M., Wolf, S., Francis, E. C., Grieb, G., Pfister, P., Reid, G., Bernhagen, J., Lindenblatt, N., Gousopoulos, E., & Kim, B.-S. (2023). Involvement of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Lipedema. Metabolites, 13(10), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101105








