Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Response to Cultivar Improvement and Nitrogen Fertilizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Plant Materials and Experimental Design
2.3. Plant Measurements and Analysis
2.3.1. Grain Quality and Yield Measurements
2.3.2. Metabolite Extraction
2.3.3. LC-MS Conditions for Non-Targeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.3.4. Data Processing for Nontargeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Improvements and N Application for Increased Cultivar Quality and Yield
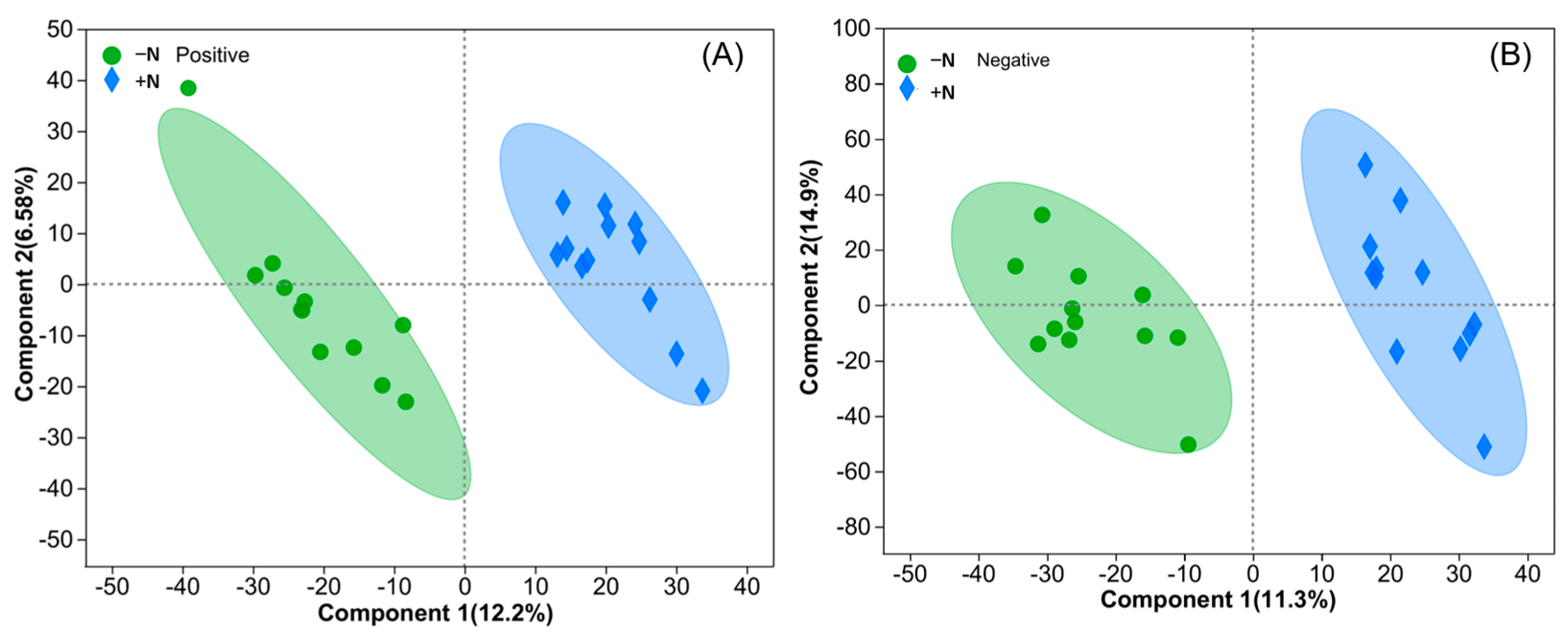
3.2. Effects of Genetic Improvement and N Application on Metabolic Profiles
3.3. Overview of Altered Metabolites under Genetic Improvement and N Application Groups
3.4. Altered Metabolic Pathways in Genetic Improvement and N Application Groups
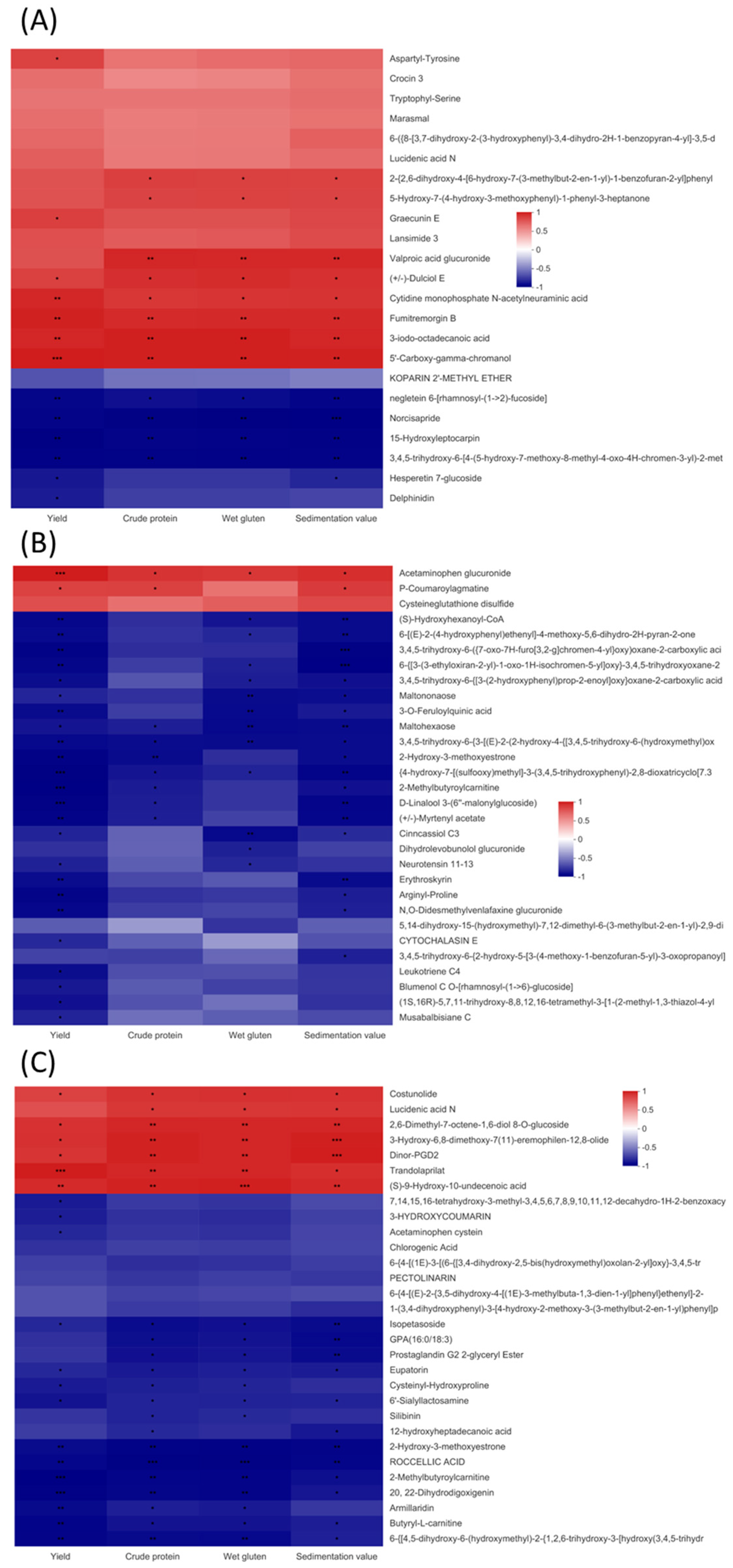
3.5. Relationships between Metabolic Profiles and Quality and Yield in Genetic Improvement and N Application Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Cultivar Improvements on Wheat Yield and Quality Based on Metabonomics
4.2. Effects of N Fertilizer Application on Wheat Yield and Quality Based on Metabonomics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakka, S.; Jugulam, M.; Peterson, D.; Asif, M. Herbicide resistance: Development of wheat production systems and current status of resistant weeds in wheat cropping systems. Crop J. 2019, 7, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radstake, F.; Ariens, M.; Luna, H.; Joy, Q.G. Dryland Ecosystems: Introducing an Integrated Management Approach in the People’s Republic of China; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong City, Philippines, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.G.; Tian, Z.W.; Yin, M.; Cai, J.; Jiang, D.; Ji, L.Y.; Dai, T.B. Variations of grain yield and quality characteristics in winter wheat cultivars from different eras and their responses to nitrogen. J. Triticeae Crop. 2014, 34, 1390–1397, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Calderini, D.F.; Reynolds, M.P.; Slafer, G.A.; Satorre, E.H.; Slafer, G.A. Genetic gains in wheat yield and associated physiological changes during the twentieth century. Wheat Ecol. Physiol. Yield Determ. 1999, 61, 351–377. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Ren, G.X.; Liu, S.C. Variation and trends in dough rheological properties and flour quality in 330 Chinese wheat varieties. Crop J. 2014, 4, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hosseini, R. The effect of nitrogen on yield and yield component in modern and old wheat cultivars. Electron. J. Crop Prod. 2011, 4, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Giunta, F.; Pruneddu, G.; Motzo, R. Grain yield and grain protein of old and modern durum wheat cultivars grown under different cropping systems. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 230, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirosavljevic, M.; Momcilovic, V.; Mikic, S.; Trkulja, D.; Brbaklic, L.; Zoric, M.; Abicic, I. Changes in stay-green and nitrogen use efficiency traits in historical set of winter barley cultivars. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 249, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P. Use of alien genetic variation for wheat improvement. In Molecular Breeding for Sustainable Crop Improvement; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár-Láng, M.; Ceoloni, C.; Doležel, J. Alien Introgression in Wheat; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.B.; Fang, Y.H.; Han, L.P.; Xv, W.G.; Hu, L. Genetic improvement analysis of nitrogen uptake, utilization, translocation, and distribution in Chinese wheat in Henan Province. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 277, 108406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.L.; Yue, S.C.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.P. In-season root-zone N management for mitigating greenhouse gas emission and reactive N losses in intensive wheat production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6015–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.N.; Ren, N.; Fu, W.; Yue, S.H. Development of nitrogen fertilizer topdressing model for winter wheat based on critical nitrogen dilution curve. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.L.; Zhong, X.H.; Yang, J.C.; Wang, G.H.; Zou, Y.B.; Zhang, F.S.; Zhu, Q.S.; Roland, B.; Christian, W. Challenge and opportunity in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China. Agric. Sci. China 2002, 1, 776–785. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.K.; Guo, W.S.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Feng, C.N.; Peng, Y.X.; Lin, Q.H. Effects of nitrogen on N uptake, grain yield and quality of medium-gluten wheat Yangmai 10. Agric. Sci. China 2005, 4, 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.P.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, C.S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Fang, B.T.; Zhang, Y.H. Improving winter wheat grain yield and water-/nitrogen-use efficiency by optimizing the micro-sprinkling irrigation amount and nitrogen application rate. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Chen, J.; Shangguan, Z.P. Photosynthetic characteristics and nitrogen distribution of largespike wheat in Northwest China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, D.Y.; Karlov, G.I.; Divashuk, M.G. Metabolomics for crop breeding: General considerations. Genes 2021, 12, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xv, S.Z.; Xv, Y.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Q.F. Metabolomic prediction of yield in hybrid rice. Plant J. 2016, 88, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Riedelsheimer, C.; Czedik-Eysenberg, A.; Grieder, C.; Lisec, J.; Technow, F.; Sulpice, R.; Altmann, T.; Stitt, M.; Willmitzer, L.; Melchinger, A.E. Genomic and metabolic prediction of complex heterotic traits in hybrid maize. Nat. Gen. 2012, 44, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, K.; Lisec, J.; Romisch-Margl, L.; Selbig, J.; Gierl, A.; Piepho, H.P.; Nikoloski, Z.; Willmitzer, L. Deducing hybrid performance from parental metabolic profiles of young primary roots of maize by using a multivariate diallel approach. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalasekera, R.; Scherer, G. Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases in abiotic stress responses in plants. In Plant Metabolites and Regulation Under Environmental Stress; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.H.; Chen, C.S.; Zhong, Q.S.; Ruan, Q.C.; Chen, Z.H.; You, X.M.; Shan, R.Y.; Li, X.L. The GC-TOF/MS-based Metabolomic analysis reveals altered metabolic profiles in nitrogen deficient leaves and roots of tea plants (Camellia sinensis). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazadeh, S.; Schildhauer, J.; Araujo, W.L.; Munne-Bosch, S.; Fernie, A.; Proost, S.; Humbeck, K.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Reversal of senescence by N resupply to N-starved Arabidopsis thaliana: Transcriptomic and metabolomic consequences. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3975–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.L.; Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Nie, L.X.; Wang, F. Genetic improvements in rice yield and concomitant increases in radiation- and nitrogen-use efficiency in middle reaches of Yangtze River. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daygon, V.D.; Calingacion, M.; Forster, L.C.; Voss, J.J.; Schwartz, B.D.; Ovenden, B.; Alonso, D.E.; McCouch, S.R.; Garson, M.J.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Metabolomics and genomics combine to unravel the pathway for the presence of fragrance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, I.; Luna, E.; Leach, J.E.; McClung, A.; Vilchez, S.; Koita, O.; Ryan, E.P. Comparative rice bran metabolomics across diverse cultivars and functional rice gene-bran metabolite relationships. Metabolites 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, H.; Chevalier, E.; Matton, D.P. Plant bioactive peptides: An expanding class of signaling molecules. Can. J. Bot. 2006, 84, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziglio, A.C.; Gonalves, D. On the use of capsaicin as a natural preservative against fungal attack on Pinus sp. and Hymenaea sp. woods. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, X.R.; Liu, Q.Y.; Bao, J.K.; Long, Z.F. Antifungal activity, main active components and mechanism of curcuma longa extract against fusarium. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.X.; Han, J.S. The analgesic effect of dynorphin a in spinal cord of the rat potentiated by dynorphin B. Sci. Bull. 1985, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, C.R.; Li, H.S.; Li, M.; Wu, A.M.; Deng, R.L. Plants with allelopathic potentials can promote the resistance of peanut to aflatoxin. J. Peanut Sci. 2010, 39, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Damisch, W.; Wiberg, A. Biomass yield-a topical issue in modern wheat breeding programmes. Plant Breed. 2010, 107, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.D.; Li, Z.P.; Feng, H. Effects of irrigation and nitrogen regimes on dry matter dynamic accumulation and yield of winter wheat. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 119–126, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Ha, S.; Song, B.; Kim, T.; Waters, B.M.; Krishnan, H.B. Metabolomic profiling from leaves and roots of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants grown under nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium-deficient condition. Plant Sci. 2015, 241, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, S.M.; Zhou, J.X.; Deng, X.; Zhu, G.R.; Cao, H.; Wang, Z.M. Metabolite profiling of the response to high-nitrogen fertilizer during grain development of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.M.; Park, N.Y.; Rostgaard-Hansen, A.L.; Huang, J.J.; Jiang, Q. Vitamin E metabolite 13′-carboxychromanols inhibit pro-inflammatory enzymes, induce apoptosis and autophagy in human cancer cells by modulating sphingolipids and suppress colon tumor development in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Simpson, A.; Nakatsu, C.; Jones-Hall, Y.; Jiang, Q. Delata-tocotrienol 13′-carboxychromanol, a vitamin E metabolite, interacts with gut microbes as indicated by its anti-colitis synergy with a lactic acid bacterium in mice. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2022, 6, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.L.; Shi, M.Z.; Xie, D.Y. Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by nitrogen in TTG1-GL3/TT8-PAP1-programmed red cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2012, 236, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, S.; Gupta, S.M.; Kumar, A. Enzymes of phenylpropanoid metabolism involved in strengthening the structural barrier for providing genotype and stage dependent resistance to karnal bunt in wheat. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shadle, G.L.; Wesley, S.V.; Korth, K.L.; Chen, F.; Lamb, C.; Dixon, R.A. Phenylpropanoid compounds and disease resistance in transgenic tobacco with altered expression of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cultivar | Pedigree/Origin | Release Period |
|---|---|---|
| ND2419 | Rieti × Wilhelmina//Akagomughi | 1950s |
| BJ8 | BM4 × Early Premium | 1960s |
| ZY1 | St1472/506 | 1970s |
| XY4 | ZY4 × ZZ17 × 6609 | 1980s |
| BN3217 | Funo × NX5//XN39 × XN64 × YD34 | 1990s |
| YM2 | ZN16 × YM14 | 2000s |
| BN207 | Z16 × BN64 | 2010s |
| Release Year | N Treatments | Plant Height (cm) | No. of Panicles (×104 m−2) | Grains Per Panicle | Grain Weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019–2020 | |||||
| 1950s | −N | 107.5 | 377.7 | 32.7 | 35.1 |
| +N | 116.7 ** | 527.0 ** | 30.6 ns | 38.3 ** | |
| 1960s | −N | 115.9 | 343.7 | 36.1 | 31.7 |
| +N | 129.0 ** | 491.7 ** | 42.4 * | 33.2 * | |
| 1970s | −N | 86.1 | 334.7 | 38.9 | 42.1 |
| +N | 95.9 ** | 530.3 ** | 36.6 * | 43.1 ns | |
| 1980s | −N | 99.9 | 364.0 | 39.8 | 42.8 |
| +N | 109.0 ** | 424.7 ** | 41.4 ns | 46.6 ** | |
| 1990s | −N | 86.4 | 369.7 | 42.5 | 42.1 |
| +N | 88.3 ns | 486.7 ** | 43.9 ns | 42.2 ns | |
| 2000s | −N | 77.4 | 339.3 | 40.8 | 45.4 |
| +N | 85.0 * | 440.0 ** | 45.0 ** | 45.7 ns | |
| 2010s | −N | 75.4 | 273.3 | 43.7 | 46.9 |
| +N | 80.8 * | 394.0 ** | 47.5 ** | 47.7 ns | |
| Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| Nitrogen (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| C × N | ns | ** | ** | ns | |
| 2020–2021 | |||||
| 1950s | −N | 110.7 | 401.0 | 32.3 | 36.2 |
| +N | 115.3 * | 558.3 ** | 30.7 ns | 39.8 * | |
| 1960s | −N | 118.5 | 381.0 | 33.7 | 29.0 |
| +N | 131.5 ** | 536.7 ** | 35.8 * | 34.2 ** | |
| 1970s | −N | 84.0 | 320.3 | 38.0 | 44.0 |
| +N | 95.2 ** | 544.0 ** | 34.9 * | 43.8 ns | |
| 1980s | −N | 101.9 | 358.7 | 40.0 | 43.1 |
| +N | 108.6 ** | 421.3 ** | 40.5 ns | 46.3 * | |
| 1990s | −N | 82.6 | 379.3 | 40.9 | 42.3 |
| +N | 85.3 * | 507.0 ** | 44.2 ** | 41.4 ns | |
| 2000s | −N | 79.2 | 326.0 | 41.8 | 44.2 |
| +N | 81.7 ns | 441.0 ** | 46.3 ** | 45.6 ns | |
| 2010s | −N | 74.0 | 254.7 | 44.7 | 46.6 |
| +N | 78.2 * | 376.0 ** | 51.4 ** | 48.1 ns | |
| Cultivar (C) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| Nitrogen (N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| C × N | ns | ** | ** | ns | |
| HMDB Superclass | Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar | N Treatment (+N vs. −N) | ||||
| 1980s vs. 1950s | 2010s vs. 1980s | 1950s | 1980s | 2010s | |
| Lipids and lipid-like molecules | 68 | 22 | 4 | 19 | 22 |
| Phenylpropanoids and polyketides | 33 | 20 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| Organoheterocyclic compounds | 15 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 2 |
| Organic oxygen compounds | 29 | 14 | 1 | 20 | 7 |
| Organic acids and derivatives | 8 | 6 | 2 | 9 | 5 |
| Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Mixed metal/non-metal compounds | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lignans, neolignans and related compounds | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Benzenoids | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Others | 11 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 5 |
| Total | 171 | 75 | 23 | 68 | 54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Shi, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y. Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Response to Cultivar Improvement and Nitrogen Fertilizer. Metabolites 2023, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010107
Zhao F, Wang Y, Hu J, Shi S, Zhang H, Wang Y, Ye Y. Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Response to Cultivar Improvement and Nitrogen Fertilizer. Metabolites. 2023; 13(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Fulin, Yifan Wang, Jiayu Hu, Shaolei Shi, Hongyan Zhang, Yang Wang, and Youliang Ye. 2023. "Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Response to Cultivar Improvement and Nitrogen Fertilizer" Metabolites 13, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010107
APA StyleZhao, F., Wang, Y., Hu, J., Shi, S., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., & Ye, Y. (2023). Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Response to Cultivar Improvement and Nitrogen Fertilizer. Metabolites, 13(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010107






