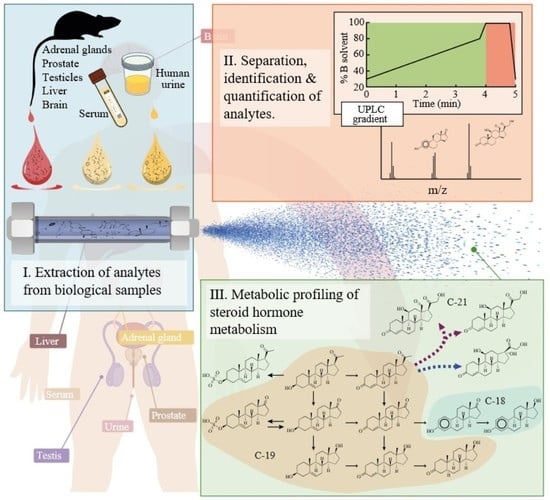
Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones Using hrLC-MS in Endocrine Tissues of Male Rats and Human Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue and Biofluid Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Standards
2.3. LCMS Sample Preparation
2.4. Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC)
2.5. Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Analyte Recovery Study
2.6.2. Study of Matrix Effect in Analyte Quantification
2.6.3. Analyte Semi-Quantification
3. Results
3.1. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Method
3.2. Analyte Recovery Optimization
3.3. Matrix Effect
3.4. Semi-Quantitation of Steroids in Animal Tissues
3.5. Quantitation of Steroid Hormones in Human Urinary Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The Molecular Biology, Biochemistry, and Physiology of Human Steroidogenesis and Its Disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereshchenko, O.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoids, Sex Hormones, and Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poschner, S.; Zehl, M.; Maier-Salamon, A.; Jäger, W. Simultaneous Quantification of Estrogens, Their Precursors and Conjugated Metabolites in Human Breast Cancer Cells by LC–HRMS without Derivatization. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, H.J.; Carvalho, T.M.A.; Fonseca, L.R.S.; Figueira, M.I.; Vaz, C.V.; Socorro, S. Revisiting Prostate Cancer Metabolism: From Metabolites to Disease and Therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 1499–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clos-Garcia, M.; Loizaga-Iriarte, A.; Zuñiga-Garcia, P.; Sánchez-Mosquera, P.; Rosa Cortazar, A.; González, E.; Torrano, V.; Alonso, C.; Pérez-Cormenzana, M.; Ugalde-Olano, A.; et al. Metabolic Alterations in Urine Extracellular Vesicles Are Associated to Prostate Cancer Pathogenesis and Progression. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1470442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonergan, P.; Tindall, D. Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating Viruses and Cellular Organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.W.; Gilligan, L.C.; Idkowiak, J.; Arlt, W.; Foster, P.A. The Regulation of Steroid Action by Sulfation and Desulfation. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, 526–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, P.A.; Mueller, J.W. Insights into Steroid Sulfation and Desulfation Pathways. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T271–T283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, R.; Hurrion, E.; Dawson, P.A. Genetics and Pathophysiology of Mammalian Sulfate Biology. J. Genet. Genom. 2017, 44, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordanaba-Florit, G.; Royo, F.; Kruglik, S.G.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M. Using Single-Vesicle Technologies to Unravel the Heterogeneity of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3163–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological Properties of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A Compendium for Extracellular Vesicles with Continuous Community Annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Fonseka, P.; Chitti, S.V.; Kang, T.; Sanwlani, R.; Van Deun, J.; Hendrix, A.; Mathivanan, S. Vesiclepedia 2019: A Compendium of RNA, Proteins, Lipids and Metabolites in Extracellular Vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D516–D519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanson, J.L.; Stander, M.A.; Pretorius, E.; Jenkinson, C.; Taylor, A.E.; Storbeck, K.H. High-Throughput Analysis of 19 Endogenous Androgenic Steroids by Ultra-Performance Convergence Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1031, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indapurkar, A.; Hartman, N.; Patel, V.; Matta, M.K. Simultaneous UHPLC-MS/MS Method of Estradiol Metabolites to Support the Evaluation of Phase-2 Metabolic Activity of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Hepatocytes. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1126–1127, 121765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, E.; Lew, B.L.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, J.; Paeng, K.J.; Chung, B.C. Simultaneous Determination of Androgens and Prostaglandins in Human Urine Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1109, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Sawyer, M.B.; Li, X.F. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Determination of Estrogen Conjugates in Human Urine. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3404–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Im, E.; Kim, H.; Lew, B.L.; Sim, W.Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, H.B.; Paeng, K.J.; Hong, J.; Chung, B.C. Untargeted Metabolomics and Steroid Signatures in Urine of Male Pattern Baldness Patients after Finasteride Treatment for a Year. Metabolites 2020, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Tanaka, E.; Suzuki, T.; Okumura, K.; Nomura, S.; Miyasho, T.; Haeno, S.; Yokota, H. Accurate Determination of Tissue Steroid Hormones, Precursors and Conjugates in Adult Male Rat. J. Biochem. 2013, 153, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.; Navarro, J.C.; Riva, C.; Bordonali, S.; Porte, C. Does Exposure to Testosterone Significantly Alter Endogenous Metabolism in the Marine Mussel Mytilus Galloprovincialis? Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Li, K. Uplc–Tof–Ms Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones in Tissue Homogenates of Zebrafish with Solid-Phase Extraction. Molecules 2021, 26, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglarek, U.; Kortz, L.; Leichtle, A.; Fiedler, G.M.; Kratzsch, J.; Thiery, J. Rapid Quantification of Steroid Patterns in Human Serum by On-Line Solid Phase Extraction Combined with Liquid Chromatography-Triple Quadrupole Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 401, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koal, T.; Schmiederer, D.; Pham-Tuan, H.; Röhring, C.; Rauh, M. Standardized LC-MS/MS Based Steroid Hormone Profile-Analysis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 129, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.F.; Le, J.; Wang, S.T.; Li, Y. An LC/MS/MS Method for Analyzing the Steroid Metabolome with High Accuracy and from Small Serum Samples. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. A UHPLC-MS/MS Method for Profiling Multifunctional Steroids in Human Hair. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4751–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, T.; Shiraishi, H.; Yasuda, M.; Shinoda, A.; Suzuki, H.; Morita, M. Determination of Estrogens and Their Conjugates in Water Using Solid-Phase Extraction Followed by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 984, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Iden, C.R.; Brownawell, B.J. Analysis of Steroid Conjugates in Sewage Influent and Effluent by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7032–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Liempd, S.; Cabrera, D.; Mato, J.M.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. A Fast Method for the Quantitation of Key Metabolites of the Methionine Pathway in Liver Tissue by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Hydrophilic Interaction Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5301–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, U.; Ermer, J.; Preu, L.; Wätzig, H. Wide Concentration Range Investigation of Recovery, Precision and Error Structure in Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 810, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordanaba-Florit, G. Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones Using hrLC-MS in Endocrine Tissues of Male Rats and Human Samples (Dataset). 2022. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/_/20231493 (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Liang, X.; Ubhayakar, S.; Liederer, B.M.; Dean, B.; Ran-Ran Qin, A.; Shahidi-Latham, S.; Deng, Y. Evaluation of Homogenization Techniques for the Preparation of Mouse Tissue Samples to Support Drug Discovery. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method Validation and Quality Control Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. 2012. Available online: https://www.eurl-pesticides.eu/library/docs/allcrl/AqcGuidance_Sanco_2011_12495.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Ghosh, C.; Shinde, C.P.; Chakraborty, B.S. Influence of Ionization Source Design on Matrix Effects during LC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 893–894, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix Effects and Application of Matrix Effect Factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrie, A.; Colombo, M.; Krumeich, S.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Diverse Subpopulations of Vesicles Secreted by Different Intracellular Mechanisms Are Present in Exosome Preparations Obtained by Differential Ultracentrifugation. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2012, 1, 18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, K.; Pringle, S.D.; Worthington, K.R.; Little, D.; Wildgoose, J.L.; Bateman, R.H. Applications of a Travelling Wave-Based Radio-Frequency-Only Stacked Ring Ion Guide. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, D.J.; Worthington, K.R.; Hoyes, J.B. Scanwave: A New Approach to Enhancing Spectral Data on a Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J. Matrix Effects: The Achilles Heel of Quantitative High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I. Adrenocortical Hormones. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 9, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosol, T.J.; Yarrington, J.T.; Latendresse, J.; Capen, C.C. Adrenal Gland: Structure, Function, and Mechanisms of Toxicity. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 29, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, W.E.; Nakamura, Y. Regulation of the Adrenal Androgen Biosynthesis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 108, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puhka, M.; Takatalo, M.; Nordberg, M.E.; Valkonen, S.; Nandania, J.; Aatonen, M.; Yliperttula, M.; Laitinen, S.; Velagapudi, V.; Mirtti, T.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles and Alternative Normalization Methods Reveal Enriched Metabolites and Strategies to Study Prostate Cancer-Related Changes. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3824–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analyte | Fraction | Recovery (%) | Matrix Effect (%) | LOD (nM) | LOQ (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnenolone | Organic | 97.2 (±1.9) | 25.2 (±3.1) | 2.5 nM | 10 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 24.0 (±2.8) | |||
| DHEA | Organic | 122.7 (±2.9) | 37.7 (±5.7) | 5.0 nM | 50 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 28.0 (±6.2) | - | - | |
| Androstenedione | Organic | 102.2 (±3.2) | 30.8 (±4.6) | 0.25 nM | 0.5 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 23.2 (±4.5) | |||
| Estrone | Organic | 103.7 (±3.8) | 25.5 (±4.8) | 5.0 nM | 10 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 25.7 (±4.0) | |||
| DHT | Organic | 74.2 (±3.4) | 23.1 (±3.9) | 0.25 nM | 1.0 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 23.4 (±2.9) | |||
| Cortisol | Organic | 114.3 (±3.8) | 25.9 (±4.2) | 0.5 nM | 1.0 nM |
| Aqueous | 22.28 (±4.5) | 17.6 (±4.7) | |||
| Aldosterone | Organic | 99.8 (±1.77) | 18.7 (±4.3) | 0.5 nM | 2.5 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 17.7 (±5.1) | |||
| Corticosterone | Organic | 109.4 (±3.1) | 25.1 (±3.6) | 0.25 nM | 1.0 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 20.2 (±3.2) | |||
| Testosterone | Organic | 126.9 (±1.7) | 14.3 (±1.9) | 0.25 nM | 0.25 nM |
| Aqueous | - | 8.0 (±2.1) | |||
| Pregnenolone sulfate | Organic | 6.9 (±2.7) | 25.2 (±3.1) | 0.25 nM | 1.0 nM |
| Aqueous | 94.8 (±1.9) | 24.0 (±2.8) | |||
| DHEAS | Organic | - | 42.6 (±1.1) | 0.25 nM | 0.5 nM |
| Aqueous | 108.0 (±1.4) | 42.5 (±0.1) |
| Analyte | Urine Volume | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnenolone | 50 µL | 92.4 (±3.6) |
| 250 µL | 99.3 (±4.8) | |
| Androstenedione | 50 µL | 93.0 (±3.9) |
| 250 µL | 79.3 (±3.8) | |
| Estrone | 50 µL | 94.2 (±3.3) |
| 250 µL | 84.8 (±4.8) | |
| DHT | 50 µL | 76.3 (±4.1) |
| 250 µL | 71.2 (±3.76) | |
| Cortisol | 50 µL | 87.0 (±3.0) |
| 250 µL | 72.4 (±3.6) | |
| Aldosterone | 50 µL | 110.7 (±2.9) |
| 250 µL | 103.1 (±3.2) | |
| Corticosterone | 50 µL | 96.2 (±2.8) |
| 250 µL | 84.3 (±3.6) | |
| Testosterone | 50 µL | 104.1 (±2.1) |
| 250 µL | 96.3 (±5.1) | |
| Pregnenolone sulfate | 50 µL | 54.9 (±1.5) |
| 250 µL | 25.5 (±1.2) | |
| DHEAS | 50 µL | 75.7 (±2.5) |
| 250 µL | 44.0 (±4.2) |
| Analyte | Quantification (nmol/g Tissue) | Adrenal Gland | Prostate | Brain | Testicle | Serum (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnenolone | Amount | 7.04 | - | Detected | Detected | - |
| St. dev. | 3.74 | |||||
| %cv | 53 | |||||
| Androstenedione | Amount | 5.97 × 10−3 | - | Detected | 1.45 × 10−3 | Detected |
| St. dev. | 3.35 × 10−3 | 1.38 × 10−3 | ||||
| %cv | 56 | 95 | ||||
| DHT | Amount | 3.47 × 10−3 | 7.57 × 10−3 | Detected | 2.70 × 10−3 | Detected |
| St. dev. | 1.02 × 10−3 | 2.40 × 10−3 | 7.92 × 10−4 | |||
| %cv | 29 | 31 | 29 | |||
| Corticosterone | Amount | 18.89 | 4.01 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−2 | 1.25 × 10−3 | 28.01 |
| St. dev. | 10.05 | 5.15 × 10−3 | 7.04 × 10−3 | 7.98 × 10−4 | 3.31 | |
| %cv | 53 | 128 | 29 | 63 | 12 | |
| Cortisol | Amount | 0.45 | - | - | - | - |
| St. dev. | 0.19 | |||||
| %cv | 43 | |||||
| Testosterone | Amount | 4.53 × 10−3 | 6.92 × 10−4 | 7.02 × 10−4 | 9.18 × 10−3 | 0.20 |
| St. dev. | 1.47 × 10−3 | 2.36 × 10−4 | 4.29 × 10−4 | 4.53 × 10−3 | 0.02 | |
| %cv | 32 | 34 | 60 | 49 |
| Sample | Collection Time | Androstenedione (nM) | Cortisol (nM) | DHEAS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. (µM) | EV-Associated DHEAS (µM) | EV-Associated DHEAS in Urine (ppm) | ||||
| Urine | Morning | 2.25 (±0.92) | 40.1 (±33.5) | 0.36 (±0.16) | - | - |
| Urine | Afternoon | 1.95 (±0.78) | 35.7 (±0.7) | 1.27 (±0.87) | - | - |
| SN100K | Morning | 2.31 (±1.53) | 29.9 (±14.7) | 1.33 (±0.94) | - | - |
| SN100K | Afternoon | 1.82 (±0.64) | 31.4 (±0.7) | 0.87 (±0.92) | - | - |
| P10K | Morning | - | - | - | 1.75 | 0.90 |
| P10K | Afternoon | - | - | - | 0.76 (±0.08) | 0.79 (±0.41) |
| P100K | Morning | - | - | - | 6.17 | 3.19 |
| P100K | Afternoon | - | - | - | 0.74 (±0.01) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bordanaba-Florit, G.; Liempd, S.v.; Cabrera, D.; Royo, F.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M. Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones Using hrLC-MS in Endocrine Tissues of Male Rats and Human Samples. Metabolites 2022, 12, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080714
Bordanaba-Florit G, Liempd Sv, Cabrera D, Royo F, Falcón-Pérez JM. Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones Using hrLC-MS in Endocrine Tissues of Male Rats and Human Samples. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080714
Chicago/Turabian StyleBordanaba-Florit, Guillermo, Sebastiaan van Liempd, Diana Cabrera, Félix Royo, and Juan Manuel Falcón-Pérez. 2022. "Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones Using hrLC-MS in Endocrine Tissues of Male Rats and Human Samples" Metabolites 12, no. 8: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080714
APA StyleBordanaba-Florit, G., Liempd, S. v., Cabrera, D., Royo, F., & Falcón-Pérez, J. M. (2022). Simultaneous Quantification of Steroid Hormones Using hrLC-MS in Endocrine Tissues of Male Rats and Human Samples. Metabolites, 12(8), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080714