MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Highlights Specific Metabolome and Lipidome Profiles in Salivary Gland Tumor Tissues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Histopathological Assessment
2.2. MALDI-MSI of Polar and Non-Polar Metabolites in Parotid Sections
2.3. Exploratory Analysis, Classification, and Model Validation
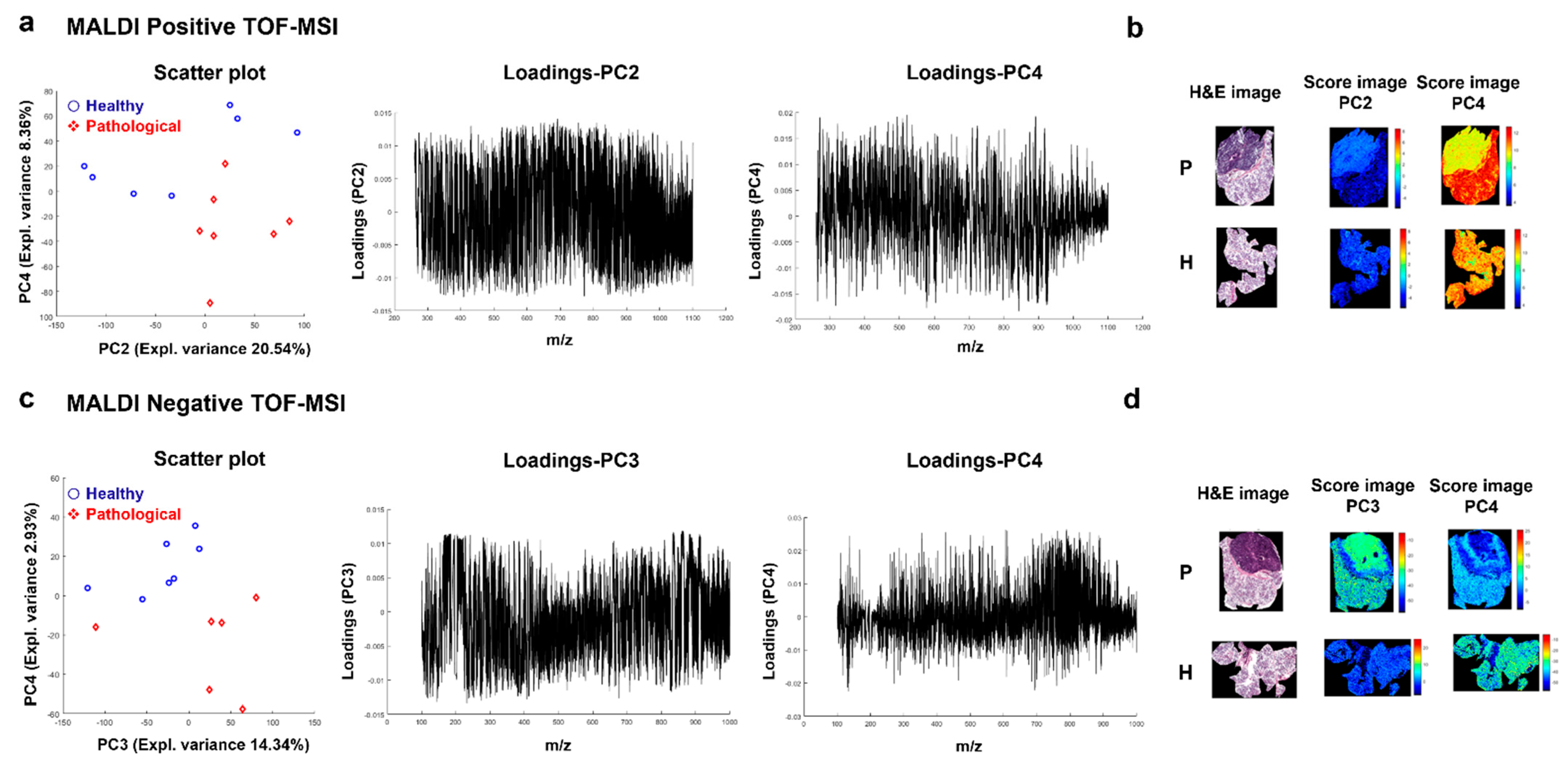
2.3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3.2. Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
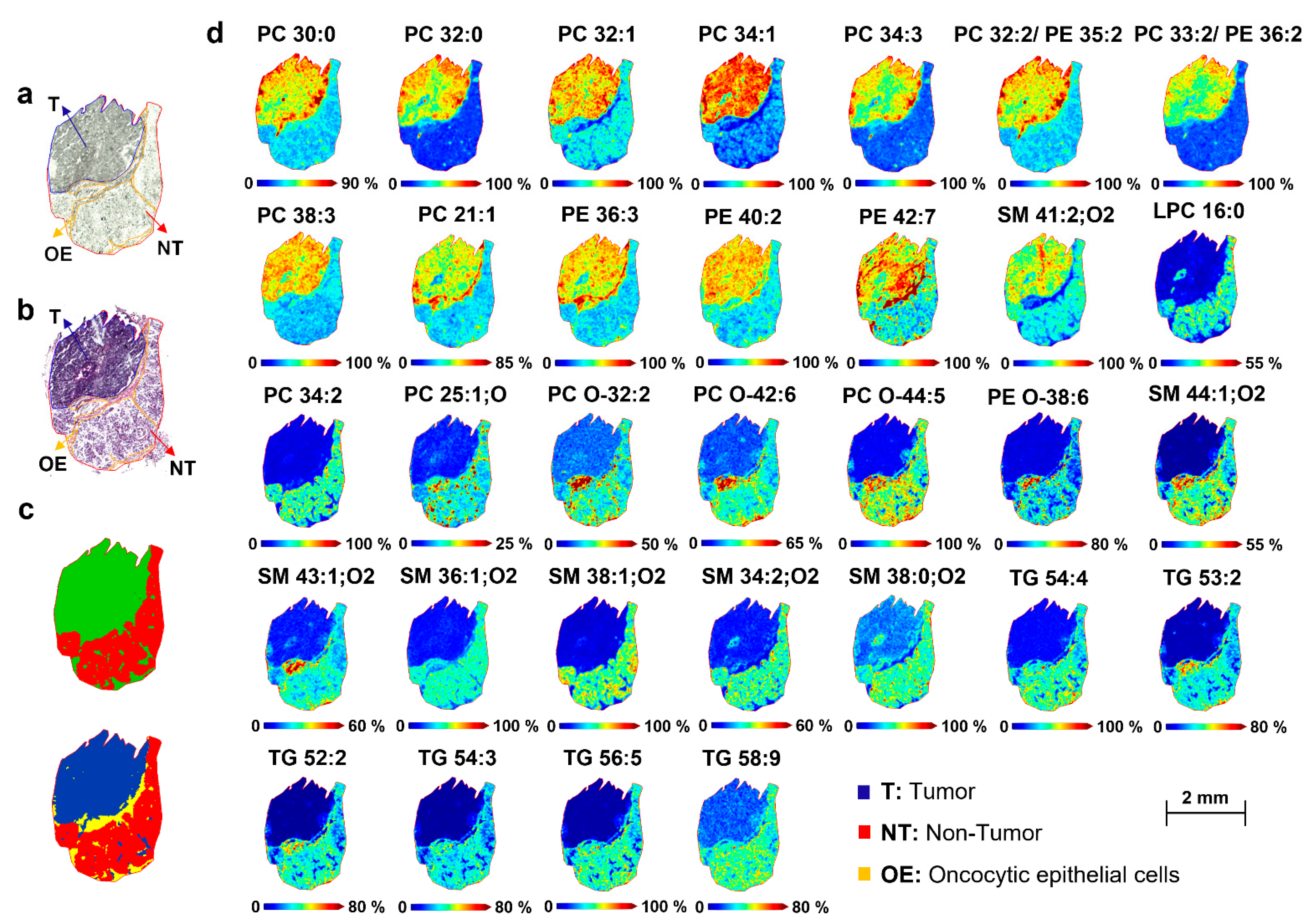
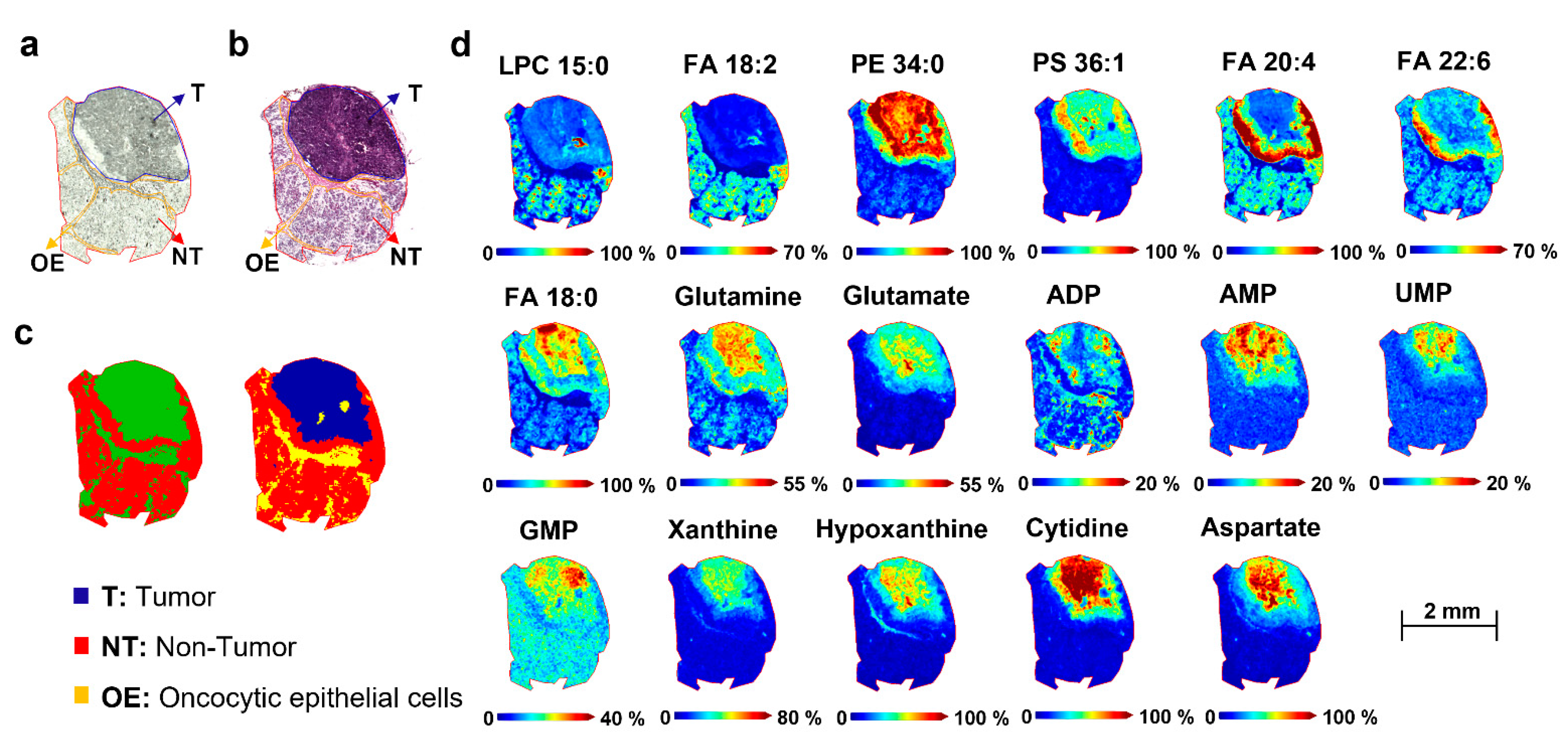
2.4. Spatial Segmentation of MALDI-MSI Data and Specific m/z Values Colocalize with Healthy or Tumor Parotid Region
2.5. Spatial Discrimination of Metabolome and Lipidome Profiles in Parotid Gland Tumor Tissues by MALDI-MSI
2.5.1. Lipidome Differences between Tumor and Non-Tumor Areas of Parotid Biopsies
2.5.2. Metabolome Differences between Tumor and Non-Tumor Areas of Parotid Biopsies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants and Sample Collection
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Tissue Sample Preparation for MALDI-MSI
3.4. Sample Preparation for MALDI-MSI Analysis of Lipids and Metabolites
3.5. MALDI-MSI Analysis
3.6. Metabolite and Lipid Annotation by MALDI-FT-ICR-MS
3.7. Imaging Data Analysis
3.8. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Stains to MSI Co-Registration
3.10. Statistical Analysis by SCiLS Lab Software
3.11. Multivariate Data Analysis
3.11.1. Data Pre-Processing
3.11.2. Exploratory Analysis
3.11.3. Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
- ○
- Classification accuracy (or percent correct classification rate), which is defined as:
- ○
- Sensitivity, i.e., the percent true positive rate:
- ○
- Specificity, i.e., the true negative rate:
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Żurek, M.; Rzepakowska, A.; Jasak, K.; Niemczyk, K. The Epidemiology of Salivary Glands Pathologies in Adult Population over 10 Years in Poland—Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatta, G.; Guzzo, M.; Locati, L.D.; McGurk, M.; Prott, F.J. Major and Minor Salivary Gland Tumours. In Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, J.L.; Ismaila, N.; Beadle, B.; Caudell, J.J.; Chau, N.; Deschler, D.; Glastonbury, C.; Kaufman, M.; Lamarre, E.; Lau, H.Y.; et al. Management of Salivary Gland Malignancy: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1909–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherl, C. Rare Diseases of the Salivary Glands and of Facial Nerve. Laryngorhinootologie 2021, 100, S1–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.P.; Wong, K.T.; King, A.D.; Ahuja, A.T. Imaging of Salivary Gland Tumours. Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 66, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.S.; Akhtar, S.; Junaid, M.; Awan, S.; Aftab, K. Diagnostic Accuracy of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Parotid Lesions. ISRN Surg. 2011, 2011, 721625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torresano, L.; Nuevo-Tapioles, C.; Santacatterina, F.; Cuezva, J.M. Metabolic Reprogramming and Disease Progression in Cancer Patients. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, R.D.; Dunn, W.; Schmidt, M.A.; Gross, S.S.; Kirwan, J.A.; Cascante, M.; Brennan, L.; Wishart, D.S.; Oresic, M.; Hankemeier, T.; et al. Metabolomics Enables Precision Medicine: “A White Paper, Community Perspective. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, D.; Vestuto, V.; Ferraro, M.R.; Ciaglia, T.; Pecoraro, C.; Sommella, E.; Cascioferro, S.; Salviati, E.; Novi, S.; Tecce, M.F.; et al. Metabolomics-Assisted Discovery of a New Anticancer GLS-1 Inhibitor Chemotype from a Nortopsentin-Inspired Library: From Phenotype Screening to Target Identification. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 234, 114233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searfoss, R.; Shah, P.; Ofori-Mensa, K.; Bussberg, V.; Tolstikov, V.; Greenwood, B.; Li, H.; Richardson, K.; Miller, G.M.; DeCicco, C.; et al. Impact of Hemolysis on Multi-OMIC Pancreatic Biomarker Discovery to Derisk Biomarker Development in Precision Medicine Studies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, J.; Tafuro, M.; Lombardi, M.; Scala, G.; Richards, S.M.; Symes, S.J.K.; Ascierto, P.A.; Delrio, P.; Tatangelo, F.; Buonerba, C.; et al. A Metabolomics-Based Screening Proposal for Colorectal Cancer. Metabolites 2022, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, M.; Marino, C.; Buonocore, M.; Santoro, A.; Sommella, E.; Merciai, F.; Salviati, E.; De Rosa, A.; Nuzzo, T.; Errico, F.; et al. Prenatal and Early Postnatal Cerebral d -Aspartate Depletion Influences l -Amino Acid Pathways, Bioenergetic Processes, and Developmental Brain Metabolism. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Toward Merging Untargeted and Targeted Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Li, T.; Song, X.; Huang, L.; Zang, Q.; Xu, J.; Bi, N.; Jiao, G.; Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Spatially Resolved Metabolomics to Discover Tumor-Associated Metabolic Alterations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández, L.P.; Gómez de Cedrón, M.; Ramírez de Molina, A. Alterations of Lipid Metabolism in Cancer: Implications in Prognosis and Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 6577420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohavanichbutr, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Gu, H.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Djukovic, D.; Buas, M.F.; Raftery, D.; Chen, C. Salivary Metabolite Profiling Distinguishes Patients with Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Normal Controls. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krasny, L.; Hoffmann, F.; Ernst, G.; Trede, D.; Alexandrov, T.; Havlicek, V.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Von Eggeling, F.; Crecelius, A.C. Spatial Segmentation of MALDI FT-ICR MSI Data: A Powerful Tool to Explore the Head and Neck Tumor in Situ Lipidome. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 26, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Răchieriu, C.; Eniu, D.T.; Moiş, E.; Graur, F.; Socaciu, C.; Socaciu, M.A.; Hajjar, N.A. Lipidomic Signatures for Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis and Progression Using Uplc-qtof-esi+ms. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanetake, H.; Kato-Kogoe, N.; Terada, T.; Kurisu, Y.; Hamada, W.; Nakajima, Y.; Hirose, Y.; Ueno, T.; Kawata, R. Short Communication: Distribution of Phospholipids in Parotid Cancer by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Imaging Mass Spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Takizawa, Y.; Hayasaka, T.; Masaki, N.; Kusama, Y.; Su, J.; Mineta, H.; Setou, M. Increased Phosphatidylcholine (16:0/16:0) in the Folliculus Lymphaticus of Warthin Tumor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5815–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiliro, C.; Firestein, B.L. Mechanisms of Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells Supporting Enhanced Growth and Proliferation. Cells 2021, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, M.; Palisi, A.; Rossi, G.; Stillitano, I.; Faiella, F.; Montoro, P.; Rodriquez, M.; Palladino, R.; D’Ursi, A.M.; Romano, R. Saliva of Patients Affected by Salivary Gland Tumour: An NMR Metabolomics Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommella, E.; Verna, G.; Liso, M.; Salviati, E.; Esposito, T.; Carbone, D.; Pecoraro, C.; Chieppa, M.; Campiglia, P. Hop-Derived Fraction Rich in Beta Acids and Prenylflavonoids Regulates the Inflammatory Response in Dendritic Cells Differently from Quercetin: Unveiling Metabolic Changes by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 12800–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-De-La-Fuente, A.; Godzien, J.; Saugar, S.; Garcia-Carmona, R.; Badran, H.; Wishart, D.S.; Barbas, C.; Otero, A. CEU Mass Mediator 3.0: A Metabolite Annotation Tool. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed Minimum Reporting Standards for Chemical Analysis: Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, O.; Strohschein, K.; Nebrich, G.; Oetjen, J.; Trede, D.; Thiele, H.; Alexandrov, T.; Giavalisco, P.; Duda, G.N.; von Roth, P.; et al. MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry: Discrimination of Pathophysiological Regions in Traumatized Skeletal Muscle by Characteristic Peptide Signatures. Proteomics 2014, 14, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, T.; Becker, M.; Deininger, S.O.; Ernst, G.; Wehder, L.; Grasmair, M.; Von Eggeling, F.; Thiele, H.; Maass, P. Spatial Segmentation of Imaging Mass Spectrometry Data with Edge-Preserving Image Denoising and Clustering. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6535–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beloribi-Djefaflia, S.; Vasseur, S.; Guillaumond, F. Lipid Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, Z. Significantly Increased Monounsaturated Lipids Relative to Polyunsaturated Lipids in Six Types of Cancer Microenvironment Are Observed by Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Han, J.; Hardie, D.B.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Borchers, C.H. Metabolomic Profiling of Prostate Cancer by Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry Imaging Using Matrix Coating Assisted by an Electric Field (MCAEF). Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, K.; Jiang, L.; Greenwood, T.R.; Glunde, K.; Heeren, R.M.A. Mass Spectrometry Images Acylcarnitines, Phosphatidylcholines, and Sphingomyelin in MDA-MB-231 Breast Tumor Models. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iorio, E.; Ricci, A.; Bagnoli, M.; Elena Pisanu, M.; Castellano, G.; Di Vito, M.; Venturini, E.; Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Mezzanzanica, D.; et al. Tumor and Stem Cell Biology Activation of Phosphatidylcholine Cycle Enzymes in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Wang, J. Lipidomics Identified Lyso-Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylethanolamine as Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Laryngeal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 646779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denti, V.; Andersen, M.K.; Smith, A.; Bofin, A.M.; Nordborg, A.; Magni, F.; Moestue, S.A.; Giampà, M. Reproducible Lipid Alterations in Patient-Derived Breast Cancer Xenograft Ffpe Tissue Identified with Maldi Msi for Pre-Clinical and Clinical Application. Metabolites 2021, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.K.; Høiem, T.S.; Claes, B.S.R.; Balluff, B.; Martin-Lorenzo, M.; Richardsen, E.; Krossa, S.; Bertilsson, H.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Rye, M.B.; et al. Spatial Differentiation of Metabolism in Prostate Cancer Tissue by MALDI-TOF MSI. Cancer Metab. 2021, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Attencourt, C.; Colin, E.; Boudahi, A.; Tebbakha, R.; Salzet, M.; Testelin, S.; Dakpé, S.; Fournier, I. Mass Spectrometry-Based Differentiation of Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Nontumor Regions With the SpiderMass Technology. Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 827360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogretmen, B.; Avenue, A. Sphingolipid Metabolism in Cancer Signalling and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Carvalho, M.; Aveiro, S.S.; Melo, T.; Domingues, M.R.; Macedo-Silva, C.; Coimbra, N.; Jerónimo, C.; Henrique, R.; Bastos, M.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomics and Lipidomics Profiling of Prostate Cancer Tissue Reveals Metabolic Dysregulations Associated with Disease Development. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Terada, N.; Inoue, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakayama, K.; Okada, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Uegaki, M.; Utsunomiya, N.; et al. Decreased Expression of Lysophosphatidylcholine (16:0/OH) in High Resolution Imaging Mass Spectrometry Independently Predicts Biochemical Recurrence after Surgical Treatment for Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2015, 75, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.Y.; Yeon, A.; Shahid, M.; Cho, E.; Sairam, V.; Figlin, R.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J. Reprogrammed Lipid Metabolism in Bladder Cancer with Cisplatin Resistance. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13231–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mika, A.; Pakiet, A.; Czumaj, A.; Kaczynski, Z.; Liakh, I.; Kobiela, J.; Perdyan, A.; Adrych, K.; Makarewicz, W.; Sledzinski, T. Decreased Triacylglycerol Content and Elevated Contents of Cell Membrane Lipids in Colorectal Cancer Tissue: A Lipidomic Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Kitabatake, K.; Sugano, A.; Nakamura, M.; Kaneko, M.; Ota, S.; Hiwatari, K.; Enomoto, A.; Soga, T.; et al. Identification of Salivary Metabolomic Biomarkers for Oral Cancer Screening. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Yang, X.; Narayanan, R.; Shankar, V.; Ethiraj, S.; Wang, X.; Duan, N.; Ni, Y.H.; Hu, Q.; Zare, R.N. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed from Saliva Metabolic Profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16167–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnikov, B.; Joo Jeon, Y.; Smith, J.W.; Ronai, Z.E.A. Right on TARGET: Glutamine metabolism in cancer. Oncoscience 2015, 2, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilillo, M.; Ait-Belkacem, R.; Esteve, C.; Pellegrini, D.; Nicolardi, S.; Costa, M.; Vannini, E.; De Graaf, E.L.; Caleo, M.; McDonnell, L.A. Ultra-High Mass Resolution MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of Proteins and Metabolites in a Mouse Model of Glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sládková, K.; Houška, J.; Havel, J. Laser Desorption Ionization of Red Phosphorus Clusters and Their Use for Mass Calibration in Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 3114–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genangeli, M.; Heijens, A.M.M.; Rustichelli, A.; Schuit, N.D.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Cifani, C.; Vittori, S.; Siegel, T.P.; Heeren, R.M.A. MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging to Investigate Lipid and Bile Acid Modifications Caused by Lentil Extract Used as a Potential Hypocholesterolemic Treatment. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid Extraction by Methyl-Terf-Butyl Ether for High-Throughput Lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sommella, E.; Carrizzo, A.; Merciai, F.; Di Sarno, V.; Carbone, D.; De Lucia, M.; Musella, S.; Vecchione, C.; Campiglia, P. Analysis of the Metabolic Switch Induced by the Spirulina Peptide SP6 in High Fat Diet ApoE-/- Mice Model: A Direct Infusion FT-ICR-MS Based Approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 195, 113865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, T.; Kobarg, J.H. Efficient Spatial Segmentation of Large Imaging Mass Spectrometry Datasets with Spatially Aware Clustering. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, i230–i238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Race, A.M.; Styles, I.B.; Bunch, J. Inclusive Sharing of Mass Spectrometry Imaging Data Requires a Converter for All. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 5111–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, P.H.C. Parametric Time Warping. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchi, M.; Biancolillo, A.; Marini, F. Chemometric Methods for Classification and Feature Selection, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indahl, U.G.; Martens, H.; Næs, T. From Dummy Regression to Prior Probabilities in PLS-DA. J. Chemom. 2007, 21, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Johansson, E.; Cocchi, M. 3D QSAR in Drug Design: Theory, Methods and Applications. ESCOM Leiden Holl. 1993, 1, 523–550. [Google Scholar]
- Capitoli, G.; Piga, I.; Galimberti, S.; Leni, D.; Pincelli, A.I.; Garancini, M.; Clerici, F.; Mahajneh, A.; Brambilla, V.; Smith, A.; et al. MALDI-MSI as a Complementary Diagnostic Tool in Cytopathology: A Pilot Study for the Characterization of Thyroid Nodules. Cancers 2019, 11, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| MALDI-Positive TOF-MSI | ||||||||
| Range | nVar | nLVs | Accuracy (CC%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |||
| Training and cross-validation (CV) | ||||||||
| Training | CV | Training | CV | Training | CV | |||
| Full | 23,694 | 3 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| VIP | 441 | 1 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Test set | ||||||||
| Full | 69.00 | 76.31 | 64.44 | |||||
| VIP | 69.00 | 76.31 | 64.44 | |||||
| MALDI-Negative TOF-MSI | ||||||||
| nLVs | nLVs | nLVs | Accuracy (CC%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | |||
| Training and cross-validation (CV) | ||||||||
| Training | CV | Training | CV | Training | CV | |||
| Full | 30,327 | 3 | 100.00 | 92.68 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 85.71 |
| VIP | 245 | 3 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Test set | ||||||||
| Full | 68.04 | 90.68 | 53.72 | |||||
| VIP | 68.04 | 90.68 | 53.72 | |||||
| Compound | m/z | Adduct | Molecular Formula | VIP Score | Pearson Correl. Coeff. (r) | Modulation in Tumor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAR 16:0 | 400.3 | [M+H]+ | C23H45NO4 | 2.580 | ↓ | |
| Cer 42:2;O | 632.6 | [M+H]+ | C42H81NO2 | 2.188 | ↑ | |
| DG O-36:4 | 603.5 | [M+H]+ | C39H70O4 | 2.001 | ↓ | |
| LPC 15:0 | 480.3 | [M-H]− | C23H48NO7P | 2.172 | ↓ | |
| LPC 16:0 | 496.3 | [M+H]+ | C24H50NO7P | 2.078 | ↓ | |
| PC 30:0 | 744.4 | [M+K]+ | C38H76NO8P | 0.563 | ↑ | |
| PC 32:0 | 772.5 | [M+K]+ | C43H82NO8P | 2.032 | 0.702 | ↑ |
| PC 32:1 | 770.5 | [M+K]+ | C40H78NO8P | 2.007 | ↑ | |
| PC 34:1 | 798.5 | [M+K]+ | C42H82NO8P | 0.687 | ↑ | |
| PC 34:3 | 756.5 | [M+H]+ | C42H78NO8P | 0.622 | ↑ | |
| PC 32:2 or PE 35:2 | 730.5 | [M+H]+ | C40H76NO8P | 2.036 | ↑ | |
| PC 33:2 or PE 36:2 | 744.5 | [M+H]+ | C41H78NO8P | 0.563 | ↑ | |
| PC 34:2 | 758.5 | [M+K]+ | C42H80NO8P | 2.282 | 0.679 | ↓ |
| PC 38:3 | 812.6 | [M+H]+ | C46H86NO8P | 0.563 | ↑ | |
| PC 21:1 | 578.4 | [M+H]+ | C29H56NO8P | 2.169 | ↑ | |
| PC 25:1;O | 650.4 | [M+H]+ | C33H64NO9P | 0.503 | ↓ | |
| PC O-32:2 | 551.5 | [M+H]+ | C35H66O4 | 3.525 | ↓ | |
| PC O-42:6 | 870.6 | [M+Na]+ | C50H90NO7P | 0.519 | ↓ | |
| PC O-44:5 | 900.7 | [M+Na]+ | C52H96NO7P | 2.086 | ↓ | |
| PE 34:0 | 718.5 | [M-H]− | C39H78NO8P | 0.592 | ↑ | |
| PE 36:3 | 742.5 | [M+H]+ | C41H76NO8P | 0.610 | ↑ | |
| PE 40:2 | 800.5 | [M+H]+ | C45H86NO8P | 0.742 | ↑ | |
| PE 42:7 | 818.4 | [M+H]+ | C47H80NO8P | 2.198 | ↑ | |
| PE O-38:6 | 750.5 | [M+H]+ | C43H76NO7P | 2.045 | 0.681 | ↓ |
| PS O-30:2 | 712.4 | [M+Na]+ | C36H68NO9P | 0.633 | ↓ | |
| PS 36:1 | 524.3 | [M-H]− | C24H48NO9P | 0.552 | ↑ | |
| SM 44:1;O2 | 881.6 | [M+K]+ | C49H99N2O6P | 4.523 | ↓ | |
| SM 41:2;O2 | 821.6 | [M+Na]+ | C46H91N2O6P | 2.425 | ↑ | |
| SM 43:2;O2 | 827.6 | [M+H]+ | C48H95N2O6P | 2.079 | ↓ | |
| SM 36:1;O2 | 731.6 | [M+H]+ | C41H83N2O6P | 2.011 | 0.667 | ↓ |
| SM 38:1;O2 | 781.5 | [M+Na]+ | C43H87N2O6P | 2.617 | 0.681 | ↓ |
| SM 34:2;O2 | 723.5 | [M+Na]+ | C39H77N2O6P | 2.055 | 0.680 | ↓ |
| SM 38:0;O2 | 761.5 | [M+H]+ | C43H89N2O6P | 2.001 | ↓ | |
| TG 54:4 | 883.7 | [M+H]+ | C57H102O6 | 2.092 | ↓ | |
| TG 53:2 | 895.7 | [M+Na]+ | C56H104O6 | 2.149 | ↓ | |
| TG 52:2 | 881.7 | [M+Na]+ | C55H102O6 | 2.551 | ↓ | |
| TG 54:3 | 907.7 | [M+Na]+ | C57H104O6 | 2.198 | ↓ | |
| TG 56:5 | 909.7 | [M+H]+ | C59H104O6 | 2.001 | ↓ | |
| TG 58:9 | 929.7 | [M+H]+ | C61H100O6 | 2.265 | ↓ | |
| FA 18:2 | 279.2 | [M-H]− | C18H32O2 | 0.529 | ↓ | |
| FA 20:4 | 303.2 | [M-H]− | C20H32O2 | 0.544 | ↓ | |
| FA 22:6 | 327.2 | [M-H]− | C22H32O2 | 0.519 | ↓ | |
| FA 18:0 | 283.2 | [M-H]− | C18H36O2 | 2.023 | ↓ | |
| Glutamine | 145.0 | [M-H]− | C5H10N2O3 | 0.662 | ↑ | |
| Glutamate | 146.0 | [M-H]− | C5H9NO4 | 0.521 | ↑ | |
| ADP | 426.0 | [M-H]− | C10H15N5O10P2 | 2.034 | ↑ | |
| AMP | 346.0 | [M-H]− | C10H14N5O7P | 2.049 | 0.623 | ↑ |
| UMP | 323.0 | [M-H]− | C9H13N2O9P | 2.089 | ↑ | |
| GMP | 362.0 | [M-H]− | C10H14N5O8P | 0.521 | ↑ | |
| Xanthine | 151.0 | [M-H]− | C5H4N4O2 | 2.013 | ↑ | |
| Hypoxanthine | 135.0 | [M-H]− | C5H4N4O | 2.038 | 0.628 | ↑ |
| Cytidine | 242.0 | [M-H]− | C9H13N3O5 | 0.553 | ↑ | |
| Aspartate | 132.0 | [M-H]− | C4H7NO4 | 2.002 | 0.563 | ↑ |
| Parotid Tumor Subjects | |
|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 64 (43–78) |
| Sex (M/F) | 3/8 |
| Tumor histological type (patient classification number): | Warthin Tumor (1, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10) |
| Pleomorphic adenoma (5) | |
| Chronic sialoadenitis (2, 6, 11) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sommella, E.; Salviati, E.; Caponigro, V.; Grimaldi, M.; Musella, S.; Bertamino, A.; Cacace, L.; Palladino, R.; Mauro, G.D.; Marini, F.; et al. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Highlights Specific Metabolome and Lipidome Profiles in Salivary Gland Tumor Tissues. Metabolites 2022, 12, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060530
Sommella E, Salviati E, Caponigro V, Grimaldi M, Musella S, Bertamino A, Cacace L, Palladino R, Mauro GD, Marini F, et al. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Highlights Specific Metabolome and Lipidome Profiles in Salivary Gland Tumor Tissues. Metabolites. 2022; 12(6):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060530
Chicago/Turabian StyleSommella, Eduardo, Emanuela Salviati, Vicky Caponigro, Manuela Grimaldi, Simona Musella, Alessia Bertamino, Luigi Cacace, Remo Palladino, Giuseppe Di Mauro, Federico Marini, and et al. 2022. "MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Highlights Specific Metabolome and Lipidome Profiles in Salivary Gland Tumor Tissues" Metabolites 12, no. 6: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060530
APA StyleSommella, E., Salviati, E., Caponigro, V., Grimaldi, M., Musella, S., Bertamino, A., Cacace, L., Palladino, R., Mauro, G. D., Marini, F., D’Ursi, A. M., & Campiglia, P. (2022). MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Highlights Specific Metabolome and Lipidome Profiles in Salivary Gland Tumor Tissues. Metabolites, 12(6), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060530














