Renin–Angiotensin System in Liver Metabolism: Gender Differences and Role of Incretins
Abstract
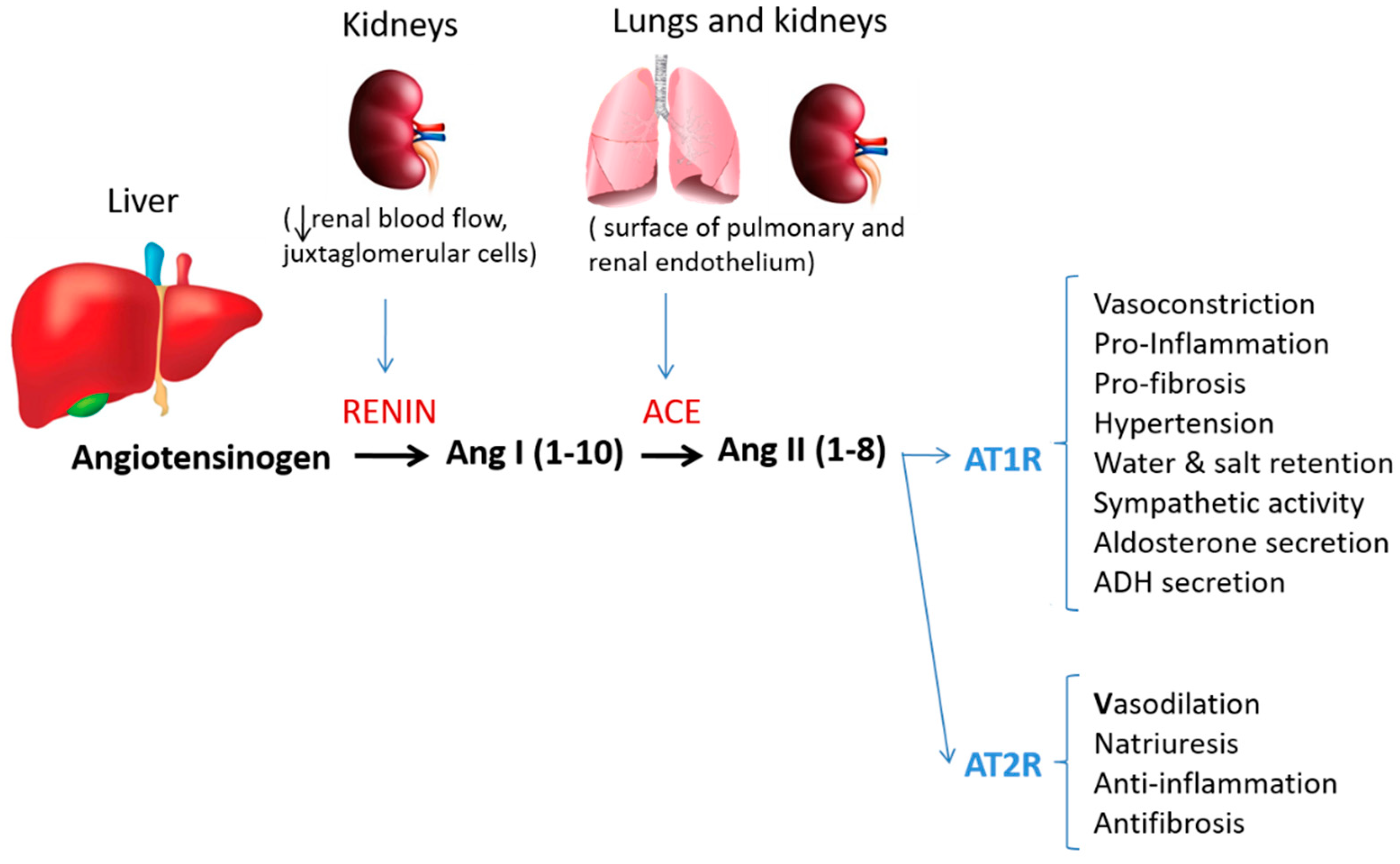
1. Introduction
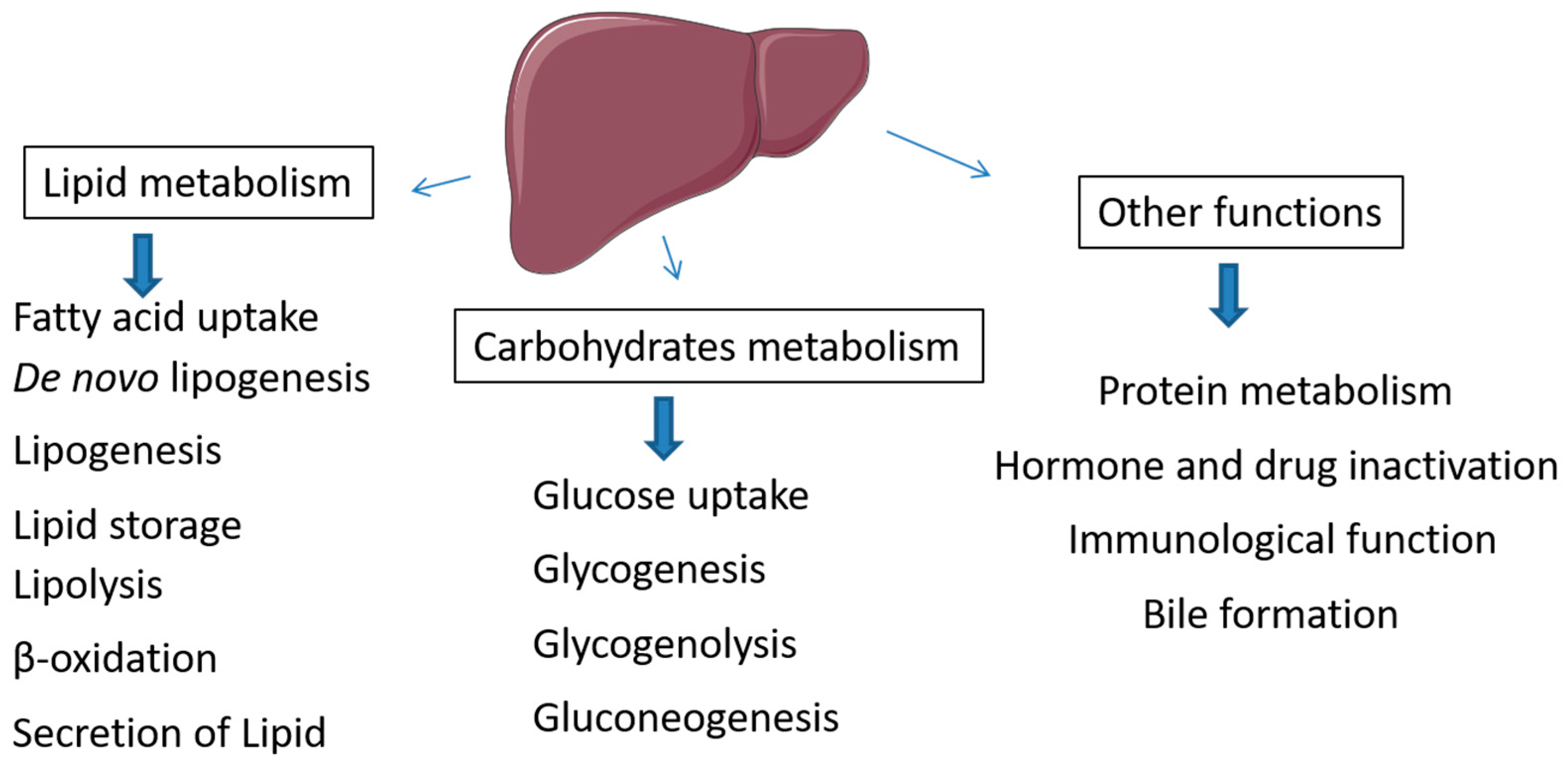
2. Metabolic Role of Liver in Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism
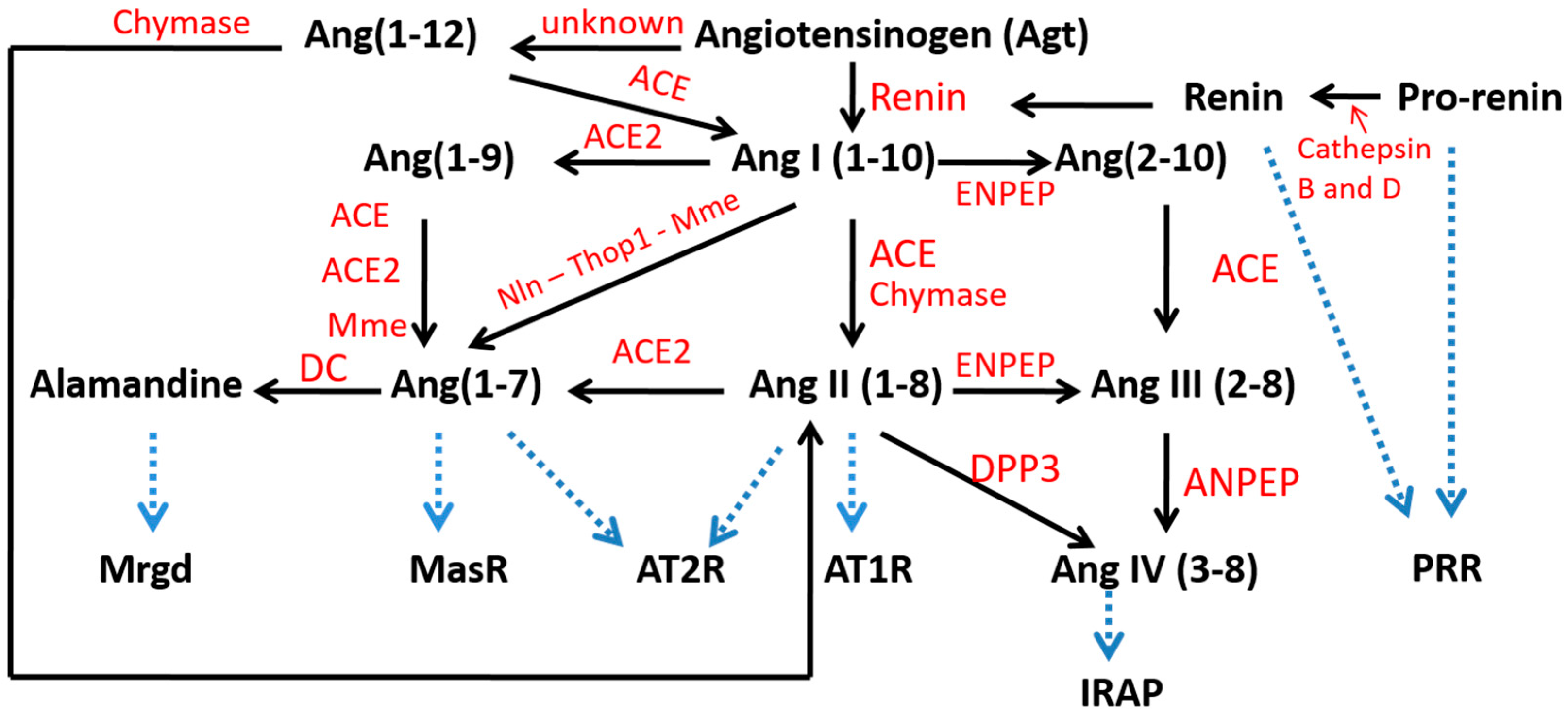
3. Local Hepatic RAS
3.1. Angiotensinogen Regulation in Liver
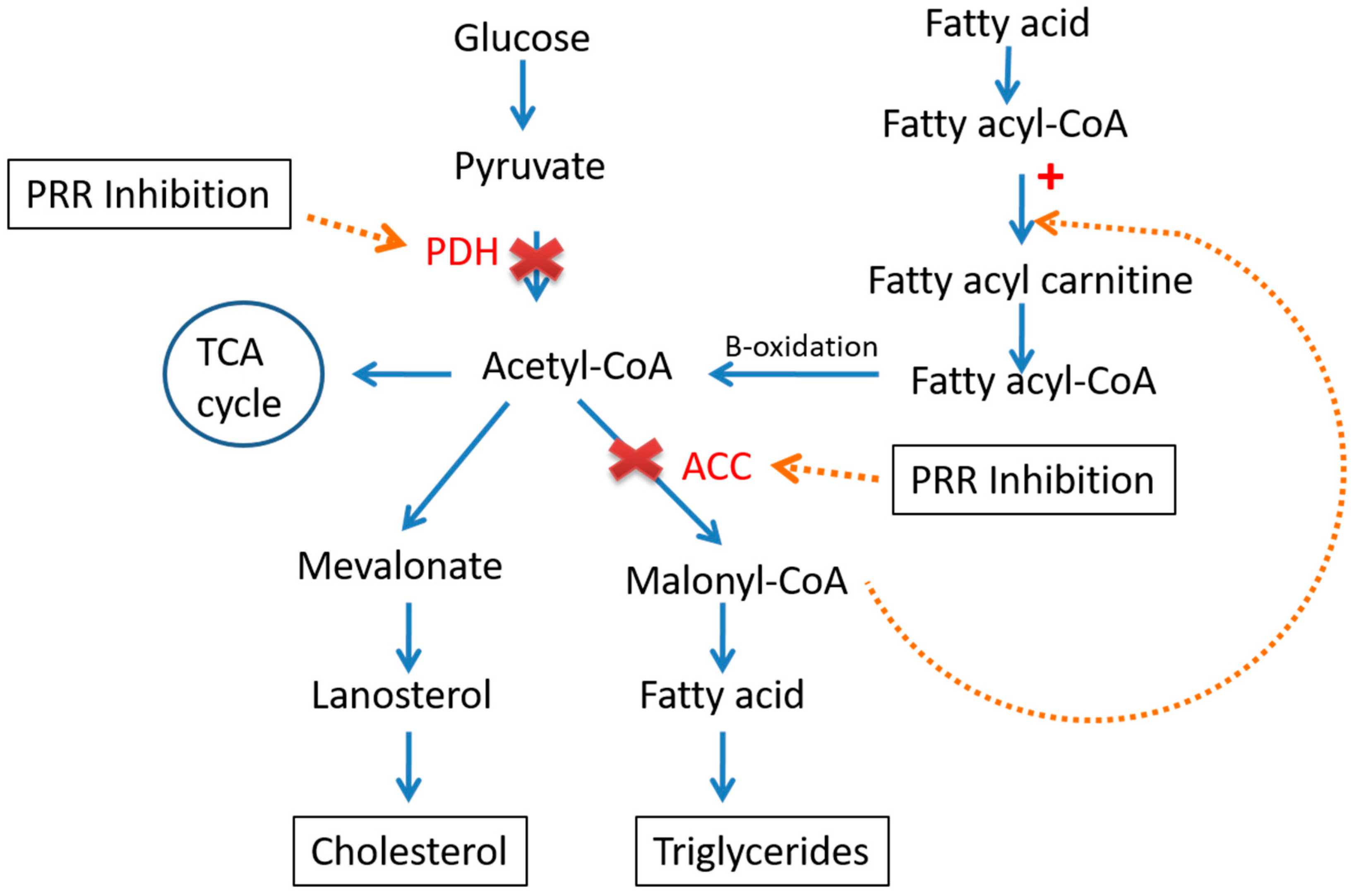
3.2. Pro-Renin Receptor in Liver Metabolism
3.3. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) and Angiotensin II
3.4. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) and Ang(1-7)
4. Crosstalk between RAS, Liver Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism
5. Gender in RAS, Liver Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism
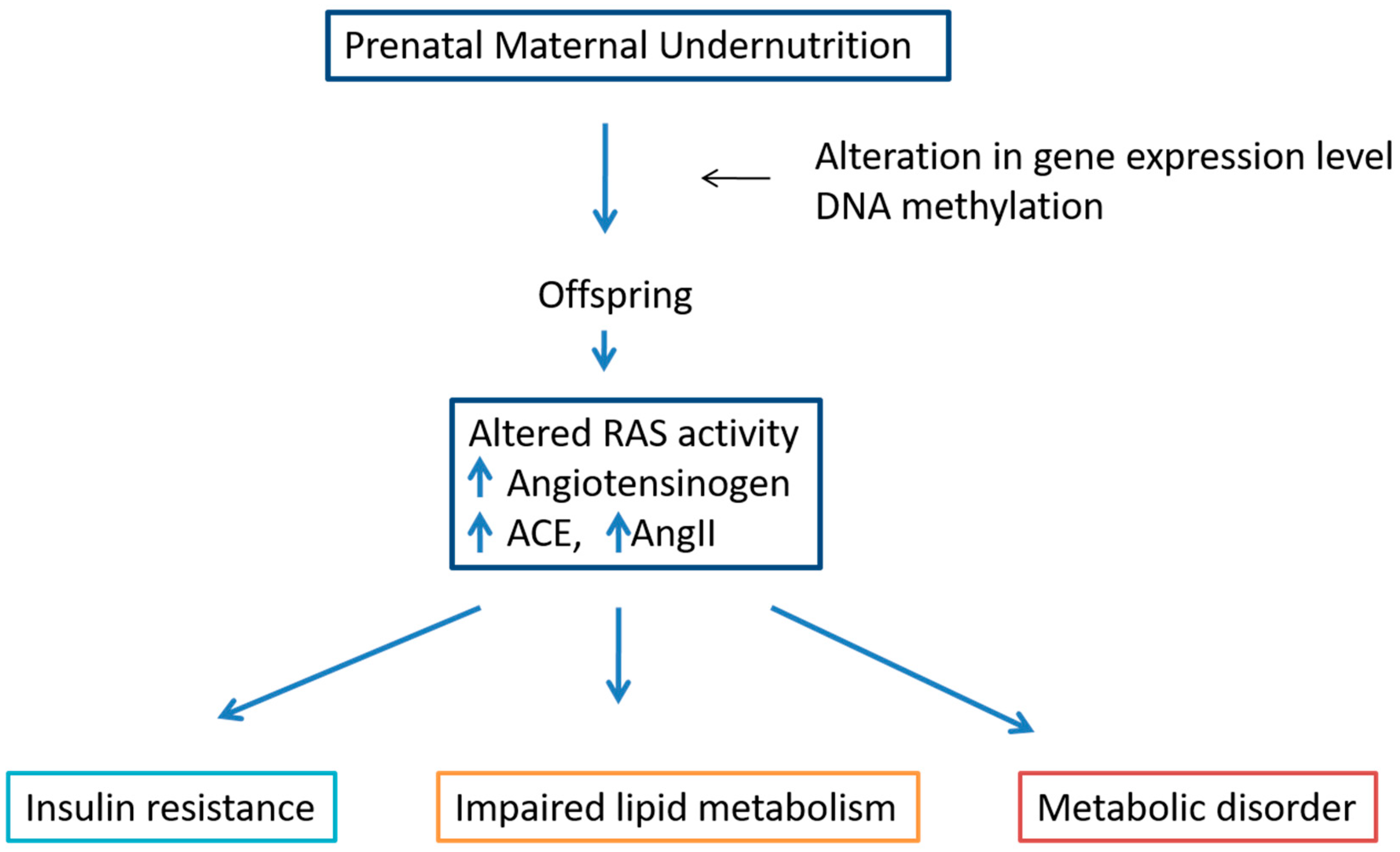
6. Effect of Perinatal Undernutrition on RAS, Liver Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism
7. GLP-1R Agonists Regulate the Liver Lipids and Carbohydrate Metabolism
8. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Silva, A.C.S.; Miranda, A.S.; Rocha, N.P.; Teixeira, A.L. Renin angiotensin system in liver diseases: Friend or foe? World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3396–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastra-Lastra, G.; Sowers, J.R.; Restrepo-Erazo, K.; Manrique-Acevedo, C.; Lastra-González, G. Role of aldosterone and angiotensin II in insulin resistance: An update. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Macêdo, S.M.; Guimarães, T.A.; Feltenberger, J.D.; Santos, S.H.S. The role of renin-angiotensin system modulation on treatment and prevention of liver diseases. Peptides 2014, 62, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadori, G.; Saile, B. Inflammation, damage repair, immune cells, and liver fibrosis: Specific or nonspecific, this is the question. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; dos Santos, R.A.S.; Dias, F.L.D.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; e Silva, A.C.S. Renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ma, X.; Xuan, X.; Deng, H.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, L. Liraglutide Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice by Regulating the Local Renin-Angiotensin System. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, P.; Nielsen, M.O. Impacts of prenatal nutrition on animal production and performance: A focus on growth and metabolic and endocrine function in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.C.; Mehrabian, M.; Lusis, A.J. Sex differences in metabolism and cardiometabolic disorders. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2018, 29, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, E.; Guven, C. Local Renin angiotensin System at liver and crosstalk with hepatic diseases. In Renin-Angiotensin System; Tolekova, A.N., Ed.; Intech Open Book Series; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorfer, B. Sexual Dimorphism in Human Lipid Metabolism. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.Y.; Tosh, D.N.; Garg, A.; Mansano, R.; Ross, M.G.; Desai, M. Gender-specific programmed hepatic lipid dysregulation in intrauterine growth-restricted offspring. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 196, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiriet, M. Hyperlipidemias and Obesity. In Vasculopathies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 331–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.S.; Sampaio, W.O.; Alzamora, A.C.; Motta-Santos, D.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1–7)/MAS Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Focus on Angiotensin-(1–7). Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 505–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidikova, P.; Svitok, P.; Herichova, I. Sex and salt intake dependent renin-angiotensin plasticity in the liver of the rat. Endocr. Regul. 2019, 53, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neo, J.H.; I Ager, E.I.; Angus, P.W.; Zhu, J.; Herath, C.B.; Christophi, C. Changes in the renin angiotensin system during the development of colorectal cancer liver metastases. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, E.F. Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of NASH/NAFLD: Could they be a first-class option? Adv. Ther. 2008, 25, 1141–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, Y.; Endoh, D.; Yamashita, T.; Watanabe, T. Expression of Renin in the Rat Liver. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 1998, 27, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Tomita, N.; Yamada, T.; Zhang, L.; Kaneda, Y.; Morishita, R.; Ogihara, T.; Dzau, V.J.; Horiuchi, M. Transcription factor decoy to study the molecular mechanism of negative regulation of renin gene expression in the liver in vivo. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.L.; Ager, E.; Christophi, C. Liver regeneration and tumour stimulation: Implications of the renin-angiotensin system. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, A.; Scavone, C.; Rafaniello, C.; De Angelis, A.; Urbanek, K.; di Mauro, G.; Cappetta, D.; Berrino, L.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. The Role of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in the Heart and Lung: Focus on COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 667254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.C.; Dzau, V.J. The Feedback Regulation of Angiotensinogen Production by Components of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Circ. Res. 1983, 52, 328–334. Available online: http://ahajournals.org (accessed on 25 September 2021). [CrossRef]
- Klett, C.; Nobiling, R.; Gierschik, P.; Hackenthal, E. Angiotensin II stimulates the synthesis of angiotensinogen in hepatocytes by inhibiting adenylyl cyclase activity and stabilizing angiotensinogen mRNA. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1993, 268, 25095–25107. [Google Scholar]
- Sernia, C.; Reid, I.A. Stimulation of angiotensinogen production: A dose-related effect of angiotensin II in the conscious dog. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1980, 239, E442–E446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.-S.; Lin, W.-H.; Lai, S.-L.; Lin, H.-Y.; Hsu, W.-M.; Chou, C.-H.; Lee, P.-H. Interleukin-6 Mediates Angiotensinogen Gene Expression during Liver Regeneration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-C.; Lee, K.-C.; Lei, H.-J.; Lan, K.-H.; Huo, T.-I.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chan, C.-C.; Schnabl, B.; Huang, Y.-H.; Hou, M.-C.; et al. (Pro)renin Receptor Knockdown Attenuates Liver Fibrosis Through Inactivation of ERK/TGF-β1/SMAD3 Pathway. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansoè, G.; Aragno, M.; Wong, F. Pathways of hepatic and renal damage through non-classical activation of the renin-angiotensin system in chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2019, 40, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.C.; Fleeman, R.; Arnold, A.C. Sex differences in the metabolic effects of the renin-angiotensin system. Biol. Sex Differ. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Sun, Y.; Lu, H.; Ye, D.; Han, L.; Wang, N.; Daugherty, A.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Su, F.; et al. (Pro)renin Receptor Inhibition Reprograms Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Protects Mice From Diet-Induced Obesity and Hepatosteatosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Li, F.; Takahashi, N. The renin angiotensin system and the metabolic syndrome. Open Hypertens. J. 2010, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.Y.; Eom, Y.W.; Kim, M.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Baik, S.K. Role of the renin-angiotensin system in hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S. Angiotensin II: A key mediator in the development of liver fibrosis and cancer. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2018, 42, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, J.R.; Clouston, A.D.; Ando, Y.; Kelemen, L.I.; Horn, M.J.; Adamson, M.D.; Purdie, D.M.; Powell, E.E. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates the Progression of Rat Hepatic Fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiao, M.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; Yu, H.-R.; Sheen, J.-M.; Lin, I.-C.; Lai, Y.-J.; Tain, Y.-L.; Huang, L.-T.; Tsai, C.-C. Resveratrol ameliorates maternal and post-weaning high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via renin-angiotensin system. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, I.; Gunarathne, L.; Angus, P.; Herath, C. Update on New Aspects of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Hepatic Fibrosis and Portal Hypertension: Implications for Novel Therapeutic Options. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Österreicher, C.H.; Taura, K.; De Minicis, S.; Seki, E.; Penz-Österreicher, M.; Kodama, Y.; Kluwe, J.; Schuster, M.; Oudit, G.Y.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme 2 inhibits liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2009, 50, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksha, I.G.; Gunarathne, L.S.; Asadi, K.; Cunningham, S.C.; Sharland, A.; Alexander, I.E.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Liver-Targeted Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Therapy Inhibits Chronic Biliary Fibrosis in Multiple Drug-Resistant Gene 2-Knockout Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1656–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Jiang, C.; Penninger, J.M. Lessons from SARS: Control of acute lung failure by the SARS receptor ACE2. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 84, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizoń, T.; Rajzer, M.; Wojciechowska, W.; Wach-Pizoń, M.; Drożdż, T.; Wróbel, K.; Gruszka, K.; Rojek, M.; Kameczura, T.; Jurczyszyn, A.; et al. The relationship between plasma renin activity and serum lipid profiles in patients with primary arterial hypertension. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2018, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Zhou, Z.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Sang, J.; Liu, Z. Therapeutic effect of renin angiotensin system inhibitors on liver fibrosis. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2016, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utba, R.M.; Hussain, S.A.; Fadhil, A.A.; Ahmed, A. Effect of Azilsartan, Aliskirenor Their Combination on Body Weightand Adipogenesis of High-fat Diet Induced Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats. Am. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 4, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-F.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.-W. The mechanisms of renin–angiotensin system in hepatocellular carcinoma: From the perspective of liver fibrosis, HCC cell proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis, and corresponding protection measures. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Mourabit, H.E.; Housset, C.; Cadoret, A.; Lemoinne, S. Role of Angiogenesis in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffelfinger, S.C. The Renin Angiotensin System in the Regulation of Angiogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakoo, A.Y.; Sidman, R.L.; Pasqualini, R.; Arap, W. Does the Renin-Angiotensin System Participate in Regulation of Human Vasculogenesis and Angiogenesis? Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9112–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, F.; Shi, T.; Yuan, M.; Xin, Z.; Xie, R.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Yang, J.-K. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1–7)/Mas axis activates Akt signaling to ameliorate hepatic steatosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Toit, E.F.; Donner, D.G. Myocardial Insulin Resistance: An Overview of Its Causes, Effects, and Potential Therapy. In Insulin Resistance; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Magkos, F.; Mittendorfer, B. Gender Differences in Lipid Metabolism and the Effect of Obesity. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 36, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, B.T.; Zhu, L.; Eckel, R.H.; Stafford, J.M. Sex differences in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, D.T.; Miquet, J.G.; González, L.; Sotelo, A.I.; Muñoz, M.C.; Geraldes, P.M.; Giani, J.F.; Dominici, F.P. Mice lacking angiotensin type 2 receptor exhibit a sex-specific attenuation of insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 498, 110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmurzynska, A. Fetal programming: Link between early nutrition, DNA methylation, and complex diseases. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoutre, S.; Montel, V.; Vallez, E.; Pourpe, C.; Delmont, A.; Eury, E.; Verbanck, M.; Dickes-Coopman, A.; Daubersies, P.; Lesage, J.; et al. Transcription profiling in the liver of undernourished male rat offspring reveals altered lipid metabolism pathways and predisposition to hepatic steatosis. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2019, 317, 1094–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Sales, V.M.; Wolf, A.R.; Subramanian, S.; Matthews, T.J.; Chen, M.; Sharma, A.; Gall, W.; Kulik, W.; Cohen, D.E.; et al. Attenuated Effects of Bile Acids on Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity in a Male Mouse Model of Prenatal Undernutrition. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, T.D.A.; Barcala-Jorge, A.S.; Andrade, J.M.O.; Ferreira, E.C.N.; Crespo, T.S.; Batista-Jorge, G.C.; Vieira, C.A.; Lelis, D.D.F.; Paraiso, A.F.; Pinheiro, U.B.; et al. Obesity and malnutrition similarly alter the renin–angiotensin system and inflammation in mice and human adipose. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-C.; Wang, L.-F.; Lu, K.-S.; Chen, C.-M. Effects of maternal undernutrition on renal angiotensin II and chymase in hypertensive offspring. Acta Histochem. 2008, 110, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.C.D.S.; De Menezes, R.C.; Chianca, D.A., Jr. The implication of protein malnutrition on cardiovascular control systems in rats. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hsu, C.-N.; Tain, Y.-L. The Double-Edged Sword Effects of Maternal Nutrition in the Developmental Programming of Hypertension. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Vieira-Rocha, M.; Quintana-Villamandos, B.; Monedero-Cobeta, I.; Prachaney, P.; de Pablo, A.L.; González, M.; Morato, M.; Diniz, C.; Arribas, S. Implication of RAS in Postnatal Cardiac Remodeling, Fibrosis and Dysfunction Induced by Fetal Undernutrition. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz-Chaves, Y.; Toba, L.; Fandiño, J.; González-Matías, L.C.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Mallo, F. The GLP-1 analog, liraglutide prevents the increase of proinflammatory mediators in the hippocampus of male rat pups submitted to maternal perinatal food restriction. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandiño, J.; Vaz, A.A.; Toba, L.; Romaní-Pérez, M.; Matías, L.C.G.; Mallo, F.; Diz-Chaves, Y. Liraglutide Enhances the Activity of the ACE-2/Ang(1–7)/Mas Receptor Pathway in Lungs of Male Pups from Food-Restricted Mothers and Prevents the Reduction of SP-A. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 6920620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; He, H.; Li, S.; Yang, L. Comparison of the Efficacy of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease: Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrinology 2021, 11, 622589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.A.; Mells, J.; Dunham, R.M.; Grakoui, A.; Handy, J.; Saxena, N.K.; Anania, F.A. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is present on human hepatocytes and has a direct role in decreasing hepatic steatosis in vitro by modulating elements of the insulin signaling pathway. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomori, H.; Ando, W. Spatial expression of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor and caveolin-1 in hepatocytes with macrovesicular steatosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghieri, M.; Christensen, A.S.; Andersen, A.; Solini, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Future Perspectives on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and GLP-1/glucagon Receptor Co-agonists in the Treatment of NAFLD. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuani, B.; Pacifici, F.; Della-Morte, D.; Lauro, D. Glucagon Like Peptide 1 and MicroRNA in Metabolic Diseases: Focusing on GLP1 Action on miRNAs. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulies, K.B.; Anstrom, K.J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Redfield, M.M.; Shah, M.R.; Braunwald, E.; Cappola, T.P. GLP-1 Agonist Therapy for Advanced Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fandiño, J.; Toba, L.; González-Matías, L.C.; Diz-Chaves, Y.; Mallo, F. GLP-1 receptor agonist ameliorates experimental lung fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.-R.; Wang, J.-L.; Ren, H.-Z.; Shi, X.-L. Lipometabolism and Glycometabolism in Liver Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1287127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowacka-Woszuk, J.; Madeja, Z.E.; Chmurzynska, A. Prenatal caloric restriction alters lipid metabolism but not hepatic Fasn gene expression and methylation profiles in rats. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, P. The Renin-Angiotensin System: Where Do We Stand, and What Is the Future? Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 125S–126S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastoor, Z.; Diz-Chaves, Y.; González-Matías, L.C.; Mallo, F. Renin–Angiotensin System in Liver Metabolism: Gender Differences and Role of Incretins. Metabolites 2022, 12, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050411
Mastoor Z, Diz-Chaves Y, González-Matías LC, Mallo F. Renin–Angiotensin System in Liver Metabolism: Gender Differences and Role of Incretins. Metabolites. 2022; 12(5):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050411
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastoor, Zainab, Yolanda Diz-Chaves, Lucas C. González-Matías, and Federico Mallo. 2022. "Renin–Angiotensin System in Liver Metabolism: Gender Differences and Role of Incretins" Metabolites 12, no. 5: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050411
APA StyleMastoor, Z., Diz-Chaves, Y., González-Matías, L. C., & Mallo, F. (2022). Renin–Angiotensin System in Liver Metabolism: Gender Differences and Role of Incretins. Metabolites, 12(5), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050411





