Metabolomic Associations of Asthma in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Sample Characteristics
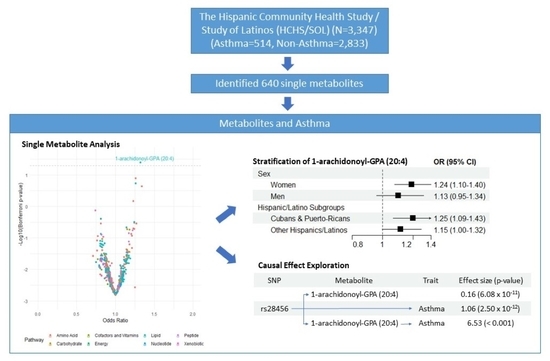
2.2. Single Metabolites and Asthma
2.3. Metabolite Modules and Asthma
2.4. Stratification Analysis by Sex and Hispanic/Latino High-Risk Backgrounds
2.5. Causal Effect Exploration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Samples
4.2. Metabolite Profiling
4.3. Ascertainment of Asthma and Covariates
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Most Recent National Asthma Data. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/asthma/most_recent_national_asthma_data.htm (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Bai, Y.; Hillemeier, M.M.; Lengerich, E.J. Racial/ethnic disparities in symptom severity among children hospitalized with asthma. J. Health Care Poor Underserved 2007, 18, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, M.; Paxson, C.; Waldfogel, J. Racial disparities in childhood asthma in the United States: Evidence from the National Health Interview Survey, 1997 to 2003. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e868–e877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forno, E.; Celedon, J.C. Asthma and ethnic minorities: Socioeconomic status and beyond. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 9, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunninghake, G.M.; Weiss, S.T.; Celedón, J.C. Asthma in Hispanics. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.B.; Zhang, Z. Allergic asthma: Influence of genetic and environmental factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32883–32889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Moon, J.Y.; Laurie, C.C.; North, K.E.; Sanchez-Johnsen, L.A.P.; Davis, S.; Yu, B.; Nyenhuis, S.M.; Kaplan, R.; Rastogi, D.; et al. Genetic predisposition to obesity is associated with asthma in US Hispanics/Latinos: Results from the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Allergy 2018, 73, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.T.; Wenzel, S.; Postma, D.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Renz, H.; Sly, P.D. Asthma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsahai, J.M.; Hansbro, P.M.; Wark, P.A.B. Mechanisms and Management of Asthma Exacerbations. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.E.; Xu, Y.J.; Xu, F.; Cheng, C.; Peh, H.Y.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Wong, W.S.; Ong, C.N. Metabolomics reveals altered metabolic pathways in experimental asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol 2013, 48, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reisdorph, N.; Wechsler, M.E. Utilizing metabolomics to distinguish asthma phenotypes: Strategies and clinical implications. Allergy 2013, 68, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, J.S.; Baurecht, H.; Stückler, F.; Krumsiek, J.; Gieger, C.; Heinrich, J.; Kabesch, M.; Prehn, C.; Peters, A.; Rodriguez, E.; et al. Integrative genetic and metabolite profiling analysis suggests altered phosphatidylcholine metabolism in asthma. Allergy 2013, 68, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Moon, H.B. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2010, 2, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.K. A Fresh Take on the “TCA” Cycle: TETs, Citrate, and Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.J.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Dong, L.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Shen, H.H. Lipid metabolism in asthma: Immune regulation and potential therapeutic target. Cell Immunol. 2021, 364, 104341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, F. Serum Metabolomics Analysis of Asthma in Different Inflammatory Phenotypes: A Cross-Sectional Study in Northeast China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2860521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Choi, Y.; Park, H.S. Potential Metabolic Biomarkers in Adult Asthmatics. Metabolites 2021, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Chen, C.; Wen, Z.; Hu, J.; Fleming, I.; Wang, D.W. Metabolism pathways of arachidonic acids: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.S.; Virkud, Y.; Giorgio, R.; Celedon, J.C.; Weiss, S.T.; Lasky-Su, J. Metabolomic profiling of lung function in Costa-Rican children with asthma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofanova, E.V.; Chen, H.; Dai, Y.; Jia, P.; Grove, M.L.; Morrison, A.C.; Qi, Q.; Daviglus, M.; Cai, J.; North, K.E.; et al. A Genome-wide Association Study Discovers 46 Loci of the Human Metabolome in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.A.R.; Mathur, R.; Vonk, J.M.; Szwajda, A.; Brumpton, B.; Granell, R.; Brew, B.K.; Ullemar, V.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Genetic Architectures of Childhood- and Adult-Onset Asthma Are Partly Distinct. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishigaki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Kawakami, E.; Sugishita, H.; Sakaue, S.; Matoba, N.; Low, S.K.; Okada, Y.; et al. Large-scale genome-wide association study in a Japanese population identifies novel susceptibility loci across different diseases. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, S.E. Arachidonic acid metabolites: Mediators of inflammation in asthma. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 3S–12S. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, R.K.; Raven, J.M.; Walters, E.H.; Abramson, M.J.; Thien, F.C. Fatty acid levels and risk of asthma in young adults. Thorax 2004, 59, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damon, M.; Chavis, C.; Daures, J.P.; Crastes de Paulet, A.; Michel, F.B.; Godard, P. Increased generation of the arachidonic metabolites LTB4 and 5-HETE by human alveolar macrophages in patients with asthma: Effect in vitro of nedocromil sodium. Eur. Respir. J. 1989, 2, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, C.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G.; Mazzarella, G. Arachidonic acid metabolism in inflammatory cells of patients with bronchial asthma. Allergy 2000, 55 (Suppl. 61), 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insuela, D.B.R.; Ferrero, M.R.; Coutinho, D.S.; Martins, M.A.; Carvalho, V.F. Could Arachidonic Acid-Derived Pro-Resolving Mediators Be a New Therapeutic Strategy for Asthma Therapy? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 580598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matysiak, J.; Klupczynska, A.; Packi, K.; Mackowiak-Jakubowska, A.; Breborowicz, A.; Pawlicka, O.; Olejniczak, K.; Kokot, Z.J.; Matysiak, J. Alterations in Serum-Free Amino Acid Profiles in Childhood Asthma. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comhair, S.A.; McDunn, J.; Bennett, C.; Fettig, J.; Erzurum, S.C.; Kalhan, S.C. Metabolomic Endotype of Asthma. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y. Serum Levels of Gamma-Glutamyltransferase During Stable and Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e927771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce-Brady, M.; Hiratake, J. Inhibiting Glutathione Metabolism in Lung Lining Fluid as a Strategy to Augment Antioxidant Defense. Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2011, 7, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuzova, M.; Jean, J.C.; Hughey, R.P.; Brown, L.A.; Cruikshank, W.W.; Hiratake, J.; Joyce-Brady, M. Inhibiting lung lining fluid glutathione metabolism with GGsTop as a novel treatment for asthma. Front. Pharm. 2014, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liss, K.H.H.; Lutkewitte, A.J.; Pietka, T.; Finck, B.N.; Franczyk, M.; Yoshino, J.; Klein, S.; Hall, A.M. Metabolic importance of adipose tissue monoacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 in mice and humans. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, R.A.; Lee, D.P. Enzymes of triacylglycerol synthesis and their regulation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 134–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessenko, A.V.; Lebedev capital A, C.T.E.C.; Kurochkin, I.N. The role of sphingolipids in cardiovascular pathologies. Biomed. Khim. 2018, 64, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.-C.; Li, Z.; Yazdanyar, A. Chapter 6—Sphingolipids and HDL Metabolism. In The HDL Handbook, 2nd ed.; Komoda, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 133–158. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, J.; Walsh, M.T.; Hammad, S.M.; Hussain, M.M. Sphingolipids and Lipoproteins in Health and Metabolic Disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grineski, S.E.; Staniswalis, J.G.; Peng, Y.; Atkinson-Palombo, C. Children’s asthma hospitalizations and relative risk due to nitrogen dioxide (NO2): Effect modification by race, ethnicity, and insurance status. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahnquist, J.; Wamala, S.P.; Lindstrom, M. Social determinants of health--a question of social or economic capital? Interaction effects of socioeconomic factors on health outcomes. Soc. Sci. Med. 2012, 74, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Braun, K.L.; Kaholokula, J.K.; Armstead, C.A.; Burch, J.B.; Thompson, B. Considering the Role of Stress in Populations of High-Risk, Underserved Community Networks Program Centers. Prog. Community Health Partn. 2015, 9, 7–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco-Mondragon, E.; Jimenez, A.; Palladino-Davis, A.G.; Davis, D.; Escamilla-Cejudo, J.A. Hispanic health in the USA: A scoping review of the literature. Public Health Rev. 2016, 37, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey Smith, G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, R.; Weiss, S.; Levy, B.; Raby, B.; Lasky-Su, J. Metabolite quantitative trait loci provide functional link between FADS2 and lung obstruction in asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, PA1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisenko, Y.; Novgorodtseva, T.; Antonyuk, M. The Activity of Fatty Acids Desaturases in Mild and Moderate ASTHMA. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56 (Suppl. 64), 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.E.; Holguin, F. Diet and Metabolism in the Evolution of Asthma and Obesity. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, I.; Williams, L.; Thompson, C.; Scott, H.; Wood, L. Evidence for lifestyle interventions in asthma. Breathe 2019, 15, e50–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiotiu, A.I.; Novakova, P.; Nedeva, D.; Chong-Neto, H.J.; Novakova, S.; Steiropoulos, P.; Kowal, K. Impact of Air Pollution on Asthma Outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S.F.; van der Sluis, S.; Kyvik, K.O.; Skytthe, A.; Backer, V. Estimates of asthma heritability in a large twin sample. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, P.; Sordillo, J.E.; Lutz, S.M.; Weiss, S.T.; Kelly, R.S.; McGeachie, M.J.; Wu, A.C.; Lasky-Su, J.A. Pharmaco-Metabolomics of Inhaled Corticosteroid Response in Individuals with Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavange, L.M.; Kalsbeek, W.D.; Sorlie, P.D.; Aviles-Santa, L.M.; Kaplan, R.C.; Barnhart, J.; Liu, K.; Giachello, A.; Lee, D.J.; Ryan, J.; et al. Sample design and cohort selection in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Ann. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorlie, P.D.; Aviles-Santa, L.M.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Kaplan, R.C.; Daviglus, M.L.; Giachello, A.L.; Schneiderman, N.; Raij, L.; Talavera, G.; Allison, M.; et al. Design and implementation of the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Ann. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.C.; Chai, J.C.; Yu, B.; Michelotti, G.A.; Grove, M.L.; Fretts, A.M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Garcia-Bedoya, O.L.; Thyagarajan, B.; Schneiderman, N.; et al. Serum sphingolipids and incident diabetes in a US population with high diabetes burden: The Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Masutomi, N.; Tsutsui, N.; Sakairi, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Beebe, K.D.; Guo, L. Untargeted metabolomic profiling as an evaluative tool of fenofibrate-induced toxicology in Fischer 344 male rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2009, 37, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.M.; DeHaven, C.D.; Barrett, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, E. Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal. Chem 2009, 81, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Jia, E.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y. Missing Value Imputation Approach for Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomics Data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Playdon, M.C.; Joshi, A.D.; Tabung, F.K.; Cheng, S.; Henglin, M.; Kim, A.; Lin, T.; van Roekel, E.H.; Huang, J.; Krumsiek, J.; et al. Metabolomics Analytics Workflow for Epidemiological Research: Perspectives from the Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS). Metabolites 2019, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barr, R.G.; Avilés-Santa, L.; Davis, S.M.; Aldrich, T.K.; Gonzalez, F., 2nd; Henderson, A.G.; Kaplan, R.C.; LaVange, L.; Liu, K.; Loredo, J.S.; et al. Pulmonary Disease and Age at Immigration among Hispanics. Results from the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, R.; Semprini, A.; Mitchell, E.A. Risk factors for asthma: Is prevention possible? Lancet 2015, 386, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Um, I.Y.; Hong, S.; Yum, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Kwon, H. Association between Household Income and Asthma Symptoms among Elementary School Children in Seoul. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2012, 27, e2012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagan, T.M.; Gulsvik, A.; Eide, G.E.; Bakke, P.S. The effect of educational level on the incidence of asthma and respiratory symptoms. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philipneri, A.; Hanna, S.; Mandhane, P.J.; Georgiades, K. Association of immigrant generational status with asthma. Can. J. Public Health 2019, 110, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toskala, E.; Kennedy, D.W. Asthma risk factors. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5 (Suppl. 1), S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daviglus, M.L.; Talavera, G.A.; Aviles-Santa, M.L.; Allison, M.; Cai, J.; Criqui, M.H.; Gellman, M.; Giachello, A.L.; Gouskova, N.; Kaplan, R.C.; et al. Prevalence of major cardiovascular risk factors and cardiovascular diseases among Hispanic/Latino individuals of diverse backgrounds in the United States. JAMA 2012, 308, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjellvik, V.; Tverdal, A.; Furu, K. Body mass index as predictor for asthma: A cohort study of 118,723 males and females. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVange, L.; Davis, S.M.; Hankinson, J.; Enright, P.; Wilson, R.; Barr, R.G.; Aldrich, T.K.; Kalhan, R.; Lemus, H.; Ni, A.; et al. Spirometry Reference Equations from the HCHS/SOL (Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, D.; Hodonsky, C.J.; Schick, U.M.; Morrison, J.V.; Minnerath, S.; Brown, L.; Schurmann, C.; Liu, Y.; Auer, P.L.; Laurie, C.A.; et al. Genome-wide association of white blood cell counts in Hispanic/Latino Americans: The Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeffermann, D. Modelling of complex survey data: Why model? Why is it a problem? How can we approach it? Stat. Can. 2011, 37, 115–136. [Google Scholar]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, W.; Shi, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Pan, H. Application of Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis for Data from Paired Design. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zuo, L.; Tao, A. Key genes and co-expression modules involved in asthma pathogenesis. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.S.; Chawes, B.L.; Blighe, K.; Virkud, Y.V.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; McGeachie, M.J.; Clish, C.B.; Bullock, K.; Celedon, J.C.; Weiss, S.T.; et al. An Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Study of Lung Function in Children With Asthma. Chest 2018, 154, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, H.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Huang, H.; Li, M. Application of weighted gene co-expression network analysis to identify key modules and hub genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 6001–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Horvath, S. Understanding network concepts in modules. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horvath, S.; Dong, J. Geometric interpretation of gene coexpression network analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modena, B.D.; Bleecker, E.R.; Busse, W.W.; Erzurum, S.C.; Gaston, B.M.; Jarjour, N.N.; Meyers, D.A.; Milosevic, J.; Tedrow, J.R.; Wu, W.; et al. Gene Expression Correlated with Severe Asthma Characteristics Reveals Heterogeneous Mechanisms of Severe Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1449–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Newcomb, D.C. Sex Bias in Asthma Prevalence and Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homa, D.M.; Mannino, D.M.; Lara, M. Asthma mortality in U.S. Hispanics of Mexican, Puerto Rican, and Cuban heritage, 1990-1995. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, F.J.; Forno, E.; Cooper, P.J.; Celedon, J.C. Asthma in Hispanics. An 8-year update. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MSEA: A web-based tool to identify biologically meaningful patterns in quantitative metabolomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W71–W77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, A.M.; Bridgewater, B.R.; Liu, Q.; Mitchell, M.W.; Robinson, R.J.; Dai, H.; Stewart, S.J.; DeHaven, C.D.; Miller, L.A.D. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Improves Data Quantity and Quality as Compared to Unit Mass Resolution Mass Spectrometry in HighThroughput Profiling Metabolomics. J. Postgenomics Drug Biomark. Dev. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehaven, C.D.; Evans, A.M.; Dai, H.; Lawton, K.A. Organization of GC/MS and LC/MS metabolomics data into chemical libraries. J. Cheminform. 2010, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Asthma (n = 514) | Non-Asthma (n = 2833) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female, N (%) | 343 (66.73) | 1561 (55.10) | <0.001 |
| Age, years ± SD | 47.14 ± 13.40 | 45.93 ± 13.37 | 0.060 |
| Ethnicity, N (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Dominican | 42 (8.17) | 286 (10.10) | |
| Central American | 47 (9.14) | 286 (10.10) | |
| Cuban | 109 (21.21) | 445 (15.71) | |
| Mexican | 93 (18.08) | 1216 (42.92) | |
| Puerto-Rican | 208 (40.47) | 404 (14.26) | |
| South American | 15 (2.92) | 196 (6.92) | |
| Cigarette Use, N (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Never | 247 (48.05) | 1710 (60.36) | |
| Former | 117 (22.76) | 566 (19.98) | |
| Current | 150 (29.18) | 557 (19.66) | |
| Less than High School Education, N (%) | 174 (33.98) | 970 (34.23) | 0.905 |
| BMI, kg/m2 ± SD | 31.48 ± 7.12 | 29.58 ± 5.90 | <0.001 |
| Lipids, mg/dL ± SD | |||
| LDL | 121.53 ± 37.27 | 123.96 ± 36.68 | 0.173 |
| HDL | 49.56 ± 13.34 | 49.70 ± 13.04 | 0.826 |
| TG | 128.20 ± 65.38 | 129.93 ± 68.39 | 0.585 |
| Immigration Status | |||
| Residence Period in US, years ± SD | 28.06 ± 16.57 | 22.24 ± 14.98 | <0.001 |
| US Born, N (%) | 134 (26.07) | 463 (16.34) | <0.001 |
| Annual Family Income, N (%) | |||
| <$20,000 | 294 (57.20) | 1306 (46.10) | <0.001 |
| Metabolite | Model (1) | Model (2) | Model (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-arachidonoyl-GPA (20:4) | 1.32 * (1.16, 1.51) | 1.33 * (1.17, 1.52) | 1.32 * (1.15, 1.51) |
| Glutamate | 1.36 * (1.17, 1.58) | 1.36 (1.16, 1.59) | 1.34 (1.14, 1.57) |
| Tyrosine | 1.28 * (1.13, 1.44) | 1.27 (1.12, 1.43) | 1.26 (1.12, 1.42) |
| Cases/Controls | Model (1) | Model (2) | Model (3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Green Module | Women | 343/1561 | 1.41 *** (1.22, 1.64) | 1.36 *** (1.17, 1.59) | 1.37 *** (1.17, 1.60) |
| Men | 171/1272 | 1.00 (0.83, 1.21) | 1.05 (0.87, 1.27) | 1.04 (0.86, 1.25) | |
| 1-arachidonoyl-GPA (20:4) | Women | 343/1561 | 1.23 *** (1.09, 1.38) | 1.22 *** (1.08, 1.37) | 1.24 *** (1.10, 1.40) |
| Men | 171/1272 | 1.12 (0.95, 1.32) | 1.15 (0.96, 1.35) | 1.13 (0.95, 1.34) | |
| Hispanic/Latino Backgrounds | |||||
| Green Module | Cuban and Puerto-Rican Backgrounds | 317/849 | 1.27 ** (1.09, 1.47) | 1.26 ** (1.08, 1.48) | 1.27 ** (1.09, 1.49) |
| Others | 197/1984 | 1.21 * (1.02, 1.45) | 1.20 * (1.00, 1.44) | 1.20 (1.00, 1.44) | |
| 1-arachidonoyl-GPA (20:4) | Cuban and Puerto-Rican Backgrounds | 317/849 | 1.26 *** (1.10, 1.44) | 1.26 *** (1.10, 1.44) | 1.25 ** (1.09, 1.43) |
| Others | 197/1984 | 1.14 (0.99, 1.30) | 1.15 * (1.00, 1.31) | 1.15 * (1.00, 1.32) | |
| Direct Association | Mendelian Randomization | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Outcome | Population | N | AF | beta | se | p | beta | se | p |
| Ferreira (2019) | Adult asthma | European | 327,253 | 0.69 | 1.06 | 0.01 | 2.5 × 10−12 | 6.53 | 0.05 | <0.001 |
| Ferreira (2019) | Childhood asthma | European | 327,253 | 0.68 | 1.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 6.30 | 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Ishigaki (2020) | Adult asthma | East Asian | 209,808 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.; Qi, Q.; Afshar, M.; Cai, J.; Daviglus, M.L.; Thyagarajan, B.; North, K.E.; London, S.J.; et al. Metabolomic Associations of Asthma in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Metabolites 2022, 12, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040359
Lee Y, Chen H, Chen W, Qi Q, Afshar M, Cai J, Daviglus ML, Thyagarajan B, North KE, London SJ, et al. Metabolomic Associations of Asthma in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Metabolites. 2022; 12(4):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040359
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yura, Han Chen, Wei Chen, Qibin Qi, Majid Afshar, Jianwen Cai, Martha L. Daviglus, Bharat Thyagarajan, Kari E. North, Stephanie J. London, and et al. 2022. "Metabolomic Associations of Asthma in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos" Metabolites 12, no. 4: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040359
APA StyleLee, Y., Chen, H., Chen, W., Qi, Q., Afshar, M., Cai, J., Daviglus, M. L., Thyagarajan, B., North, K. E., London, S. J., Boerwinkle, E., Celedón, J. C., Kaplan, R. C., & Yu, B. (2022). Metabolomic Associations of Asthma in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos. Metabolites, 12(4), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12040359