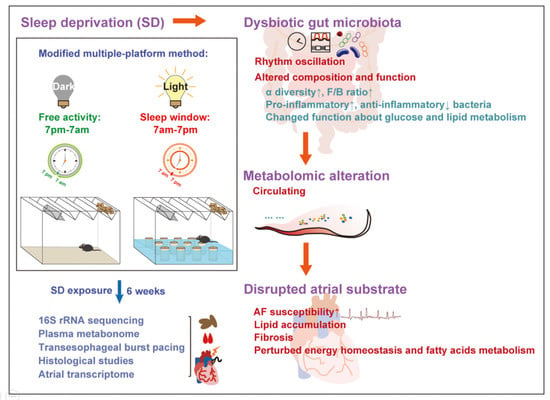
The Impact of Sleep Disturbance on Gut Microbiota, Atrial Substrate, and Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility in Mice: A Multi-Omics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. AF Inducibility by Transesophageal Burst Pacing
2.3. Histology
2.4. Gut Microbiota Profile of 16s rRNA
2.5. Plasma Metabolomic Analyses Based on LC-MS
2.6. Atrial Transcriptomic Signatures
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enhanced AF Inducibility, Atrial Lipid Accumulation, and Fibrosis in SD Mice
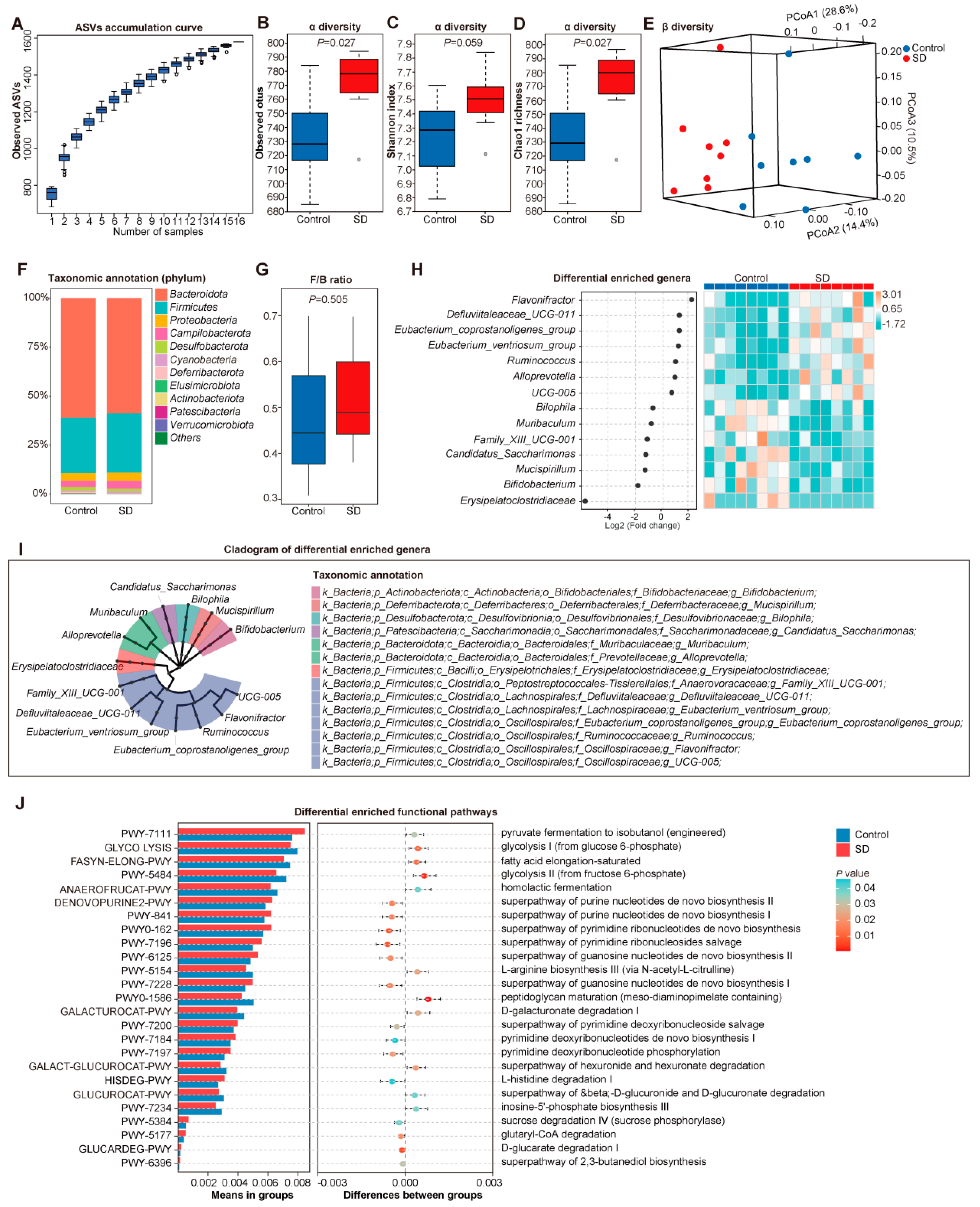
3.2. Altered Gut Microbiota in SD Mice
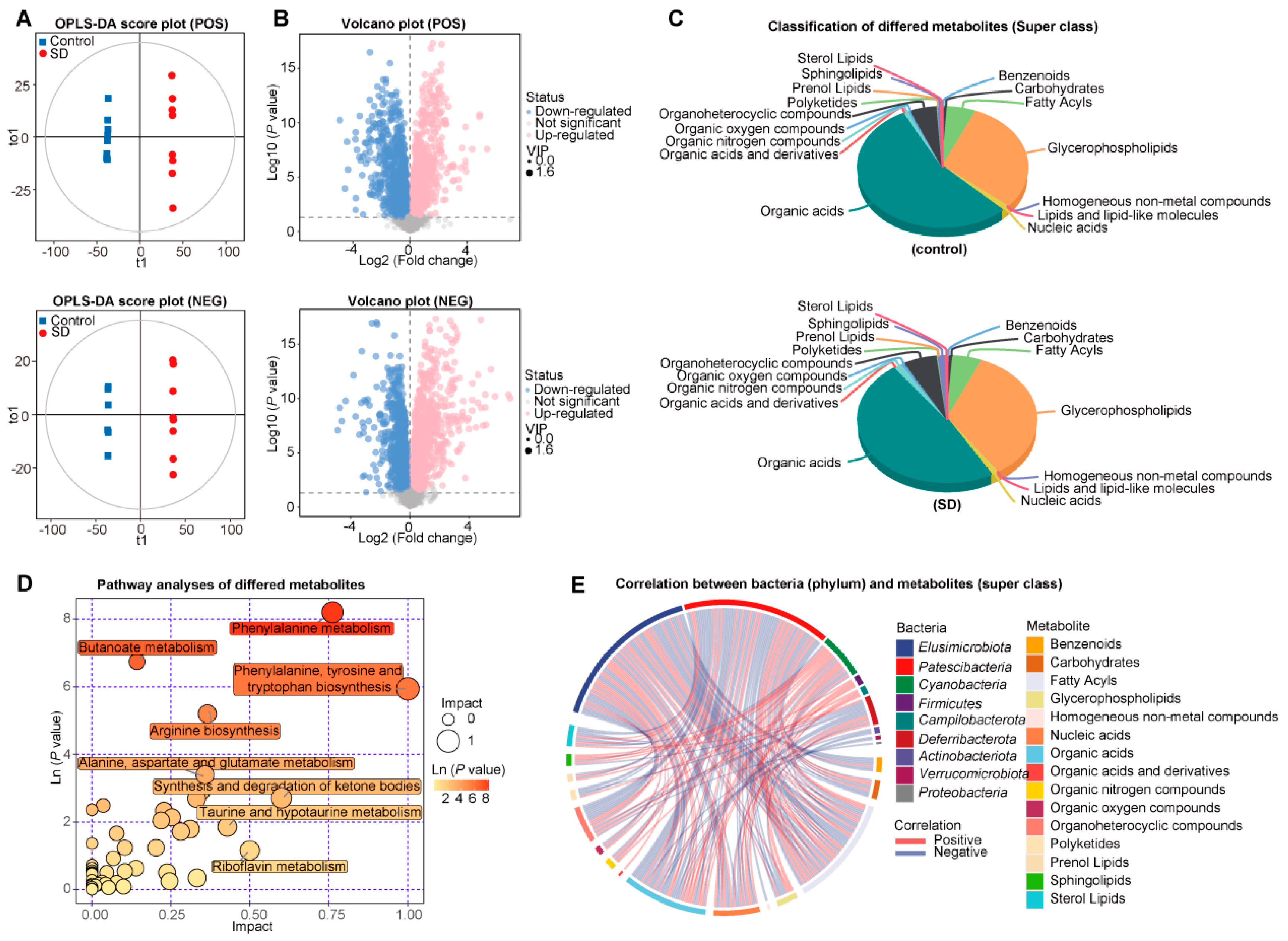
3.3. Changed Metabolic Patterns in Plasma of SD Mice
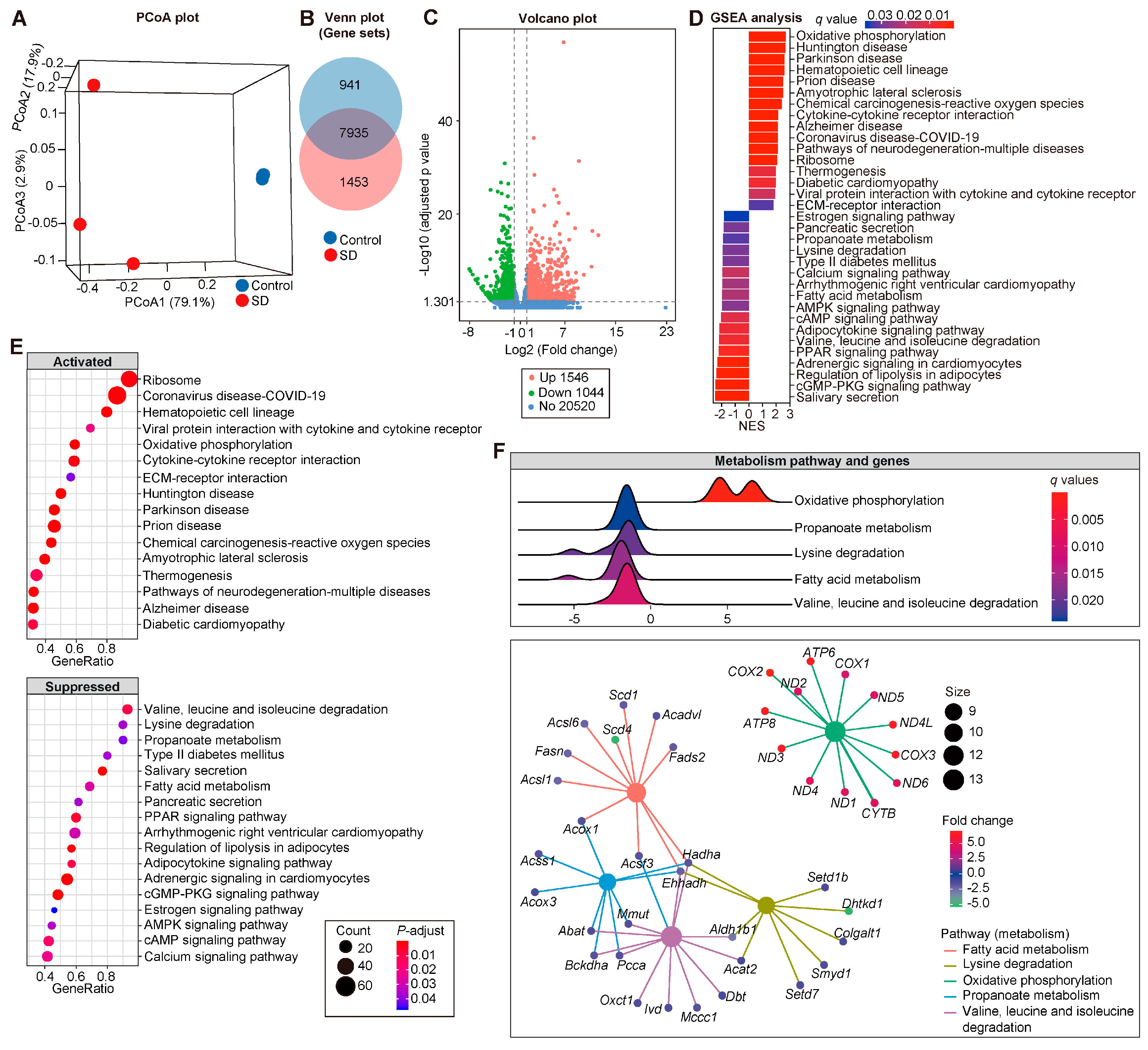
3.4. Modified Transcriptional Signatures in Atria of SD Mice
3.5. The Linkage between GM, Plasma Metabolism, and Atrial Transcriptome
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, D.; Zhou, J.; Ma, J.; Chang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zeng, L. Sleep disturbance mediates the relationship between depressive symptoms and cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Geriatr. Nurs. 2021, 42, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Bai, A.; Huang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, L. Association between Sleep and Motoric Cognitive Risk Syndrome Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results From the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 774167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hua, D.; Tang, X.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; et al. The Role of Perioperative Sleep Disturbance in Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2021, 13, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AV, S.G.E.F.; de Lima Cavalcanti, M.P.; de Passos Junior, M.A.; Vechio Koike, B.D. The association between sleep deprivation and arterial pressure variations: A systematic literature review. Sleep Med. X 2022, 4, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Hoshide, S.; Kario, K. Sleep duration as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease- a review of the recent literature. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2010, 6, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandner, M.A. Sleep, Health, and Society. Sleep Med. Clin. 2020, 15, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, X.; Zhang, J.; Xia, F.; et al. Long-term night shift work is associated with the risk of atrial fibrillation and coronary heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4180–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.; Chang, S.H.; Ko, Y.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Young, J.D.; Ojcius, D.M. Gut barrier disruption and chronic disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, A.; Kaplan Dor, Y.; Nambara, K.; Pollina, E.A.; Lin, C.; Greenberg, M.E.; Rogulja, D. Sleep Loss Can Cause Death through Accumulation of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Gut. Cell 2020, 181, 1307–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delli Bovi, A.P.; Marciano, F.; Mandato, C.; Siano, M.A.; Savoia, M.; Vajro, P. Oxidative Stress in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. An Updated Mini Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 595371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dudley, S.C., Jr. Evidence for Inflammation as a Driver of Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrev, D.; Heijman, J.; Hiram, R.; Li, N.; Nattel, S. Inflammatory signalling in atrial cardiomyocytes: A novel unifying principle in atrial fibrillation pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korantzopoulos, P.; Letsas, K.; Fragakis, N.; Tse, G.; Liu, T. Oxidative stress and atrial fibrillation: An update. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, K.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Hu, C.; Gao, Y.; Chen, M.; Hu, R.; Liu, Y.; Chi, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Disordered gut microbiota and alterations in metabolic patterns are associated with atrial fibrillation. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, K.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, X. Duration of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Is Associated with Alterations in Human Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Phenotypes. mSystems 2019, 4, e00422-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, K.; Yin, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; et al. Different Types of Atrial Fibrillation Share Patterns of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis. mSphere 2020, 5, e00071-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawałko, M.; Agbaedeng, T.A.; Saljic, A.; Müller, D.N.; Wilck, N.; Schnabel, R.; Penders, J.; Rienstra, M.; van Gelder, I.; Jespersen, T.; et al. Gut microbiota, dysbiosis and atrial fibrillation. Arrhythmogenic mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2415–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Su, J.; Li, R.; Luo, F. Changes in Intestinal Flora Structure and Metabolites Are Associated with Myocardial Fibrosis in Patients with Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautkramer, K.A.; Fan, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbial metabolites as multi-kingdom intermediates. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Aquino-Martinez, R.; Hutchison, E.; Allayee, H.; Lusis, A.J.; Rey, F.E. Role of gut microbe-derived metabolites in cardiometabolic diseases: Systems based approach. Mol. Metab. 2022, 64, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertli, S.; Zimmermann, P. Molecular interactions between the intestinal microbiota and the host. Mol. Microbiol. 2022, 117, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabney, S.M.; Henagan, T.M. Short Chain Fatty Acids in the Colon and Peripheral Tissues: A Focus on Butyrate, Colon Cancer, Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Dai, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, L.; Tian, H.; et al. Reconstruction and Dynamics of the Human Intestinal Microbiome Observed In Situ. Engineering 2022, 15, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. The Role of Microbiome in Insomnia, Circadian Disturbance and Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, B.H.P.; Novaes, E.B.R.R.; Paslar Leal, T.; Piqueira Garcia, N.; Martins Dos Santos, R.M.; Alvares-Saraiva, A.M.; Perez Hurtado, E.C.; Braga Dos Reis, T.C.; Duarte Palma, B. Chronic Sleep Restriction Impairs the Antitumor Immune Response in Mice. Neuroimmunomodulation 2018, 25, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, B.M.; Rechtschaffen, A.; Gilliland, M.A.; Quintans, J. Effect of extended sleep deprivation on tumor growth in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, R1460–R1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchecki, D.; Tufik, S. Social stability attenuates the stress in the modified multiple platform method for paradoxical sleep deprivation in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 2000, 68, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.B.; Tufik, S.; Suchecki, D. Chronic stress during paradoxical sleep deprivation increases paradoxical sleep rebound: Association with prolactin plasma levels and brain serotonin content. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.B.; Hipólide, D.C.; Benedito-Silva, A.A.; Tufik, S. Sleep deprivation induced by the modified multiple platform technique: Quantification of sleep loss and recovery. Brain. Res. 2004, 1004, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Lange, T.; Hansen, K.; Mölle, M.; Fehm, H.L. Effects of sleep and circadian rhythm on human circulating immune cells. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 4454–4464. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.H.; Abílio, V.C.; Takatsu, A.L.; Kameda, S.R.; Grassl, C.; Chehin, A.B.; Medrano, W.A.; Calzavara, M.B.; Registro, S.; Andersen, M.L.; et al. Role of hippocampal oxidative stress in memory deficits induced by sleep deprivation in mice. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, L.; Ruan, Y.; Zuo, S.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xia, S.; Bai, R.; et al. Ibrutinib promotes atrial fibrillation by inducing structural remodeling and calcium dysregulation in the atrium. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2893–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Fu, C.; Wei, Q. The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zuo, K.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, P.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Z.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; et al. Shifts in gut microbiome and metabolome are associated with risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13356–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Zou, X.; Zhang, H. The Relationship between Atrial Fibrillation and Intestinal Flora with Its Metabolites. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 948755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Yan, L.; Lei, Y. The Gut Microbial-Derived Metabolite Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Atrial Fibrillation: Relationships, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Gawałko, M.; Sanders, P.; Penders, J.; Li, N.; Nattel, S.; Dobrev, D. Does gut microbiota affect atrial rhythm? Causalities and speculations. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3521–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. The Four Key Genes Participated in and Maintained Atrial Fibrillation Process via Reprogramming Lipid Metabolism in AF Patients. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 821754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhuo, L.B.; He, Y.; Fu, Y.; Shen, L.; Xu, F.; Gou, W.; Miao, Z.; Shuai, M.; Liang, Y.; et al. The gut microbiota-bile acid axis links the positive association between chronic insomnia and cardiometabolic diseases. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, S.; Liang, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Q. Different effects of norepinephrine and nerve growth factor on atrial fibrillation vulnerability. J. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, D.; Carter, J.R.; Van Cauter, E.; Leproult, R. Adverse Impact of Sleep Restriction and Circadian Misalignment on Autonomic Function in Healthy Young Adults. Hypertension 2016, 68, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.J.; Purvis, T.E.; Hu, K.; Scheer, F.A. Circadian misalignment increases cardiovascular disease risk factors in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1402–E1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Jang, E.C.; Kwon, S.C.; Han, W.; Kang, M.S.; Nam, Y.H.; Lee, Y.J. Night shift work and inflammatory markers in male workers aged 20-39 in a display manufacturing company. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 28, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, K.R.C.; Dos Santos, C.P.; de Medeiros, L.A.; Mendes, J.A.; Cunha, T.M.; De Angelis, K.; Penha-Silva, N.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Crispim, C.A. Night workers have lower levels of antioxidant defenses and higher levels of oxidative stress damage when compared to day workers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, B.S.; Chavez-Moreno, A.; Koh, W.; Akar, J.G.; Akar, F.G. Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, J.; Ellis, D.; Braddock, A.; Roberts, E.; Ingram, K.; Perez, E.; Short, A.; Brown, D.; Hutzley, V.; Webb, C.; et al. Temporal and region-specific effects of sleep fragmentation on gut microbiota and intestinal morphology in Sprague Dawley rats. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.X.; He, Z.M.; Zhu, W.L.; Ji, Y.B.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.M.; Yuan, K.; Bao, Y.P.; et al. Gut microbiota modulates the inflammatory response and cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6277–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishehsari, F.; Voigt, R.M.; Keshavarzian, A. Circadian rhythms and the gut microbiota: From the metabolic syndrome to cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulose, J.K.; Wright, J.M.; Patel, A.G.; Cassone, V.M. Human Gut Bacteria Are Sensitive to Melatonin and Express Endogenous Circadian Rhythmicity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulose, J.K.; Cassone, C.V.; Graniczkowska, K.B.; Cassone, V.M. Entrainment of the Circadian Clock of the Enteric Bacterium Klebsiella aerogenes by Temperature Cycles. iScience 2019, 19, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix, A.; Zarrinpar, A.; Miu, P.; Panda, S. Time-restricted feeding is a preventative and therapeutic intervention against diverse nutritional challenges. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix, A.; Lin, T.; Le, H.D.; Chang, M.W.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Feeding Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice Lacking a Circadian Clock. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Zeb, F.; Huang, Y.; An, J.; Ren, J.; Yang, F.; Feng, Q. Regulation of circadian rhythms by NEAT1 mediated TMAO-induced endothelial proliferation: A protective role of asparagus extract. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 382, 111451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitmeier, S.; Kiessling, S.; Clavel, T.; List, M.; Almeida, E.L.; Ghosh, T.S.; Neuhaus, K.; Grallert, H.; Linseisen, J.; Skurk, T.; et al. Arrhythmic Gut Microbiome Signatures Predict Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichman, E.M.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. When Rhythms Meet the Blues: Circadian Interactions with the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 448–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Ward, R.E.; Martin, R.J.; Lefevre, M.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ye, J. Butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure in mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellahcene, M.; O’Dowd, J.F.; Wargent, E.T.; Zaibi, M.S.; Hislop, D.C.; Ngala, R.A.; Smith, D.M.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Stocker, C.J.; Arch, J.R. Male mice that lack the G-protein-coupled receptor GPR41 have low energy expenditure and increased body fat content. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, M.; Khalyfa, A.; Ericsson, A.; Puech, C.; McAdams, Z.; Bender, S.B.; Gozal, D. Gut microbiota mediate vascular dysfunction in a murine model of sleep apnea: Effect of probiotics. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 2200002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, M.N.; Rader, T.A.; Park, S.; Bastin, J.; McCune, S.A.; Kelly, D.P. Fatty acid oxidation enzyme gene expression is downregulated in the failing heart. Circulation 1996, 94, 2837–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bilsen, M.; van Nieuwenhoven, F.A.; van der Vusse, G.J. Metabolic remodelling of the failing heart: Beneficial or detrimental? Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 81, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wei, H.; Li, C.; Zhan, R.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Yi, Y.; Cui, X.; Shan, W.; Ji, L.; et al. Gut microbiota production of trimethyl-5-aminovaleric acid reduces fatty acid oxidation and accelerates cardiac hypertrophy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houten, S.M.; Denis, S.; Argmann, C.A.; Jia, Y.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Reddy, J.K.; Wanders, R.J. Peroxisomal L-bifunctional enzyme (Ehhadh) is essential for the production of medium-chain dicarboxylic acids. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Chang, J.P.; Lin, Y.S.; Pan, K.L.; Ho, W.C.; Liu, W.H.; Chang, T.H.; Huang, Y.K.; Fang, C.Y.; Chen, C.J. Deciphering the gene expression profile of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signaling pathway in the left atria of patients with mitral regurgitation. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Kim, I.M.; Weintraub, N.L.; Tang, Y. The Impaired Bioenergetics of Diabetic Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 642857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, K.; Fang, C.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, X.; Liu, X.; et al. The Impact of Sleep Disturbance on Gut Microbiota, Atrial Substrate, and Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility in Mice: A Multi-Omics Analysis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111144
Zuo K, Fang C, Fu Y, Liu Z, Liu Y, Liu L, Wang Y, Wang H, Yin X, Liu X, et al. The Impact of Sleep Disturbance on Gut Microbiota, Atrial Substrate, and Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility in Mice: A Multi-Omics Analysis. Metabolites. 2022; 12(11):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111144
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Kun, Chen Fang, Yuan Fu, Zheng Liu, Ye Liu, Lifeng Liu, Yuxing Wang, Hongjiang Wang, Xiandong Yin, Xiaoqing Liu, and et al. 2022. "The Impact of Sleep Disturbance on Gut Microbiota, Atrial Substrate, and Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility in Mice: A Multi-Omics Analysis" Metabolites 12, no. 11: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111144
APA StyleZuo, K., Fang, C., Fu, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Yin, X., Liu, X., Li, J., Zhong, J., Chen, M., Yang, X., & Xu, L. (2022). The Impact of Sleep Disturbance on Gut Microbiota, Atrial Substrate, and Atrial Fibrillation Inducibility in Mice: A Multi-Omics Analysis. Metabolites, 12(11), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111144