Impact of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Pancreatic Neuro-Endocrine Tumors: Causes, Consequences, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Is Diabetes Mellitus a Risk Factor for the Development of pNETS?
3. What Is the Prevalence and Physiopathology of Diabetes in Patients with pNETs?
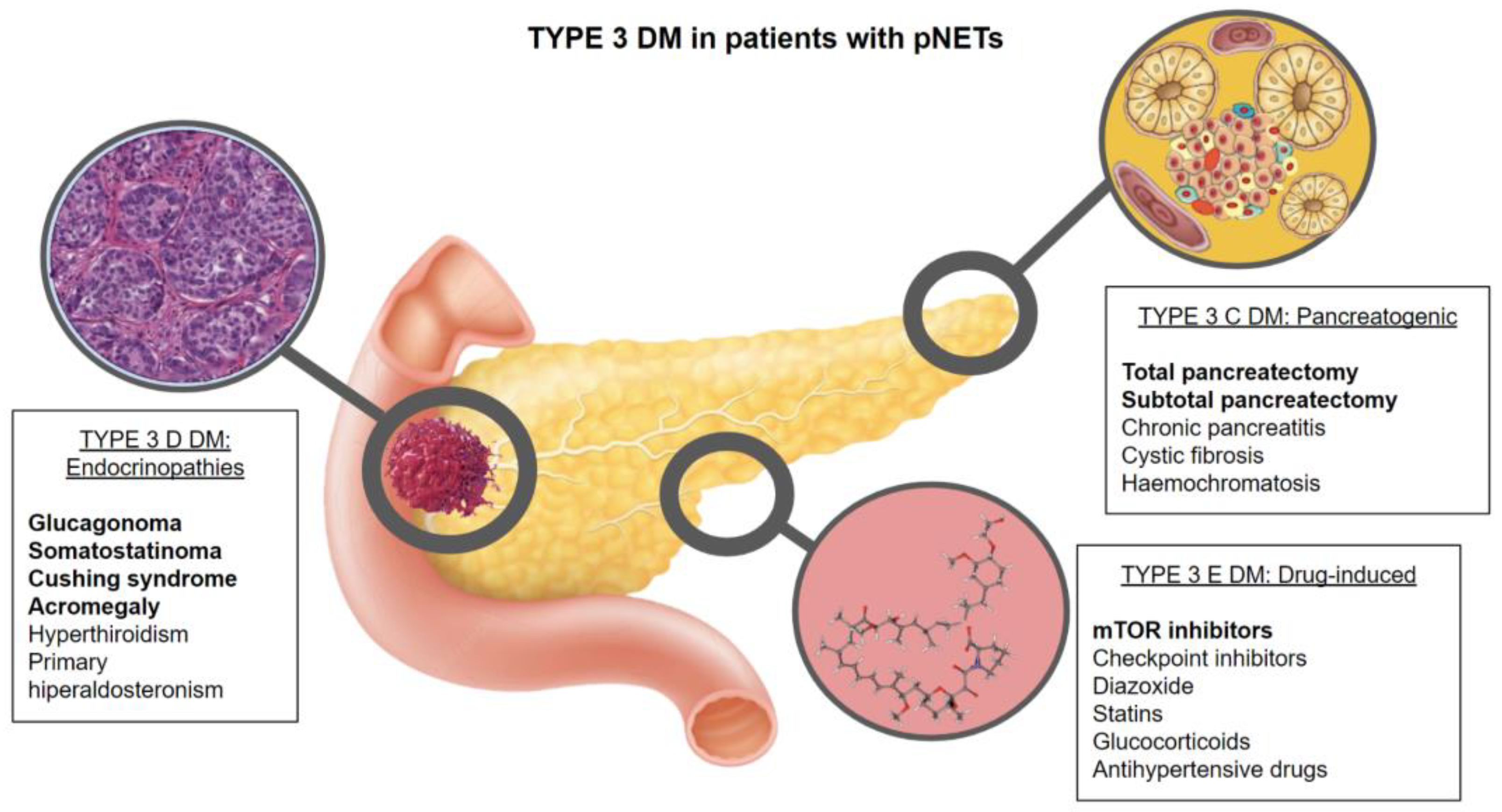
3.1. Type 3C DM (Exocrine Pancreas Disease or Pancreatogenic Diabetes) (T3CDM)
3.2. Type 3D DM (Endocrinopathies) (T3DDM)
3.2.1. Glucagonoma
3.2.2. Somatostatinoma
3.2.3. Other Ectopic Hormone Secretion
3.3. Type 3E DM
3.3.1. Somatostatin Analogues (SSA)
3.3.2. Everolimus
3.3.3. Interferon Alpha
3.3.4. Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
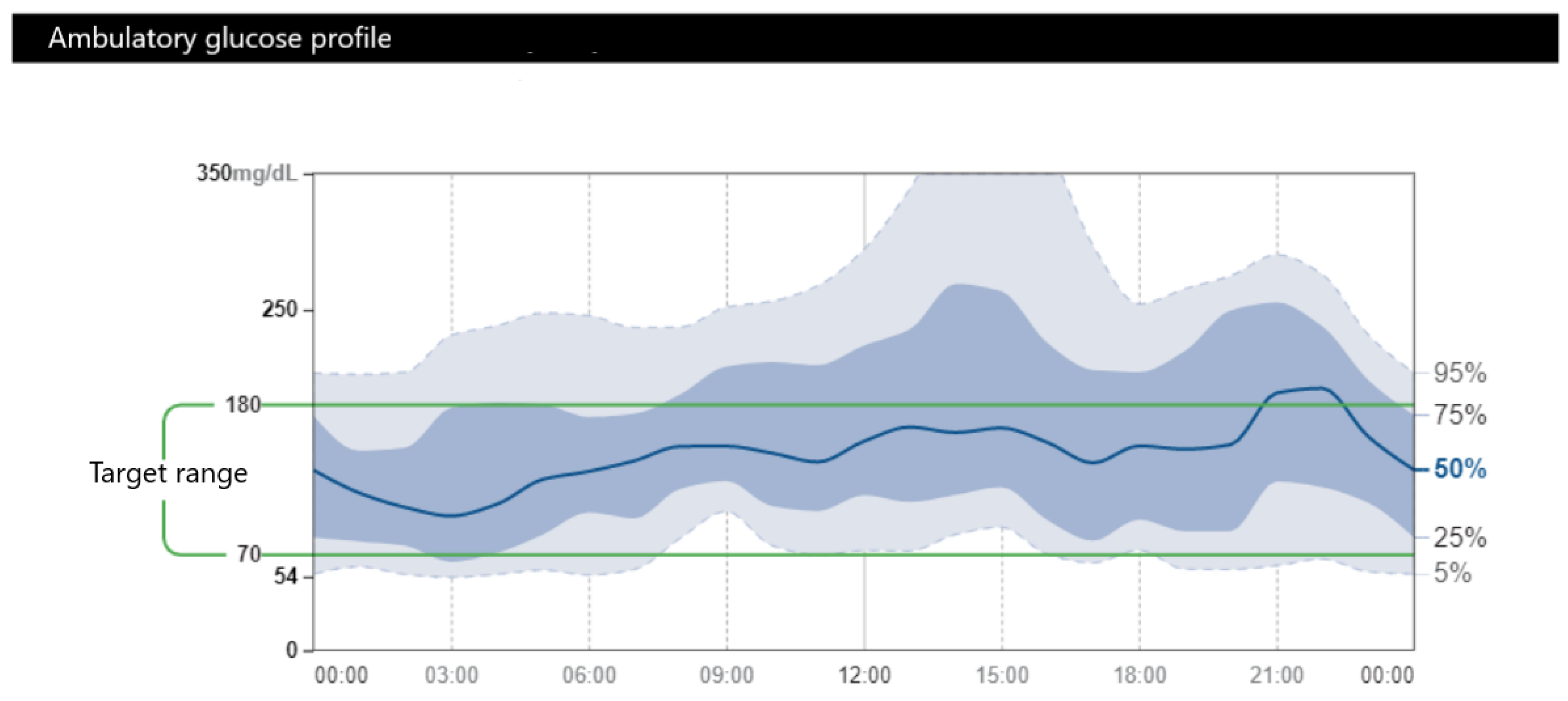
4. Glycemic Goals and Management of DM in Patients with pNETs
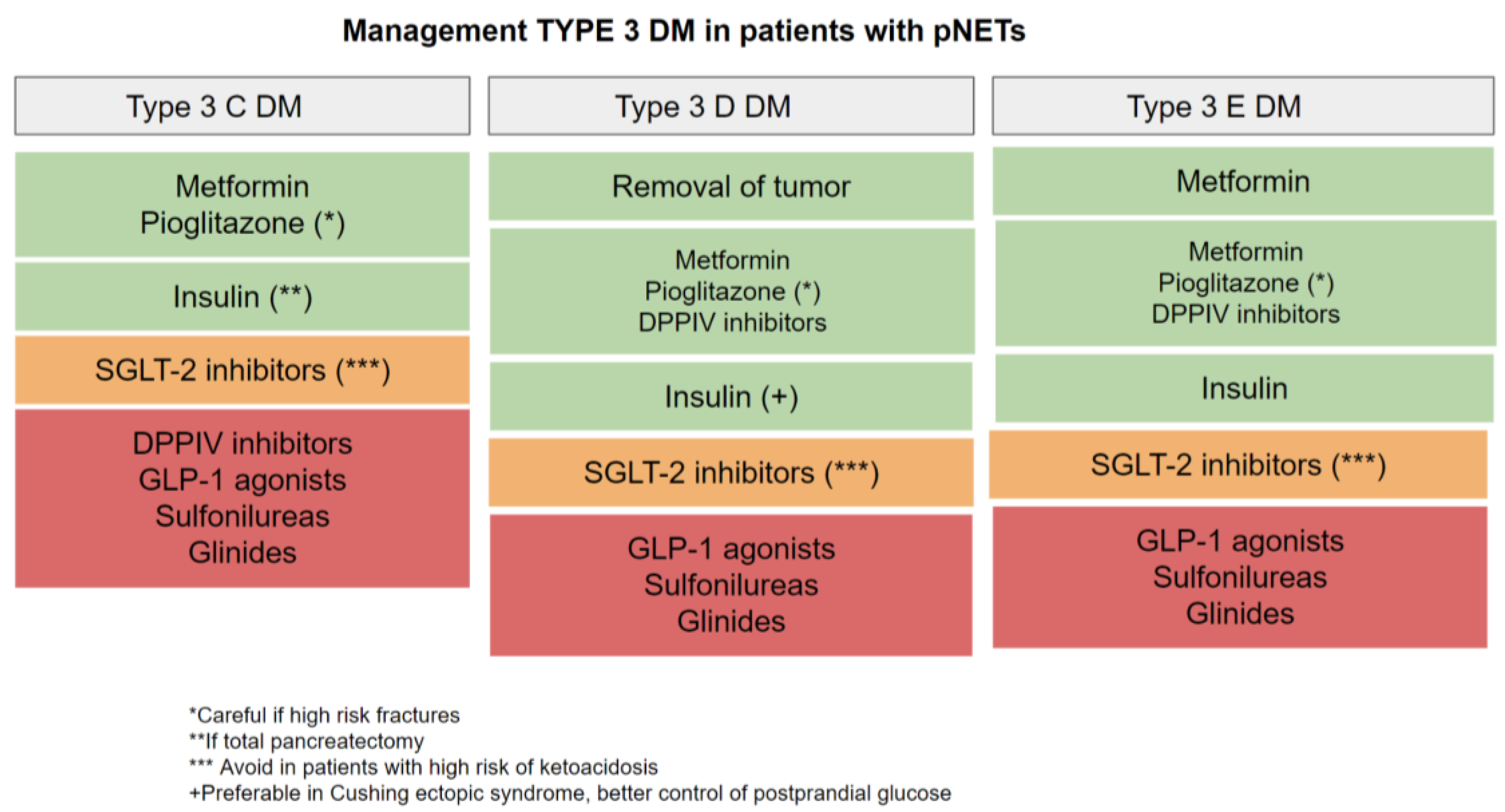
4.1. Type 3C DM
4.2. Type 3D DM
4.3. Type 3E DM
5. Impact of Neuroendocrine Tumors on the Survival, Tumor Stage, and Tumoral Growth in Patients with Diabetes
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawrence, B.; Gustafsson, B.I.; Chan, A.; Svejda, B.; Kidd, M.; Modlin, I.M. The epidemiology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocrinol. Metab Clin. N. Am. 2011, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauso, O.; Gustafsson, B.I.; Kidd, M.; Waldum, H.L.; Drozdov, I.; Chan, A.K.; Modlin, I.M. Neuroendocrine tumor epidemiology: Contrasting Norway and North America. Cancer 2008, 113, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Harris, C.; Baeg, K.J.; Aronson, A.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Kim, M.K. Incidence Trends of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2212.e1–2217.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Survival Outcomes in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röder, P.V.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugvik, S.P.; Hedenström, P.; Korsæth, E.; Valente, R.; Hayes, A.; Siuka, D.; Maisonneuve, P.; Gladhaug, I.P.; Lindkvist, B.; Capurso, G. Diabetes, smoking, alcohol use, and family history of cancer as risk factors for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroendocrinology 2015, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yang, C.; Cheng, H.; Jin, K.; Fan, K.; Ni, Q.; Yu, X.; Luo, G.; et al. Diabetes Is Associated with the Metastasis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas 2020, 49, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, M.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pizza, G.; Faggiano, A.; Colao, A. Diabetes and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: Which interplays, if any? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusceddu, S.; Vernieri, C.; Prinzi, N.; Torchio, M.; Coppa, J.; Antista, M.; Niger, M.; Milione, M.; Giacomelli, L.; Corti, F.; et al. The potential role of metformin in the treatment of patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A review of preclinical to clinical evidence. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820927271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, G.; Falconi, M.; Panzuto, F.; Rinzivillo, M.; Boninsegna, L.; Bettini, R.; Corleto, V.; Borgia, P.; Pederzoli, P.; Scarpa, A.; et al. Risk factors for sporadic pancreatic endocrine tumors: A case-control study of prospectively evaluated patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 3034–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Phan, A.; Li, D.; Dagohoy, C.G.; Leary, C.; Yao, J.C. Risk factors associated with neuroendocrine tumors: A U.S.-based case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfdanarson, T.R.; Bamlet, W.R.; Hobday, T.J.; McWilliams, R.R.; Petersen, G.M. Risk factors for sporadic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): A single-center case control study. Pancreas 2010, 39, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoncini, E.; Carioli, G.; La Vecchia, C.; Boccia, S.; Rindi, G. Risk factors for neuroendocrine neoplasms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.X.; Cong, L.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhang, T.P.; Chen, G. Risk factors for the occurrence of insulinoma: A case-control study. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2013, 12, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, R.; Hayes, A.J.; Haugvik, S.P.; Hedenström, P.; Siuka, D.; Korsæth, E.; Kämmerer, D.; Robinson, S.M.; Maisonneuve, P.; Delle Fave, G.; et al. Risk and protective factors for the occurrence of sporadic pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, R.P.; Nagpal, S.J.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chari, S.T. New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Q.; Zhong, J.; Fei, J.; Chen, H.; Yv, L.; Tan, L.; Yuan, Y. Risk Factors for sporadic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuge, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, C. Diabetes in Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 615082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makuc, J. Management of pancreatogenic diabetes: Challenges and solutions. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2016, 9, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshimizu, H.; Omori, H.; Funase, Y.; Tsukada, Y.; Tauchi, K.; Furukawa, T.; Oguchi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Higuchi, K.; Aizawa, T. Pancreatic nonfunctioning neuroendocrine tumor with the main pancreatic duct obstruction presenting as excessive hyperglycemia: A case report and review of the literature. Pancreas 2012, 41, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapi, S.; Baeg, K.; Kim, M.K.; Gallagher, E.J. Survival of Patients with Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Diabetes Mellitus. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, P.D.; Brendel, M.D.; Kloer, H.U.; Bretzel, R.G. Is pancreatic diabetes (type 3c diabetes) underdiagnosed and misdiagnosed? Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S165–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, N.; Bretzel, R.G. Diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (Type 3c)—Are we neglecting an important disease? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Nahm, C.; Jamieson, N.; Samra, J.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Mittal, A.; Tsang, V. Risk factors for development of diabetes mellitus (type 3c) after partial pancreatectomy: A systematic review. Clin. Endocrinol. 2020, 92, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A.; Schrader, H.; Breuer, T.G.; Dabrowski, Y.; Uhl, W.; Schmidt, W.E.; Meier, J.J. Metabolic consequences of a 50% partial pancreatectomy in humans. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Carmichael, K.A.; Schallom, M.E.; Klinkenberg, W.D. Retrospective review of postoperative glycemic control in patients after distal pancreatectomy. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 41, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconi, M.; Eriksson, B.; Kaltsas, G.; Bartsch, D.K.; Capdevila, J.; Caplin, M.; Kos-Kudla, B.; Kwekkeboom, D.; Rindi, G.; Klöppel, G.; et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines Update for the Management of Patients with Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermers, R.A.; Fatourechi, V.; Wynne, A.G.; Kvols, L.K.; Lloyd, R.V. The glucagonoma syndrome. Clinical and pathologic features in 21 patients. Medicine 1999, 75, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Atypical Forms of Diabetes. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, I.; Carvalho, A.; Amaral, C.; Machado, S.; Carvalho, R. Glucagonoma syndrome and necrolytic migratory erythema. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrau, F.; Kobornits, M. Metabolic syndrome in Cushing’s Syndrome Patients. Front. Horm Res. 2018, 49, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davi’, M.V.; Cosaro, E.; Piacentini, S.; Reimondo, G.; Albiger, N.; Arnaldi, G.; Faggiano, A.; Mantovani, G.; Fazio, N.; Piovesan, A.; et al. Prognostic factors in ectopic Cushing’s syndrome due to neuroendocrine tumors: A multicenter study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freites-Martinez, A.; Santana, N.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Viera, A. Using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE—Version 5.0) to Evaluate the Severity of Adverse Events of Anticancer Therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr. Engl. Ed. 2021, 112, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Brendel, M.D.; Zacharias, S.; Mergler, S.; Jahr, H.; Wiedenmann, B.; Bretzel, R.G.; Plöckinger, U.; Strowski, M.Z. Characterization of somatostatin receptor subtype-specific regulation of insulin and glucagon secretion: An in vitro study on isolated human pancreatic islets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinke, A.; Müller, H.H.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Klose, K.J.; Barth, P.; Wied, M.; Mayer, C.; Aminossadati, B.; Pape, U.F.; Bläker, M.; et al. Placebo-controlled, double-blind, prospective, randomized study on the effect of octreotide LAR in the control of tumor growth in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine midgut tumors: A report from the PROMID Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplin, M.E.; Pavel, M.; Ćwikła, J.B.; Phan, A.T.; Raderer, M.; Sedláčková, E.; Cadiot, G.; Wolin, E.M.; Capdevila, J.; Wall, L.; et al. Lanreotide in metastatic enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolin, E.M.; Jarzab, B.; Eriksson, B.; Walter, T.; Toumpanakis, C.; Morse, M.A.; Tomassetti, P.; Weber, M.M.; Fogelman, D.R.; Ramage, J.; et al. Phase III study of pasireotide long-acting release in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors and carcinoid symptoms refractory to available somatostatin analogues. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5075–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.C.; Shah, M.H.; Ito, T.; Bohas, C.L.; Wolin, E.M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Hobday, T.J.; Okusaka, T.; Capdevila, J.; de Vries, E.G.; et al. RAD001 in Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors, Third Trial (RADIANT-3) Study Group. Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Ito, T.; Jensen, R.T. Everolimus in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors: Efficacy, side-effects, resistance, and factors affecting its place in the treatment sequence. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, K.; Hirakawa, K.; Sasazaki, K.; Tanaka, H.; Hori, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Time-to-onset of diabetes with everolimus use: Analysis of a spontaneous reporting system database. Pharmazie 2021, 76, 515–518. [Google Scholar]
- Sivendran, S.; Agarwal, N.; Gartrell, B.; Ying, J.; Boucher, K.M.; Choueiri, T.K.; Sonpavde, G.; Oh, W.K.; Galsky, M.D. Metabolic complications with the use of mTOR inhibitors for cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Baudin, E.; Kvols, L.K.; Rougier, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Hoosen, S.; St. Peter, J.; Haas, T.; Lebwohl, D..; et al. Daily oral everolimus activity in patients with metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy: A phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulke, M.H.; Ruszniewski, P.; Van Cutsem, E.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Valle, J.W.; De Herder, W.W.; Pavel, M.; Degtyarev, E.; Brase, J.C.; Bubuteishvili-Pacaud, L.; et al. A randomized, open-label, phase 2 study of everolimus in combination with pasireotide LAR or everolimus alone in advanced, well-differentiated, progressive pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: COOPERATE-2 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1309–1315, Erratum in Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.; Tsomos, E.; Hammerstad, S.S.; Tomer, Y. Interferon alpha: The key trigger of type 1 diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 94, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S. The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, N.; Hardt, P.D. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7276–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Andersen, D.K.; Bradley, D.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Forsmark, C.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Habtezion, A.; Korc, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, S.N.; Ewald, N.; Kelleher, L.; Griffin, O.; Gibney, J.; Conlon, K.C. The nutritional management of type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes in chronic pancreatitis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattamisra, S.K.; Siang, T.C.; Rong, C.Y.; Annan, N.C.; Sean, E.H.Y.; Xi, L.W.; Lyn, O.S.; Shan, L.H.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; et al. Type-3c Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes of Exocrine Pancreas—An Update. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2019, 15, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y. DPP-4 (CD26) inhibitor sitagliptin exerts anti-inflammatory effects on rat insulinoma (RINm) cells via suppressing NF-κB activation. Endocrine 2017, 55, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.E.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Gurlo, T.; Dawson, D.W.; Atkinson, M.; Butler, P.C. Marked expansion of exocrine and endocrine pancreas with incretin therapy in humans with increased exocrine pancreas dysplasia and the potential for glucagon-producing neuroendocrine tumors. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pizza, G.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Barrea, L.; Faggiano, A.; Colao, A.; NIKE Group. The management of neuroendocrine tumours: A nutritional viewpoint. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koritzinsky, M. Metformin: A novel biological modifier of tumor response to radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiant Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Martínez, A.D.; Pedraza-Arevalo, S.; L-López, F.; Gahete, M.D.; Gálvez-Moreno, M.A.; Castaño, J.P.; Luque, R.M. Type 2 Diabetes in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Are Biguanides and Statins Part of the Solution? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, S.; Buzzoni, R.; Vernieri, C.; Concas, L.; Marceglia, S.; Giacomelli, L.; Milione, M.; Leuzzi, L.; Femia, D.; Formisano, B.; et al. Metformin with everolimus and octreotide in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor patients with diabetes. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, S.; Vernieri, C.; Di Maio, M.; Prinzi, N.; Torchio, M.; Corti, F.; Coppa, J.; Buzzoni, R.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Milione, M.; et al. Impact of Diabetes and Metformin Use on Enteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Post Hoc Analysis of the CLARINET Study. Cancers 2021, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT02294006. Activity and Safety of Everolimus+Octreotide LAR + Metformin in Advanced Pancreatic Well-Differentiated NETs (MetNET1). 9 September 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02294006 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- NCT02823691. The MetNET-2 Trial (MetNET-2). 7 June 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02823691 (accessed on 20 October 2022).

| Major Criteria (All Must Be Fulfilled) | Minor Criteria |
|---|---|
| Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | Absence of pancreatic polypeptide secretion |
| Alteration of the anatomical appearance of the pancreas as evidenced by imaging studies (endoscopy, ultrasound, MRI, or scanner) | Decreased insulin secretion |
| Absence of anti-beta cell antibodies (positive in type 1 diabetes/LADA) | Low levels of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) |
| Nutrient malabsorption requiring pancreatic enzyme supplementation |
| Severity Grade | Glucose Intolerance | Hyperglycemia |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | Asymptomatic; clinical or diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated | Abnormal glucose above baseline with no medical intervention |
| G2 | Symptomatic; dietary modification or oral agent indicated | Change in daily management from baseline for a diabetic; oral antiglycemic agent initiated; workup for diabetes |
| G3 | Severe symptoms; insulin indicated | Insulin therapy initiated; hospitalization indicated |
| G4 | Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated | Life-threatening consequences; urgent intervention indicated |
| G5 | Death | Death |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez-Rienda, L.; del Olmo-García, M.I.; Merino-Torres, J.F. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Pancreatic Neuro-Endocrine Tumors: Causes, Consequences, and Future Perspectives. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111103
Hernandez-Rienda L, del Olmo-García MI, Merino-Torres JF. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Pancreatic Neuro-Endocrine Tumors: Causes, Consequences, and Future Perspectives. Metabolites. 2022; 12(11):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111103
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez-Rienda, Lorena, Maria Isabel del Olmo-García, and Juan Francisco Merino-Torres. 2022. "Impact of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Pancreatic Neuro-Endocrine Tumors: Causes, Consequences, and Future Perspectives" Metabolites 12, no. 11: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111103
APA StyleHernandez-Rienda, L., del Olmo-García, M. I., & Merino-Torres, J. F. (2022). Impact of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with Pancreatic Neuro-Endocrine Tumors: Causes, Consequences, and Future Perspectives. Metabolites, 12(11), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111103





