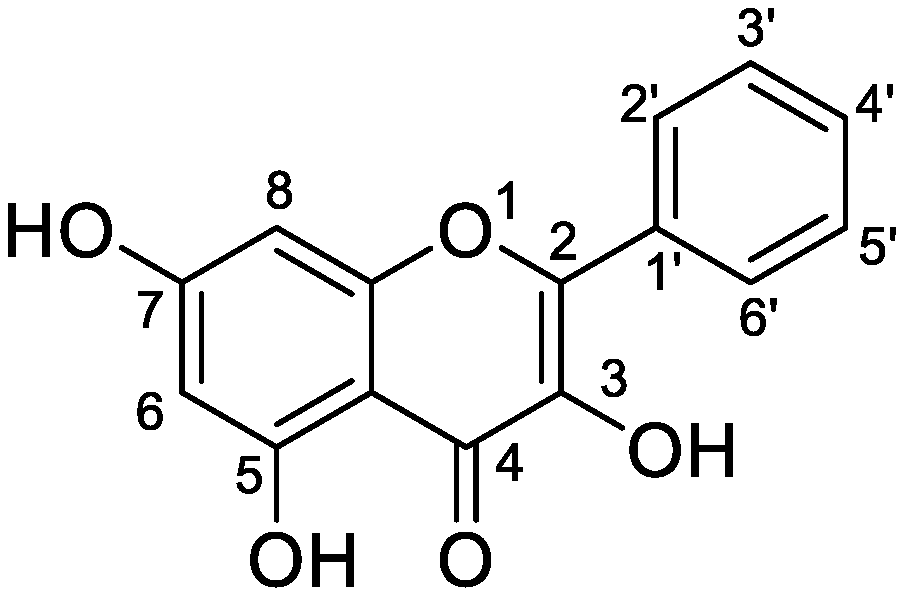
Analysis of Galangin and Its In Vitro/In Vivo Metabolites via Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. In Vivo Metabolism
2.2.1. Animal and Drug Administration
2.2.2. Sample Collection of Plasma, Urine, Feces, Bile, and Tissue
2.2.3. Preparation of Plasma, Urine, Feces, Bile, and Tissue Sample Solutions
2.3. In Vitro Metabolism by Rat Liver Microsomes
2.4. In Vitro Metabolism by Rat Intestinal Flora
2.5. Instruments and Analytical Conditions
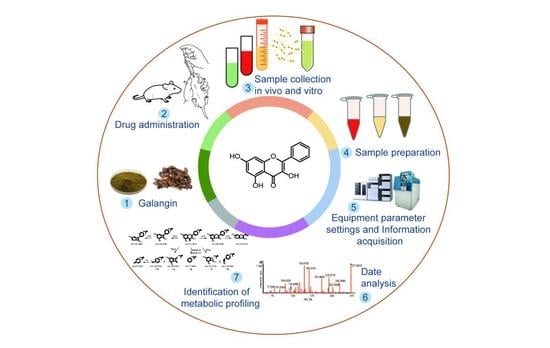
2.6. Analytical Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of LC-MS Conditions
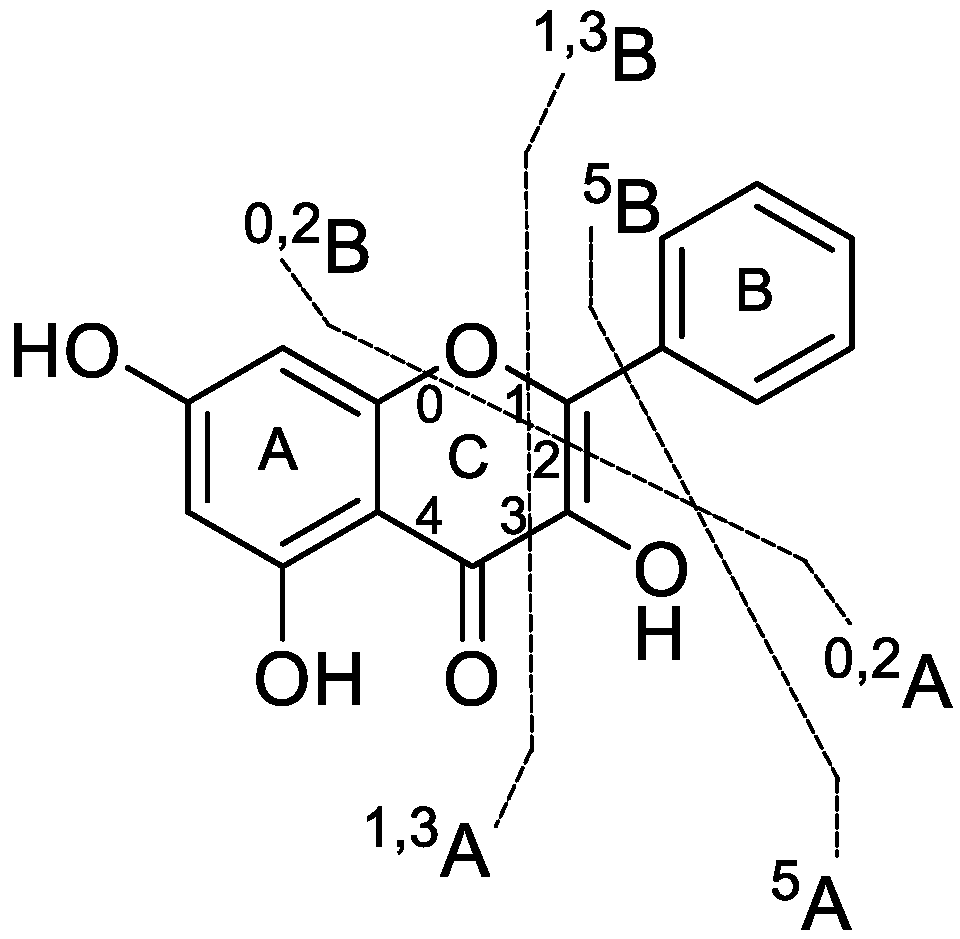
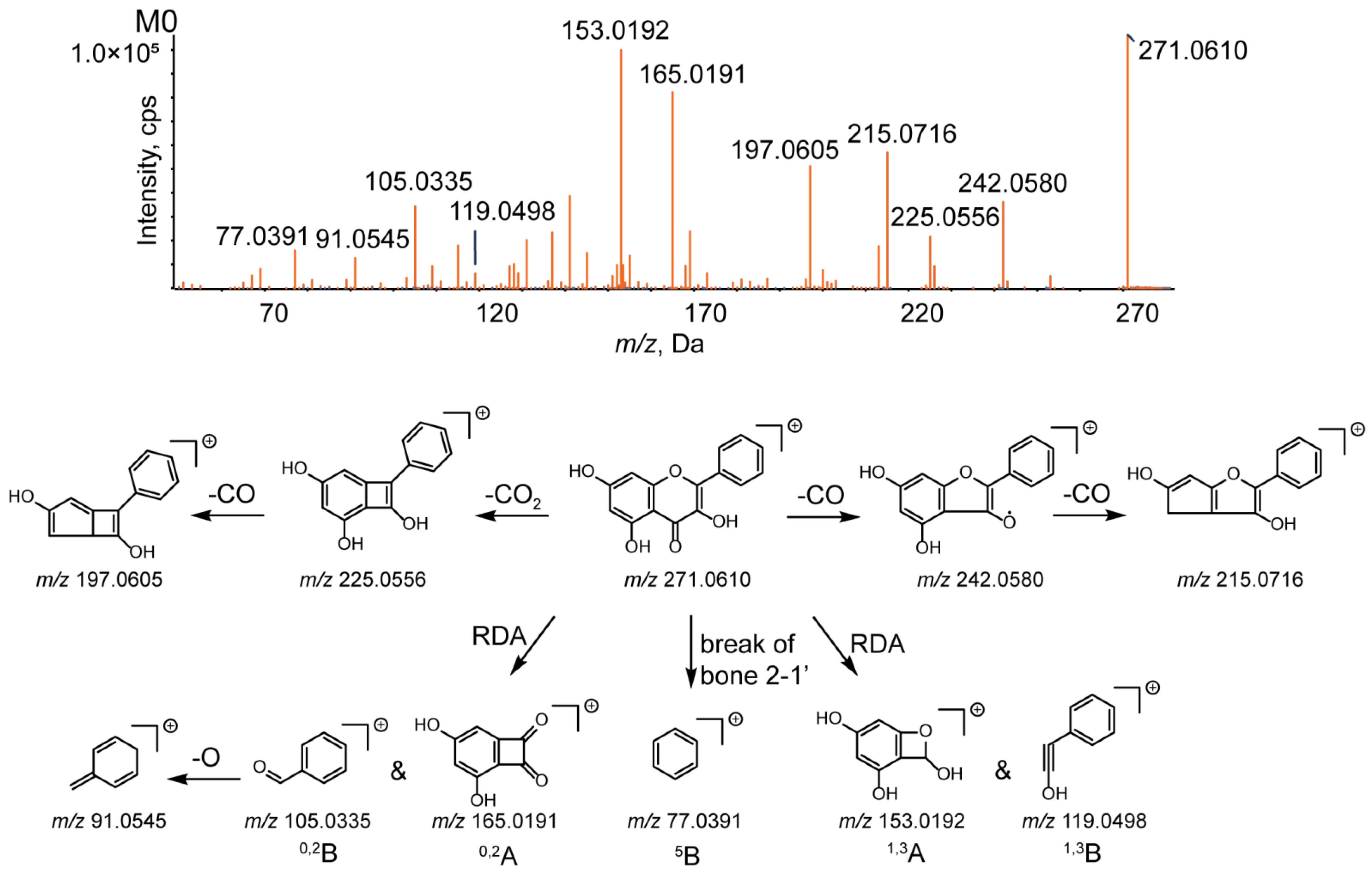
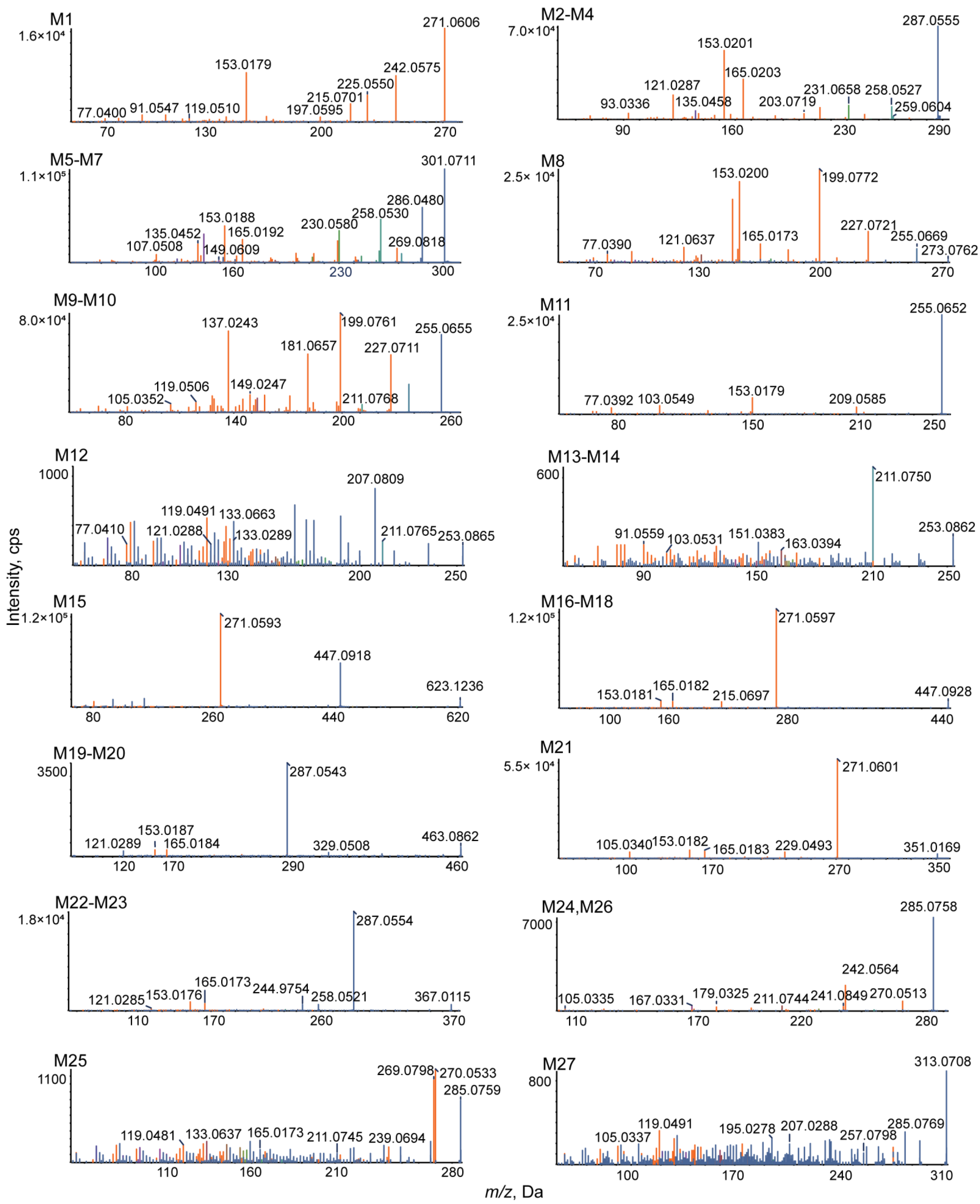
3.2. Analytical Strategy and Metabolite Identification
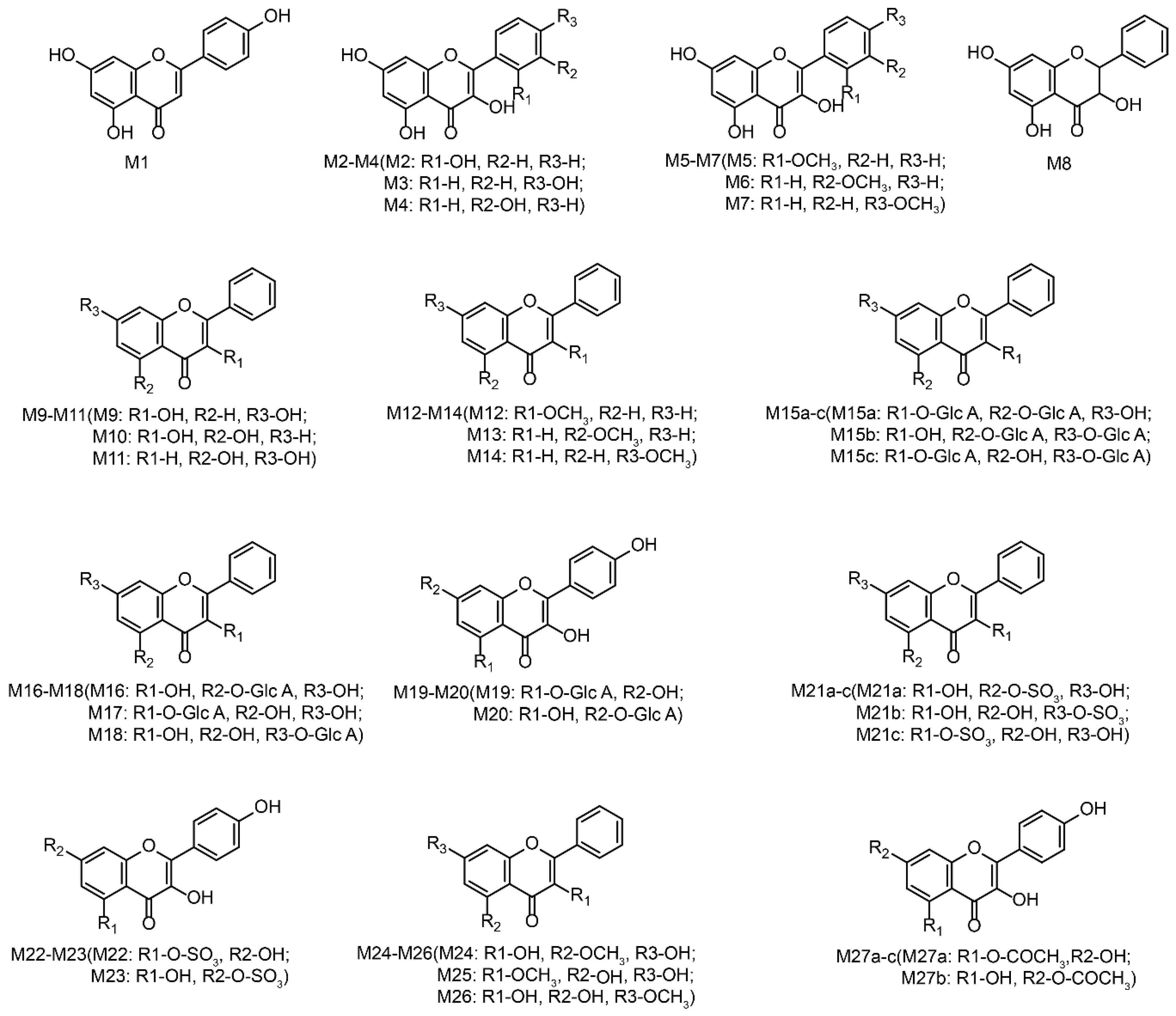
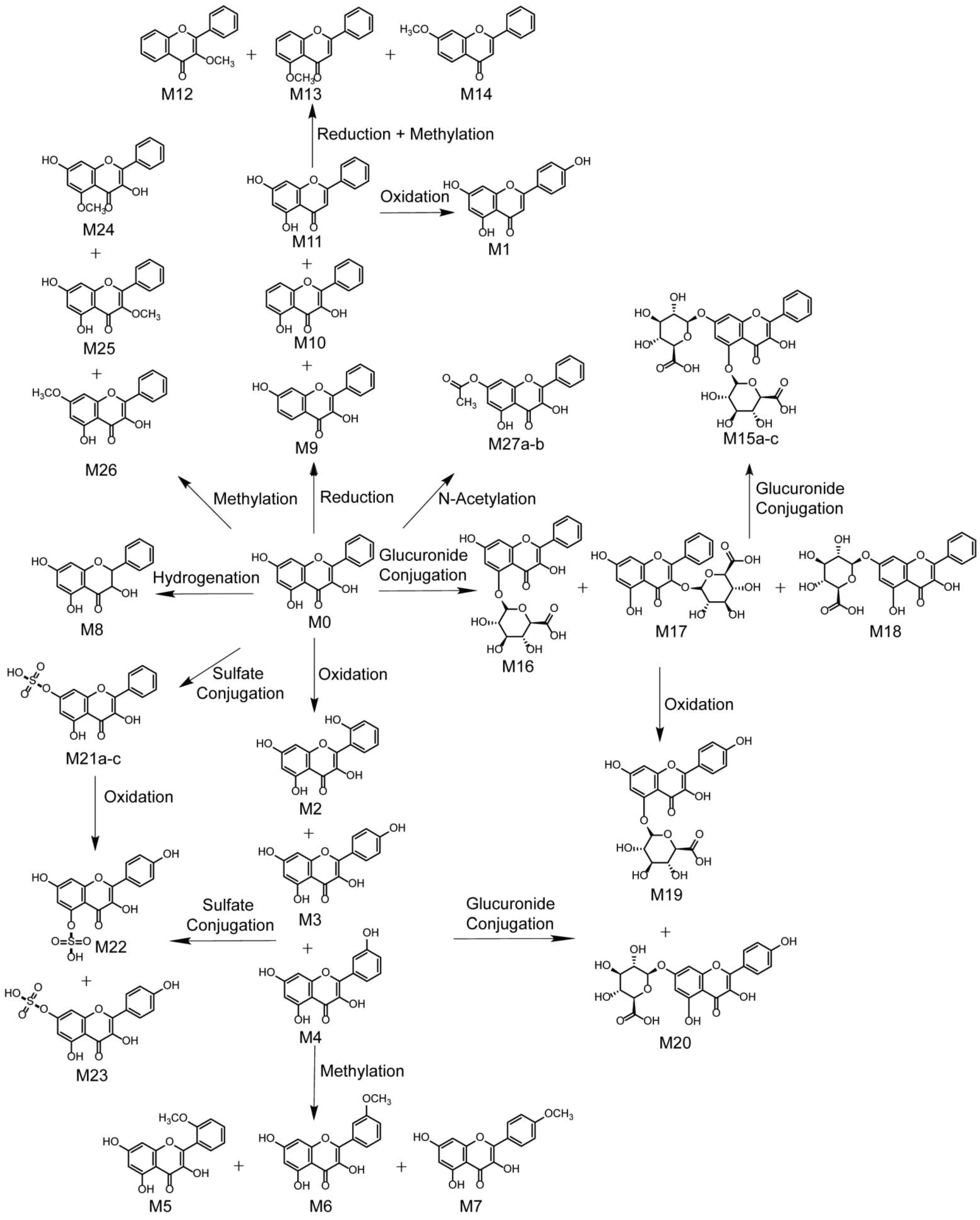
3.3. Identification of Phase I Metabolites
3.3.1. Oxidation Reaction
3.3.2. Reduction Reaction
3.4. Identification of Phase II Metabolites
3.5. Proposed Metabolic Pathways of Galangin
3.6. Comparison of Metabolites in Different Matrices
3.7. Biological Activity of Galangin and Its Metabolites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyer, J.J.M.; Afolayan, A.J.; Taylor, M.B.; Erasmus, D. Antiviral activity of galangin isolated from the aerial parts of Helichrysum aureonitens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1997, 56, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalani, S.; Poh, C.L. Flavonoids as antiviral agents for enterovirus A71 (EV-A71). Viruses 2020, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Hamilton, V.E.S.; Lamb, A.J. Assessment of the antibacterial activity of selected flavonoids and consideration of discrepancies between previous reports. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Yan, C.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-Q.; Zhen, L.-L. Galangin potentiates human breast cancer to apoptosis induced by TRAIL through activating AMPK. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, A.Y.; Ye, X.; Guan, R.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C. Galangin, a flavonoid from lesser galangal, induced apoptosis via p53-dependent pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Tiku, A.B. Galangin induces cell death by modulating the expression of glyoxalase-1 and Nrf-2 in HeLa cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 279, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-X.; Tang, C. Galangin suppresses human laryngeal carcinoma via modulation of caspase-3 and AKT signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.K.; Kim, M.E.; Yoon, J.H.; Bae, S.J.; Yeom, J.; Lee, J.S. Galangin induces human colon cancer cell death via the mitochondrial dysfunction and caspase-dependent pathway. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.A.; Lee, D.H.; Woo, S.M.; Seo, B.R.; Min, K.-J.; Kim, S.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kwon, T.K. Galangin sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis through down-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins in renal carcinoma Caki cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Hua, Z. Galangin and TRAIL cooperate to suppress A549 lung cancer proliferation via apoptosis and p38 MAPK activation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zhang, W.; Wu, G.; Ren, J.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Han, X. Synergistic anti-cancer effects of galangin and berberine through apoptosis induction and proliferation inhibition in oesophageal carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Tan, Y.-F.; Li, H.-L.; Qin, Z.-M.; Cai, H.-D.; Lai, W.-Y.; Zhang, X.-P.; Li, Y.-H.; Guan, W.-W.; Li, Y.-B.; et al. Differential systemic exposure to galangin after oral and intravenous administration to rats. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, H.; Wei, N.; Tan, Y. Simultaneous determination of two galangin metabolites from Alpinia officinarum Hance in rat plasma by UF LC-MS/MS and its application in pharmacokinetics study. PeerJ 2021, 9, 11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.L.; Zhao, F.; Yin, J.-T.; Liang, C.-J.; Niu, X.-L.; Qiu, Z.-H.; Zhang, L.-T. Two approaches for evaluating the effects of galangin on the activities and mRNA expression of seven CYP450. Molecules 2019, 24, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Stonik, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Metabolite profiling of triterpene glycosides of the far eastern sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix and their distribution in various body components using LC-ESI QTOF-MS. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Garg, A.; Takwani, H.; Singh, S. Metabolite identification by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 360–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Cao, G. Identification of metabolites of gardenin A in rats by combination of high-performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometer based on multiple data processing techniques. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Du, P.; Chen, Y. Identification of in vivo and in vitro metabolites of triptolide by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Guang, C.; Qiao, M.; Wang, T.; Chai, L.; Qiu, F. Characterization of the in vivo and in vitro metabolites of linarin in rat biosamples and intestinal flora using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2018, 23, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaouguaou, F.-E.; Ahl Bebaha, M.A.; Yadlapalli, S.; Taghzouti, K.; Es-safi, N.E. Structural characterization of bioactive compounds in Cotula cinerea extracts by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array and high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry detectors. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizah, M.; Pripdeevech, P.; Thongkongkaew, T.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS-based molecular networking guided isolation and dereplication of antibacterial and antifungal constituents of Ventilago denticulata. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, S.I.; Vale, N.; Gomes, P.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Freire, C.; Cardoso, S.M.; Vilas-Boas, M. Phenolic profiling of Portuguese propolis by LC-MS spectrometry: Uncommon propolis rich in flavonoid glycosides. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Li, H.-L.; Tan, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-H.; Lai, W.-Y.; Guan, W.-W.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-S.; Qin, Z.-M. Identification of known chemicals and their metabolites from Alpinia oxyphylla fruit extract in rat plasma using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with selected reaction monitoring. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 97, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-J.; Deinzer, M.L. Tandem mass spectrometry for sequencing proanthocyanidins. Anal Chem. 2007, 79, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, R.; Williamson, G.; Bennett, R.N.; Davis, B.D.; Brodbelt, J.S.; Kroon, P.A. Absorption, conjugation and efflux of the flavonoids, kaempferol and galangin, using the intestinal CACO-2/TC7 cell model. J. Funct. Foods 2009, 1, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Mao, F.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yamamoto, K. Interaction of dietary polyphenols with bovine milk proteins: Molecular structure-affinity relationship and influencing bioactivity aspects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, E.R.; Ang, H.L.; Asnaf, S.E.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Yavari, M.; Esmaeili, H.; Zarrabi, A.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Kumar, A.P. Broad-Spectrum Preclinical Antitumor Activity of Chrysin: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sinha, S.; Rathaur, P.; Vora, J.; Jha, P.C.; Johar, K.; Rawal, R.M.; Shrivastava, N. Reckoning apigenin and kaempferol as a potential multi-targeted inhibitor of EGFR/HER2-MEK pathway of metastatic colorectal cancer identified using rigorous computational workflow. Mol. Divers. 2022; Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Suchal, K.; Khan, S.I.; Bhatia, J.; Kishore, K.; Dinda, A.K.; Arya, D.S. Apigenin ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via MAPK-NF-κB-TNF-α and TGF-β1-MAPK-fibronectin pathways. Am. J. Physiology. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kumar Tekade, R.; Kalia, K. Kaempferol in ameliorating diabetes-induced fibrosis and renal damage: An in vitro and in vivo study in diabetic nephropathy mice model. Phytomedicine 2020, 76, 153235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhong, Y.; Feng, N.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Xing, D. New horizons in the roles and associations of COX-2 and novel natural inhibitors in cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Compound Formula | Molecular Weight (Da) | Width (Da) | Mass Loss (mDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C15H10O5 | 270.0528 | 100 | 52.8236 |
| 2 | C15H10O5 C6H8O6 | 446.0849 | 100 | 84.9118 |
| 3 | C15H10O5 SO3 | 350.0096 | 100 | 9.6393 |
| 4 | C15H10O5 CH2 | 284.0685 | 100 | 68.4737 |
| 5 | C15H10O5 C2H2O | 312.0634 | 100 | 63.3883 |
| Report | Name | Formula | m/z | ppm | R.T. (min) | % Score | MS/MS | Clog P | P | B | U | F | H | T | M | Li | Bo | Lu | K | St | Br | S | Me | RML | IB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Isomer | C15H10O5 | 271.0606 | 1.8 | 8.45 | 94.3 | 271.0606, 242.0575, 225.0550, 215.0701, 197.0595, 153.0179, 119.0510, 91.0547, 77.0400 | 2.90529 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| M2 | Oxidation | C15H10O6 | 287.0555 | 1.6 | 6.47 | 69.1 | 287.0555, 259.0604, 258.0527, 231.0658, 203.0719, 165.0203, 153.0201, 135.0458, 121.0287, 93.0336 | 1.79989 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| M3 | Oxidation | C15H10O6 | 287.0547 | −1.2 | 9.39 | 75.6 | 287.0547, 259.0607, 258.0523, 231.0655, 203.0717, 165.0193, 153.0194, 135.0455, 121.0288, 93.0334 | 2.09989 | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| M4 | Oxidation | C15H10O6 | 287.0556 | 2.1 | 10.4 | 70.8 | 287.0556, 259.0606, 258.0528, 231.0656, 203.0721, 165.0197, 153.0196, 135.0456, 121.0285, 93.0331 | 2.09989 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| M5 | Oxidation and Methylation | C16H12O6 | 301.0711 | 1.3 | 8.08 | 78.1 | 301.0711, 286.0480, 269.0818, 258.0530, 230.0580, 165.0192, 153.0188, 149.0609, 135.0452, 107.0508 | 2.13699 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| M6 | Oxidation and Methylation | C16H12O6 | 301.0715 | 2.8 | 8.77 | 74.9 | 301.0715, 286.0484, 269.0822, 258.0533, 230.0584, 165.0195, 153.0189, 149.0613, 135.0456, 107.0512 | 2.69699 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| M7 | Oxidation and Methylation | C16H12O6 | 301.0712 | 1.7 | 12.15 | 67.7 | 301.0712, 286.0485, 269.0819, 258.0532, 230.0581, 165.0193, 153.0187, 149.0611, 135.0453, 107.0509 | 2.69699 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| M8 | Hydrogenation | C15H12O5 | 273.0762 | 1.8 | 6.63 | 80.8 | 273.0762, 255.0669, 227.0721, 199.0772, 165.0173, 153.0200, 121.0637, 77.0390 | 2.03495 | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| Report | Name | Formula | m/z | ppm | R.T. (min) | % Score | MS/MS | Clog P | P | B | U | F | H | T | M | Li | Bo | Lu | K | St | Br | S | Me | RML | IB |
| M9 | Loss of O | C15H10O4 | 255.0655 | 1.1 | 7.74 | 89.8 | 255.0655, 227.0711, 211.0768, 199.0761, 181.0657 149.0247, 137.0243, 119.0506, 105.0352 | 2.49525 | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| M10 | Loss of O | C15H10O4 | 255.0654 | 0.7 | 9.15 | 76.4 | 255.0654, 227.0709, 211.0766, 199.0759, 149.0245, 137.0241 | 3.39525 | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| M11 | Loss of O | C15H10O4 | 255.0652 | 0.2 | 11.73 | 81.8 | 255.0652, 209.0585, 153.0179, 103.0549, 77.0392 | 3.56275 | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| M12 | Loss of O and O + Methylation | C16H12O3 | 253.0865 | 2.3 | 6.55 | 86.4 | 253.0865, 211.0765, 207.0809, 133.0663, 133.0289, 121.0288, 119.0491, 77.0410 | 3.089 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| M13 | Loss of O and O + Methylation | C16H12O3 | 253.0862 | 1.2 | 6.90 | 87 | 253.0862, 211.0750, 163.0394, 151.0383, 103.0531, 91.0559 | 3.5865 | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| M14 | Loss of O and O + Methylation | C16H12O3 | 253.0861 | 0.6 | 8.43 | 58.8 | 253.0861, 211.0749, 163.0391, 151.0382, 103.0530, 91.0558 | 3.5865 | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| M15 a | Bis-Glucuronide Conjugation | C27H26O17 | 623.1236 | −1.1 | 4.45 | 84.4 | 623.1236, 447.0918, 271.0593 | −2.44921 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| M15 b | −2.08677 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M15 c | −1.54921 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M16 | Glucuronidation | C21H18O11 | 447.0928 | 1.4 | 4.10 | 93.5 | 447.0928, 271.0597, 215.0697, 165.0182, 153.0181 | −0.0529127 | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| M17 | Glucuronidation | C21H18O11 | 447.0922 | 0 | 4.79 | 88.9 | 447.0922, 271.0595, 215.0694, 165.0180, 153.0183 | 0.444445 | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| M18 | Glucuronidation | C21H18O11 | 447.0920 | −0.5 | 8.48 | 75 | 447.0920, 271.0593, 215.0691, 165.0177, 153.0179 | 0.847087 | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| M19 | Oxidation and Glucuronide Conjugation | C21H18O12 | 463.0862 | −1.8 | 3.41 | 75.6 | 463.0862, 329.0508, 287.0543, 165.0184, 153.0187, 121.0289 | −0.717049 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| M20 | Oxidation and Glucuronide Conjugation | C21H18O12 | 463.0859 | −2.6 | 3.82 | 74.1 | 463.0859, 329.0506, 287.0540, 165.0181, 153.0184, 121.0285 | 0.182951 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Report | Name | Formula | m/z | ppm | R.T. (min) | % Score | MS/MS | Clog P | P | B | U | F | H | T | M | Li | Bo | Lu | K | St | Br | S | Me | RML | IB |
| M21 a | Sulfate Conjugation | C15H10O8S | 351.0169 | −0.2 | 5.68 | 96.4 | 351.0169, 271.0601, 229.0493, 165.0183, 153.0182, 105.0340 | 0.362386 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| M21 b | 1.26239 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M21 c | 1.41974 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M22 | Oxidation and Sulfate Conjugation | C15H10O9S | 367.0115 | −0.8 | 5.03 | 79.6 | 367.0115, 287.0554, 258.0521, 244.9754, 165.0173, 153.0176, 121.0285 | −0.301752 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| M23 | Oxidation and Sulfate Conjugation | C15H10O9S | 367.0121 | 0.8 | 5.44 | 82.1 | 367.0121, 287.0558, 258.0526, 244.9759, 165.0177, 153.0179, 121.0287 | 0.598248 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| M24 | Methylation | C16H12O5 | 285.0758 | 0.3 | 8.01 | 74.4 | 285.0758, 270.0513, 242.0564, 241.0849, 211.0744, 179.0325, 167.0331, 105.0335 | 2.50839 | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| M25 | Methylation | C16H12O5 | 285.0759 | 0.5 | 12.55 | 96.3 | 285.0759, 270.0533, 269.0798, 239.0694, 211.0745, 165.0173, 133.0637, 119.0481 | 3.00574 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| M26 | Methylation | C16H12O5 | 285.0755 | −0.9 | 14.82 | 97.1 | 285.0755, 270.0511, 242.0561, 241.0845, 211.0742, 179.0322, 167.0328, 105.0331 | 3.40839 | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| M27 a | N-Acetylation | C17H12O6 | 313.0708 | 0.6 | 13.13 | 84.9 | 313.0708, 285.0769, 257.0798, 207.0288, 195.0278, 119.0491, 105.0337 | 1.93839 | + | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, F.; Ma, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L. Analysis of Galangin and Its In Vitro/In Vivo Metabolites via Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111032
Zhao F, Ma Y, Yin J, Li Y, Cao Y, Zhang L. Analysis of Galangin and Its In Vitro/In Vivo Metabolites via Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2022; 12(11):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111032
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Feng, Yinling Ma, Jintuo Yin, Ying Li, Yanli Cao, and Lantong Zhang. 2022. "Analysis of Galangin and Its In Vitro/In Vivo Metabolites via Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 12, no. 11: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111032
APA StyleZhao, F., Ma, Y., Yin, J., Li, Y., Cao, Y., & Zhang, L. (2022). Analysis of Galangin and Its In Vitro/In Vivo Metabolites via Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 12(11), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111032