Metabolic Alterations Associated with γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and the Potential of Metabolites as Biomarkers of Its Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of GHB
3. Analytical Issues of GHB in Biological Samples
4. GHB-Associated Metabolic Changes in AA, OA, and Polyamine (PA)
5. Changes in the Levels of GHB Conjugates upon GHB Exposure
6. Future Directions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Califf, R.M. Biomarker definitions and their applications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiaghi, A.; Ferrario, M.; Masseroli, M. Analysis of metabolomic data: Tools, current strategies and future challenges for omics data integration. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, R.; Struck-Lewicka, W.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Kaliszan, R. Metabolomics for laboratory diagnostics. J. Pharm. BioMed. Anal. 2015, 113, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jang, W.J.; Shakya, R.; Choi, B.; Jeong, C.H.; Lee, S. Current Understanding of Methamphetamine-associated metabolic changes revealed by the metabolomics approach. Metabolites 2019, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Kim, S.P.; Hwang, S.; Hwang, J.; Yang, C.H.; Lee, S. Metabolic characterization in urine and hair from a rat model of methamphetamine self- administration using LC-QTOF-MS-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, B.; Seo, J.H.; Seo, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Jeong, C.H. Hair Metabolomics in Animal Studies and Clinical Settings. Molecules 2019, 24, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jang, W.J.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, C.H.; Lee, S. Revealing Metabolic Perturbation Following Heavy Methamphetamine Abuse by Human Hair Metabolomics and Network Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jang, W.J.; Yu, H.; Ryu, I.S.; Jeong, C.H.; Lee, S. Integrated Non-targeted and Targeted Metabolomics Uncovers Dynamic Metabolic Effects during Short-Term Abstinence in Methamphetamine Self-Administering Rats. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3913–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.L.; Telving, R.; Andreasen, M.F.; Hasselstrøm, J.B.; Johannsen, M. A Metabolomics Study of Retrospective Forensic Data from Whole Blood Samples of Humans Exposed to 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine: A New Approach for Identifying Drug Metabolites and Changes in Metabolism Related to Drug Consumption. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsu, K.; Miyawaki, I.; Bando, K.; Horie, H.; Shima, N.; Katagi, M.; Tatsuno, M.; Bamba, T.; Sato, T.; Ishii, A.; et al. Metabolic profiling of urine and blood plasma in rat models of drug addiction on the basis of morphine, methamphetamine, and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. Anal. BioAnal. Chem. 2014, 406, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Chong, E.Y.; Walker, D.I.; Chandler, J.D.; Michalski, E.S.; Grossmann, R.E.; Uppal, K.; Li, S.; Frediani, J.K.; Tirouvanziam, R.; et al. Plasma metabolomics in adults with cystic fibrosis during a pulmonary exacerbation: A pilot randomized study of high-dose vitamin D(3) administration. Metabolism 2017, 70, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, R.M.; van Iwaarden, S.; Dijkstra, B.A.; de Jong, C.A. Decision rules for GHB (γ-hydroxybutyric acid) detoxification: A vignette study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 135, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, P.C.; Yoong, F.F. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid: An emerging recreational drug. Anaesthesia 1998, 53, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Berto, R.; Viel, G.; Montagnese, S.; Raduazzo, D.I.; Ferrara, S.D.; Dauvilliers, Y. Narcolepsy and effectiveness of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB): A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schep, L.J.; Knudsen, K.; Slaughter, R.J.; Vale, J.A.; Mégarbane, B. The clinical toxicology of γ-hydroxybutyrate, γ-butyrolactone and 1,4-butanediol. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila) 2012, 50, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snead, O.C., 3rd; Gibson, K.M. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2721–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitány-Fövény, M.; Zacher, G.; Posta, J.; Demetrovics, Z. GHB-involved crimes among intoxicated patients. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 275, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvosec, D.L.; Smith, S.W.; Porrata, T.; Strobl, A.Q.; Dyer, J.E. Case series of 226 γ-hydroxybutyrate-associated deaths: Lethal toxicity and trauma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 29, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, C.A.; Kamal, R.; Dijkstra, B.A.; de Haan, H.A. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate detoxification by titration and tapering. Eur. Addict. Res. 2012, 18, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.E.; Roth, B.; Hyma, B.A. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate withdrawal syndrome. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 37, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.; Gomez, H.F.; McManus, J.L.; Bania, T.C. Severe gamma-hydroxybutyrate withdrawal: A case report and literature review. J. Emerg. Med. 2000, 18, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerts, E.M.; Goodwin, A.K.; Griffiths, R.R.; Brown, P.R.; Froestl, W.; Jakobs, C.; Gibson, K.M. Spontaneous and precipitated withdrawal after chronic intragastric administration of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in baboons. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldicott, D.G.; Kuhn, M. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate overdose and physostigmine: Teaching new tricks to an old drug? Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 37, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, S.W.; Viera, A.J. Physostigmine in the treatment of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid overdose. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2000, 75, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvosec, D.L.; Smith, S.W.; Litonjua, R.; Westfal, R.E. Physostigmine for gamma-hydroxybutyrate coma: Inefficacy, adverse events, and review. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoto, P.; Colombo, G.; Cappai, F.; Gessa, G.L. Naloxone antagonizes ethanol- but not gamma-hydroxybutyrate-induced sleep in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 1994, 252, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.; Satz, W.A.; Dougherty, T.; Greene, T. An investigation of flumazenil to antagonize gamma-hydroxybutyrate intoxication in a murine model. J. Med. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carai, M.A.; Colombo, G.; Gessa, G.L. Resuscitative effect of a gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor antagonist on gamma-hydroxybutyric acid mortality in mice. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2005, 45, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S. Nonfatal instances of intoxication with gamma-hydroxybutyrate in the United Kingdom. Drug Monit. 2004, 26, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelberg, F.C.; Holmgren, A.; Eklund, A.; Jones, A.W. Forensic toxicology findings in deaths involving gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2010, 124, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Seo, C.; Kim, Y.-A.; Park, M.; Choi, B.; Ji, M.; Lee, S.; Paik, M.-J. Metabolomic study of polyamines in rat urine following intraperitoneal injection of γ-hydroxybutyric acid. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Schätzlein, M.; Wang, Y.; Brailsford, A.D.; Parella, T.; Cowan, D.A.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Pérez-Trujillo, M. Direct Monitoring of Exogenous γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid in Body Fluids by NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8343–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.; Na, M.; Jang, J.; Park, M.; Choi, B.; Lee, S.; Paik, M.-J. Monitoring of altered amino acid metabolic pattern in rat urine following intraperitoneal injection with γ-hydroxybutyric acid. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, S.; Stachel, N.; Skopp, G. A potential new metabolite of gamma-hydroxybutyrate: Sulfonated gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2016, 130, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, I.N.; Tortzen, C.; Kristensen, J.L.; Pedersen, D.S.; Breindahl, T. Identification of a new metabolite of GHB: Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid glucuronide. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascali, J.P.; Fais, P.; Vaiano, F.; Ciolini, A.; Bertol, E. Zwitterionic HILIC stationary phase as a valuable alternative in separative techniques: Application to the analysis of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid and its metabolite in hair. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. BioMed. Life Sci. 2019, 1134–1135, 121876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.S.; Castro, A.L.; Melo, P.; Tarelho, S.; Domingues, P.; Franco, J.M. A fast method for GHB-GLUC quantitation in whole blood by GC-MS/MS (TQD) for forensic purposes. J. Pharm. BioMed. Anal. 2018, 150, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Gottardi, M.; Tini, A.; Mortali, C.; Giorgetti, R.; Pichini, S. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Determination of Endogenous GHB and GHB-Glucuronide in Nails. Molecules 2018, 23, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Mehling, L.M.; Spottke, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Young, P.; Madea, B.; Hess, C.; Schänzer, W.; Thevis, M. Potential of GHB phase-II-metabolites to complement current approaches in GHB post administration detection. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 279, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.E.; Raeber, J.; Steuer, C.; Boxler, M.I.; Dornbierer, D.A.; Bosch, O.G.; Quednow, B.B.; Seifritz, E.; Kraemer, T. Identification of new urinary gamma-hydroxybutyric acid markers applying untargeted metabolomics analysis following placebo-controlled administration to humans. Drug Test Anal. 2019, 11, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.; Park, M.; Choi, B.; Lee, S.; Paik, M.-J. Metabolomic analysis of urinary organic acids following intraperitoneal injection with γ-hydroxybutyric acid in rats. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunnicliff, G. Sites of action of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB)--a neuroactive drug with abuse potential. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.G.; Chan, K.F.; Gibson, K.M.; Snead, O.C. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid: Neurobiology and toxicology of a recreational drug. Toxicol. Rev. 2004, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamelak, M. Gammahydroxybutyrate: An endogenous regulator of energy metabolism. NeuroSci. Biobehav. Rev. 1989, 13, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, M. The gamma-hydroxybutyrate signalling system in brain: Organization and functional implications. Prog. NeuroBiol. 1997, 51, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogema, B.M.; Gupta, M.; Senephansiri, H.; Burlingame, T.G.; Taylor, M.; Jakobs, C.; Schutgens, R.B.; Froestl, W.; Snead, O.C.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; et al. Pharmacologic rescue of lethal seizures in mice deficient in succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, H.; Aydin, B.E.; Mueller, A.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S. An overview of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid: Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, toxic effects, addiction, analytical methods, and interpretation of results. Drug Test Anal. 2011, 3, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBeau, M.A.; Miller, M.L.; Levine, B. Effect of storage temperature on endogenous GHB levels in urine. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 119, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneisen, R.; Elsohly, M.A.; Murphy, T.P.; Passarelli, J.; Russmann, S.; Salamone, S.J.; Watson, D.E. Pharmacokinetics and excretion of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in healthy subjects. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.; Goullé, J.P.; Cirimele, V.; Ludes, B. Window of detection of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in blood and saliva. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 2033–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, C.; Thai, D.; Jacob, P., 3rd; Dyer, J.E. GHB urine concentrations after single-dose administration in humans. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Pichini, S.; Zaami, S.; Pacifici, R.; Kintz, P. Hair testing of GHB: An everlasting issue in forensic toxicology. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, I.J.; Lusthof, K.J. Forensic cases involving the use of GHB in The Netherlands. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 133, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elian, A.A. Determination of endogenous gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) levels in antemortem urine and blood. Forensic Sci. Int. 2002, 128, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatman, D.T.; Reid, K. A study of urinary endogenous gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) levels. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2003, 27, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Steinecke, H. Beitrag zur Bewertung von Gamma-Hydroxybuttersa¨ure (GHB)-Konzentrationen im Blut lebender Personen sowie in postmortalen Blutproben. ToxiChem. Krimtech. 2007, 74, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Crookes, C.E.; Faulds, M.C.; Forrest, A.R.; Galloway, J.H. A reference range for endogenous gamma-hydroxybutyrate in urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, R.R.; Paget-Wilkes, H.; Chronister, C.W.; Goldberger, B.A. Analysis of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in urine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1999, 23, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, P.V.; Kenny, P.; Feely, J. The urinary excretion of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in man. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2001, 53, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, H.; Sprys, N.; Schmoldt, A.; Mueller, A.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate in urine and serum: Additional data supporting current cut-off recommendations. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 200, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Oh, S.M.; Chung, K.H.; Lee, S. A surrogate analyte-based LC-MS/MS method for the determination of γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in human urine and variation of endogenous urinary concentrations of GHB. J. Pharm. BioMed. Anal. 2014, 98, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.M. Pharmacologic, pharmacokinetic, and clinical assessment of illicitly used gamma-hydroxybutyrate. J. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 57, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardo, F.P.; Kyriakou, C. GHB in biological specimens: Which cut-off levels should be taken into consideration in forensic toxicological investigation? Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2014, 8, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.R.; Ainslie, G.R.; Walters, D.C.; McConnell, A.; Dhamne, S.C.; Rotenberg, A.; Roullet, J.B.; Gibson, K.M. Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency, a disorder of GABA metabolism: An update on pharmacological and enzyme-replacement therapeutic strategies. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBacco, M.L.; Roullet, J.B.; Kapur, K.; Brown, M.N.; Walters, D.C.; Gibson, K.M.; Pearl, P.L. Age-related phenotype and biomarker changes in SSADH deficiency. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beránková, K.; Mutnanská, K.; Balíková, M. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid stability and formation in blood and urine. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 161, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailsford, A.D.; Cowan, D.A.; Kicman, A.T. Urinary γ-hydroxybutyrate concentrations in 1126 female subjects. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2010, 34, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, S.; Farré, M.; Segura, M.; Pichini, S.; Pastor, A.; Pacifici, R.; Pellegrini, M.; de la Torre, R. Disposition of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in conventional and nonconventional biologic fluids after single drug administration: Issues in methodology and drug monitoring. Drug Monit. 2007, 29, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paoli, G.; Walker, K.M.; Pounder, D.J. Endogenous γ-hydroxybutyric acid concentrations in saliva determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Castro, A.L.; Dias, M.; Reis, F.; Teixeira, H.M. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid endogenous production and post-mortem behavior–The importance of different biological matrices, cut-off reference values, sample collection and storage conditions. J. Forensic Leg Med. 2014, 27, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, S. The presence of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) in postmortem biological fluids. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2001, 25, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kintz, P.; Villain, M.; Cirimele, V.; Ludes, B. GHB in postmortem toxicology. Discrimination between endogenous production from exposure using multiple specimens. Forensic Sci. Int. 2004, 143, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadones, N.; Capiau, S.; De Kesel, P.M.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C. Spot them in the spot: Analysis of abused substances using dried blood spots. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2211–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stove, C.P.; Ingels, A.S.; De Kesel, P.M.; Lambert, W.E. Dried blood spots in toxicology: From the cradle to the grave? Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2012, 42, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò, F.P.; Vergallo, G.M.; Plazzi, G. GHB Pharmacology and Toxicology: From Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics to Applications: In Clinical and Forensic Toxicology. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 1054–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.A. Novel Approach to Document Single Exposure to GHB: Hair Analysis after Sweat Contamination. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, J.; Shen, J. Differences in cytocompatibility between collagen, gelatin and keratin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 59, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, N.; Miki, A.; Kamata, T.; Katagi, M.; Tsuchihashi, H. Urinary endogenous concentrations of GHB and its isomers in healthy humans and diabetics. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 149, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBeau, M.A.; Montgomery, M.A.; Morris-Kukoski, C.; Schaff, J.E.; Deakin, A.; Levine, B. A comprehensive study on the variations in urinary concentrations of endogenous gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB). J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raknes, G.; Aronsen, L.; Fuskevåg, O.M. Urinary concentrations of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid and related compounds in pregnancy. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2010, 34, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailsford, A.D.; Cowan, D.A.; Kicman, A.T. Pharmacokinetic properties of γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in whole blood, serum, and urine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 36, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.R.; Olsen, K.M.; Strand, D.H. Determination of γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), pregabalin, 1,4-butane-diol (1,4BD) and γ-butyrolactone (GBL) in whole blood and urine samples by UPLC-MSMS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. BioMed. Life Sci. 2012, 885-886, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S.S.; Windberg, C.N. Simultaneous determination of γ-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) and its analogues (GBL, 1.4-BD, GVL) in whole blood and urine by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeld, B.; Burns, M.L.; Karinen, R.; Larssen, B.; Smith-Kielland, A.; Vindenes, V. Long-term stability of GHB in post-mortem samples and samples from living persons, stored at -20°C, using fluoride preservatives. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 222, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struys, E.A.; Verhoeven, N.M.; Jansen, E.E.; Ten Brink, H.J.; Gupta, M.; Burlingame, T.G.; Quang, L.S.; Maher, T.; Rinaldo, P.; Snead, O.C.; et al. Metabolism of gamma-hydroxybutyrate to d-2-hydroxyglutarate in mammals: Further evidence for d-2-hydroxyglutarate transhydrogenase. Metabolism 2006, 55, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebich, H.M. Gas chromatographic profiling of ketone bodies and organic acids in diabetes. J. Chromatogr. 1986, 379, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, H.; Paik, M.J.; Xuan, Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Ham, I.H.; Yun, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, G.; Han, S.U. Quantitative measurement of organic acids in tissues from gastric cancer patients indicates increased glucose metabolism in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhara, T. Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric urinary metabolome analysis to study mutations of inborn errors of metabolism. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, M.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.R. Simultaneous retention index analysis of urinary amino acids and carboxylic acids for graphic recognition of abnormal state. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. BioMed. Life Sci. 2005, 821, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Lee, G.; Moon, S.-M.; Park, M.-J.; Hong, S.K.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Kim, K.-R.; Paik, M.-J. Metabolomic screening and star pattern recognition by urinary amino acid profile analysis from bladder cancer patients. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Fleming, L.; Olin-Sandoval, V.; Campbell, K.; Ralser, M. Remaining Mysteries of Molecular Biology: The Role of Polyamines in the Cell. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 3389–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, N. Catabolism of polyamines. Amino Acids 2004, 26, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, C.W.; Tabor, H. Polyamines. Annu. Rev. BioChem. 1984, 53, 749–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.A.; Turecki, G. Suicide and the polyamine system. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotarski, S.L.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A., Jr. Polyamines and cancer: Implications for chemotherapy and chemoprevention. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2013, 15, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, M.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, H.D.; Pack, J.K.; Kim, N.; Ahn, Y.H. Metabolomic study of urinary polyamines in rat exposed to 915 MHz radiofrequency identification signal. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehling, L.M.; Wang, X.; Johansen, S.S.; Spottke, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Young, P.; Madea, B.; Hess, C. Determination of GHB and GHB-β-O-glucuronide in hair of three narcoleptic patients-Comparison between single and chronic GHB exposure. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 278, e8–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehling, L.M.; Piper, T.; Spottke, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Young, P.; Madea, B.; Thevis, M.; Hess, C. GHB-O-β-glucuronide in blood and urine is not a suitable tool for the extension of the detection window after GHB intake. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 35, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, C.A.; Nieman, D.C.; Signini, E.F.; Abreu, R.M.; Catai, A.M. Metabolomics-Based Studies Assessing Exercise-Induced Alterations of the Human Metabolome: A Systematic Review. Metabolites 2019, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.D.; Sha, W.; Meaney, M.P.; John, C.; Pappan, K.L.; Kinchen, J.M. Metabolomics-Based Analysis of Banana and Pear Ingestion on Exercise Performance and Recovery. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Scherr, J.; Luo, B.; Meaney, M.P.; Dréau, D.; Sha, W.; Dew, D.A.; Henson, D.A.; Pappan, K.L. Influence of pistachios on performance and exercise-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, immune dysfunction, and metabolite shifts in cyclists: A randomized, crossover trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, G.; Vinaixa, M.; McGovern, R.; Beltran, A.; Novials, A.; Correig, X.; McClean, C. Metabolomic response to acute hypoxic exercise and recovery in adult males. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, R.; Zhao, X.; Weigert, C.; Simon, P.; Fehrenbach, E.; Fritsche, J.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Wang, J.; Hoene, M.; et al. Medium chain acylcarnitines dominate the metabolite pattern in humans under moderate intensity exercise and support lipid oxidation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.D.; Knab, A.M.; Shanely, R.A.; Pappan, K.L.; Jin, F.; Lila, M.A. Influence of a polyphenol-enriched protein powder on exercise-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in athletes: A randomized trial using a metabolomics approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, F.A.; Lawler, N.; Peiffer, J.J.; Maker, G.L.; Boyce, M.C.; Fairchild, T.J.; Broadhurst, D. Characterizing the plasma metabolome during and following a maximal exercise cycling test. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Farrell, L.; Wood, M.J.; Martinovic, M.; Arany, Z.; Rowe, G.C.; Souza, A.; Cheng, S.; McCabe, E.L.; Yang, E.; et al. Metabolic signatures of exercise in human plasma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 33ra37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knab, A.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.D.; Shanely, R.A.; Cialdella-Kam, L.; Henson, D.A.; Sha, W. Effects of a flavonoid-rich juice on inflammation, oxidative stress, and immunity in elite swimmers: A metabolomics-based approach. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2013, 23, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, F.M.; Le Moyec, L.; Santi, C.; Gaston, A.F.; Triba, M.N.; Roca, E.; Durand, F. The impact of moderate altitude on exercise metabolism in recreational sportsmen: A nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomic approach. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Shanely, R.A.; Gillitt, N.D.; Pappan, K.L.; Lila, M.A. Serum metabolic signatures induced by a three-day intensified exercise period persist after 14 h of recovery in runners. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stander, Z.; Luies, L.; Mienie, L.J.; Keane, K.M.; Howatson, G.; Clifford, T.; Stevenson, E.J.; Loots, D.T. The altered human serum metabolome induced by a marathon. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.D.; Sha, W. Identification of a select metabolite panel for measuring metabolic perturbation in response to heavy exertion. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
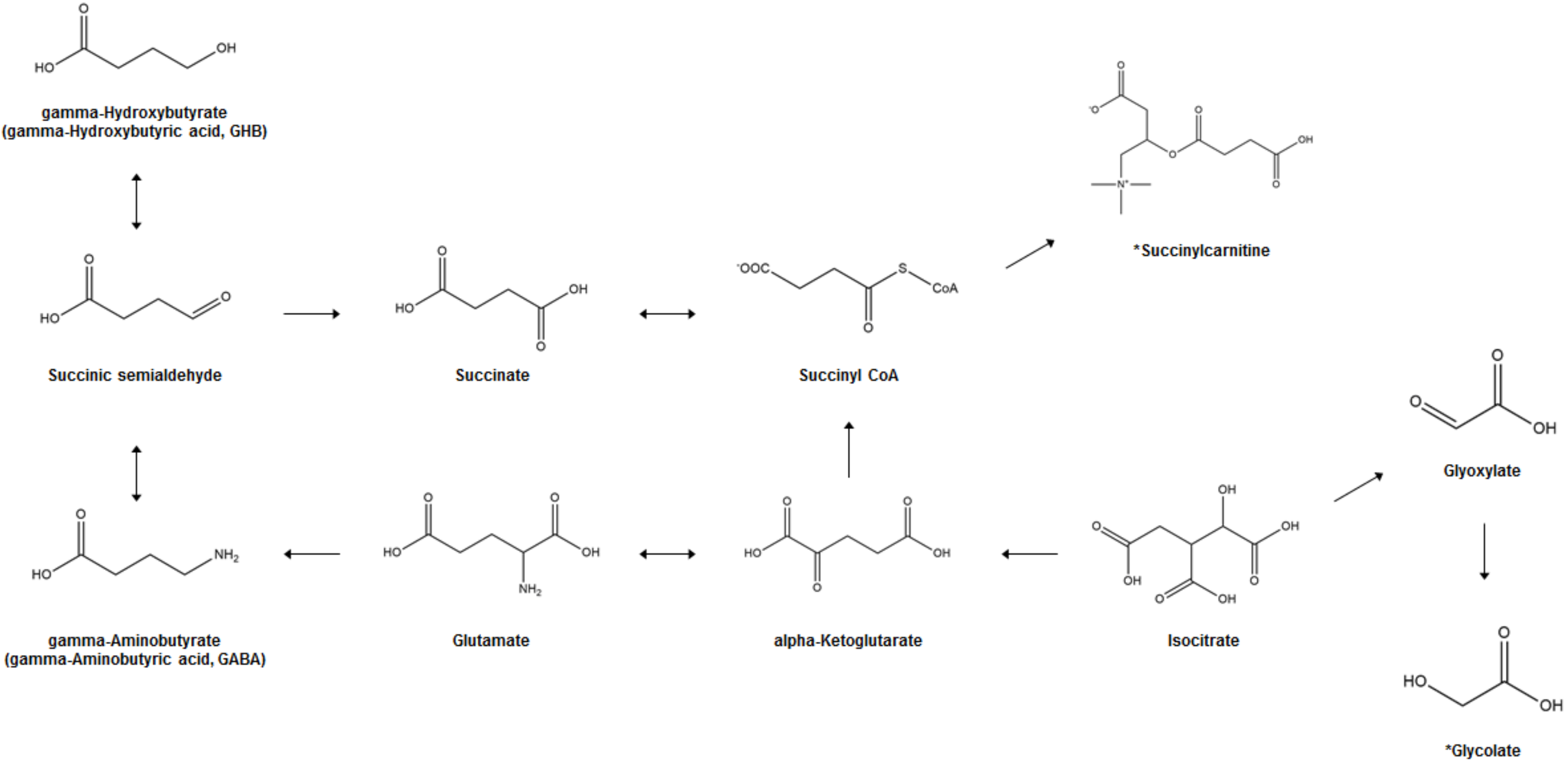
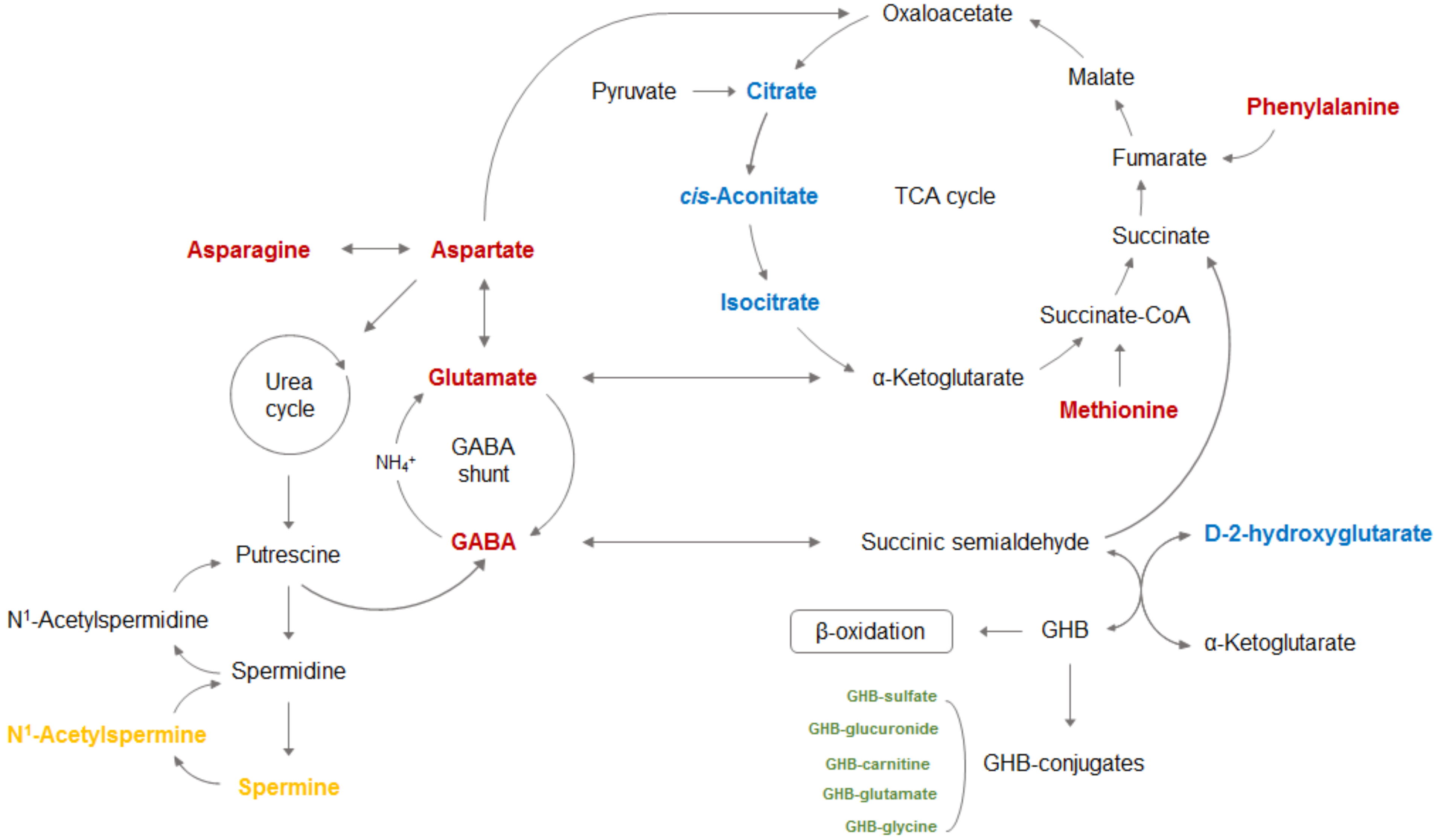
| Reference No. | Sample | Sample Preparation | Analytical Platform (Untargeted or Targeted) | Treatment (Administration Dose, Route, and No. of Doses) | Sampling Time | Metabolic Changes | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | Male SD rat (n = 18), urine | Methoxime/tert-butyldimethylsilyl derivatization | GC-SIM-MS(targeted) | 600 mg/kg GHB, i.p. once per day for 10 days | For 12 h following single administration | Pyruvic acid (↑), acetoacetic acid (↓), lactic acid (↑), glycolic acid (↑), 2-hydroxybutyric acid (↓), malonic acid (↓), succinic acid (↑), fumaric acid (↑), oxaloacetic acid (↑), malic acid (↑), α-ketoglutaric acid (↑), 2-hydroxyglutaric acid (↑), cis-aconitic acid (↑), citric acid (↑), isocitric acid (↑), γ-hydroxybutyric acid (↑) | Alteration of organic acid metabolism related with tricarboxylic acid cycle Key metabolite: 2-hydroxyglutaric acid |
| For 12 h following multiple administration (10 times) | Pyruvic acid (↑), acetoacetic acid (↑), lactic acid (↑), glycolic acid (↑), 2-hydroxybutyric acid (↑), malonic acid (↑), succinic acid (↑), fumaric acid (↑), oxaloacetic acid (↑), malic acid (↑), α-ketoglutaric acid (↑), 2-hydroxyglutaric acid (↑), cis-aconitic acid (↑), citric acid (↑), isocitric acid (↑), γ-hydroxybutyric acid (↑) | ||||||
| [34] | Male SD rat (n = 25), urine | Ethoxycarbonyl/tert-butyldimethylsilyl derivatization | GC-SIM-MS(targeted) | 600 mg/kg GHB, i.p. once per day for 10 days | For 12 h following single administration | Alanine (↑), glycine (↑), α-aminobutyric acid (↑), valine (↑), β-aminoisobutyric acid (↑), leucine, isoleucine (↑), serine (↑), proline (↑), γ-aminobutyric acid (↑), pipecolic acid (↑), 4-hydroxyproline (↑), methionine (↑), phenylalanine (↑), aspartic acid (↑), glutamic acid (↑), asparagine (↑), ornithine (↑), lysine (↑), histidine (↑), tyrosine (↑), tryptophan (↑), glutamine (↓) | Alteration of amino acid metabolism Key metabolite(s): phenylalanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, asparagine, and methionine |
| For 12 h following multiple administration (10 times) | Leucine (↑), isoleucine (↑), serine (↑), proline (↑), histidine (↓), phenylalanine (↓), γ-aminobutyric acid (↑), pyroglutamic acid (↑), α-aminoadipic acid (↑), glycine (↓), methionine (↓), tyrosine (↓) 4-hydroxyproline (↓), aspartic acid (↓), glutamic acid (↓), asparagine (↓), ornithine (↓), glutamine (↓), lysine (↓) | ||||||
| [32] | Male SD rat (n = 18), urine | N-ethoxylcarbonyl-N-pentafluoropropionyl derivatization | GC-SIM-MS(targeted) | 600 mg/kg GHB, i.p. once per day for 10 days | For 12 h following single administration | Putrescine (↑), N1-acetylspermidine (↑), spermine (↑), N1-acetylspermine (↑) | Alteration of polyamine metabolism Key metabolite(s): N1-acetylspermine and spermine |
| For 12 h following multiple administration (10 times) | Putrescine (↓), N1-acetylspermidine (↓), spermine (↑), N1-acetylspermine (↑) | ||||||
| [33] | Healthy men & women (n = 12, each), urine | Lyophilization and reconstitution in D2O | NMR(untargeted) | 25 mg/kg GHB (Xyrem®) | Urine: 10 min, 1, 2, 4, 6, 14, 20, 24, and 30 h post dose | Glycolate (↑), succinate (↑) | Confirmation of glycolate and succinate as potent markers for GHB, Slower elimination of glycolate (even after 24 h) than succinate (at time point of 6 h) |
| Reference No. | Sample | Sample Preparation | Analytical Platform | Concentration Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | Anonymous clinical urine samples (n = 50) | Dilution | LC-MS/MS | GHB-GLUC, 0.11–5.0 mgL (mean, 1.3 ± 1.2 mgL). |
| [35] | Authentic urine samples (n = 5) | Protein precipitation | LC-MS/MS | GHB-SUL, 70–170 mgL |
| [38] | Post-mortem peripheral blood samples (n = 12) | Protein precipitation followed by trimethylsilyl derivatization | GC-MS/MS | GHB, 0.8–23 mg/L; GHB-GLUC, ND |
| [39] | Healthy adults & children nail samples (n = 90) | Digestion followed by solid phase extraction | LC-MS/MS | GHB, 0.3–3.8 ng/mg in fingernails and 0.3–2.4 ng/mg in toenails; GHB-GLUC, 0.08–0.252 ng/mg in fingernails |
| [37] | Healthy adults & children hair samples (n = 65) | Solvent extraction | LC-MS/MS | GHB, 0.11–0.96 ng/mg (mean, 0.38 ± 0.25 ng/mg, n = 44); GHB-GLUC, <LOQ (n = 3) |
| [40] | Athletes (n = 100) & sports students (n = 50) urine samples | Dilution | LC-QTOF-MS | GHB-SUL, 0.009–11.5 mgL; GHB-GLUC, 0.5–19.8 mgL |
| Reference No. | Sample | Sample Preparation | Analytical Platform (Untargeted or Targeted) | Treatment (Administration Dose, Route, and No. of Doses) | Sampling Time | Metabolic Changes | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | Volunteers (n = 3), urine | Dilution | LC-QTOF-MS (untargeted) | 2.25 g Xyrem® (equal to 1.86 g of GHB) or 10 mL Somsanit (equal to 2 g of GHB) | Before and 72 h after administration | GHB-SUL (↑ but detected in non-GHB users), GHB-GLUC (fluctuate, lower than thresholds), GHB-GLUC/β-citryl glutamic acid ratio (↑) | Failure of GHB-SUL and GHB-GLUC as potent markers for GHB, GHB-GLUC/β-citryl glutamic acid ratio as a potential biomarker for GHB administration |
| [41] | Healthy men (n = 20), urine | Dilution | LC-QTOF-MS (untargeted) | 50 mg/kg GHB (Xyrem®) | 4.5 h after administration | Glycolate (↑), succinylcarnitine (↑), GHB-carnitine (↑), GHB-glutamate (↑), GHB-glycine (↑) | Discovery of new metabolites of GHB (GHB-carnitine, GHB-glutamate, and GHB-glycine) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.; Kim, S.; Seo, Y.; Lee, S. Metabolic Alterations Associated with γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and the Potential of Metabolites as Biomarkers of Its Exposure. Metabolites 2021, 11, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020101
Jung S, Kim S, Seo Y, Lee S. Metabolic Alterations Associated with γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and the Potential of Metabolites as Biomarkers of Its Exposure. Metabolites. 2021; 11(2):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020101
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Suryun, Suji Kim, Yujin Seo, and Sooyeun Lee. 2021. "Metabolic Alterations Associated with γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and the Potential of Metabolites as Biomarkers of Its Exposure" Metabolites 11, no. 2: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020101
APA StyleJung, S., Kim, S., Seo, Y., & Lee, S. (2021). Metabolic Alterations Associated with γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and the Potential of Metabolites as Biomarkers of Its Exposure. Metabolites, 11(2), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020101






