Abstract
The bottleneck for taking full advantage of metabolomics data is often the availability, awareness, and usability of analysis tools. Software tools specifically designed for metabolomics data are being developed at an increasing rate, with hundreds of available tools already in the literature. Many of these tools are open-source and freely available but are very diverse with respect to language, data formats, and stages in the metabolomics pipeline. To help mitigate the challenges of meeting the increasing demand for guidance in choosing analytical tools and coordinating the adoption of best practices for reproducibility, we have designed and built the MSCAT (Metabolomics Software CATalog) database of metabolomics software tools that can be sustainably and continuously updated. This database provides a survey of the landscape of available tools and can assist researchers in their selection of data analysis workflows for metabolomics studies according to their specific needs. We used machine learning (ML) methodology for the purpose of semi-automating the identification of metabolomics software tool names within abstracts. MSCAT searches the literature to find new software tools by implementing a Named Entity Recognition (NER) model based on a neural network model at the sentence level composed of a character-level convolutional neural network (CNN) combined with a bidirectional long-short-term memory (LSTM) layer and a conditional random fields (CRF) layer. The list of potential new tools (and their associated publication) is then forwarded to the database maintainer for the curation of the database entry corresponding to the tool. The end-user interface allows for filtering of tools by multiple characteristics as well as plotting of the aggregate tool data to monitor the metabolomics software landscape.
1. Introduction
The need to list and categorize software tools used in different phases of data analysis is recognized in the metabolomics and bioinformatics communities [1,2,3,4,5]. Technological advances, both in instrumentation and computation, have allowed for more comprehensive and sensitive measurements of metabolites. This has driven the growth of metabolomics applications to study biological mechanisms, discover biomarkers, diagnose disease, and monitor treatment responses [6,7,8]. The diversity of applications is matched by a diversity of instrumental approaches, experimental designs, as well as the expansion of statistical and computational methods applied to the growing amount of generated and curated data from metabolomics studies. This translates to a large, complex, and expanding collection of software tools used in metabolomics [1,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Unfortunately, it also translates into the fragmentation of software and data resources, blunting the full advantage of the expanded capabilities of modern metabolomics research [2,5,23]. Further, as metabolomic data are to be integrated into multiple -omics datasets (e.g., multiomics or mixomics) or as a tool for systems biology, the problem of finding the right tools and data resources is compounded [24,25,26,27].
The size, complexity, and variety of the set of software tools applicable to metabolomics studies introduce some difficulty in delineating their optimal use and adoption as well as their incorporation into best practices for reproducible science and data reuse. Metabolomics researchers may not have dedicated bioinformatics support to help navigate the toolsets, let alone to iterate the development of analysis workflows [5]. Multiple efforts have sought to provide a reasonably up-to-date overview of the software tools being developed [1,14,16,17,18,19,21,28]. However, these have relied on either labor-intensive human curation of the most notable tools as they are released and/or on crowdsourcing of the most recommended tools available. The pace of metabolomics and software development combined with the already-mentioned diversity of the field itself means that these efforts cannot cover the entirety of the tool landscape, and they are bound to be quickly out of date. Inspired by the work being conducted in other areas of bioinformatics tool development [2,29], we propose that surveying and assessing the current landscape of metabolomics software tools with respect to their functionality, interoperability, and reusability can be a “force multiplier” for the metabolomics methods development community and for researchers in general. To that end, we have developed MSCAT, a curated database of metabolomics software tools that uses Machine Learning (ML) and text mining to automatically assist the curator by scanning the literature for publications describing metabolomics tools and identifying new metabolomics tools by name (Figure 1).
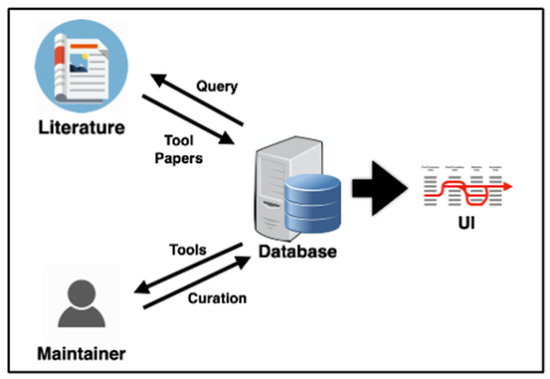
Figure 1.
Schematic of MSCAT function. A semi-automated process is implemented where the database server periodically queries the literature and extracts new published tools to be displayed in the user interface (UI). The tools classification is then curated by the database maintainer.
2. Results
2.1. Categorization of Software Tools
Given the large variety of instruments, approaches, and applications represented in metabolomics research, any survey or catalog of software benefits from a framework to categorize these tools. Different schemes have been explicitly and implicitly proposed (see Table 1) by previous reviews and surveys. Two basic aspects emerge as criteria for tool categorization: instrumentation used and step in the analysis pipeline. However, many differences emerge among the schemes in their details. Another pitfall of an a priori granular categorization of tools is that the structure may limit representation of the kinds of workflows possible in metabolomics studies. This is especially a concern as the discipline develops new approaches and refinements. Thus, when categorizing tools for MSCAT, we opted for a coarse categorization based on seven functionality categories: Pre-processing, Post-processing, Statistical Analysis, Annotation, Database, Visualization/Network, and Data/Workflow Management. Within the first four categories listed, each software tool may implement multiple specific methodologies or tasks (e.g., Pre-processing tools may be for peak detection, normalization, batch correction, etc.), and these are cataloged in a separate field for each of the first four functionality categories for the user to further filter the results in the main UI table or search for them in the Workflow Builder. Suite solutions (tools that function at multiple pipeline stages) are curated as belonging to multiple pipeline categories.

Table 1.
Categorization (rows) of metabolomics software tools in previous surveys (columns).
Table 1.
Categorization (rows) of metabolomics software tools in previous surveys (columns).
| Kusonmano et al. [30] | Spicer et al. [1] | Stanstrup et al. [31] | Misra et al. [18] | Chang et al. [32] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition Instrument | Pre-Processing LC-MS GC-MS NMR | Metabolite Profiling MS Data ProcessingNMR Data ProcessingUV Data Processing | Data Preprocessing | Data Preprocessing |
| Data Preprocessing Normalization Identification Binning | Annotation Identification Quantification | Metabolite Annotation Ion grouping MS/MS Structure Databases | Statistical Tools | Statistical Analysis |
| Data Analysis PCA Clustering SVM PLS | Post-Processing | Data Analysis Statistics Network Analysis Pathway Analysis | Annotation Tools | Identification |
| Data Interpretation Databases Network Visualization Pathway Analysis | Statistical Analysis | Biological Interpretation | Functional Analysis | |
| Workflow and other tools | Databases | Metabolic Modeling | ||
| Instrument-based | ||||
| Workflows |
To supplement the stage-based categorization of tools, these are also curated by instrumentation category (LC-MS, GC-MS, MS, NMR) and by biomolecule type to accommodate tools that are used in multi-omics (i.e., not strictly the analysis of metabolite data). Further software tool characteristics (OS, programming language, version, user interface type, etc.) are curated to ensure “findability” of software and to be compatible with a simple software ontology (https://github.com/allysonlister/swo, accessed on 20 September 2021).
2.2. Database Design
We designed a relational database using PostgreSQL [33,34] (version 12.1) housing 17 tables that were normalized to the fifth normal form [35]. Following these normalization guidelines allows for a database that can be updated frequently while preventing data inconsistency and minimizing redundancy. The tables in the database are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Structure of the MSCAT database consisting of 17 tables and their descriptions.
We chose to base MSCAT on a relational database model rather than as a single flat table to allow for extensibility. The software tool’s name was chosen as the primary key or foreign key across tables, giving the data model a primarily one-to-many relation structure.
2.3. Literature Mining: Tool Publications
To begin populating our database, we defined a scope of the metabolomics tools to find and curate. As dictated by best practices, we limited our survey to open-source software tools. Additionally, in order to ensure both findability of documentation and to obtain rich information for tool curation, we limited ourselves to metabolomics software tools that have a publication associated with them (i.e., a publication announcing and describing a tool or its development). Thus we needed to mine the metabolomics literature to find a specific type of publication, also known as a Document Classification Problem. As a first approach, we built a PubMed query comprising the main concepts of metabolomics and software through keywords and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Outline of first PubMed query to obtain metabolomics software tools papers based on metabolomics and software-related keywords and MeSH terms.
The query defined by Table 3 returned 987 results as of 16 June 2021, and upon manual curation of titles and abstracts, 45.3% of them were publications of the desired type (i.e., publications primarily about a metabolomics software tool or tools, as opposed to metabolomics applications where a software tool is talked about in the abstract).
Manual checking of some previously logged publications with this literature search quickly revealed, however, that this simple query was not capturing all of the metabolomics software literature. We then formulated a second version of the PubMed query to cast a wider net. (Table 4).

Table 4.
Outline of second PubMed query to obtain metabolomics software tools papers based on metabolomics and software-related keywords and MeSH terms.
This second query returns 9698 results (as of 16 June 2021), and upon manual curation of the titles and abstracts, 39.2% of them were publications of the desired type. This number is close to that obtained by the first query, however, it includes more software papers in areas outside of metabolomics, thus, while the second query catches more relevant papers, the “signal-to-noise” ratio is lower. As we will see in the following section, this may also affect the performance of our tool name identification method.
As mentioned above, the primary key in the MSCAT main database table is the tool’s name since multiple papers can talk about the same tool, and we want to be able to detect tools named anywhere in the metabolomics literature. Further, although FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) Principles for Research Software [36,37] call for unique identifiers for software, adoption of this metadata standard is not complete. Thus, in order to properly track the tools to curate as they are published, in practice, we needed a way of detecting the tool name in the literature query results. In other words, on top of our literature query, we needed to solve a Named Entity Recognition (NER) problem [38,39].
2.4. Literature Mining: Tool Name Detection
Using the information that is retrieved by mining PubMed, our goal now was to detect metabolomics software tools contained within the text. For this reason, we employed a Named Entity Recognition model to extract predicted probabilities that a certain token, usually a word, is a metabolomics software tool name.
The title often contains information about the metabolomics tool name if the article is a true positive. Thus, we concatenated all titles with their respective abstracts obtained from the first PubMed query above. To train a NER model, we needed to first split the data into training and testing sets. We opted for an 80% for training and 20% for the testing split. To generate both the training and testing sets, we tokenized the words in the concatenated title and abstracts, then we removed English stop words, as defined by the Python Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) package [40], and we tagged each token with a part of speech (POS) tag. We also identified where sentences end for each collection of tokens, and we created our label by tagging tokens that match a predefined list of known metabolomics software tools (combining [1] and our manual curation). An example of the processing can be seen in Table 5 (see Materials and Methods). Finally, we formatted the training and testing data to conform to the conference on natural language learning (CoNLL) format. We used a pre-trained deep learning model, provided by the Python spark-nlp package [41], to produce ELMo embeddings [42] for each sentence’s tokens. These word embeddings were used as features in the deep learning NER model. The deep learning (neural network) architecture that the NER model was built on starts with a character convolutional neural network (CNN) followed by a bi-directional long short-term memory (LSTM) layer followed by conditional random fields (CRF) layer [43,44]. The F1 score (see Materials and Methods) is an evaluation metric that aims to balance a model’s predictive correctness (precision) and its ability to identify the relevant data (recall). Against the dataset obtained from the first PubMed query, the CNN-LSTM-CRF model performs with an F1 of 76.5% versus an F1 of 64% using the CRF layer alone. When applied against a dataset from the second, broader PubMed query, the CNN-LSTM-CRF model performs with an F1 of 63.5% while using only the CRF layer performs with an F1 score of 45%. The poorer performance of the model on the second query may be partly due to the sparseness in tool name tokens in the dataset text. However, the size of the curated training set used to test the second query was also much smaller in relation to the size of the dataset (600 out of 9698 abstracts) compared to the curated training set used for the first query (600 out of 987 abstracts). Thus, this may also indirectly affect the NER performance. In the end, we chose to use the first, narrower PubMed query in the currently available version of MSCAT, and future updates will feature an optimized literature query.

Table 5.
Example of processed training data. Where each row corresponds to a word from the collection of abstracts in the training data. The Part of Speech column (POS) tag tokens as a common noun (NN), adjective (JJ), etc. The sentence ID column identifies a training example (i.e., all tokens with the same Sentence ID are inserted into the model as one training example. The label column describes whether a token is a software tool (T) or not (O).
2.5. Database User Interface
The current version of the MSCAT presents the user with three different views of the data (Figure 2). The user interface (UI) communicates with the PostgreSQL backend and is built using the Dash web framework. The main tab presents the tools and a subset of their characteristics sorted by how recently the tool has been updated and by the number of citations from the corresponding publication. The user is able to filter the table view by any combination of matching values in multiple fields. The user is also able to extract the full dataset of MSCAT as a single table in csv format from this tab.
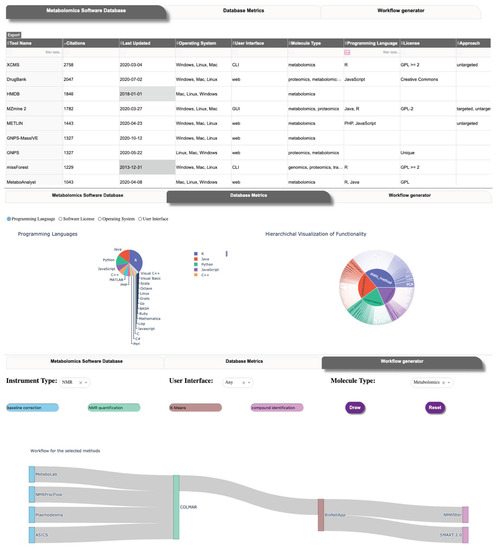
Figure 2.
User interface of MSCAT. Top: main table view. Middle: aggregate tool data visualization. Bottom: workflow builder.
In the middle tab of the application, we displayed aggregate data from the curated tools in MSCAT detailing the proportion of programming languages, methodologies, the timeline of release, and others. It is our intention to motivate from this view future detailed assessment of the software landscape (using the curated data in MSCAT) that may help identify gaps or overrepresentation of the kinds of metabolomics software being developed and areas where interoperability can be improved.
The third tab in the user interface is our first approach to providing the user with a way to design a metabolomics pipeline or workflow. In the current implementation, the user chooses specific methods within two or more functionality categories from among those most often linked together as pipelines or workflows (i.e., Pre-processing, Post-processing, Statistical Analysis, and Annotation) as well as other optional, additional discriminants (Instrument type, UI type, Molecule type) if needed. The interface then draws a Sankey-type diagram [45] representing the possible tool combinations that can constitute such a pipeline. This workflow generator interface does not present the other functionality categories (Database, Workflow Management, Visualization) since tools in those categories are largely agnostic or independent from the pipeline categories. The end-user can still perform a custom search of tools in those categories via the main interface tab.
2.6. Curation Workflow
We based our initial scan of the literature to start populating the database on the first query described above, plus previous reviews of metabolomics software tools [1,14,17,18,19,20,21,31]. From this scan of publications and NER identification of tools, we see that there are approximately 500 published metabolomics software tools (as of 16 June 2021), of which we have curated 400 thus far. For automation of updates of the landscape, MSCAT runs a script that calls the R functions that re-run the PubMed query and the Python code that detects the predicted tool names. The script then checks the updated results against previously predicted tokens, logged publications, and tools already in our database to prepare a report that it sends to the database curator with a list of possible new metabolomics tools (and their publication) to add. The script also runs an R function that queries the CrossRef API [46] for the citation numbers of each publication listed in MSCAT. Currently, we are running the literature mining script monthly and incorporating its results alongside the backlog of known tools still being curated. We are also using the ticket/issue feature of the code repository of MSCAT for community members to submit tool suggestions or data corrections.
3. Discussion
We have built MSCAT and its associated ML and automation parts in order to provide a catalog of metabolomics software tools that can be updated in a sustainable fashion without exclusive reliance on crowdsourced data or literature reviews. The database and its associated web interfaces are hosted at the Metabolomics Workbench website [47], an international repository for the metabolomics community. The catalog has three main purposes: make metabolomics tools more findable even if user requirements are very specific, providing a bird’s-eye-view of the efforts of the metabolomics software community, and, lastly, provide a way to determine interoperability between tools. Aside from the benefits to the user in finding and choosing compatible software for analysis workflows, our database project brings a structured framework to conduct surveys of metabolomics software tool development. We thus see the database also as a platform for the community to discuss needs and trends in the field and identify gaps in functionality as well as best practices for tool documentation and deployment.
The interoperability determination goal is represented in the current MSCAT implementation, as the workflow builder Table Currently, the determination of interoperability depends on salient features of the software tool (e.g., operating system dependencies, compatible file formats) and its classification of chief functionality (e.g., annotation, pre-processing, statistical analysis). Relying on this chiefly syntactic definition of interoperability is not error-proof, it depends strongly on user metabolomics expertise, and it does not adequately describe all the meaningful analysis workflows that can be assembled. We initially tried mitigating the lack of semantics by matching input and output file formats between tools in a pipeline. However, the file formats used in metabolomics do not provide a sufficient specification for this. The recent development of newer, more metadata-rich file formats [48,49,50] for metabolomics tells us there is an increasingly urgent need to standardize the knowledge representation and metadata elements in this community to achieve better interoperability and information exchange. There is a similar problem being worked on in the healthcare space [51], and a similar effort is likely needed when dealing with large, diverse datasets as in metabolomics and multi-omics. Future work will aim to build some semantic characterization of the software tools into their curation into MSCAT. This characterization could combine the metadata in the new file formats together with a Software Description Ontology [52] thus that future versions of the MSCAT can characterize software tools by their input and output variables to programmatically assess interoperability and outline all possible meaningful analysis pipelines [53]. We expect that this future capability would help improve the compliance of metabolomics studies to FAIR principles as well as provide an entry point for researchers with less specialized expertise to formulate a sophisticated data analyses workflow that takes full advantage of what the metabolomics software community has to offer.
4. Materials and Methods
We surveyed the landscape of available metabolomics tools by mining the literature repository PubMed. PubMed citations come from MEDLINE indexed journals as well as journals and manuscripts deposited in PubMed Central. We used the easyPubMed R package [54] to make API calls to PubMed, retrieving the abstracts that matched the PubMed query that we defined. The first PubMed query used for model training and initial scanning was:
((software [MeSH Terms] OR “programming language” [All Fields]) AND (metabolomics [MeSH Terms] OR “metabolomics” [All Fields] OR “metabolomics” [All Fields] OR “metabolomic” [All Fields] OR “metabonomic” [All Fields] OR “metabonomics” [All Fields])).
The second PubMed query, which collects many more publications but at a lower percentage of relevant ones, was:
(((“metabolomic” [All Fields] OR “metabolomics” [All Fields] OR “metabonomic” [All Fields] OR “metabonomics” [All Fields] OR “metabolonics” [All Fields] OR “metabolite” [All Fields] OR “metabolites” [All Fields] OR “multiomic” [All Fields] OR “multiomics” [All Fields] OR “mixomic” [All Fields] OR “mixomics” [All Fields] OR “metabolome”[All Fields] OR “metabolomes”[All Fields] OR Metabolomics[Mesh] OR metabolome [Mesh])) AND (((algorithm OR toolkit) AND (code OR software)) OR “open source” OR “source code” OR “web app” OR “web application” OR “command line” OR “programming language” OR (software AND (framework OR pipeline OR tool OR package OR suite OR workflow)) OR github OR gitlab OR sourceforge OR Bioconductor OR biopython OR biojava OR bioruby OR “Computing Methodologies” [Mesh])).
The mined data included the article’s PMID, the title, and the abstract. Publication types were curated manually using Endnote software (Clarivate).
We concatenated all titles with their respective abstracts. To train a NER model, we split the 600 manually curated abstracts retrieved from mining PubMed using Query 1 into training and testing sets. We opted for an 80% for training and 20% for testing split and further pulled 10% from the training as a validation set. To both the training and testing sets we tokenized the words in the concatenated title and abstracts, then we removed English stop words, as defined by the Python NLTK package, and we tagged each token with a part of speech (POS) tag. We also identified where sentences end for each collection of tokens, and we created our label by tagging tokens that matched a curated list of known metabolomics software tools derived from the 600 manually curated abstracts. An example of the processing is shown in Table 5. Finally, we formatted the training and testing data to conform to the conference on natural language learning (CoNLL) format. We then used a pre-trained deep learning model, provided by the Python “sparknlp” package [41], to produce ELMo embeddings for each sentence’s tokens. These word embeddings were used as features in the deep learning NER model that was generated using the “sparknlp” package.
The deep learning (neural network) architecture that the NER model is built on includes a character convolutional neural network (CNN) followed by a bi-directional long short-term memory (LSTM) layer followed by conditional random fields (CRF) layer [55]. The parameters of the character CNN take 100 number of characters, a filter size of 25, and a kernel of 3 × 3, and the LSTM cells are of size 128 for the bi-directional LSTM layer. We evaluate model performance using the f1 score statistic.
where TP, FP, and FN are the true positive, false positive, and false negative predictions, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.G., K.K. and W.L.; data curation, J.D. and W.L.; formal analysis, J.D.; methodology, J.D. and W.L.; software, J.D.; supervision, D.G. and K.K.; writing—original draft, W.L.; writing—review and editing, D.G., J.D., K.K. and W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Development of MSCAT was supported by the NIH Metabolomics Common Fund Program U01 CA235488 under the administrative supplement U01CA235488-02S1.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The code and data behind MSCAT are hosted in a version control repository (https://gitlab.com/metabolomics-tools-database/database-container, accessed on 20 September 2021).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Charmion Cruickshank-Quinn and Julie Haines for input in the categorization of metabolomics tools and methods. Parts of the second PubMed query are derived from Ben Harnke’s work in searching for open-source bioinformatics publications.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Spicer, R.; Salek, R.M.; Moreno, P.; Canueto, D.; Steinbeck, C. Navigating freely-available software tools for metabolomics analysis. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, V.J.; Bandrowski, A.E.; Pepin, A.S.; Gonzalez, B.J.; Desfeux, A. OMICtools: An informative directory for multi-omic data analysis. Database 2014, 2014, bau069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellinger, J.J.; Chylla, R.A.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L. Databases and Software for NMR-Based Metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannata, N.; Merelli, E.; Altman, R.B. Time to organize the bioinformatics resourceome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, R.J.M.; Lawson, T.N.; Salek, R.M.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Glen, R.C.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; Haug, K.; Koulman, A.; Moreno, P.; et al. Computational tools and workflows in metabolomics: An international survey highlights the opportunity for harmonisation through Galaxy. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, S.; Yoo, H.J. Understanding Metabolomics in Biomedical Research. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Spangler, S.; Fang, M.; Johnson, C.H.; Forsberg, E.M.; Granados, A.; Martin, R.L.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Huan, T.; Rinehart, D.; et al. Exposome-Scale Investigations Guided by Global Metabolomics, Pathway Analysis, and Cognitive Computing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11505–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Marsal, S.; Julia, A. Analytical methods in untargeted metabolomics: State of the art in 2015. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Theis, F.J. Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 4, e201301009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Benton, H.P.; Siuzdak, G. Bioinformatics: The next frontier of metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uppal, K.; Walker, D.I.; Liu, K.; Li, S.; Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Computational Metabolomics: A Framework for the Million Metabolome. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1956–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blazenovic, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, B.B. New tools and resources in metabolomics: 2016–2017. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B. Data normalization strategies in metabolomics: Current challenges, approaches, and tools. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 26, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B. Open-Source Software Tools, Databases, and Resources for Single-Cell and Single-Cell-Type Metabolomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2064, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, B.B.; Mohapatra, S. Tools and resources for metabolomics research community: A 2017–2018 update. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B.; van der Hooft, J.J. Updates in metabolomics tools and resources: 2014–2015. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Shea, K.; Misra, B.B. Software tools, databases and resources in metabolomics: Updates from 2018 to 2019. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Grapov, D. Review of emerging metabolomic tools and resources: 2015–2016. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2257–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B. New software tools, databases, and resources in metabolomics: Updates from 2020. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Kawakami, M.; Robert, M.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Bioinformatics Tools for Mass Spectroscopy-Based Metabolomic Data Processing and Analysis. Curr. Bioinform. 2012, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Bradbury, J.; Bergmann, S.; Capuccini, M.; Cascante, M.; de Atauri, P.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Foguet, C.; Glen, R.; Gonzalez-Beltran, A.; et al. PhenoMeNal: Processing and analysis of metabolomics data in the cloud. Gigascience 2019, 8, giy149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krassowski, M.; Das, V.; Sahu, S.K.; Misra, B.B. State of the Field in Multi-Omics Research: From Computational Needs to Data Mining and Sharing. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 610798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, E.L.; Billings, E.M.; Benton, H.P.; Martin, R.L.; Palermo, A.; Guijas, C.; Rinschen, M.M.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Tagtow, B.A.; et al. Cognitive analysis of metabolomics data for systems biology. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1376–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabonomics: Systems biology in pharmaceutical research and development. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2004, 6, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Misra, A.; Sriram, G. Genome-scale models of plant metabolism. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1083, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappia, L.; Phipson, B.; Oshlack, A. Exploring the single-cell RNA-seq analysis landscape with the scRNA-tools database. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusonmano, K.; Vongsangnak, W.; Chumnanpuen, P. Informatics for Metabolomics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2016, 939, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanstrup, J.; Broeckling, C.D.; Helmus, R.; Hoffmann, N.; Mathe, E.; Naake, T.; Nicolotti, L.; Peters, K.; Rainer, J.; Salek, R.M.; et al. The metaRbolomics Toolbox in Bioconductor and beyond. Metabolites 2019, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.Y.; Colby, S.M.; Du, X.; Gomez, J.D.; Helf, M.J.; Kechris, K.; Kirkpatrick, C.R.; Li, S.; Patti, G.J.; Renslow, R.S.; et al. A Practical Guide to Metabolomics Software Development. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PostgreSQL: The World’s Most Advanced Open Source Relational Database. Available online: https://www.postgresql.org/ (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Stonebraker, M.; Rowe, L.A. The design of Postgres. ACM Sigmod Rec. 1986, 15, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W. A simple guide to five normal forms in relational database theory. Commun. ACM 1983, 26, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, D.S.; Gruenpeter, M.; Honeyman, T. Taking a fresh look at FAIR for research software. Patterns 2021, 2, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lample, G.; Ballesteros, M.; Subramanian, S.; Kawakami, K.; Dyer, C. Neural architectures for named entity recognition. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.01360. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, A.; Han, J.; Li, C. A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S. NLTK: The natural language toolkit. In Proceedings of the COLING/ACL 2006 Interactive Presentation Sessions, Sydney, Australia, 17–18 July 2006; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kocaman, V.; Talby, D. Spark NLP: Natural Language Understanding at Scale. Softw. Impacts 2021, 8, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep contextualized word representations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05365. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yu, K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.01991. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Jayasumana, S.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Vineet, V.; Su, Z.; Du, D.; Huang, C.; Torr, P.H.S. Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Las Condes, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1529–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Riehmann, P.; Hanfler, M.; Froehlich, B. Interactive sankey diagrams. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 23–25 October 2005; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain, S.; Zhu, H.; Jahn, N.; Boettiger, C.; Ram, K. rcrossref: Client for Various ‘CrossRef’ ‘APIs’, 1.1.0. 2020. Available online: https://docs.ropensci.org/rcrossref/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Azam, K.; Vadivelu, I.; Burant, C.; Edison, A.; Fiehn, O.; Higashi, R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Metabolomics Workbench: An international repository for metabolomics data and metadata, metabolite standards, protocols, tutorials and training, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D463–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhamber, R.S.; Jankevics, A.; Deutsch, E.W.; Jones, A.R.; Dowsey, A.W. mzMLb: A Future-Proof Raw Mass Spectrometry Data Format Based on Standards-Compliant mzML and Optimized for Speed and Storage Requirements. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larralde, M.; Lawson, T.N.; Weber, R.J.; Moreno, P.; Haug, K.; Rocca-Serra, P.; Viant, M.R.; Steinbeck, C.; Salek, R.M. mzML2ISA & nmrML2ISA: Generating enriched ISA-Tab metadata files from metabolomics XML data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2598–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, L.; Chambers, M.; Sturm, M.; Kessner, D.; Levander, F.; Shofstahl, J.; Tang, W.H.; Römpp, A.; Neumann, S.; Pizarro, A.D. mzML—a community standard for mass spectrometry data. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, R110.000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saripalle, R.; Runyan, C.; Russell, M. Using HL7 FHIR to achieve interoperability in patient health record. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 94, 103188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garijo, D.; Ratnakar, V.; Gil, Y.; Khider, D. The Software Description Ontology. Available online: https://w3id.org/okn/o/sd/1.9.0 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Carvalho, L.A.M.C.; Garijo, D.; Medeiros, C.B.; Gil, Y. Semantic Software Metadata for Workflow Exploration and Evolution. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 14th International Conference on e-Science (e-Science), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 Octtober–1 November 2018; pp. 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Fantino, D. easyPubMed. 2019. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/easyPubMed/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Chiu, J.P.; Nichols, E. Named entity recognition with bidirectional LSTM-CNNs. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2016, 4, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).