Systemic Metabolic Alterations Correlate with Islet-Level Prostaglandin E2 Production and Signaling Mechanisms That Predict β-Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
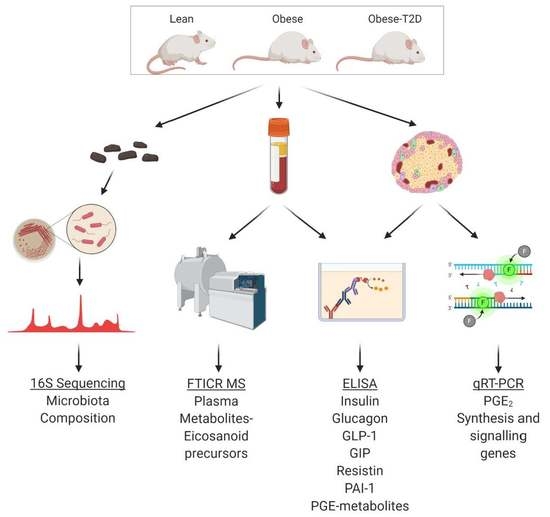
2. Results
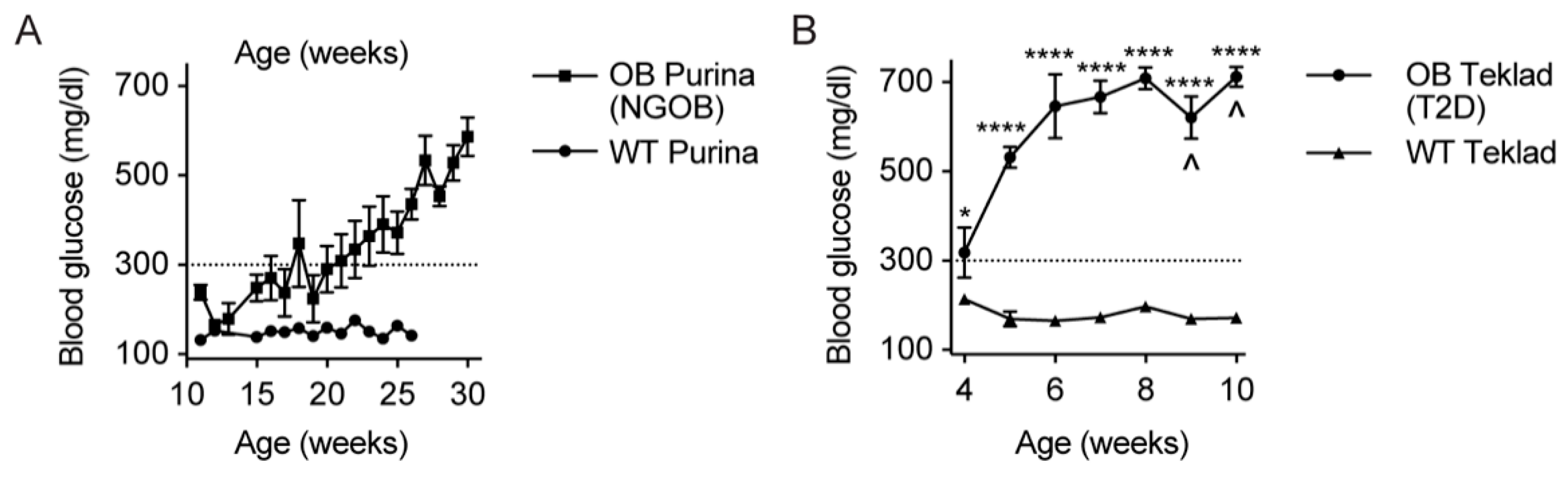
2.1. Initial Observation That Metabolic Phenotype Can Be Indpendent of Genotype in the BTBRob Mouse Model of T2D
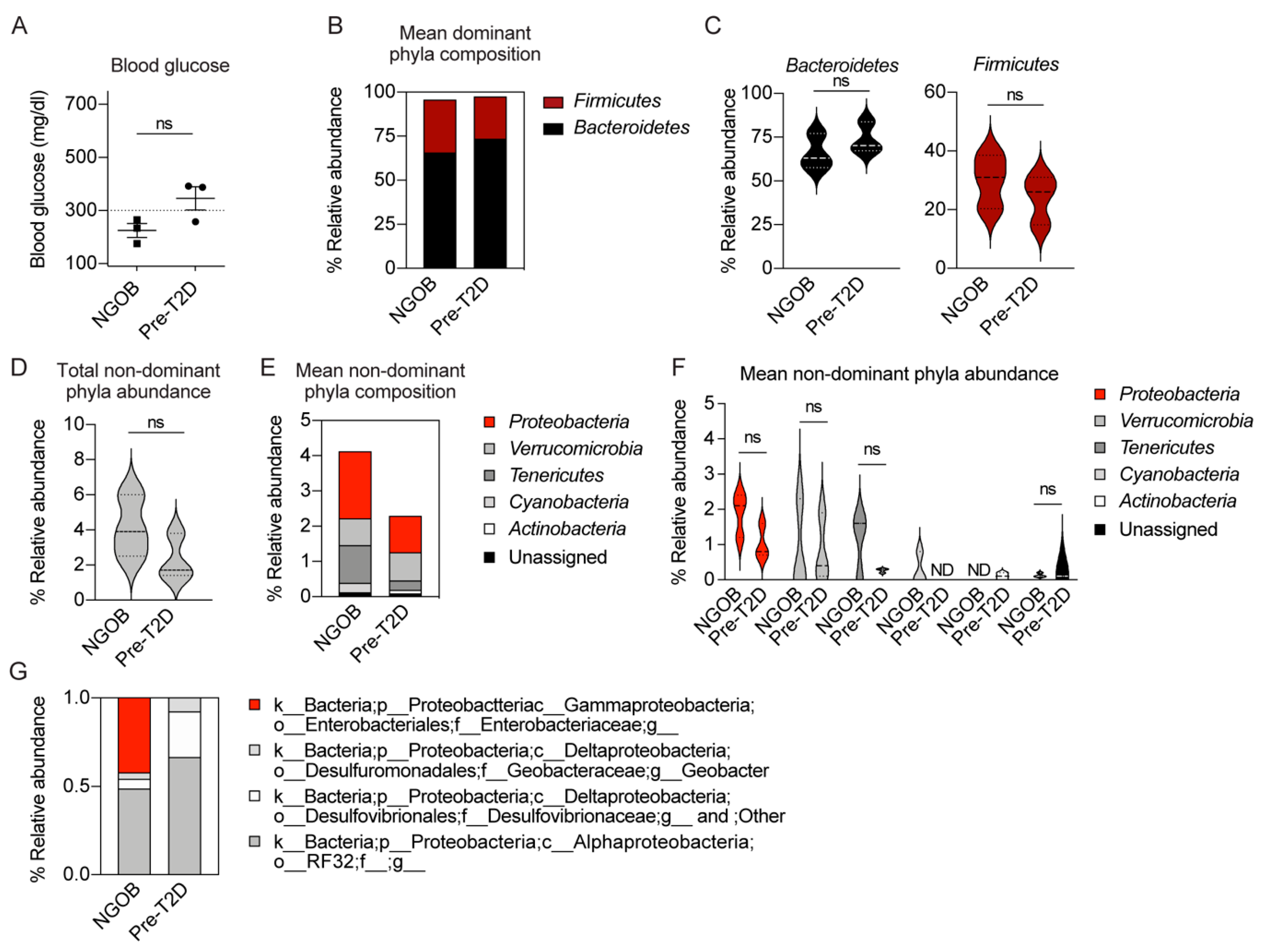
2.2. An Altered Gut Microbiota Composition Is Associated with T2D Resistance vs. Susceptiblity BTBROb Mice
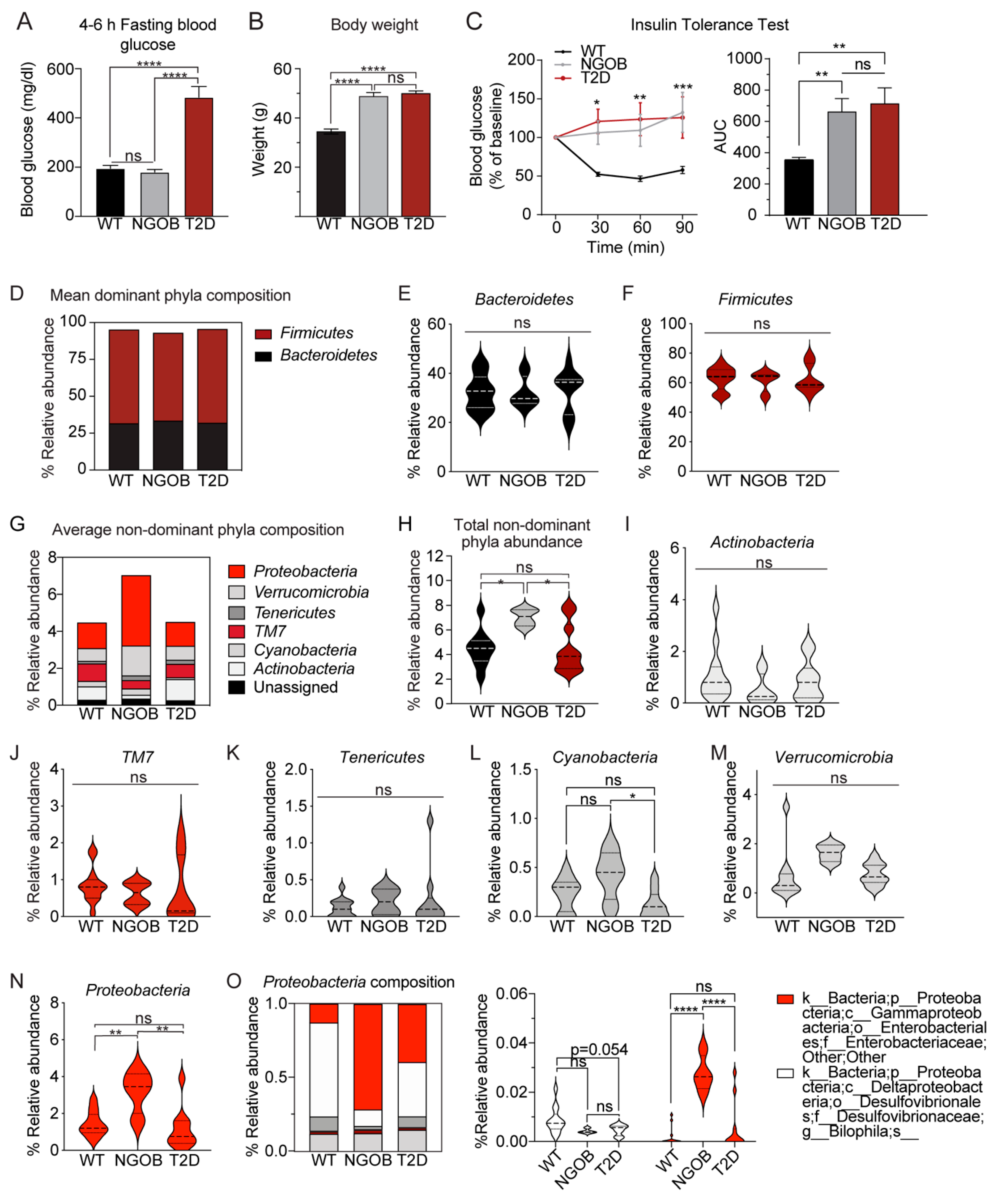
2.3. The Gut Microbiota Composition of Normoglycemic BTBROb Mice Is Significantly Different Compared to Both T2D BTBROb and WT Controls, At Least Partially Independent of Diet
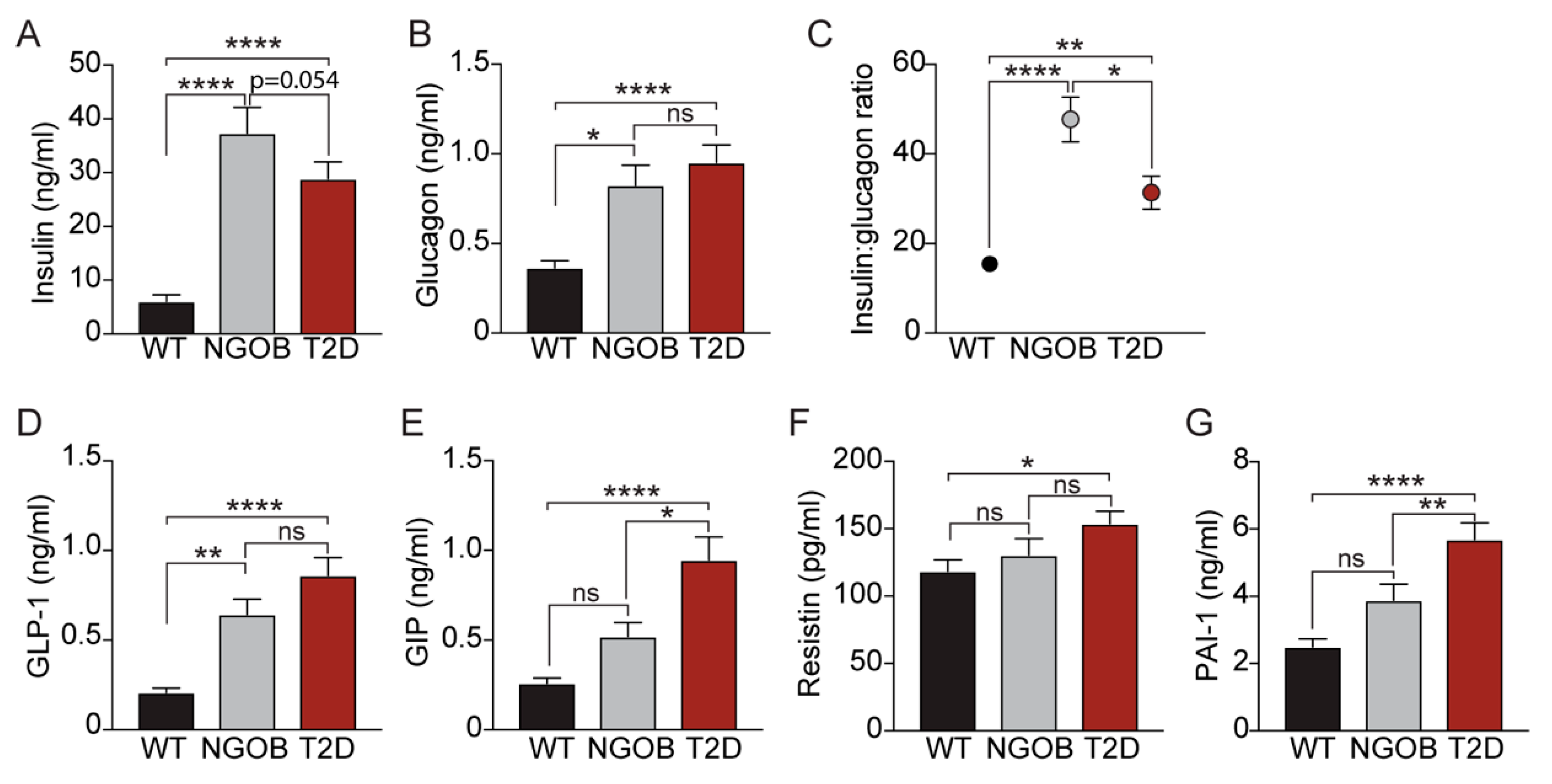
2.4. The T2D Phenotype Is Associated with Altered Circulating Incretin and Adipokine Levels
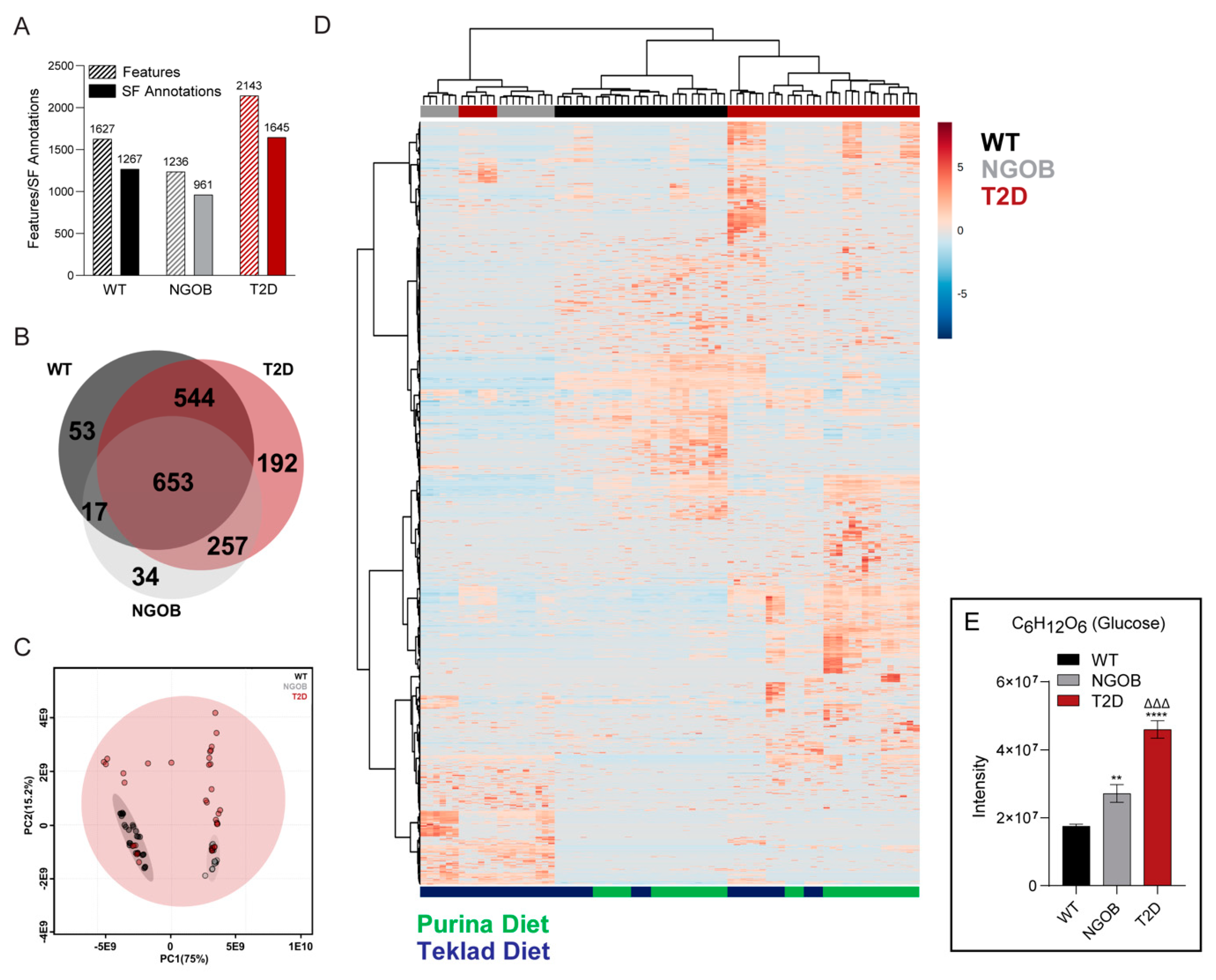
2.5. An Integrated Ultrahigh-Resolution FIE-FTCIR MS Metabolomics Approach Accurately Clusters Mouse Plasma Samples by Disease State
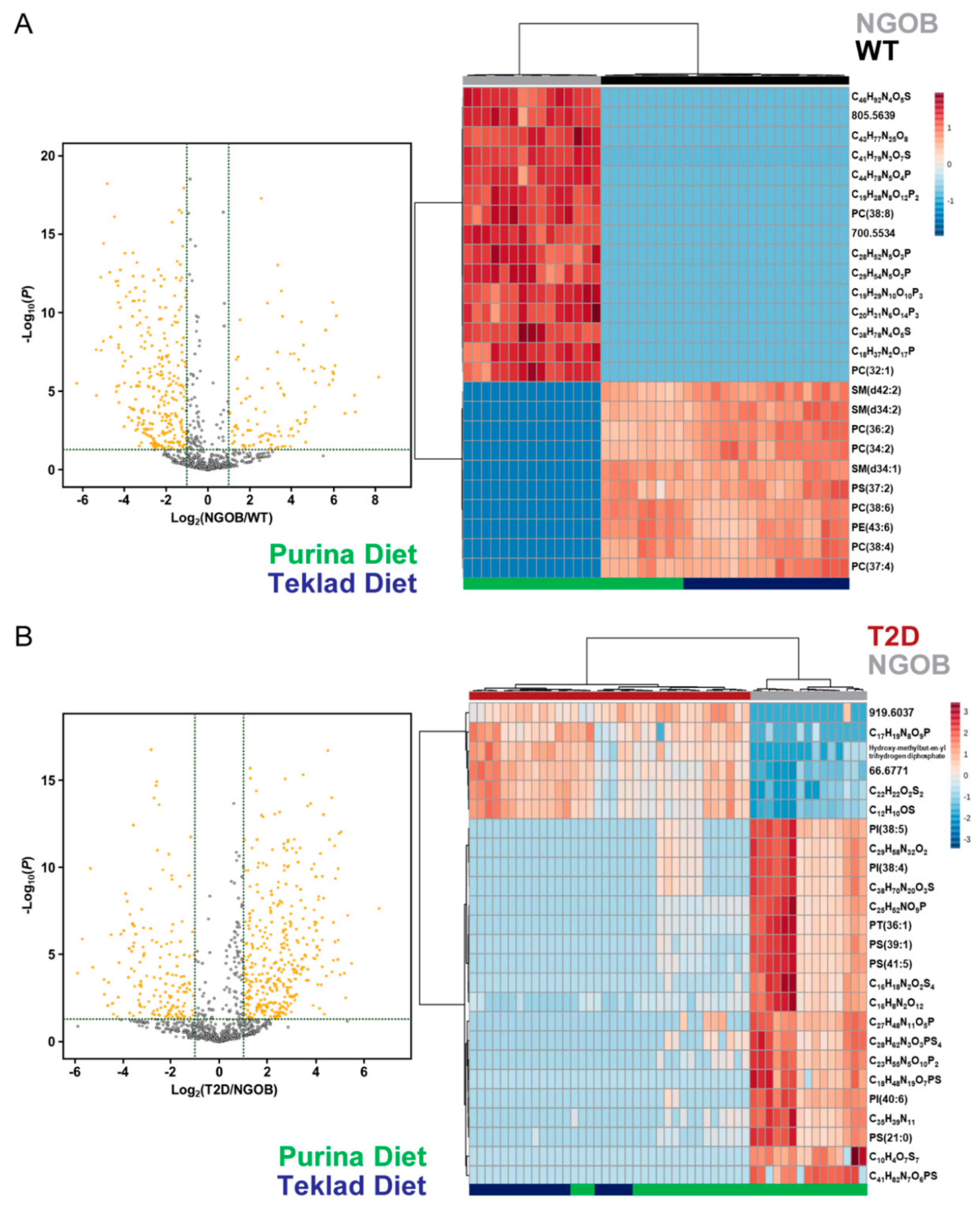
2.6. Diet Alone Does Not Explain the Phenotype of Male BTBRob Mice at 10 Weeks of Age
2.7. FIE-FTCIR MS Metabolomics Reveals That Elevations in Circulating Eicosanoid Precursors Correlate Directly with Agonist-Dependent EP3 Signaling in T2D β-Cell Dysfunction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Care and Husbandry
4.2. Blood Glucose Measurements and Insulin Tolerance Tests
4.3. Ex Vivo Islet Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion Assays
4.4. Quantitative PCR for Gene Expression Analyses
4.5. Terminal Blood Collection and Plasma Hormone/Metabolite Assays
4.6. Gut Microbial DNA Preparation, Sequencing, and Analysis
4.7. FIE-FTCIR MS for Unbiased Plasma Metabolomics
4.8. Statistical Analyses
4.9. Data Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerf, M.E. Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, M. Insulin resistance and pancreatic β cell failure. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, J.C.; Schaid, M.D.; Brill, A.L.; Fenske, R.J.; Kibbe, C.R.; Fontaine, D.A.; Sdao, S.M.; Brar, H.K.; Connors, K.M.; Wienkes, H.N.; et al. Enriching islet phospholipids with eicosapentaenoic acid reduces prostaglandin E2 signaling and enhances diabetic β-cell function. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimple, M.E.; Keller, M.P.; Rabaglia, M.R.; Pasker, R.L.; Neuman, J.C.; Truchan, N.A.; Brar, H.K.; Attie, A.D. Prostaglandin E2 receptor, EP3, is induced in diabetic islets and negatively regulates glucose- and hormone- stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Prostaglandin E2 confers protection against diabetic coronary atherosclerosis by stimulating M2 macrophage polarization via the activation of the CREB/BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7360–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clee, S.M.; Nadler, S.T.; Attie, A.D. Genetic and genomic studies of the BTBR ob/ob mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Ther. 2005, 12, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wancewicz, B.; Schaid, M.; Tiambeng, T.N.; Wenger, K.; Jin, Y.; Heyman, H.; Thompson, C.J.; Barsch, A.; Cox, E.D.; et al. Ultrahigh-Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Platform for Plasma Metabolomics Applied to Type 2 Diabetes Research. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 20, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harsch, I.; Konturek, P. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Type 2 and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: New Insights into “Old” Diseases. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falinska, A.M.; Tan, T.; Bloom, S. Gut hormones and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Manag 2014, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.L.; Wang, H.W.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Lin, H.H. Roles of adipocyte derived hormone adiponectin and resistin in insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorsman, P.; Huising, M.O. The somatostatin-secreting pancreatic δ-cell in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hædersdal, S.; Lund, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. The Role of Glucagon in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Gilbert, E.R.; Liu, D. Regulation of Insulin Synthesis and Secretion and Pancreatic Beta-Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2012, 9, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Gupta, Y. The Insulin:Glucagon Ratio and the Choice of Glucose-Lowering Drugs. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Pessin, J.E. Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanapure, S.; Garvey, D.; Janero, D.; Letts, G. Eicosanoids in Inflammation: Biosynthesis, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Frontiers. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Nilsson, Å. Sources of eicosanoid precursor fatty acid pools in tissues. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1521–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Pillinger, M.H.; Abramson, S.B. Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: The role of PGE2 synthases. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parazzoli, S.; Harmon, J.S.; Vallerie, S.N.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Robertson, R.P. Cyclooxygenase-2, not microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1, is the mechanism for interleukin-1-β-induced prostaglandin E2 production and inhibition of insulin secretion in pancreatic islets. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 32246–32253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.O.T.; Gleason, C.E.; Poitout, V.; Robertson, R.P. Prostaglandin E2 mediates inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1β. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31245–31248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tran, P.O.T.; Gleason, C.E.; Paul Robertson, R. Inhibition of interleukin-1β-induced COX-2 and EP3 gene expression by sodium salicylate enhances pancreatic islet β-cell function. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maedler, K.; Sergeev, P.; Ris, F.; Oberholzer, J.; Joller-Jemelka, H.I.; Spinas, G.A.; Kaiser, N.; Halban, P.A.; Donath, M.Y. Glucose-induced β cell production of IL-1β contributes to glucotoxicity in human pancreatic islets. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwdorp, M.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Pai, N.; Kaplan, L.M. Role of the microbiome in energy regulation and metabolism. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; Van Den Berg, F.W.J.; Sandris Nielsen, D.; Andreasen, A.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, L.H.; Jakobsen, M. Gut Microbiota in Human Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Differs from Non-Diabetic Adults. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzatti, G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Gibiino, G.; Binda, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Proteobacteria: A common factor in human diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S.; Inagaki, N. Regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 sensitivity by gut microbiota dysbiosis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of Incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, M.L.G.; Haynes, W.G. A role for plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in obesity: From pie to PAI? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2183–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martin, A.M.; Sun, E.W.; Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J. The influence of the gut microbiome on host metabolism through the regulation of gut hormone release. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, J.I.; Guo, L.; Von Montfort, C.; Kaiser, J.P.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Arteel, G.E. New role of resistin in lipopolysaccharide-induced liver damage in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, S.; Gamble, J.; Lyons, S.; Vlatković, N.; Dimaline, R.; Varro, A.; Dockray, G.J. Gastric expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 is associated with hyperphagia and obesity in mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byberg, L.; Smedman, A.; Vessby, B.; Lithell, H. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and relations to fatty acid composition in the diet and in serum cholesterol esters. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 2086–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Pahor, M.; Incalzi, R.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1): A key factor linking fibrinolysis and age-related subclinical and clinical conditions. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, S.; Duval, C.; Sammut, S.J.; Steele, I.; Pritchard, D.M.; Atherton, J.C.; Argent, R.H.; Dimaline, R.; Dockray, G.J.; Varro, A. Increased expression of the urokinase plasminogen activator system by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyot, J.; Semache, M.; Ferdaoussi, M.; Fontés, G.; Poitout, V. Lipopolysaccharides impair insulin gene expression in isolated islets of langerhans via toll-like receptor-4 and nf-κb signalling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.C.; Shieh, W.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, S.C.; Chen, H.L. Lipopolysaccharide increases resistin gene expression in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett. 2002, 530, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poreba, M.; Rostoff, P.; Siniarski, A.; Mostowik, M.; Golebiowska-Wiatrak, R.; Nessler, J.; Undas, A.; Gajos, G. Relationship between polyunsaturated fatty acid composition in serum phospholipids, systemic low-grade inflammation, and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimple, M.E.; Moss, J.B.; Brar, H.K.; Rosa, T.C.; Truchan, N.A.; Pasker, R.L.; Newgard, C.B.; Casey, P.J. Deletion of Gαz protein protects against diet-induced glucose intolerance via expansion of β-cell mass. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20344–20355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, J.C.; Truchan, N.A.; Joseph, J.W.; Kimple, M.E. A method for mouse pancreatic islet isolation and intracellular cAMP determination. J. Vis. Exp. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchan, N.A.; Brar, H.K.; Gallagher, S.J.; Neuman, J.C.; Kimple, M.E. A single-islet microplate assay to measure mouse and human islet insulin secretion. Islets 2015, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brill, A.L.; Wisinski, J.A.; Cadena, M.T.; Thompson, M.F.; Fenske, R.J.; Brar, H.K.; Schaid, M.D.; Pasker, R.L.; Kimple, M.E. Synergy between Gαz deficiency and GLP-1 analog treatment in preserving functional β-cell mass in experimental diabetes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pak, H.H.; Cummings, N.E.; Green, C.L.; Brinkman, J.A.; Yu, D.; Tomasiewicz, J.L.; Yang, S.E.; Boyle, C.; Konon, E.N.; Ong, I.M.; et al. The Metabolic Response to a Low Amino Acid Diet is Independent of Diet-Induced Shifts in the Composition of the Gut Microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Desantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schaid, M.D.; Zhu, Y.; Richardson, N.E.; Patibandla, C.; Ong, I.M.; Fenske, R.J.; Neuman, J.C.; Guthery, E.; Reuter, A.; Sandhu, H.K.; et al. Systemic Metabolic Alterations Correlate with Islet-Level Prostaglandin E2 Production and Signaling Mechanisms That Predict β-Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2021, 11, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010058
Schaid MD, Zhu Y, Richardson NE, Patibandla C, Ong IM, Fenske RJ, Neuman JC, Guthery E, Reuter A, Sandhu HK, et al. Systemic Metabolic Alterations Correlate with Islet-Level Prostaglandin E2 Production and Signaling Mechanisms That Predict β-Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites. 2021; 11(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchaid, Michael D., Yanlong Zhu, Nicole E. Richardson, Chinmai Patibandla, Irene M. Ong, Rachel J. Fenske, Joshua C. Neuman, Erin Guthery, Austin Reuter, Harpreet K. Sandhu, and et al. 2021. "Systemic Metabolic Alterations Correlate with Islet-Level Prostaglandin E2 Production and Signaling Mechanisms That Predict β-Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes" Metabolites 11, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010058
APA StyleSchaid, M. D., Zhu, Y., Richardson, N. E., Patibandla, C., Ong, I. M., Fenske, R. J., Neuman, J. C., Guthery, E., Reuter, A., Sandhu, H. K., Fuller, M. H., Cox, E. D., Davis, D. B., Layden, B. T., Brasier, A. R., Lamming, D. W., Ge, Y., & Kimple, M. E. (2021). Systemic Metabolic Alterations Correlate with Islet-Level Prostaglandin E2 Production and Signaling Mechanisms That Predict β-Cell Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites, 11(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11010058