A Python-Based Pipeline for Preprocessing LC–MS Data for Untargeted Metabolomics Workflows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
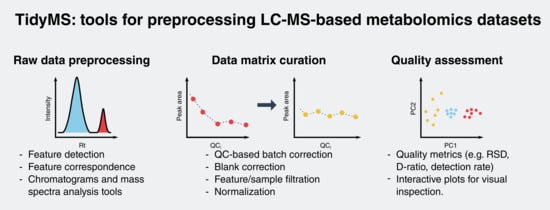
2.1. Package Implementation
2.1.1. Raw Data Analysis Tools
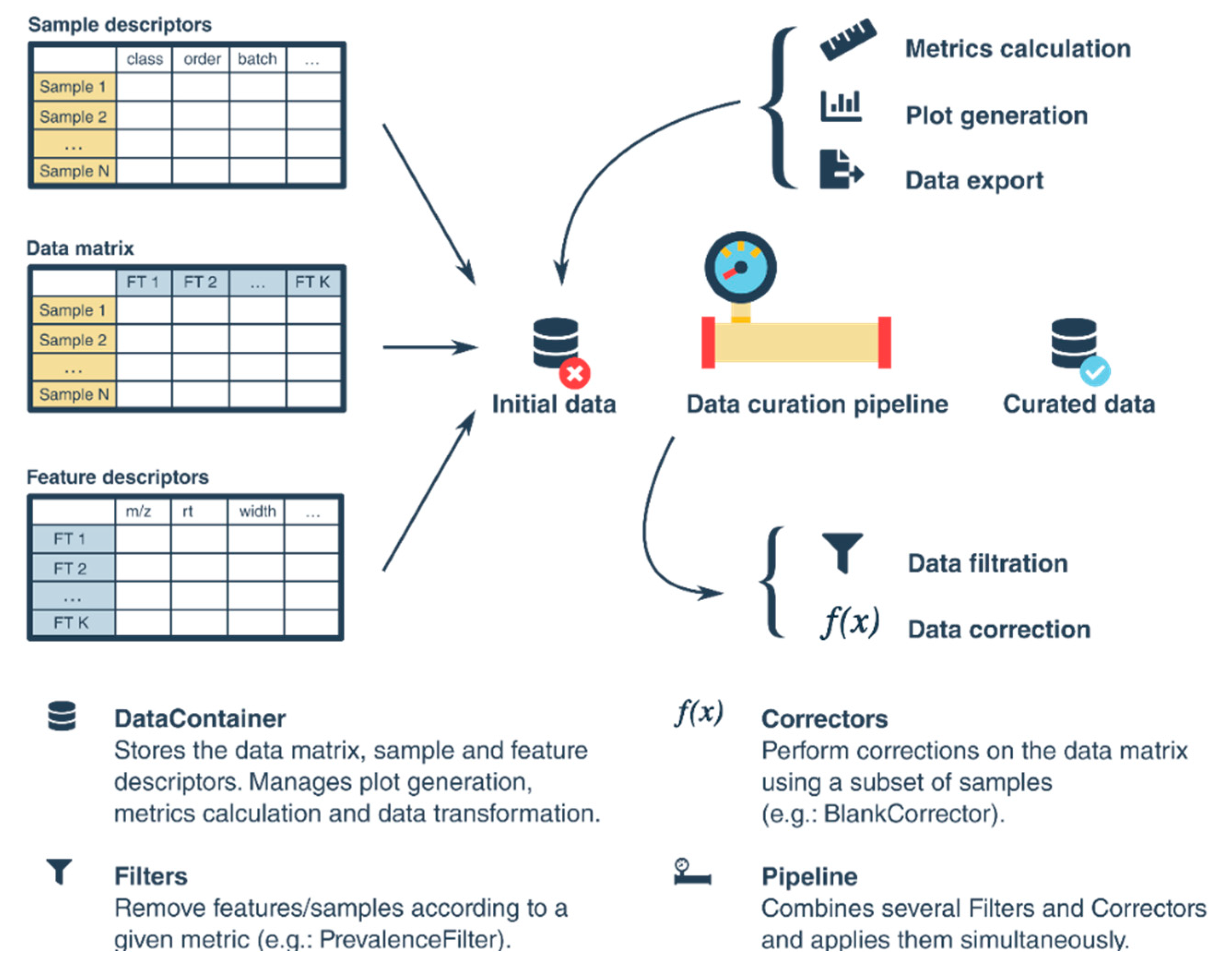
2.1.2. Data Matrix Curation Tools
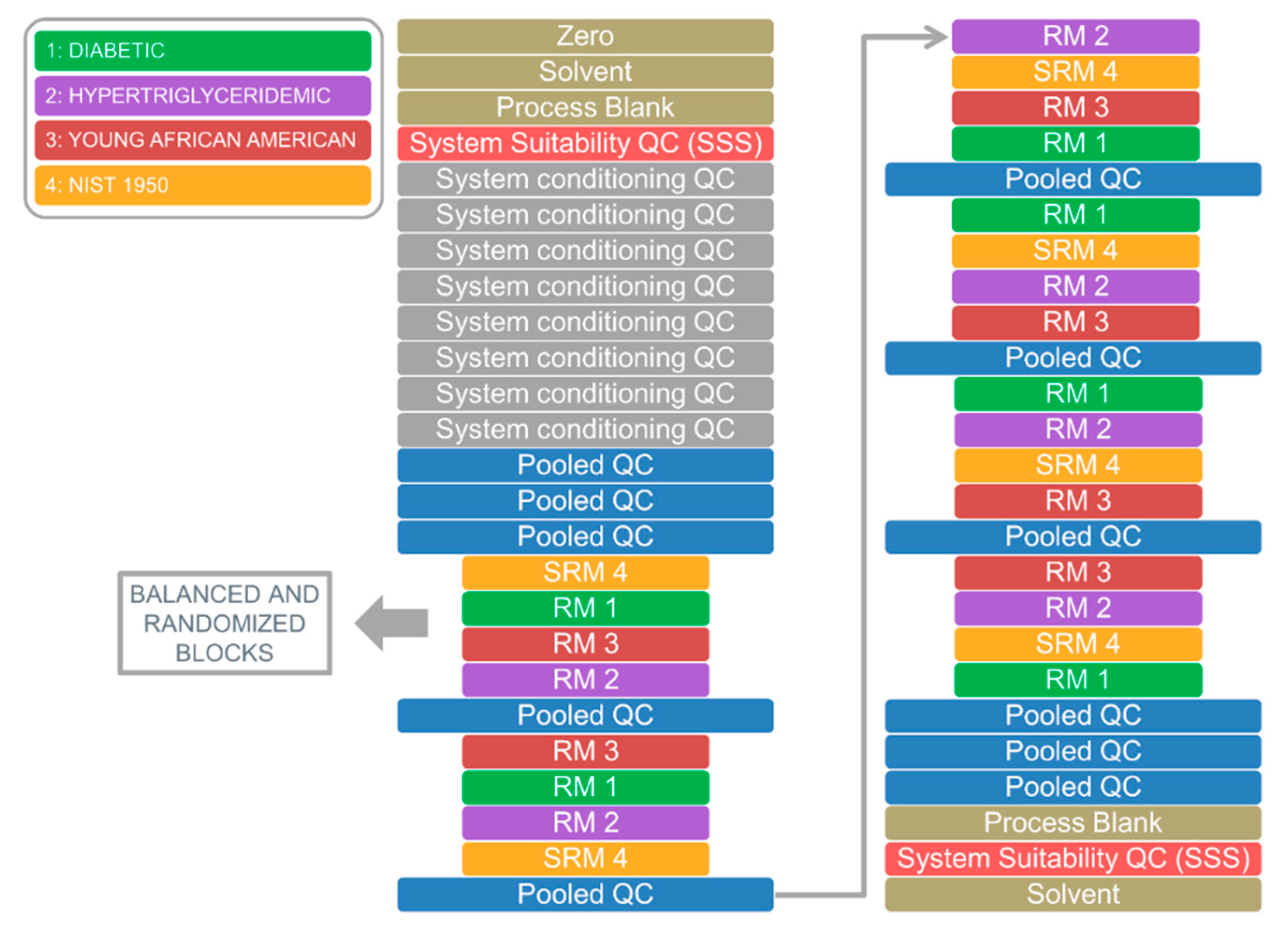
2.2. Application 1: System Suitability Check and Signal Drift Evaluation
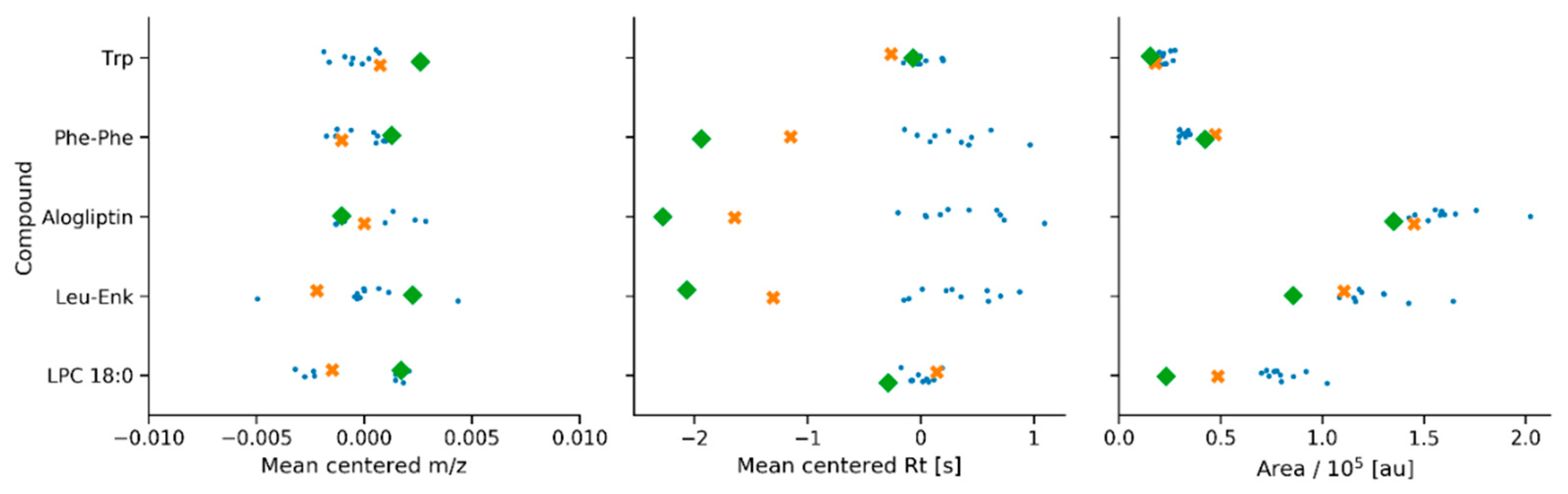
2.3. Application 2: Analysis of Candidate Reference Standard Materials
2.4. Running Times
2.5. Comparable Software Alternatives
2.6. Limitations and Perspectives
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plasma Samples
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography−Mass Spectrometry (UPLC–MS)
4.5. Raw Data Conversion
4.6. Python Package
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Disclaimer
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- González-Riano, C.; Dudzik, D.; Garcia, A.; Gil-De-La-Fuente, A.; Gradillas, A.; Godzien, J.; López-Gonzálvez, Á.; Rey-Stolle, F.; Rojo, D.; Rupérez, F.J.; et al. Recent Developments along the Analytical Process for Metabolomics Workflows. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzik, D.; Barbas-Bernardos, C.; García, A.; Barbas, C. Quality assurance procedures for mass spectrometry untargeted metabolomics. a review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playdon, M.C.; Joshi, A.D.; Tabung, F.K.; Cheng, S.; Henglin, M.; Kim, A.; Lin, T.; Van Roekel, E.H.; Huang, J.; Krumsiek, J.; et al. Metabolomics Analytics Workflow for Epidemiological Research: Perspectives from the Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS). Metabolities 2019, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beger, R.D.; Dunn, W.B.; Bandukwala, A.; Bethan, B.; Broadhurst, D.; Clish, C.B.; Dasari, S.; Derr, L.; Evans, A.; Fischer, S.; et al. Towards quality assurance and quality control in untargeted metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.; O’Donovan, C.; Playdon, M.; Beecher, C.; Beger, R.D.; Bowden, J.A.; Broadhurst, D.; Clish, C.B.; Dasari, S.; Dunn, W.B.; et al. On behalf of the Metabolomics Quality Assurance and Quality Control Consortium (mQACC), Dissemination and Analysis of the Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) Practices of LC-MS Based Untargeted Metabolomics practitioners. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge, M.E.; Dodds, J.N.; Baker, E.S.; Edison, A.S.; Fernández, F.M. Challenges in Identifying the Dark Molecules of Life. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 12, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzatti, J.; Boccard, J.; Codesido, S.; Gagnebin, Y.; Joshi, A.; Picard, D.; González-Ruiz, V.; Rudaz, S. Implementation of liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry methods for untargeted metabolomic analyses of biological samples: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1105, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klåvus, A.; Kokla, M.; Noerman, S.; Koistinen, V.M.; Tuomainen, M.; Zarei, I.; Meuronen, T.; Häkkinen, M.R.; Rummukainen, S.; Babu, A.F.; et al. “Notame”: Workflow for non-targeted lc–ms metabolic profiling. Metabolities 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Want, E.J. From Samples to Insights into Metabolism: Uncovering Biologically Relevant Information in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Data. Metabolities 2019, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomoni, F.; Le Corguillé, G.; Monsoor, M.; Landi, M.; Pericard, P.; Pétéra, M.; Duperier, C.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Martin, J.-F.; Jacob, D.; et al. Workflow4Metabolomics: A collaborative research infrastructure for computational metabolomics. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, R.; Broadhurst, D.; Smilde, A.K.; Kristal, B.S.; Baker, J.D.; Beger, R.; Bessant, C.; Connor, S.; Capuani, G.; Craig, A.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindelar, M.; Patti, G.J. Chemical Discovery in the Era of Metabolomics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9097–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SECIMTools: A Suite of Metabolomics Data Analysis Tools. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5910624/ (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Sands, C.; Wolfer, A.M.; Correia, G.D.S.; Sadawi, N.; Ahmed, A.; Jiménez, B.; Lewis, M.R.; Glen, R.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Pearce, J.T.M. The nPYc-Toolbox, a Python module for the pre-processing, quality-control and analysis of metabolic profiling datasets. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 5359–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Goodacre, R.; Reinke, S.N.; Kuligowski, J.; Wilson, I.D.; Lewis, M.R.; Dunn, W.B. Guidelines and considerations for the use of system suitability and quality control samples in mass spectrometry assays applied in untargeted clinical metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Beger, R.D.; Ekman, D.R.; Epps, D.J.T.; Kamp, H.; Leonards, P.; Loizou, G.D.; Macrae, J.I.; Van Ravenzwaay, B.; et al. Use cases, best practice and reporting standards for metabolomics in regulatory toxicology. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, C.R.; Camara, J.E.; Carney, J.; Choquette, S.J.; Cole, K.D.; Derose, P.C.; Duewer, D.L.; Epstein, M.S.; Kline, M.C.; Lippa, K.A.; et al. Metrological Tools for the Reference Materials and Reference Instruments of the NIST Material Measurement Laboratory. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. Spec. Publ. 2020, 260, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Manso, Y.; Lowenthal, M.S.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Sampson, M.; Telu, K.H.; Rudnick, P.A.; Mallard, W.G.; Bearden, D.W.; Schock, T.B.; Tchekhovskoi, D.V.; et al. Metabolite Profiling of a NIST Standard Reference Material for Human Plasma (SRM 1950): GC-MS, LC-MS, NMR, and Clinical Laboratory Analyses, Libraries, and Web-Based Resources. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11725–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Delgado, P.; Dudzik, D.; Miguel, V.; Lamas, S.; Barbas, C. Data-dependent normalization strategies for untargeted metabolomics—A case study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6391–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, B.B. Data normalization strategies in metabolomics: Current challenges, approaches, and tools. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 26, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millman, K.J.; Aivazis, M. Python for Scientists and Engineers. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Designs and Implementation (OSDI 16), Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bokeh Development Team Python Library for Interactive Visualization. Available online: https://bokeh.org (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Röst, H.L.; Sachsenberg, T.; Aiche, S.; Bielow, C.; Weisser, H.; Aicheler, F.; Andreotti, S.; Ehrlich, H.-C.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Kenar, E.; et al. OpenMS: A flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.; Ijsbrand, J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.; Bourne, P.; et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic database annotations via query of elemental compositions: Mass accuracy is insufficient even at less than 1 ppm. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TidyMS Repository. Available online: https://github.com/griquelme/tidyms. (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- TidyMS Application Examples. Available online: https://github.com/griquelme/tidyms-notebooks (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Du, P.; Kibbe, W.A.; Lin, S.M. Improved peak detection in mass spectrum by incorporating continuous wavelet transform-based pattern matching. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Neumann, S. Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; The Human Serum Metabolome (HUSERMET) Consortium; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, K.; Cochrane, K.; Nainala, V.C.; Williams, M.; Chang, J.; Jayaseelan, K.V.; O’Donovan, C. MetaboLights: A resource evolving in response to the needs of its scientific community. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D440–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.C.; MacLean, B.; Burke, R.; Amode, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python Software Foundation. Python Language Reference, Version 3.6. Available online: http://www.python.org (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Van Der Walt, S.; Colbert, S.C.; Varoquaux, G. The NumPy Array: A Structure for Efficient Numerical Computation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and Statistical Modeling with Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar]

| Tool | TidyMS | MZmine2 | XCMS a | MS-DIAL | nPYc- Toolbox | SECIM TOOLS | Notame | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | ||||||||
| Language | Python | Java | R | C# | Python | Python | R | |
| Raw data preprocessing Tools (e.g., feature detection and correspondence) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | |
| Data curation | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| QC-based batch correction | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | |
| Quality metrics (e.g., RSD in samples and references, PCA plots) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Normalization, imputation, scaling | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Feature annotation | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riquelme, G.; Zabalegui, N.; Marchi, P.; Jones, C.M.; Monge, M.E. A Python-Based Pipeline for Preprocessing LC–MS Data for Untargeted Metabolomics Workflows. Metabolites 2020, 10, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100416
Riquelme G, Zabalegui N, Marchi P, Jones CM, Monge ME. A Python-Based Pipeline for Preprocessing LC–MS Data for Untargeted Metabolomics Workflows. Metabolites. 2020; 10(10):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100416
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiquelme, Gabriel, Nicolás Zabalegui, Pablo Marchi, Christina M. Jones, and María Eugenia Monge. 2020. "A Python-Based Pipeline for Preprocessing LC–MS Data for Untargeted Metabolomics Workflows" Metabolites 10, no. 10: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100416
APA StyleRiquelme, G., Zabalegui, N., Marchi, P., Jones, C. M., & Monge, M. E. (2020). A Python-Based Pipeline for Preprocessing LC–MS Data for Untargeted Metabolomics Workflows. Metabolites, 10(10), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100416