Wild Harvesting vs. Cultivation: Total Petasin Content in Petasites hybridus Rhizome Extracts Determines Spasmolytic Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extract Preparation
2.2. Gas Chromatography
2.3. Animals
2.4. Tissue Preparation
2.5. Contractile Activity Measurement
2.6. Ethics
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. P. hybridus Rhizome Extract Exerts Dose-Dependent Antispasmodic Effects
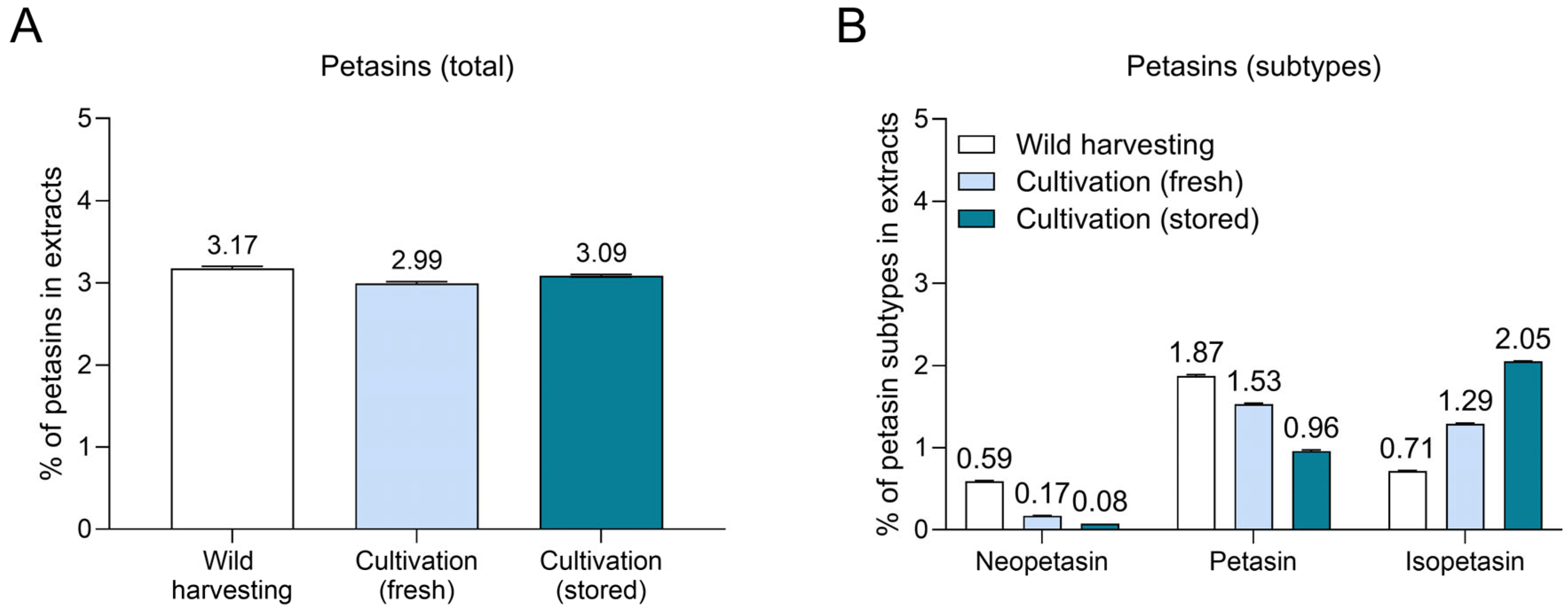
3.2. Petasin Composition Varies in P. hybridus Rhizome Extracts Derived from Wild Harvesting and Cultivation
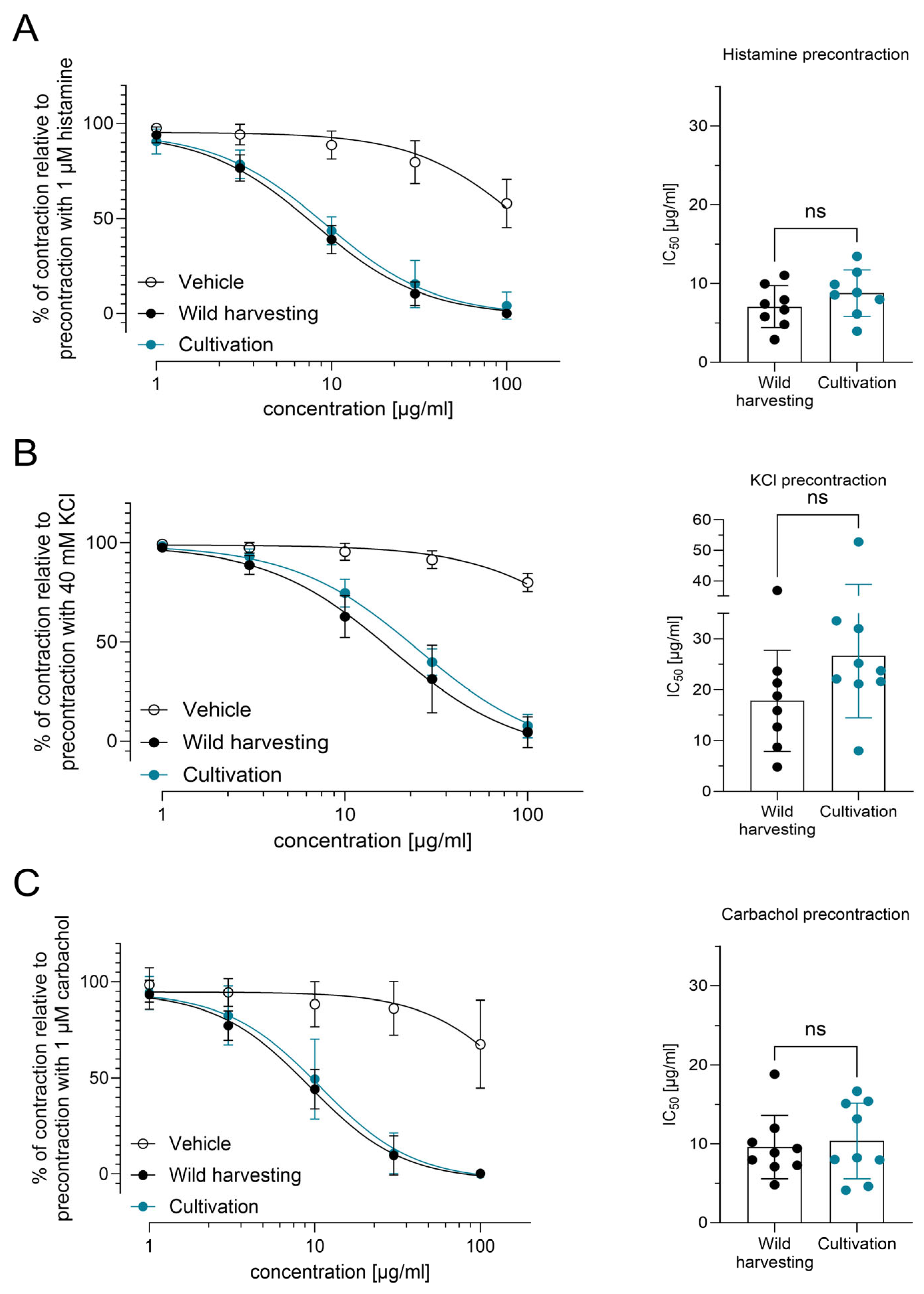
3.3. Spasmolytic Effects of P. hybridus Rhizome Extracts Derived from Wild Harvesting and Cultivation Are Comparable
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-LOX | 5-lipoxygenase |
| P. hybridus | Petasites hybridus |
| FID | Flame ionization detector |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| PA | Pyrrolizidine alkaloids |
| TRPs | Transient receptor potential channels |
| VDCC | Voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels |
References
- Zeller Medical AG CH-Romanshorn. Patienteninformation Relaxane(R) Filmtabletten Swissmedic Approved 2009. Available online: https://www.swissmedicinfo.ch/ViewMonographie (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- HMPC (Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products—European Medicines Agency). Community Herbal Monographs on Melissa officinalis L., folium (2013; Doc RefEMEA/HMPC/196745/2012), Passiflora incarnata L., herba (2014; Doc Ref. EMEA/HMPC/669740/2013), Valeriana officinalis L., radix (2016; Doc Ref. EMEA/HMPC/150848/2015). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/search?f%5B0%5D=ema_search_categories%3A85&f%5B1%5D=herbal_outcome%3A254 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Kälin, P. The common butterbur (Petasites hybridus)—Portrait of a medicinal herb. Forsch Komplementarmed Kl. Naturheilkd 2003, 10 (Suppl. 1), 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, M.E.; Nicolussi, S.; Spura, K.; Blohm, C.; Zahner, C.; Drewe, J. Effect of the fixed combination of valerian, lemon balm, passionflower, and butterbur extracts (Ze 185) on the prescription pattern of benzodiazepines in hospitalized psychiatric patients-A retrospective case-control investigation. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, S.; Haschke, M.; Zahner, C.; Kruttschnitt, E.; Drewe, J.; Liakoni, E.; Hammann, F.; Gaab, J. Effects of a fixed herbal drug combination (Ze 185) to an experimental acute stress setting in healthy men—An explorative randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Phytomedicine 2018, 39, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, U.; Hobi, V.; Kocher, R.; König, C. Die sedative Akutwirkung eines pflanzlichen Entspannungsdragées im Vergleich zu Bromazepam. Schweiz. Rundschau Med. 1991, 52, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg, R.; Sauer, S.; Brattström, B. Pflanzlicher Tagestranquilizer Ze 185 und Oxazepam im klinischen und neurophysiologischen Vergleich bei Patienten mit psychovegetativen Beschwerden. Z. Für Phytother. 2004, 25, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Melzer, J.; Schrader, E.; Brattström, A.; Schellenberg, R.; Saller, R. Fixed herbal drug combination with and without butterbur (Ze 185) for the treatment of patients with somatoform disorders: Randomized, placebo-controlled pharmaco-clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, G.; Opwis, K. Wirkung von Relax® auf Angst und kognitive Leistungsfähigkeit-Eine plazebokontrollierte Doppelblindstudie. Ars. Medici. 2000, 25/26, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschek, W. Wichtl–Teedrogen und Phytopharmaka; Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Mihajilov-Krstev, T.; Jovanovic, B.; Zlatkovic, B.; Matejic, J.; Vitorovic, J.; Cvetkovic, V.; Ilic, B.; Dordevic, L.; Jokovic, N.; Miladinovic, D.; et al. Phytochemistry, Toxicology and Therapeutic Value of Petasites hybridus Subsp. Ochroleucus (Common Butterbur) from the Balkans. Plants 2020, 9, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinowski, L.; Luca, S.V.; Minceva, M.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K. A review on the ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of butterbur species (Petasites L.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlak, J.; Diener, H.C.; Kleeberg-Hartmann, J.; Messlinger, K.; Silberstein, S. Petasites for Migraine Prevention: New Data on Mode of Action, Pharmacology and Safety. A Narrative Review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 864689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapowal, A. Randomised controlled trial of butterbur and cetirizine for treating seasonal allergic rhinitis. BMJ 2002, 324, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitru, A.F.; Shamji, M.; Wagenmann, M.; Hindersin, S.; Scheckenbach, K.; Greve, J.; Klenzner, T.; Hess, L.; Nebel, S.; Zimmermann, C.; et al. Petasol butenoate complex (Ze 339) relieves allergic rhinitis-induced nasal obstruction more effectively than desloratadine. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1515–1521-e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blosa, M.; Uricher, J.; Nebel, S.; Zahner, C.; Butterweck, V.; Drewe, J. Treatment of Early Allergic and Late Inflammatory Symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis with Petasites hybridus Leaf Extract (Ze 339): Results of a Noninterventional Observational Study in Switzerland. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, A.; Siewert, B.; Toff, S.; Drewe, J. UPLC TOF MS for sensitive quantification of naturally occurring pyrrolizidine alkaloids in Petasites hybridus extract (Ze 339). J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 997, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomet, O.A.; Wiesmann, U.N.; Schapowal, A.; Bizer, C.; Simon, H.U. Role of petasin in the potential anti-inflammatory activity of a plant extract of Petasites hybridus. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomet, O.A.; Wiesmann, U.N.; Blaser, K.; Simon, H.U. Differential inhibition of inflammatory effector functions by petasin, isopetasin and neopetasin in human eosinophils. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattström, A.; Schapowal, A.; Maillet, I.; Schnyder, B.; Ryffel, B.; Moser, R. Petasites extract Ze 339 (PET) inhibits allergen-induced Th2 responses, airway inflammation and airway hyperreactivity in mice. Phytother. Res. 2009, 24, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, K. Über ein antispastisches Prinzip in Petasites officinalis Moench. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Für Exp. Pathol. Und Pharmakol. 1951, 213, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.C.; Lei, C.B.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, C.F. Relaxant effects of petasins in isolated guinea pig trachea and their structure-activity relationships. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.J.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, X.C.; Liao, J.F.; Ren, J. Cellular calcium regulatory machinery of vasorelaxation elicited by petasin. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.C.; Lei, C.B.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, C.F. Mechanisms of Relaxant Action of S-Petasin and S-Isopetasin, Sesquiterpenes of Petasites formosanus, in Isolated Guinea Pig Trachea. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.J.; Wu, X.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Jun, R.; Shum, A.Y.C.; Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, C.F. Ca2+ channel blocking effect of iso-S-petasin in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 445, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esberg, L.B.; Wang, G.J.; Lin, Y.L.; Ren, J. Iso-S-petasin, a hypotensive sesquiterpene from Petasites formosanus, depresses cardiac contraction and intracellular Ca2+ transients in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodjadjiku, U.; Nagele, B.; Halbsguth, C.; Butterweck, V. Extract matrix composition does not affect in vitro leukotriene inhibitory effects of the Petasites hybridus extract Ze 339. Fitoterapia 2021, 153, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapowal, A.; Engel, J.P.; Horn, J.; Kaiser, W.D.; Kortüm, M.; Martin, R.; Massing, A.; Nemec-Held, U.; Sauer, S.; Schellenberg, R.; et al. Treating intermittent allergic rhinitis: A prospective, randomized, placebo and antihistamine-controlled study of Butterbur extract Ze 339. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benemei, S.; De Logu, F.; Li Puma, S.; Marone, I.M.; Coppi, E.; Ugolini, F.; Liedtke, W.; Pollastro, F.; Appendino, G.; Geppetti, P.; et al. The anti-migraine component of butterbur extracts, isopetasin, desensitizes peptidergic nociceptors by acting on TRPA1 cation channel. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2897–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeberg-Hartmann, J.; Vogler, B.; Messlinger, K. Petasin and isopetasin reduce CGRP release from trigeminal afferents indicating an inhibitory effect on TRPA1 and TRPV1 receptor channels. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urda, L.; Kreuter, M.H.; Drewe, J.; Boonen, G.; Butterweck, V.; Klimkait, T. The Petasites hybridus CO2 Extract (Ze 339) Blocks SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro. Viruses 2022, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakwerth, C.A.; Grass, V.; Erb, A.; Pichlmair, A.; Boonen, G.; Butterweck, V.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication by Petasites hybridus CO2-extract (Ze 339). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 115959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesugi, S.; Hakozaki, M.; Kanno, Y.; Shiraishi, A.; Suzuki, M.; Kimura, K.I.; Shiono, Y.; Yano, A. Petasin is the main component responsible for the anti-adipogenic effect of Petasites japonicus. Fitoterapia 2022, 157, 105130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Song, A.L.; Bai, Y.L.; Xu, X.D.; He, D.Q.; Zhang, Y.C. Inhibitory effects of petasin on human colon carcinoma cells mediated by inactivation of Akt/mTOR pathway. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heishima, K.; Sugito, N.; Soga, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Ito, Y.; Honda, R.; Kuranaga, Y.; Sakai, H.; Ito, R.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Petasin potently inhibits mitochondrial complex I-based metabolism that supports tumor growth and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e139933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halbsguth, C.; Merk, V.M.; Drewe, J.; Boonen, G.; Butterweck, V. Wild Harvesting vs. Cultivation: Total Petasin Content in Petasites hybridus Rhizome Extracts Determines Spasmolytic Effects. Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020015
Halbsguth C, Merk VM, Drewe J, Boonen G, Butterweck V. Wild Harvesting vs. Cultivation: Total Petasin Content in Petasites hybridus Rhizome Extracts Determines Spasmolytic Effects. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2025; 93(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalbsguth, Christiane, Verena M. Merk, Jürgen Drewe, Georg Boonen, and Veronika Butterweck. 2025. "Wild Harvesting vs. Cultivation: Total Petasin Content in Petasites hybridus Rhizome Extracts Determines Spasmolytic Effects" Scientia Pharmaceutica 93, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020015
APA StyleHalbsguth, C., Merk, V. M., Drewe, J., Boonen, G., & Butterweck, V. (2025). Wild Harvesting vs. Cultivation: Total Petasin Content in Petasites hybridus Rhizome Extracts Determines Spasmolytic Effects. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 93(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93020015





