Abstract
The roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. have been widely used both for industrial and medicinal purposes for centuries. The primary biologically active substances from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes are anthraquinone derivatives such as ruberythric acid and lucidin-3-primeveroside. Their identification and quantification are carried out by various analytical methods, requiring a complicated sample preparation as well as special reagents and reference samples. However, NMR spectroscopy has no limitations of this kind. In this work, we have developed and validated a new express and standard-free method for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of ruberythric acid and lucidin-3-primeveroside by 1H NMR spectroscopy in the extracts from the roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. In this work, we have optimized the conditions of the sample preparation and registration of 1H NMR spectra, determined the optimal solvent and reference compound and confirmed the obtained results by HPLC-UV-MS.
1. Introduction
Rubia tinctorum L. is an herbaceous perennial plant with a woody horizontal rhizome and branched climbing shoots up to 1.5–2 m high, belonging to the family Rubiaceae and the genus Rubia. Typically, species of the Rubia genus are referred to as madder. Rubia tinctorum L. grows in Eastern Europe, the Mediterranean, Asia Minor and Central Asia. In Russia, it is native to the south-eastern part of the country and to the Caucasus region. From prehistoric times to the end of the 19th century, when synthetic dyes were introduced, the roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. have been used as a natural red dye source. The root of Rubia tinctorum L. was highly sought after by artisans in ancient Greece, Rome, Egypt and Persia. The reliable red dye extracted from the roots was used for dyeing various kinds of textiles, including cotton, wool and silk. Toward the end of the nineteenth century, natural dyes derived from Rubia tinctorum L. gradually began to disappear, being replaced by their synthetic counterparts [1]. However, the oldest known identification of madder (with an abundant content of purpurine) was found on a fragment of an Egyptian leather quiver that was recovered at Thebes and dates to the Middle Kingdom Dynasty (2100–1980 BC) [2].
Alizarin-poor madder mixed with Egyptian blue was found in a Hellenistic sculpture using an LC-MS analysis of purple pigments [3].
In the Tarim Basin of western China, certain found textiles (dating to the late 2nd millennium BC) were probably dyed using Rubia tinctorum L. Additionally, certain textiles founded at Timna, Israel (dating to the eleventh and tenth centuries BC), contained red dye sourced from madder species [2].
At present, Rubia tinctorum L. is mostly utilized as a medicinal plant. It is reported to exert the nephrolithic effect, has antidiabetic potential in type II diabetes, possesses antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities and significantly reduces the genotoxicity of several carcinogens [4,5,6,7,8,9,10].
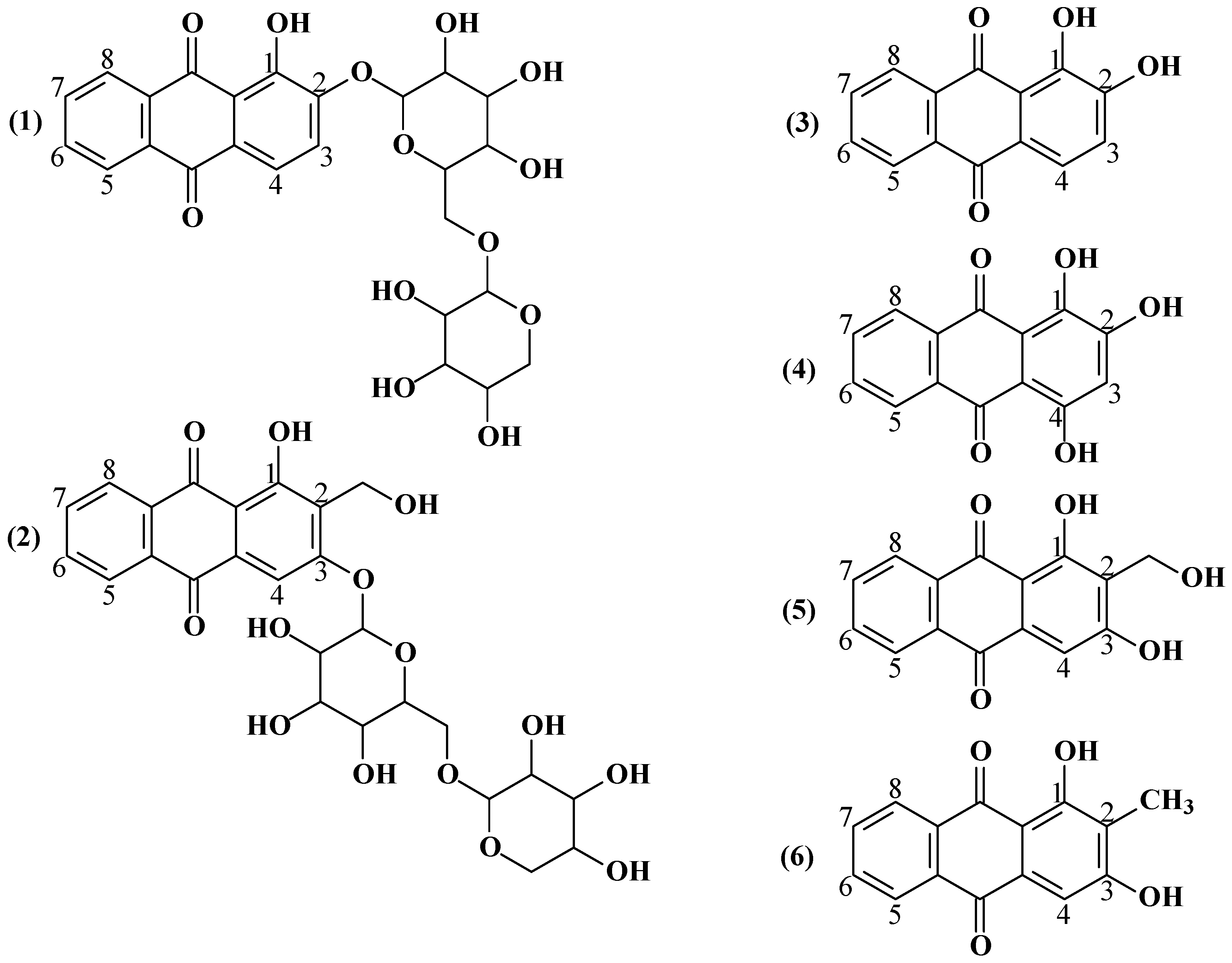
The roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. contain organic acids (malic, tartaric, citric), triterpenoids, anthraquinones, flavonoids, iridoids, sugars, proteins, ascorbic acid, pectin substances and other compounds [5,10,11]. Among the biologically active substances of Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes, anthraquinone derivatives are of particular interest due to their staining bioactivity. Based on the pertinent literature [12], the primary anthraquinone compounds from the extract from the Rubia tinctorum L. root and rhizomes are ruberythric acid (RA) and lucidin-3-primeveroside (LP), the glycated derivatives of alizarin and lucidin at positions 2 and 3, respectively; their structures as well as the structures of several other anthraquinone compounds in the extracts of Rubia tinctorum L. root and rhizomes are shown in Figure 1.
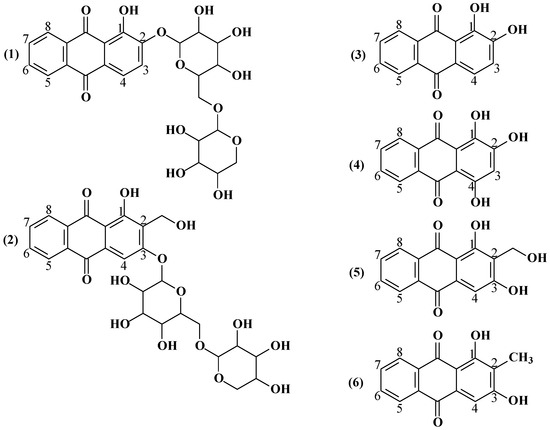
Figure 1.
Anthraquinone derivatives from the extract of Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes: (1) ruberythric acid (M = 534.47 g/mol), (2) lucidin-3-primeveroside (M = 564.49 g/mol), (3) alizarin (M = 240.21 g/mol), (4) purpurin (M = 256.21 g/mol), (5) lucidin (M = 270.24 g/mol), and (6) rubiadin (M = 254.24 g/mol).
RA and LP are shown to exert toxic effects. Shukla V. et al. [13] showed that RA can be processed by liver enzymes and NADPH producing alizarin and 1-hydroxyanthraquinone. Chronic treatment with 1-hydroxyanthraquinone induces unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) in primary rat hepatocytes (PRHs) and increases the incidence of intestinal and liver tumors in rats [13]. In the presence of the rat liver extract and NADPH, LP can be converted into lucidin and rubiadin, which have been shown to induce mutations in Salmonella typhimurium [13]. Information compiled from several studies and investigations carried out by the EMA evaluating the toxic potential of herbal extracts shows that the roots of Rubia tinctorum L. contain lucidin with probable carcinogenic and genotoxic activity thus ruling out its benefit [14].
On the other hand, Houari et al. showed that the oral administration of the Rubia tinctorum L. root extract up to 400 mg·kg−1 is safe for nutritional and therapeutic purposes, and the LD50 of the aqueous extract was much higher than 2000 mg·kg−1. Moreover, it is possible that the root of Rubia tinctorum L. inhibits red blood cell hemolysis, hence having an antianemic effect [10].
In recent research carried out by Nguyen et al., the antigenotoxic activity of alizarin isolated from Rubia tinctorum L. tested on human colon cancer cells shows and suppresses tumor cell proliferation. The experiment revealed no carcinogenic characteristics or tumor-promoting action, such as enhancing malignant transformation or stimulating cell proliferation. Alizarin demonstrated selective efficacy against cancer cells since it had a much weaker inhibitory effect on normal cells [15].
This implicates the paramount importance of precisely determining these anthraquinone compounds in Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes.
According to the monograph 2.5.0083.18 of the 14th edition of the Russian Pharmacopoeia, the primary methods for identifying, quantifying and determining the anthraquinone derivatives in the extracts from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes are as follow: qualitative specific reaction, thin-layer chromatography and UV spectrophotometry [16]. These methods allow for determining only the total content of anthraquinone derivatives but not the content of the individual compounds. Previously, anthraquinone derivatives in Rubia tinctorum L. were also analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography combined with UV detection (HPLC-UV) [17,18]. High-performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS), which allows for determining several components with a similar structure at the same time, can also be used for this purpose [5,19]. Dercsen et al. determined anthraquinone derivatives by both methods, HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS [11]. Langa-Lomba et al. used IR spectroscopy and gas chromatography combined with mass spectrometry to identify 58 compounds in the hydromethanolic extracts of Rubia tinctorum L. including anthraquinone derivatives such as alizarin, α-hydroxyanthraquinone, β-methylanthraquinone, 1-hydroxy-4-methylanthraquinone and 1,8-dihydroxy-3-methyl anthraquinone [20]. However, most analytical methods mentioned above have certain disadvantages, since they require the purification of the target component or its chemical modification, complex and time-consuming sample preparation, reference samples and have low accuracy. NMR spectroscopy does not require complicated sample preparation, derivatization or reference samples. Due to its sufficient sensitivity, informativeness and precision, as the signals in the NMR spectrum have a mole ratio, the NMR spectroscopy method is preferable to any of the above-mentioned methods. The signals from the reference compounds added in known amounts can be used as reference signals, in particular, the signals of residual protons from the deuterated solvents, which are utilized for the quantitative determination of target compounds [21].
According to the literature, quantitative NMR spectroscopy has been widely used for natural product analysis over the past 10 years. AbouZid et al. quantitatively analyzed the content of taxifolin and seven major flavonolignans including silybin A, silybin B, isosilybin A, isosilybin B, silychristin, isosilychristin and silydiani in Silybum marianum by NMR using DMSO-d6 as a solvent and its residual proton signal for quantification [22]. Imai et al. investigated the cycloartane triterpene content in the roots/rhizomes and aerial parts of Actaea racemosa, A. podocarpa and A. cordifolia by quantitative 1H NMR using the same methodology [23]. Feng et al. showed the potential of using the quantitative 1H NMR method for the simultaneous determination of osthol, columbianadin and isoimperatorin in Angelicae Pubescentis Radix using DMSO-d6 as a solvent and pyrazine as an internal standard [24]. Using quantitative NMR coumarins in Angelica dahurica, actinodaphnine in Illigera aromatica and Illigera henry, catechins in green tea were also determined [25,26,27].
In this work, we aimed to develop and validate an appropriate technique for identifying and quantifying RA and LP in the extracts from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Previously, NMR spectroscopy has only been used to determine the structures of novel anthraquinone derivatives extracted and purified from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes [17,28,29], whereas their quantification in crude extracts by NMR spectroscopy has not been previously described.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
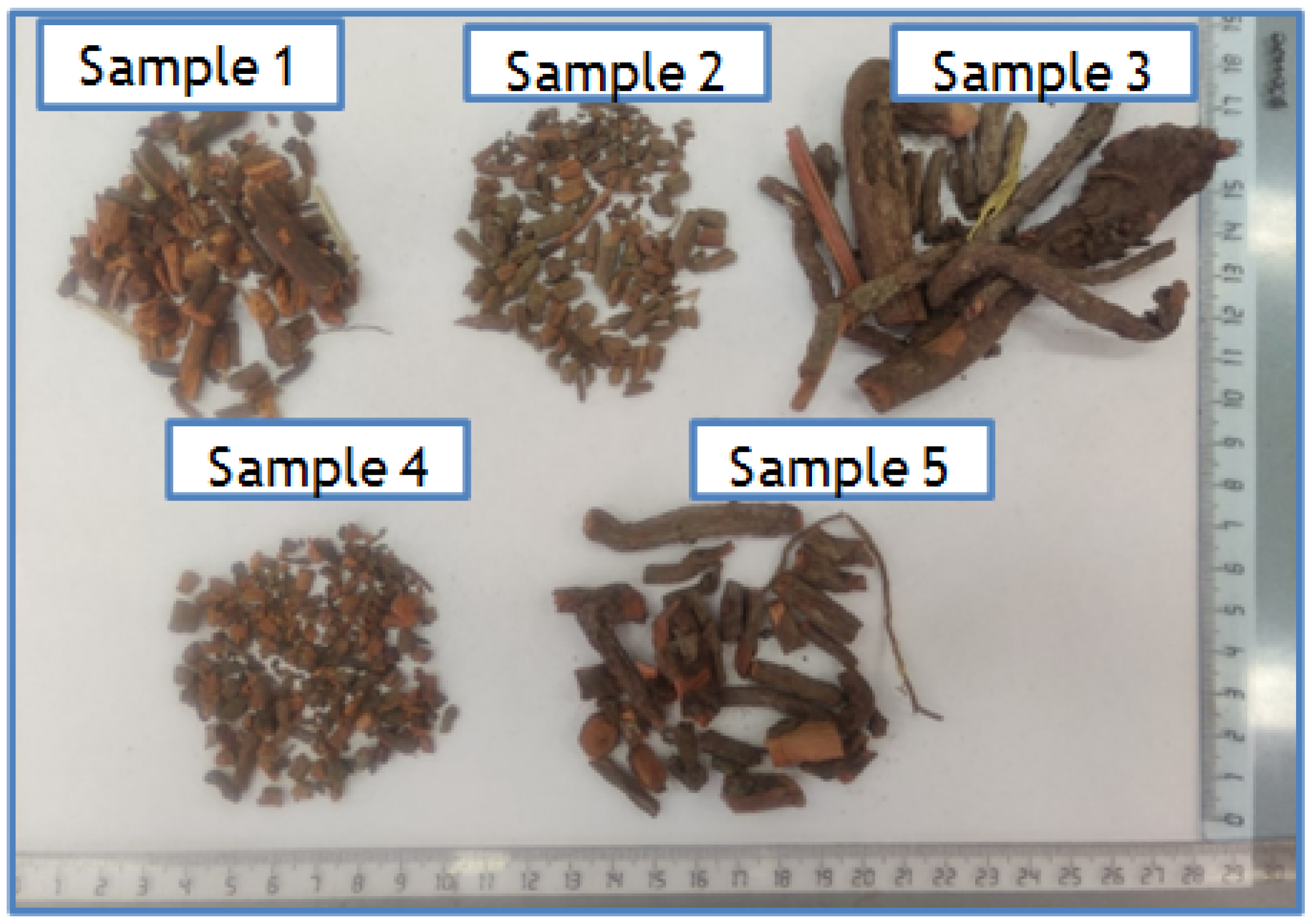
Five commercial samples of whole or cut Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes were purchased in online stores and drugstores in Russia. All of them were sealed and contained instructions for use. They varied in length, had a cylindrical shape and a thickness of 2–18 mm and had reddish-brown bark and orange-red wood (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Cut Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes from 5 different vendors.
2.2. Reagents
The following solvents and standard samples were used: dimethyl sulfoxide -d6 (≥99,9%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), ruberythric acid internal standard (PhytoLab, Vestenbergsgreuth, Germany), lucidin-3-primeveroside internal standard (PhytoLab, Vestenbergsgreuth, Germany), lucidin internal standard (PhytoLab, Vestenbergsgreuth, Germany), purpurin internal standard (PhytoLab, Vestenbergsgreuth, Germany), alizarin internal standard (PhytoLab, Vestenbergsgreuth, Germany) and dimethyl sulfone internal standard (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.3.1. NMR Spectroscopy
The roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. were ground into powder using the laboratory grinder (IKA A11 basic, Staufen, Germany). Approximately 20 mg (exact weight) of the powder was placed into a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube, and 1 mL of deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide was added. The sample was sonicated for 30 min in an ultrasonic bath (Sapphire-9.5 TTC, Moscow, Russia), placed into the laboratory shaker (IKA VXR S0000, Staufen, Germany), mixed and then centrifuged (Eppendorf Mini Spin, Hamburg, Germany) for 5 min (14,000 rpm). The supernatant was collected and transferred to a 5 mm NMR tube prior to analysis.
2.3.2. HPLC-UV-MS
Approximately 30 mg (exact weight) of the powder was placed into a 10 mL measuring flask. A total of 6 mL of the solvent mixture (methanol/water—70/30, v/v) was added, and after mixing, the flask was filled up to the mark with the same solvent, the final suspension was mixed again and then filtered through the nylon membrane filter with a 0.45 µm pore size. A total of 5 µL of the solution was injected into HPLC-UV-MS.
2.4. Experimental
2.4.1. NMR Spectroscopy
1H NMR spectra were registered at 298 K on the JNM ECA-600 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) (600 MHz) NMR spectrometer under the following conditions: relaxation delay—20 s; the number of data points—32768; spectral width—22 ppm; acquisition time—1.98 s; the number of scans—16; and the pulse angle—30°.
All 1H NMR spectra were manually phased, baseline corrected and integrated using Delta IV software, version 4.3.6 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4.2. HPLC-UV-MS
The high-performance liquid chromatograph with UV and MS detector Agilent 6430 LC/MS QQQ (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used. The chromatographic conditions were as follows: the column—Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan); ShimPack FC-ODS (150 × 2 mm × 3.0 μm); the mobile phase—0.1% formic acid (A), the acetonitrile HPLC-MS grade (B); the elution type—gradient elution (0 min, 95% A; 5 min, 95% A; 30 min, 70% A; 40 min, 30% A; 45 min, 10% A; 47 min, 95% A; 50 min, 95% A); column equilibration—95% A–5% B, for at least 60 min; flow rate—0.25 mL/min; column temperature—(30 ± 2) °C; detectors—triplequad QQQ, DAD wavelengths 340, 290, 254, 474 nm; and analysis time—50 min. The MS detection conditions were as follows: interface—(ESI+); (ESI−); detection—the registration of total ion current (TIC) in the range of 100-2000 Da; drying gas temperature—320 °C; drying gas flow—12.0 L/min; nebulizer pressure—30 psi; drying gas and nebulizing gas—nitrogen; interface voltage—4.0 kV; and fragmentor voltage—135 V.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The results are presented as the mean ± relative standard deviation (RSD, %) of three replicates (n = 3) of each test sample. Statistical analysis was performed using the Microsoft Excel 2016 program.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Quantification Signals of Analytes
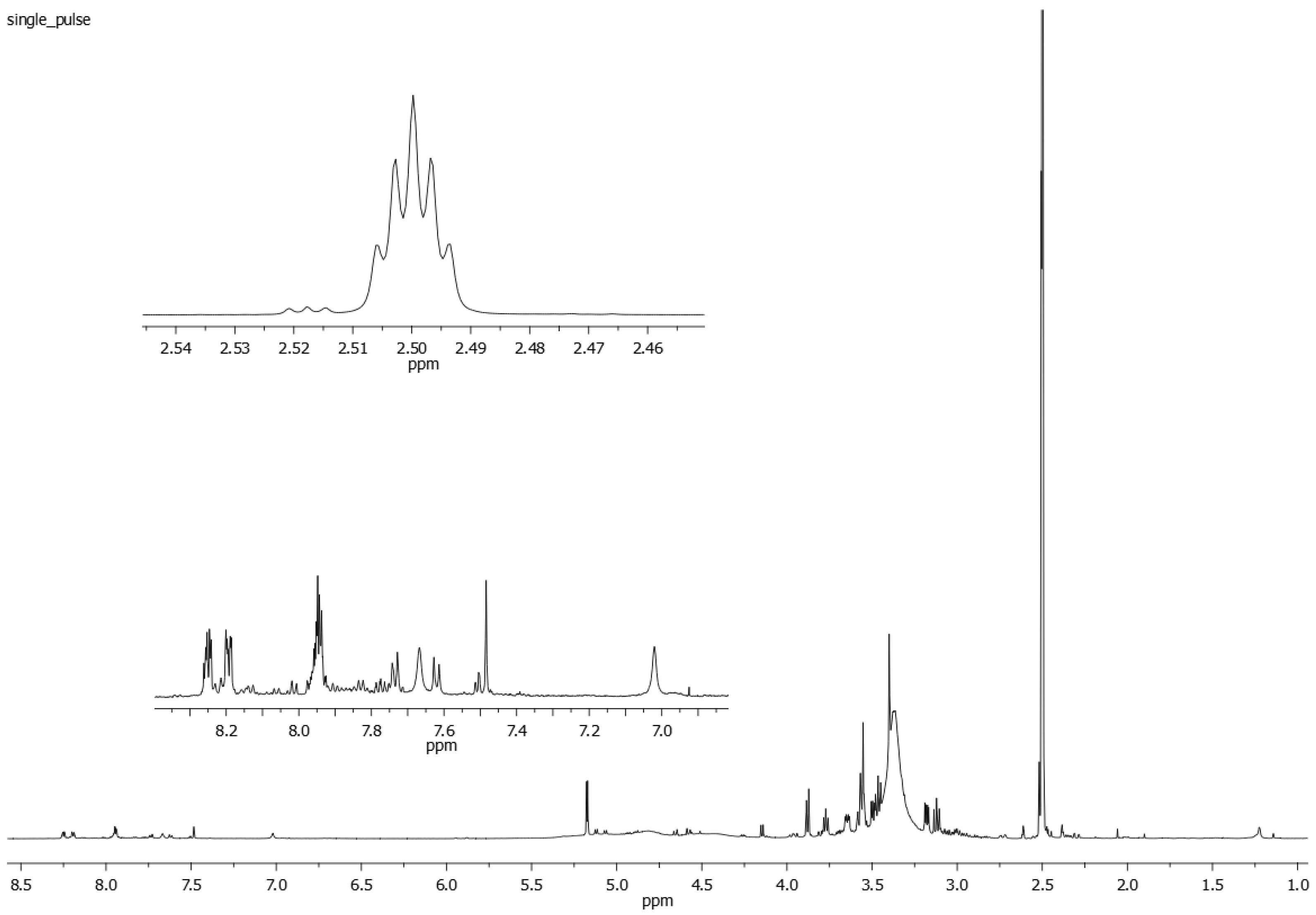
The 1H NMR spectrum of the extract from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes (Figure 3), apart from the signals of anthraquinone derivatives’ protons, contains a number of overlapping and separate signals from the protons belonging to different biologically active substances (organic acids, sugars, etc.) in a wide range of chemical shifts (0.5–17.5 ppm).
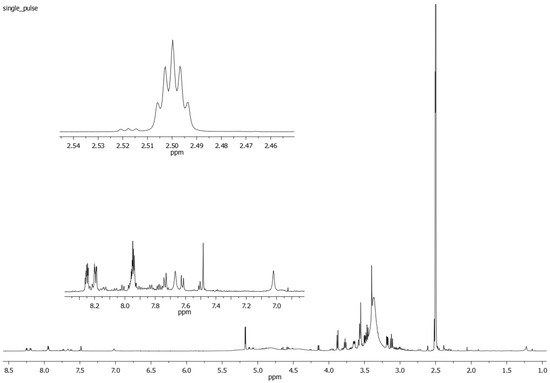
Figure 3.
A 1H NMR spectrum of the Rubia tinctorum L. extract in DMSO-d6. The enlarged spectral fragments in the 2.46–2.54 ppm and 6.9–8.3 ppm regions are also shown.
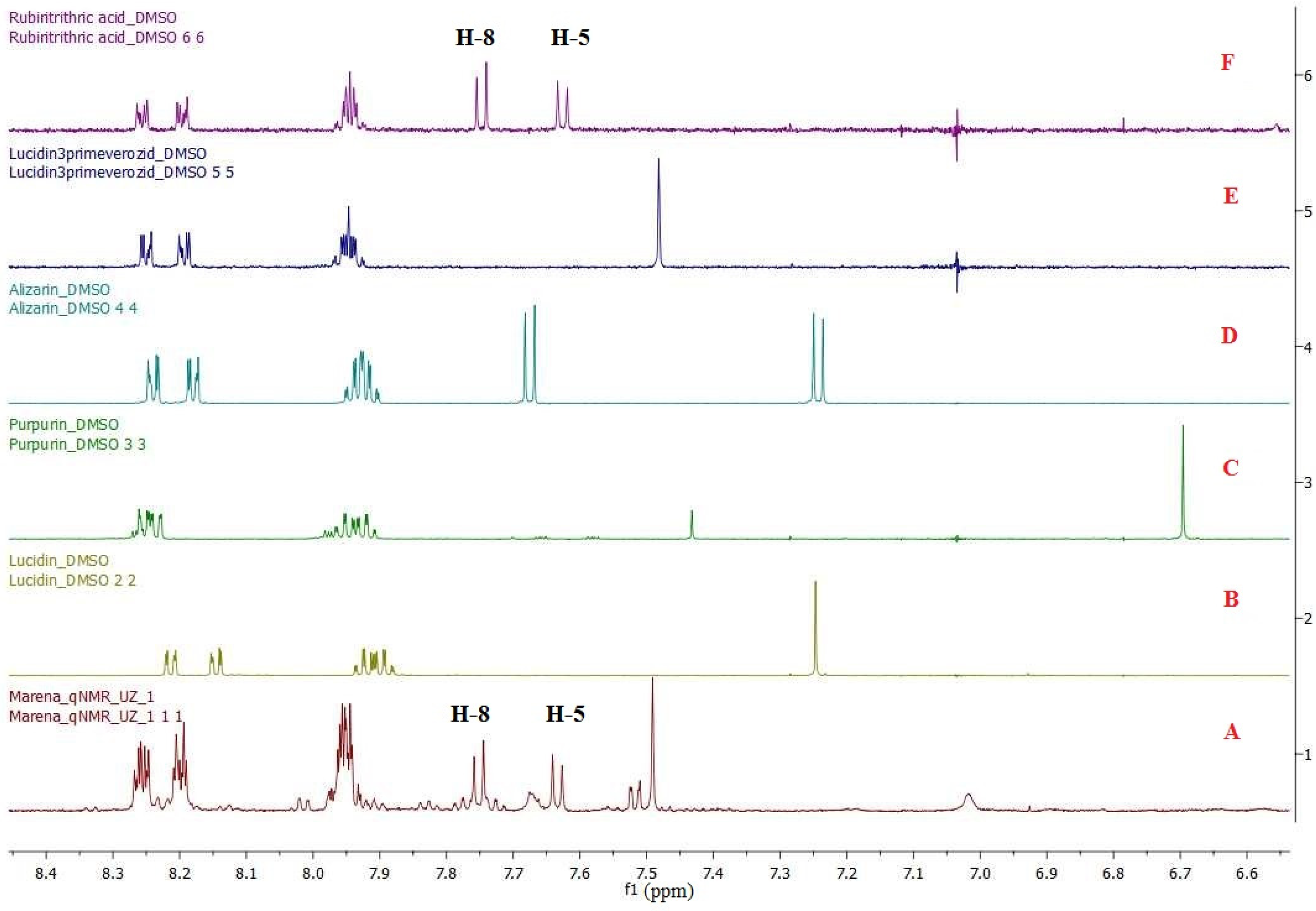
To develop a method for identifying and quantifying individual biologically active substances in complex mixtures, at least one signal of each biologically active substance should not overlap with the others. For this purpose, we registered the individual 1H NMR spectra of RA, LP, alizarin, lucidin, and purpurin reference samples (Figure 4, Supplementary Material A) as well as the 1H NMR spectra of the Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes extract obtained in the laboratory via direct extraction with DMSO-d6.
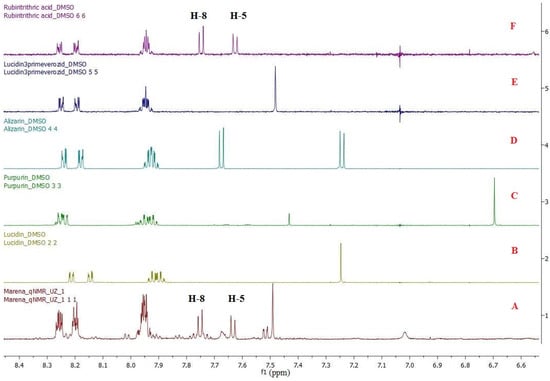
Figure 4.
1H NMR spectrum stack in DMSO-d6: (A) extract of roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L., (B) internal standard of lucidin, (C) internal standard of purpurin, (D) internal standard of alizarin, (E) internal standard of LP, and (F) internal standard of RA.
A spectrum stack showed two doublet proton signals from RA at 7.62 ppm and 7.74 ppm (J = 8.5 Hz each), which did not overlap with the other aromatic proton signals in the 1H NMR spectra of the Rubia tinctorum L. extract. The obtained data imply that these signals can be used for the identification and quantification of RA in the extract. Similarly, a non-overlapping singlet signal from LP at 7.48 ppm was also observed in the 1H NMR spectra of the extract and can be used to identify and quantify LP in the extract by 1H NMR spectroscopy.
3.2. Solvent Selection
We used several different polar solvents for extracting anthraquinone derivatives from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes. The extractants used for the separation of biologically active substances from the roots of Rubia tinctorum L. include ethanol, water and their combination at various ratios [12,28]. The most common procedure described for extracting anthraquinone derivatives from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes is performed with the 37% hydrochloric acid/methanol/water (2:1:1, v/v/v) mixture [30]. But the presence of water in extractant solutions leads to the degradation of the primary anthraquinone derivatives such as RA [12], which makes analyzing the primary anthraquinone derivatives impossible.
To reduce the sample preparation time and chemical conversion of the primary biologically active substances, we performed a direct extraction of anthraquinone derivatives with deuterated solvents. Anhydrous deuterated ethanol is rarely used in NMR spectroscopy since it is expensive and there are other solvents suitable for extracting or dissolving analytes. Additionally, 95–98% deuterated ethanol in water is less expensive; however, the presence of water in the solvent or sample complicates interpreting the 1H NMR spectra of polyphenolic compounds due to an elevated exchange rate of the protons from hydroxyl groups. This results in wider signals from the OH-group protons or their absence in the spectrum. Observing the signals of the OH-group protons from polyphenolic compounds is important, because it means that the glycosidic linkage between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of the saccharide and the hydroxyl group of polyphenolic compounds is formed. To reduce the proton exchange rate and retain the hydroxyl group signals in 1H NMR spectra, we selected an aprotonic solvent, dimethyl sulfoxide, as an extractant.
3.3. Selecting a Reference Sample
To accurately determine the chemical shifts in 1H NMR spectra, the chemical shift scale must be calibrated. Trimethylsilyl propanoic acid, trimethylsilyl propane sodium sulfonate (TSP) and other organosilicon compounds are commonly used for these purposes. A method for calibrating the scale of chemical shifts in 1H NMR spectra with the signals of residual protons in deuterated solvents has been also described, since the value of a chemical shift is constant for each deuterated solvent [31,32]. The quantitative measurement by 1H NMR spectroscopy is performed by comparing the signal from an analyte with the reference compound signal. This method requires the absence of overlap between the particular signal and the other signals from analyzed substances. If the solvent residual proton signal is used as a reference [21], it is necessary to determine the exact concentration of residual protons in the solvent. In this work, we used the residual proton signal of dimethylsulfoxide-d6 (2.5 ppm) to calibrate the chemical shift scale and quantify the target biologically active substances in the test samples. We determined the exact concentration of residual solvent protons using dimethylsulfone as an internal standard.
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Parameters
Relaxation delay (D1) and a pulse angle are crucial for accurate quantification and are correlated with each other. In general, the highest sensitivity is obtained at the 90° pulse angle and D1 must be five times greater than the longest longitudinal relaxation time (T1) of the quantification protons; at the 30° pulse angle, D1 should be seven-thirds times higher than T1 [33,34]. We selected the 30° pulse angle to save time and increase the efficiency. It is necessary to assess T1 of both selected protons from RA and LP as well as a residual proton of DMSO-d6 used as an internal standard. T1 from RA and LP did not exceed 2 s, while T1 of DMSO-d6 was about 8 s. T1 of DMSO-d6 was used to determine D1. Experiment D1 was set to 20 s. The number of scans is also an important parameter closely related to S/N ratio values. In this experiment, the number of scans was set to 8, 16, 32 and 64. The obtained results showed that 16 scans could ensure obtaining S/N values above 150 [34]. The S/N ratio was determined following Santosh et al. [33].
3.5. Sample Preparation Conditions
To study the exhaustive extraction of the analyzed biologically active substances, we evaluated the effects of heating and ultrasound treatment.
For these purposes, three equal amounts of the ground powder were dissolved in equal volumes of DMSO-d6 and shaken for 10 min. The first sample was heated at 60 °C for 15 min. The second sample was sonicated in an ultrasonic bath for 30 min. The third sample was used as a control sample, which was not exposed to either ultrasound or heating. All samples were centrifuged, and the supernatants were transferred into clean tubes to register 1H NMR spectra. RA and LP contents as well as their sum (total content) are presented in Table S1. The results indicate that unlike ultrasound, heating did not have any significant effects on the sample.
To select the conditions for the ultrasound treatment, we tested different times (0, 15, 30, 45 and 60 min). RA and LP contents and their total contents are shown in Table S2. RA and LP concentrations in sonicated samples increase in a time-dependent manner, reaching a plateau after 30 min exposure (Figure S1). The ultrasound treatment promotes the diffusion of bioactive substances into an extractant, thus reducing the extraction time of target analytes in the test samples. We selected the 30 min exposure to ultrasound for the following sample preparations.
3.6. Determination of RA and LP in Crude Extracts
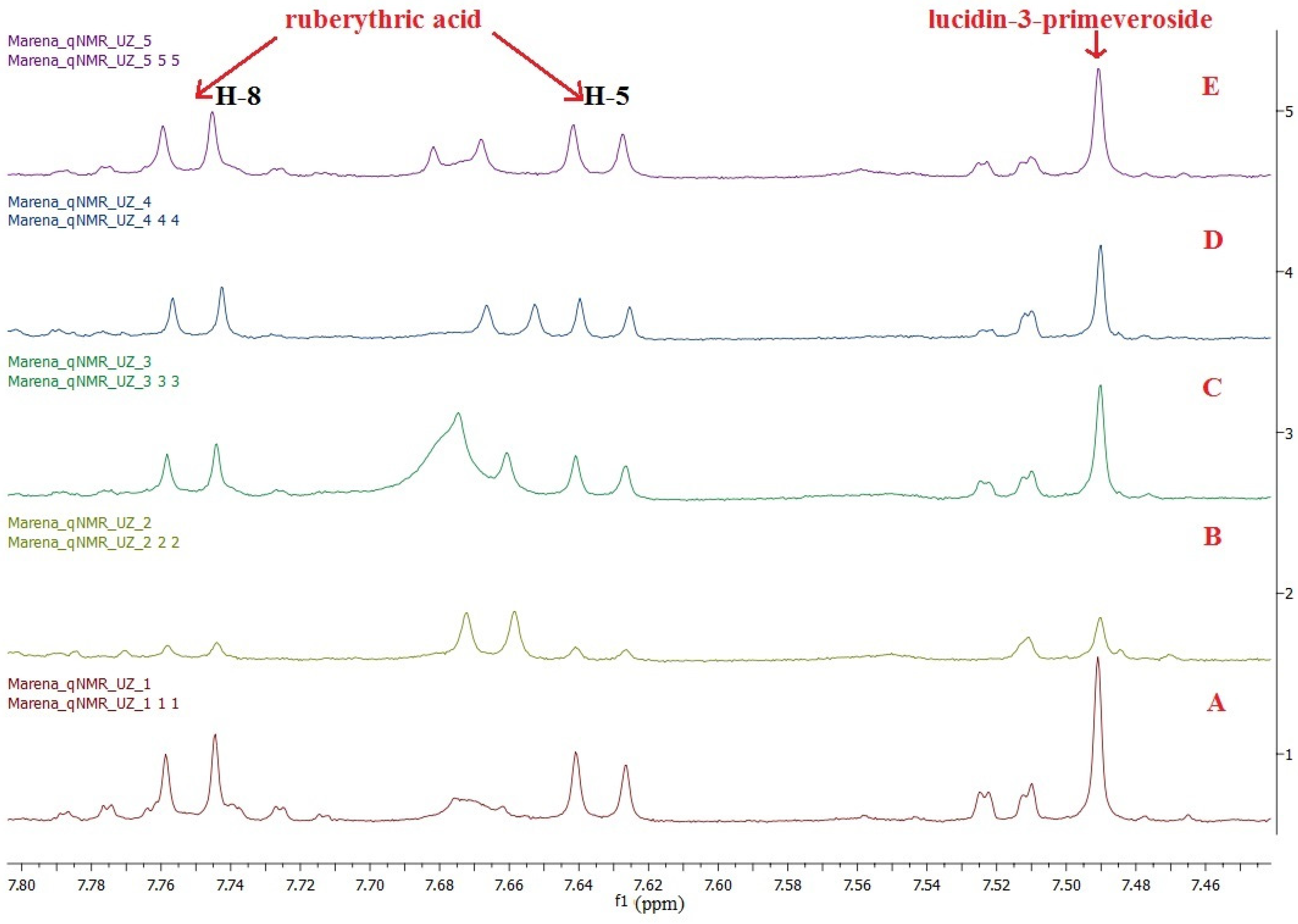
To identify and quantify RA and LP in the extracts from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes by 1H NMR spectroscopy, we used a doublet signal at 7.62 ppm and a singlet signal at 7.48 ppm. Quantification was performed by comparing the integral signal of the target biologically active substances with the DMSO-d6 residual proton signal using the equation presented in Santosh et al. [33]. Measurements were performed in triplicate for all extracts tested. The 1H NMR spectra of five commercial samples in DMSO-d6 are shown in Figure 5. The RA and LP quantification results and their total content are presented in Table 1.
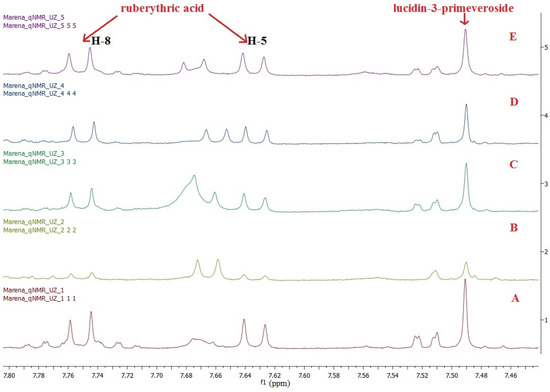
Figure 5.
A 1H NMR spectrum stack of the extracts from the roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. in DMSO-d6: (A) sample 1; (B) sample 2; (C) sample 3; (D) sample 4; and (E) sample 5.

Table 1.
RA, LP and their total content in 5 commercial samples of Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes (n = 3).
3.7. HPLC-UV-MS Experiment
HPLC-UV-MS was used to verify the data obtained by NMR spectroscopy. The obtained results are presented in Table 1.
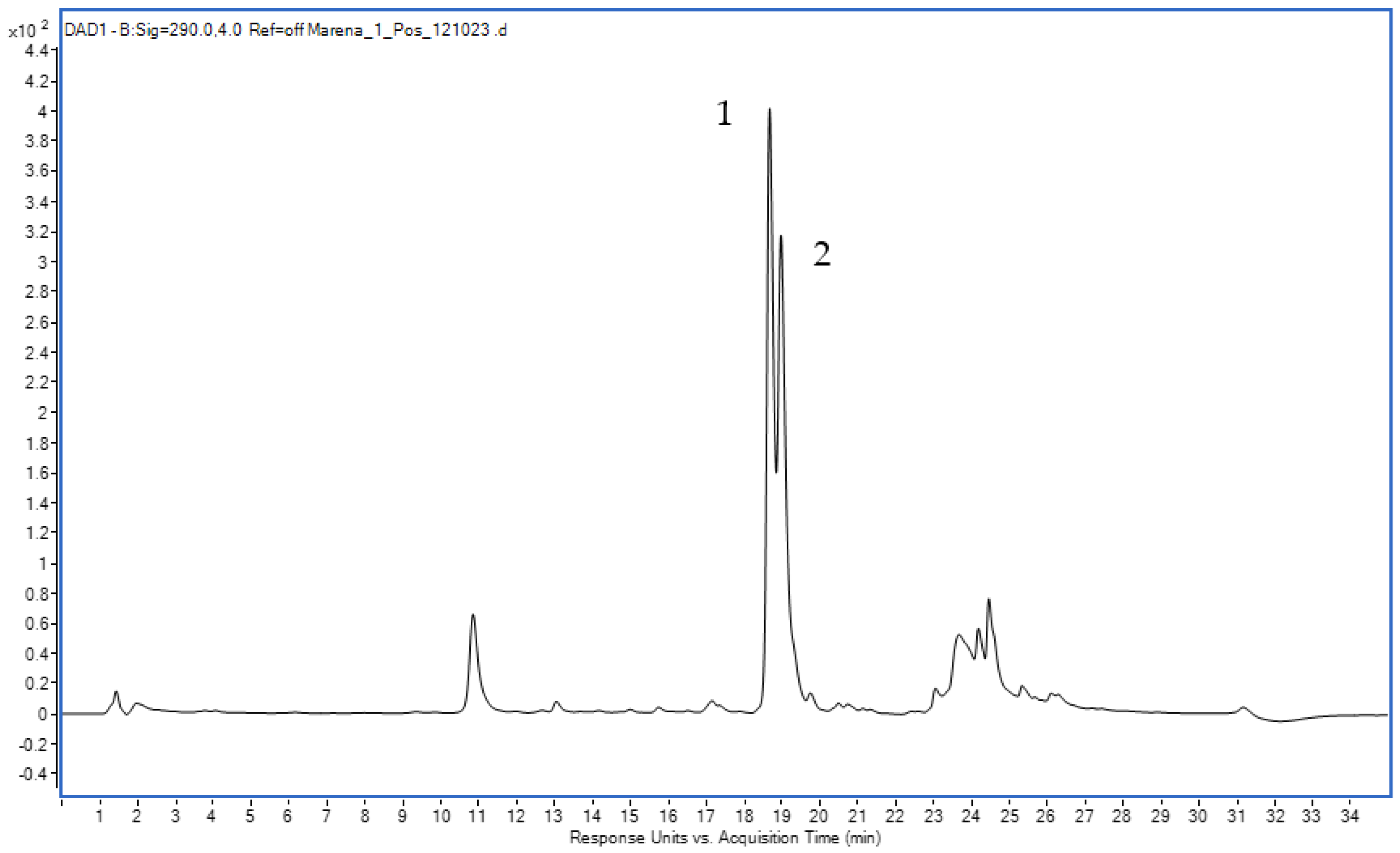
The DAD chromatogram of the roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. extracts (Figure 6) confirmed the presence of LP (Rt = 18.803 min) and RA (Rt = 19.098 min).
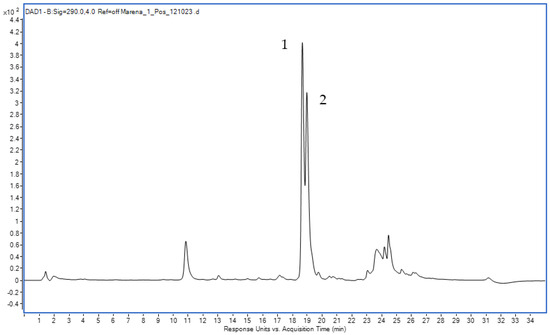
Figure 6.
The DAD chromatogram of the extract from Rubia tinctorum L. of roots and rhizomes ((1)—LP, (2)—RA).
In the electrospray ionization mass spectrum (negative ion detection mode) that corresponded to the chromatographic peak with a retention time of 18.803 min, the observed signal with m/z 563 Da (Figure S2) matches the [M-H]− ions, which complies with the molecular mass of LP (564 Da).
Likewise, in the electrospray ionization mass spectrum (negative ion detection mode) that corresponded to the chromatographic peak with an output time of 19.098 min, a signal with m/z 533 (Figure S3) matches the [M-H]− ions, which complies with the molecular mass of RA (534 Da).
The mass spectral information confirms the presence of LP and RA in the extract from the roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L.
According to the Russian State Pharmacopoeia (edition XIV), the total content of anthraquinone derivatives in the roots and rhizomes of Rubia tinctorum L. exceeds 3% [16]. In test samples 1, 3 and 5, the total content of RA and LP was 3.85 ± 0.03, 3.00 ± 0.04 and 3.10 ± 0.03, respectively, which complies well with the reference values. However, in samples 2 and 4, the total content of RA and LP was below 3%. This might result from the improper harvesting or storage of the raw materials, since we observed a doublet signal at 7.66 ppm related to alizarin in the 1H NMR spectrum. Alizarin is an aglycone of RA produced as a result of glycosidic linkage destroyed during acidic hydrolysis. Meanwhile, we did not observe the proton signals from lucidin in the 1H NMR spectrum. This is in line with the idea that LP is converted to lucidin only under highly acidic conditions [12].
3.8. Method Validation
The validation of the developed method was carried out according to [34,35].
3.8.1. Specificity
The specificity of the method was determined by comparing the 1H NMR spectra of test sample 1 of the extract (Figure 4A) and the standard samples of RA and LP (Figure 4F and Figure 4E, respectively). Two doublet signals from the RA protons at 7.62 ppm and 7.74 ppm were detected in the spectra (J = 8.5 Hz each), each representing one proton that did not overlap with the other aromatic proton signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of test sample 1. The spin coupling constants of these doublet signals were matched as well. A singlet signal at 7.48 ppm (1H) was also detected in the 1H NMR spectra of test sample 1 and the standard LP sample.
3.8.2. Linearity
The linearity was estimated using standard sample solutions with different concentrations (0.5 mg/mL; 1.0 mg/mL; 1.5 mg/mL; 2.0 mg/mL; 2.5 mg/mL; 3.0 mg/mL). The proton signals at 7.48 ppm (1H) and at 7.62 ppm (1H) were used for the quantification of LP and RA, respectively, as described above. The linearity curve was plotted, and the correlation coefficients obtained from the linear regression curves were 0.9986 and 0.9993 for LP and RA, respectively. The linear regression yielded a regression line of y = 0.012x + 0.0003 and y = 0.0123x − 2 × 10−5 for LP and RA, respectively (Figures S4 and S5).
3.8.3. Accuracy
The accuracy was determined by comparing the RA and LP content in sample 1 obtained by NMR spectroscopy with the data from the validated HPLC-UV method. The accuracy values were 98.24% and 102.83% for ruberythric acid and lucidin-3-primeveroside, respectively.
3.8.4. Reproducibility
The reproducibility of the results obtained from RA and LP quantification was assessed using test sample 1 by determining the RSD% for three replicates. Its values were equal to 1.06% and 0.75% for RA and LP, respectively.
3.8.5. Sensitivity
The sensitivity of the method was evaluated by determining the limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ) of sequentially diluted RA and LP standard samples. The LOD at the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) = 3/1 was equal to 0.04 mg/mL for RA and 0.035 mg/mL for LP. The LOQ at the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) = 10/1 was 0.95 mg/mL for RA and 0.85 mg/mL for LP.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we showed a possibility of developing novel unconventional express methods for identifying and quantifying the primary biologically active substances from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes such as ruberythric acid and lucidin-3-primeveroside. We optimized the conditions of sample preparation and 1H NMR spectrum registration. We proposed to use the calibrated residual proton signal of the DMSO-d6 solvent as a reference signal. Hence, we developed and validated a method for the qualitative and quantitative determination of ruberythric acid and lucidin-3-primeveroside in the extracts from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes using NMR spectroscopy. The results were confirmed by HPLC-UV-MS data. Since NMR spectroscopy has multiple advantages (rapid sample preparation, the high reproducibility of results, the exclusion of the use of an authentic internal standard) over other analytical platforms, it is a promising alternative method for identifying and quantifying the biologically active substances in the raw materials of plant origin. However, the method is rarely used for pharmacopeial routine analysis due to the high cost of the spectrometer.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/scipharm92020024/s1, Supplementary Material A: 1H NMR spectral parameters of ruberythric acid, lucidin-3-primeveroside, alizarin, purpurin, lucidin internal standards; Table S1: RA and LP content in the untreated sample and the samples either heated at 60 °C for 15 min or exposed to the ultrasound for 30 min; Table S2: RA and LP and their total content after the ultrasound treatment for 0, 15, 30, 45, and 60 min; Figure S1: The dependence of the concentration of ruberythric acid and lucidin-3-primeveroside on the ultrasound exposure time; Figure S2: ESI (−) Mass spectrum of LP in extract from Rubia tinctorum L. roots and rhizomes; Figure S3: ESI (−) Mass spectrum of ruberythric acid in extract from Rubia tinctorum L. of roots and rhizomes, registration of negative ions; Figure S4: Linear dependence of lucedin-3-primeveroside proton signal integral on concentration; Figure S5: Linear dependence of ruberythric acid proton signal integral on concentration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.V. and G.K.; data curation, A.K. (Arkadiy Khromov); formal analysis, E.P.; funding acquisition, V.R.; investigation, A.S.; methodology, V.I.; project administration, V.I.; resources, A.K. (Alexandr Kolesnov); software, S.G.; supervision, G.K.; validation, V.V., A.S., F.H. and C.E.; visualization, V.V.; writing—original draft, A.S.; writing—review and editing, V.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Acknowledgments
This publication was prepared with the support of the “RUDN University Strategic Academic Leadership Program”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ford, L.L. Chemical Analysis and Elucidation of Anthraquinone and Flavonoid Type Compounds with Applications to Historical Artefacts and Sustainability. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, R.; Gates, G.A. The Matter of madder in the ancient world. In Mummy Portraits of Roman Egypt: Emerging Research from the APPEAR Project; Svoboda, M., Cartwright, C.R., Eds.; Getty Publications: Los Angeles, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, J.; Tamburini, D.; Sotiropoulou, S. The Identification of Lac as a Pigment in Ancient Greek Polychrome: The Case of a Hellenistic Oinochoe from Canosa di Puglia. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 149, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, G.C.H.; Van Beek, T.A. Rubia tinctorum L. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, 1st ed.; Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 26 (part G), pp. 629–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltamany, E.E.; Nafie, M.S.; Khodeer, D.M.; El-Tanahy, A.H.H.; Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Badr, J.M.; Abdelhameed, R.F.A. Rubia tinctorum root extracts: Chemical profile and management of type II diabetes mellitus. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.N.; Huang, M.P.; Lee, H. Structure-activity relationships of anthraquinones as inhibitors of 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase and mutagenicity of 2-amino-3-methylimidazox [4,5-f] quinolone. Mutat. Res. 1995, 328, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczylo, T.H.; Hayatsu, T.; Arimoto-Kobayashi, S.; Tada, M.; Fujita, K.; Kamataki, T.; Nakayama, K.; Hayatsu, H. Protection against the bacterial mutagenicity of heterocyclic amines by purpurin, a natural anthraquinone pigment. Mutat. Res. 1999, 444, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczylo, T.H.; Arimoto-Kobayashi, S.; Hayatsu, H. Protection against Trp-P-2 mutagenicity by purpurin: Mechanism of in vitro antimutagenesis. Mutagenesis 2000, 15, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manojlović, N.T.; Solujić, S.; Sukdolak, S.; Milošev, M. Antifungal activity of Rubia tinctorum, Rhamnus frangula and Caloplaca cerina. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houari, F.Z.; Erenler, R.; Bakir, S.; Capanoglu, E.; Hariri, A. LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis, toxicity and anti-anaemic activity of Rubia tinctorum L. aqueous extract. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2022, 21, e978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, G.C.H.; Niederlander, H.A.G.; van Beek, T.A. Analysis of anthraquinones in Rubia tinctorum L. by liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array UV and mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 978, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, L.; Rayner, C.M.; Blackburn, R.S. Isolation and extraction of ruberythric acid from Rubia tinctorum L. and crystal structure elucidation. Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Asthana, S.; Gupta, P.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Tripathi, A.; Das, M. Toxicity of Naturally Occurring Anthraquinones. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Fishbein, J.C., Heilman, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 11, pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cpmp List of Herbal Drugs with Serious Risks; EMEA: London, UK, 1992.
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Han, J.M.; Jung, H.J.; Pandey, R.P.; Park, Y.I.; Sohng, J.K. Regio-specific biotransformation of alizarin to alizarin methoxide with enhanced cytotoxicity against proliferative cells. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 47, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russian Pharmacopoeia, 14th ed.; Emshanova, S.V., Potanina, O.G., Budanova, E.V., Chistyakov, V.V., Goryun, M.I., Eds.; Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 2018; Volume 4, pp. 6243–6252. Available online: https://docs.rucml.ru/feml/pharma/v14/vol4/1061/ (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Marković, Z.S.; Manojlović, N.T.; Jeremić, S.R.; Živić, M. HPLC, UV-vis and NMR spectroscopic and DFT characterization of purpurin isolated from Rubia tinctorum L. Hem. Ind. 2013, 67, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, L.G.; Pistelli, L.; Belloni, P.; Bertoli, A.; Panconesi, S. Rubia tinctorum a source of natural dyes: Agronomic evaluation, quantitative analysis of alizarin and industrial assays. Ind. Crop. Prod. 1997, 6, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of quinones in multi-origin Rubia species by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langa-Lomba, N.; Sánchez-Hernández, E.; Buzón-Durán, L.; González-García, V.; Casanova-Gascón, J.; Martín-Gil, J.; Martín-Ramos, P. Activity of Anthracenediones and Flavoring Phenols in Hydromethanolic Extracts of Rubia tinctorum against Grapevine Phytopathogenic Fungi. Plants 2021, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierens, G.K.; Carroll, A.R.; Davis, R.A.; Palframan, M.E.; Ronald, J. Determination of Analyte Concentration Using the Residual Solvent Resonance in 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Quinn J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbouZid, S.F.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Silymarin content in Silybum marianum populations growing in Egypt. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, A.; Lankin, D.C.; Godecke, T.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. NMR based quantitation of cycloartane triterpenes in black cohosh extracts. Fitoterapia 2020, 141, 104846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, D. The Use of H-1-qNMR Method for Simultaneous Determination of Osthol, Columbianadin, and Isoimperatorin in Angelicae Pubescentis Radix. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Qiu, D. Simultaneous Determination of Three Coumarins in Angelica dahurica by H-1-qNMR Method: A Fast and Validated Method for Crude Drug Quality Control. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8987560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.-W.; Li, X.-J.; Shi, J.-Y.; Liu, K.-Q. Application of a proton quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method for the determination of actinodaphnine in Illigera aromatica and Illigera henryi. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 73, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, J.G.; Godecke, T.; Lankin, D.C.; Jaki, B.U.; McAlpine, J.B.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Orthogonal analytical methods for botanical standardization: Determination of green tea catechins by qNMR and LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 93, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkin, V.A.; Shmygareva, A.A.; Rybalko, M.V.; Daeva, E.D.; Kadentse, V.I. Xanthopurposide, A New Anthraglycoside from Rubia tinctorum Rhizomes. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.L.; Rayner, C.M.; Blackburn, R.S. Isolation and extraction of lucidin primeveroside from Rubia tinctorum L. and crystal structure elucidation. Phytochemistry 2013, 95, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, L.; Rayner, C.M. Degradation of lucidin: New insights into the fate of this natural pigment present in Dyer’s madder (Rubia tinctorum L.) during the extraction of textile artefacts. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 154, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabin, G.; Vasil’ev, V.; Ivlev, V.; Babkin, V. Fast screening of some flavonoids content in raw plant materials: Opportunities of 1H NMR spectroscopy. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 169, 02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’ev, V.G.; Prokop’ev, A.S.; Kalabin, G.A. Identification of Terpene Lactones and Flavonol Glycosides in Preparations Based on Ginkgo Biloba Extract and a New Way of Semi-Quantitative Determination of Flavonol Glycosides by 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, K.B.; Raja, R. Quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy. TrAC 2012, 35, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malz, F.; Jancke, H. Validation of quantitative NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 38, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Topic Q 2 (R1). Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodolog; EMEA: London, UK, 1995.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).