Abstract
Easy access to over-the-counter (OTC) drugs makes it possible to procure active substances that normally used in therapeutic doses do not raise health problems. The use of high doses of OTC drugs containing codeine, loperamide, pseudoephedrine, diphenhydramine or dimenhydrinate, as well as the use of benzidamine systemically raises concerns regarding the increase in units sold. These drugs are used for recreational or euphorizing purposes, including by young women of childbearing age, psychoactive substance users representing a risk group in terms of the possibility of an unplanned pregnancy. Abusive consumption of OTC products during pregnancy is harmful, with consequences for both fetal and late development that can occur in the infant. This literature review presents the risks (teratogenicity, fetal toxicity, neonatal abstinence syndrome, etc.) associated with the use of potentially psychoactive OTC drugs to emphasize the importance of re-evaluating OTC classification and dispensing.
1. Introduction
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are pharmaceutical products that are dispensed from pharmacies without a prescription. More and more people turn to self-medication due to the easy access to treatment and the speed with which a minor condition can be treated because it does not require medical consultation beforehand. Another advantage of self-medication is represented by reducing the pressure exerted on the medical system by decreasing the number of patients seeking medical advice [1]. Because these products can be purchased very easily, and, in the absence of a control of the number of units sold, the risk of abuse/misuse is increased. Used in therapeutic doses over short periods of time in the standard indications set out in the Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC), they are risk-free. However, their use for purposes other than therapeutic, usually to obtain a psychostimulant effect, raises major problems considering their pharmacological features.
Things become more complicated, however, if misuse occurs, or does not stop, during pregnancy, because, in addition to maternal risks, there is the possibility that the medication could affect pregnancy, in utero development of the fetus or present late risks in the child after delivery. In addition, the risk of an unplanned pregnancy is higher in psychoactive substance users [2,3]. It should not be overlooked that the consumption of psychotropic substances, unfortunately, can start in adolescence. The risk of an unplanned pregnancy is increased among sexually active minors mostly due to lack of sexual education. In these cases, in addition to the risks associated with the consumption of the active substances, there are also risks specifically associated with uterine immaturity such as preeclampsia, preterm labor, spontaneous abortion, premature birth, low birth weight or neonatal death [4].
Among the active substances released OTC, there are some where the frequency of misuse, outside the indications provided by the manufacturer, is higher, such as codeine, loperamide, pseudoephedrine, benzydamine, diphenhydramine, and dimenhydrinate [5,6,7]. Unfortunately, there is no data on the abuse of OTC drugs during pregnancy. In 2022, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, published the National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Women, in which references have been made to the use of substances for euphoric purposes by pregnant women. In 2020, only the consumption of marijuana (8%), opioids (0.4%) and cocaine (0.3%) were reported [8]. Precisely the lack of data regarding the abuse of OTC preparations should draw attention to the accessibility of these products, but also to the associated risks.
The purpose of this review is to present the possible consequences of the abusive use of OTC products containing the above-mentioned active substances, including the possible consequences of their use during pregnancy.
2. Getting High on Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs
Opioid drugs are misused/abused to achieve a euphorizing effect. These compounds are μ (mu), κ (kappa), and δ (delta) opioid receptor agonists. The physiological agonists of these receptors are the endogenous opioids (enkephalins, dynorphins, and endorphins). Opioid receptors are located both centrally and peripherally, their stimulation contributing to the occurrence of central (e.g., analgesia, miosis, respiratory depression, euphoria) and peripheral (e.g., decreased intestinal transit, urinary retention) effects [9]. The euphorizing effect of opioid derivatives is associated with the release of dopamine at the reward system [10].
OTC release of codeine and loperamide is possible due to a favorable benefit/risk ratio in therapeutic doses, the two substances being considered to have no serious side effects, in the age categories for which they are recommended by the manufacturers, based on existing safety data. When misused, doses which exceed the recommended ones are used [11]. This predisposes to risks that will be detailed further.
2.1. Codeine
2.1.1. Pharmacological Features of Codeine
Codeine is an opioid receptor agonist with increased affinity for the μ opioid receptor and lower affinity for κ and δ receptors. Due to the higher affinity for μ receptors, codeine is indicated as cough suppressant (in doses of 15 mg, max 45 mg/24 h) or analgesic (in doses of 15–30 mg, max 90 mg/24 h) [11].
Structurally, codeine is a morphine derivative, the only structural difference between the two compounds being a methoxy group in position 3 of morphinan nucleus in the case of codeine. Codeine has a complex metabolism with many active metabolites, including morphine, a compound known to have addictive potential (Figure 1). Precisely because of these metabolic transformations, in doses above 100 mg, codeine has a euphorizing effect, if used in doses exceeding the maximum recommended daily intake of 240 mg [12].
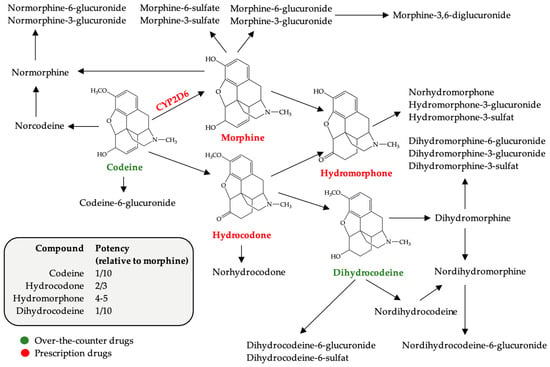
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of codeine and its metabolites (modified after [11]). The potency of codeine and its active metabolites compared to morphine (according to WHO Guidelines for the Pharmacological and Radiotherapeutic Management of Cancer Pain in Adults and Adolescents [13]).
In OTC products recommended for the control of low and/or moderate pain, codeine is frequently associated with acetaminophen (paracetamol) or ibuprofen, substances with analgesic effect, with the aim of obtaining a drug synergism. Thus, by combining two or more analgesics, an action of superior intensity and duration is obtained [14]. In addition to products with analgesic effects, in some countries, codeine is also found in cough syrups, also sold OTC. These syrups have been identified as the main source of codeine misused by students of medical faculties (medicine, pharmacy) in Nigeria [15].
Since they can be purchased from the pharmacy at the request of the patient, the existence of OTC drugs with codeine facilitates the access of the population to this opioid. In a prospective study conducted in 2021, Richards GC et al. reported sales of 31.5 billion units of OTC codeine containing products between 2013–2019 in 31 countries, including Argentina, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Latvia, Lithuania, Mexico, The Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, Thailand, the UK, and the USA [16]. The alarming increase in the sold number of OTC units containing codeine has led to changes in the regime for the release of these products in many countries [17].
Although the abuse of OTC drugs containing codeine are recognized worldwide, in many countries there is no data on the prevalence of the use of these products. The scarce number of articles report the prevalence of non-medical consumption of codeine from OTC products, this being 6.3% in Spain (in 2018), 4.5% in the UK (in 2018) [18] 2.4% in Nigeria (in 2017) [19].
2.1.2. Over-the-Counter Codeine Drugs and Pregnancy Risks
Codeine is one of the most prescribed opioids during pregnancy for high intensity pain, either alone [20,21] or in combination with acetaminophen [22]. However, the safety of codeine in pregnant women has not yet been fully elucidated. In a study published in 2019, Fishman B et al. report that intrauterine exposure to codeine could not be associated with an increase in the risk of major malformations, but a 4-fold increase in the risk of spina bifida could be identified [23]. In other studies, codeine administration during pregnancy was associated with increased risk of minor abnormalities (hemangioma, plagiocephaly, ankyloglossia), and major ones such as ventricular septal, pulmonary artery stenosis or hypertrophic pyloric stenosis [24]. An increase in the risk of developing cardiac, musculoskeletal, or chromosomal abnormalities has also been reported by Brogly S et al., (2023) [21], as well as an increase in the risk of gastrointestinal abnormalities, namely ankyloglossia, reported by Bowie A et al. (2022) [24]. Regarding delivery outcome, codeine consumption in the last trimester of pregnancy was associated with an increased risk of acute cesarean delivery and postpartum hemorrhage [25]. Since the CYP2D6 isoform exhibits genetic polymorphism, the metabolic activation of codeine, and, implicitly, the intensity of the effects varies depending on the type of metabolizer, rapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizer. European Caucasians and their descendants are generally poor metabolizers [26]. Thus, in slow metabolizers, it can be inferred that the risks of taking codeine during pregnancy is lower.
Nor should it be overlooked that opioids, as µ receptor agonists, increase the tone of intestinal smooth muscles having a constipating effect, as well as having emetic effect. All these side effects raise problems for a pregnant woman, pregnancy being anyway associated with these symptoms [20]. The constipating effect is due to stimulation of peripherally located µ receptors, in myenteric and submucosal plexus neurons, G-protein-coupled receptors (Gi/Go). As a result of stimulation of these receptors the level of cyclic 3′,5′ adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) decreases, Ca2+ channels are inhibited, and K+ channels are opened. The consequence of these changes is inhibition of acetylcholine and prostaglandins release from enteric nerves, as well as inhibition of the nerve impulse as a result of membrane hyperpolarization, a decrease in peristalsis and an increase in intestinal transit time [27,28]. Pregnant women may suffer from constipation as a result of an increase in progesterone levels, a decrease in motilin levels, and an increase in the amount of water absorbed from the intestine. All these lead to a decrease in intestinal transit as well as slow bowel propulsive movement [29].
Most of the data reported in the literature on the safety of codeine during pregnancy relate to exposure to therapeutic doses. When misused for recreational purposes, maternal doses are much higher, and the risks are more difficult to assess. In addition to teratogenic effects, intrauterine exposure to opioids can also have late side effects, manifested in offspring such as withdrawal syndrome [20,30] or neurobehavior disorders [31,32].
Because it is less potent than other opioids used as pain relievers, infant withdrawal syndrome is less likely to occur at therapeutic doses. In high doses it can produce withdrawal syndrome similar to more potent opioids manifested by respiratory depression, sedation, sucking disorders, irritability, inability to regulate body temperature, tremor and diarrhea, symptoms that appear in the first day’s post-partum and last for several weeks [20].
There are several mechanisms proposed in the literature that explain the neurobehavioral teratogenicity of opioids, that affect fetal brain development [33]. Previous studies have shown that exposure to heroin during intrauterine life contributes to a decrease in the diameter of axons and the density of nerve fibers [34]. The substance also directly influences the myelination process with connectivity disorders identified between different brain regions such as the cortical regions and the amygdala. These abnormalities in signal transmission between different regions of the brain may be the consequence of myelination disorders. Opioids appear to have opposite effects on the myelination process depending on the dose. Thus, in therapeutic doses it causes the formation of compact myelin sheaths around oligodendrocytes, more precisely an accelerated maturation of immature pro-oligodendrocytes, while in high doses it inhibits the myelination process [35]. These results were obtained in animal models therefore extrapolation of the results to the human species should be made with caution. Moreover, there is a major difference between the potency of codeine and heroin, for this reason the results may be relevant in the context of OTC drug abuse only to explain the mechanism of neurotoxicity.
2.2. Loperamide
2.2.1. The Pharmacological Features of Loperamide
Loperamide is an OTC oral antidiarrheal agent. Structurally, loperamide is a synthetic phenylpiperidine opioid receptor agonist [36]. Even if it is an opioid derivative, in therapeutic doses it possesses only peripheral effects because it is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp), an efflux pump that manages to remove the substance from the central nervous system after it crosses the blood-brain barrier. However, in doses exceeding therapeutic recommendations, due to the saturation of the transport capacity of P-gp, loperamide also has central effects [37].
Among the pharmacological possibilities by which the central effect of loperamide can be potentiated is the concomitant administration of P-gp inhibitors, thus increasing the amount of substance that crosses the blood-brain barrier and is available to stimulate opioid receptors in the central nervous system. Among the P-gp inhibitors reported in the literature as being used simultaneously with loperamide are dextromethorphan, diphenidramine, omeprazole, and cimetidine [38]. In the presence of enzyme inhibitors, the pharmacokinetic profile of loperamide undergoes changes. If in doses of max 16 mg the reported elimination half-life is 4–20 h, depending on the pharmaceutical form ingested [39,40], in high doses its elimination occurs more slowly due to distribution in several water compartments as a result of inhibition of P-gp [41]. The oral bioavailability of loperamide is decreased due to the fact that it is metabolized by the CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 pathways during the first hepatic passage with the formation of desmethylloperamide. However, hepatic metabolism of loperamide may be inhibited, thereby increasing its bioavailability [42].
The antidiarrheal effect is due to the agonist action on receptors located in the myenteric and submucosal plexus neurons thus increasing the tone of the smooth muscles and implicitly diminishing intestinal peristalsis, as previously described in codeine [27]. The recommended dosage of loperamide is 4 mg (2 tablets) after the first loose bowel movement, followed by 2 mg after each loose stool, but not exceeding 8 mg/day [36]. Abusive consumption, however, involves ingesting doses of up to 1600 mg/day [43,44,45].
Between 2005–2017, approximately 2000 cases of adverse drug reaction related to loperamide misuse, abuse, addiction, or withdrawal were reported in the European Medicines Agency (EMA) EudraVigilance database [38].
Loperamide can also be used with the aim of relieving the symptoms of opioid withdrawal syndrome in doses greater than 100 mg. In even higher doses, the euphorizing effect is manifested, including loperamide dependence and withdrawal syndrome on cessation. Unfortunately, in these doses, side effects related to cardiac episodes are also visible [11,46]. As early as 2016, the FDA published a safety announcement concerning the cardiotoxicity of loperamide describing prolongation of the corrected QT interval (QTc), torsade de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, and sudden cardiac death [47]. The exact mechanism by which loperamide produces heart rhythm disturbances has not been elucidated, but since it is a piperidine derivative it may behave similarly to Vaughan-Williams class IA, III, and IV antiarrhythmics. It blocks hERG/Ikr potassium channel, cardiac sodium channels, and L-type calcium channels [48]. Blocking these ion channels causes changes on the electrocardiogram, prolongation of the QRS complex due to sodium channel blockade, and prolongation of the QTc interval by blocking hERG potassium channels, which explains the cardiac toxic effects reported for loperamide [49].
2.2.2. Loperamide and Pregnancy Risks
The safety of loperamide in pregnant women has not yet been fully elucidated and data reported in the literature are inconsistent. In some studies, no significant differences in the risk of major malformations were identified between the loperamide-exposed group in the first trimester of pregnancy and the control group. However, a low risk of harmful effects for gestational age could be identified [50]. Another study proved an increased risk of hypospadias, placenta previa, large for gestational age and caesarean section [51]. If these are the risks reported for therapeutic doses, there are no data on the risks in pregnant women who consume high doses of loperamide for recreational purposes. First, as also described in codeine, a problem is represented by the decrease in intestinal transit which is anyway affected during pregnancy. Loperamide in high doses also poses cardiac risks; there has been a reported case of acute heart failure mimicking peripartum cardiomyopathy as a result of loperamide misuse during pregnancy. The condition required prompt delivery of the fetus [52]. In the absence of precise data it is difficult to estimate the degree of exposure of the fetus to loperamide, since P-gp is also found in the placenta [53] which would limit the distribution of the substance in the fetal compartment. However, as described above, in high doses, the P-gp transport capacity is exceeded, as a result, loperamide can remain in the fetal compartment with consequences on fetal cardiac function.
Even if the use of loperamide for recreational purposes is widely recognized, the risks in pregnant women are still unclear.
3. Getting High on Over-the-Counter Pseudoephedrine
3.1. The Pharmacological Features of Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine, the stereoisomer of ephedrine, is used in therapy as an oral decongestant. Both are vasoconstricting agents, even though there are differences in their mechanism of action and potency. Ephedrine is a directly acting and indirectly acting sympathomimetic. The direct action refers to the ability of the substance to bind to alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors whereas the indirect effect involves inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake from the synaptic cleft. Norepinephrine will stay longer at in the synaptic cleft and stimulate postsynaptic receptors. In the case of pseudoephedrine, the main mechanism is the indirect one [54].
Pseudoephedrine is completely absorbed after oral administration reaching its maximum plasma concentration in less than 2 h and it crosses the blood-brain barrier [55].
There are scarce data in the literature on the misuse of pseudoephedrine, most of which are case studies. The information is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Data on misuse of pseudoephedrine for recreational purposes.
The risk of developing hallucinations is increased in patients prone to mental disorders [59] even in therapeutic doses [61]. The symptoms experienced by patients taking high doses of pseudoephedrine are similar to those found in patients suffering from schizophrenia and can be explained based on the increase in the availability of norepinephrine in the central nervous system. Even if in the etiology of schizophrenia, the excess of dopamine and/or serotonin was initially incriminated, nowadays the noradrenergic theory, and the interrelations between the noradrenergic and serotonergic system are increasingly being considered [62].
Regarding the consumption of pseudoephedrine, risks are reported even when taking therapeutic doses. At the request of the French Medicines Agency (under Article 31 of Directive 2001/83/EC), on 10 February 2023 EMA’s safety committee (PRAC) “has started a review of medicines containing pseudoephedrine following concerns about the risk of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) and reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS)”, as posted on the EMA website [63].
These side effects are explainable by the mechanism of action. As an alpha 1-adrenergic receptors agonist, it produces vasoconstriction (which also explains its nasal decongestant action) [64]. In addition, the action on beta-1 adrenergic receptors explains cardiovascular side effects such as tachycardia [65].
It should also be mentioned that pseudoephedrine can be oxidized in the presence of potassium permanganate to ephedrone, which is considered a psychostimulant “designer drug” [66]. It also can be used as a precursor in methamphetamine synthesis [67] or as an anorexigenic drug [68].
3.2. Over-the-Counter Pseudoephedrine Drugs and Pregnancy Risks
Even though about 25% of pregnant women are exposed during pregnancy to pseudoephedrine [69], the associated risks are still unclear. Older studies suggest that therapeutic doses are risk-free [64], but there are also data reported regarding the consequences of exposure to pseudoephedrine during pregnancy, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Pseudoephedrine and risks of birth defects reported in the literature.
As follows from Table 2, the main risk during pregnancy is represented by gastroschisis, a paraumbilical abdominal wall defect through which loops of intestines (sometimes stomach) can protrude [74]. One of the theories that explains this malformation, postulated since the 1980s, would be the impairment of the vascular function of the omphalomesenteric artery that irrigates the abdominal wall during intrauterine life [75].
This theory can explain the risk observed in the case of taking pseudoephedrine during pregnancy, especially since the substance produces vasoconstriction, the risks are obviously higher with the use of high doses for recreational purposes.
4. Getting High on Over-the-Counter Antihistamines
Antihistamines, due to their ability to antagonize histaminergic H1 receptors, are recommended for the relief of symptoms associated with various types of allergies, kinetopathies/vertigo (only those that also possess anticholinergic effects) [76]. OTC antihistamines include loratadine (low-lipophilic antihistamine with no central effect at therapeutic doses), dimenhydrinate and diphenhydramine (high-lipophilic antihistamines with sedative and anticholinergic effects). The first-generation antihistamines, due to their increased lipophilicity, cross the blood-brain barrier and have central effects even in therapeutic doses [77].
In some countries, diphenhydramine is available as an OTC for seasonal allergies, motion sickness, or insomnia. Short-term side effects are directly related to its anticholinergic effect, with patients experiencing confusion, impaired vision, coordination, or urinary hesitancy. In the long-term use, coordination/tremor and vision disorders may worsen. In addition, cardiovascular side effects such as heart rhythm disturbances and hypotension can also occur. In case of overdose, in addition to the symptoms already mentioned (with greater intensity this time), the following may also occur: tinnitus, mydriasis, convulsions, delirium, paranoia, marked sedative effect, nausea, and vomiting [78]. Withdrawal syndrome has been described after sudden discontinuation of treatment characterized by tremor, convulsions, hallucinations, hypersalivation, diaphoresis, mydriasis, hypomimia, dysarthria, and hypophonia [79].
Although there are no data on the safety of misuse of diphenhydramine during pregnancy, the fetal risk from exposure to high doses can be assessed from case reports in which the substance has been used for suicidal purposes. Thus Shenai N. (2014), reported the case of a 19-year-old woman, 27 weeks pregnant who ingested 3000 mg of diphenhydramine that led to the vaginal delivery of a stillborn fetus. In addition to the miscarriage, detected on sonography at the time of admission, respiratory failure, wide QRS complex, tachycardia, psychomotor agitation, and confusion (aggravated on the second day after admission to the intensive care unit) were also reported. These symptoms are due to the fact that, in high doses, selectivity for histaminergic receptors is lost and anticholinergic effects predominate (delirium, hallucinations, psychosis, especially in patients with other mental disorders). Premature onset of labor can be attributed to the oxytocin-like effect of diphenhydramine [80]. Increase in uterine contractions was reported after a diphenhydramine overdose at 26-week gestation [81]. If administered close to the time of birth, the newborn may suffer withdrawal syndrome characterized by respiratory depression and sedation. This was observed after taking 25 mg doses of diphenhydramine at 4 h, which confirms the distribution of the substance in the fetal compartment even in low doses [82]. Fortunately, in cases of overdose, parenteral administration of physostigmine can antagonize maternal and fetal cardiovascular side effects and improve mental status [80,83].
Dimenhydrinate is an antihistamine recommended for the treatment of motion sickness or vertigo. Structurally, it is the chlorotheophylline salt of diphenhydramine, and is considered safe in therapeutic doses being recommended for the management of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy [84].
In the 1950s and 60s, dimenhydrinate was used to induce labor for its presumable oxytocin-like effect. However, its use as a useful labor and delivery medication has been discontinued due to its uncontrollable and dose-dependent effect on the uterine musculature, with cases of prolonged uterine tetany associated with fetal distress [81], although Watt LO, 1961, showed that it is effective and safe as antiemetic and oxytocic in doses up to 1000 mg [85].
5. Getting High on Over-the-Counter Local Antiseptic (Benzydamine)
Benzydamine is a compound with anti-inflammatory properties used locally (mouthwashes, oral sprays, vaginal solutions, vaginal solution powder, etc.) for the symptomatic treatment of oropharyngeal or vaginal condition. In recent years, pharmaceutical products have been diverted and used, orally, for recreational purposes [86].
The psychoactive effects of benzydamine, characterized as hallucinations and nonspecific sensory changes after oral administration [87,88,89,90,91] occur in doses greater than 100 mg/day; numerous cases of misuse of doses up to 3000 mg have been described in the literature [89,92].
Although the exact mechanism of these hallucinations is still unclear, due to the structural similarity of benzydamine with serotonin and lysergic acid diethylamine (LSD), it is assumed that it mimics the effect of the psychedelic compound at the level of serotonin receptors, the hallucinations being a result of the stimulation of 5-HT2A receptors [93,94]. This pathway leads to dopamine release in nucleus accumbens.
The safety of benzydamine in the pregnant woman is not yet established, in the absence of controlled studies it is difficult to hypothesize, even in therapeutic doses and local administration, the potential consequences of use during pregnancy. Older studies in rodents have shown that, after oral administration, benzydamine does not affect organogenesis even in doses of 200 mg/kg body weight [95]. There are only a few case reports that refer to the safety of the use of benzydamine during pregnancy, including premature constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus as a result of maternal treatment [96], an effect similar to that of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the last trimester of pregnancy. The decrease in prostaglandin availability as a result of inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX1) by NSAIDs explains this side effect [97].
6. Additional Considerations
Since high doses of codeine or pseudoephedrine are required to achieve a psychoactive effect, consumers take several tablets at once, which predisposes to a risk of overdosing of the active drugs that are usually associated (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid). Of the 3 analgesic substances, overdose of acetaminophen poses the greatest concerns, because in doses greater than 4 g/day it can dramatically affect liver function. The hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen occurs as a result of the accumulation of its hepatotoxic metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone-imine (NAPQI), an oxidizing metabolite. Less than 10% of the ingested paracetamol dose is metabolized in the liver by the NAPQI-forming cytochrome P450 (CYP450) isoform CYP2E1. In therapeutic doses, the liver antioxidant systems (reduced glutathione—GSH) manage to reduce this oxidizing metabolite, but in high doses (over 4 g/day in those without liver disease, respectively over 2 g/day in those with impaired liver function), as a result of the existence of a limited available GSH, the metabolite accumulates and damages hepatocytes [98]. Literature describes methods by which codeine can be extracted from OTC products in order not to ingest increased doses of paracetamol [99].
In high doses, ibuprofen also raises health concerns regarding gastrointestinal (gastric, duodenal, and gastroduodenal ulcers), renal (acute and chronic renal failure) or cardiac (acute coronary syndrome, heart failure and myocardial infarction) side effects [99]. In short, they can be explained based on the mechanism of action of ibuprofen, namely the non-selective inhibition of cyclooxygenases (COX1 and COX2) and implicitly the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, mediators that have various physiological functions such as: maintaining the integrity of the gastrointestinal mucosa (by stimulating the synthesis of gastric protective mucus and inhibiting gastric acid secretion) or controlling the glomerular filtration rate. Impaired renal function contributes to the appearance of hydro-electrolyte imbalances, changes in arterial pressure with consequences on cardiac function. Although in the case of ibuprofen hepatic toxicity is described less frequently, in cases of prolonged use or over-therapeutic doses hepatic function should also be assessed [100,101]. In the last trimester of pregnancy, a decrease in prostaglandin synthesis causes premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and an increase in the risk of developing pulmonary hypertension in the newborn [97].
The study has limitations because the risks associated with prenatal exposure to the substances discussed in the manuscript have not been evaluated in epidemiological studies. The data presented are mainly based on case reports or preclinical studies.
7. Conclusions
The easy availability of OTC products containing substances with psychoactive potential raises serious problems. Even though risks in the general population are studied, there are limited data on maternal and fetal risks when ingested during pregnancy. Adverse pregnancy outcomes vary depending on the substance used, from malformations in the case of codeine (minor or major malformations) and pseudoephedrine (gastroschisis), to fetal toxic effects in the case of loperamide (arrhythmias) and benzydamine (premature closure of the ductus arteriosus) or withdrawal syndrome in the newborn (especially in the case of codeine). At the same time, the substances can affect the pregnancy due to an increased bleeding risk (codeine) or oxytocic effect (diphenhydramine and dimenhydrinate) which could lead to stillbirth and fetal death. For these reasons, we believe it is necessary to re-evaluate the release of OTC drugs containing substances with psychoactive potential to limit the population’s access to substances that possess increased toxicity at high doses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: B.-E.Ő.; writing—original draft preparation: B.-E.Ő., R.Ș., A.S. and G.J.; writing—review and editing: B.-E.Ő. and C.-E.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by George Emil Palade University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science, and Technology of Targu Mures, Research Grant number 163/6/10.01.2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Adrian Naznean for the English language revision of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chautrakarn, S.; Khumros, W.; Phutrakool, P. Self-Medication with Over-the-Counter Medicines Among the Working Age Population in Metropolitan Areas of Thailand. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 726643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, S.H.; Jones, H.E.; Arria, A.; Kaltenbach, K.; Coyle, M.; Fischer, G.; Stine, S.; Selby, P.; Martin, P.R. Unintended Pregnancy in Opioid-Abusing Women. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2011, 40, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K.I.; Day, C.A. Improving Access to Long-Acting Contraceptive Methods and Reducing Unplanned Pregnancy Among Women with Substance Use Disorders. Subst. Abus. 2016, 10, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosdzol-Cop, A.; Staniczek, J.; Orszulak, D.; Kowalczyk, K.; Fuchs, A.; Sieroszewski, P.; Wielgos, M.; Kalinka, J.; Huras, H.; Wegrzyn, P.; et al. The Polish Society of Gynecologists and Obstetricians’ Expert Group Recommendations regarding adolescent pregnancy. Ginekol. Pol. 2023, 94, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirguis, A. Misuse of prescription and over-the-counter drugs to obtain illicit highs: How pharmacists can prevent abuse. Pharm. J. 2020, 305, 7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S.; Miuli, A.; Mosca, A.; Santovito, M.C.; Corkery, J.M.; Guirguis, A.; Pettorruso, M.; Di Giannantonio, M.; Martinotti, G. Focus on Over-the-Counter Drugs’ Misuse: A Systematic Review on Antihistamines, Cough Medicines, and Decongestants. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 7, 657397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, N.A.; Whyte, I.M.; Dawson, A.H.; Cruickshank, D.A. Pheniramine-a Much Abused Drug. Med. J. Aust. 1994, 160, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delphin-Rittmon, M.E. 2022 The National Survey on Drug Use and Health. 2020. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/slides-2020-nsduh/2020NSDUHNationalSlides072522.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Pathan, H.; Williams, J. Basic Opioid Pharmacology: An Update. Br. J. Pain 2012, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrer, J.L.; Becker, J.A.J.; Befort, K.; Kieffer, B.L. Reward Processing by the Opioid System in the Brain. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1379–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczak, Ł.; Goryński, K. Pharmacological Aspects of Over-the-Counter Opioid Drugs Misuse. Molecules 2020, 25, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hout, M.C.V.; Horan, A.; Santlal, K.; Rich, E.; Bergin, M. ‘Codeine Is My Companion’: Misuse and Dependence on Codeine Containing Medicines in Ireland. Ir. J. Psychol. Med. 2018, 35, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines for the Pharmacological and Radiotherapeutic Management of Cancer Pain in Adults and Adolescents; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-92-4-155039-0.
- Lyngstad, G.; Skjelbred, P.; Swanson, D.M.; Skoglund, L.A. Analgesic Effect of Oral Paracetamol 1000 Mg/Ibuprofen 400 Mg, Paracetamol 1000 Mg/Codeine 60 Mg, Paracetamol 1000 Mg/Ibuprofen 400 Mg/Codeine 60 Mg, or Placebo on Acute Postoperative Pain: A Single-Dose, Randomized, and Double-Blind Study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 79, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akande-Sholabi, W.; Adisa, R.; Ilesanmi, O.S.; Bello, A.E. Extent of misuse and dependence of codeine-containing products among medical and pharmacy students in a Nigerian University. BMC Public. Health 2019, 19, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, G.C.; Aronson, J.K.; MacKenna, B.; Goldacre, B.; Hobbs, F.R.; Heneghan, C. Sales of Over-the-Counter Products Containing Codeine in 31 Countries, 2013–2019: A Retrospective Observational Study. Drug Saf. 2022, 45, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Van Hout, M.C. Over-the-Counter Codeine—From Therapeutic Use to Dependence, and the Grey Areas in Between. In Non-Medical and Illicit Use of Psychoactive Drugs; Nielsen, S., Bruno, R., Schenk, S., Eds.; Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 59–75. ISBN 978-3-319-60016-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hockenhull, J.; Wood, D.M.; Fonseca, F.; Guareschi, M.; Scherbaum, N.; Iwanicki, J.L.; Dart, R.C.; Dargan, P.I. The Association between the Availability of over the Counter Codeine and the Prevalence of Non-Medical Use. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNODC. Drug Use in Nigeria 2018, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, Vienna. 2018. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/data-and-analysis/statistics/Drugs/Drug_Use_Survey_Nigeria_2019_BOOK.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Shah, S.; Banh, E.T.; Koury, K.; Bhatia, G.; Nandi, R.; Gulur, P. Pain Management in Pregnancy: Multimodal Approaches. Pain. Res. Treat. 2015, 2015, 987483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogly, S.B.; Bowie, A.C.; Li, W.; Camden, A.; Velez, M.P.; Guttmann, A.; Werler, M.M. Safety of Prenatal Opioid Analgesics: Do Results Differ between Public Health Insurance Beneficiary and Population-Based Cohorts? Birth Defects Res. 2023, 115, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werler, M.M.; Kerr, S.M.; Ailes, E.C.; Reefhuis, J.; Gilboa, S.M.; Browne, M.L.; Kelley, K.E.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Smith-Webb, R.S.; Garcia, M.H.; et al. Patterns of Prescription Medication Use during the First Trimester of Pregnancy in the United States, 1997–2018. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 114, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, B.; Daniel, S.; Koren, G.; Lunenfeld, E.; Levy, A. Pregnancy outcome following opioid exposure: A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, A.C.; Werler, M.M.; Velez, M.P.; Li, W.; Camden, A.; Guttmann, A.; Brogly, S.B. Prescribed Opioid Analgesics in Early Pregnancy and the Risk of Congenital Anomalies: A Population-Based Cohort Study. CMAJ 2022, 194, E152–E162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezvalová-Henriksen, K.; Spigset, O.; Nordeng, H. Effects of Codeine on Pregnancy Outcome: Results from a Large Population-Based Cohort Study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, L.; Kane, M. Codeine Therapy and CYP2D6 Genotype. In Medical Genetics Summaries; Pratt, V.M., Scott, S.A., Pirmohamed, M., Esquivel, B., Kattman, B.L., Malheiro, A.J., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Galligan, J.J.; Sternini, C. Insights into the Role of Opioid Receptors in the GI Tract: Experimental Evidence and Therapeutic Relevance. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 239, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.E. Loperamide: A Pharmacological Review. Rev. Gastroenterol. Disord. 2007, 7 (Suppl. 3), S11–S18. [Google Scholar]
- Rungsiprakarn, P.; Laopaiboon, M.; Sangkomkamhang, U.S.; Lumbiganon, P.; Pratt, J.J. Interventions for Treating Constipation in Pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD011448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.; Soraisham, A.S.; Akierman, A. Neonatal Withdrawal Syndrome Due to Maternal Codeine Use. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 17, e40-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, W.; Jang, F.F.; Teng, C.; Tai-Zhen, H. Apoptosis may involve in prenatally heroin exposed neurobehavioral teratogenicity? Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 976–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotkin, T.A.; Seidler, F.J.; Yanai, J. Heroin Neuroteratogenicity: Targeting Adenylyl Cyclase as an Underlying Biochemical Mechanism. Dev. Brain Res. 2001, 132, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.; Sud, N.; Nobile, Z.; Bhattacharya, D. Teratogenic Effects of Maternal Drug Abuse on Developing Brain and Underlying Neurotransmitter Mechanisms. Neurotoxicology 2021, 86, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnelly, V.J.; Anblagan, D.; Quigley, A.; Cabez, M.B.; Cooper, E.S.; Mactier, H.; Semple, S.I.; Bastin, M.E.; Boardman, J.P. Prenatal Methadone Exposure Is Associated with Altered Neonatal Brain Development. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestal-Laborde, A.A.; Eschenroeder, A.C.; Bigbee, J.W.; Robinson, S.E.; Sato-Bigbee, C. The Opioid System and Brain Development: Methadone Effects on the Oligodendrocyte Lineage and the Early Stages of Myelination. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahi, N.; Nguyen, R.; Santos, C. Loperamide. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wandel, C.; Kim, R.; Wood, M.; Wood, A. Interaction of Morphine, Fentanyl, Sufentanil, Alfentanil, and Loperamide with the Efflux Drug Transporter P-Glycoprotein. Anesthesiology 2002, 96, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Chiappini, S. Is There Such a Thing as a “lope” Dope? Analysis of Loperamide-Related European Medicines Agency (EMA) Pharmacovigilance Database Reports. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doser, K.; Meyer, B.; Nitsche, V.; Binkert-Graber, P. Bioequivalence Evaluation of Two Different Oral Formulations of Loperamide (Diarex Lactab vs Imodium Capsules). Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 33, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Kim, W.; Moon, C.J. LC-MS Determination and Bioavailability Study of Loperamide Hydrochloride after Oral Administration of Loperamide Capsule in Human Volunteers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 36, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapaganti, S.; Anwar Ansari, S.; Saba, R.; Elkhouly, A.; Hassib, M. A Rare Case of Loperamide-Induced Cardiac Arrest. Cureus 2020, 12, e9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.E.; Juurlink, D.N. Clinical Review: Loperamide Toxicity. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 70, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasoff, D.R.; Koh, C.H.; Corbett, B.; Minns, A.B.; Cantrell, F.L. Loperamide Trends in Abuse and Misuse over 13 Years: 2002–2015. Pharmacotherapy 2017, 37, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, W.; Clark, K.H.; Marraffa, J.M. Loperamide Abuse Associated With Cardiac Dysrhythmia and Death. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borron, S.W.; Watts, S.H.; Tull, J.; Baeza, S.; Diebold, S.; Barrow, A. Intentional Misuse and Abuse of Loperamide: A New Look at a Drug with “Low Abuse Potential”. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 53, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.R.; Vera, A.; Alexander, A.; Ruck, B.; Nelson, L.S.; Wax, P.; Campleman, S.; Brent, J.; Calello, D.P. Loperamide Misuse to Avoid Opioid Withdrawal and to Achieve a Euphoric Effect: High Doses and High Risk. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Warns about Serious Heart Problems with High Doses of the Antidiarrheal Medicine Loperamide (Imodium), Including from Abuse and Misuse; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021.
- Rasla, S.; Parikh, P.; Hoffmeister, P.; Amand, A.S.; Garas, M.K.; Meligy, A.E.; Minami, T.; Shah, N.R. Unexpected Serious Cardiac Arrhythmias in the Setting of Loperamide Abuse. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2017, 100, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Compton, D.R.; Vaz, R.J.; Rampe, D. Proarrhythmic Mechanisms of the Common Anti-Diarrheal Medication Loperamide: Revelations from the Opioid Abuse Epidemic. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einarson, A.; Mastroiacovo, P.; Arnon, J.; Ornoy, A.; Addis, A.; Malm, H.; Koren, G. Prospective, Controlled, Multicentre Study of Loperamide in Pregnancy. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 14, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Källén, B.; Nilsson, E.; Otterblad Olausson, P. Maternal Use of Loperamide in Early Pregnancy and Delivery Outcome. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Nguyen, M.; Diaz, J.; Smith, T. Loperamide toxicity mimicking peripartum cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 693.e5–693.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceckova-Novotna, M.; Pavek, P.; Staud, F. P-Glycoprotein in the Placenta: Expression, Localization, Regulation and Function. Reprod. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statler, A.K.; Maani, C.V.; Kohli, A. Ephedrine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer, I.; Dowse, R.; Vuma, V. Pharmacokinetics of Oral Decongestants. Pharmacotherapy 1993, 13, 116S–128S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alevizos, B. Dependence and Chronic Psychosis with D-nor-Pseudoephedrine. Eur. Psychiatry 2003, 18, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, K.M. Paranoid Psychosis after Abuse of Actifed. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1982, 284, 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pugh, C.R.; Howie, S.M. Dependence on Pseudoephedrine. Br. J. Psychiatry 1986, 149, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, R. Mixed Bipolar Disorder Precipitated by Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride. South. Med. J. 1990, 83, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G. Acute Psychosis Following Intravenous Abuse of Pseudoephedrine: A Case Report. J. Psychopharmacol. 1996, 10, 324–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, H.; Woods, D. Pseudoephedrine Causing Mania-like Symptoms. N. Z. Med. J. 2002, 115, 86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mäki-Marttunen, V.; Andreassen, O.A.; Espeseth, T. The Role of Norepinephrine in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency: EMA/535476/2023—PRAC Recommends Measures to Minimise the Risk of Serious Side Effects with Medicines Containing Pseudoephedrine. 1 December 2023. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/referrals/pseudoephedrine-containing-medicinal-products (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Werler, M.M. Teratogen Update: Pseudoephedrine. Birth Defects Res. Part. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2006, 76, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghiev, M.D.; Hosseini, F.; Moran, J.; Cooper, C.E. Effects of Pseudoephedrine on Parameters Affecting Exercise Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. Open. 2018, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikk, K.; Haldre, S.; Aquilonius, S.-M.; Taba, P. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism Due to Ephedrone Abuse. Parkinsons Dis. 2011, 2011, 865319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Is Methamphetamine Manufactured? Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/methamphetamine/how-methamphetamine-manufactured (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Munafò, A.; Frara, S.; Perico, N.; Di Mauro, R.; Cortinovis, M.; Burgaletto, C.; Cantarella, G.; Remuzzi, G.; Giustina, A.; Bernardini, R. In Search of an Ideal Drug for Safer Treatment of Obesity: The False Promise of Pseudoephedrine. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werler, M.M.; Mitchell, A.A.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Honein, M.A. Use of over-the-counter medications during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 193 Pt 1, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werler, M.M.; Mitchell, A.A.; Shapiro, S. First Trimester Maternal Medication Use in Relation to Gastroschisis. Teratology 1992, 45, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werler, M.M.; Sheehan, J.E.; Mitchell, A.A. Maternal Medication Use and Risks of Gastroschisis and Small Intestinal Atresia. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torfs, C.P.; Katz, E.A.; Bateson, T.F.; Lam, P.K.; Curry, C.J.R. Maternal medications and environmental exposures as risk factors for gastroschisis. Teratology 1996, 54, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werler, M.M.; Sheehan, J.E.; Hayes, C.; Mitchell, A.A.; Mulliken, J.B. Vasoactive Exposures, Vascular Events, and Hemifacial Microsomia. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2004, 70, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentea, R.M.; Gupta, V. Gastroschisis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyme, H.E.; Higginbottom, M.C.; Jones, K.L. The Vascular Pathogenesis of Gastroschisis: Intrauterine Interruption of the Omphalomesenteric Artery. J. Pediatr. 1981, 98, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Attali, P. Management of Peripheral Vertigo with Antihistamines: New Options on the Horizon. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, B.G.; Berning, S.; Dudden, R.; Milgrom, H.; Tran, Z.V. Sedation and Performance Impairment of Diphenhydramine and Second-Generation Antihistamines: A Meta-Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, M.E.; Pinnick, R.V.; Terhes, J.M. Life-Threatening Diphenhydramine Overdose Treated With Charcoal Hemoperfusion and Hemodialysis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1999, 33, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, J.S.; Barbano, R.L.; Schult, R.; Wiegand, T.J.; Selioutski, O. Chronic Diphenhydramine Abuse and Withdrawal. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2017, 7, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenai, N.; Shulman, J.; Gopalan, P.; Cheng, E.; Cerimele, J.M. Fetal Outcomes in Intentional Over-the-Counter Medication Overdoses in Pregnancy. Psychosomatics 2018, 59, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brost, B.C.; Scardo, J.A.; Newman, R.B. Diphenhydramine Overdose during Pregnancy: Lessons from the Past. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 175, 1376–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.A. Diphenhydramine Toxicity in a Newborn: A Case Report. J. Perinatol. 2000, 20, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellpflug, S.J.; Bangh, S.A.; Cole, J.B. The Treatment of Maternal and Fetal Anticholinergic Toxicity with Physostigmine. Toxicol. Commun. 2018, 2, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Einarson, A. Managing Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy with Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatments. Womens Health 2006, 2, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, L.O. Oxytocic Effects of Dimenhydrinate in Obstetrics. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1961, 84, 533–534. [Google Scholar]
- Ősz, B.-E.; Jîtcă, G.; Sălcudean, A.; Rusz, C.M.; Vari, C.-E. Benzydamine—An Affordable Over-the-Counter Drug with Psychoactive Properties—From Chemical Structure to Possible Pharmacological Properties. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefania, C.; Andrea, M.; Alessio, M.; Mauro, P.; Amira, G.; Martin, C.J.; Giovanni, M.; Massimo, D.G.; Fabrizio, S. The Benzydamine Experience: A Systematic Review of Benzydamine Abuse. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaprutko, T.; Koligat, D.; Michalak, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Józiak, M.; Ratajczak, M.; Szydłowska, K.; Miazek, J.; Kus, K.; Nowakowska, E. Misuse of OTC Drugs in Poland. Health Policy 2016, 120, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opaleye, E.S.; Noto, A.R.; van der Meer Sanchez, Z.; de Moura, Y.G.; Galduróz, J.C.F.; Carlini, E.A. Recreational Use of Benzydamine as a Hallucinogen among Street Youth in Brazil. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2009, 31, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürü, M.; Şafak, Y.; Cengiz, G.F.; Kuru, E.; Örsel, S. Chronic Psychosis Related to Benzydamine Hydrochloride Abuse. Neurocase 2019, 25, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, B.; Oz, I.; Ozer, H.; Simsek, T. Hallucinations after Ingesting a High Dose of Benzydamine Hydrochloride. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2016, 14, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, Y.A.; Kalkan, M.; Çetin, R.; Çevik, E.; Çınar, O. Acute Psychotic Symptoms Due to Benzydamine Hydrochloride Abuse with Alcohol. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2014, 2014, 290365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaban, O.D.; Atagun, M.I.; Yilmaz, H.; Yazar, M.S.; Alpkan, L.R. Benzydamine Abuse as a Hallucinogen: A Case Report. Bull. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Howell, L.L.; Cunningham, K.A. Serotonin 5-HT2 Receptor Interactions with Dopamine Function: Implications for Therapeutics in Cocaine Use Disorder. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankes, R.; Abraham, R.; LeFevre, R. Reproductive Inhibition Caused by the Anti-Inflammatory Analgesic Benzydamine in the Rat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1981, 5, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzeszowski, W.; Wilczyński, J.; Grzesiak, M.; Nowakowska, D. Prenatal Sonographic Diagnosis of Premature Constriction of the Fetal Ductus Arteriosus after Maternal Self-Medication with Benzydamine Hydrochloride: Report of 3 Cases and Review of the Literature. J. Ultrasound Med. 2015, 34, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, A.M.; Healy, H.M.; Bell, K.A.; Brown, D.W.; Mullen, M.; Scheid, A. Prenatal Duct Closure Leading to Severe Pulmonary Hypertension in a Preterm Neonate—A Case Report. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E.M.; Hiatt, J.R.; Zarrinpar, A. Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity: An Updated Review. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnett, J.T.; Dines, A.M.; Wood, D.M.; Archer, J.R.H.; Dargan, P.I. Cold Water Extraction of Codeine/Paracetamol Combination Products: A Case Series and Literature Review. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Dureja, G.P.; Kadhe, G.; Mane, A.; Phansalkar, A.A.; Sawant, S.; Kapatkar, V. Cross-Sectional Study for Prevalence of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Gastrointestinal, Cardiac and Renal Complications in India: Interim Report. Gastroenterol. Res. 2015, 8, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, N.K.; Prince Sabina, E. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): A current insight into its molecular mechanism eliciting organ toxicities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 172, 113598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).