Abstract
CYP2C19 is a highly polymorphic gene responsible for the metabolism of commonly used drugs. CYP2C19*1, the wild-type allele, is associated with normal enzyme activity, whereas CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*17 lead to null and increased enzyme activity, respectively. The use of different instruments to perform the same pharmacogenetic tests should not affect the reliability of the results reported to clinicians, as required by the ISO 15189 standard. Genotyping assays allowed for the identification of gene variants corresponding to the CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*17 haplotypes in 44 selected samples. Each sample was analyzed in duplicate using the Thermo Fisher Taqman Drug Metabolism probes CYP2C19*2: c_25986767_70 (rs4244285) and CYP2C19*17: c_469857_10 (rs12248560). The experiments were performed on two widely used types of real-time PCR analyzers: ABI PRSIM™7500 and QuantStudioTM12KFlex (both from Applied Biosystems, Thermofisher). The data were analyzed in a Thermo Fisher Cloud facility. The analysis was performed independently by two qualified professionals. Both different instruments and analysts’ interpretations were consistent in identifying the native homozygous, heterozygous, and mutant homozygous variants for CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*17. The results provided by both the primary and backup analyzers showed a perfect correlation. This would allow for the use of the backup analyzer in case the main one is not available.
1. Introduction
Interindividual variability in drug response is a major clinical problem. Cytochromes P450 (CYP) catalyze a wide variety of drugs, enabling their bioactivation and elimination from the body. The CYP superfamily consists of 18 families and 44 subfamilies. The CYP 1 to 3 families are involved in phase I drug metabolism, whereas CYP 4 to 51 are associated with endobiotic metabolism. CYP2C19 is responsible for the metabolism of commonly used drugs, including clopidogrel and voriconazole [1].
The CYP2C19 gene is highly polymorphic and contains up to 36 star (*) alleles, as currently catalogued by the Pharmacogene Variation Consortium (PharmVar) [2]. CYP2C19*1 is considered to be the wild-type allele, which is associated with a “normal metabolizer” phenotype or normal enzyme activity. Heterozygous carriers of non-functional alleles (e.g., *2 and *3) are classified as “intermediate metabolizers”. Finally, two non-functional alleles (e.g., *2/*2, *2/*3, and *3/*3) result in null enzyme activity and are therefore classified as “poor metabolizers”. Conversely, CYP2C19*17 increases enzyme activity and is associated with “rapid” (*1/*17) and "ultrarapid" (*17/*17) metabolizer phenotypes. The distribution of CYP2C19 alleles varies in different populations, with overall frequencies of 15%, 0.02%, and 22% for CYP2C19*2, *3, and *17, respectively [3].
The anticoagulant clopidogrel is used to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with acute coronary syndromes and/or after percutaneous coronary intervention. Clopidogrel is a prodrug that requires hepatic biotransformation via CYP2C19 to produce the active metabolite. According to the recommendations of the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC), poor metabolizers treated with standard doses of this drug may have significantly reduced clopidogrel active metabolite formation, leading to increased on-treatment platelet reactivity and an increased risk of adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events. Alternatively, rapid and ultrarapid metabolizers show an increased formation of clopidogrel active metabolite and lower on-treatment platelet reactivity, although there is no association with an increased bleeding risk [4].
Voriconazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent used to treat invasive fungal infections (IFI), including aspergillosis, candidiasis, and infections caused by Scedosporium aspiospermum and Fusarium spp. IFIs are an important cause of morbidity and mortality in critically ill children and immunocompromised individuals. The therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole is necessary to ensure its efficacy and to avoid adverse effects. Low serum concentrations have been associated with treatment failure, while high serum concentrations lead to adverse effects, such as neurotoxicity [5,6,7]. The therapeutic drug monitoring of voriconazole has become the standard practice in many hospitals. In addition, the CYP2C19 genotype can significantly reduce subtherapeutic and supratherapeutic voriconazole concentrations in individuals at risk of serious infections [8].
Ensuring the best patient care requires the reliable performance of laboratory techniques. In this regard, the medical report sent to the clinician should be accurate regardless of the equipment used, and ISO 15189 [9]-ccredited laboratories must define a mechanism to allow for a comparison of results when they are provided by different analyzers [10]. Moreover, the compatibility of different analytical systems allows for faster results when needed. The aim of this study was to describe the compatibility, accuracy, and correlation of CYP2C19 genotyping results obtained from two different types of automated analyzers used in daily practice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
The Navarra Health Research Institute (IdiSNA) is a multidisciplinary and translational biomedical research institute focused on basic, clinical, epidemiological, and health services research located in Pamplona (Navarra, Spain). IdisNA research groups are located at the Universitary Hospital of Navarra (HUN), the Public University of Navarra (UPNA), the University Clinic of Navarra (CUN), the University of Navarra (UN), the Center for Biomedical research (Navarrabiomed), the Center for Applied Medical Research (CIMA), and the Institute of Public and Occupational Health and Primary Care of the Navarra Health Service. Two types of real-time PCR analyzers are available for CYP2C19 analysis: the ABI PRIM™7500 detection system and the QuantStudioTM12KFlex (both from Applied Biosystems, ThermoFisher Scientif, Inc., Walthman, MA, USA). The ABI PRISM™7500 is the reference analyzer, while the QuantStudioTM12KFlex would be used as the backup system.
These two analyzers use the same reagents and have similar methodologies and software. However, the QuantStudio 12KFlex is a more versatile analyzer as it maximizes throughput with minimal resources, since it allows for the use of 96-well, 384-well, and open array plates using interchangeable adapters without the need for additional tools, while the ABI PRIM™7500 only allows for the use of 96-well plates. In addition, up to four open arrays can be run simultaneously in a single experiment in the QuantStudio 12KFlex. It also features a faster start-up, with the possibility of starting an experiment with 12,000 data points in up to 20 min and the possibility of automation thanks to its compatibility with the Thermo Scientific Orbitor RS2 microplate handler for open array systems.
Knowing the CYP2C19*2, *3, and *17 allele frequencies and taking into account the population in our community, only CYP2C19*2 and *17 are routinely analyzed in daily practice.
2.2. Materials
A total of 44 samples were selected for genotyping for CYP2C19*2 (23 samples) and *17 (21 samples). In total, 18 out of 23 samples for CYPC19*2 and 18 out of 21 samples for CYP2C19*17 were of good quality. Samples with low DNA quality or quantity were also tested in order to evaluate the resolution of the analyzers.
All the research procedures were conducted in agreement with the Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent revisions.
2.3. Methods
The study was based on the analysis of 44 samples (23 samples for CYP2C19*2 and 21 samples for CYP2C19*17). The DNA extraction methods varied according to sample availability: (a) DNA extraction from filter paper using the Dried Blood Spot DANA Isolation Kit (Norgen Biotek Corp. ™, Thorold, ON, Canada) and (b) DNA extraction from 5 mL of peripheral blood using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen). The filter paper method required an amplification step in order to improve the DNA quality and quantity. Previously described protocols by Itoh K. et al. and Balwin R.M. et al. were used [11,12,13], with the primers listed in Table 1. The sample quality and quantity were assessed using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific).

Table 1.
List of primers used in CYP2C19*2 and *17 genotyping.
Genotyping was performed according to the RT-PCR protocol specified by the manufacturer, using Thermo-Fisher Taqman Drug Metabolism probes: c_25986767_70 (rs4244285) for CYP2C19*2, and c_469857_10 (rs12248560) for CYP2C19*17. Both samples and standard controls were run as duplicates in the two different RT-PCR setups described above. The data were uploaded and analyzed in the Thermo Fisher Cloud platform. Analyses were carried out independently by two qualified professionals to assess the inter-personal deviation in the post-analytical phase, as described in the flowchart in Figure 1.
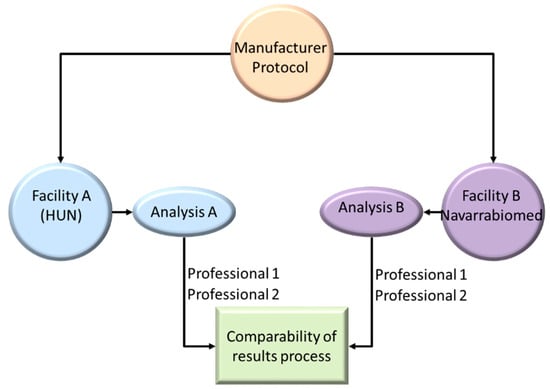
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the comparability process used.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Cohen’s kappa coefficient (κ) was calculated using Microsoft Excel v.16.50. An almost perfect agreement was considered if κ was above 0.8.
3. Results
The analysis of the 44 samples resulted in the identification of native, heterozygous, and homozygous configurations for CYP2C19*2 and CYP2C19*17. The results from both instruments (Table 2 and Table 3) and both analysts were in full agreement (κ = 1). In addition, samples analyzed as having too low DNA quantity or quality were classified as “undetermined or no amplification” by both analyzers.

Table 2.
Genotyping results for CYP2C19*2.

Table 3.
Genotyping results for CYP2C19*17.
4. Discussion
Although most laboratory errors occur during the preanalytical (68.2%) or postanalytical (18.5%) phase [14,15], the laboratory performance and selected analysis device can jeopardize the quality and reliability of data. This scenario often leads to confusion and distrust, potentially compromising patient care.
When deciding to use one piece of equipment or another, the characteristics of the laboratory where the installation is to be carried out must be taken into account, as well as the economic aspects. The choice of the methodology to be used is also important, as it is necessary to balance the economic cost and the reliability of the results. Currently, in pharmacogenetic studies, the use of real-time PCR techniques is considered to be the technique of choice in routine situations due to their availability and low cost compared to other technologies [16].
Regarding the consumption of reagents, the economic cost will be similar for both ABI PRISM™7500 and QuantStudio 12KFlex, since they are from the same manufacturer and use the same model of probes. Regarding the installation, although it is true the initial investment in the QuantStudio 12KFlex is higher, its versatility and compatibility with more modern resources make it more viable in the long term. In the clinical laboratory of the HUN, an ABI PRISM™7500 was already installed, which is why it was decided to continue to use this equipment, while in Navarrabiomed, it was recently decided to install real-time PCR equipment, so equipment in which a greater number of applications could be developed was chosen.
According to the ISO 15189 standard [9], laboratories must ensure that the results provided by different analyzers are comparable [10]. Even if the results of two devices from the same manufacturer are expected to be identical, quality standards require this to be verified. Such verification must be carried out even when the model used is the same, but two different devices are involved. In order to set-up a routine for the CYP2C19 analysis, we performed a comparability process between the two RT-PCR analysis instruments.
In our analysis, the results showed a perfect agreement between the two instruments. Furthermore, the analysis of the samples in duplicate ensured intra-sample reproducibility. These results allow us to rely on one of the analysis set-ups in case the other one is not available. Additionally, we verified that the analysis carried out by different professionals was also reproducible, ensuring part of the post-analytical phase. These reliable and comparable results, on a daily basis, provide the high-quality reporting of results in a suitable time for the best the patient care.
5. Conclusions
Our intercomparative analysis guarantees that the samples analyzed in our laboratory will provide the same result regardless of the equipment used to process them. This is a requirement for laboratories that want to establish a reliable quality management system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.L., J.S.G., O.T.H., F.G.A., A.V.M., A.F.V. and J.V.R.; methodology, A.A.L., J.S.G., O.T.H., F.G.A. and A.V.M.; software, A.A.L., J.S.G., O.T.H., F.G.A. and A.V.M.; investigation, A.A.L., J.S.G., O.T.H., F.G.A. and A.V.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.L., F.G.A., A.F.V. and J.V.R.; writing—review and editing, A.A.L., A.F.V. and J.V.R.; visualization, A.A.L., J.S.G., O.T.H., F.G.A., A.V.M., A.F.V. and J.V.R.; supervision, A.A.L., A.F.V. and J.V.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Samer, C.F.; Lorenzini, K.I.; Rollason, V.; Daali, Y.; Desmeules, J.A. Applications of CYP450 testing in the clinical setting. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2013, 17, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmacogene Variation Consortium (PharmVar). CYP2C19 [Internet]. Children Mercy. Available online: https://www.pharmvar.org/gene/CYP2C19 (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Ionova, Y.; Ashenhurst, J.; Zhan, J.; Nhan, H.; Kosinski, C.; Tamraz, B.; Chubb, A. CYP2C19 Allele Frequencies in Over 2.2 Million Direct-to-Consumer Genetics Research Participants and the Potential Implication for Prescriptions in a Large Health System. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Luzum, J.A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Gammal, R.S.; Sabatine, M.S.; Stein, C.M.; Kisor, D.F.; Limdi, N.A.; Lee, Y.M.; Scott, S.A.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2C19 Genotype and Clopidogrel Therapy: 2022 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SlateRunPharma. Inventor VORICONAZOLE- Voriconazole Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, for Solution [Packet Insert]. 2019. Available online: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=7f2e0784-8e48-f565-e053-2991aa0a0746 (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Moriyama, B.; Kadri, S.; Henning, S.A.; Danner, R.L.; Walsh, T.J.; Penzak, S.R. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Genotypic Screening in the Clinical Use of Voriconazole. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2015, 9, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Job, K.M.; Olson, J.; Stockmann, C.; Constance, J.E.; Enioutina, E.Y.; Rower, J.E.; Linakis, M.W.; Balch, A.H.; Yu, T.; Liu, X.; et al. Pharmacodynamic studies of voriconazole: Informing the clinical management of invasive fungal infections. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, B.; Obeng, A.O.; Barbarino, J.; Penzak, S.R.; Henning, S.A.; Scott, S.A.; Agúndez, J.; Wingard, J.R.; McLeod, H.L.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for CYP2C19 and Voriconazole Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15189:2022; Medical laboratories–Particular Requirements for Quality and Competence. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/76677.html (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Miler, M.; Šimundić, A.M.; Štefanović, M.; Ferenec-Ružić, D.; Kvaternik, M.; Topic, E.; Vrkic, N. A model for results comparison on two different biochemistry analyzers in laboratory accredited according to the ISO 15189. Biochem. Med. 2009, 19, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Inoue, K.; Yanagiwara, S.; Kyoya, H.; Suzuki, T. A rapid and simple detection of genetic defects responsible for the phenotypic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 2C19. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 22, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, R.; Kumari, R.; Singh, K.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K.; Mittal, B. Possible role of CYP2C9 & CYP2C19 single nucleotide polymorphisms in drug refractory epilepsy. Indian J. Med. Res. 2011, 134, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, R.M.; Ohlsson, S.; Pedersen, R.S.; Mwinyi, J.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Eliasson, E.; Bertilsson, L. Increased omeprazole metabolism in carriers of the CYP2C19*17 allele; a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plebani, M. Laboratory errors: How to improve pre- and post-analytical phases? Biochem. Med. 2007, 17, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiñón, L.; Soler, A.; López, R.M.; Pajares, S.; de Aledo, J.M.G.; Argudo-Ramírez, A.; Marín, J.L.; García-Villoria, J.; Sahuquillo, Á.; Alvarez, L. Inter-rater reliability assessment for the new-born screening quality assurance. Biochem. Medica 2022, 32, 030901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunno, N.; Esposito, M.; Argo, A.; Salerno, M.; Sessa, F. Pharmacogenetics and Forensic Toxicology: A New Step towards a Multidisciplinary Approach. Toxics 2021, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

