Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Activity of Dual COX-2/5-LOX Inhibitor Darbufelon and Its Novel Analogues
Abstract
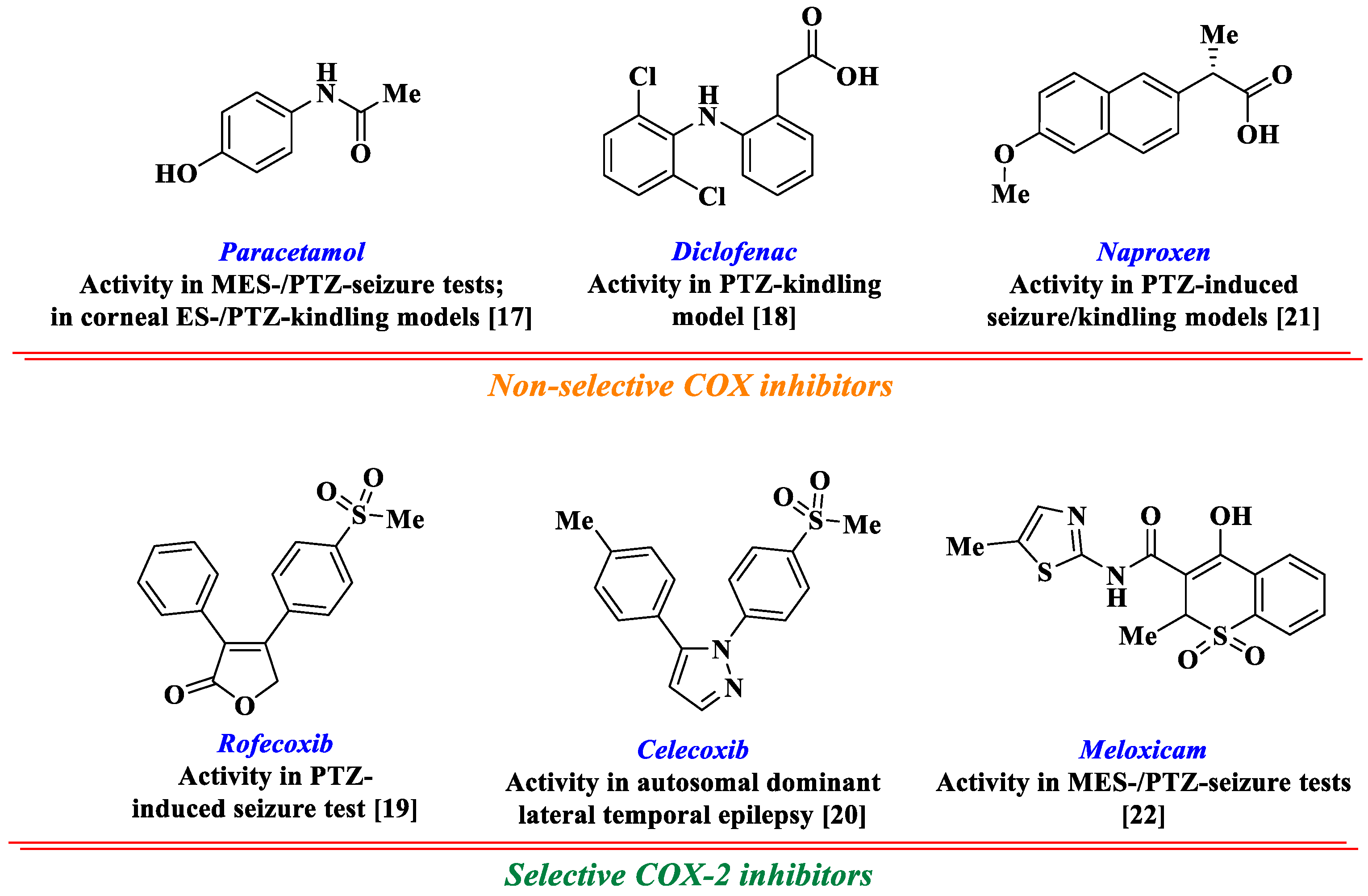
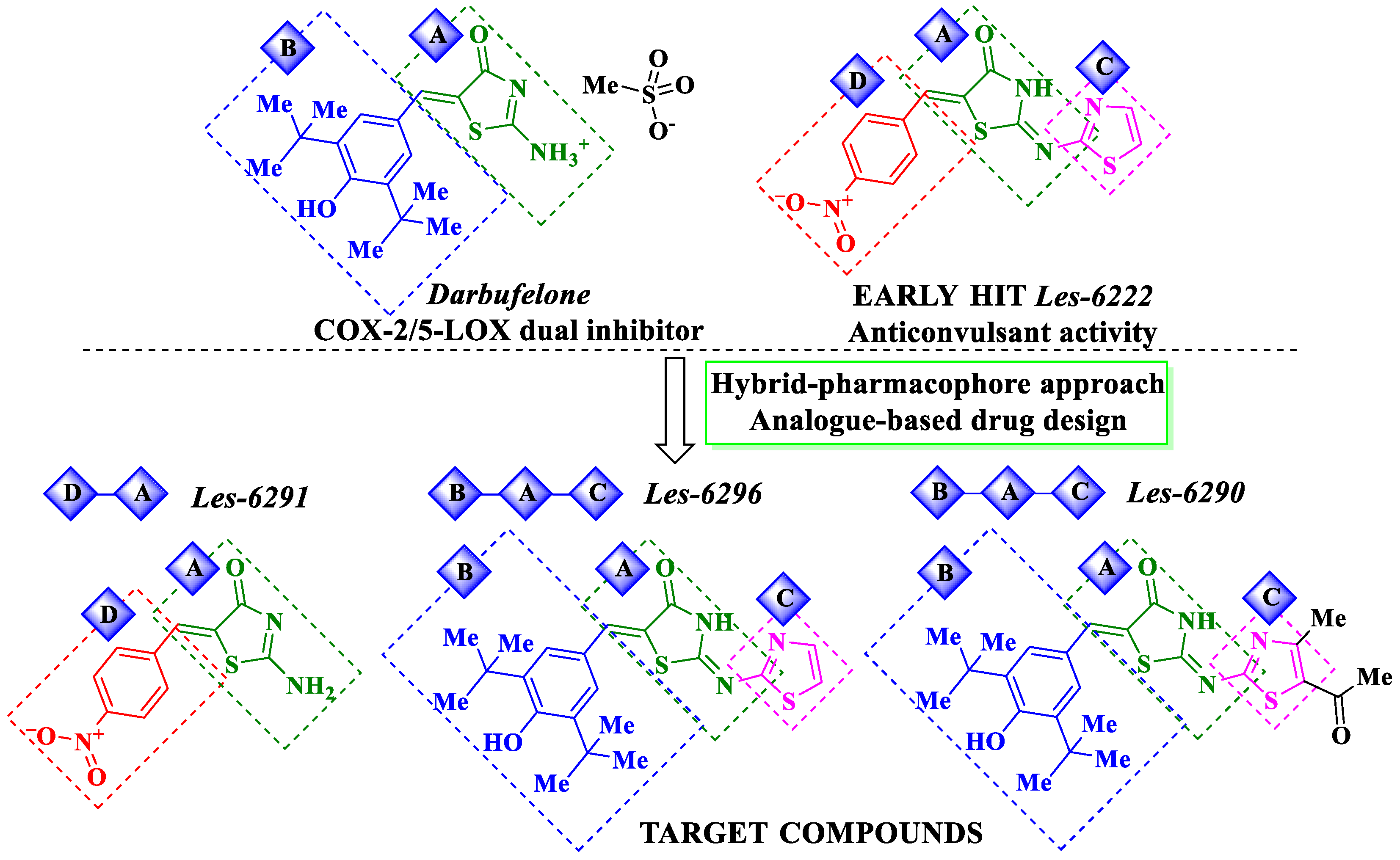
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information
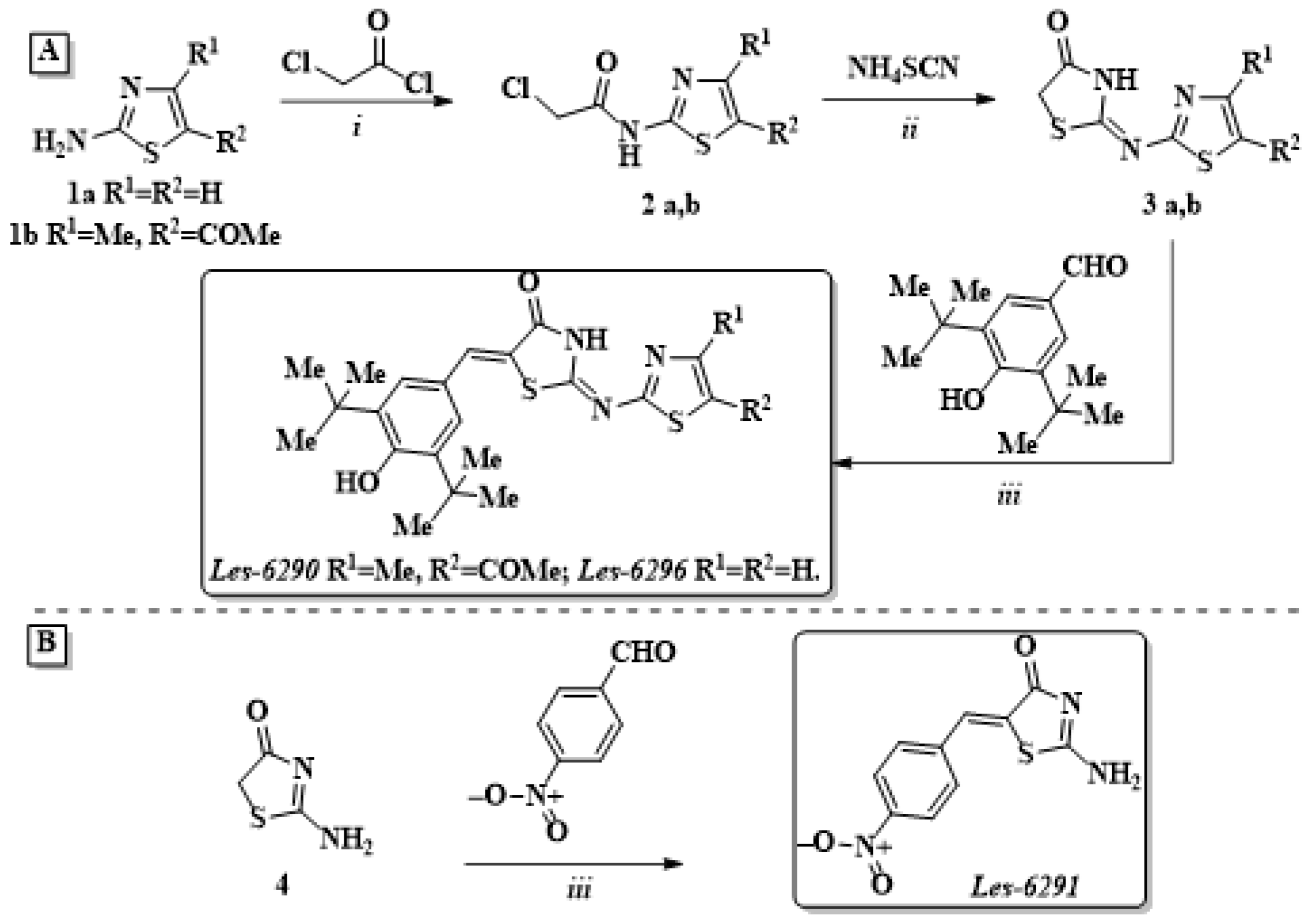
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Compounds
2.2.1. Synthesis of (thiazol-2-ylamino/5-acetyl-4-methyl-thiazol-2-ylamino)-acetyl chlorides (2a,b)
2.2.2. Characterization of Compounds Les-6296, Les-6290, Les-6291
2.3. Pharmacology Assay
2.3.1. Animals
2.3.2. Subcutaneous Pentylenetetrazole Model (scPTZ)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Synthesis and Drug-Likeness Properties
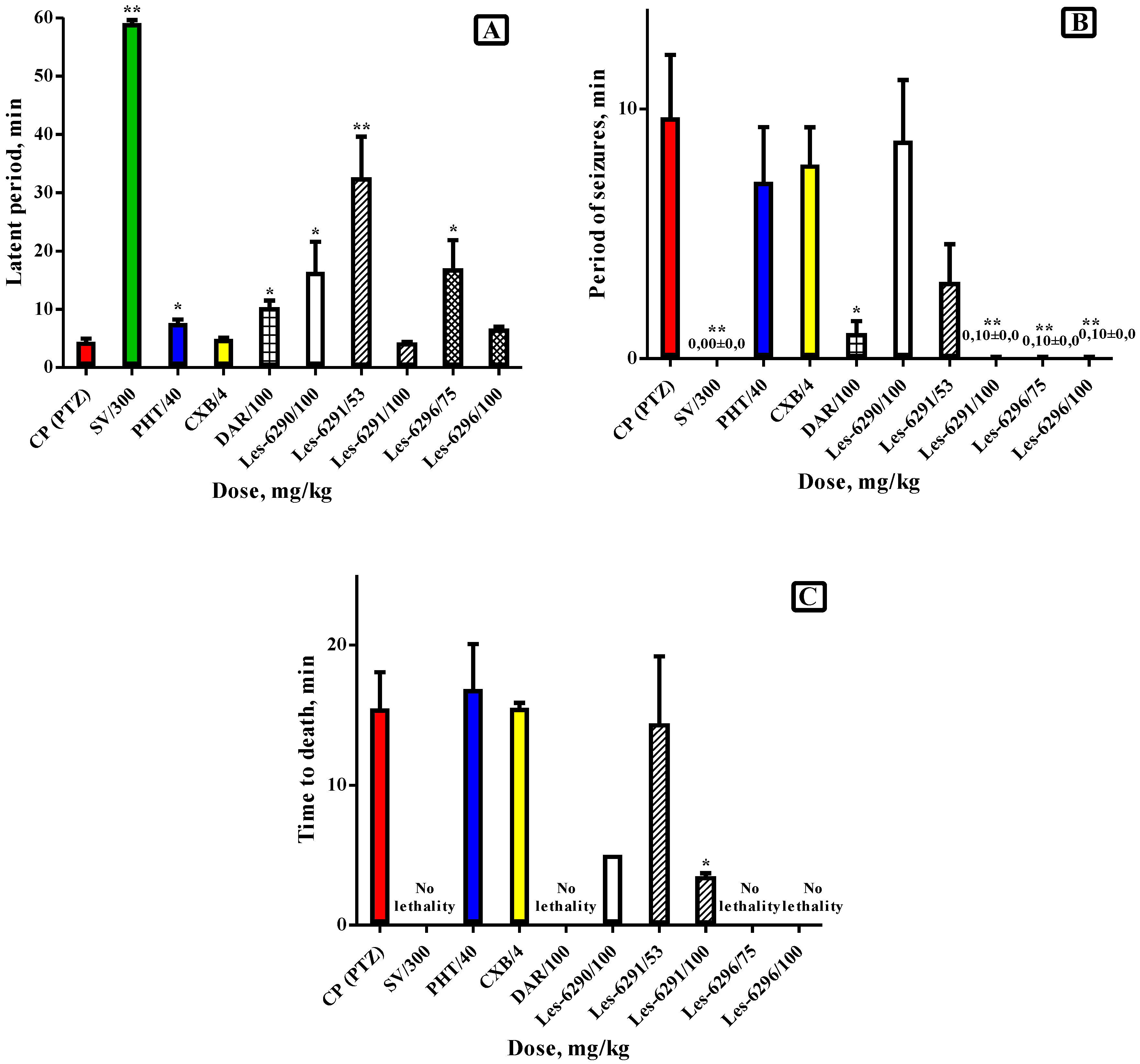
3.2. Anticonvulsant Activity of Synthesized Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thijs, R.D.; Surges, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy in adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A. Difficulties in treatment and management of epilepsy and challenges in new drug development. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2090–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalic, L.; Cook, M.J. Managing drug-resistant epilepsy: Challenges and solutions. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.B.; Kaminski, R.M. A systems-level framework for anti-epilepsy drug discovery. Neuropharmacology 2020, 170, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. An update for epilepsy research and antiepileptic drug development: Toward precise circuit therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 201, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker-Haliski, M.L.; Löscher, W.; White, H.S.; Galanopoulou, A.S. Neuroinflammation in epileptogenesis: Insights and translational perspectives from new models of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Balosso, S.; Ravizza, T. Neuroinflammatory pathways as treatment targets and biomarkers in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleen, J.K.; Holmes, G.L. Brain inflammation initiates seizures. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1309–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Hussain, M.D.; Yan, L.J. Microglia, neuroinflammation, and beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Neurosci. 2014, 124, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinewietfeld, M.; Hafler, D.A. Regulatory T cells in autoimmune neuroinflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 259, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becher, B.; Spath, S.; Goverman, J. Cytokine networks in neuroinflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, P.; Cunha, R.A.; Oliveira, C. Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Xiong, G.; Lin, B. Cyclooxygenase-1 mediates neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, C.; Kukal, S.; Dahiya, U.R.; Kukreti, R. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors: Future therapeutic strategies for epilepsy management. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, B.M.; Epureanu, F.B.; Radu, M.; Fabene, P.F.; Bertini, G. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in clinical and experimental epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 131, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A. An update of cyclooxygenase (COX)-inhibitors in epilepsy disorders. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemaru, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Tanaka, A.; Araki, H.; Aso, H.; Watanabe, M. Anticonvulsant effects of acetaminophen in mice: Comparison with the effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 140, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, V.; Glassmann, D.; Marafon, P.; Pereira, P.; Gomez, R.; Coitinho, A.S. Effect of diclofenac sodium on seizures and inflammatory profile induced by kindling seizure model. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 127, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, K.K.; Dhir, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Rofecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor increases pentylenetetrazol seizure threshold in mice: Possible involvement of adenosinergic mechanism. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 78, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, L.; Cao, S.L.; Xie, Y.J.; Wang, N.; Shao, C.Y.; Wang, Y.-N.; Zhou, J.-H.; Cowell, J.K.; Shen, Y. Celecoxib ameliorates seizure susceptibility in autosomal dominant lateral temporal epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3346–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A.; Naidu, P.S.; Kulkarni, S.K. Effect of naproxen, a non-selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor, on pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2005, 32, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, H.; Rezaei, M.; Khodayar, M.J.; Reza Zargar, H.; Dehghani, M.A.; Rajabi Vardanjani, H.; Ghanbari, S. Differential effects of meloxicam on pentylenetetrazole-and maximal electroshock-induced convulsions in mice. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2017, 12, e36412. [Google Scholar]
- Barbalho, P.G.; Carvalho, B.S.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; Maurer-Morelli, C.V. Cyclooxygenase-1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Seizure Suppression: Evidences from Zebrafish Pentylenetetrazole-Seizure Model. Front Neurol. 2016, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun, M.; Tratrat, C.; Kolokotroni, A.; Petrou, A.; Geronikaki, A.; Ivanov, M.; Kostic, M.; Sokovic, M.; Carazo, A.; Mladěnka, P.; et al. 5-Benzyliden-2-(5-Methylthiazol-2-Ylimino)Thiazolidin-4-Ones as Antimicrobial Agents. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, K.; Geronikaki, A.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Camoutsis, C.; Soković, M.; Ćirić, A.; Glamočlija, J. Novel 4-thiazolidinone derivatives as potential antifungal and antibacterial drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.; Shtrygol, S.; Kaminskyy, D.; Lesyk, R. Thiazole-bearing 4-thiazolidinones as new anticonvulsant agents. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadich, E.; Kryshchyshyn-Dylevych, A.; Holota, S.; Polishchuk, P.; Džubak, P.; Gurska, S.; Hajduch, M.; Lesyk, R. Assessing different thiazolidine and thiazole based compounds as antileishmanial scaffolds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklyarova, Y.; Fomenko, I.; Lozynska, I.; Lozynskyi, A.; Lesyk, R.; Sklyarov, A. Hydrogen sulfide releasing 2-mercaptoacrylic acid-based derivative possesses cytoprotective activity in a small intestine of rats with medication-induced enteropathy. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaras, K.; Fesatidou, M.; Geronikaki, A. Thiazoles and thiazolidinones as COX/LOX inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishchenko, M.V.; Shtrygol, S.Y.; Lesyk, R.B.; Lozynskyi, A.V.; Holota, S.M. Screening study of new thiazolidinone derivatives for anticonvulsant activity. Zaporozhye Med. J. 2020, 22, 840–846. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Sarkis, G.Y.; Al-Azawe, S. Preparation and spectral characterization of substituted 2-aminothiazoles. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1973, 18, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapiuk, Y.V.; Obushak, M.D.; Matiychuk, V.S.; Naskrent, M.; Gzella, A.K. A convenient method for the synthesis of 2-[(5-benzyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)imino]-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subtel’na, I.; Atamanyuk, D.; Szymańska, E.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Zimenkovsky, B.; Vasylenko, O.; Gzella, A.; Lesyk, R. Synthesis of 5-arylidene-2-amino-4-azolones and evaluation of their anticancer activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5090–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hock, F.J. Drug Discovery and Evaluation: Pharmacological Assays; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; 4314p. [Google Scholar]
- Paronikyan, R.G.; Avagyan, M.N.; Harutyunyan, A.A.; Avakyan, G.G.; Litvinova, S.A.; Voronina, T.A. Experimental study of the anticonvulsant and psychotropic properties of pufemid, piratidine and N3212 in comparison with known antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Paroxysmal Cond. 2019, 11, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Furian, A.F.; Royes, L.F.F.; Fighera, M.R.; Fiorenza, N.G.; Castelli, M.; Machado, P.; Bohrer, D.; Veiga, M.; Ferreira, J.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2/PGE2 pathway facilitates pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 79, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bespalov, A.; Michel, M.C.; Steckler, T. Good Research Practice in Non-Clinical Pharmacology and Biomedicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; 423p. [Google Scholar]
- SwissADME. Available online: http://www.swissadme.ch/ (accessed on 27 March 2021).
- Katyal, J.; Kumar, H.; Gupta, Y.K. Anticonvulsant activity of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor etoricoxib in pentylenetetrazole-kindled rats is associated with memory impairment. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 44, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compounds/ Drugs | Lipinski Rules | Veber Rules | Violations of Rules | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW ≤ 500 | Log P ≤ 5 | NHD ≤ 5 | NHA ≤ 10 | NBR ≤ 10 | TPSA ≤ 140 | ||
| Darbufelon | 332.46 | 2.88 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 100.98 | 0 |
| Les-6290 | 471.64 | 3.81 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 145.19 | 1 |
| Les-6291 | 249.25 | 1.19 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 126.57 | 0 |
| Les-6296 | 415.57 | 3.41 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 128.12 | 0 |
| Group of Animals | Dose, mg/kg | Number of Clonic-Tonic Seizures per Mouse | Mice with Seizures, % | Seizure Severity, Points | Lethality, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clonic | Tonic | |||||
| СP(PTZ) | 90 | 2.29 ± 0.52 | 100 | 85.71 | 5.57 ± 0.43 | 85.71 |
| SV | 300 | 0.00 ± 0.00 ** | 0 ** | 0 ** | 0 ** | 0 ** |
| PHT | 40 | 1.17 ± 0.17 | 100 | 66.67 | 5.00 ± 0.63 | 66.67 |
| CXB | 4 | 2.00 ± 0.37 | 100 | 66.67 | 4.67 ± 0.62 | 50.00 |
| DAR | 100 | 1.17 ± 0.17 | 100 | 100 | 4.00 ± 0.00 * | 0.00 ** |
| Les-6290 | 100 | 1.67 ± 0.56 | 83.33 ** | 50.00 | 3.67 ± 0.84 * | 16.67 ** |
| Les-6291 | 100 | 1.00 ± 0.00 * | 100 | 66.67 | 4.33 ± 0.56 | 33.33 * |
| 53 | 1.00 ± 0.63 | 50.00 ** | 33.33 * | 2.50 ± 1.20 * | 33.33 * | |
| Les-6296 | 100 | 1.00 ± 0.00 * | 100 | 33.33 * | 3.33 ± 0.21 ** | 0.00 ** |
| 75 | 0.83 ± 0.17 * | 83.33 ** | 16.67 ** | 2.67 ± 0.56 ** | 0.00 ** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishchenko, M.; Shtrygol’, S.; Lozynskyi, A.; Khomyak, S.; Novikov, V.; Karpenko, O.; Holota, S.; Lesyk, R. Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Activity of Dual COX-2/5-LOX Inhibitor Darbufelon and Its Novel Analogues. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89020022
Mishchenko M, Shtrygol’ S, Lozynskyi A, Khomyak S, Novikov V, Karpenko O, Holota S, Lesyk R. Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Activity of Dual COX-2/5-LOX Inhibitor Darbufelon and Its Novel Analogues. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2021; 89(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishchenko, Mariia, Sergiy Shtrygol’, Andrii Lozynskyi, Semen Khomyak, Volodymyr Novikov, Olexandr Karpenko, Serhii Holota, and Roman Lesyk. 2021. "Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Activity of Dual COX-2/5-LOX Inhibitor Darbufelon and Its Novel Analogues" Scientia Pharmaceutica 89, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89020022
APA StyleMishchenko, M., Shtrygol’, S., Lozynskyi, A., Khomyak, S., Novikov, V., Karpenko, O., Holota, S., & Lesyk, R. (2021). Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Activity of Dual COX-2/5-LOX Inhibitor Darbufelon and Its Novel Analogues. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 89(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm89020022








