Abstract
Introduction: Bioactive encapsulation and drug delivery systems have already found their way to the market as efficient therapeutics to combat infections, viral diseases and different types of cancer. The fields of food fortification, nutraceutical supplementation and cosmeceuticals have also been getting the benefit of encapsulation technologies. Aim: Successful formulation of such therapeutic and nutraceutical compounds requires thorough analysis and assessment of certain characteristics including particle number and surface area without the need to employ sophisticated analytical techniques. Solution: Here we present simple mathematical formulas and equations used in the research and development of drug delivery and controlled release systems employed for bioactive encapsulation and targeting the sites of infection and cancer in vitro and in vivo. Systems covered in this entry include lipidic vesicles, polymeric capsules, metallic particles as well as surfactant- and tocopherol-based micro- and nanocarriers.
1. Introduction
Drug delivery systems emerged around six decades ago with the aim of improving Human and livestock health and well-being. Also known as encapsulation protocols and controlled release systems, they can be broadly categorized into different groups such as lipidic, polymeric, metallic particles, surfactant-based and tocopherol-based carriers (Table 1). The drug delivery systems are very versatile in terms of their ingredients, size, surface characteristics, charge, elasticity, number of coats, layers or bilayers surrounding the drug molecules, encapsulation capacity, release profile and stability/shelf-life. Based on this versatility, drug carriers are being applied in many areas of biological and medical research, diagnosis and therapy as well as a number of different industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food, nutrition, cosmetics and skincare) as highly valuable ingredients [1,2,3,4,5]. Formulations of benzoyl peroxide microsponge have been reported to find applications in the treatment of mild to moderate acne [6], while polymeric hydrogel carriers are recently reported to show promise in targeting colon cancer [7,8]. Polymeric nanoparticles [9], niosomes [10] and the recently introduced drug carrier “tocosome” [11,12] are other formulations with potential use to combat cancer, viral and some other health issues.

Table 1.
Main classes of bioactive encapsulation systems.
Formulation and optimization of potent drug delivery systems necessitate thorough analysis of certain physicochemical and biological characteristics [13,14]. The disposition properties of intravenously injected carrier systems and those applied via other routes of administration are complicated and depend in part on dose, particle size, charge, number of carriers, and total surface area [15,16,17]. Consequently, parameters such as particle number and surface area must be precisely fine-tuned to ensure successful formulations and their quality assurance. This entry presents simple mathematical formula and equations used in the calculation of the aforementioned parameters along with some available techniques employed to characterize the micro- and nanocarrier systems.
2. Particle Number Determination
The tangible number of particles in drug delivery formulations (number concentration, N) is of importance for quality assurance, comprehensive physicochemical characterization, and pharmacodynamics [15]. The number of particles in a certain volume of sample, rather than merely their size, could affect their absorption, clearance and disposition [16,18]. The number of particles affects effective uptake of a targeted carrier system by specific cells (e.g., phagocytic cells) and the cumulative drug content of the particles determines their bioactivity and therapeutic efficacy. Knowledge of particle quantity enables the precise assessment of drug concentration in each solid (rigid, e.g., liposomes made of lipids with high phase transition temperature) or liquid (elastic) particle [15]. Concentration of the bioactive agent or its distribution between phases determines if the system is of dissolved or dispersed type, and accordingly, it defines the drug release kinetics and mechanism. Among the techniques used for the quantification of particle number is nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), which is able to track and measure particles moving under Brownian motion [17,19]. This high-resolution method is effective in determining the size, size distribution, and concentration of colloidal and particulate drug delivery systems. It can be employed to assess particles and vesicles within the size range of 30–1000 nm [20]. Samples are injected into the special cell of the apparatus and then it is illuminated by laser light (635 nm) that passes through a liquid layer on the optical surface [19,20]. Refraction occurs and the region in which the vesicles or particles are present is illuminated and visualized under microscopy. A charge-coupled device camera records a video (30 frames/sec) wherein the movement of particles under Brownian motion can be visualized. Special software identifies and tracks the center of each particle throughout the length of the video and relates it to the particle characteristics [21]. Mathematical equations used to calculate the quantity of some examples of carrier systems are described below. Simple equations are given for both solid particles (e.g., metallic particles, polymeric microcapsules and nanocapsules) and soft vesicles (e.g., liposomes, nanoliposomes, lipospheres, solid lipid nanoparticles, niosomes and tocosomes).
2.1. Quantification of Number of Metallic Particles
Particles of gold, silver, iron, copper and other metals are popular colloidal substrates employed in various sensor, imaging, and drug delivery applications. They can be synthesized and modified with several different chemical functional groups, which allow them to be conjugated with antibodies, ligands, and other bioactive agents or drugs of interest [22]. Particle number or concentration of metallic particles determines crucial features of the formulations including stability, bioactivity and cytotoxicity. The number of metallic particles (NMP) in solution can be calculated from the ratio of the number of initial metal atoms (Nma) and the number of metal atoms per one, single metallic particle Nma/smp as described in Equation (1):
NMP = Nma / Nma/smp
Hinterwirth and co-workers [23] employed a similar mathematical equation to calculate number concentration of the gold nanoparticles in their formulation. Taking their study as an instance, if initially 55 mL of 1.14 mM Au(III) atoms was used in the construction of particles and the number of metal atoms per single metallic particle is calculated to be 30.89602 (see Equation (2) below), the number of gold nanoparticles in 1 L sample will be:
in which NA is Avogadro’s constant (i.e., 6.02E23). The average number of metal atoms per metallic particle of gold is calculated according to the following equation [24,25]:
where ρ is the density for a face-centered cubic (FCC) gold (19.3 g/cm3), D is the average size (31 ± 1.6 nm) and M stands for atomic weight of gold (197 g/mol). The average number of gold atoms per nanoparticle can also be calculated from high-resolution microscopic analysis. Rajakumar et al. [25] reported that images of their synthesized gold nanoparticles depicted particles in the range of 23 to 46 nm, with an average size of 31 ± 1.6 nm (D, nm) [25]. Assuming a spherical shape and a uniform face-centered cubic (FCC) structure [26], the average number of gold atoms for each type of nanosphere was calculated by Equation (2) [27,28].
1.14 × 10−3 mol L−1 × 0.055 L × NA / 30.89602 = 1.2221 × 1018
Nma/smp = π ρ D3 / 6M = 30.89602 D3
The mathematical approach and the related Equation (1) explained above can be extrapolated to be used for other metallic micro- and nanoparticles including copper [29] and silver [30].
2.2. Particle Number of Vesicular Carriers
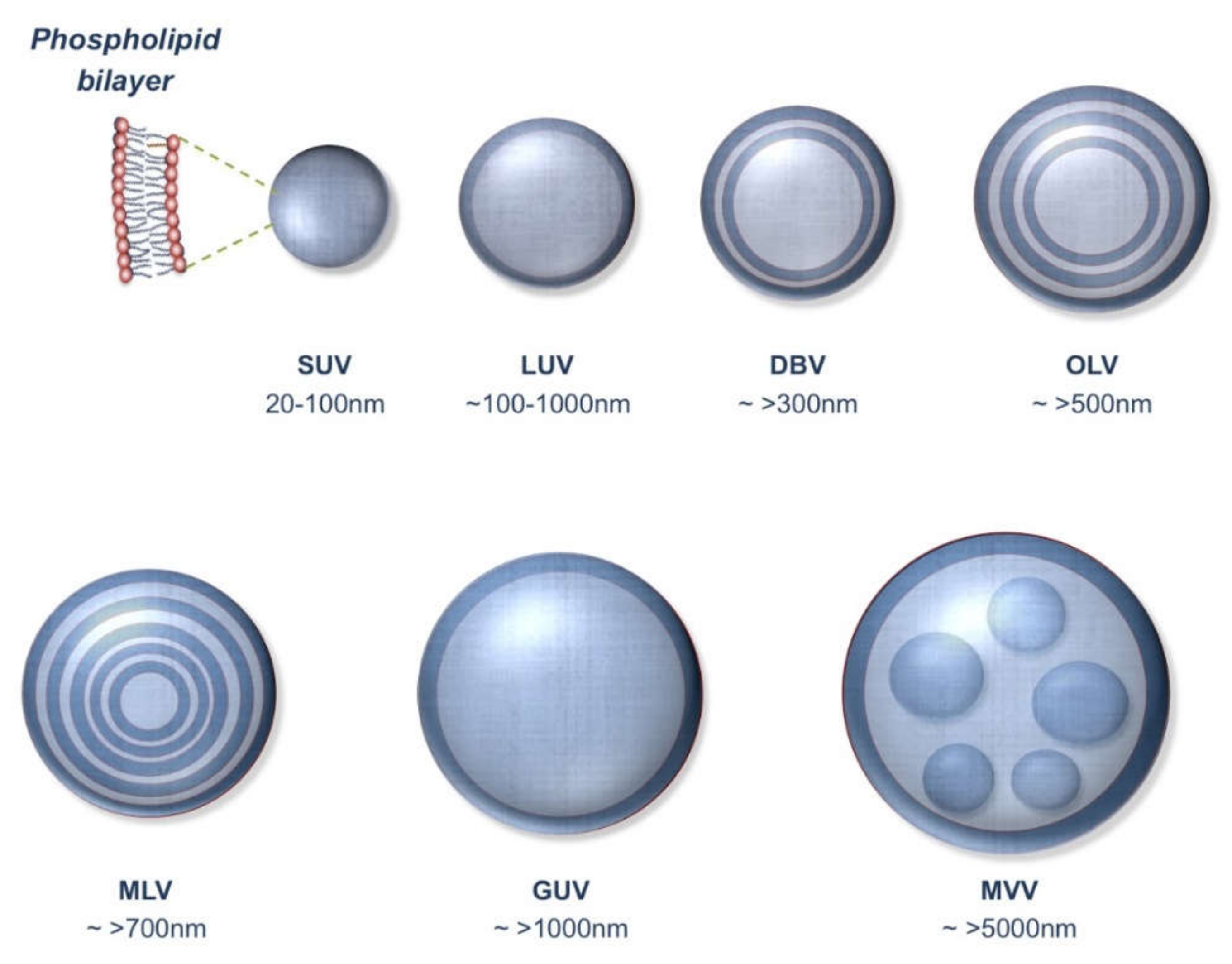
Vesicular drug-delivery carriers comprise liposomes, nanoliposomes, micelles, tocosomes, niosomes, solid lipid nanoparticles and archaeosomes to name a few [16,31]. Among the vesicular carriers, liposomes (and nanoliposomes) are the most applied encapsulation techniques with the highest number of products approved for Human use on the market. Also known as a bilayer phospholipid vesicle, liposome is a mesomorphic structure mainly composed of lipid, phospholipid and water molecules [32]. The main chemical components of liposomes and nanoliposomes are amphiphilic lipid/phospholipid molecules (Figure 1). They improve the efficacy of pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and other bioactive compounds by entrapment and release of water-soluble, lipid-soluble and amphipathic materials, as well as targeting the encapsulated drug molecules to particular cells or tissues [33,34]. Vesicular drug carriers, including liposomes, can be prepared in different forms with respect of their number of lamella (phospholipid bilayers) as depicted in Figure 2.
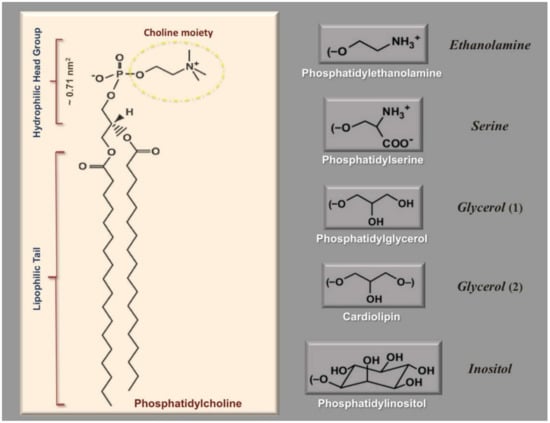
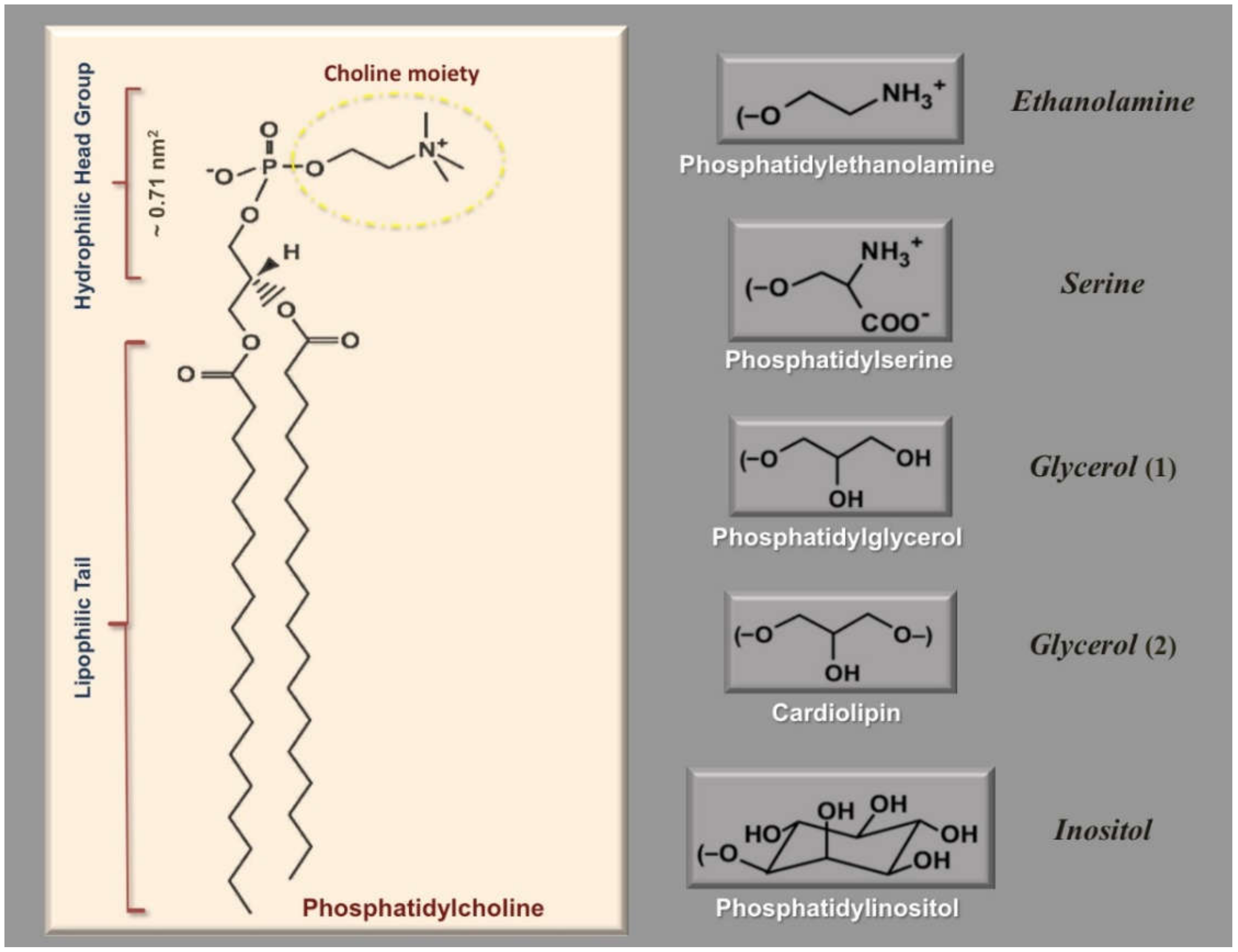
Figure 1.
Structural formula of phosphatidylcholine molecule and its derivatives/related phospholipids. The chemical moieties on the right panel replace the Choline moiety depicted on the left panel, and hence each phospholipid molecule is named based on its specific moiety on its hydrophilic head group.
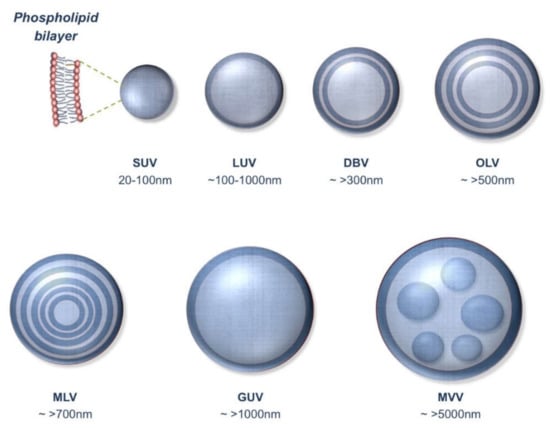
Figure 2.
Different types of lipid vesicles. SUV: small unilamellar vesicle; LUV: large unilamellar vesicle; DBV: double bilayer vesicle; OLV: oligolamellar vesicle; MLV: multilamellar vesicle; GUV: giant unilamellar vesicle; MVV: multivesicular vesicle.
Currently, there are no validated experimental approaches for the determination of the particle number-concentration of liposomal and nanoliposomal formulations [15]. Here we present a simple mathematical approach to calculate the number of phospholipid vesicles, in the form of unilamellar vesicle, in any certain volume of sample. Once the total concentration of phospholipids, lipids and other ingredients of our vesicles (such as cholesterol, phytosterols, vitamin E, etc.) in the suspending media are known, then the total number of particles per ml can easily be calculated using Equation (3).
where: NVes is the number of drug delivery vesicles per milliliter; Ming is the molar concentration of ingredients of the vesicles; NA is the Avogadro Number (6.02E23); and Ntot is the total number of ingredients per vesicle. Equation (3) is the main equation by which particle number of vesicular bioactive carrier systems can be easily calculated once we know Ntot.
NVes = [Ming × NA] / [Ntot × 1000]
Ntot can be calculated using the following equation:
in which: [4π(d/2)2] is the surface area of vesicle’s monolayer; d is the diameter of the vesicle; h is the thickness of the phospholipid bilayer (i.e., ~5 nm); a is the phospholipid head group area and E2 is exponent two (to the power 2). The headgroup area of phosphatidylcholine (a generally used ingredient in the manufacture of lipid vesicles, niosomes, tocosomes, etc.) is about 0.71 nm square, as depicted in Figure 1 [35,36,37]. Accordingly, Equation (4) can be simplified to:
in which 17.69 is 4π/a.
Ntot = [4 π (d/2)E2 + 4 π [(d/2)−h)]E2] / a
Ntot = 17.69 × [(d/2)E2 + (d/2 − 5)E2]
As an example the total number of ingredients for a unilamellar formulation with 400 nm mean particle size is:
and using this number as Ntot in Equation (3), we will find out the number of vesicles in a milliliter of the prepared sample, assuming molar concentration (Ming) of 1 micromole:
17.69 × [(400 / 2)2 + (400 / 2 - 5) 2] = 1,022,088.89 = Ntot
NVes = [10−6 × (6.02 × 1023)] / [1,022,088.89 × 1000] =
~ 588,989,868 vesicles/ml
~ 588,989,868 vesicles/ml
Exceptional cases for the use of Equation (3) for quantification of particle number of vesicular drug carriers would be multilamellar vesicles (MLV) or multivesicular vesicles (MVV) (see Figure 2). The mathematical equations described above are straightforward means for calculation of particle number. Other approaches mentioned in the literature are complicated and involve multistep calculations. For instance, Pidgeon and Hunt [38] have presented formulas based on the volume of the entrapped water by liposomal vesicles, which involve solving several equations in order to find the estimated particle number.
2.3. Particle Number of Polymeric Carriers
A method used to assess the number concentration of polymeric carriers is scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS) [39,40]. In this method, the formulations are atomized to aerosol droplets that are then dried in a silica-gel diffusion drier. The dry particles flow into the SMPS apparatus, which is composed of the differential mobility analyzer (DMA) unit. DMA provides size information according to the size-dependent electric mobility of the particles. The particles then move into the condensation particle counter (CPC) section, which counts the number of particles in each size group. The combined measurements result in a highly resolved particle count for the full-size distribution range. Integrating the counts over the full-size range yields the total particle number concentration Nc using Equation (5):
in which N’c is the number of particles per cm3 measured by SMPS, CF is the calibration factor for the particle size, Fg is the flow rate (cm3 min−1) of the carrier gas (e.g., nitrogen). Rev is the measured evaporation rate of the sample solution (ml min−1) and is calculated by measuring the rate of solution loss from the atomizer compartment for the calibrated gas flow through the atomizer. The calibration factor (CF) is employed to account for the loss of particles in the system.
Nc = N’c × CF × Fg / Rev
3. Surface Area Determination
When bioactive carriers come in contact with cells and tissues, their external surface is obviously the first contact point, which determines drug pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Knowledge of the surface area of drug delivery systems is of high importance in the assessment of their release and permeation behavior and their stability, as well as their interaction with the target cells and tissues, and hence their cytotoxicity profile. Once we know the number of our spherical or near-spherical particles/vesicles (N) and the mean particle size of the formulation (d) we can calculate the surface area (S) employing Equation (6):
in which [4 π (d/2)E2] is the surface area of one single spherical or semispherical particle. Equation (6) can be applied for both solid particles (e.g., metallic particles, polymeric capsules) and soft vesicular systems (e.g., tocosomes, liposomes, nanoliposomes, lipospheres, solid lipid nanoparticles, vesicular lipid gels, niosomes and archaeosomes).
S = N × 4 π (d/2)E2
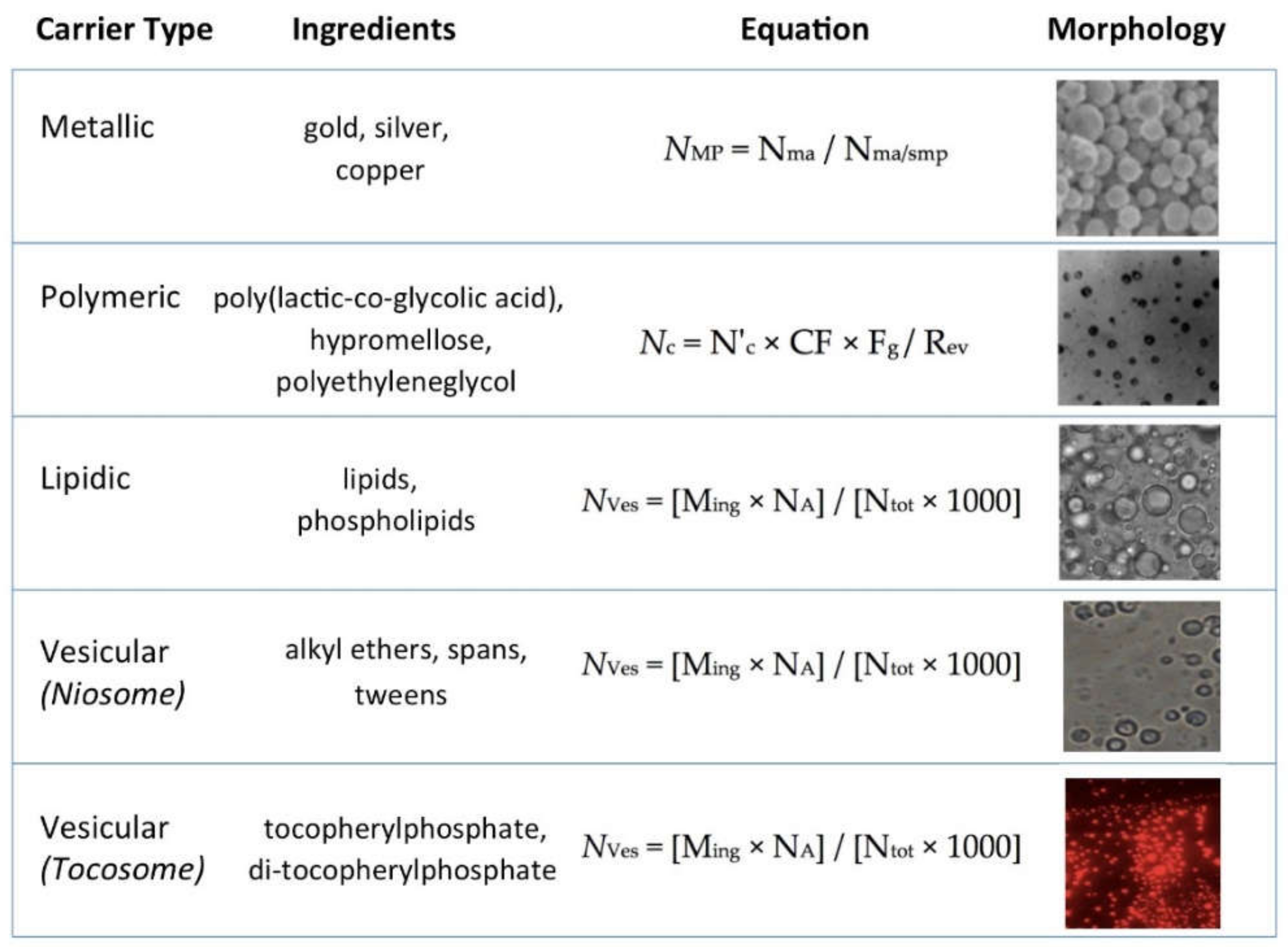
While Equation (6) can be used universally to measure surface area of all type of spherical drug carriers, quantification of particle number requires specific equations for different carrier systems based on their ingredients (and as a result their physicochemical properties) as explained throughout this article and simplified in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Simple equations for the quantification of particle number of major groups of bioactive carrier systems, generally used ingredients for their manufacture and microscopic image of each class of carrier system.
4. Conclusions
Calculations of the particle number and surface area towards formulation of the drug delivery/encapsulation systems is of importance for quality assurance, comprehensive physicochemical characterization, safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics. Some calculation methods that have been previously employed are limited because they rely on several assumptions and are not applicable for certain formulations of drug carriers. In this entry, we presented simple mathematical equations for the calculation of particle size and surface area of a whole range of bioactive encapsulation systems. Employing data on these characteristics of solid and soft drug carriers will assist in the optimization of formulations intended for pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and skincare applications.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the compilation and editing of the text and tables, as well as graphical designs of figures of this article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, J.; Wu, S.H.; Herman, C.J. Combinational Liposome Compositions for Cancer Therapy. U.S. Patent 16/279,977, 8 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, M.; Khan, H.U.; Afzal, S.; Majeed, A.; Iqbal, N.; Afzal, K.; Andleeb, M.; Rauf, A.; Farooq, A. Formulation, characterization and optimization of nebivolol-loaded sustained release lipospheres. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R.; Johnson, C.; Hatziantoniou, S.; Demetzos, C. Nanoliposomes and Their Applications in Food Nanotechnology. J. Liposome Res. 2008, 18, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemnejad, S.M.; Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Zarket, B.; Castaneda, C.R.; Doyle, P.S. Thermoresponsive nanoemulsion-based gel synthesized through a low-energy process. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Ronchi, M.; Petrangolini, G.; Bosisio, S.; Allegrini, P. Improved Oral Absorption of Quercetin from Quercetin Phytosome®, a New Delivery System Based on Food Grade Lecithin. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 44, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokhodchi, A.; Jelvehgari, M.; Siahi, M.R.; Mozafari, M.R. Factors affecting the morphology of benzoyl peroxide microsponges. Micron 2007, 38, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnani, G.P.; Bahekar, J.; Kokare, C.R. Development of novel pH–responsive dual crosslinked hydrogel beads based on Portulaca oleracea polysaccharide-alginate-borax for colon specific delivery of 5-fluorouracil. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnani, G.P.; Kokare, C.R. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of colon cancer targeted epichlorohydrin crosslinked Portulaca-alginate beads. Biomol. Concepts 2018, 9, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moku, G.; Layek, B.; Trautman, L.; Putnam, S.; Panyam, J.; Prabha, S. Improving Payload Capacity and Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using TAT Peptide Functionalized Polymeric Nanoparticles. Cancers 2019, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, I.; Parizi, M.H.; Farajzadeh, S.; Pardakhty, A.; Parizi, M.D.; Sharifi, H.; Keyhani, A.; Mostafavi, M.; Bamorovat, M.; Khosravi, A.; et al. Tioxolone niosomes exert antileishmanial effects on Leishmania tropica by promoting promastigote apoptosis and immunomodulation. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2019, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.; Javanmard, R.; Raji, M. Tocosome: Novel drug delivery system containing phospholipids and tocopheryl phosphates. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrabi, A.; Alipoor Amro Abadi, M.; Khorasani, S.; Mohammadabadi, M.; Jamshidi, A.; Torkaman, S.; Taghavi, E.; Mozafari, M.R.; Rasti, B. Nanoliposomes and tocosomes as multifunctional nanocarriers for the encapsulation of nutraceutical and dietary molecules. Molecules 2020, 25, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R.; Reed, C.J.; Rostron, C.; Kocum, C.; Piskin, E. Formation and characterisation of non-toxic anionic liposomes for delivery of therapeutic agents to the pulmonary airways. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2002, 7, 243–244. [Google Scholar]
- ElMeshad, A.N.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Mozafari, M.R. Formulation and characterization of nanoliposomal 5-fluorouracil for cancer nanotherapy. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, H.; Afergan, E.; Moise, T.; Richter, Y.; Rudich, Y.; Golomb, G. Number-concentration of nanoparticles in liposomal and polymeric multiparticulate preparations: Empirical and calculation methods. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Davarani, F.H.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, M.; Kalantari, M.; Raji, M.; Fekri, H.S.; Saber, R.; Asnani, G.; Mortazavi, S.; Mozafari, M.; Rasti, B.; Taheriazam, A. Probing nanoliposomes using single particle analytical techniques: Effect of excipients, solvents, phase transition and zeta potential. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkiewicz, P.; Okruszek, A.; Hof, M.; Langner, M. Associating oligonucleotides with positively charged liposomes. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2003, 8, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saveyn, H.; De Baets, B.; Thas, O.; Hole, P.; Smith, J.; Van der Meeren, P. Accurate particle size distribution determination by nanoparticle tracking analysis based on 2-D Brownian dynamics simulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, V.; Hawe, A.; Jiskoot, W. Critical Evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the Measurement of Nanoparticles and Protein Aggregates. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.N.D.M.; Couto, V.M.; Fraceto, L.F.; De Paula, E. Use of nanoparticle concentration as a tool to understand the structural properties of colloids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, V.V.; Siwale, R.; Singh, A.K.; Mody, H.R. Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinterwirth, H.; Wiedmer, S.K.; Moilanen, M.; Lehner, A.; Allmaier, G.; Waitz, T.; Lindner, W.; Lämmerhofer, M. Comparative method evaluation for size and size-distribution analysis of gold nanoparticles. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakumar, G.; Gomathi, T.; Rahuman, A.A.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Mydhili, G.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, T.-J.; Chung, I.-M. Biosynthesis and Biomedical Applications of Gold Nanoparticles Using Eclipta prostrata Leaf Extract. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucic, R.C.; Storhoff, J.J.; Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L. DNA-Directed Synthesis of Binary Nanoparticle Network Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12674–12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hussain, I.; Brust, M.; Cooper, A.I. Emulsion-Templated Gold Beads Using Gold Nanoparticles as Building Blocks. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarutti, C.; Raj, G.; Fogolari, F.; Giorgetti, S.; Corazza, A.; Bellotti, V.; Esposito, G. Interference of cit-rate-stabilized gold nanoparticles with β2-microglobulin oligomeric association. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5422–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Pan, D.; Cai, X.; Yang, X.; Senpan, A.; Allen, J.S.; Lanza, G.M.; Wang, L.V. ανβ3-targeted Copper Nanoparticles Incorporating an Sn 2 Lipase-Labile Fumagillin Prodrug for Photoacoustic Neovascular Imaging and Treatment. Theranostics 2015, 5, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Siddiqui, M. Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoabediny, G.; Haghiralsadat, F.; Naderinezhad, S.; Helder, M.N.; Akhoundi Kharanaghi, E.; Mohammadnejad Arough, J.; Zandieh-Doulabi, B. Overview of preparation methods of polymeric and lipid-based (niosome, solid lipid, lip-osome) nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2018, 67, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R. Nanoliposomes: Preparation and analysis. In Liposomes; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 29–50. [Google Scholar]
- Maherani, B.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Mozafari, M.R.; Gaiani, C.; Linder, M. Liposomes: A Review of Manufacturing Techniques and Targeting Strategies. Curr. Nanosci. 2011, 7, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveling, E.; Zhou, J.; Lim, Y.F.; Mozafari, M.R. Targeting lipidic nanocarriers: Current strategies and problems. Pharmakeftiki 2006, 19, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchell, D. A model for the packing of lipids in bilayer membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1975, 389, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edholm, O.; Nagle, J.F. Areas of Molecules in Membranes Consisting of Mixtures. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapay, N.; Bennett, W.F.D.; Tieleman, D.P. Thermodynamics of flip-flop and desorption for a systematic series of phosphatidylcholine lipids. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3295–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidgeon, C.; Hunt, C.A.; Huntx, C. Calculating Number and Surface Area of Liposomes in Any Suspension. J. Pharm. Sci. 1981, 70, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kwak, D.B.; Kim, S.C.; Pui, D.Y. Characterization of colloidal nanoparticles in mixtures with poly-disperse and multimodal size distributions using a particle tracking analysis and electrospray-scanning mobility particle sizer. Powder Technol. 2019, 355, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwak, M.; Song, N.W.; Kim, J. Effect of colloidal nanoparticle concentration on sizing analysis with an electrospray scanning mobility particle sizer. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).