The major chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Thin layer chromatography and column chromatography were performed using Merck 60 F254 silica gel and 60 (70–230 mesh) silica gel, respectively (Darmstadt, Germany). FT-IR spectroscopy was conducted using a Bruker ALPHA spectrometer with Ge-ATR (Billerica, MA, USA). 1H- and 13C-NMR analysis was carried out using a JEOL JNM ECS-400 spectrometer (Tokyo, Japan) in deuterated chloroform at 400 MHz. Mass spectroscopy was performed on an Agilent 5977B MSD-7890 GC System (Santa Clara, CA, USA). High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) was carried out using Waters Xevo QToF MS (Milford, MA, USA). Melting points were measured using a Fisher-Johns apparatus and are uncorrected. All commercial reagents and solvents used were of analytical grade.
2.1. Synthesis of 3,4-Dimethoxy-β-Nitrostyrene Derivatives
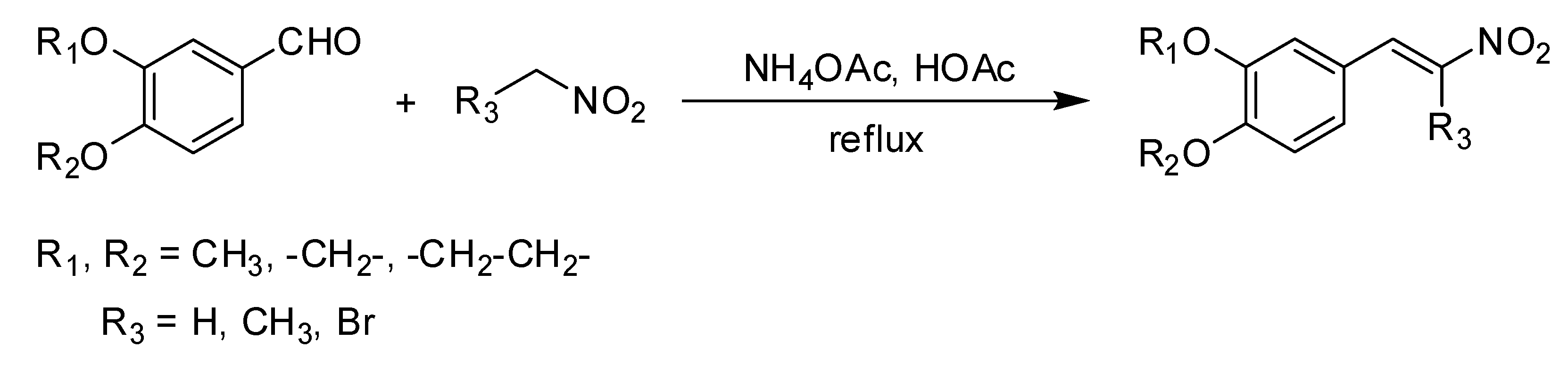
2.1.1. Synthesis of β-Nitrostyrene Series
The methods of Mee et al. [
19], were slightly modified and adapted for the synthesis of the compounds. The corresponding aldehyde was dissolved in stirred glacial acetic acid. Ammonium acetate and nitromethane (
p = 1.14 g/cm
3) were added, then the mixture was refluxed while stirring for 2 h at 50 °C (reaction progress monitored by TLC). The dark orange mixture was cooled to room temperature, and distilled water was added. The crude orange product was filtered off, washed with water, then extracted with dichloromethane. The phase of organic extract was dried over MgSO
4, filtered, and evaporated under a vacuum. The yellow solid was recrystallized twice from ethanol to yield the product, with the melting point being determined and identified through spectrometric analysis.
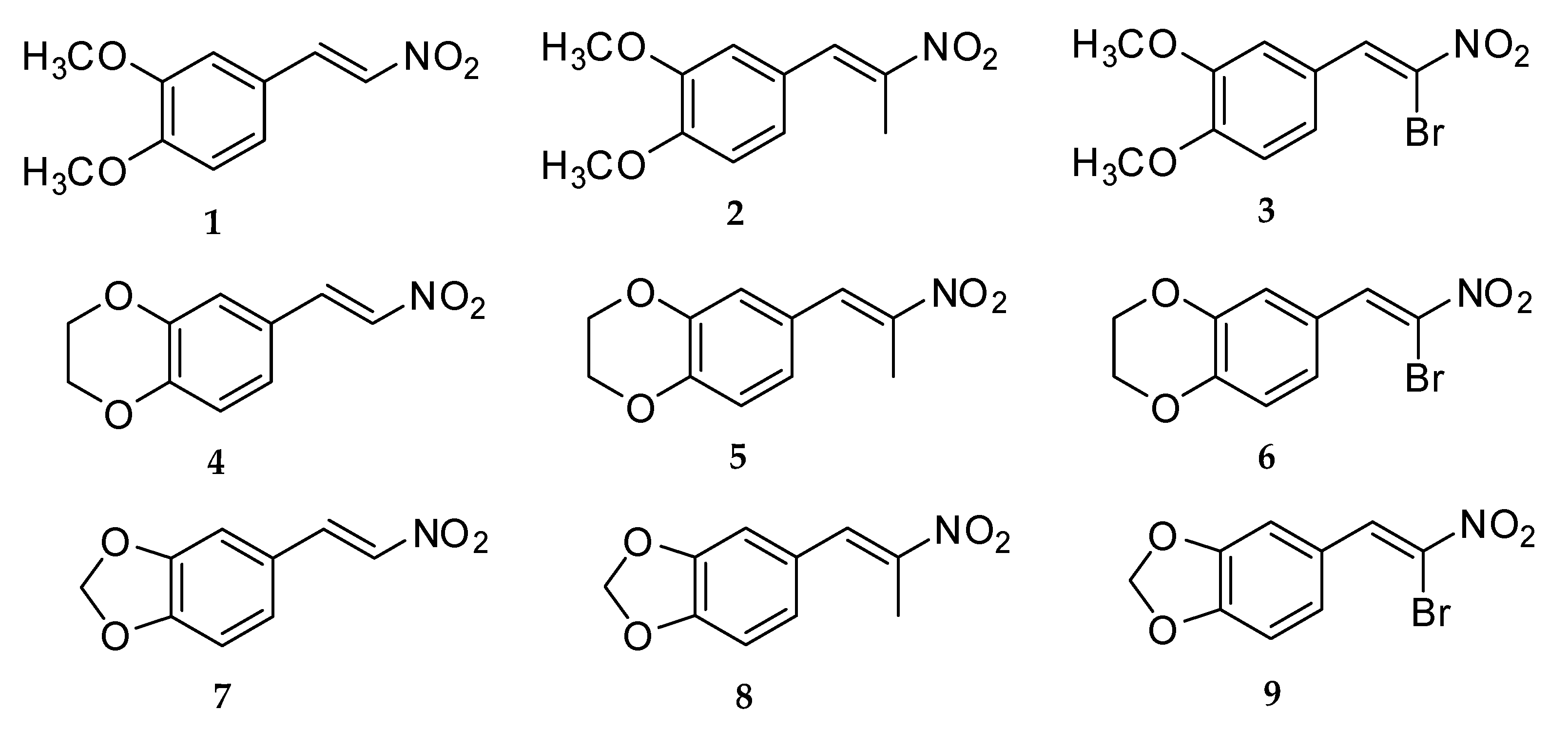
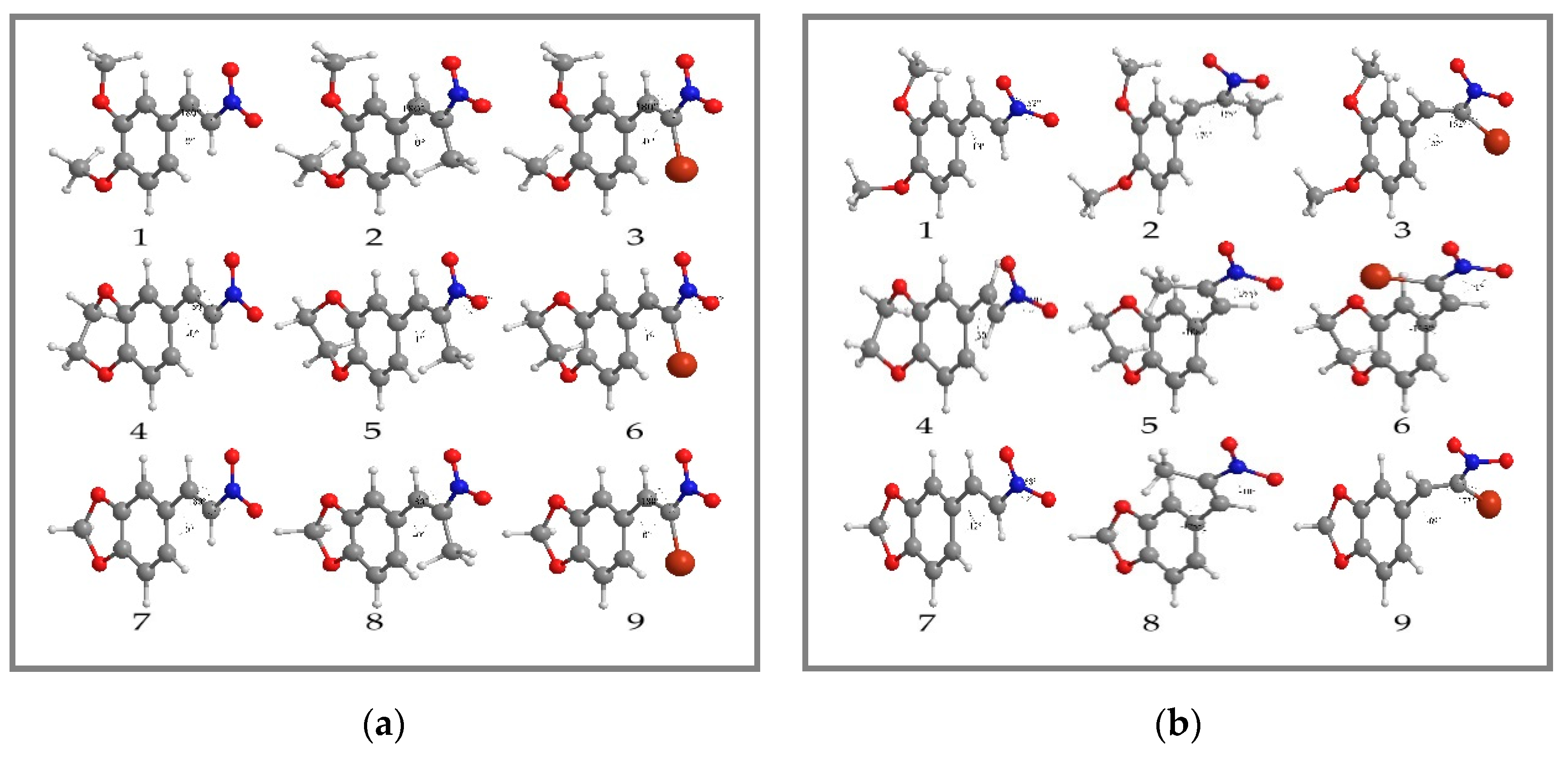
Compound 1: A mixture of 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (2.29 g, 14 mmol) and nitromethane (15.96 g, 256 mmol) with ammonium acetate (3.70 g, 48 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (5 mL) was reacted, and light yellow crystals were obtained, 1.48 g, 50.5% yield, mp 139 °–141 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1491 (asymmetric NO2), 1358 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 7.94 (1H, d, J = 13.6 Hz, H-β), 7.52 (1H, d, J = 13.6 Hz, H-α), 7.16 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, 8.0 Hz, H-6), 6.99 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-2), 6.89 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-5), 3.92 (3H, s, C3-OCH3), 3.91 (3H, s, C4-OCH3); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 152.9 (C-3), 149.6 (C-4), 139.4 (C-α), 135.2 (C-β), 124.7 (C-1), 122.9 (C-6), 111.4 (C-5), 110.3 (C-2), 56.2 (C3-OCH3), 56.1 (C4-OCH3); GC/MS m/z (%): 209 (M, 100), 162 (51), 119 (14), 91 (16). HRMS: C10H11NO4Na [M+Na]+; calculated: 232.0586, found: 232.0604.
Compound 4: A mixture of 3,4-ethylenedioxybenzaldehyde (1.29 g, 8 mmol) and nitromethane (9.12 g, 146 mmol) with ammonium acetate (2.11 g, 27.4 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (3 mL) was reacted, and light yellow crystals were obtained, 1.20 g, 72.5% yield, mp 147 °–149 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1509 (asymmetric NO2), 1338 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 7.89 (1H, d, J = 13.2 Hz, H-β), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 13.6 Hz, H-α), 7.06 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-2), 7.05 (1H, d, J = 6.8 Hz, H-5), 6.90 (1H, dd, J = 2.4, 6.4 Hz, H-6), 4.33-4.27 (2H, m, C3-OCH2), 4.33–4.27 (2H, m, C4-OCH2); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 147.5 (C-4), 144.1 (C-3), 139.1 (C-α), 135.6 (C-β), 123.6 (C-1), 123.5 (C-6), 118.4 (C-5), 117.9 (C-2), 64.8 (C3-OCH2), 64.2 (C4-OCH2); GC/MS m/z (%): 207 (M, 100), 160 (66), 89 (26), 77 (19). HRMS: C10H9NO4Na [M+Na]+; calculated: 230.0429, found: 230.0439.
Compound 7: A mixture of 3,4-methylenedioxybenzaldehyde (1.18 g, 8 mmol) and nitromethane (9.12 g, 146 mmol) with ammonium acetate (2.11 g, 27.4 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (4 mL) was reacted, and brownish yellow crystals were obtained, 0.80 g, 52% yield, mp 158 °–160 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1492 (asymmetric NO2), 1332 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 7.91 (1H, d, J = 13.6 Hz, H-β), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 13.6 Hz, H-α), 7.07 (1H, dd, J = 1.6, 7.6 Hz, H-6), 6.99 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-2), 6.86 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5), 6.05 (2H, s, C3-OCH2O-C4); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 151.5 (C-3), 148.8 (C-4), 139.2 (C-α), 135.5 (C-β), 126.8 (C-1), 124.2 (C-6), 109.2 (C-2), 107.1 (C-5), 102.2 (C3-OCH2O-C4); GC/MS m/z (%): 193 (M, 92), 146 (100), 89 (61), 63 (31). HRMS: C9H7NO4Na [M+Na]+; calculated: 216.0273, found: 216.0269.
2.1.2. Synthesis of β-Methyl-β-Nitrostyrene Series
The corresponding aldehyde was dissolved in stirred glacial acetic acid. Ammonium acetate and nitroethane (p = 1.045 g/cm3) were added, then the mixture was refluxed while stirring for 2 h at 50 °C (reaction progress monitored by TLC). The dark orange mixture was then cooled to room temperature, extracted with dichloromethane, and washed with distilled water. The layer of organic extract was dried over MgSO4 then filtered and concentrated under a vacuum. The crude orange solid was recrystallized twice from ethanol to yield the product, with the melting point determined and identified using spectrometric analysis.
Compound 2: A mixture of 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (1.66 g, 10 mmol) and nitroethane (14.63 g, 200 mmol) with ammonium acetate (2.71 g, 35 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (5 mL) was reacted, and light yellow crystals were obtained, 1.26 g, 56.5% yield, mp 66 °–68 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1511 (asymmetric NO2), 1313 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 8.06 (1H, s, H-α), 7.08 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, 8.8 Hz, H-6), 6.94 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-2), 6.93 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-5), 3.93 (3H, s, C3-OCH3), 3.91 (3H, s, C4-OCH3), 2.48 (3H, s, H-γ); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 150.8 (C-3), 149.1 (C-4), 133.9 (C-α), 145.9 (C-β), 125.1 (C-1), 124.1 (C-6), 113.1 (C-5), 111.3 (C-2), 56.1 (C3-OCH3), 56.1 (C4-OCH3), 14.3 (C-γ); GC/MS m/z (%): 223 (M, 100), 176 (51), 131 (25), 91 (16). HRMS: C11H13NO4Na [M+Na]+; calculated: 246.0742, found: 246.0735.
Compound 5: A mixture of 3,4-ethylenedioxybenzaldehyde (0.70 g, 4.3 mmol) and nitroethane (8.36 g, 100 mmol) with ammonium acetate (2.00 g, 26 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (5 mL) was reacted, and light yellow crystals were obtained, 0.28 g, 30.3% yield, mp 73 °–75 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1503 (asymmetric NO2), 1284 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 7.98 (1H, s, H-α), 6.98 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-2), 6.96 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, 8.4 Hz, H-6), 6.91 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz, H-5), 4.32-4.27 (2H, m, C3-OCH2), 4.32–4.27 (2H, m, C4-OCH2), 2.44 (3H, s, H-γ); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 146.2 (C-4), 145.5 (C-3), 133.6 (C-α), 143.7 (C-β), 125.7 (C-1), 124.4 (C-6), 119.2 (C-5), 117.9 (C-2), 64.7 (C3-OCH2), 64.3 (C4-OCH2), 14.2 (C-γ); GC/MS m/z (%): 221 (M, 100), 174 (78), 103 (38), 91 (29). HRMS: C11H11NO4Na [M+Na]+; calculated: 244.0586, found: 244.0575.
Compound 8: A mixture of 3,4-methylenedioxybenzaldehyde (1.50 g, 10 mmol) and nitroethane (14.63 g, 200 mmol) with ammonium acetate (2.71 g, 35 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (5 mL) was reacted and light yellow crystals were obtained, 0.99 g, 47.6% yield, mp 88 °–90 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1508 (asymmetric NO2), 1319 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH(ppm): 8.01 (1H, s,H-α), 6.97 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, 8.0 Hz, H-6), 6.93 (1H, d, J = 1.2 Hz, H-2), 6.88 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5), 6.04 (2H, s, C3-OCH2O-C4), 2.45 (3H, s, H-γ); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 149.4 (C-3), 148.3 (C-4), 133.8 (C-α), 146.2 (C-β), 126.3 (C-1), 126.1 (C-6), 109.6 (C-2), 108.9 (C-5), 101.9 (C3-OCH2O-C4), 14.3 (C-γ); GC/MS m/z (%): 207 (M, 83), 160 (87), 103 (100), 77 (43). HRMS: C10H9NO4Na [M+Na]+; calculated: 230.0429, found: 230.0431.
2.1.3. Synthesis of β-Bromo-β-Nitrostyrene Series
The corresponding aldehyde was dissolved in stirred glacial acetic acid. Ammonium acetate and bromo-nitromethane (p = 2.007 g/cm3) were added, then the mixture was refluxed while stirring for 2 h at 50 °C (reaction progress monitored by TLC). The dark orange mixture was cooled to room temperature then extracted with dichloromethane and washed with distilled water. The organic extracts were dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated under a vacuum. The crude residue was purified using column chromatography over silica gel with eluent of n-hexane-chloroform (1:4) to yield the product with the melting point determined and identified through spectrometric analysis.
Compound 3: A mixture of 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (0.92 g, 5.5 mmol) and bromo-nitromethane (2.01 g, 12.9 mmol) with ammonium acetate (0.70 g, 9 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (1.5 mL) was reacted, and orange crystals were obtained, 0.31 g, 19.6% yield, mp 110 °–112 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1517 (asymmetric NO2), 1307 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 8.63 (1H, s, H-α), 7.59 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz, H-2), 7.51 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, 8.8 Hz, H-6), 6.96 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-5), 3.95 (3H, s, C3-OCH3), 3.93 (3H, s, C4-OCH3); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 152.7 (C-3), 149.0 (C-4), 136.7 (C-α), 127.0 (C-1), 125.5 (C-6), 122.7 (C-β), 112.8 (C-5), 111.1 (C-2), 56.2 (C3-OCH3), 56.1 (C4-OCH3); GC/MS m/z (%): 289 (M, 81Br, 55), 287 (M, 79Br, 56), 162 (100), 147 (45), 91 (29). HRMS, C10H10NO4NaBr [M+Na]+; calculated: 309.9691, found: 309.9687.
Compound 6: A mixture of 3,4-ethylenedioxybenzaldehyde (0.90 g, 5.5 mmol) and bromo-nitromethane (2.61 g, 17 mmol) with ammonium acetate (0.70 g, 9 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (2 mL) was reacted, and light yellow crystals were obtained, 0.90 g, 57.3% yield, mp 129 °–131 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1509 (asymmetric NO2), 1277 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 8.55 (1H, s, H-α), 7.59 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-2), 7.39 (1H, dd, J = 2.4, 8.8 Hz, H-6), 6.95 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz, H-5), 4.34–4.28 (2H, m, C3-OCH2), 4.34-4.28 (2H, m, C4-OCH2); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 147.4 (C-4), 143.7 (C-3), 136.3 (C-α), 126.3 (C-1), 125.9 (C-β), 123.3 (C-6), 119.8 (C-5), 117.9 (C-2), 64.8 (C3-OCH2), 64.2 (C4-OCH2); GC/MS m/z (%): 287 (M, 81Br, 51), 285 (M, 79Br, 53), 160 (100), 104 (45), 76 (35). HRMS: C10H8NO4NaBr [M+Na]+; calculated: 307.9534, found: 307.9537.
Compound 9: A mixture of 3,4-methylenedioxybenzaldehyde (1.66 g, 11 mmol) and bromo-nitromethane (4.82 g, 30 mmol) with ammonium acetate (1.4 g, 18 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (4 mL) was reacted, and brown crystals were obtained, 0.61 g, 20.3% yield, mp 93 °–95 °C. FT-IR (ATR; υ, cm−1): 1495 (asymmetric NO2), 1295 (symmetric NO2); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δH (ppm): 8.58 (1H, s, H-α), 7.62 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-2), 7.34 (1H, dd, J = 1.2, 8.0 Hz, H-6), 6.91 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5), 6.08 (2H, s, C3-OCH2O-C4); 13C NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δC (ppm): 151.2 (C-3), 148.3 (C-4), 136.5 (C-α), 129.1 (C-1), 125.8 (C-6), 124.1 (C-β), 109.4 (C-2), 108.9 (C-5), 102.2 (C3-OCH2O-C4); GC/MS m/z (%): 273 (M, 81Br, 32), 271 (M, 79Br, 32), 226 (81Br, 30), 224 (79Br, 30), 146 (100). HRMS: C9H6NO4NaBr [M+Na]+; calculated: 293.9378, found: 293.9382.