Structural Insight into the In Vitro Anti-Intravasative Properties of Flavonoids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. 3D Co-Cultivation of MCF-7 Cancer Cells with LECs
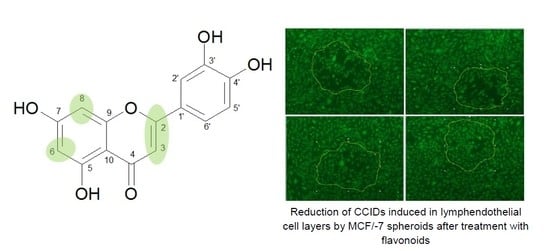
2.4. Circular Chemo-Repellent Induced Defect (CCID) Assay
2.5. Statistical Analyses
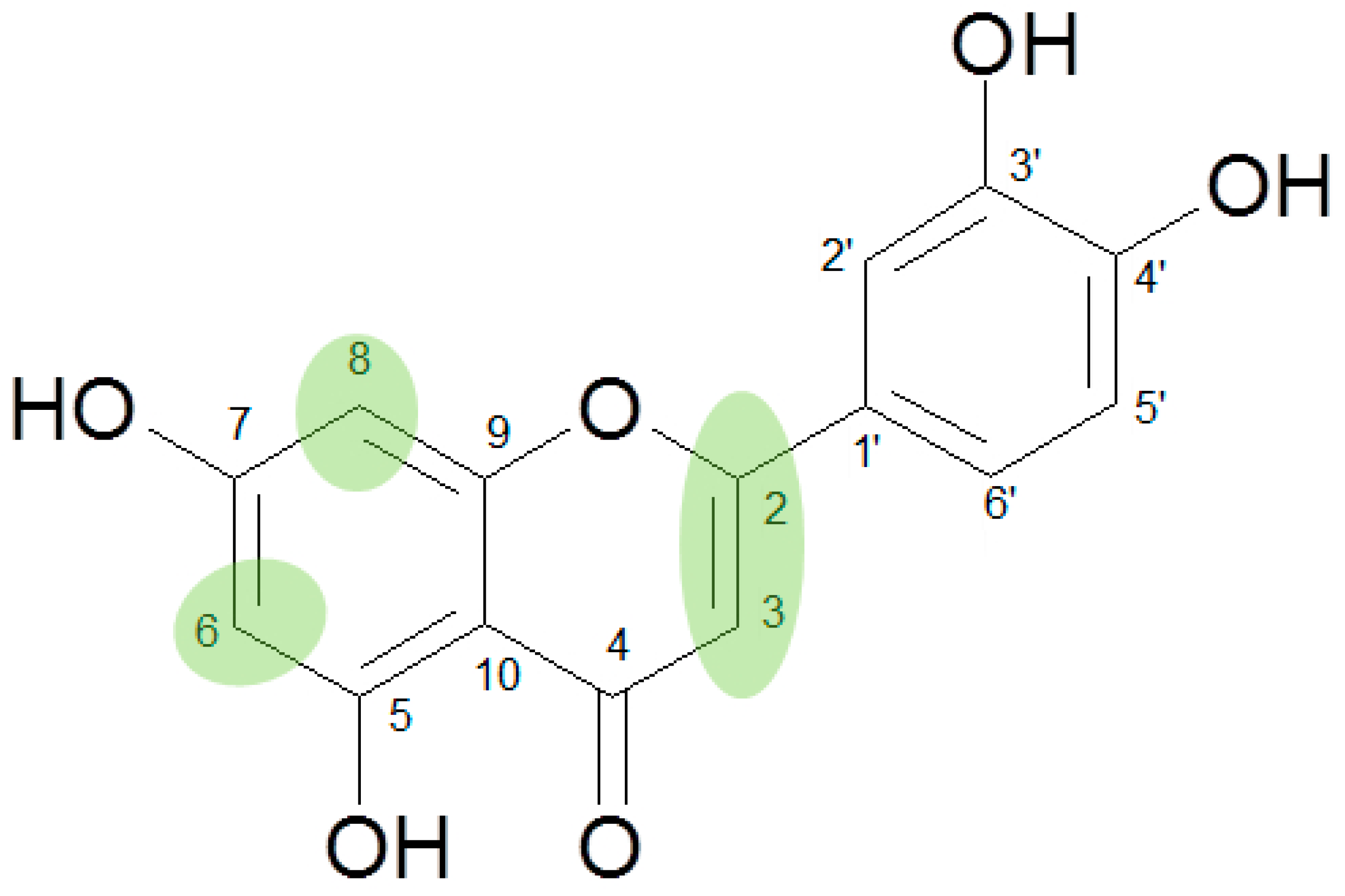
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madlener, S.; Saiko, P.; Vonach, C.; Viola, K.; Huttary, N.; Stark, N.; Popescu, R.; Gridling, M.; Vo, N.T.; Herbacek, I.; et al. Multifactorial anticancer effects of digalloyl-resveratrol encompass apoptosis, cell-cycle arrest, and inhibition of lymphendothelial gap formation in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonach, C.; Viola, K.; Giessrigl, B.; Huttary, N.; Raab, I.; Kalt, R.; Krieger, S.; Vo, T.P.; Madlener, S.; Bauer, S.; et al. NF-kappaB mediates the 12(S)-HETE-induced endothelial to mesenchymal transition of lymphendothelial cells during the intravasation of breast carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, K.; Kopf, S.; Huttary, N.; Vonach, C.; Kretschy, N.; Teichmann, M.; Giessrigl, B.; Raab, I.; Stary, S.; Krieger, S.; et al. Bay11-7082 inhibits the disintegration of the lymphendothelial barrier triggered by MCF-7 breast cancer spheroids; the role of ICAM-1 and adhesion. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özmen, A.; Bauer, S.; Gridling, M.; Singhuber, J.; Krasteva, S.; Madlener, S.; Vo, T.P.N.; Stark, N.; Saiko, P.; Fritzer-Szekeres, M.; et al. In vitro anti-neoplastic activity of the ethno-pharmaceutical plant Hypericum adenotrichum Spach endemic to Western Turkey. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 22, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gridling, M.; Popescu, R.; Kopp, B.; Wagner, K.H.; Krenn, L.; Krupitza, G. Anti-leukaemic effects of two extract types of Lactuca sativa correlate with the activation of Chk2, induction of p21, downregulation of cyclin D1 and acetylation of α-tubulin. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozmen, A.; Madlener, S.; Bauer, S.; Krasteva, S.; Vonach, C.; Giessrigl, B.; Gridling, M.; Viola, K.; Stark, N.; Saiko, P.; et al. In vitro anti-leukemic activity of the ethno-pharmacological plant Scutellaria orientalis ssp. carica endemic to western Turkey. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessrigl, B.; Yazici, G.; Teichmann, M.; Kopf, S.; Ghassemi, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Dirsch, V.M.; Grusch, M.; Jäger, W.; Özmen, A.; et al. Effects of Scrophularia extracts on tumor cell proliferation, death and intravasation through lymphoendothelial cell barriers. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewenhofer, V.; Schweighofer, L.; Ledermüller, T.; Eichsteininger, J.; Kählig, H.; Zehl, M.; Nguyen, C.H.; Krupitza, G.; Özmen, A.; Krenn, L. Chemical Composition of Scrophularia lucida and the Effects on Tumor Invasiveness in Vitro. Front Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravishankar, D.; Rajora, A.K.; Greco, F.; Osborn, H.M. Flavonoids as prospective compounds for anti-cancer therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, C.J.; Yen, G.C. Flavonoids, a ubiquitous dietary phenolic subclass, exert extensive in vitro anti-invasive and in vivo anti-metastatic activities. Cancer Metastasis. Rev. 2012, 31, 323–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, M.; Scherzer, M.; Walter, S.; Holzner, S.; Pudelko, K.; Riedl, A.; Unger, C.; Kramer, N.; Weil, B.; Neesen, J.; et al. Exclusion from spheroid formation identifies loss of essential cell-cell adhesion molecules in colon cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerjaschki, D.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Rudas, M.; Sexl, V.; Schneckenleithner, C.; Wolbank, S.; Bartel, G.; Krieger, S.; Kalt, R.; Hantusch, B.; et al. Lipoxygenase mediates invasion of intrametastatic lymphatic vessels and propagates lymph node metastasis of human mammary carcinoma xenografts in mouse. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2000–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzner, S.; Brenner, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Senfter, D.; Stadler, S.; Nguyen, C.H.; Fristiohady, A.; Milovanovic, D.; Huttary, N.; Krieger, S.; et al. Intravasation of SW620 colon cancer cell spheroids through the blood endothelial barrier is inhibited by clinical drugs and flavonoids in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 111, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, S.; Nguyen, C.H.; Schachner, H.; Milovanovic, D.; Holzner, S.; Brenner, S.; Eichsteininger, J.; Stadler, M.; Senfter, D.; Krenn, L.; et al. Colon cancer cell-derived 12(S)-HETE induces the retraction of cancer-associated fibroblast via MLC2, RHO/ROCK and Ca(2+) signalling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Fristiohady, A.; Nguyen, C.H.; Milovanovic, D.; Huttary, N.; Krieger, S.; Hong, J.; Geleff, S.; Birner, P.; Jager, W.; et al. Apigenin and Luteolin Attenuate the Breaching of MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Spheroids Through the Lymph Endothelial Barrier in Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chang, E.; Cherry, A.M.; Bangs, C.D.; Oei, Y.; Bodnar, A.; Bronstein, A.; Chiu, C.P.; Herron, G.S. Human endothelial cell life extension by telomerase expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26141–26148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoppmann, S.F.; Kalt, R.; Okubo, Y.; Benisch, C.; Nagavarapu, U.; Herron, G.S.; Geleff, S. Telomerase-immortalized lymphatic and blood vessel endothelial cells are functionally stable and retain their lineage specificity. Microcirculation 2004, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ci, Y.; Qiao, J.; Han, M. Molecular Mechanisms and Metabolomics of Natural Polyphenols Interfering with Breast Cancer Metastasis. Molecules 2016, 21, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.A.; Hwang, K.A.; Choi, K.C. Roles of Dietary Phytoestrogens on the Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Diverse Cancer Metastasis. Toxins 2016, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badolato, M.; Carullo, G.; Cione, E.; Aiello, F.; Caroleo, M.C. From the hive: Honey, a novel weapon against cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, F.; Armentano, B.; Polera, N.; Carullo, G.; Loizzo, M.R.; Bonesi, M.; Cappello, M.S.; Capobianco, L.; Tundis, R. From Vegetable Waste to New Agents for Potential Health Applications: Antioxidant Properties and Effects of Extracts, Fractions and Pinocembrin from Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Aerial Parts on Viability of Five Human Cancer Cell Lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7944–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogiatzoglou, A.; Mulligan, A.A.; Lentjes, M.A.; Luben, R.N.; Spencer, J.P.; Schroeter, H.; Khaw, K.T.; Kuhnle, G.G. Flavonoid intake in European adults (18 to 64 years). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.D.; Kim, J. Dietary flavonoid intake and risk of stomach and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, C.; Qi, X.; Qianyong, Z.; Xiaoli, P.; Jundong, Z.; Mantian, M. Flavonoids, flavonoid subclasses and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Li, L.P.; Luo, S.Q.; Jiang, H.D.; Zeng, S. Intestinal absorption of luteolin from peanut hull extract is more efficient than that from individual pure luteolin. J. Agric Food Chem. 2008, 56, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Song, J.; Cheng, X.D.; Jiang, J.; Jia, X.B. Enhanced bioavailability of apigenin via preparation of a carbon nanopowder solid dispersion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2327–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.P.; Chen, A.L.; Hung, H.C.; Chien, Y.H.; Huang, J.S.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, C.N. Chrysin: A histone deacetylase 8 inhibitor with anticancer activity and a suitable candidate for the standardization of Chinese propolis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11748–11758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Sakurai, H.; Abdelhamed, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Maruyama, T.; Athikomkulchai, S.; Viriyaroj, A.; Awale, S.; Yagita, H.; Ruchirawat, S.; et al. A flavonoid chrysin suppresses hypoxic survival and metastatic growth of mouse breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Lim, H.K.; Shim, S.H.; Jung, J. Improved chemotherapeutic efficacy of injectable chrysin encapsulated by copolymer nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Xiang, T.; Yin, X.; Luo, X.; Huang, J.; Luo, F.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Ren, G. Chrysin inhibits metastatic potential of human triple-negative breast cancer cells by modulating matrix metalloproteinase-10, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Lian, S.; Khoi, P.N.; Yoon, H.J.; Joo, Y.E.; Chay, K.O.; Kim, K.K.; Do Jung, Y. Chrysin inhibits tumor promoter-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking AP-1 via suppression of ERK and JNK pathways in gastric cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, P.J.; Beale, P.; Noney, L.; Liddell, S.; Rivory, L.P.; Clarke, S. A pilot study on the safety of combining chrysin, a non-absorbable inducer of UGT1A1, and irinotecan (CPT-11) to treat metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrutha, K.; Nanjan, P.; Shaji, S.K.; Sunilkumar, D.; Subhalakshmi, K.; Rajakrishna, L.; Banerji, A. Discovery of lesser known flavones as inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells--A SAR study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4735–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Mastriani, E.; Li, Q.H.; Bao, H.X.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Main components of pomegranate, ellagic acid and luteolin, inhibit metastasis of ovarian cancer by down-regulating MMP2 and MMP9. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attoub, S.; Hassan, A.H.; Vanhoecke, B.; Iratni, R.; Takahashi, T.; Gaben, A.M.; Bracke, M.; Awad, S.; John, A.; Kamalboor, H.A.; et al. Inhibition of cell survival, invasion, tumor growth and histone deacetylase activity by the dietary flavonoid luteolin in human epithelioid cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 651, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Senfter, D.; Basilio, J.; Holzner, S.; Stadler, S.; Krieger, S.; Huttary, N.; Milovanovic, D.; Viola, K.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; et al. NF-κB contributes to MMP1 expression in breast cancer spheroids causing paracrine PAR1 activation and disintegrations in the lymph endothelial barrier in vitro. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 39262–39275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Kuang, G.; Wan, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Gong, X.; Li, H. Luteolin suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by reversing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via downregulation of beta-catenin expression. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, H.G.; Wang, X.H.; Zhong, W.L.; Chen, S.; Gu, W.G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.H.; Liu, Y.R.; et al. Apigenin inhibits NF-κB and snail signaling, EMT and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41421–41431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmeyer, F.; Li, H.; Menashi, S.; Soria, C.; Lu, H. Apigenin acts on the tumor cell invasion process and regulates protease production. Nutr. Cancer 2001, 39, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.F.; Rao, Y.K.; Tzeng, Y.M. Aqueous extract of Anisomeles indica and its purified compound exerts anti-metastatic activity through inhibition of NF-kappaB/AP-1-dependent MMP-9 activation in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Ong, C.N.; Yang, X.F.; Shen, H.M. Chrysin sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis in human tumor cells via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB. Cancer Lett. 2010, 293, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.F.; Xu, N.N.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Guo, M.Y. Luteolin reduces inflammation in Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis by inhibiting NF-kB activation and MMPs expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28481–28493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T. Methylation of dietary flavones increases their metabolic stability and chemopreventive effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5002–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Miao, H.; Zhu, R. Diosmetin inhibits the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.A.; Choi, K.C.; Hwang, K.A. Kaempferol, a phytoestrogen, suppressed triclosan-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastatic-related behaviors of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.; Yu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yin, X. Inhibitory effects of kaempferol on the invasion of human breast carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.F.; Yao, X. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of galangin on breast cancer metastasis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2016, 47, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.C.; Kim, M.E.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, P.R.; Youn, H.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of galangin on lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages via ERK and NF-κB pathway regulation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 36, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, O.; Nass, J.; Saeed, M.E.M.; Schuler, B.; Efferth, T. Kaempferol is an anti-inflammatory compound with activity towards NF-ℵB pathway proteins. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar]
- Barve, A.; Chen, C.; Hebbar, V.; Desiderio, J.; Saw, C.L.; Kong, A.N. Metabolism, oral bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of chemopreventive kaempferol in rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2009, 30, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Tan, Y.F.; Li, H.L.; Qin, Z.M.; Cai, H.D.; Lai, W.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, Y.H.; Guan, W.W.; Li, Y.B.; et al. Differential systemic exposure to galangin after oral and intravenous administration to rats. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biteau, F.; Nisse, E.; Hehn, A.; Miguel, S.; Hannewald, P.; Bourgaud, F. A rapid and efficient method for isolating high quality DNA from leaves of carnivorous plants from the Drosera genus. Mol. Biotechnol. 2012, 51, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yao, J.; Wu, X.P.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; You, Q.D.; Guo, Q.L.; Lu, N. Wogonin suppresses human alveolar adenocarcinoma cell A549 migration in inflammatory microenvironment by modulating the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, E81–E93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Song, Y.W.; Cho, S.K. Baicalein Inhibits Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition via Downregulation of Cyr61 and LOXL-2 in MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.L.; Feng, F.; You, Q.D.; Lu, N.; Guo, Q.L. Flavonoid baicalein suppresses adhesion, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 297, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Lu, N.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hui, H.; Lu, Z.; Song, X.; Li, Z.; You, Q.; Guo, Q. Inhibitory effects of wogonin on the invasion of human breast carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Toxicology 2011, 282, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Lu, N.; Li, C.; Li, F.; Zhao, K.; Lin, B.; Guo, Q. Oroxylin A inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 expression and activation by up-regulating tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and suppressing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett. 2012, 209, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yan, W.; Dai, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S. Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Hou, W.C.; Shen, S.C.; Juan, S.H.; Ko, C.H.; Wang, L.M.; Chen, Y.C. Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via suppressing PKC delta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation in breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Chueh, F.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Lin, J.P.; Lien, J.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Chung, J.G. Quercetin inhibits migration and invasion of SAS human oral cancer cells through inhibition of NF-κB and matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 signaling pathways. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Hong, W.; Fan, P.; Qian, D.; Zhu, J.; Bai, B. Quercetin Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igura, K.; Ohta, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Kaji, K. Resveratrol and quercetin inhibit angiogenesis in vitro. Cancer Lett. 2001, 171, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Budhraja, A.; Son, Y.O.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, S.; Wang, L.; Hitron, A.; Lee, J.C.; Xu, M.; et al. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGFR- 2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravishankar, D.; Watson, K.A.; Boateng, S.Y.; Green, R.J.; Greco, F.; Osborn, H.M.I. Exploring quercetin and luteolin derivatives as antiangiogenic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobuchi, H.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K.; Nguyen, H.G.; Packer, L. Quercetin inhibits inducible ICAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells through the JNK pathway. Am. J. Physiol.- Cell Physiol. 1999, 277, C403–C411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyuga, S.; Hyuga, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y.; Goda, Y.; Hanawa, T. Herbacetin, a constituent of ephedrae herba, suppresses the HGF-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting c-Met and Akt phosphorylation. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Brenner, S.; Huttary, N.; Li, Y.; Atanasov, A.G.; Dirsch, V.M.; Holzner, S.; Stadler, S.; Riha, J.; Krieger, S.; et al. 12(S)-HETE increases intracellular Ca(2+) in lymph-endothelial cells disrupting their barrier function in vitro; stabilization by clinical drugs impairing calcium supply. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Flavanones | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Compound | Formula | IC50 µM | logP(o/w) |
| 1 | Pinocembrin | 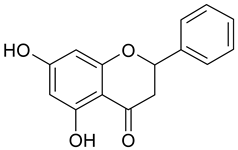 | n.a. | 2.69 |
| 2 | Naringenin | 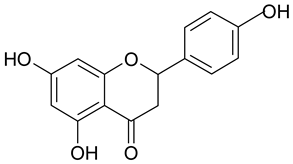 | n.a. | 2.38 |
| 3 | Eriodictyol | 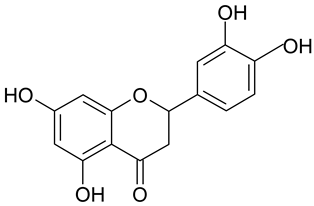 | n.a. | 2.11 |
| 4 | Homoeriodictyol | 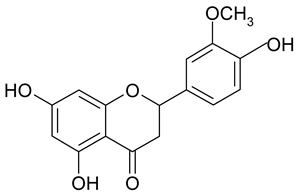 | 99.46 µM | 2.37 |
| Flavones and Flavonols | ||||
| 5 | Chrysin | 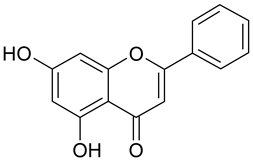 | 24.76 µM | 2.84 |
| 6 | Galangin |  | 39.61 µM | 2.61 |
| 7 | Baicalein | 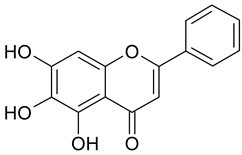 | >100 µM | 2.49 |
| 8 | Oroxylin A | 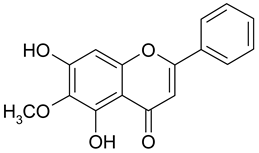 | 74.78 µM | 2.76 |
| 9 | Norwogonin | 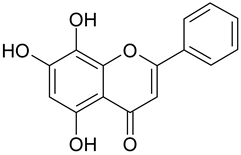 | n.a. | 2.49 |
| 10 | Wogonin |  | >100 µM | 2.76 |
| 11 | Apigenin | 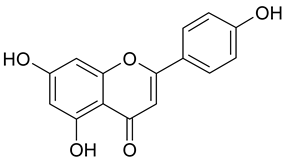 | 34.11 µM | 2.53 |
| 12 | Kämpferol | 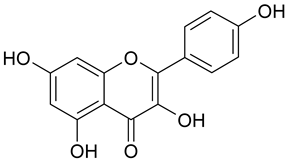 | 44.67 µM | 2.31 |
| 13 | Hispidulin | 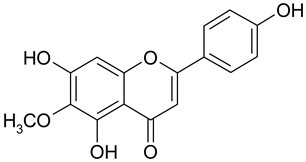 | 88.65 µM | 2.45 |
| 14 | Luteolin |  | 19.31 µM | 2.26 |
| 15 | Diosmetin |  | >100 µM | 2.53 |
| 16 | Nepetin | 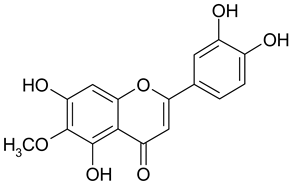 | 78.97 µM | 2.18 |
| 17 | Quercetin | 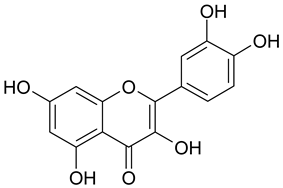 | n.a. | 2.03 |
| 18 | Gossypetin | 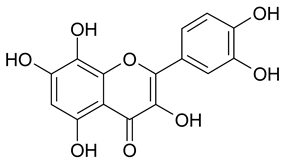 | n.a. | 1.68 |
| No. | Compound | Formula | IC50 µM | logP(o/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | Acacetin | 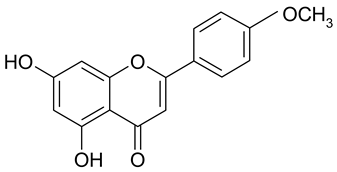 | 36.92 µM | 2.80 |
| 20 | Scutellarein | 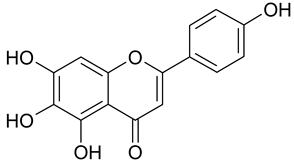 | n.a. | 2.19 |
| 21 | Herbacetin | 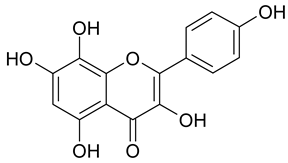 | n.a. | 1.96 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eichsteininger, J.; Kirisits, K.; Smöch, C.; Stadlbauer, C.; Nguyen, C.H.; Jäger, W.; Özmen, A.; Ecker, G.; Krupitza, G.; Krenn, L. Structural Insight into the In Vitro Anti-Intravasative Properties of Flavonoids. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030023
Eichsteininger J, Kirisits K, Smöch C, Stadlbauer C, Nguyen CH, Jäger W, Özmen A, Ecker G, Krupitza G, Krenn L. Structural Insight into the In Vitro Anti-Intravasative Properties of Flavonoids. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2019; 87(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleEichsteininger, Julia, Kerstin Kirisits, Claudia Smöch, Christa Stadlbauer, Chi Huu Nguyen, Walter Jäger, Ali Özmen, Gerhard Ecker, Georg Krupitza, and Liselotte Krenn. 2019. "Structural Insight into the In Vitro Anti-Intravasative Properties of Flavonoids" Scientia Pharmaceutica 87, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030023
APA StyleEichsteininger, J., Kirisits, K., Smöch, C., Stadlbauer, C., Nguyen, C. H., Jäger, W., Özmen, A., Ecker, G., Krupitza, G., & Krenn, L. (2019). Structural Insight into the In Vitro Anti-Intravasative Properties of Flavonoids. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 87(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030023