An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Assays of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and α-Glucosidase Inhibition by Stellasterol from Ganoderma australe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
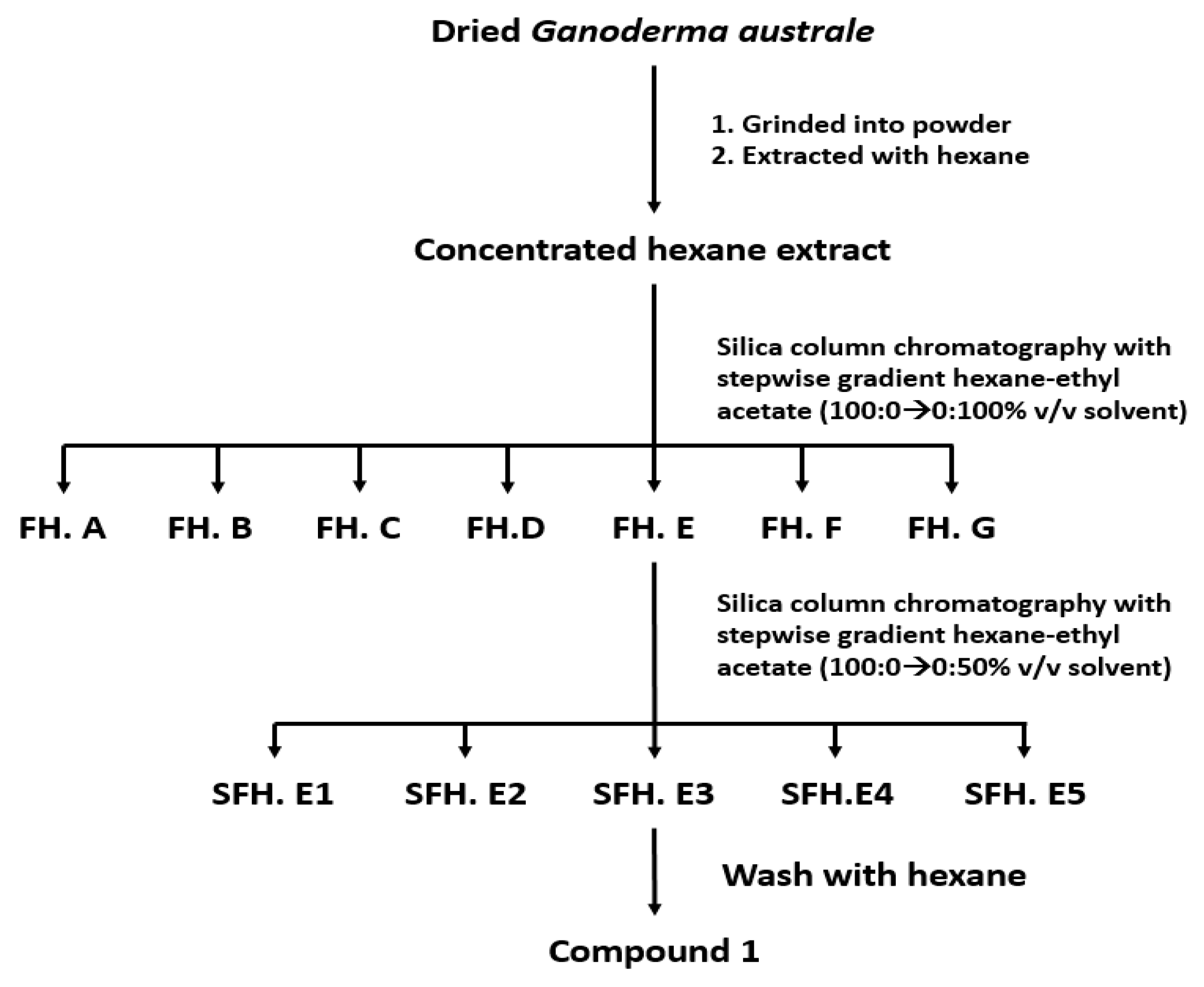
2.2. Extraction and Isolation
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. In Vitro Study of DPP-4 Inhibition
2.5. In Vitro Study of α-Glucosidase Inhibition
2.6. In Silico Study
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
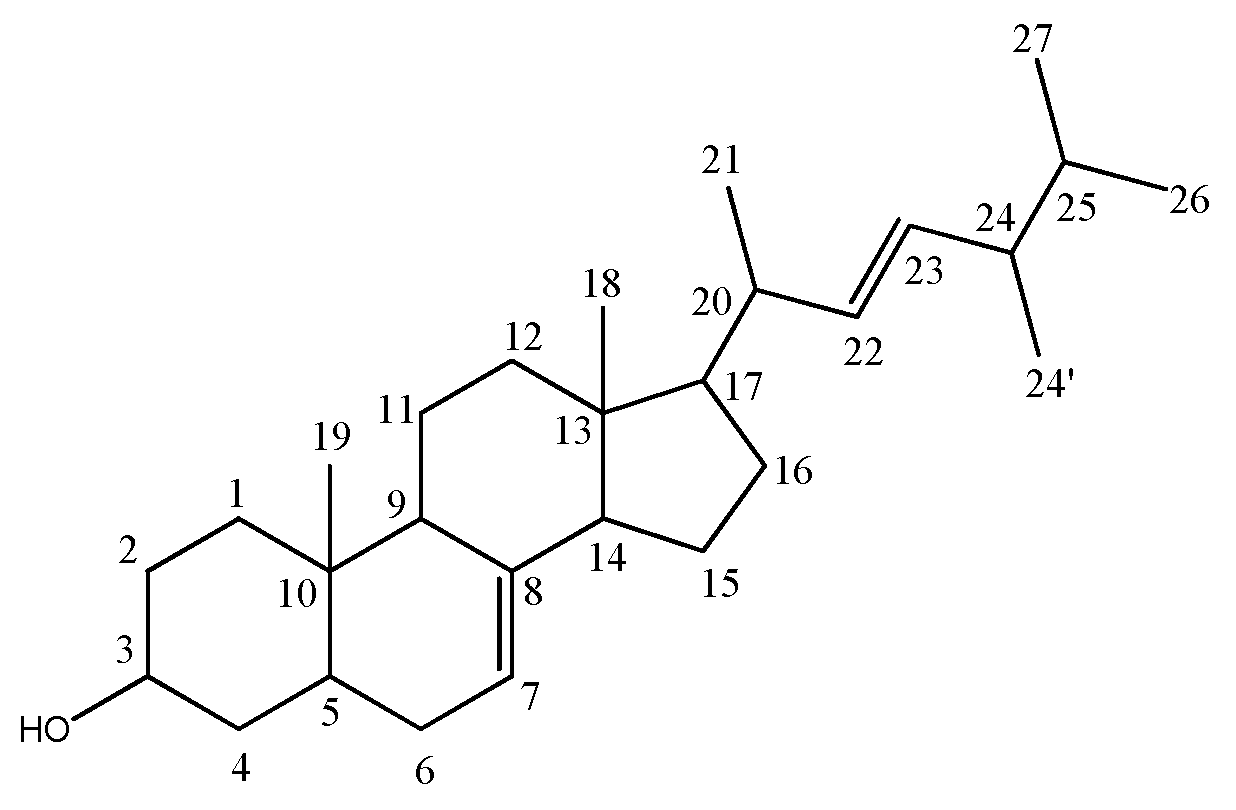
3.1. Structure Elucidation
3.2. Assay of DPP-4 and α-Glucosidase Inhibition
3.3. Stellasterol In Silico Study for DPP-4 Enzyme
3.4. Stellasterol In Silico Study for α-Glucosidase Enzyme
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottlieb, A.M.; Ferrer, E.; Wright, J.E. rDNA analyses as an aid to the taxonomy of species of Ganoderma. Mycol. Res. 2000, 104, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Z. Antihyperglycemic effect of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6135–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatmawati, S.; Shimizu, K.; Kondo, R. Ganoderol B: A potent α-glucosidase inhibitor isolated from the fruiting body of Ganoderma lucidum. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Bao, L.; Xiong, W.; Ma, K.; Han, J.; Wang, W.; Yin, W.; Liu, H. Lanostane triterpenes from the Tibetan medicinal mushroom Ganoderma leucocontextum and their inhibitory effects on HMG-CoA reductase and α-glucosidase. J. Nat. Pro. 2015, 78, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, K.S.; Kao, C.H.; Xu, Y.; Glucina, M.P.; Paterson, R.R.; Ferguson, L.R. From 2000 years of Ganoderma lucidum to recent developments in nutraceuticals. Phytochemistry 2015, 114, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, C.; Wittsein, K.; Kirk, P.M.; Stadler, M. An assessment of the taxonomy and chemotaxonomy of Ganoderma. Fungal Divers. 2015, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J. Treating insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes with metformin and thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2005, 7, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Bridgeman, M.B. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors in the management of diabetes. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Verspohl, E.J. Novel therapeutics for type 2 diabetes: Incretin hormone mimetics (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 124, 113–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Jin, T. The incretin hormone GLP-1 and mechanisms underlying its secretion. J. Diabetes 2016, 8, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Jun, H.S. Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells. Metabolism 2014, 63, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahren, B. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: Clinical data and clinical implications. Diabetes Care. 2007, 30, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, T. Recent advances in non-peptidomimetic dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors: Medicinal chemistry and preclinical aspects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3982–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, R.N.; Haq, W. Sixteen-years of clinically relevant dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors for treatment of type-2 diabetes: A perspective. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K. Trelagliptin: First global approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 1161–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, I.; Mckay, G.; Fisher, M. Omarigliptin. Pract. Diabetes 2017, 34, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, B. DPP-4 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In Progress in Medicine 2017; The Asscociation of Physicians of India: Mumbai, India, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, M.M.; Dias, T. Commonly used endocrine drugs. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 3rd ed.; Biller, J., Ferro, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 120, pp. 809–824. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, R.; Bhavtaran, S.; Narendra, P.; Varghese, N.; Vanchhawng, L.; Hyder, M.S.; Shihabudeen, H.; Thirumurugan, K. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity of Berberis aristata. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 4, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Masri, I.M.; Mohammad, M.K.; Tahaa, M.O. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) is one of the mechanisms explaining the hypoglycemic effect of berberine. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munim, A.; Katrin; Azizahwati; Andriani, A.; Mahmudah, K.F.; Mashita, M. Screening of alpha glucosidase inhibitory activity of some Indonesian medicinal plants. Int. J. Med. Arom. Plants. 2013, 3, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlagdan, M.; de Castro, M.E.; van Altena, I.; Ragasa, C. Sterols from Trametes versicolor. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 740–744. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H.W.; Hung, T.M.; Na, M.; Junga, H.J.; Kim, J.C.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, I.; Bae, K.; et al. Steroids and triterpenes from the fruit bodies of Ganoderma lucidum and their anti-complement activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levita, J.; Rositama, M.R.; Alias, N.; Khalida, N.; Saptarini, N.M.; Megantara, S. Discovering COX-2 inhibitors from flavonoids and diterpenoids. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Marvaniya, H.M.; Patel, H.U. Role of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-4) inhibitor in the management of type 2 diabetes. World J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2017, 6, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, Z.W.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Kong, L.; Wen, X.; Sun, H. Discovery of highly potent DPP-4 inhibitors by hybrid compound design based on linagliptin and alogliptin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 83, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmozhiraja, S.; Matsuo, N.; Ishitsubo, E.; Okazaki, S.; Shimano, H.; Tokiwa, H. Comparative binding analysis of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) with antidiabetic drugs—An Ab Initio fragment molecular orbital study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, M. Teneligliptin: A DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2013, 6, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhotra, P.; Chittepu, V.C.S.R.; Osorio-Revilla, G.; Gallardo-Velázquez, T. Structure—activity relationship and molecular docking of natural product library reveal Chrysin as a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor. Molecules 2018, 23, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhotra, P.; Chittepu, V.C.S.R.; Osorio-Revilla, G.; Gallardo-Velázquez, T. Discovery of galangin as a potential DPP-4 inhibitor that improves insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose uptake: A combinational therapy for diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Jafri, L.; Haq, I.U.; Chang, L.C.; Calderwood, D.; Green, B.D.; Mirza, B. Plants Fagonia cretica L. and Hedera nepalensis K. Koch contain natural compounds with potent dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, T.; Yamashita, K.; Okuyama, M.; Mori, H.; Yao, M.; Kimura, A. Molecular basis for the recognition of long-chain substrates by plant α-glucosidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19296–19303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Tam, N.; Thiện, Đ.; Van Sung, T.; Nguyen, T.H.A.; Thi Thuy, T.; Huu Trung, K.; Dang Xuan, T.; Khanh, T. Evaluation of ursolic acid as the main component isolated from Catharanthus roseus against hyperglycemia. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2016, 50, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagri, P.; Ali, M.; Aeri, V.; Bhowmik, M. Isolation and antidiabetic activity of new lanostenoids from the leaves of Psidium guajava L. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
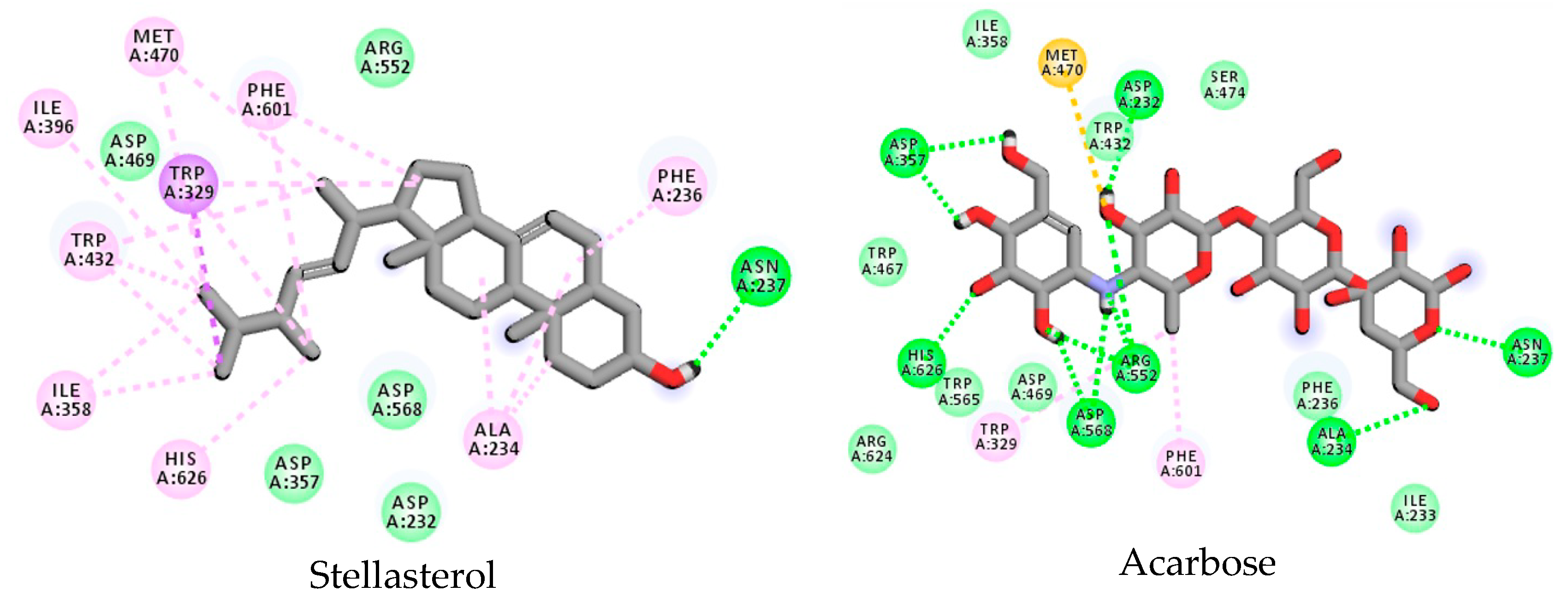
| Ligand | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Bond | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glu206 | Glu205 | Arg358 | Arg125 | Asn710 | Tyr585 | Tyr631 | Tyr547 | Tyr666 | Tyr662 | Val711 | Val656 | Trp659 | Phe357 | |
| Stellasterol | - | - | - | - | - | + | π–alkyl | π–alkyl | π–alkyl | π–alkyl | Alkyl–alkyl | Alkyl–alkyl | π–alkyl | π–alkyl |
| Sitagliptin | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | π-π | π-π | - | - | - | π–π |
| Amino Acid Residues | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2’ | S1’ | S1 | S2 | S2 Ext | |
| Trp629 | Tyr547 | Tyr666 | Arg125 | Phe357 | |
| His740 | Tyr631 | Ser630 | Arg669 | Arg358 | |
| Ser630 | Phe357 | Val656 | Glu205 | Ser209 | |
| Tyr547 | Pro550 | Trp659 | Glu206 | Val207 | |
| Tyr666 | Tyr662 | Phe357 | |||
| Val711 | Arg358 | ||||
| Asn710 | |||||
| Ligand | Hydrogen Bond | Hydrophobic Bond | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arg552 | Asp568 | Asp367 | His626 | Asp232 | Asn237 | Ala234 | Ile358 | Ile233 | Ile396 | Trp467 | Trp329 | Trp432 | Trp329 | Phe601 | Phe236 | Ph3476 | Met470 | |
| Stellasterol | - | - | - | π–alkyl | - | + | π–alkyl | + | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | π–alkyl |
| Acarbose | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | + |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budipramana, K.; Junaidin, J.; Ruslan Wirasutisna, K.; Budi Pramana, Y.; Sukrasno, S. An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Assays of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and α-Glucosidase Inhibition by Stellasterol from Ganoderma australe. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030021
Budipramana K, Junaidin J, Ruslan Wirasutisna K, Budi Pramana Y, Sukrasno S. An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Assays of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and α-Glucosidase Inhibition by Stellasterol from Ganoderma australe. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2019; 87(3):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudipramana, Krisyanti, Junaidin Junaidin, Komar Ruslan Wirasutisna, Yanatra Budi Pramana, and Sukrasno Sukrasno. 2019. "An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Assays of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and α-Glucosidase Inhibition by Stellasterol from Ganoderma australe" Scientia Pharmaceutica 87, no. 3: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030021
APA StyleBudipramana, K., Junaidin, J., Ruslan Wirasutisna, K., Budi Pramana, Y., & Sukrasno, S. (2019). An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Assays of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 and α-Glucosidase Inhibition by Stellasterol from Ganoderma australe. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 87(3), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm87030021




