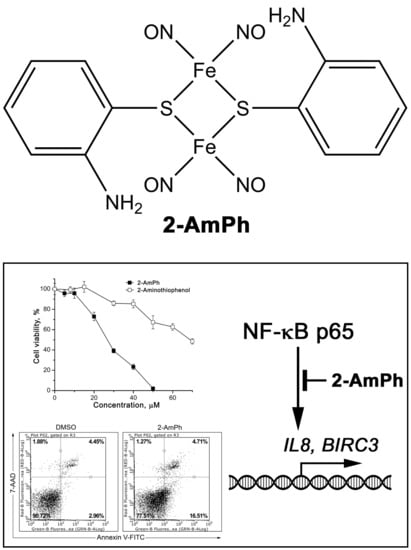
NO-Donor Nitrosyl Iron Complex with 2-Aminophenolyl Ligand Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits NF-κB Function in HeLa Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of 2-AmPh
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cytotoxicity Studies
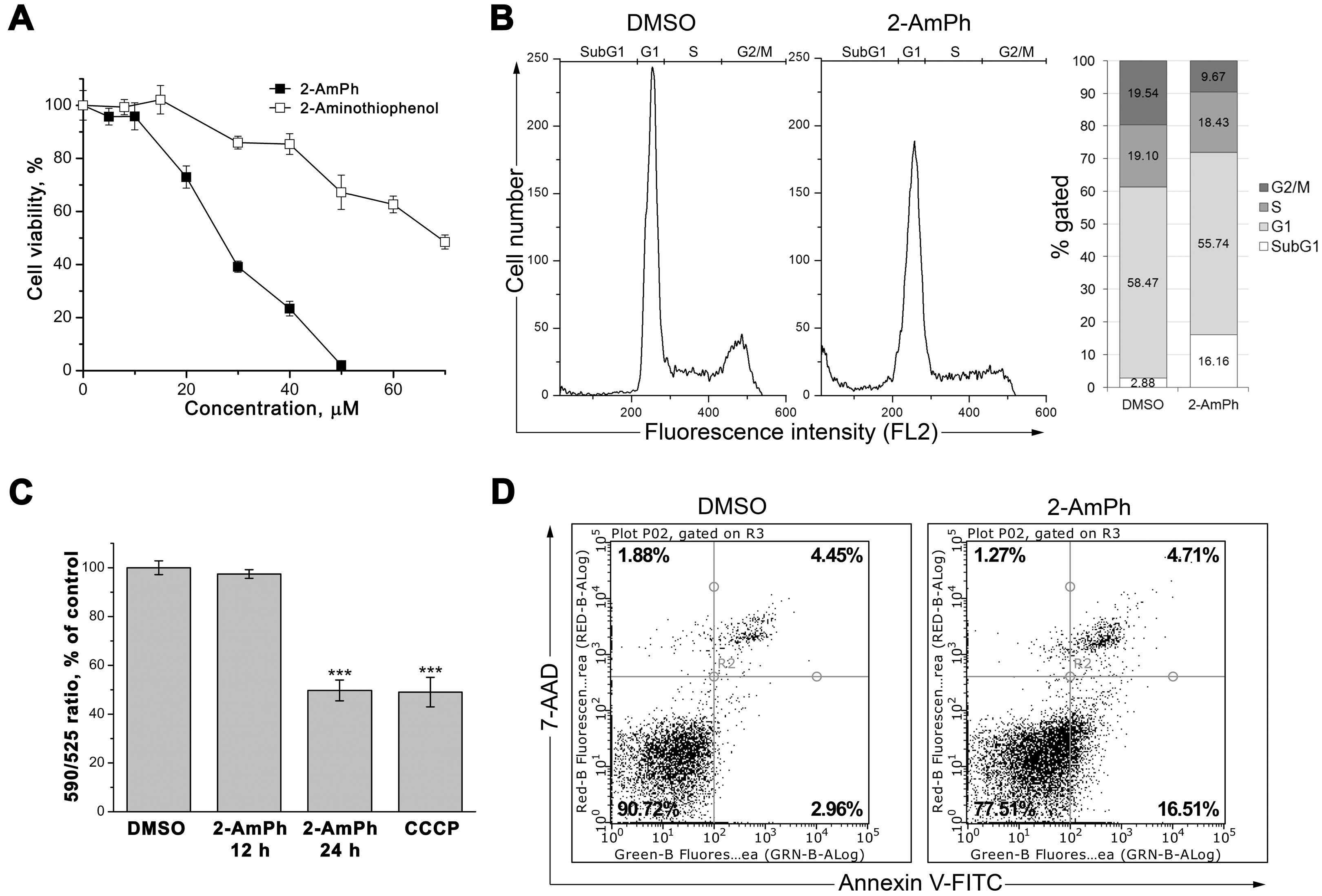
2.4. Flow Cytometry
2.5. Evaluation of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
2.6. Preparation of Nuclear Extracts and Immunoblotting
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. 2-AmPh Induces Apoptosis in HeLa Cells
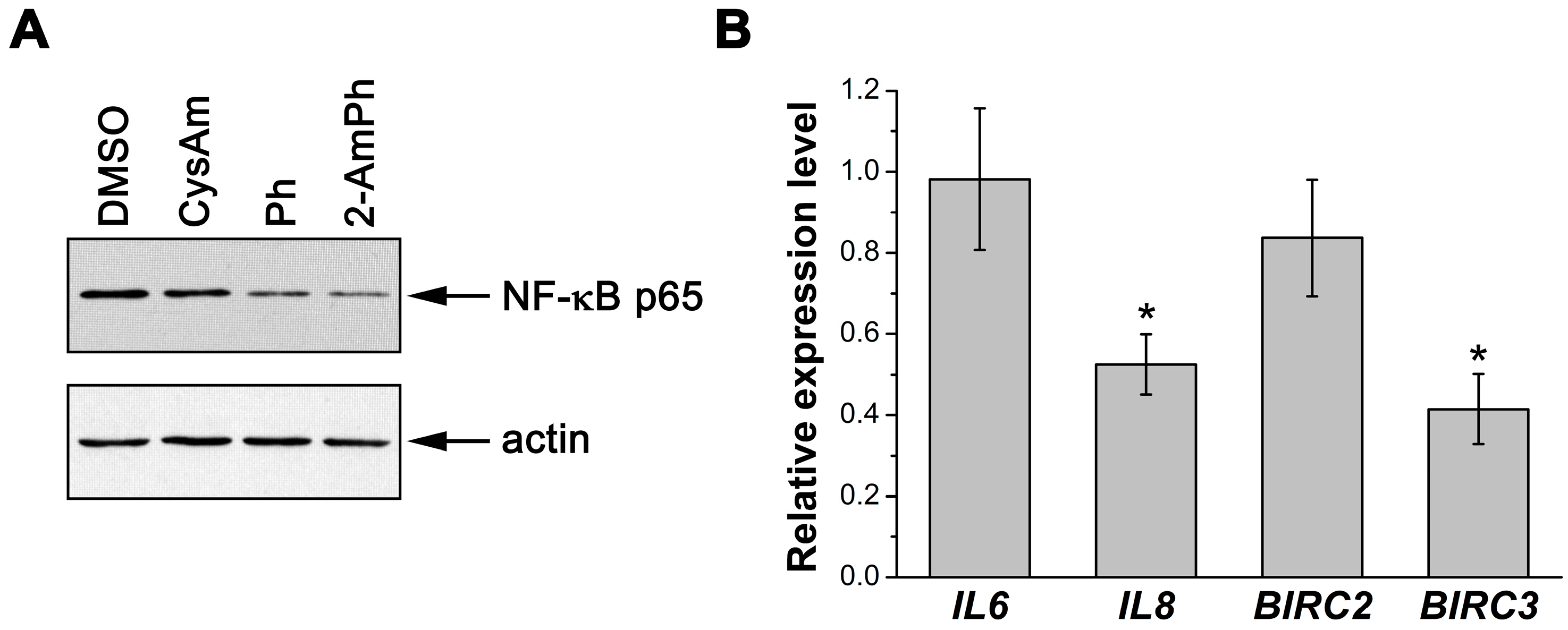
3.2. Effects of 2-AmPh on NF-κB Functions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ignarro, L.J. Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology, 1st ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780080525037. [Google Scholar]
- Batler, A.; Nicholson, R. Life, Death and Nitric Oxide; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2003; ISBN 978-1-84755-123-8. [Google Scholar]
- McCleverty, J.A. Chemistry of nitric oxide relevant to biology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowiak, J.C. Metals in Medicine; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0470681961. [Google Scholar]
- Mingos, D.; Michael, P. (Eds.) Nitrosyl Complexes in Inorganic Chemistry, Biochemistry and Medicine II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-41160-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowska, H.; Kalinowska, M.; Brzoska, K.; Wojciuk, K.; Wojciuk, G.; Kruszewski, M. Nitrosyl iron complexes—Synthesis, structure and biology. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 8273–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanin, A.F. Dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiolate ligands: Physico-chemistry, biochemistry and physiology. Nitric Oxide 2009, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.T.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Li, B.H.; Lu, Y.H.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, H.T.; Weng, T.C.; Sokaras, D.; Chen, H.Y.; et al. To transfer or not to transfer? Development of a dinitrosyl iron complex as a nitroxyl donor for the nitroxylation of an Fe(III)-porphyrin center. Chemistry 2015, 49, 17570–17573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.T.; Weng, T.C.; Liaw, W.F. X-ray emission spectroscopy: A spectroscopic measure for the determination of NO oxidation states in Fe-NO complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 43, 11562–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, C.C.; Lin, Z.S.; Lu, T.T.; Liaw, W.F. Transformation of dinitrosyl iron complexes [(NO)2Fe(SR)2]- (R = Et, Ph) into [4Fe-4S] Clusters [Fe4S4(SPh)4]2-: Relevance to the repair of the nitric oxide-modified ferredoxin [4Fe-4S] clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 50, 17154–17160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, C.C.; Lu, T.T.; Liaw, W.F. EPR, UV-Vis, IR, and X-ray demonstration of the anionic dimeric dinitrosyl iron complex [(NO)2Fe(μ-StBu)2Fe(NO)2]-: Relevance to the products of nitrosylation of cytosolic and mitochondrial aconitases, and high-potential iron proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 42, 12626–12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, J.; Kim, E. Synthetic modeling chemistry of iron-sulfur clusters in nitric oxide signaling. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 8, 2453–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burks, P.T.; Garcia, J.V.; GonzalezIrias, R.; Tillman, J.T.; Niu, M.; Mikhailovsky, AA.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Ford, P.C. Nitric oxide releasing materials triggered by near-infrared excitation through tissue filters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 48, 18145–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.C.; Iretskii, A.V.; Han, R.M.; Ford, P.C. Dinitrosyl iron complexes with cysteine. Kinetics studies of the formation and reactions of DNICs in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 1, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanina, N.A.; Aldoshin, S.M. Structure and properties of iron nitrosyl complexes with functionalized sulfur-containing ligands. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2011, 60, 1223–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanina, N.A.; Serebryakova, L.I.; Shul’zhenko, V.S.; Pisarenko, O.I.; Roudneva, T.N.; Аldoshin, S.М. The use of sulfur-binuclear nitrosyl cation type iron complex as a vasodilator drug. RU. Patent 2460531, 10 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vasil’eva, S.V.; Streltsova, D.A.; Starostina, I.A.; Sanina, N.A. Nitrogen oxide is involved in the regulation of the Fe–S cluster assembly in proteins and the formation of biofilms by Escherichia coli cells. Biol. Bull. 2013, 40, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanina, N.A.; Lysenko, K.A.; Zhukova, O.S.; Roudneva, T.N.; Emel’yanova, N.S.; Aldoshin, S.M. Water-soluble binuclear nitrosyl iron complexes with natural aliphatic thiolyls possessing cytotoxic, apoptotic and NO donor activity. US Patent 8,067,628 B2, 29 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sanina, N.A.; Kozub, G.I.; Zhukova, O.S.; Emel’yanova, N.S.; Kondrat’eva, T.A.; Korchagin, D.V.; Shilov, G.V.; Ovanesyan, N.S.; Aldoshin, S.M. Synthesis, structure, NO donor activity of iron–sulfur nitrosyl complex with 2-aminophenol-2-yl and its antiproliferative activity against human cancer cells. J. Coord. Chem. 2013, 66, 3602–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, O.S.; Smirnova, Z.S.; Chikileva, I.O.; Kiselevskii, M.V. Antiproliferative activity of a new nitrosyl iron complex with cysteamine in human tumor cells in vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 162, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaSalle, M.; Billen, D. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in murine bone-marrow cells by AET and cysteamine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1964, 114, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigdestad, C.P.; Guilford, W.; Perrin, J.; Grdina, D.J. Cell cycle redistribution of cultured cells after treatment with chemical radiation protectors. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1988, 21, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffray, P.; Ronot, X.; Adolphe, M.; Fontagne, J.; Lechat, P. Effects of D-penicillamine on growth and cell cycle kinetics of cultured rabbit articular chondrocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1984, 43, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüne, B. The intimate relation between nitric oxide and superoxide in apoptosis and cell survival. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Q.; Wogan, G.N. Nitric oxide as a modulator of apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2005, 226, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, J.M.; Eggleton, P.; Winyard, P.G. Nitric oxide and the regulation of apoptosis in tumour cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4445–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, S.Y.; Garbán, H.J. Regulation of apoptosis-related genes by nitric oxide in cancer. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, L.; Jeannin, J.F.; Bettaieb, A. Post-translational modifications induced by nitric oxide (NO): Implication in cancer cells apoptosis. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.D.; Ridnour, L.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Flores-Santana, W.; Switzer, C.H.; Donzelli, S.; Hussain, P.; Vecoli, C.; Paolocci, N.; Ambs, S.; et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: Implications in cellular signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigert, A.; Brüne, B. Nitric oxide, apoptosis and macrophage polarization during tumor progression. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavida, B.; Garban, H. Nitric oxide-mediated sensitization of resistant tumor cells to apoptosis by chemo-immunotherapeutics. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntané, J.; De la Rosa, A.J.; Marín, L.M.; Padillo, F.J. Nitric oxide and cell death in liver cancer cells. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Arfuso, F.; Chinnathambi, A.; Zayed, M.E.; Alharbi, S.A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. NF-κB in cancer therapy. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Greiner, J.F.W.; Kadhim, H.M.; Kaltschmidt, C. Subunit-Specific Role of NF-κB in Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Bishr, M.K.; Almutairi, F.M.; Ali, A.G. Inhibitors of apoptosis: Clinical implications in cancer. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1487–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.S. Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-κB: Critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Valacchi, G.; Gohil, K.; Akaike, T.; van der Vliet, A. S-nitrosothiols inhibit cytokine-mediated induction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 27, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Silva, M.C.; Sampaio de Freitas, M.; Assreuy, J. Killing of lymphoblastic leukemia cells by nitric oxide and taxol: Involvement of NF-κB activity. Cancer Lett. 2001, 173, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishi, L.; Dhiman, R.; Raje, M.; Majumdar, S. Nitric oxide induces apoptosis in cutaneous T cell lymphoma (HuT-78) by downregulating constitutive NF-κB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 8, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.Z.; Tsukahara, H.; Hayakawa, K.; Todoroki, Y.; Tamura, S.; Ohshima, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Mayumi, M. Effects of antioxidants and NO on TNF-alpha-induced adhesion molecule expression in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuyama, K.; Shichiri, M.; Marumo, F.; Hirata, Y. NO inhibits cytokine-induced iNOS expression and NF-κB activation by interfering with phosphorylation and degradation of IκB-alpha. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkita, M.; Takaoka, M.; Shiota, Y.; Nojiri, R.; Matsumura, Y. Nitric oxide inhibits endothelin-1 production through the suppression of nuclear factor κB. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2002, 103 (Suppl. 48), 68S–71S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla-Sarkar, M.; Bauer, J.A.; Lupica, J.A.; Morrison, B.H.; Tang, Z.; Oates, R.K.; Almasan, A.; DiDonato, J.A.; Borden, E.C.; Lindner, D.J. Suppression of NF-κB survival signaling by nitrosylcobalamin sensitizes neoplasms to the anti-tumor effects of Apo2L/TRAIL. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39461–39469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaert, N.L.; Ckless, K.; Korn, S.H.; Vos, N.; Guala, A.S.; Wouters, E.F.; van der Vliet, A.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M. Nitric oxide represses inhibitory κB kinase through S-nitrosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibe, W.; Bartels, W.; Lindemann, S.; Grosser, T.; Buerke, M.; Boissel, J.P.; Meyer, J.; Darius, H. Involvement of PKC and NF-κB in nitric oxide induced apoptosis in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 5, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.R.; Botting, C.H.; Panico, M.; Morris, H.R.; Hay, R.T. Inhibition of NF-κB DNA binding by nitric oxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 12, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, S.B.; Park, S.K.; Park, J.S. Exogenous nitric oxide inhibits VCAM-1 expression in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Role of cyclic GMP and NF-κB. Nephron 2002, 4, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradkar, P.N.; Roth, J.A. Nitric oxide transcriptionally down-regulates specific isoforms of divalent metal transporter (DMT1) via NF-κB. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, H.E.; Hess, D.T.; Stamler, J.S. S-nitrosylation: Physiological regulation of NF-κB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8841–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, M.; Goswami, S.; Rodes, D.B.; Kodela, R.; Velazquez, C.A.; Boring, D.; Crowell, J.A.; Kashfi, K. NO-releasing NSAIDs suppress NF-κB signaling in vitro and in vivo through S-nitrosylation. Cancer Lett. 2010, 298, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Huq, M.D.; Hu, X.; Wei, L.N. Tyrosine nitration on p65: A novel mechanism to rapidly inactivate nuclear factor-κB. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2005, 4, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozarowski, P.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Analysis of cell cycle by flow cytometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2004, 281, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, M.S.; Paris, A.; Codron, P.; Cassereau, J.; Procaccio, V.; Lenaers, G.; Reynier, P.; Chevrollier, A. Current mechanistic insights into the CCCP-induced cell survival response. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, L.; Kunkel, S.; Nabel, G.J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor κB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupina, T.S.; Terent’ev, A.A.; Antonova, N.O.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Sanina, N.A.; Aldoshin, S.M. Influence of sulfur-nitrosyl iron complexes of “µ-S” structural type on NF-κB nuclear factor. Int. Sci. J. Med. Biol. Sci. 2014, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Stupina, T.S.; Parkhomenko, I.I.; Balalaeva, I.V.; Kostyuk, G.V.; Sanina, N.A.; Terent’ev, A.A. Cytotoxic properties of the nitrosyl iron complex with phenylthiyl. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2011, 60, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, N.; Marchetti, P.; Castedo, M.; Decaudin, D.; Macho, A.; Hirsch, T.; Susin, S.A.; Petit, P.X.; Mignotte, B.; Kroemer, G. Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell death. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermes, I.; Haanen, C.; Steffens-Nakken, H.; Reutelingsperger, C. A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 184, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Z.; Tsukahara, H.; Ohshima, Y.; Todoroki, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Maeda, M.; Mayumi, M. Effects of antioxidants and nitric oxide on TNF-alpha-induced adhesion molecule expression and NF-κB activation in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Life Sci. 2004, 10, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.F.; Carvalho, A.P.; Caramona, M.M.; Lopes, M.C. Role of nitric oxide in the activation of NF-κB, AP-1 and NOS II expression in articular chondrocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2002, 7, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, A.; Bardelli, C.; Fresu, L.G.; Poletti, E.; Palma, A.; Federici Canova, D.; Zeng, H.W.; Ongini, E.; Brunelleschi, S. The nitric oxide-donating pravastatin, NCX 6550, inhibits cytokine release and NF-κB activation while enhancing PPARγ expression in human monocyte/macrophages. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 5, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavida, B.; Baritaki, S. Dual role of NO donors in the reversal of tumor cell resistance and EMT: downregulation of the NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP circuitry. Nitric Oxide 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemish, J.; Nakaya, N.; Mittal, V.; Enikolopov, G. Nitric oxide activates diverse signaling pathways to regulate gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42321–42329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Role of the NFκB-signaling pathway in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begalli, F.; Bennett, J.; Capece, D.; Verzella, D.; D’Andrea, D.; Tornatore, L.; Franzoso, G. Unlocking the NF-κB conundrum: Embracing complexity to achieve specificity. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ignazio, L.; Batie, M.; Rocha, S. Hypoxia and inflammation in cancer, focus on HIF and NF-κB. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Hong, J.T. Roles of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cells 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeligs, K.P.; Neuman, M.K.; Annunziata, C.M. Molecular pathways: The balance between cancer and the immune system challenges the therapeutic specificity of targeting nuclear factor-κB signaling for cancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4302–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sung, B. NF-κB in cancer: A matter of life and death. Cancer Discov. 2011, 6, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sundaram, C.; Reuter, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirvanappa, A.C.; Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Ananda, H.; Sukhorukov, A.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Sundaram, M.S.; Nayaka, S.C.; Girish, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; et al. Novel synthetic oxazines target NF-κB in colon cancer in vitro and inflammatory bowel disease in vivo. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Lee, Y.R.; Chenm, T.C.; Chen, C.L.; Lee, C.C.; Shiau, C.Y.; Chiang, C.H.; Huang, H.S. Novel anthra[1,2-c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-6,11-diones as promising anticancer lead compounds: Biological evaluation, characterization & molecular targets determination. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.; Maher, M.; Temkin, A.; Pitts, T.; Wright, A. Spongiatriol inhibits nuclear factor κB activation and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, K.R.; Mohapatra, P.; Patel, H.M.; Goyal, S.N.; Ojha, S.; Kundu, C.N.; Patil, C.R. Pentacyclic triterpenoids inhibit IKKβ mediated activation of NF-κB pathway: In silico and in vitro evidences. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.A.; Maers, K.; Roberts, J.; Kemami-Wangun, H.V.; Harmody, D.; Wright, A.E. The marine natural product microsclerodermin A is a novel inhibitor of the nuclear factor κB and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 1, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.D.; Anilkumar, N.C.; Rangappa, S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Mishra, S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole induces anticancer activity by targeting NF-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Song, L.; Pu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, G.; Liu, X.; Bai, M.; Li, S.; Gao, F.; et al. Natural cyclopeptide RA-V inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting TAK1. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 7, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saud, S.M.; Li, W.; Gray, Z.; Matter, M.S.; Colburn, N.H.; Young, M.R.; Kim, Y.S. Diallyl disulfide (DADS), a constituent of garlic, inactivates NF-κB and prevents colitis-induced colorectal cancer by inhibiting GSK-3β. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 2016, 7, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.T.; Wong, P.F.; He, H.; Hooper, J.D.; Mustafa, M.R. Alpha-tomatine attenuation of in vivo growth of subcutaneous and orthotopic xenograft tumors of human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells is accompanied by inactivation of nuclear factor-κB signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 2, e57708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Prasad, S.; Sethumadhavan, D.R.; Nair, M.S.; Mo, Y.Y.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nimbolide, a limonoid triterpene, inhibits growth of human colorectal cancer xenografts by suppressing the proinflammatory microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 16, 4465–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kannappan, R.; Kim, J.; Rahman, G.M.; Francis, S.K.; Raveendran, R.; Nair, M.S.; Das, J.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bharangin, a diterpenoid quinonemethide, abolishes constitutive and inducible nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation by modifying p65 on cysteine 38 residue and reducing inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB α kinase activation, leading to suppression of NF-κB-regulated gene expression and sensitization of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolou, A.; Liousia, M.; Kalamida, D.; Pouliliou, S.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Koukourakis, M. Inhibition of IKK-NFκB pathway sensitizes lung cancer cell lines to radiation. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 3, 293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Prasad, S.; Reuter, S.; Kannappan, R.; Yadav, V.R.; Ravindran, J.; Hema, P.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Nair, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Modification of cysteine 179 of IkBα kinase by nimbolide leads to down-regulation of NF-κB-regulated cell survival and proliferative proteins and sensitization of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 46, 35406–35417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravindan, N.; Mohan, S.; Herman, T.S.; Natarajan, M. Nitric oxide-mediated inhibition of NF-κB regulates hyperthermia-induced apoptosis. J. Cell Biochem. 2009, 6, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdagul, A., Jr.; Chen, J.; Funk, S.D.; Albert, P.; Kevil, C.G.; Orr, A.W. Altered nitric oxide production mediates matrix-specific PAK2 and NF-κB activation by flow. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 3, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.J.; Liu, T.Z.; Lu, F.J.; Hsieh, P.Y.; Chen, C.H. Actinodaphnine induces apoptosis through increased nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species and down-regulation of NF-κB signaling in human hepatoma Mahlavu cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 3, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushnareva, Y.; Newmeyer, D.D. Bioenergetics and cell death. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1201, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brat, D.J.; Bellail, A.C.; Van Meir, E.G. The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 2005, 2, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, F.; Longo, A.M.; de Boer, W.I.; Rabe, K.F.; Hiemstra, P.S. Interleukin-8 stimulates cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer through epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Lung Cancer 2007, 1, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anestakis, D.; Petanidis, S.; Kalyvas, S.; Nday, C.M.; Tsave, O.; Kioseoglou, E.; Salifoglou, A. Mechanisms and applications of interleukins in cancer immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1691–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndubaku, C.; Cohen, F.; Varfolomeev, E.; Vucic, D. Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins for therapeutic intervention. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 8, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Vucic, D. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: Fascinating biology leads to attractive tumor therapeutic targets. Future Oncol. 2011, 5, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gressot, L.V.; Doucette, T.; Yang, Y.; Fuller, G.N.; Manyam, G.; Rao, A.; Latha, K.; Rao, G. Analysis of the inhibitors of apoptosis identifies BIRC3 as a facilitator of malignant progression in glioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12695–12704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Vucic, D. Targeting IAP proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silke, J.; Vucic, D. IAP family of cell death and signaling regulators. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 545, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stupina, T.; Balakina, A.; Kondrat’eva, T.; Kozub, G.; Sanina, N.; Terent’ev, A. NO-Donor Nitrosyl Iron Complex with 2-Aminophenolyl Ligand Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits NF-κB Function in HeLa Cells. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86040046
Stupina T, Balakina A, Kondrat’eva T, Kozub G, Sanina N, Terent’ev A. NO-Donor Nitrosyl Iron Complex with 2-Aminophenolyl Ligand Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits NF-κB Function in HeLa Cells. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2018; 86(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleStupina, Tatiana, Anastasia Balakina, Tatiana Kondrat’eva, Galina Kozub, Natalia Sanina, and Alexei Terent’ev. 2018. "NO-Donor Nitrosyl Iron Complex with 2-Aminophenolyl Ligand Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits NF-κB Function in HeLa Cells" Scientia Pharmaceutica 86, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86040046
APA StyleStupina, T., Balakina, A., Kondrat’eva, T., Kozub, G., Sanina, N., & Terent’ev, A. (2018). NO-Donor Nitrosyl Iron Complex with 2-Aminophenolyl Ligand Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits NF-κB Function in HeLa Cells. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 86(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86040046