Ocular Delivery System for Propranolol Hydrochloride Based on Nanostructured Lipid Carrier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
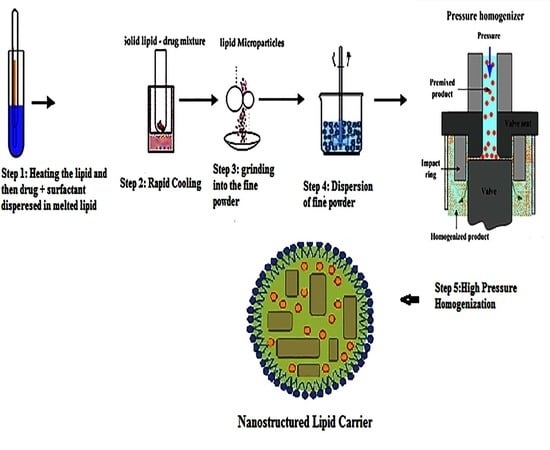
2.2.1. Preparation of Drug-Loaded Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC)
2.2.2. Particle Size Measurement
2.2.3. Entrapment Efficiency (EE%) and Loading Capacity (LC%) Determination
2.2.4. Drug Release Profile of Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC) Formulations
2.2.5. Drug Permeability through Isolated Rabbit Cornea
2.2.6. Effect of Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC) on the Cornea
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Formulation Components, Entrapment Efficiency (EE%) and Loading Capacity (LC%)
3.2. Nanostructure Lipid Carrier(NLC) Particle Size Distribution
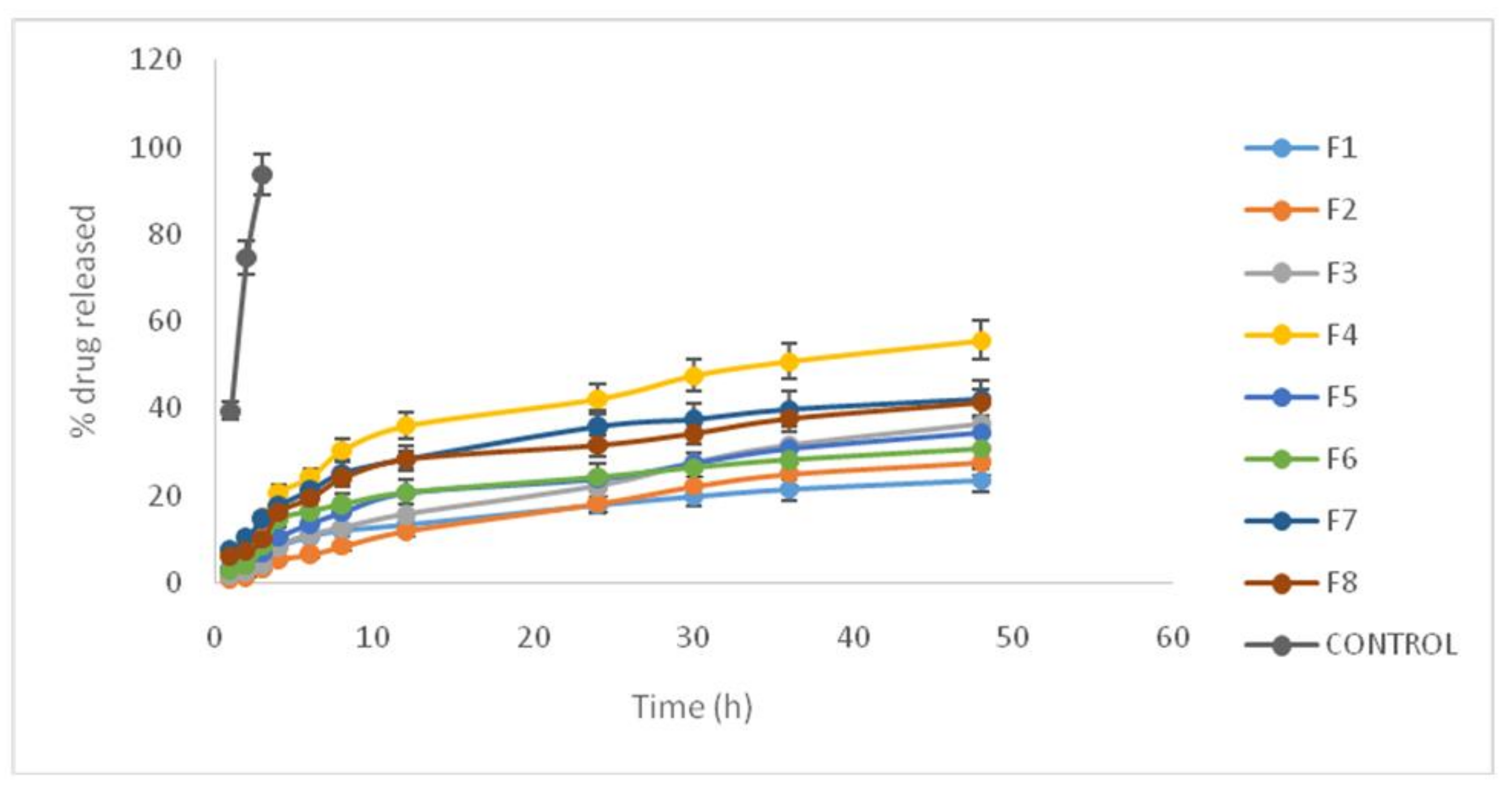
3.3. Drug Release from Lipid Nanoparticle Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC)
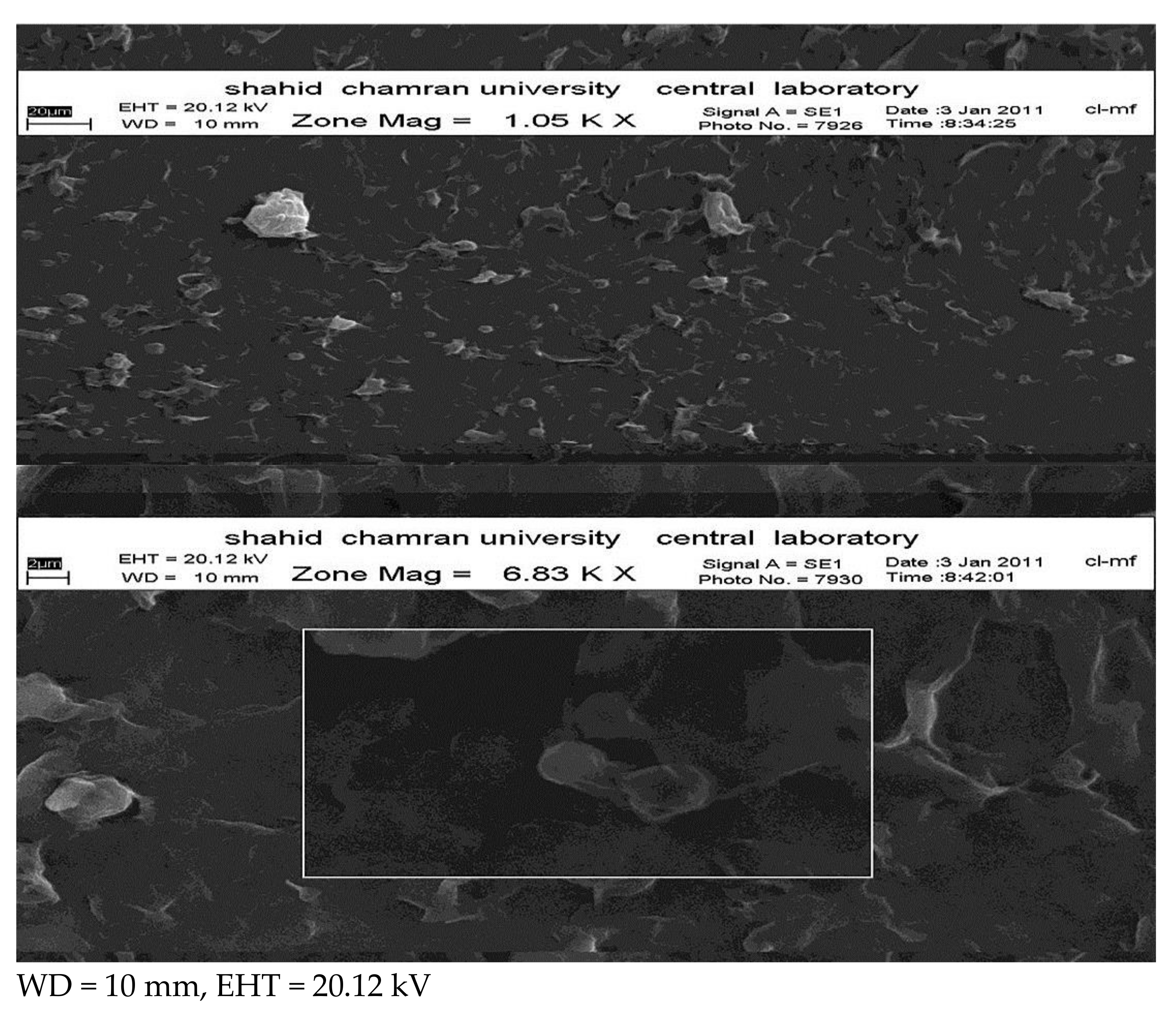
3.4. Nanoparticle Morphology
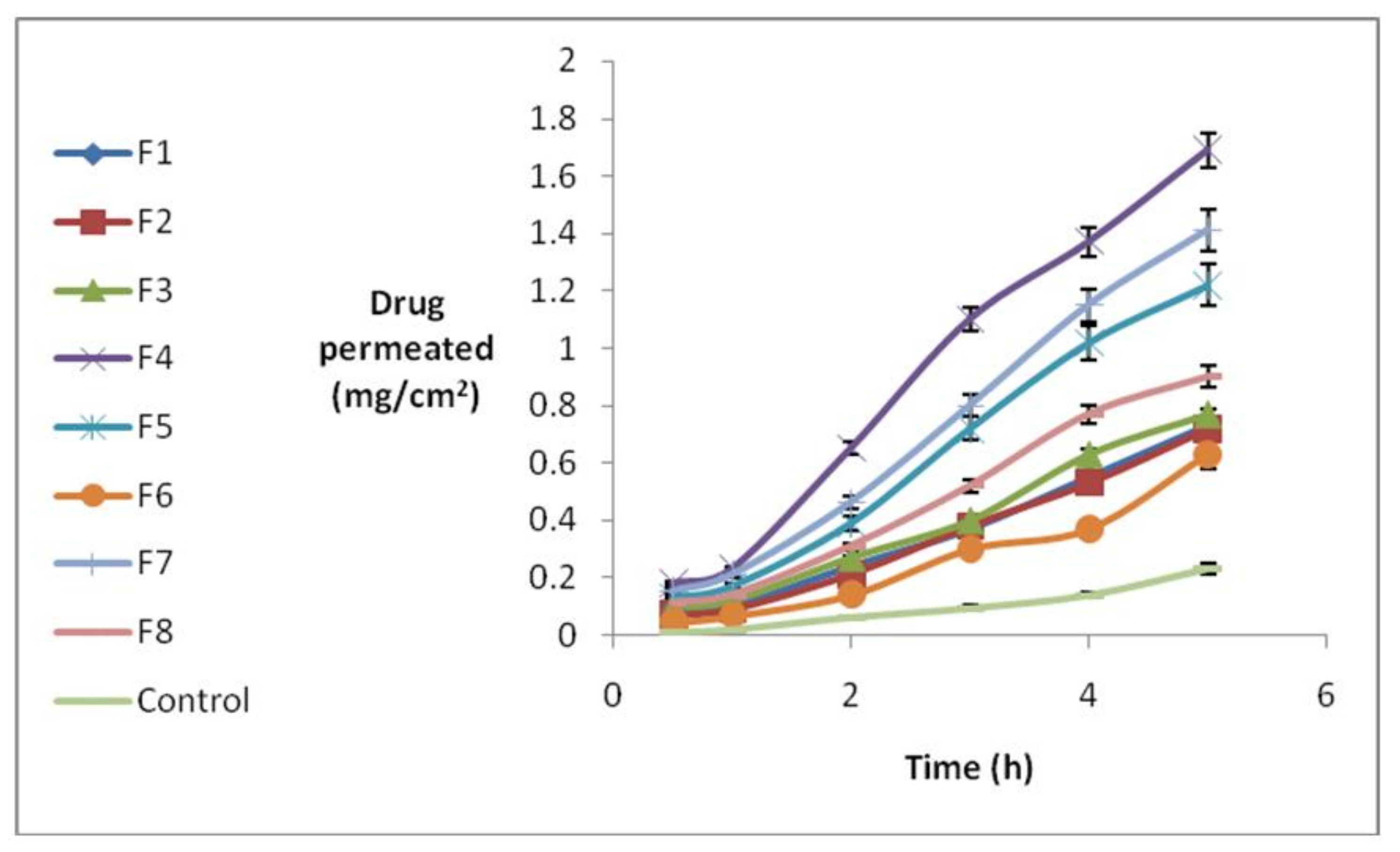
3.5. Nanostructure Lipid Carrier (NLC) Permeation through Rabbit Cornea
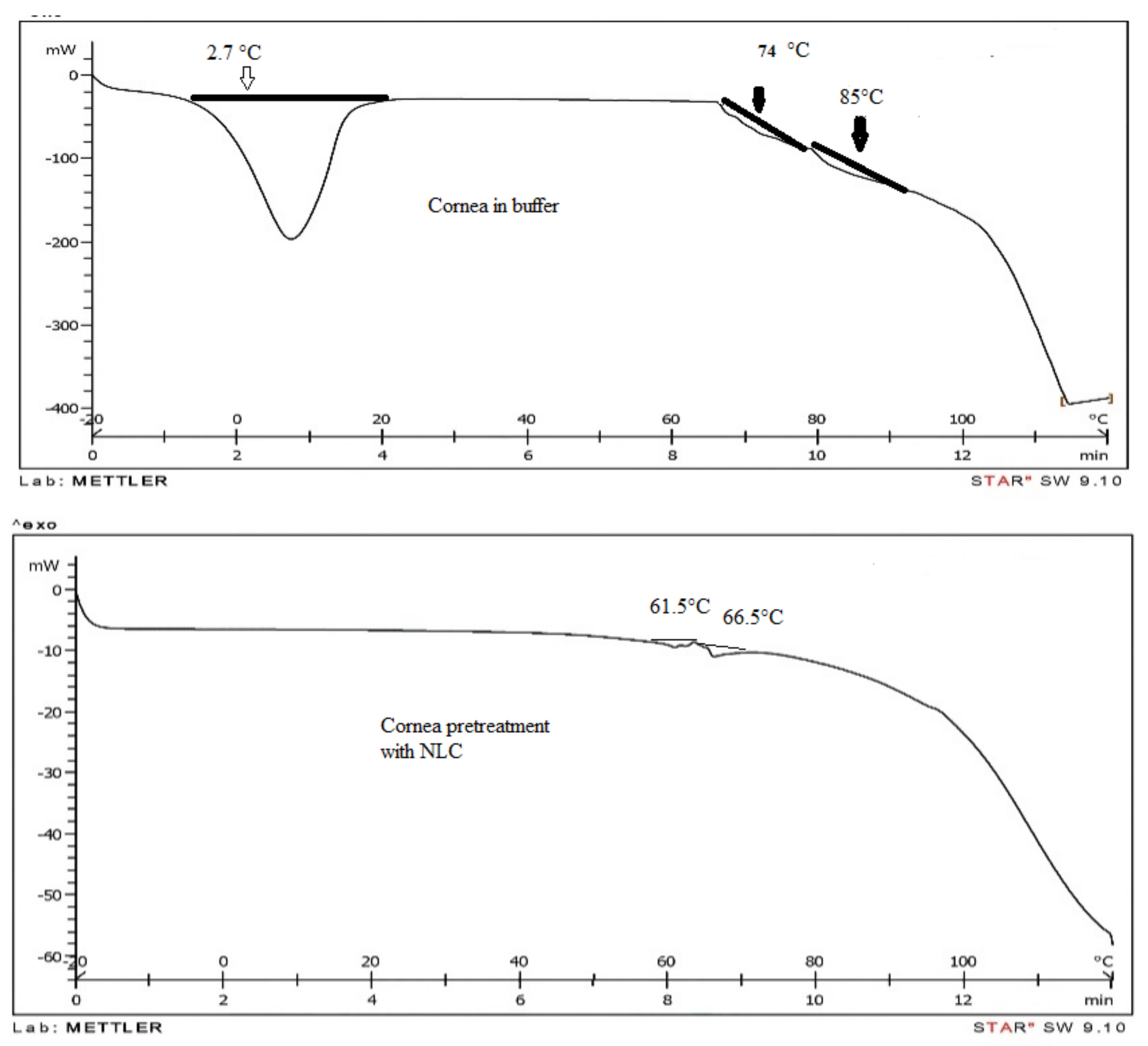
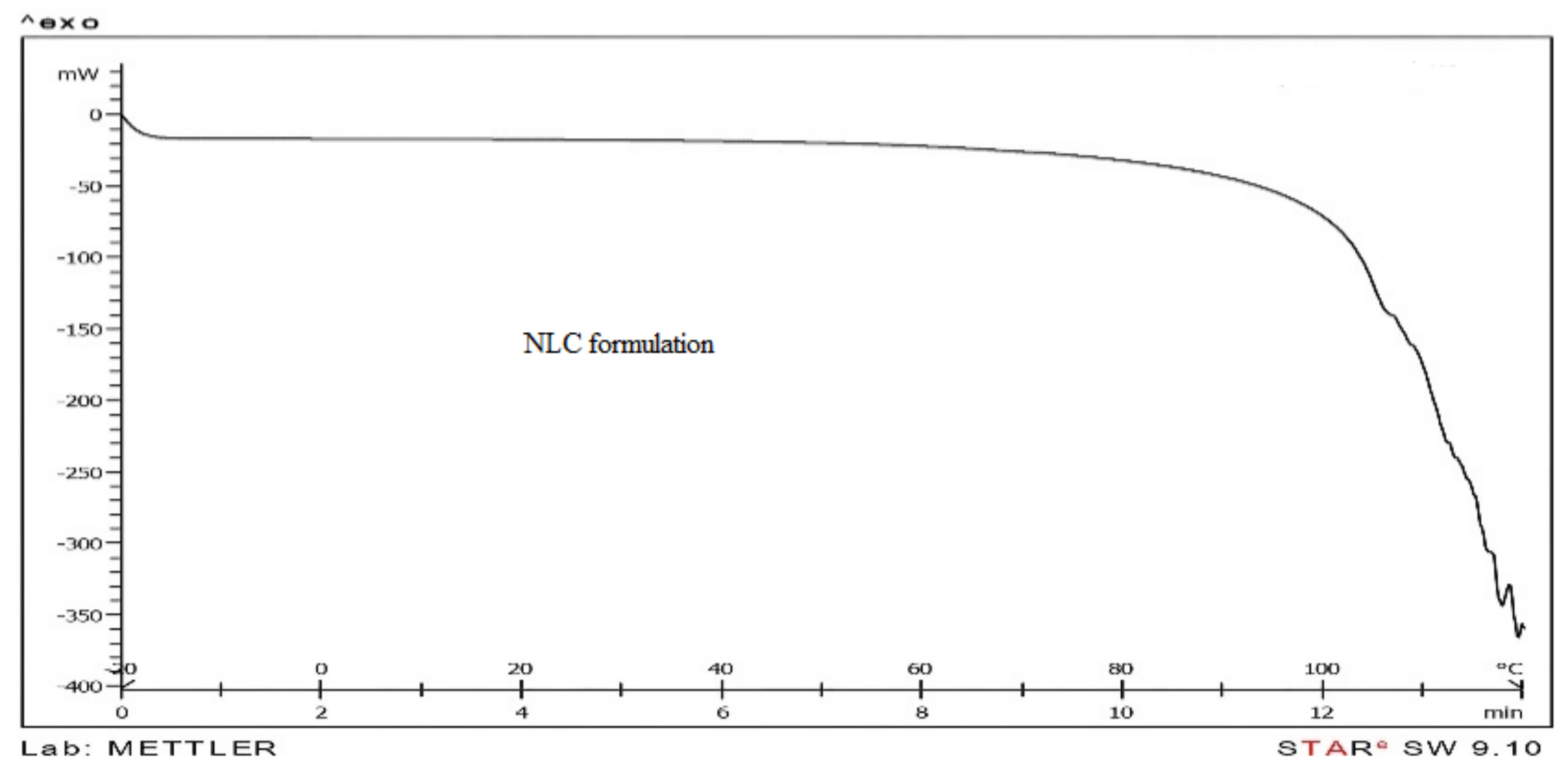
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetric (DSC) of Rabbit Cornea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitra, A.K. Ophthalmic Drug Delivery Systems; Taylor & Francis Inc: New York, NY USA, 2003; Volume 130, pp. 178–197. [Google Scholar]
- Macha, S.; Hughes, P.; Mitra, A. Overview of ocular drug delivery. In Drugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; Volume 130, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pijls, R.T.; Sonderkamp, T.; Daube, G.W.; Krebber, R.; Hanssen, H.H.; Nuijts, R.M.; Koole, L.H. Studies on a new device for drug delivery to the eye. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 59, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Espina, M.; Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.; García, M. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC): Overcoming the anatomical and physiological barriers of the eye–part i–barriers and determining factors in ocular delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 110, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudana, R.; Jwala, J.; Boddu, S.H.; Mitra, A.K. Recent perspectives in ocular drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandervoort, J.; Ludwig, A. Ocular drug delivery: Nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepić, I.; Hafner, A.; Lovrić, J.; Filipović-Grčić, J. Bioavailability of dexamethasone from nonionic surfactant/chitosan micelle system. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blass, S.; Teubl, B.; Frohlich, E.; Meindl, C.; Rabensteiner, D.; Trummer, G.; Schmut, O.; Zimmer, A.; Roblegg, E. Permeability studies on the ocular absorbance of nanostructured materials across the cornea. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, M.; Pawar, P.K. Preparation and in vitro/ex vivo evaluation of moxifloxacin-loaded plga nanosuspensions for ophthalmic application. Sci. Pharm. 2013, 81, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Suresh, P.K. Drug delivery to eye: Special reference to nanoparticles. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 2010, 2, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balguri, S.P.; Adelli, G.R.; Majumdar, S. Topical ophthalmic lipid nanoparticle formulations (SLN, NLC) of indomethacin for delivery to the posterior segment ocular tissues. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousry, C.; Fahmy, R.H.; Essam, T.; El-Laithy, H.M.; Elkheshen, S.A. Nanoparticles as tool for enhanced ophthalmic delivery of vancomycin: A multidistrict-based microbiological study, solid lipid nanoparticles formulation and evaluation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üner, M.; Yener, G. Importance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Chetoni, P.; Burgalassi, S.; Monti, D.; Tampucci, S.; Tullio, V.; Cuffini, A.M.; Muntoni, E.; Spagnolo, R.; Zara, G.P.; Cavalli, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles as promising tool for intraocular tobramycin delivery: Pharmacokinetic studies on rabbits. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, I.; Reichl, S.; Müller-Goymann, C. Drug release and permeation studies of nanosuspensions based on solidified reverse micellar solutions (SRMS). Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 305, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.C.; Roehrs, R.E.; Rodeheaver, D.P.; Missel, P.J.; Jani, R.; Chowhan, M.A. Design and evaluation of ophthalmic pharmaceutical products. Drugs Pharm. Sci. 2002, 121, 415–478. [Google Scholar]
- Liedtke, S.; Wissing, S.; Müller, R.; Mäder, K. Influence of high pressure homogenisation equipment on nanodispersions characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 196, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, D.; Chetoni, P.; Burgalassi, S.; Najarro, M.; Saettone, M. Increased corneal hydration induced by potential ocular penetration enhancers: Assessment by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and by desiccation. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 232, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Nie, S.-F.; Kong, J.; Li, N.; Ju, C.-Y. A controlled-release ocular delivery system for ibuprofen based on nanostructured lipid carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburahma, M.H.; Badr-Eldin, S.M. Compritol 888 ATO: A multifunctional lipid excipient in drug delivery systems and nanopharmaceuticals. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthélémy, P.; Farah, N.; Laforet, J. Transcutol-product profile. In Product Information; Gattefosse Company: Saint-Priest, France, 1995; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Solid lipid nanoparticles for oral drug delivery: Chitosan coating improves stability, controlled delivery, mucoadhesion and cellular uptake. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, H.A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Hamidi, M.; Jalali, M.B. Repaglinide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Effect of using different surfactants/stabilizers on physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignati’eva, N.Y.; Danilov, N.; Lunin, V.; Obrezkova, M.; Averkiev, S.; Chaikovskii, T. Alteration of the thermodynamic characteristics of corneal collagen denaturation as a result of nonenzymatic glycation. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2007, 62, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Sun, M.; Ping, Q.; Ying, Z.; Liu, W. Incorporation of liquid lipid nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery enhancement. Nanotechnology 2009, 21, 025101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.H.; MaÈder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zur Mühlen, A.; Mehnert, W. Drug incorporation and delivery of prednisolone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 1st World Meeting APGI/APV, Budapest, Hungary, 9–11 May 1995; pp. 455–456. [Google Scholar]
- Sanad, R.A.; Abdelmalak, N.S.; elBayoomy, T.S.; Badawi, A.A. Formulation of a novel oxybenzone-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasango, K.W.; Pardeike, J.; Muller, R.H.; Walker, R.B. Selection and characterization of suitable lipid excipients for use in the manufacture of didanoside–loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carrires. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5185–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhmalzadeh, B.S.; Barati, N.; Hassani, M.; Rahim, F. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles as eschar delivery system for nitrofurazone using taguchi design approach. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 1, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Ye, T.; Chen, F.; Sun, X.; Kong, J.; Yang, X.; Pan, W.; Li, S. Design, characterization and in vitro cellular inhibition and uptake of optimized genistein–loaded NLC for prevention of posterior capsular opacification using surface methodology. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, M.; Singh, D.; Murthy, S.N.; Singh, M.R. Design, characterization and skin permeating potential of fluocinolone acetonide loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical treatment of psoriasis. Steroids 2015, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, L.; Serpe, L.; Foglietta, F.; Muntoni, E.; Gallarate, M.; Del Pozo Rodriguez, A.; Solinis, M.A. Application of lipid nanoparticles to ocular drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Formulation No. | State in Full Factorial Design | Drug% | %L (Oleic Acid%) | Transcutol% | Surfactant% | Compritol% | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +++ | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1 | 3 | 13.5 | 61.23 ± 3.12 |
| 2 | ++− | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 3 | 13.5 | 58.13 ± 2.29 |
| 3 | +−+ | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 14.5 | 48.98 ± 1.72 |
| 4 | −−+ | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 14.5 | 28.53 ± 2.44 |
| 5 | −+− | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 1.5 | 13.5 | 39.72 ± 3.05 |
| 6 | +−− | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 3 | 14.5 | 45.11 ± 1.52 |
| 7 | −++ | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 13.5 | 40.88 ± 2.25 |
| 8 | −−− | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0 | 1.5 | 14.5 | 35.95 ± 1.47 |
| Formulation No. | State in Full Factorial Design | Particle Size (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +++ | 385 ± 30 | 0.44 ± 0.04 |
| 2 | −++ | 491 ± 51 | 0.51 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | +−+ | 554 ± 29 | 0.29 ± 0.018 |
| 4 | +−− | 840 ± 33 | 0.38 ± 0.035 |
| 5 | −+− | 462 ± 28 | 0.5 ± 0.025 |
| 6 | −−+ | 686 ± 56 | 0.56 ± 0.011 |
| 7 | ++− | 706 ± 19 | 0.22 ± 0.02 |
| 8 | −−− | 880 ± 66 | 0.4 ± 0.03 |
| Formulation No. | State in Full Factorial Design | R4 (%) | R48 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +++ | 8.21 ± 0.37 | 23.38 ± 1.15 |
| 2 | −++ | 5.4 ± 0.59 | 27.66 ± 1.38 |
| 3 | +−+ | 8.45 ± 0.61 | 36.29 ± 1.57 |
| 4 | +−− | 20.71 ± 1.33 | 55.64 ± 4.11 |
| 5 | −+− | 10.4 ± 0.36 | 34.5 ± 3.05 |
| 6 | −−+ | 14.5 ± 0.94 | 30.6 ± 1.96 |
| 7 | ++− | 17.67 ± 1.42 | 42.2 ± 3.12 |
| 8 | −−− | 16.05 ± 0.95 | 41.17 ± 1.64 |
| Formulation No. | State in Full Factorial Design | Zero-Order Kinetic | First-Order Kinetic | Higuchi Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | k | r2 | k | r2 | k | ||
| 1 | +++ | 0.674 | 0.423 | 0.44 | 0.017 | 0.85 | 3.71 |
| 2 | −++ | 0.663 | 0.506 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.86 | 4.49 |
| 3 | +−+ | 0.776 | 0.708 | 0.39 | 0.024 | 0.92 | 6.04 |
| 4 | +−− | 0.726 | 0.92 | 0.53 | 0.013 | 0.9 | 7.95 |
| 5 | −+− | 0.88 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.027 | 0.96 | 5.65 |
| 6 | −−+ | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.009 | 0.85 | 3.74 |
| 7 | ++− | 0.7 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.013 | 0.88 | 5.96 |
| 8 | −−− | 0.72 | 0.665 | 0.54 | 0.013 | 0.89 | 5.81 |
| Formulation No. | State in Full Factorial Design | Q5 (mg/cm2) | Jss (mg/cm·s−1) | Tlag (h) | P (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +++ | 0.7 ± 0.055 | 0.181 ± 0.012 | 0.95 ± 0.066 | 0.012 ± 0.002 |
| 2 | −++ | 0.725 ± 0.038 | 0.178 ± 0.014 | 0.85 ± 0.09 | 0.0123 ± 0.0014 |
| 3 | +−+ | 0.761 ± 0.062 | 0.185 ± 0.016 | 1.05 ± 0.095 | 0.015 ± 0.0009 |
| 4 | +−− | 1.705 ± 0.12 | 0.493 ± 0.025 | 0.95 ± 0.059 | 0.068 ± 0.001 |
| 5 | −+− | 1.220 ± 0.088 | 0.331 ± 0.014 | 0.88 ± 0.072 | 0.033 ± 0.0001 |
| 6 | −−+ | 0.625 ± 0.055 | 0.155 ± 0.009 | 0.75 ± 0.083 | 0.014 ± 0.0006 |
| 7 | ++− | 1.42 ± 0.13 | 0.417 ± 0.027 | 0.95 ± 0.047 | 0.041 ± 0.0008 |
| 8 | −−− | 0.885 ± 0.035 | 0.24 ± 0.017 | 1.10 ± 0.087 | 0.027 ± 0.0005 |
| Control | − | 0.229 ± 0.011 | 0.053 ± 0.002 | 0.85 ± 0.069 | 0.002 ± 0.00005 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharif Makhmal Zadeh, B.; Niro, H.; Rahim, F.; Esfahani, G. Ocular Delivery System for Propranolol Hydrochloride Based on Nanostructured Lipid Carrier. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86020016
Sharif Makhmal Zadeh B, Niro H, Rahim F, Esfahani G. Ocular Delivery System for Propranolol Hydrochloride Based on Nanostructured Lipid Carrier. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2018; 86(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharif Makhmal Zadeh, Behzad, Hassan Niro, Fakher Rahim, and Golbarg Esfahani. 2018. "Ocular Delivery System for Propranolol Hydrochloride Based on Nanostructured Lipid Carrier" Scientia Pharmaceutica 86, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86020016
APA StyleSharif Makhmal Zadeh, B., Niro, H., Rahim, F., & Esfahani, G. (2018). Ocular Delivery System for Propranolol Hydrochloride Based on Nanostructured Lipid Carrier. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 86(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm86020016