The Effects of Job Mismatch on Pay, Job Satisfaction, and Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Job Fit Theory
2.2. Pay, Job Satisfaction, and Job Performance
3. Method
3.1. Research Model
3.2. Samples and Method
3.3. Measuring Instruments
4. Findings and Discussion
4.1. Factor Analysis and Reliability Testing
4.2. Structure Equation Analysis Results
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Monetary Fund (IMF). Jobs and Growth: Analytical and Operational Considerations for the Fund; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dabla-Norris, E.; Guo, S.; Haksar, V.; Kim, M.; Kochhar, K.; Wiseman, K.; Zdzienicka, A. The New Normal: A Sector-Level Perspective on Productivity Trends in Advanced Economies; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- International Monetary Fund (IMF). IMD World Talent Report 2016; Institute for Management Development: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.Y. Is It Ready for Talent War, Korea? Report vol. 17; Hyundai Research Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.; Van der Velden, R. Educational mismatch versus skill mismatch: Effects on wages, job satisfaction, and on-the-job search. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 2001, 3, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.R. Person-job fit: A conceptual integration, literature review, and methodological critique. Int. Rev. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 1991, 6, 283–357. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, B.; Goldstein, J.R.; Smith, D.B. The ASA framework: An update. Pers. Psychol. 1995, 48, 747–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristof-Brown, A.L.; Zimmerman, R.; Johnson, E.C. Consequences of Individuals’ Fit at Work: A Meta-Analysis of Person-Job, Person-Organization, Person-Group, and Person-Supervisor Fit. Pers. Psychol. 2005, 58, 281–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R. The Overeducated American; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, J.; Kalleberg, A. Matching Training and Jobs: The Fit between Vocational Education and Employment in the German labour market. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 1995, 11, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackman, R.; Oldham, G.R. Development of the job diagnostic survey. J. Appl. Psychol. 1975, 60, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.R. Literature Review Exploring Job Mismatch and Income; Human Resources and Skills Development Canada (HRSDC): Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, G.; Hoffman, S.D. The incidence and wage effects of overeducation. Econ. Educ. Rev. 1981, 1, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Weert, E. What do educational mismatches tell us about skill mismatches? A Cross-country analysis. Eur. J. Educ. 2007, 42, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoung, N.I.; Eun, L. Job mismatches of youth employees: Determinants, relationship with wage, and adjustment strategies. J. Vocat. Educ. Res. 2009, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wolbers Maarten, H.J. Job Mismatches and their Labour-Market Effects among School-Leavers in Europe. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 2003, 19, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, A. Measuring over-education. Economica 2003, 70, 509–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, A.; Mañée, F. Misusing our talent? Overeducation, overskilling and skill underutilisation among Spanish Ph. D. graduates. Econ. Labour Relat. Rev. 2016, 27, 432–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostas, M.; Mcguinness, S.; O’leary, N. Job Mismatches and Labour Market Outcomes: Panel Evidence on University Graduates. Econ. Soc. Aust. 2013, 89, 382–395. [Google Scholar]
- Felix, B.; de Grip, A.; Mertens, A. Overeducation in Europe: Current Issues in Theory and Policy; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK; Northampton, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Clogg, C.C.; Shockey, J.W. Mismatch between occupation and schooling: A prevalence measure, recent trends and demographic analysis. Demography 1984, 21, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaeta, G.L.; Lavadera, G.L.; Pastore, F. Much Ado about Nothing? The Wage Penalty of Holding a Ph.D. Degree but Not a Ph.D. Job Position; GLO Discussion Paper; Global Labor Organization: Bonn, Germany, 2016; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Montt, G. Field-of-study mismatch and overqualification: Labour market correlates and their wage penalty. IZA J. Labor Econ. 2017, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandulli, F.D.; Baker, P.M.; López-Sánchez, J.I. Jobs mismatch and productivity impact of information technology. Serv. Ind. J. 2014, 34, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, M.R.; Parent, M.R. Relationships between Job Skills and Performance: A Study of Webmasters. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2002, 18, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, A.H.; Bichang’a, W.O.; Atambo, W.N. Effects of educational mismatch on employee performance: A case study of Co-operative Bank of Kenya Ltd. Glob. Bus. Econ. Res. J. 2015, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Locke, E.A. Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology. The Nature and Cause of Job Satisfaction; Dunnette, M.D., Ed.; Rand McNally: Chicago, IL, USA, 1976; pp. 1293–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, H.M.; Cropanzano, R. Research in organizational behavior: An annual series of analytical essays and critical reviews. In Affective Events Theory: A Theoretical Discussion of the Structure, Causes and Consequences of Affective Experiences at Work; Staw, B.M., Cummings, L.L., Eds.; Elsevier Science/JAI Press: Stamford, CT, USA, 1996; Volume 18, pp. 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Inkeun, H. A Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Performance Pay between Public and Private Organizations. J. Gov. Stud. 2013, 8, 87–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrow, C. A framework for the comparative analysis of organization. Am. Social. Rev. 1967, 32, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.M. Technological differences in job characteristics, employee satisfaction, and motivation: A synthesis of job design research and social technical system theory. Organ. Behav. Hum. Perform. 1978, 19, 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igalens, J.; Roussel, P. A study of the relationships between compensation package, work motivation and job satisfaction. J. Organ. Behav. 1999, 20, 1003–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberg, F.; Mausner, B.; Snyderman, B.B. The Motivation to Work, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.C.; Kendall, L.M.; Hulin, C.C. The Measurement of Satisfaction in Work and Retirement; Rand McNally: Chicago, IL, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, D.; Dawis, R.; England, G.; Lofquist, L.J. Manual for the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire; Industrial Relations Center, University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, P.E. Measurement of human service staff satisfaction: Development of the job satisfaction survey. Am. J. Community Psychol. 1985, 13, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furnham, A.; Eracleous, A.; Chamorro-Premuzic, T. Personality, motivation and job satisfaction: Hertzberg meets the Big Five. J. Manag. Psychol. 2009, 24, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millette, V.; Gagnè, M. Designing volunteers’ tasks to maximize motivation, satisfaction and performance: The impact of job characteristics on volunteer engagement. Mot. Emot. 2008, 32, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Van de Vliert, E. Where intrinsic job satisfaction fails to work: National moderators of intrinsic motivation. J. Organ. Behav. 2003, 24, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNall, L.A.; Masuda, A.D.; Nicklin, J.M. Flexible Work Arrangements, Job Satisfaction, and Turnover Intentions: The Mediating Role of Work-to-Family Enrichment. J. Sychol. 2010, 144, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae-Soon, U.; Hyun-Sil, K. Impacts of Job Stress and Job Satisfaction on Depression among Local Public Servants. Health Soc. Sci. 2013, 34, 135–158. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, T.A.; Thoresen, C.J.; Bono, J.E.; Patton, G.K. The job satisfaction-job performance relationship: A qualitative and quantitative review. Psychol. Bull. 2001, 127, 376–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgensen, C.E. Job preferences (What makes a job good or bad?). J. Appl. Psychol. 1978, 50, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneman, H.G., III; Schwab, D.P. Pay satisfaction: Its multidimensional nature and measurement. Int. J. Psychol. 1985, 20, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Judge, T.A.; Piccolo, R.F.; Podsakoff, N.P.; Shaw, J.C.; Rich, B.L. The relationship between pay and job satisfaction: A meta-analysis of the literature. J. Vocat. Behav. 2010, 77, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.N.; Brummel, B.J. Examining the curvilinear relationship between income and job and pay satisfaction. J. Pers. Psychol. 2016, 1, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhart, B.; Rynes, S.L. Compensation: Theory, Evidence, and Strategic Implications; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Currall, S.C.; Towler, A.J.; Judge, T.A.; Kohn, L. Pay Satisfaction and Organizational Outcomes. Pers. Psychol. 2005, 58, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, S.; Pouliakas, K.; Redmond, P. How Useful Is the Concept of Skills Mismatch? Skills and Employability Branch International Labour Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kristo-Brown, A.L. Person-organization fit: An integrative review of its conceptualizations, measurement, and implications. Pers. Psychol. 1996, 49, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, D.M.; Judge, T.A. Interviewers’ Perceptions of person-organization fit and organizational selection decisions. J. Appl. Psychol. 1997, 82, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, N.; West, M. Managerial Job Change, Men and Women in Transition; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, K.A.; Heywood, J.S. Educational Mismatch among Ph.D.s: Determinants and Consequences. Science and Engineering Careers in the United States; Freeman, R.B., Goroff, D.L., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 229–256. [Google Scholar]
- Canal Domínguez, J.F.; Rodríguez Gutiérrez, C. Wage differences among Ph. Ds by area of knowledge: Are science areas better paid than humanities and social ones? The Spanish case. J. Educ. Work 2013, 26, 187–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si-jeoung, K.; Ok, C.S.; Yoonkyo, S. The Effects of Job Mismatch on Job Satisfaction and Performance. Gov. Stud. 2017, 23, 125–150. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristics | N (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 2019 | (88.8) |
| Female | 254 | (11.2) | |
| Age | 20 s | 1 | (0) |
| 30 s~40 s | 533 | (23.4) | |
| 50 s~60 s | 1608 | (70.7) | |
| over 70 s | 131 | (5.8) | |
| Major | Science | 429 | (18.9) |
| Technology | 1005 | (44.2) | |
| Medical science | 213 | (9.4) | |
| Agriculture | 115 | (5.1) | |
| Social Science | 362 | (15.9) | |
| Humanities | 149 | (6.6) | |
| Organization | Private | 477 | (21.0) |
| Public | 485 | (21.3) | |
| University | 1209 | (53.2) | |
| NPO (Non Profit Organization) | 65 | (2.9) | |
| Etc. | 37 | (1.6) | |
| Dimension | Explanation | Variables | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Job mismatch | The gap between the qualities and capacities of individuals recognized at the time of doctoral degree acquisition versus the qualifications and capacities recognized as necessary for the current job | MISMATCH | |
| Pay | Current annual salary | ln_PAY | |
| Job satisfaction | Rated on a 5-point Likert scale of satisfaction on 10 items in total: Welfare, job security, geographical location, working environment, promotion opportunities, intellectual stimulation, level of responsibility, level of independence, social contribution, social status | JOBSATIS_1~JOBSATIS_10 | |
| Performance | Research performance | Publications in domestic and international journals, translation works | ln_OUT, ln_IN, ln_CNT |
| Patent performance | Patent applications, registration outcomes | ln_PATENTCNTln_PATENTRCNT | |
| Dimension | Factor Loading | Communality | Eigen Value | Cumulative | Cronbach’s α | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research performance | OUT | 0.651 | 0.516 | 1.367 | 27.34 | 0.516 |
| IN | 0.331 | 0.735 | ||||
| CNT | 0.041 | 0.720 | ||||
| Patent performance | PATENTCNT | 0.901 | 0.823 | 2.231 | 44.61 | 0.854 |
| PATENTRCNT | 0.893 | 0.804 | ||||
| KMO = 0.606, Bartlett’s = 3263 *** | ||||||
| Model Fit | Absolute Fit Index | Relative Fit Index | ||||
| GFI | AGFI | IFI | RMSEA | NFI | CFI | |
| 0.935 | 0.901 | 0.909 | 0.063 | 0.902 | 0.909 | |
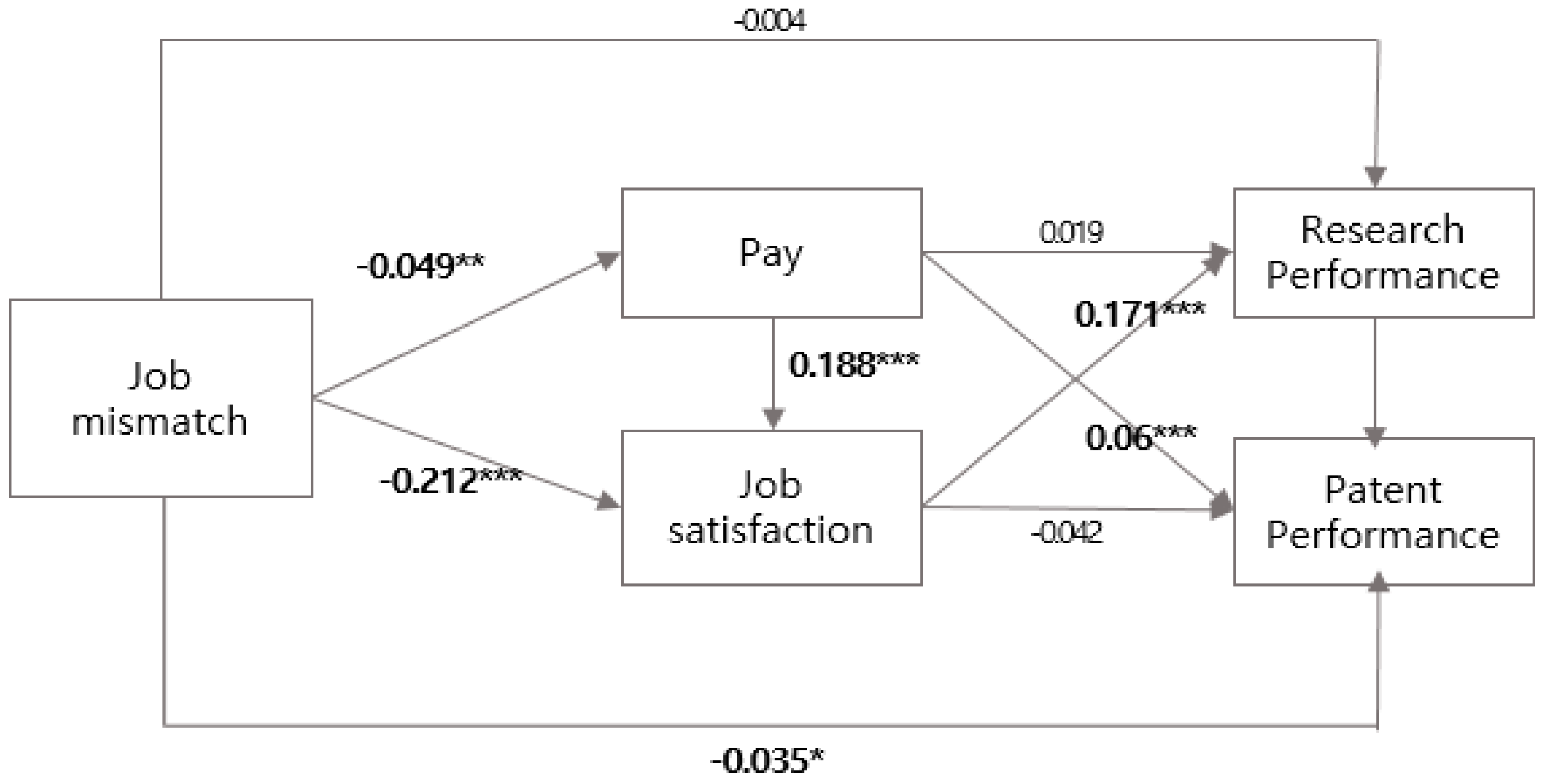
| Path | Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | S.E. | C.R. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pay | ← | jobmismatch | H1 | −0.006 | −0.049 | 0.002 | −2.437 ** |
| Job satisfaction | ← | jobmismatch | H1 | −0.018 | −0.212 | 0.00 | −9.902 *** |
| research | ← | jobmismatch | H2 | −0.637 | −0.004 | 3.244 | −0.196 |
| patent | ← | jobmismatch | H2 | −3.980 | −0.035 | 2.311 | −1.722 * |
| Job satisfaction | ← | Pay | H3 | 0.132 | 0.188 | 0.016 | 8.508 *** |
| research | ← | Pay | H4 | 23.554 | 0.019 | 27.301 | 0.863 |
| patent | ← | Pay | H4 | 55.460 | 0.060 | 19.467 | 2.849 *** |
| research | ← | Job satisfaction | H5 | 304.475 | 0.171 | 42.958 | 7.088 *** |
| Patent | ← | Job satisfaction | H5 | −54.357 | −0.042 | 32.199 | −1.688 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-J.; Choi, S.O. The Effects of Job Mismatch on Pay, Job Satisfaction, and Performance. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2018, 4, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc4040049
Kim S-J, Choi SO. The Effects of Job Mismatch on Pay, Job Satisfaction, and Performance. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity. 2018; 4(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc4040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Si-Jeoung, and Sang Ok Choi. 2018. "The Effects of Job Mismatch on Pay, Job Satisfaction, and Performance" Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 4, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc4040049
APA StyleKim, S.-J., & Choi, S. O. (2018). The Effects of Job Mismatch on Pay, Job Satisfaction, and Performance. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 4(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc4040049





