Short-Term Effect of a New Oral Sodium Hyaluronate Formulation on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Criteria for Eligibility of Patients
2.3. Treatment
2.4. Outcome Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
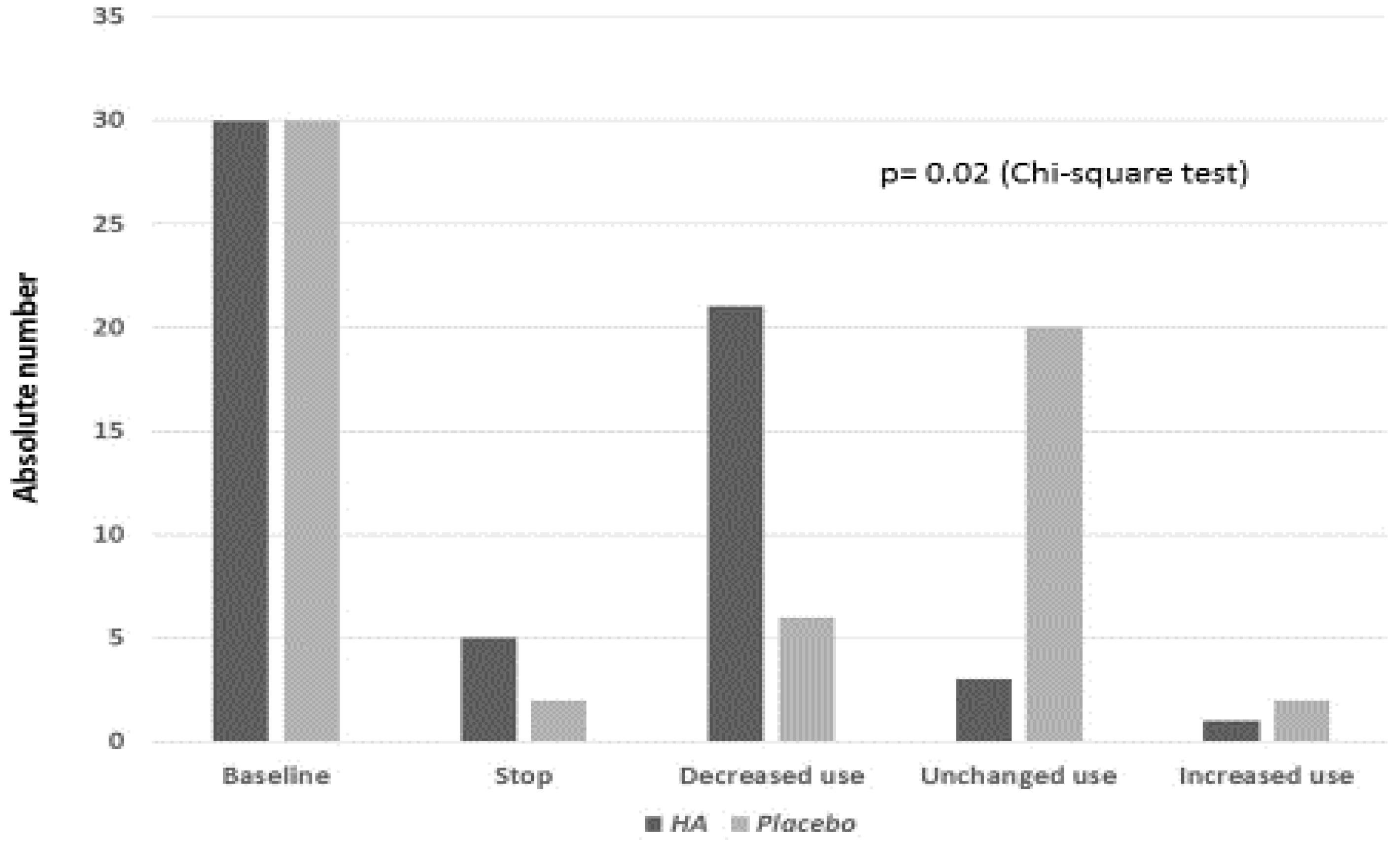
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, D.J. Osteoarthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 25, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arden, N.; Nevitt, M. Osteoarthritis: Epidemiology. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckwalter, J.A.; Mankin, H.J. Articular cartilage: Degeneration and osteoarthritis, repair, regeneration, and transplantation. Instr. Course Lect. 1998, 47, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, J.; Berenbaum, F.; Lafeber, F.P. Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet 2011, 377, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peat, G.; McCarney, R.; Croft, P. Knee pain and osteoarthritis in older adults: A review of community burden and current use of primary health care. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Abraham, J. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 dis-eases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.J.; McCabe, P.; McBeth, J. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Hartrick, C.; Edelsberg, J.; Sadosky, A.; Oster, G. Direct and indirect economic costs among private-sector em-ployees with osteoarthritis. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 53, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Junoy, J.; Zamora, A.R. Socio-economic costs of osteoarthritis: A systematic review of cost-of-illness studies. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 44, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Hawker, G.A.; Laporte, A.; Croxford, R.; Coyte, P.C. The economic burden of disabling hip and knee osteoarthritis (OA) from the perspective of individuals living with this condition. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarz, H.; Gunnarsson, C.L.; Fang, H.; Rizzo, J. Insurer, and out-of-pocket costs of osteoarthritis in the US: Evidence from national survey data. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3546–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevsevar, D.S. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: Evidence-based guideline. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2013, 21, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Recommendations for the medical management of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: 2000 update. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 1905–1915. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Nuki, G.; Moskowitz, R.; Abramson, S.; Altman, R.; Arden, N.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Brandt, K.; Croft, P.; Doherty, M.; et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 476–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazs, E.A.; Denlinger, J.L. Viscosupplementation: A new concept in the treatment of osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1993, 39, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Legré-Boyer, V. Viscosupplementation: Techniques, indications, results. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, S101–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, H.; Burkhardt, D.; Sambrook, P.; March, L. Longterm effects of intraarticular hyaluronan on syno-vial fluid in osteoarthritis of the knee. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 946–950. [Google Scholar]
- Brosseau, L.; Taki, J.; Desjardins, B.; Thevenot, O.; Fransen, M.; Wells, G.A.; Imoto, A.M.; Toupin-April, K.; Westby, M.; Gallardo, I.C.Á.; et al. The Ottawa panel clinical practice guidelines for the management of knee osteoarthritis. Part one: Introduction, and mind-body exercise programs. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Rannou, F.; Richette, P.; Bruyère, O.; Al-Daghri, N.; Altman, R.D.; Brandi, M.L.; Basset, S.C.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Migliore, A.; et al. Use of Intraarticular Hyaluronic Acid in the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis in Clinical Practice. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 69, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.; Awad, M.E.; Hamrick, M.W.; Hunter, M.; Fulzele, S. Recent advances in hyaluronic acid-based therapy for os-teoarthritis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.P.; Martel-Pelletier, J. The pathophysiology of osteoarthritisc and the implication of the use of hyaluronan and hylan as therapeutic agents in viscosupplementation. J. Rheumatol. 1993, 39, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Natov, N.S.; Obadan, L.E. Therapeutic trajectory of hyaluronic acid versus cortico-steroids in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, T.; Seino, S.; Sato, T.; Matsuoka, R.; Masuda, Y.; Fukui, N. Oral Administration of Polymer Hyaluronic Acid Alleviates Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study over a 12-Month Period. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 167928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, F.; Zvirbulis, R.A.; Zonca, B.; Li, K.W.; Turner, S.M.; Pasierb, M.; Wilton, P.; Martínez-Puig, D.; Wu, W. The effects of an oral preparation containing hyaluronic acid (Oralvisc®) on obese knee osteoarthritis patients determined by pain, function, bradykinin, leptin, inflammatory cytokines, and heavy water analyses. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 35, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Micheloni, G.M.; Berti, M.; Perusi, E.; Sambugaro, E.; Vecchini, B. Clinical comparison of oral administration and viscosupplemen-tation of hyaluronic acid (HA) in early knee osteoarthritis. Musculoskelet Surg. 2017, 101, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francomanno, F.; Puoci, F.; Amone, F. Technological development of a jaluronic acid with a large spec-trum of molecular weight and high bioavailability. Pharmanutr. Funct. Food 2019, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Schmid, C.H.; Kent, D.M.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Wong, J.B.; McAlindon, T.E. Comparative Effectiveness of Pharmacologic Interventions for Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.D.; Manjoo, A.; Fierlinger, A.; Niazi, F.; Nicholls, M. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, M.K.; Ludwig, T.E.; Liebisch, G.; Zhang, R.; Siebert, H.C.; Wilhelm, J.; Rickert, M. Articular joint lubricants during osteoarthritis and rheu-matoid arthritis display altered levels and molecular species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.R.E.; Laurent, T.C. Hyaluronan: Its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, E.A. The physical properties of synovial fluid and the special role of hyaluronic acid. In Disorders of the Knee, 2nd ed.; Helfet, A.J., Ed.; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1982; pp. 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Balazs, E.A.; Denlinger, J.L. Sodium hyaluronate acid and joint function. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1985, 5, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D. Laboratory findings in osteoarthritis. In Osteoarthritis-Diagnosis and Medical Surgical Manage-Ment, 2nd ed.; Moskowtz, R., Howell, D., Goldberg, V., Mankin, J., Saunders, W.B., Eds.; Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; pp. 313–328. [Google Scholar]
- Balazs, E.A.; Watson, D.; Duff, I.F.; Roseman, S. Hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid. I. Molecular parameters of hyaluronic acid in normal and arthritic human fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1967, 10, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazs, E.A.; Briller, S.; Denlinger, J.L. Na-hyaluronate molecular size variations in equine arthritis and human arthritic synovial fluid and the effect on phagocytic cells. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Talbot, J., Ed.; Grune and Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, L.S. Viscosupplementation therapy with intra-articular hyaluronic acid: Fact or fantasy? Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 25, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.E.; Allen, K.D.; Golightly, Y.M.; Goode, A.P.; Jordan, J.M. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: The Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmeier, S.F.; Shaffer, B.S. Viscosupplementation Therapy for Osteoarthritis. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2006, 14, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, N.; Campbell, J.; Robinson, V.; Gee, T.L.; Bourne, R.; Wells, G.; Welch, V.; Wells, G.A. Viscosupplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 2, CD005321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finelli, I.; Chiessi, E.; Galesso, D.; Renier, D.; Paradossi, G. A new viscosupplement based on partially hydrophobic hyaluronic acid: A comparative study. Biorheology 2011, 48, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, A.; Stellavato, A.; Busico, T.; Papa, A.; Tirino, V.; Papaccio, G.; la Gatta, A.; de Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. In vitro analysis of the effects on wound healing of high- and low-molecular weight chains of hyaluronan and their hybrid H-HA/L-HA complexes. BMC Cell Boil. 2015, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, G.S.; Attridge, V.L.; Lenninger, M.R.; Benson, K.F. Oral intake of a liquid high-molecular-weight hyaluronan associated with relief of chronic pain and reduced use of pain medication: Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind pilot study. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, E.A. Viscosupplementation for treatment of osteoarthritis: From initial discovery to status and results. Surg. Technol. Int. 2004, 12, 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Asari, A.; Kanemitsu, T.; Kurihara, H. Oral Administration of High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan (900 kDa) Controls Immune System via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Intestinal Epithelium. J. Boil. Chem. 2010, 285, 24751–24758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendzerska, T.; King, L.K.; Lipscombe, L.; Croxford, R.; Stanaitis, I.; Hawker, G.A. The impact of hip and knee osteoarthritis on the subsequent risk of incident diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetology 2018, 61, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Sang, L.; Wu, D.; Rong, J.; Jiang, L. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosseau, L.; Taki, J.; Desjardins, B.; Thevenot, O.; Fransen, M.; Wells, G.A.; Imoto, A.M.; Toupin-April, K.; Westby, M.; Gallardo, I.C. Álvarez; et al. The Ottawa panel clinical practice guidelines for the management of knee osteoarthritis. Part two: Strengthening exercise programs. Clin. Rehabil. 2017, 31, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harirforoosh, S.; Asghar, W.; Jamali, F. Adverse effects of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: An update of gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and renal complications. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 16, 821–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Rassen, J.A.; Glynn, R.J.; Lee, J.; Levin, R.; Schneeweiss, S. The comparative safety of analgesics in older adults with arthritis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conaghan, P.G. A turbulent decade for NSAID’s: Update on current concepts of classification, epidemiology, comparative efficacy, and toxicity. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 32, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Advani, S.M.; Peng, H.-L.; Banfield, E.; Hawk, E.T.; Chang, S.; Frazier-Wood, A.C. Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in US adults: Changes over time and by demographic. Open Hear. 2017, 4, e000550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasciuškevičiūtė, S.; Gumbrevičius, G.; Vendzelytė, A.; Sčiupokas, A.; Petrikonis, K.; Kadusevicius, E. Impact of the World Health Organization Pain Treatment Guidelines and the European Medicines Agency Safety Recommendations on Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Use in Lithuania: An Observational Study. Medicina 2018, 54, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FS-HA (n: 30) | Placebo (n: 30) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | T28 | T56 | T0 | T28 | T56 | |
| VAS-p (mean ± SD) | 6.7 ± 1.0 | 5.5 * ± 0.9 | 4.1 *,° ± 0.6 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 6.0 ± 1.3 |
| Pain WOMAC (mean ± SD) | 9.6 ± 1.2 | 9.0 * ± 1.2 | 8.8 *,° ± 0.9 | 9.3 ± 1.4 | 9.1 ± 1.2 | 9.3 ± 1.1 |
| Function WOMAC (mean ± SD) | 22.8 ± 2.4 | 22.1 ± 2.5 | 20.3 ± 1.9 * | 23.1 ± 2.7 | 22.9 ± 2.8 | 22.7 ± 2.1 |
| Total WOMAC (mean ± SD) | 40.3 ± 3.8 | 36.8 * ± 4.3 | 33.9 *,° ± 4.1 | 40.5 ± 3.8 | 39.3 ± 4.1 | 38.9 ± 4.4 |
| Lequesne Functional Index (mean ± SD) | 6.5 ± 0.9 | 6.3 ± 1.0 | 6.1 * ± 1.1 | 6.7 ± 1.1 | 6.5 ± 1.0 | 6.5 ± 1.2 |
| Extension ROM (mean ± SD) | 86 ± 11 | 88 ± 12 | 91 ± 15 * | 85 ± 13 | 84 ± 11 | 82 ± 13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cicero, A.F.G.; Girolimetto, N.; Bentivenga, C.; Grandi, E.; Fogacci, F.; Borghi, C. Short-Term Effect of a New Oral Sodium Hyaluronate Formulation on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Diseases 2020, 8, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8030026
Cicero AFG, Girolimetto N, Bentivenga C, Grandi E, Fogacci F, Borghi C. Short-Term Effect of a New Oral Sodium Hyaluronate Formulation on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Diseases. 2020; 8(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleCicero, Arrigo F. G., Nicolò Girolimetto, Crescenzio Bentivenga, Elisa Grandi, Federica Fogacci, and Claudio Borghi. 2020. "Short-Term Effect of a New Oral Sodium Hyaluronate Formulation on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial" Diseases 8, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8030026
APA StyleCicero, A. F. G., Girolimetto, N., Bentivenga, C., Grandi, E., Fogacci, F., & Borghi, C. (2020). Short-Term Effect of a New Oral Sodium Hyaluronate Formulation on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Diseases, 8(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases8030026








