Genetic Substrate Reduction Therapy: A Promising Approach for Lysosomal Storage Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
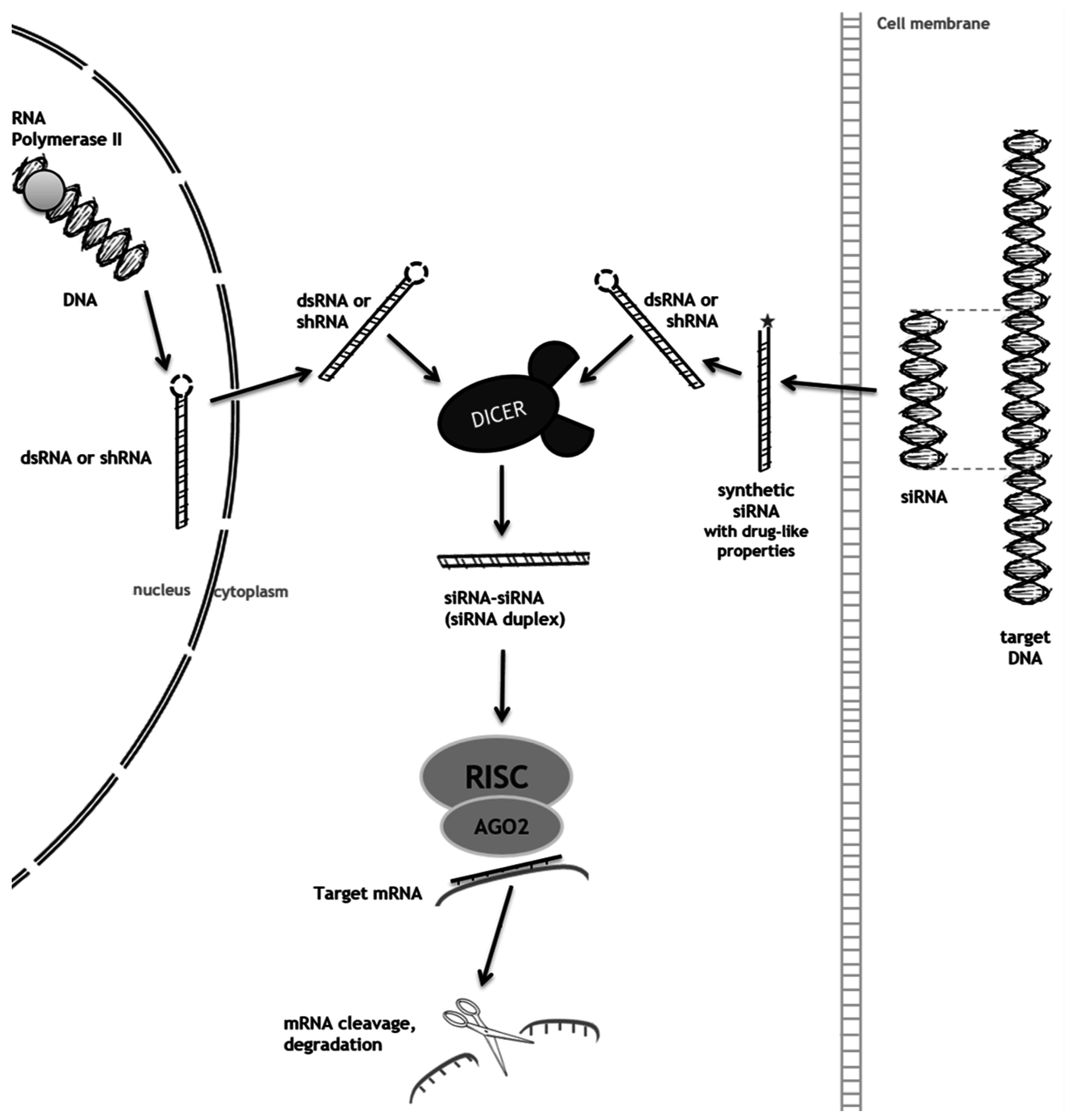
2. RNA Interference (RNAi) as a Mechanism to Promote Substrate Reduction
2.1. RNAi-Mediated SRT for Gaucher Disease
2.2. RNAi-Mediated SRT for Mucopolysaccharidoses
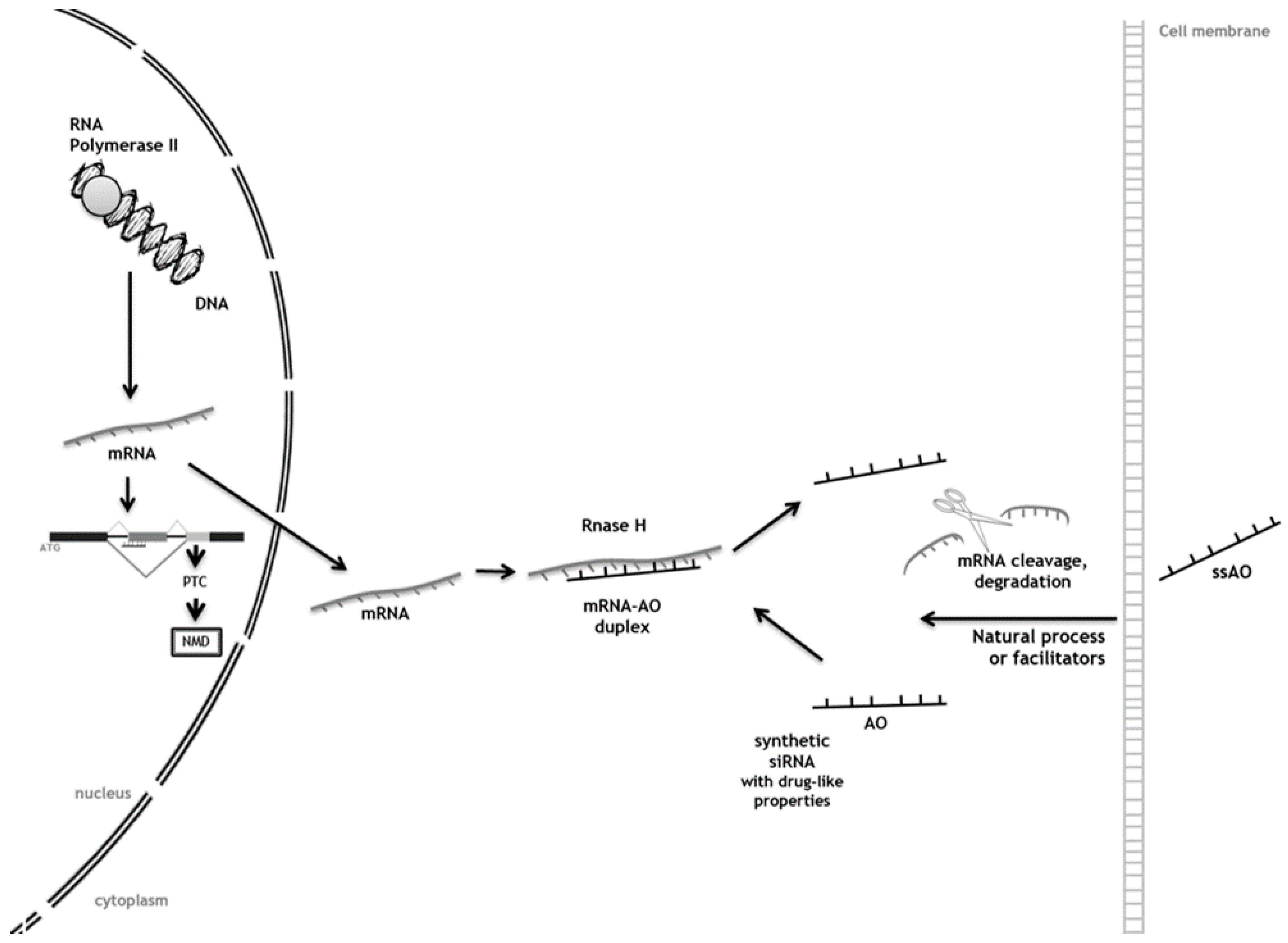
3. Antisense Oligonucleotides (AOs) as Tools to Achieve Substrate Reduction
Antisense Oligonucleotide-Mediated SRT for Pompe Disease
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radin, N.S. Treatment of gaucher disease with an enzyme inhibitor. Glycoconj. J. 1996, 13, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Wegrzyn, A.; Wegrzyn, G. Substrate deprivation therapy: A new hope for patients suffering from neuronopathic forms of inherited lysosomal storage diseases. J. Appl. Genet. 2007, 48, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, T.M. Current treatments. In Lysosomal Storage Disorders—A Practical Guide, 1th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Malden, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, H.; Lee, J.I. Current and potential therapeutic strategies for mucopolysaccharidoses. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabig-Ciminska, M.; Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Malinowska, M.; Kloska, A.; Piotrowska, E.; Chmielarz, I.; Moskot, M.; Wegrzyn, A.; Wegrzyn, G. Combined therapies for lysosomal storage diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 2015, 15, 746–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venier, R.E.; Igdoura, S.A. Miglustat as a therapeutic agent: Prospects and caveats. J. Med. Genet. 2012, 49, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayman, J.A. Eliglustat tartrate: Glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor treatment of type 1 gaucher disease. Drugs Future 2010, 35, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Piotrowska, E.; Gabig-Ciminska, M.; Borysiewicz, E.; Slominska-Wojewodzka, M.; Narajczyk, M.; Wegrzyn, A.; Wegrzyn, G. Substrate reduction therapies for mucopolysaccharidoses. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1860–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.V.; Ignacimuthu, S. RNA interference—A silent but an efficient therapeutic tool. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 1774–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClorey, G.; Wood, M.J. An overview of the clinical application of antisense oligonucleotides for RNA-targeting therapies. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 24, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobbin, M.L.; Rossi, J.J. RNA interference (RNAi)-based therapeutics: Delivering on the promise? Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Font, A.; Chabas, A.; Grinberg, D.; Vilageliu, L. RNAi-mediated inhibition of the glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) gene: A preliminary study towards a therapeutic strategy for gaucher disease and other glycosphingolipid storage diseases. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2006, 37, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziedzic, D.; Wegrzyn, G.; Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J. Impairment of glycosaminoglycan synthesis in mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA cells by using siRNA: A potential therapeutic approach for sanfilippo disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2010, 18, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canals, I.; Beneto, N.; Cozar, M.; Vilageliu, L.; Grinberg, D. EXTL2 and EXTL3 inhibition with siRNAs as a promising substrate reduction therapy for sanfilippo C syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, N.P.; Nelson, C.A.; Weeden, T.; Taylor, K.M.; Moreland, R.J.; Scheule, R.K.; Phillips, L.; Leger, A.J.; Cheng, S.H.; Wentworth, B.M. Antisense oligonucleotide-mediated suppression of muscle glycogen synthase 1 synthesis as an approach for substrate reduction therapy of pompe disease. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barata, P.; Sood, A.K.; Hong, D.S. RNA-targeted therapeutics in cancer clinical trials: Current status and future directions. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 50, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, M.; Arenz, C.; Schmitz, K.; Sandhoff, K.; Schepers, U. Long endogenous dsRNAs can induce complete gene silencing in mammalian cells and primary cultures. Oligonucleotides 2003, 13, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaidonis, X.; Liaw, W.C.; Roberts, A.D.; Ly, M.; Anson, D.; Byers, S. Gene silencing of EXTL2 and EXTL3 as a substrate deprivation therapy for heparan sulphate storing mucopolysaccharidoses. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2010, 18, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Hopwood, J.J.; Clague, A.E.; Carey, W.F. Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 1999, 281, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Grabowski, G.A. Gaucher disease: Perspectives on a prototype lysosomal disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2002, 59, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederickson, D.S.; Sloan, H.R. Glucosyl ceramide lipidoses: Gaucher’s disease. In The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease; Stanbury, J.B., Wyngaarden, J.B., Frederickson, D.S., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 730–759. [Google Scholar]
- Dreborg, S.; Erikson, A.; Hagberg, B. Gaucher disease—norrbottnian type. I. General clinical description. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1980, 133, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidransky, E.; Sherer, D.M.; Ginns, E.I. Gaucher disease in the neonate: A distinct gaucher phenotype is analogous to a mouse model created by targeted disruption of the glucocerebrosidase gene. Pediatr. Res. 1992, 32, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.D.; Nelson, P.V.; Robertson, E.F.; Morris, C.P. Mutation analysis of 28 gaucher disease patients: The australasian experience. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1994, 49, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangas, M.; Nogueira, C.; Prata, M.J.; Lacerda, L.; Coll, M.J.; Soares, G.; Ribeiro, G.; Amaral, O.; Ferreira, C.; Alves, C.; et al. Molecular analysis of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB in portugal: Evidence of a single origin for a common mutation (R234C) in the iberian peninsula. Clin. Genet. 2008, 73, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, M.F.; Lacerda, L.; Prata, M.J.; Ribeiro, H.; Lopes, L.; Ferreira, C.; Alves, S. Molecular characterization of portuguese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis IIIC: Two novel mutations in the hgsnat gene. Clin. Genet. 2008, 74, 194–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.; Mangas, M.; Prata, M.J.; Ribeiro, G.; Lopes, L.; Ribeiro, H.; Pinto-Basto, J.; Lima, M.R.; Lacerda, L. Molecular characterization of portuguese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II shows evidence that the ids gene is prone to splicing mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrow, T.A.; Grabowski, G.A. Emerging treatments and future outcomes. In Lysosomal Storage Disorders—A Practical Guide, 1th ed.; Wiley: Malden, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, M.F.; Santos, J.I.; Alves, S. Less is more: Substrate reduction therapy for lysosomal storage disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziedzic, D.; Narajczyk, M.; Gabig-Ciminska, M.; Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J. Simultaneous siRNA-mediated silencing of pairs of genes coding for enzymes involved in glycosaminoglycan synthesis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chmielarz, I.; Gabig-Ciminska, M.; Malinowska, M.; Banecka-Majkutewicz, Z.; Wegrzyn, A.; Jakobkiewicz-Banecka, J. Comparison of siRNA-mediated silencing of glycosaminoglycan synthesis genes and enzyme replacement therapy for mucopolysaccharidosis in cell culture studies. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paterson, B.M.; Roberts, B.E.; Kuff, E.L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 4370–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chery, J.; Naar, A. RNA therapeutics: RNAi and antisense mechanisms and clinical applications. Postdoc. J. 2016, 4, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, M.M.; Toonen, L.J.; van Roon-Mom, W.M. Antisense oligonucleotides in therapy for neurodegenerative disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 87, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehr, B. Fomivirsen approved for CMV retinitis. J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care 1998, 4, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magen, I.; Hornstein, E. Oligonucleotide-based therapy for neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. 2014, 1584, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gragoudas, E.S.; Adamis, A.P.; Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Feinsod, M.; Guyer, D.R. Pegaptanib for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2805–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooke, S.T.; Geary, R.S. Clinical pharmacological properties of mipomersen (kynamro), a second generation antisense inhibitor of apolipoprotein B. Br. J. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 76, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompe, J.C. Over idiopathische hypertrophie van het hart. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 1932, 76, 304–312. [Google Scholar]
- Amalfitano, A.; Bengur, A.R.; Morse, R.P.; Majure, J.M.; Case, L.E.; Veerling, D.L.; Mackey, J.; Kishnani, P.; Smith, W.; McVie-Wylie, A.; et al. Recombinant human acid alpha-glucosidase enzyme therapy for infantile glycogen storage disease type II: Results of a phase I/II clinical trial. Genet. Med. 2001, 3, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winkel, L.P.; Kamphoven, J.H.; van den Hout, H.J.; Severijnen, L.A.; van Doorn, P.A.; Reuser, A.J.; van der Ploeg, A.T. Morphological changes in muscle tissue of patients with infantile pompe’s disease receiving enzyme replacement therapy. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinge, L.; Straub, V.; Neudorf, U.; Voit, T. Enzyme replacement therapy in classical infantile pompe disease: Results of a ten-month follow-up study. Neuropediatrics 2005, 36, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeberl, D.D.; Kishnani, P.S.; Chen, Y.T. Glycogen storage disease types I and II: Treatment updates. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishnani, P.S.; Corzo, D.; Nicolino, M.; Byrne, B.; Mandel, H.; Hwu, W.L.; Leslie, N.; Levine, J.; Spencer, C.; McDonald, M.; et al. Recombinant human acid [alpha]-glucosidase: Major clinical benefits in infantile-onset pompe disease. Neurology 2007, 68, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolino, M.; Byrne, B.; Wraith, J.E.; Leslie, N.; Mandel, H.; Freyer, D.R.; Arnold, G.L.; Pivnick, E.K.; Ottinger, C.J.; Robinson, P.H.; et al. Clinical outcomes after long-term treatment with alglucosidase alfa in infants and children with advanced pompe disease. Genet. Med. 2009, 11, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishnani, P.S.; Corzo, D.; Leslie, N.D.; Gruskin, D.; Van der Ploeg, A.; Clancy, J.P.; Parini, R.; Morin, G.; Beck, M.; Bauer, M.S.; et al. Early treatment with alglucosidase alpha prolongs long-term survival of infants with pompe disease. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prater, S.N.; Banugaria, S.G.; DeArmey, S.M.; Botha, E.G.; Stege, E.M.; Case, L.E.; Jones, H.N.; Phornphutkul, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Young, S.P.; et al. The emerging phenotype of long-term survivors with infantile pompe disease. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard-Guilloux, G.; Raben, N.; Takikita, S.; Batista, L.; Caillaud, C.; Richard, E. Modulation of glycogen synthesis by RNA interference: Towards a new therapeutic approach for glycogenosis type II. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 3876–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashe, K.M.; Taylor, K.M.; Chu, Q.; Meyers, E.; Ellis, A.; Jingozyan, V.; Klinger, K.; Finn, P.F.; Cooper, C.G.; Chuang, W.L.; et al. Inhibition of glycogen biosynthesis via mTORC1 suppression as an adjunct therapy for pompe disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 100, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, H.M.; Moulton, J.D. Morpholinos and their peptide conjugates: Therapeutic promise and challenge for duchenne muscular dystrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantounas, I.; Phylactou, L.A.; Uney, J.B. RNA interference and the use of small interfering RNA to study gene function in mammalian systems. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 33, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.D.; Vorhies, J.S.; Senzer, N.; Nemunaitis, J. SiRNA vs. ShRNA: Similarities and differences. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussecker, D. Stacking up CRISPR against RNAi for therapeutic gene inhibition. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 3249–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voytas, D.F.; Gao, C. Precision genome engineering and agriculture: Opportunities and regulatory challenges. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayudham, A.; Dolganiuc, A.; Ellis, M.; Petrasek, J.; Kodys, K.; Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. Vsl#3 probiotic treatment attenuates fibrosis without changes in steatohepatitis in a diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model in mice. Hepatology 2009, 49, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polyak, D.; Krivitsky, A.; Scomparin, A.; Eliyahu, S.; Kalinski, H.; Avkin-Nachum, S.; Satchi-Fainaro, R. Systemic delivery of siRNA by aminated poly(α)glutamate for the treatment of solid tumors. J. Control. Release 2016, 16, 30411–30414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.; Gao, X. Functional peptides for siRNA delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Yang, N.; Nadithe, V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: Current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boado, R.J. RNA interference and nonviral targeted gene therapy of experimental brain cancer. NeuroRx J. Am. Soc. Exper. NeuroTher. 2005, 2, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, J.J. RNAi therapeutics: Snalping siRNAs in vivo. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. Recent advances of using polyhydroxyalkanoate-based nanovehicles as therapeutic delivery carriers. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.C.; Ezzat, K.; El Andaloussi, S.; Weinberg, M.S. Synthetic siRNA delivery: Progress and prospects. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1364, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruun, J.; Larsen, T.B.; Jolck, R.I.; Eliasen, R.; Holm, R.; Gjetting, T.; Andresen, T.L. Investigation of enzyme-sensitive lipid nanoparticles for delivery of siRNA to blood-brain barrier and glioma cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5995–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Serramia, M.J.; Alvarez, S.; Fuentes-Paniagua, E.; Clemente, M.I.; Sanchez-Nieves, J.; Gomez, R.; de la Mata, J.; Munoz-Fernandez, M.A. In vivo delivery of siRNA to the brain by carbosilane dendrimer. J. Control. Release 2015, 200, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck, J.; Pascolo, S.; Fuchs, K.; Kellerer, C.; Glocova, I.; Geisel, J.; Dengler, K.; Yazdi, A.S.; Rocken, M.; Ghoreschi, K. Cholesterol modification of p40-specific small interfering RNA enables therapeutic targeting of dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, M.M.; Dar, G.H.; Jeyalakshmi, D.; Venkatraman, U.; Saba, K.; Rangaraj, N.; Patel, A.B.; Gopal, V. A designed recombinant fusion protein for targeted delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain. J. Control. Release 2016, 228, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabathuler, R.; Ho, L.; Tian, M.M.; Hutchison, R.; Jefferies, W. Using a Peptide Derived from Transcend (mtf, p97) to Deliver Biologics to the CNS Using a Physiologic Pathway. Available online: http://www.brains4brain.eu/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/9th-B4B-Workshop-Scientific-Programme.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- Haskins, M.E.; Giger, U.; Patterson, D.F. Animal models of lysosomal storage diseases: Their development and clinical relevance. In Fabry Disease: Perspectives from 5 Years of FOS; Mehta, A., Beck, M., Sunder-Plassmann, G., Eds.; Oxford Pharmagenesis: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
| Drug | Target | Condition | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNAi | ||||
| DCR-MYC | Myc | Solid tumors Hepatocellular carcinoma | I | Recruiting |
| I/II | Recruiting | |||
| ALN-TTRSC (Revusiran) | Transthyretin | TTR-mediated familial amyloidotic cardiomyopathy | I | Completed |
| II | Active | |||
| III | Active | |||
| ALN-CC5 | Complement component C5 | Paroxysmal nocturnal Hemoglobinuria | I/II | Active |
| ALN-AS1 | ALAS-1 | Acute intermittent porphyria | I | Recruiting |
| ALN-PCSSC | PCSK9 | Hypercholesterolemia | I | Completed |
| ALN-TTR02 (Patisiran) | Transthyretin | TTR-mediated amyloidosis | II | Active |
| III | Active | |||
| ALN-AT3SC | Antithrombin | Hemophilia A/B | I | Recruiting |
| TKM-080301 | Polo-like kinase 1 | Hepatocellular carcinoma Neuroendocrine tumors | I | Active |
| I/II | Recruiting | |||
| TKM-100802 | Ebola genome | Ebola virus | I/II | Terminated |
| QPI-1007 | Caspase 2 | Primary angle-closure glaucoma | II | Completed |
| RXI-109 | CTGF | Hypertrophic scar keloid excision surgery | II | Completed |
| II | Completed | |||
| Atu027 | PKN3 | Pancreatic ductal carcinoma | I/II | Completed |
| SYL040012 | Β2-adrenergic receptor | Ocular hypertension | II | Completed |
| Antisense | ||||
| Mipomersen * | ApoB 100 | Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia atherosclerosis | III | Completed |
| III | Completed | |||
| ISIS-TTRRX | Transthyretin | Familial amyloid polyneuropathy | III | Active |
| ISIS-ApoC-IIIRX | ApoCIII | Hypertriglyceridemia | II | Completed |
| ISIS-DMPKRX | DMPK | Myotonic dystrophy type 1 | I/II | Recruiting |
| ISIS APO(a)-LRX | Apoliprotein (a) | Elevated lipoprotein (a) | I | Completed |
| II | Completed | |||
| Curtirsen | Clusterin | Non-small cell lung cancer Prostate cancer | III | Recruiting |
| III | Active |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coutinho, M.F.; Santos, J.I.; Matos, L.; Alves, S. Genetic Substrate Reduction Therapy: A Promising Approach for Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Diseases 2016, 4, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4040033
Coutinho MF, Santos JI, Matos L, Alves S. Genetic Substrate Reduction Therapy: A Promising Approach for Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Diseases. 2016; 4(4):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4040033
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoutinho, Maria Francisca, Juliana Inês Santos, Liliana Matos, and Sandra Alves. 2016. "Genetic Substrate Reduction Therapy: A Promising Approach for Lysosomal Storage Disorders" Diseases 4, no. 4: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4040033
APA StyleCoutinho, M. F., Santos, J. I., Matos, L., & Alves, S. (2016). Genetic Substrate Reduction Therapy: A Promising Approach for Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Diseases, 4(4), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4040033









