New Tools for Molecular Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Alterations in HCC
2.1. Cell-Autonomous Changes
2.2. Non-Cell-Autonomous Cues
3. Gene Therapy of HCC: Is It a Good Deal?
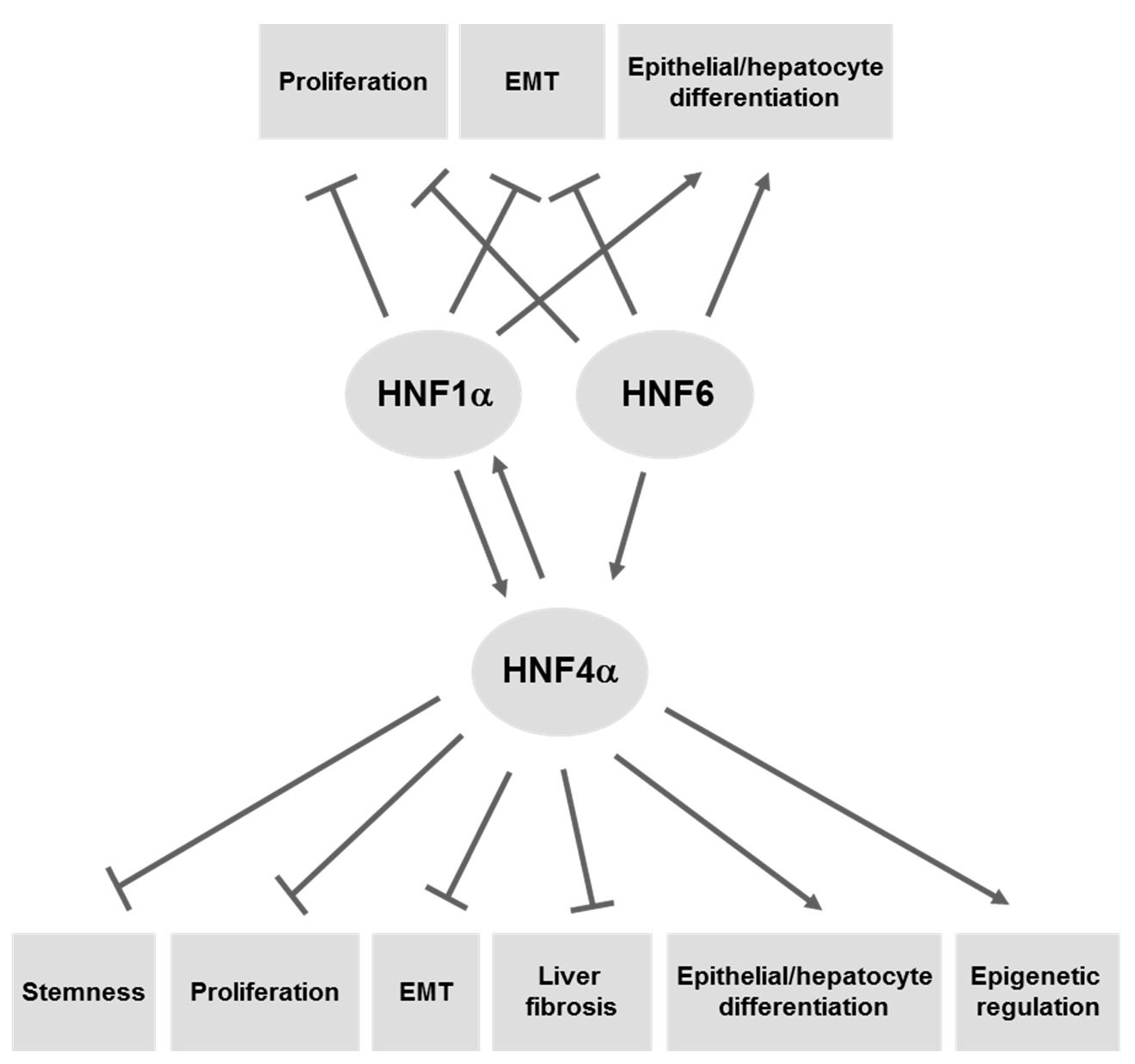
4. LETFs as Molecular Tools for Gene Therapy of HCC
4.1. HNF4α
4.2. HNF1α
4.3. HNF6/ONECUT1
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farazi, P.A.; DePinho, R.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangenberg, H.C.; Thimme, R.; Blum, H.E. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; Lam, M.G. Delivery approaches of gene therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 4711–4718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friemel, J.; Rechsteiner, M.; Frick, L.; Bohm, F.; Struckmann, K.; Egger, M.; Moch, H.; Heikenwalder, M.; Weber, A. Intratumor heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Goel, A. Genetic and epigenetic signatures in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hayashi, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Ohta, K.; Nakabayashi, H.; Tamaoki, T.; Itoh, H. Expression of HNF-1α and HNF-1β in various histological differentiations of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pathol. 1998, 184, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevich, N.L.; Shavochkina, D.A.; Fleishman, D.I.; Kustova, I.F.; Morozova, O.V.; Chuchuev, E.S.; Patyutko, Y.I. Deregulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF4)as a marker of epithelial tumors progression. Exp. Oncol. 2010, 32, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yumoto, Y.; Hanafusa, T.; Hada, H.; Morita, T.; Ooguchi, S.; Shinji, N.; Mitani, T.; Hamaya, K.; Koide, N.; Tsuji, T. Loss of heterozygosity and analysis of mutation of p53 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1995, 10, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zen, K.; Yasui, K.; Nakajima, T.; Zen, Y.; Zen, K.; Gen, Y.; Mitsuyoshi, H.; Minami, M.; Mitsufuji, S.; Tanaka, S.; et al. ERK5 is a target for gene amplification at 17p11 and promotes cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating mitotic entry. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2009, 48, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yan, H.X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; He, Y.Q.; Yu, L.X.; Zhang, S.H.; Huang, D.D.; Tang, L.; Kong, X.N.; et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling contributes to activation of normal and tumorigenic liver progenitor cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4287–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Hibino, S.; Saito, H. Alterations of epigenetics and microRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amicone, L.; Citarella, F.; Cicchini, C. Epigenetic regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma requires long noncoding RNAs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Vargas, H.; Lambert, M.P.; le Calvez-Kelm, F.; Gouysse, G.; McKay-Chopin, S.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Herceg, Z. Hepatocellular carcinoma displays distinct DNA methylation signatures with potential as clinical predictors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, D.; Ye, H.; Xiao, Z.; Cai, M.; Xu, K.; Zeng, Y.; Li, H.; et al. High expression of trimethylated histone H3 lysine 4 is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.Y.; Hou, J.H.; Rao, H.L.; Luo, R.Z.; Li, M.; Pei, X.Q.; Lin, M.C.; Guan, X.Y.; Kung, H.F.; Zeng, Y.X.; et al. High expression of H3K27me3 in human hepatocellular carcinomas correlates closely with vascular invasion and predicts worse prognosis in patients. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ladeiro, Y.; Couchy, G.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Pelletier, L.; Rebouissou, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhu, A.; Jia, H.L.; Forgues, M.; Liu, C.G.; Goldstein, D.; Lam, A.; Zanetti, K.A.; Ye, Q.H.; Qin, L.X.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zijl, F.; Zulehner, G.; Petz, M.; Schneller, D.; Kornauth, C.; Hau, M.; Machat, G.; Grubinger, M.; Huber, H.; Mikulits, W. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimachi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Kameyama, T.; Taguchi, K.; Aishima, S.; Shimada, M.; Sugimachi, K.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Transcriptional repressor snail and progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2657–2664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.K.; Poon, R.T.; Yuen, A.P.; Ling, M.T.; Kwok, W.K.; Wang, X.H.; Wong, Y.C.; Guan, X.Y.; Man, K.; Chau, K.L.; et al. Twist overexpression correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5369–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Xu, S.C.; Li, J.; Han, K.Q.; Pi, H.F.; Zheng, L.; Zuo, G.H.; Huang, X.B.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, H.Z.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers expressed in circulating tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with different stages of disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, A.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Rodrigo, I.; Locascio, A.; Blanco, M.J.; del Barrio, M.G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchini, C.; Filippini, D.; Coen, S.; Marchetti, A.; Cavallari, C.; Laudadio, I.; Spagnoli, F.M.; Alonzi, T.; Tripodi, M. Snail controls differentiation of hepatocytes by repressing HNF4α expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 209, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibaldi, F.; Cicchini, C.; Conigliaro, A.; Santangelo, L.; Cozzolino, A.M.; Grassi, G.; Marchetti, A.; Tripodi, M.; Amicone, L. An epistatic mini-circuitry between the transcription factors Snail and HNF4α controls liver stem cell and hepatocyte features exhorting opposite regulation on stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 19, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, A.N.; Johnson, G.L. Implications of Mesenchymal Cells in Cancer Stem Cell Populations: Relevance to EMT. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2014, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Lee, T.K.; Zheng, B.J.; Chan, K.W.; Guan, X.Y. CD133+ HCC cancer stem cells confer chemoresistance by preferential expression of the Akt/PKB survival pathway. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.F.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.R.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, S.J.; Shi, R.Y.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J. Circulating stem cell-like epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive tumor cells indicate poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.C.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, W.; Fu, B.S.; Hua, X.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, T.J.; Li, X.; Wu, X.Y.; Tai, Y.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts from hepatocellular carcinoma promote malignant cell proliferation by HGF secretion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocca, A.; Dituri, F.; Lupo, L.; Quaranta, M.; Antonaci, S.; Giannelli, G. Tumor-secreted lysophostatidic acid accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by promoting differentiation of peritumoral fibroblasts in myofibroblasts. Hepatology 2011, 54, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, Y.; Kawata, S.; Tamura, S.; Ito, N.; Tsushima, H.; Takaishi, K.; Kiso, S.; Matsuzawa, Y. Plasma transforming growth factor-β1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Comparison with chronic liver diseases. Cancer 1994, 73, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, N.; Kawata, S.; Tamura, S.; Shirai, Y.; Kiso, S.; Tsushima, H.; Matsuzawa, Y. Positive correlation of plasma transforming growth factor-β1 levels with tumor vascularity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 1995, 89, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, D.; Jang, M.K.; Kim, K.M.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, Y.S. Transforming growth factor β1 overexpression is closely related to invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2012, 82, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocca, A.; Fransvea, E.; Lavezzari, G.; Antonaci, S.; Giannelli, G. Inhibition of transforming growth factor β receptor I kinase blocks hepatocellular carcinoma growth through neo-angiogenesis regulation. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caja, L.; Bertran, E.; Campbell, J.; Fausto, N.; Fabregat, I. The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) mediates acquisition of a mesenchymal stem cell-like phenotype in human liver cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichl, P.; Haider, C.; Grubinger, M.; Mikulits, W. TGF-β in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis of liver carcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4135–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Transforming growth factor-β gene expression signature in mouse hepatocytes predicts clinical outcome in human cancer. Hepatology 2008, 47, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Park, S.H.; Yi, Y.; Choi, S.G.; Lee, C.; Parks, W.T.; Cho, H.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Shaul, Y.; Roberts, A.B.; et al. The hepatitis B virus encoded oncoprotein pX amplifies TGF-β family signaling through direct interaction with Smad4, potential mechanism of hepatitis B virus-induced liver fibrosis. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikula, M.; Proell, V.; Fischer, A.N.; Mikulits, W. Activated hepatic stellate cells induce tumor progression of neoplastic hepatocytes in a TGF-β dependent fashion. J. Cell Physiol. 2006, 209, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leask, A.; Abraham, D.J. TGF-β signaling and the fibrotic response. Faseb. J. 2004, 18, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirmaz, C.; Terzioglu, E.; Topalak, O.; Bayrak, P.; Yilmaz, O.; Ersoz, G.; Sebik, F. Serum transforming growth factor-β1(TGF-β1) in patients with cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis C. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2004, 15, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akpolat, N.; Yahsi, S.; Godekmerdan, A.; Demirbag, K.; Yalniz, M. Relationship between serum cytokine levels and histopathological changes of liver in patients with hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3260–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocca, A.; Fransvea, E.; Dituri, F.; Lupo, L.; Antonaci, S.; Giannelli, G. Down-regulation of connective tissue growth factor by inhibition of transforming growth factor β blocks the tumor-stroma cross-talk and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Sandrin, L. Liver stiffness: A novel parameter for the diagnosis of liver disease. Hepat. Med. 2010, 2, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Tumaneng, K.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, K.F.; Zhang, X.; Thomas, D.M. The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.Z.; Yao, T.J.; Lee, N.P.; Ng, I.O.; Chan, Y.T.; Zender, L.; Lowe, S.W.; Poon, R.T.; Luk, J.M. Yes-associated protein is an independent prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2009, 115, 4576–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zender, L.; Spector, M.S.; Xue, W.; Flemming, P.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Silke, J.; Fan, S.T.; Luk, J.M.; Wigler, M.; Hannon, G.J.; et al. Identification and validation of oncogenes in liver cancer using an integrative oncogenomic approach. Cell 2006, 125, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Chen, X.; Latzko, P.; Malz, M.; Gaida, M.M.; Felix, K.; Ladu, S.; Singer, S.; Pinna, F.; Gretz, N.; et al. Yes-associated protein up-regulates Jagged-1 and activates the Notch pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitamant, J.; Kottakis, F.; Benhamouche, S.; Tian, H.S.; Chuvin, N.; Parachoniak, C.A.; Nagle, J.M.; Perera, R.M.; Lapouge, M.; Deshpande, V.; et al. YAP Inhibition Restores Hepatocyte Differentiation in Advanced HCC, Leading to Tumor Regression. Cell Rep. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, O.; Cullum, R.; Lee, S.; Kan, A.C.; Wei, W.; Yi, Y.; Garside, V.C.; Bilenky, M.; Griffith, M.; Morrissy, A.S.; et al. Hippo signaling influences HNF4A and FOXA2 enhancer switching during hepatocyte differentiation. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardee, A.D.; Butterfield, L.H. Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: Unique challenges and clinical opportunities. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Marrero, J.A.; Rudolph, L.; Reddy, K.R. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyra-Gonzalez, I.; Flores-Fong, L.E.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Medina-Preciado, D.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Adenoviral gene therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbuthnot, P.B.; Bralet, M.P.; le Jossic, C.; Dedieu, J.F.; Perricaudet, M.; Brechot, C.; Ferry, N. In vitro and in vivo hepatoma cell-specific expression of a gene transferred with an adenoviral vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 1996, 7, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanger, K.; Knigin, D.; Zong, Y.; Maggs, L.; Gu, G.; Akiyama, H.; Pikarsky, E.; Stanger, B.Z. Adult hepatocytes are generated by self-duplication rather than stem cell differentiation. Cell Stem. Cell 2014, 15, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, J.R.; Malato, Y.; Gormond, C.; Willenbring, H. Evidence against a stem cell origin of new hepatocytes in a common mouse model of chronic liver injury. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odom, D.T.; Dowell, R.D.; Jacobsen, E.S.; Nekludova, L.; Rolfe, P.A.; Danford, T.W.; Gifford, D.K.; Fraenkel, E.; Bell, G.I.; Young, R.A. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human hepatocytes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.J.; Conley, P.B.; Chen, L.; Sladek, F.M.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Crabtree, G.R. A transcriptional hierarchy involved in mammalian cell-type specification. Nature 1992, 355, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrmizi, I.; Hatzis, P.; Katrakili, N.; Tronche, F.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Talianidis, I. Plasticity and expanding complexity of the hepatic transcription factor network during liver development. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2293–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parviz, F.; Matullo, C.; Garrison, W.D.; Savatski, L.; Adamson, J.W.; Ning, G.; Kaestner, K.H.; Rossi, J.M.; Zaret, K.S.; Duncan, S.A. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α controls the development of a hepatic epithelium and liver morphogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayhurst, G.P.; Lee, Y.H.; Lambert, G.; Ward, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (nuclear receptor 2A1) is essential for maintenance of hepatic gene expression and lipid homeostasis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.; Mane-Padros, D.; Bolotin, E.; Jiang, T.; Sladek, F.M. Identification of a binding motif specific to HNF4 by comparative analysis of multiple nuclear receptors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5343–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, L.; Marchetti, A.; Cicchini, C.; Conigliaro, A.; Conti, B.; Mancone, C.; Bonzo, J.A.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Alonzi, T.; Amicone, L.; et al. The stable repression of mesenchymal program is required for hepatocyte identity: A novel role for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α. Hepatology 2011, 53, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonzo, J.A.; Ferry, C.H.; Matsubara, T.; Kim, J.H.; Gonzalez, F.J. Suppression of hepatocyte proliferation by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in adult mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7345–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walesky, C.; Gunewardena, S.; Terwilliger, E.F.; Edwards, G.; Borude, P.; Apte, U. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α in adult mice results in increased hepatocyte proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G26–G37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiba, H.; Gotoh, T.; Kojima, T.; Satohisa, S.; Kikuchi, K.; Osanai, M.; Sawada, N. Hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-4α triggers formation of functional tight junctions and establishment of polarized epithelial morphology in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 286, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, S.; Suzuki, A. Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors. Nature 2011, 475, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, W.N.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Guo, Z.C.; Hao, D.L.; Liu, G.; Feng, L.; Chen, H.Z.; et al. Positive regulation of hepatic miR-122 expression by HNF4α. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutay, H.; Bai, S.; Datta, J.; Motiwala, T.; Pogribny, I.; Frankel, W.; Jacob, S.T.; Ghoshal, K. Downregulation of miR-122 in the rodent and human hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Cell Biochem. 2006, 99, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Andersen, J.B.; Durkin, M.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, P.W.; Lai, T.C.; Chau, G.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, C.M.; Lin, C.D.; Liao, Y.L.; Wang, J.L.; Chau, Y.P.; et al. MicroRNA-122, a tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Lin, X.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, H.Y.; Shi, J.W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, W.T.; Xie, R.Y.; Wei, F.; et al. MicroRNA-122 triggers mesenchymal-epithelial transition and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasion by targeting RhoA. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Luo, J.; Chen, Q.; Qian, C. Expression of miR-122 mediated by adenoviral vector induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Giovannini, C.; Veronese, A.; Ferracin, M.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Croce, C.M.; Tavolari, S.; et al. MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p. 53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, F.; Ma, L.; Shan, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y.; Bian, X.; Bie, P.; et al. MicroRNA-122 sensitizes HCC cancer cells to adriamycin and vincristine through modulating expression of MDR and inducing cell cycle arrest. Cancer Lett. 2011, 310, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.H.; Wang, B.; Kota, J.; Yu, J.; Costinean, S.; Kutay, H.; Yu, L.; Bai, S.; La Perle, K.; Chivukula, R.R.; et al. Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Fu, H.; Tie, Y.; Hu, Z.; Kong, W.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, X. miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 275, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhayat, S.A.; Mardin, W.A.; Kohler, G.; Bahde, R.; Vowinkel, T.; Wolters, H.; Senninger, N.; Haier, J.; Mees, S.T. The microRNA-200 family—A potential diagnostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma? J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.S.; Liu, H.H.; Liu, J.J.; Yeh, C.T.; Chang, T.C.; Wu, C.H.; Ho, Y.S.; Wei, P.L.; Chang, Y.J. MicroRNA-200a and -200b mediated hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration through the epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. S3), S360–S368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Luo, D.; Rong, M.; Chen, G. Underexpression of miR-34a in hepatocellular carcinoma and its contribution towards enhancement of proliferating inhibitory effects of agents targeting c-MET. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H. MicroRNA-34a: A potential therapeutic target in human cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gougelet, A.; Sartor, C.; Bachelot, L.; Godard, C.; Marchiol, C.; Renault, G.; Tores, F.; Nitschke, P.; Cavard, C.; Terris, B.; et al. Antitumour activity of an inhibitor of miR-34a in liver cancer with β-catenin-mutations. Gut 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchini, C.; de Nonno, V.; Battistelli, C.; Cozzolino, A.M.; de Santis Puzzonia, M.; Ciafre, S.A.; Brocker, C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Amicone, L.; Tripodi, M. Epigenetic control of EMT/MET dynamics: HNF4α impacts DNMT3s through miRs-29. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, T.; Kondo, Y.; Kakazu, E.; Ninomiya, M.; Kimura, O.; Shimosegawa, T. Involvement of miRNA-29a in epigenetic regulation of transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parpart, S.; Roessler, S.; Dong, F.; Rao, V.; Takai, A.; Ji, J.; Qin, L.X.; Ye, Q.H.; Jia, H.L.; Tang, Z.Y.; et al. Modulation of miR-29 expression by α-fetoprotein is linked to the hepatocellular carcinoma epigenome. Hepatology 2014, 60, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, F.J.; Davalos, V.; Vidal, E.; Gomez, A.; Heyn, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Vizoso, M.; Martinez-Cardus, A.; Sayols, S.; Ferreira, H.J.; et al. A comprehensive DNA methylation profile of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5608–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Kanai, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Saito, H.; Ishii, H.; Hirohashi, S. Expression of mRNA for DNA methyltransferases and methyl-CpG-binding proteins and DNA methylation status on CpG islands and pericentromeric satellite regions during human hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2001, 33, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatziapostolou, M.; Polytarchou, C.; Aggelidou, E.; Drakaki, A.; Poultsides, G.A.; Jaeger, S.A.; Ogata, H.; Karin, M.; Struhl, K.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; et al. An HNF4α-miRNA inflammatory feedback circuit regulates hepatocellular oncogenesis. Cell 2011, 147, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarevich, N.L.; Cheremnova, O.A.; Varga, E.V.; Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Kudrjavtseva, E.I.; Morozova, O.V.; Fleishman, D.I.; Engelhardt, N.V.; Duncan, S.A. Progression of HCC in mice is associated with a downregulation in the expression of hepatocyte nuclear factors. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, B.F.; Ding, J.; Yin, C.; Zhong, W.; Wu, K.; Zeng, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, X.; et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α suppresses the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7640–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.Y.; Yin, C.; Hou, J.L.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhong, W.; Hu, P.F.; Deng, X.; Tan, Y.X.; Zhang, J.P.; et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut 2010, 59, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.X.; Zeng, X.; Yue, H.Y.; Hou, J.L.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J.P.; Han, Z.G.; et al. Differentiation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice with recombinant adenovirus carrying hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α gene. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, A.M.; Alonzi, T.; Santangelo, L.; Mancone, C.; Conti, B.; Steindler, C.; Musone, M.; Cicchini, C.; Tripodi, M.; Marchetti, A. TGFβ overrides HNF4α tumor suppressing activity through GSK3β inactivation: Implication for hepatocellular carcinoma gene therapy. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odom, D.T.; Zizlsperger, N.; Gordon, D.B.; Bell, G.W.; Rinaldi, N.J.; Murray, H.L.; Volkert, T.L.; Schreiber, J.; Rolfe, P.A.; Gifford, D.K.; et al. Control of pancreas and liver gene expression by HNF transcription factors. Science 2004, 303, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereghini, S.; Yaniv, M.; Cortese, R. Hepatocyte dedifferentiation and extinction is accompanied by a block in the synthesis of mRNA coding for the transcription factor HNF1/LFB1. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, J.; Song, N.; Xiang, C.; Xu, J.; Hou, Z.; Su, X.; Liu, B.; Jiang, T.; et al. Human hepatocytes with drug metabolic function induced from fibroblasts by lineage reprogramming. Cell Stem. Cell 2014, 14, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeonov, K.P.; Uppal, H. Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by synthetic modified mRNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluteau, O.; Jeannot, E.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Marques, J.M.; Blanc, J.F.; Bui, H.; Beaudoin, J.C.; Franco, D.; Balabaud, C.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Bi-allelic inactivation of TCF1 in hepatic adenomas. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacq, Y.; Jacquemin, E.; Balabaud, C.; Jeannot, E.; Scotto, B.; Branchereau, S.; Laurent, C.; Bourlier, P.; Pariente, D.; de Muret, A.; et al. Familial liver adenomatosis associated with hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α inactivation. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontoglio, M.; Barra, J.; Hadchouel, M.; Doyen, A.; Kress, C.; Bach, J.P.; Babinet, C.; Yaniv, M. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 inactivation results in hepatic dysfunction, phenylketonuria, and renal Fanconi syndrome. Cell 1996, 84, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lin, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhang, X.; Ning, B.F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.P.; Qiu, L.; Qin, X.R.; Chen, Y.X.; et al. Recombinant adenovirus carrying the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α gene inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft growth in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, L.; Rebouissou, S.; Vignjevic, D.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J. HNF1α inhibition triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human liver cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzis, P.; Talianidis, I. Regulatory mechanisms controlling human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α gene expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 7320–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Adami, G.; Costa, R.H. Maintaining HNF6 expression prevents AdHNF3β-mediated decrease in hepatic levels of Glut-2 and glycogen. Hepatology 2002, 35, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Tan, Y.; Costa, R.H.; Holterman, A.X. In vivo regulation of murine CYP7A1 by HNF-6, a novel mechanism for diminished CYP7A1 expression in biliary obstruction. Hepatology 2004, 40, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudadio, I.; Manfroid, I.; Achouri, Y.; Schmidt, D.; Wilson, M.D.; Cordi, S.; Thorrez, L.; Knoops, L.; Jacquemin, P.; Schuit, F.; et al. A feedback loop between the liver-enriched transcription factor network and miR-122 controls hepatocyte differentiation. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.W.; Wang, D.M.; Hu, Y.; Tang, Y.N.; Shi, W.W.; Guo, X.J.; Song, J.G. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 suppresses the migration and invasive growth of lung cancer cells through p53 and the inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31206–31216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, F.; Kulik, U.; Klempnauer, J.; Borlak, J. Inhibition of the liver enriched protein FOXA2 recovers HNF6 activity in human colon carcinoma and liver hepatoma cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, R.; He, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, G.; Liu, D.; Cui, L.; Yu, G.; Yu, W.; Chen, Y.; Guo, D. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by hepatocyte nuclear factor 6. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4345–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumb-Rudewiez, N.; Clotman, F.; Strick-Marchand, H.; Pierreux, C.E.; Weiss, M.C.; Rousseau, G.G.; Lemaigre, F.P. Transcription factor HNF-6/OC-1 inhibits the stimulation of the HNF-3α/Foxa1 gene by TGF-β in mouse liver. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clotman, F.; Jacquemin, P.; Plumb-Rudewiez, N.; Pierreux, C.E.; Van der Smissen, P.; Dietz, H.C.; Courtoy, P.J.; Rousseau, G.G.; Lemaigre, F.P. Control of liver cell fate decision by a gradient of TGF β signaling modulated by Onecut transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchetti, A.; Bisceglia, F.; Cozzolino, A.M.; Tripodi, M. New Tools for Molecular Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diseases 2015, 3, 325-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040325
Marchetti A, Bisceglia F, Cozzolino AM, Tripodi M. New Tools for Molecular Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diseases. 2015; 3(4):325-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040325
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchetti, Alessandra, Francesca Bisceglia, Angela M. Cozzolino, and Marco Tripodi. 2015. "New Tools for Molecular Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Diseases 3, no. 4: 325-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040325
APA StyleMarchetti, A., Bisceglia, F., Cozzolino, A. M., & Tripodi, M. (2015). New Tools for Molecular Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diseases, 3(4), 325-340. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3040325




