Ginseng Metabolites on Cancer Chemoprevention: An Angiogenesis Link?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. American Ginseng is a Commonly Used Antioxidant Botanical
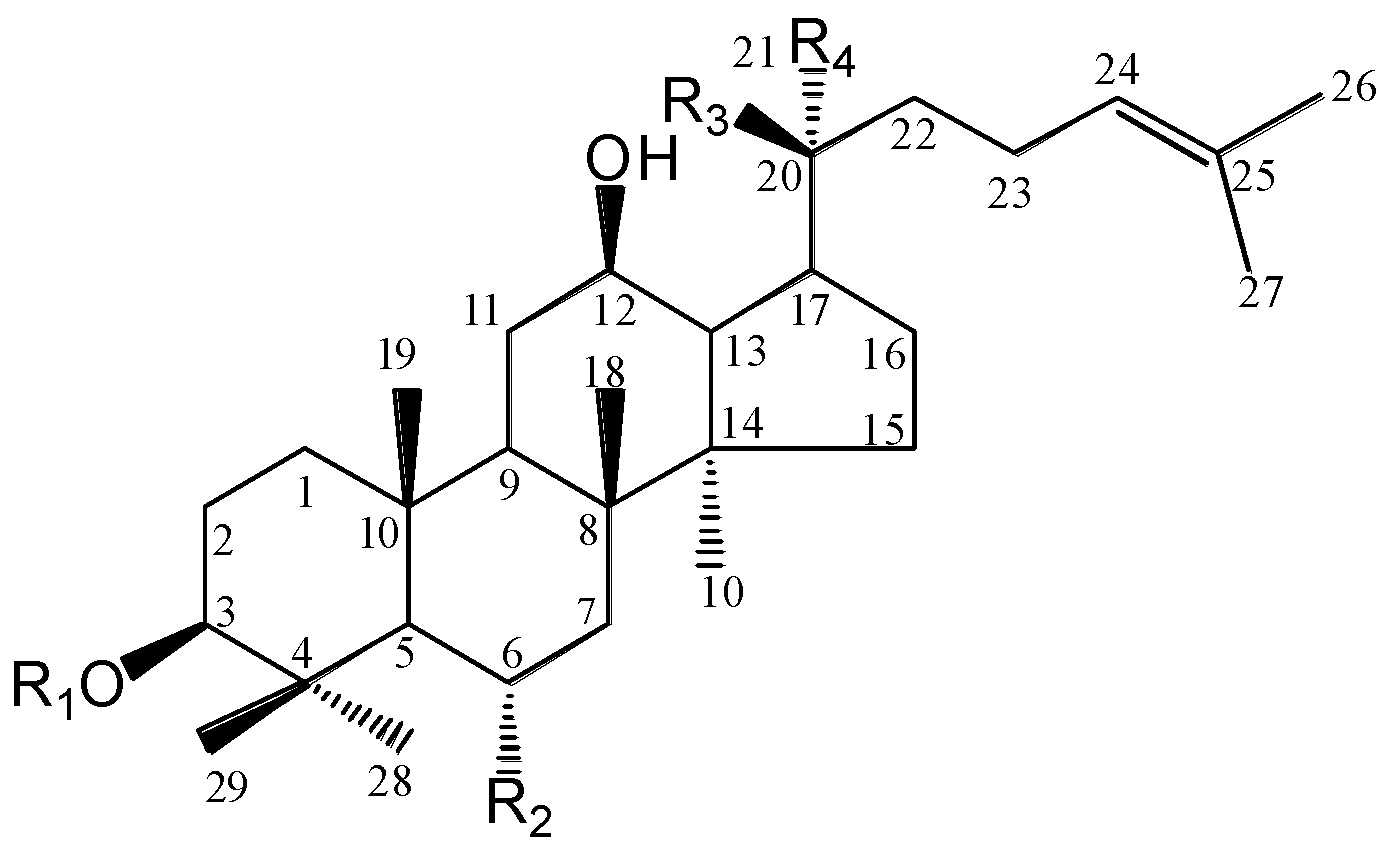
| Group | Saponin | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPT | Rg1 | H | O-glc | O-glc | CH3 |
| Re | H | O-glc2 → 1rha | O-glc | CH3 | |
| Rh1 | H | O-glc | OH | CH3 | |
| 20S-Rg2 | H | O-glc2 → 1rha | OH | CH3 | |
| 20R-Rg2 | H | O-glc2 → 1rha | CH3 | OH | |
| PPD | Rb1 | glc2 → 1glc | H | O-glc6 → 1glc | CH3 |
| Rc | glc2 → 1glc | H | O-glc6 → 1araf | CH3 | |
| Rb2 | glc2 → 1glc | H | O-glc6 → 1arap | CH3 | |
| Rb3 | glc2 → 1glc | H | O-glc6 → 1xyl | CH3 | |
| Rd | glc2 → 1glc | H | O-glc | CH3 | |
| Rg3 | glc2 → 1glc | H | OH | CH3 | |
| F2 | glc | H | O-glc | CH3 | |
| CK | H | H | O-glc | CH3 |
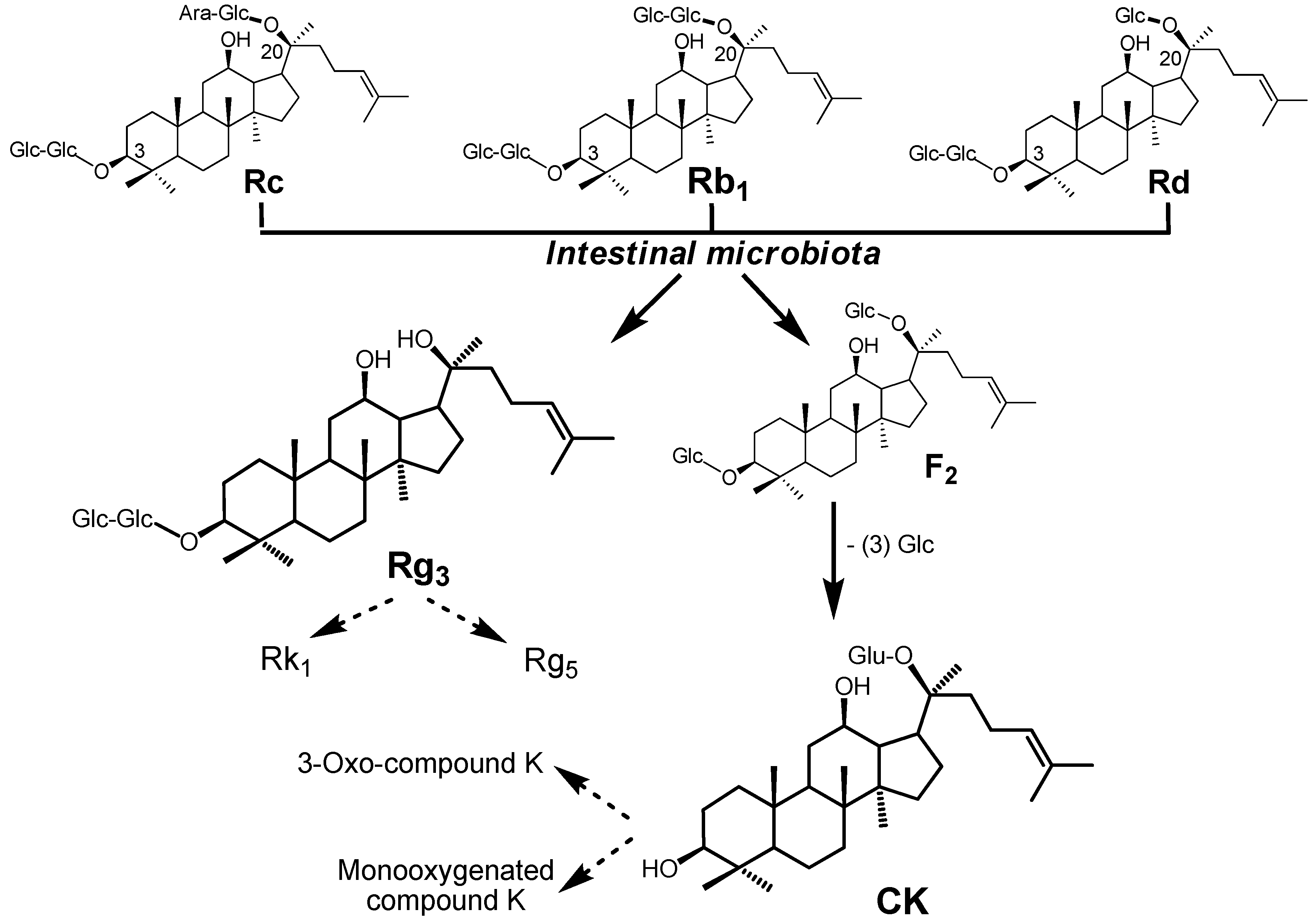
3. Biotransformation of American Ginseng Saponins
4. Effects of Ginsenoside Metabolites on Cancer Cell Death Induction
5. The Role of Ginsenoside Metabolites in Angiogenesis for Cancer Treatment
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, C.E.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Siegel, R.L.; Stein, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Alteri, R.; Robbins, A.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesketh, P.J. Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, C.B.; Micheel, C.M.; Levy, M.A.; Lovly, C.M.; Horn, L.; Warner, J.L.; Johnson, D.B.; Zhao, Z.; Anderson, I.A.; Sosman, J.A.; et al. Beyond histology: Translating tumor genotypes into clinically effective targeted therapies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2264–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biselli-Chicote, P.M.; Oliveira, A.R.; Pavarino, E.C.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M. VEGF gene alternative splicing: Pro- and anti-angiogenic isoforms in cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Miao, Z.H. Marine-derived angiogenesis inhibitors for cancer therapy. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 903–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.L.; Oh, B.; Butow, P.N.; Mullan, B.A.; Clarke, S. Cancer patient disclosure and patient-doctor communication of complementary and alternative medicine use: A systematic review. Oncologist 2012, 17, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Calway, T.; Yuan, C.S. Herbal medicines as adjuvants for cancer therapeutics. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 40, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, C.S. Trends in scientific publications of Chinese medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 40, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.M. A review of complementary and alternative medicine practices among cancer survivors. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2010, 14, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.G.; Chen, Y.H. The role of acupuncture in cancer supportive care. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 40, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hait, W.N.; Hambley, T.W. Targeted cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides: Immunomodulation and potential anti-tumor activities. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Chae, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Eo, W.; Kim, S.; Choi, W.; Cheon, S.H. The efficacy and safety of standardized allergen-removed Rhus verniciflua extract as maintenance therapy after first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, T.; Paterson, R.; Moore, V.; Carlsson, A.; Abrahamsson, B.; Basit, A.W. The gastrointestinal microbiota as a site for the biotransformation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiser, H.J.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Is it time for a metagenomic basis of therapeutics? Science 2012, 336, 1253–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shergis, J.L.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhou, W.; Xue, C.C. Quality and risk of bias in Panax ginseng randomized controlled trials: A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Qiao, J.; Zhu, M.; Du, J.; Shang, W.; Yin, W.; Wang, W.; Han, M.; Lu, W. Preliminary evaluation of the interactions of Panax ginseng and Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge with 5-fluorouracil on pharmacokinetics in rats and pharmacodynamics in human cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Ni, M.; Sun, S.; Li, X.L.; He, H.; Mehendale, S.R.; Yuan, C.S. Detection of adulteration of notoginseng root extract with other panax species by quantitative HPLC coupled with PCA. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2363–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, L.; Tang, L.; Zheng, M.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Meng, W.; Wang, W. Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates hypoxia and hypercapnia-induced vasoconstriction in isolated rat pulmonary arterial rings by reducing the expression of ERK. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Kim, K.E.; Du, G.J.; Qi, L.W.; Wen, X.D.; Li, P.; Bauer, B.A.; Bissonnette, M.B.; Musch, M.W.; Chang, E.B.; et al. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography and time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis of ginsenoside metabolites in human plasma. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, E.K.; Park, I.S.; Yang, D.C.; Jun, H.S. Efficacy comparison of Korean ginseng and American ginseng on body temperature and metabolic parameters. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhou, C.J.; Wang, B.; Han, L.; Zhang, C.F.; Wu, X.H.; Yuan, C.S. Adulteration and cultivation region identification of American ginseng using HPLC coupled with multivariate analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 99, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuzzati, N. Analysis methods of ginsenosides. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 812, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Shoyama, Y.; Tanaka, H. Pharmacokinetic study of ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 in rat by ELISA using anti-ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 monoclonal antibodies. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2006, 34, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; McEntee, E.; Wicks, S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.S. Phytochemical and analytical studies of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. J. Nat. Med. 2006, 60, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.W.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Isolation and analysis of ginseng: Advances and challenges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 467–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Qi, L.W.; Du, G.J.; Mehendale, S.R.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Red notoginseng: Higher ginsenoside content and stronger anticancer potential than Asian and American ginseng. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Aung, H.H.; Ni, M.; Wu, J.A.; Tong, R.; Wicks, S.; He, T.C.; Yuan, C.S. Red American ginseng: Ginsenoside constituents and antiproliferative activities of heat-processed Panax quinquefolius roots. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H.L.; Yu, X.F.; Qu, S.C.; Sui, D.Y. 20(S)-protopanaxadiol triggers mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.S.; Dey, L. Multiple effects of American ginseng in clinical medicine. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2001, 29, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, G.; Giardina, E.G. Benefits, adverse effects and drug interactions of herbal therapies with cardiovascular effects. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attele, A.S.; Zhou, Y.P.; Xie, J.T.; Wu, J.A.; Zhang, L.; Dey, L.; Pugh, W.; Rue, P.A.; Polonsky, K.S.; Yuan, C.S. Antidiabetic effects of Panax ginseng berry extract and the identification of an effective component. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.T.; Aung, H.H.; Wu, J.A.; Attele, A.S.; Yuan, C.S. Effects of American ginseng berry extract on blood glucose levels in ob/ob mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2002, 30, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.T.; Zhou, Y.P.; Dey, L.; Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Polonsky, K.S.; Yuan, C.S. Panax ginseng berry extract reduces blood glucose and body weight in db/db mice. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Xu, X.H.; Jiang, Y.P. Protective effects of ginsenoside on myocardiac ischemic and reperfusion injuries. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 1994, 74, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.H.; Xie, J.T.; Vanden Hoek, T.L.; Mehendale, S.; Aung, H.; Li, C.Q.; Qin, Y.; Schumacker, P.T.; Becker, L.B.; Yuan, C.S. Antioxidant effects of American ginseng berry extract in cardiomyocytes exposed to acute oxidant stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1670, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehendale, S.R.; Aung, H.H.; Yin, J.J.; Lin, E.; Fishbein, A.; Wang, C.Z.; Xie, J.T.; Yuan, C.S. Effects of antioxidant herbs on chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in a rat-pica model. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2004, 32, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehendale, S.; Aung, H.; Wang, A.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, C.Z.; Xie, J.T.; Yuan, C.S. American ginseng berry extract and ginsenoside Re attenuate cisplatin-induced kaolin intake in rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 56, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compare, D.; Nardone, G. Contribution of gut microbiota to colonic and extracolonic cancer development. Digit. Dis. 2011, 29, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Ji, G.E. Transformation of ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sung, J.H.; Benno, Y. Role of human intestinal Prevotella oris in hydrolyzing ginseng saponins. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, H.Y.; Qi, L.W.; Wang, C.Z.; Li, P.; Yuan, C.S. Biotransformation and metabolic profile of American ginseng saponins with human intestinal microflora by liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1286, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Du, G.J.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X.D.; Calway, T.; Zhen, Z.; Musch, M.W.; Bissonnette, M.; Chang, E.B.; Yuan, C.S. Ginsenoside compound K, not Rb1, possesses potential chemopreventive activities in human colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.A.; Choo, M.K.; Park, E.K.; Park, S.Y.; Shin, H.Y.; Kim, D.H. Metabolism of ginsenoside R(c) by human intestinal bacteria and its related antiallergic activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Aung, H.H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, S.; Li, X.L.; He, H.; Xie, J.T.; He, T.C.; Du, W.; Yuan, C.S. Chemopreventive effects of heat-processed Panax quinquefolius root on human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, E.; Kim, D.; Yoo, J.; Koh, B. Studies on absorption, distribution and metabolism of ginseng in humans after oral administration. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawab, M.A.; Bahr, U.; Karas, M.; Wurglics, M.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M. Degradation of ginsenosides in humans after oral administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, D.; Ge, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L. Ginsenoside metabolites inhibit p-glycoprotein in vitro and in situ using three absorption models. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.L.; Lv, G.Y.; He, B.C.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.Z.; Du, W.; Yuan, C.S.; He, T.C. Ginseng saponin metabolite 20(S)-protopanaxadiol inhibits tumor growth by targeting multiple cancer signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Li, B.; Wen, X.D.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Calway, T.D.; He, T.C.; Du, W.; Yuan, C.S. Paraptosis and NF-kappaB activation are associated with protopanaxadiol-induced cancer chemoprevention. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Su, W.; Miao, Z.H.; Niu, H.R.; Liu, J.; Hua, Q.L. Effect and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg3 on postoperative life span of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2008, 14, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, Y.S.; Han, S.S.; Chun, K.S.; Park, K.K.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Surh, Y.J. Inhibitory effects of the ginsenoside Rg3 on phorbol ester-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression, NF-kappaB activation and tumor promotion. Mutat. Res. 2003, 523–524, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Cho, J.S.; Son, S.M.; Choi, S.S.; Yun, Y.P.; Yoo, H.S.; Yoon Do, Y.; Oh, K.W.; Han, S.B.; et al. Combination of ginsenoside Rg3 with docetaxel enhances the susceptibility of prostate cancer cells via inhibition of NF-kappaB. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 631, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.C.; Gao, J.L.; Luo, X.; Luo, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Luu, H.H.; Haydon, R.C.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits colorectal tumor growth through the down-regulation of Wnt/ss-catenin signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.H.; Chung, K.S.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, K.T. Compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, induces apoptosis via caspase-8-dependent pathway in HL-60 human leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim do, Y.; Park, M.W.; Yuan, H.D.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, S.H. Compound K induces apoptosis via CAMK-IV/AMPK pathways in HT-29 colon cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10573–10578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim do, Y.; Yuan, H.D.; Chung, I.K.; Chung, S.H. Compound K, intestinal metabolite of ginsenoside, attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation via AMPK activation in human hepatoma cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, M.K.; Sakurai, H.; Kim, D.H.; Saiki, I. A ginseng saponin metabolite suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-promoted metastasis by suppressing nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in murine colon cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Song, H.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, E.O.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, S.H. Inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 signaling mediates compound K-induced apoptosis in human multiple myeloma U266 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.D.; Kang, K.A.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, S.J.; Hyun, J.W. A ginseng metabolite, compound K, induces autophagy and apoptosis via generation of reactive oxygen species and activation of JNK in human colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, G.J.; Wang, C.Z.; Wen, X.D.; Calway, T.; Li, Z.; He, T.C.; Du, W.; Bissonnette, M.; Musch, M.W.; et al. Compound K, a Ginsenoside Metabolite, Inhibits Colon Cancer Growth via Multiple Pathways Including p53–p21 Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 2980–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, M.; Yoo, Y.C.; Matsuzawa, K.; Sato, K.; Saiki, I.; Tono-oka, S.; Samukawa, K.; Azuma, I. Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3, of red ginseng. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbel, R.S. Tumor angiogenesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, P.Y.; Wong, D.Y.; Wu, P.K.; Leung, P.Y.; Mak, N.K.; Yeung, H.W.; Liu, L.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, Z.H.; Fan, T.P.; et al. The angiosuppressive effects of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3. Biol. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.J.; Zhang, M.Z.; Wang, L.X. Gensenoside Rg3 inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression in human cancer cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Li, X. Hepatic arterial administration of ginsenoside Rg3 and transcatheter arterial embolization for the treatment of VX2 liver carcinomas. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Teng, L.; Meng, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Lu, J.; Lee, R.J.; Teng, L. Development of liposomal Ginsenoside Rg3: Formulation optimization and evaluation of its anticancer effects. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.G.; Huang, Y.; Cui, D.D.; Huang, X.B.; Mao, S.H.; Ji, L.L.; Song, H.B.; Yi, C. Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 combined with gemcitabine on angiogenesis and growth of lung cancer in mice. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Kang, X.; Zhao, W. Antiangiogenic effect of low-dose cyclophosphamide combined with ginsenoside Rg3 on Lewis lung carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Kang, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, F. Antiangiogenic effect of capecitabine combined with ginsenoside Rg3 on breast cancer in mice. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2008, 23, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.S.; Lai, K.C.; Hsu, S.C.; Yang, J.S.; Kuo, C.L.; Lin, J.P.; Ma, Y.S.; Wu, C.C.; Chung, J.G. Curcumin inhibits the migration and invasion of human A549 lung cancer cells through the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, R.; Go, Y.; Kyritisis, A.P.; Uhm, J.; Venkaiah, B.; Mohanam, S.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Rao, J.S. Elevated levels of Mr 92,000 type IV collagenase during tumor growth in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.H.; Woo, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, W.K.; Hyun, J.W.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S. Ginseng saponin metabolite suppresses phorbol ester-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through inhibition of activator protein-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in human astroglioma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, A.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Lee, E.O.; Bae, H.; Kim, S.H. Compound K inhibits basic fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenesis via regulation of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase and AKT in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.O.; Seo, C.H.; Cho, H.H.; Oh, S.; Hong, S.P.; Yoo, H.S.; Hong, J.T.; Oh, K.W.; Lee, Y.M. Ginsenoside compound K inhibits angiogenesis via regulation of sphingosine kinase-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.-Z.; Cai, Y.; Anderson, S.; Yuan, C.-S. Ginseng Metabolites on Cancer Chemoprevention: An Angiogenesis Link? Diseases 2015, 3, 193-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3030193
Wang C-Z, Cai Y, Anderson S, Yuan C-S. Ginseng Metabolites on Cancer Chemoprevention: An Angiogenesis Link? Diseases. 2015; 3(3):193-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3030193
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chong-Zhi, Yi Cai, Samantha Anderson, and Chun-Su Yuan. 2015. "Ginseng Metabolites on Cancer Chemoprevention: An Angiogenesis Link?" Diseases 3, no. 3: 193-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3030193
APA StyleWang, C.-Z., Cai, Y., Anderson, S., & Yuan, C.-S. (2015). Ginseng Metabolites on Cancer Chemoprevention: An Angiogenesis Link? Diseases, 3(3), 193-204. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases3030193




