Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of the Exercise-Induced Myokine Irisin in Cancer Biology: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
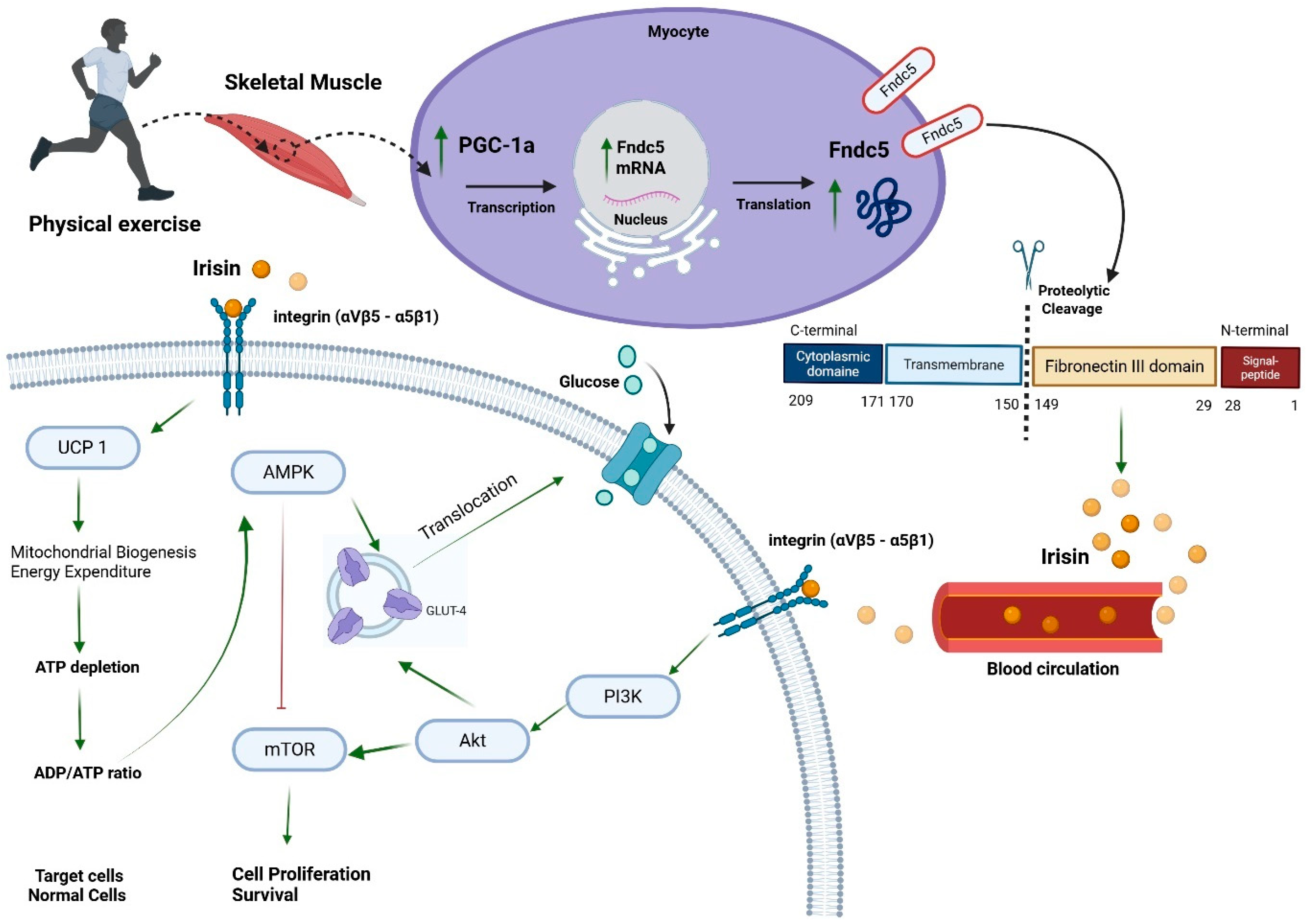
3. Structure, Source, Half-Life, and Biological Actions of Irisin
4. Obesity-Induced Carcinogenesis
5. In Vitro Effects of Irisin on Cancer Cells
5.1. Irisin’s Role in Proliferation
5.2. Molecular Mechanisms of Irisin-Induced Growth Inhibition
5.3. Irisin and Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis
6. Systemic Irisin Levels and Its Expression in Clinical Cancer Specimens
| Tumour Tissue | Fndc5/Irisin | Main Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast, Cervix, Ovaries, Endometrium | ↑ irisin expression IHC | Breast and reproductive tract cancer | [60] |
| Colorectal Cancer | ↑ irisin expression IHC | CRC compared to normal tissue | [62] |
| Oesophagus, Stomach, Liver, Pancreas, Brain | ↑ irisin expression IHC | Gastrointestinal cancer, grade II astrocytoma | [69] |
| Thyroid Cancer | ↑ irisin expression IHC | In oncolytic papillary carcinoma, anaplastic carcinoma | [72] |
| Lung Cancer | ↑ Fndc5 mRNA | In malignant tissue compared to non-malignant Higher in AC in comparison to SSC | [73] |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | ↑ Fndc5 mRNA | HCC patients compared to donors | [55] |
| ↑ Fndc5 mRNA | HCC patients compared to controls | [65] | |
| ↓ Fndc5 mRNA | Extracted data from TCGA for HCC patients compared to controls | [66] | |
| Renal Cancer | ↓ irisin expression IHC | Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma | [71] |
| Type of Cancer | Serum Irisin Levels | Number of Patients | Study Details | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | ↓ | 101 | Patients with invasive ductal | [58] |
| ↓ | 148 | Patients with spinal metastases | [59] | |
| Colorectal cancer | ↓ | 116 | Obese and non-obese patients | [61] |
| Bladder cancer | ↓ | 150 | 75 patients vs. 75 apparently healthy subjects | [63] |
| Prostate cancer | ↓ | 80 | 50 primary patients vs. 30 healthy male subjects | [64] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | ↔ | 36 | HCC patients vs. healthy control | [65] |
| ↔ | 20 | [55] | ||
| ↓ | 219 | [66] | ||
| ↓ | 43 | [67] | ||
| Gastric cancer | ↑ | 51 | Newly diagnosed cases vs. healthy control | [68] |
| Renal cancer | ↑ | 176 | Different types of renal cancers vs. heathy samples | [70] |
7. Conclusions
8. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Ibrahim, R.S.; Arabi, B.; Brockmueller, A.; Shakibaei, M.; Büsselberg, D. The effect of GLP-1R agonists on the medical triad of obesity, diabetes, and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 1297–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Patel, H.; Alanazi, S.; Kilroy, M.K.; Garrett, J.T. PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer: Clinical Implications and Adverse Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashadul Sk, M.; Hemalatha, K.; Matada, G.S.P.; Pal, R.; Manjushree, B.V.; Mounika, S.; Haripriya, E.; Viji, M.P.; Anjan, D. Current developments in PI3K-based anticancer agents: Designing strategies, biological activity, selectivity, structure-activity correlation, and docking insight. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 154, 108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocianova, E.; Piatrikova, V.; Golias, T. Revisiting the Warburg Effect with Focus on Lactate. Cancers 2022, 14, 6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, E.S.; Aromolaran, R.F.; Atoyebi, A.D.; Adeleke, F.C.; Otuyalo, A.I.; Edozie, P.K. Mechanism of the Warburg effect and its role in breast cancer immunotherapy. Discov. Med. 2024, 1, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, S. Hypoxia-inducible factor in breast cancer: Role and target for breast cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1370800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetta, P.; Sriram, R.; Zadra, G. Lactate as Key Metabolite in Prostate Cancer Progression: What Are the Clinical Implications? Cancers 2023, 15, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakici, C.; Daylan, B.; Unluer, R.S.; Emekli-Alturfan, E.; Ayla, S.; Gozel, H.E.; Yigit, P.; Dokgoz, E.Y.; Yigitbasi, T. LDH-A Inhibitor as a Remedy to Potentiate the Anticancer Effect of Docetaxel in Prostate Cancer. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaimani, R.A.; Aslam, A.; Ahmad, J.; El-Readi, M.Z.; El-Boshy, M.E.; Abdelghany, A.H.; Idris, S.; Alhadrami, M.; Althubiti, M.; Almasmoum, H.A.; et al. In Vivo and In Vitro Enhanced Tumoricidal Effects of Metformin, Active Vitamin D(3), and 5-Fluorouracil Triple Therapy against Colon Cancer by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR Network. Cancers 2022, 14, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrash, W.F.; Aslam, A.; Almaimani, R.; Minshawi, F.; Almasmoum, H.; Alsaegh, A.; Iqbal, M.S.; Tabassum, A.; Elzubier, M.E.; El-Readi, M.Z.; et al. Metformin and thymoquinone co-treatment enhance 5-fluorouracil cytotoxicity by suppressing the PI3K/mTOR/HIF1α pathway and increasing oxidative stress in colon cancer cells. Biofactors 2023, 49, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, S.; Refaat, B.; Almaimani, R.A.; Ahmed, H.G.; Ahmad, J.; Alhadrami, M.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Elzubier, M.E.; Alaufi, H.A.; Al-Amin, B. Enhanced in vitro tumoricidal effects of 5-Fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and active vitamin D3 triple therapy against colon cancer cells by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Life Sci. 2022, 296, 120442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Sarwer, D.B.; Troxel, A.B.; Sturgeon, K.; DeMichele, A.M.; Denlinger, C.S.; Schmitz, K.H. A randomized trial of exercise and diet on body composition in survivors of breast cancer with overweight or obesity. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 189, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciałowicz, M.; Woźniewski, M.; Murawska-Ciałowicz, E.; Dzięgiel, P. The Influence of Irisin on Selected Organs-The Liver, Kidneys, and Lungs: The Role of Physical Exercise. Cells 2025, 14, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.; Serrano, M.; Guerra, E.; Pardo, G.; Tinahones, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E769–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili-Tanha, G.; Shoari, A.; Nazari, E. The role of Irisin in modulating hypoxia-related disorders: New insights and implications for cancer therapy. Asp. Mol. Med. 2025, 5, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, R.; Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Hassan, M.I.; Kazim, S.N.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Al-Zharani, M.; Ahmad, F.; Islam, A. FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Molecules 2022, 27, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrash, W.; Brook, M.; Crossland, H.; Phillips, B.E.; Cegielski, J.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Smith, K.; Cleasby, M.; et al. Impacts of rat hindlimb Fndc5/irisin overexpression on muscle and adipose tissue metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E943–E955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maak, S.; Norheim, F.; Drevon, C.A.; Erickson, H.P. Progress and Challenges in the Biology of FNDC5 and Irisin. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 436–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cui, F.; Ning, K.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Wang, D.; Xu, H. Role of irisin in physiology and pathology. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 962968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Tang, N.; Huang, F.; Kong, X.; Tan, X.; Shi, G. Irisin functions to inhibit malignant growth of human pancreatic cancer cells via downregulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 7243–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Irisin Enhances Doxorubicin-Induced Cell Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 6085–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, E.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Zhang, P. Irisin/FNDC5 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of epithelial ovarian cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 306, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Taaffe, D.R.; Galvão, D.A.; Clay, T.D.; Redfern, A.D.; Hart, N.H.; Gray, E.S.; Ryan, C.J.; Kenfield, S.A.; Saad, F.; et al. Acute effect of high-intensity interval aerobic exercise on serum myokine levels and resulting tumour-suppressive effect in trained patients with advanced prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023, 26, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Chinnam, N.; Ohashi, T.; Shah, R.S.; Erickson, H.P. The structure of irisin reveals a novel intersubunit β-sheet fibronectin type III (FNIII) dimer: Implications for receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33738–33744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Dai, B.; Guo, X.; Liu, D. Cleavage of FNDC5 and insights into its maturation process. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 510, 110840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korta, P.; Pocheć, E.; Mazur-Biały, A. Irisin as a Multifunctional Protein: Implications for Health and Certain Diseases. Medicina 2019, 55, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalouf, G.E.; El Khoury, D. Exercise-Induced Irisin, the Fat Browning Myokine, as a Potential Anticancer Agent. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 6561726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S. Adipo-oncology: Adipocyte-derived factors govern engraftment, survival, and progression of metastatic cancers. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhou, X. The evolving tumor-associated adipose tissue microenvironment in breast cancer: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 27, 2778–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liermann-Wooldrik, K.T.; Kosmacek, E.A.; Oberley-Deegan, R.E. Adipose Tissues Have Been Overlooked as Players in Prostate Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, E.; Deng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Yan, Y.; Han, J.Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Immunological roles for resistin and related adipokines in obesity-associated tumors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian-Jastrzębska, A.; Malczewska-Herman, A.; Kos-Kudła, B. Role of Leptin and Adiponectin in Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, R.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Decombat, C.; Delort, L.; Caldefie-Chezet, F. Targeting Adiponectin in Breast Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Long, S.; Cao, Z. Role of Adiponectin in prostate cancer. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2019, 45, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolaki, D.; Katsibardi, K.; Efthymiou, V.; Stefanaki, C.; Mantzou, A.; Papadodima, S.; Chrousos, G.P.; Kattamis, A.; Bacopoulou, F. Irisin Concentrations in Children and Adolescent Cancer Survivors and Their Relation to Metabolic, Bone, and Reproductive Profile: A Pilot Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuğral, A.; Arıbaş, Z.; Kaya Uçar, G.; Arslan, F.D.; Bakar, Y.; Karakoyun, I.; Akyol, M. The effect of supervised aerobic exercise on adipokine and myokine biomarkers in patients with cancer during systemic chemotherapy: A single-blinded prospective controlled trial. Support. Care Cancer 2025, 33, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, N.P.; Vaughan, R.A.; Garcia-Smith, R.; Bisoffi, M.; Trujillo, K.A. Effects of the exercise-inducible myokine irisin on malignant and non-malignant breast epithelial cell behavior in vitro. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E197–E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, S.; Erden, Y.; Sandal, S.; Yilmaz, B. Is Irisin an Anticarcinogenic Peptide? Med. Sci. Int. Med. J. 2015, 4, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshanqiti, K.H.; Alomar, S.F.; Alzoman, N.; Almomen, A. Irisin Induces Apoptosis in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Cells and Inhibits Tumor Growth In Vivo. Cancers 2023, 15, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi Sadr, A.; Ehteram, H.; Seyed Hosseini, E.; Alizadeh Zarei, M.; Hassani Bafrani, H.; Haddad Kashani, H. The Effect of Irisin on Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Expression of Metastasis Markers in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Oncol. Ther. 2022, 10, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.C.; Leung, P.S. Irisin Is a Positive Regulator for Ferroptosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 18, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, N.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Irisin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth via the AMPK-mTOR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh Zarei, M.; Seyed Hosseini, E.; Haddad Kashani, H.; Ahmad, E.; Nikzad, H. Effects of the exercise-inducible myokine irisin on proliferation and malignant properties of ovarian cancer cells through the HIF-1 α signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, H.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Huang, J.X.; Chung, Y.H.; Hsu, S.T.; Chow, L.P.; Wei, K.C.; Huang, F.T. Irisin, an exercise myokine, potently suppresses tumor proliferation, invasion, and growth in glioma. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9678–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, G. Irisin reverses the IL-6 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion through the STAT3/Snail signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Xu, D.; Chu, K.; Cao, Z.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y. The Effects of MiR-214-3p and Irisin/FNDC5 on the Biological Behavior of Osteosarcoma Cells. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; et al. Irisin suppresses the migration, proliferation, and invasion of lung cancer cells via inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.H.; Zhu, T.Y.; Huang, J. FNDC5 promotes paclitaxel sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancers via inhibiting MDR1. Cell. Signal. 2020, 72, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Regulation of cell proliferation and malignant potential by irisin in endometrial, colon, thyroid and esophageal cancer cell lines. Metabolism 2014, 63, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Tang, N.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Ding, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, P.; Tan, X. Irisin stimulates cell proliferation and invasion by targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provatopoulou, X.; Georgiou, G.P.; Kalogera, E.; Kalles, V.; Matiatou, M.A.; Papapanagiotou, I.; Sagkriotis, A.; Zografos, G.C.; Gounaris, A. Serum irisin levels are lower in patients with breast cancer: Association with disease diagnosis and tumor characteristics. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Li, H.; Liu, T.J.; Zhao, Q.P.; Huang, L.H.; Cao, Z.J.; He, L.M.; Hao, D.J. Serum irisin associates with breast cancer to spinal metastasis. Medicine 2018, 97, e0524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuloglu, T.; Celik, O.; Aydin, S.; Hanifi Ozercan, I.; Acet, M.; Aydin, Y.; Artas, G.; Turk, A.; Yardim, M.; Ozan, G.; et al. Irisin immunostaining characteristics of breast and ovarian cancer cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, N.; Pan, H.; Lin, G.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Yan, K.; Gong, F. Serum and Adipose Tissue mRNA Levels of ATF3 and FNDC5/Irisin in Colorectal Cancer Patients With or Without Obesity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, S.; Nowinska, K.; Chabowski, M.; Dziegiel, P. Significance of Irisin (FNDC5) Expression in Colorectal Cancer. In Vivo 2022, 36, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esawy, M.M.; Abdel-Samd, K.M. The diagnostic and prognostic roles of serum irisin in bladder cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2020, 44, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, R.; Alp, H.H.; Eryılmaz, R.; Huyut, Z.; Sevim, M.; Araz, Ş.; Ertas, K.; Taken, K. Can the Irisin be a Biomarker for Prostate Cancer? A Case Control Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggini, M.; Cabiati, M.; Del Turco, S.; Navarra, T.; De Simone, P.; Filipponi, F.; Del Ry, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Basta, G. Increased FNDC5/Irisin expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Peptides 2017, 88, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ke, M.; Ren, Y.; Bi, J.; Du, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Lv, Y.; et al. Serum Irisin Predicts Posthepatectomy Complications in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 9850191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazgan-Simon, M.; Zuwała-Jagiełło, J.; Kukla, M.; Grzebyk, E.; Simon, K. Serum concentrations of selected adipokines in virus-related liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 6, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, S.; Hejazi, J.; Moghimi, M.; Borji, S.; Zabihian, S.; Fathi, M. Circulating Irisin Levels and Redox Status Markers in Patients with Gastric Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 2847–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Ozercan, M.R.; Albayrak, S.; Aydin, S.; Bakal, U.; Yilmaz, M.; Kalayci, M.; Yardim, M.; Sarac, M.; et al. Irisin immunohistochemistry in gastrointestinal system cancers. Biotech. Histochem. 2016, 91, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altay, D.U.; Keha, E.E.; Karagüzel, E.; Menteşe, A.; Yaman, S.O.; Alver, A. The Diagnostic Value of FNDC5/Irisin in Renal Cell Cancer. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuloğlu, T.; Artaş, G.; Yardim, M.; Sahin, I.; Aydin, Y.; Beyoğlu, N.; Özercan, I.H.; Yalcin, M.H.; Ugur, K.; Aydin, S. Immunostaining characteristics of irisin in benign and malignant renal cancers. Biotech. Histochem. 2019, 94, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, K.; Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Artas, G.; Kocdor, M.A.; Sahin, İ.; Yardim, M.; Ozercan, İ.H. Comparison of irisin hormone expression between thyroid cancer tissues and oncocytic variant cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowinska, K.; Jablonska, K.; Pawelczyk, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Partynska, A.; Gomulkiewicz, A.; Ciesielska, U.; Katnik, E.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Glatzel-Plucinska, N.; et al. Expression of Irisin/FNDC5 in Cancer Cells and Stromal Fibroblasts of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkowska, A.; Podhorska-Okołów, M.; Dzięgiel, P.; Nowińska, K. The Role of Irisin in Cancer Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, E.; Norheim, F.; Thiede, B.; Holen, T.; Ohashi, T.; Schering, L.; Lee, S.; Brenmoehl, J.; Thomas, S.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Irisin—A myth rather than an exercise-inducible myokine. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crujeiras, A.B.; Pardo, M.; Casanueva, F.F. Irisin: ‘fat’ or artefact. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, E.; Schering, L.; Buck, F.; Vlach, K.; Schober, H.C.; Drevon, C.A.; Maak, S. Irisin: Still chasing shadows. Mol. Metab. 2020, 34, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebratie, D.Y.; Dagnaw, G.G. Review of immunohistochemistry techniques: Applications, current status, and future perspectives. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 41, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Cancer | Cell Lines | Effective Concentration | Cell Viability | Cell Cycle | Apoptosis | EMT | Invasion | Migration | Signalling Pathway | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate | LNCaP DU-145 PC3 | 0.1–100 nM Effective: 10–100 nM | ↓ | _NI | NI_ | NI_ | NI_ | NI_ | NI_ | [43] |
| PC3 | 5–100 nM Effective: 100 nM | ↓ | NI | ↑ | NI | NI | NI | ↑ BAX ↑ Caspase-3 ↓ BCL2 | [44] | |
| LNCaP DU-145 | 5–40 nM Effective: 5 and 10 nM | ↓ | NI_ | ↑ | ↓ MMP2 and 9 | NI_ | NI_ | NI_ | [45] | |
| Pancreatic | Panc-1 | 0–200 nM Effective: 100–200 nM | ↓ | NI | Ferroptosis | NI | NI | NI | ↓ NF-kB ↑ LC3 II | [46] |
| PANC-1 BxPC-3 | 0–50 nM Effective: 50 nM | ↓ | NI | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ BAX ↓ BCL2 ↓ PI3K/Akt | [24] | |
| MIAPaCa-2 Panc03.27 | 0–100 nM Effective: 10 and 100 nM | ↓ | Arrest in G0/G1 | NI | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ AMPK ↓ mTOR | [47] | |
| Ovarian | OVCAR3 SKOV3 Caov4 | 5–70 nM | ↓ | NI | ↑ 10 nM on OVCAR3 | ↓ MMP2 and 9 | ↓ | NI | ↓ HIFI-α pathway | [48] |
| A2780 SKOV3 | 5–100nM_ | ↓ | NI | _NI | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ PI3K/Akt | [26] | |
| Glioblastoma | U-87 MG T98G LN-18 | 200–1000 nM Effective: 1000 nM | ↓ | Arrest in G2/M | No effect | NI | ↓ | NI | ↓ MMP-2 activity | [49] |
| Osteosarcoma | U2O2 MG-63 | 25–200 ng/mL Effective = 100 and 200 ng/ml | ↓ | NI | NI | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ p-STAT3/Snail | [50] |
| U2OS | 25–200 ng/ml | ↓ | NI | NI | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | NI | [51] | |
| Lung | A549 | 10–50 nM Effective = 20–50 nM | ↓ | NI | NI | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ PI3K/Akt/Snail | [52] |
| NSCLCs | A549 H358 H1299 H1650 | ↓ | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | ↓ NF-kB | [53] | |
| Breast | MDA-MB-231 MCF-7 | 0.62–20 nM Effective: 2.5–20 nM | ↓ | NI | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ NF-kB ↑ Caspase-3/7 cleavage | [42] |
| Endometrial Colon Thyroid Oesophageal | KLE and RL95-2 HT29 and MCA38 SW579 OE13 and OE33 and BHP7 | 5–10 nmol/L 50–100 nmol/L | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [54] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | HepG2 SMCC7721 | 0.625–20 nM Effective: 20 nM | ↑ | NI | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ PI3K/Akt | [55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farrash, W.F.; Obaid, A.A. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of the Exercise-Induced Myokine Irisin in Cancer Biology: A Comprehensive Review. Diseases 2025, 13, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090304
Farrash WF, Obaid AA. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of the Exercise-Induced Myokine Irisin in Cancer Biology: A Comprehensive Review. Diseases. 2025; 13(9):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090304
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarrash, Wesam F., and Ahmad A. Obaid. 2025. "Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of the Exercise-Induced Myokine Irisin in Cancer Biology: A Comprehensive Review" Diseases 13, no. 9: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090304
APA StyleFarrash, W. F., & Obaid, A. A. (2025). Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of the Exercise-Induced Myokine Irisin in Cancer Biology: A Comprehensive Review. Diseases, 13(9), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13090304






