PIEZO Channels in Mechano-Inflammation: Gatekeepers of Neuroimmune Crosstalk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural and Functional Overview of PIEZO Channels
3. PIEZO1 in Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Responses
4. PIEZO in Neuroinflammation and Glial Activation
Dual Role of PIEZO Channels in Inflammation: A Context-Sensitive Paradigm
5. PIEZO2: Pain Sensation and Sensory Neuroinflammation
6. PIEZO1 and Vascular Inflammation in the Central Nervous System
7. PIEZO and Connective Tissue: Mechanotransduction and Fibrotic Regulation
8. Clinical and Translational Perspectives
9. Discussion: PIEZO Channels as Converging Hubs of Neuroimmune Mechanotransduction
10. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| JNK1 | c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 |
| CXCL8 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 |
| NFAT1 | Nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| PI3K-Akt | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase—protein kinase B |
| IRF5 | Interferon regulatory factor 5 |
| CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 |
| MMP13 | Matrix metalloproteinase-13 |
| ICAM | Intercellular adhesion molecule |
| VCAM | Vascular cell adhesion molecule |
References
- Liu, H.; Bian, W.; Yang, D.; Yang, M.; Luo, H. Inhibiting the Piezo1 channel protects microglia from acute hyperglycaemia damage through the JNK1 and mTOR signalling pathways. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, P.; Parpaite, T.; Coste, B. PIEZO channels and newcomers in the mammalian mechanosensitive ion channel family. Neuron 2022, 110, 2713–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Du, H.; Winer, D.A.; Clemente-Casares, X.; Tsai, S. Mechanosensing in macrophages and dendritic cells in steady-state and disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1044729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, R.; Fu, W.; Vasylyev, D.; Waxman, S.G.; Liu, C.J. Ion channels in osteoarthritis: Emerging roles and potential targets. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Feng, X.; Zhan, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Hua, F. Piezo1 Channels as Force Sensors in Mechanical Force-Related Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 816149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, W.; Waxman, S.G.; Liu, C.J. Ion channels as therapeutic targets in osteoarthritis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2025, S0165-6147, 00121-X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoepp, F.; Abid, S.; Houssaini, A.; Lipskaia, L.; Gökyildirim, M.Y.; Born, E.; Marcos, E.; Arhatte, M.; Glogowska, E.; Vienney, N.; et al. Piezo1 in PASMCs: Critical for Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension Development. Circ. Res. 2025, 136, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coste, B.; Xiao, B.; Santos, J.S.; Syeda, R.; Grandl, J.; Spencer, K.S.; Kim, S.E.; Schmidt, M.; Mathur, J.; Dubin, A.E.; et al. Piezo proteins are pore-forming subunits of mechanically activated channels. Nature 2012, 483, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pathak, M.M.; Nourse, J.L.; Tran, T.; Hwe, J.; Arulmoli, J.; Le, D.T.; Bernardis, E.; Flanagan, L.A.; Tombola, F. Stretch-activated ion channel Piezo1 directs lineage choice in human neural stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16148–16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhong, M.; Komarova, Y.; Rehman, J.; Malik, A.B. Mechanosensing Piezo channels in tissue homeostasis including their role in lungs. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 2045894018767393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, F.; Lin, Z.; Lu, W.; Luo, H.; Feng, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Mo, S.; et al. Deficiency of Endothelial Piezo2 Impairs Pulmonary Vascular Angiogenesis and Predisposes Pulmonary Hypertension. Hypertension 2025, 82, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selezneva, A.; Gibb, A.J.; Willis, D. The contribution of ion channels to shaping macrophage behaviour. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 970234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Savadipour, A.; Palmer, D.; Ely, E.V.; Collins, K.H.; Garcia-Castorena, J.M.; Harissa, Z.; Kim, Y.S.; Oestrich, A.; Qu, F.; Rashidi, N.; et al. The role of PIEZO ion channels in the musculoskeletal system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C728–C740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cox, C.D.; Bae, C.; Ziegler, L.; Hartley, S.; Nikolova-Krstevski, V.; Rohde, P.R.; Ng, C.A.; Sachs, F.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Martinac, B. Removal of the mechanoprotective influence of the cytoskeleton reveals PIEZO1 is gated by bilayer tension. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ellefsen, K.L.; Holt, J.R.; Chang, A.C.; Nourse, J.L.; Arulmoli, J.; Mekhdjian, A.H.; Abuwarda, H.; Tombola, F.; Flanagan, L.A.; Dunn, A.R.; et al. Myosin-II mediated traction forces evoke localized Piezo1-dependent Ca2+ flickers. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, Z.; Graber, Z.T.; Baumgart, T.; Stone, H.A.; Cohen, A.E. Cell Membranes Resist Flow. Cell 2018, 175, 1769–1779.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jo, M.J.; Son, J.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Ju, J.S.; Park, M.K.; Lee, M.K.; Ahn, D.K. Blockade of Piezo2 Pathway Attenuates Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain in the Orofacial Area. Pain Res. Manag. 2024, 2024, 9179928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giniatullin, R. Ion Channels of Nociception. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Yu, W.; Su, Z.; Xiao, Z.; et al. Mechanical stretch promotes the neutrophil recruitment potential of fibroblasts through the Piezo/NFAT1/LIF axis. Cell Signal. 2025, 131, 111718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Hai, H.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Lei, M.; Cui, L.; Liu, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Piezoelectric-IL-4 programmed regulation of immuno-microenvironment-induced mesenchymal stem cell recruitment and differentiation for bone regeneration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 120, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Bai, W.; Dong, D.; Wang, H.; Qi, X.; Thanabalasuriar, A.; Ye, Y.; Xu, T.L.; Li, H.; et al. PIEZO1 mediates mechanical reprogramming of neutrophils for proangiogenic specialization in the lung. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e183796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, G.; Dong, B.B.; Devanarayana, S.; Chen, R.C.; Liu, Q. Emerging roles of mechanosensitive ion channels in ventilator induced lung injury: A systematic review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1479230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, Q.; Liu, H.; Yu, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Deng, W.; Hua, F. Mechanical properties of the brain: Focus on the essential role of Piezo1-mediated mechanotransduction in the CNS. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Csemer, A.; Sokvári, C.; Maamrah, B.; Szabó, L.; Korpás, K.; Pocsai, K.; Pál, B. Pharmacological Activation of Piezo1 Channels Enhances Astrocyte-Neuron Communication via NMDA Receptors in the Murine Neocortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cieśluk, M.; Pogoda, K.; Piktel, E.; Wnorowska, U.; Deptuła, P.; Bucki, R. Mechanical Properties of the Extracellular Environment of Human Brain Cells Drive the Effectiveness of Drugs in Fighting Central Nervous System Cancers. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, J.; Hou, B.; Tumova, S.; Muraki, K.; Bruns, A.; Ludlow, M.J.; Sedo, A.; Hyman, A.J.; McKeown, L.; Young, R.S.; et al. Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature 2014, 515, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nagase, T.; Nagase, M. Piezo ion channels: Long-sought-after mechanosensors mediating hypertension and hypertensive nephropathy. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2786–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, L.; Balogh, N.; Tóth, A.; Angyal, Á.; Gönczi, M.; Csiki, D.M.; Tóth, C.; Balatoni, I.; Jeney, V.; Csernoch, L.; et al. The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channels contribute to the arterial medial calcification. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1037230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procès, A.; Luciano, M.; Kalukula, Y.; Ris, L.; Gabriele, S. Multiscalemechanobiology in brain physiology and diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 823857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.R.; Yang, G.Y.; Ahn, M.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ju, J.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Blockade of microglial activation reduces mechanical allodynia in rats with compression of the trigeminal ganglion. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 36, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkodi, B.; Marsovszky, L.; Csorba, A.; Balog, A.; Kopper, B.; Keller-Pintér, A.; Nagy, Z.Z.; Resch, M.D. Disrupted Neural Regeneration in Dry Eye Secondary to Ankylosing Spondylitis-with a Theoretical Link between Piezo2 Channelopathy and Gateway Reflex, WDR Neurons, and Flare-Ups. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Chu, M.; et al. Mechanosensory Piezo2 regulated by gut microbiota participates in the development of visceral hypersensitivity and intestinal dysmotility. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2497399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, C.; Ma, L.; Gao, S.; Yang, M.Y.; Mu, M.D.; Chang, L.; Huang, P.; Ye, X.; Wang, W.; Tao, X.; et al. PPP1R3A inhibits osteogenesis and negatively regulates intracellular calcium levels in calcific tendinopathy. iScience 2023, 26, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schröder, A.; Engelhardt, H.; Nogueira, A.; Clausen, B.; Kirschneck, C.; Jantsch, J.; Proff, P.; Renner, K.; Paddenberg-Schubert, E. The Mechanosensitive PIEZO1 Channel Contributes to the Reaction of RAW264.7 Macrophages to Mechanical Strain. Mediat. Inflamm. 2025, 2025, 9998838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, J.; Xu, C.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, P. Roles of Piezo1 in chronic inflammatory diseases and prospects for drug treatment (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 32, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, W.; Huang, M.; Huang, X.; Ma, K.; Luo, M.; Yang, N. GsMTx4-blocked PIEZO1 channel promotes myogenic differentiation and alleviates myofiber damage in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Skelet. Muscle 2025, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mikhailov, N.; Leskinen, J.; Fagerlund, I.; Poguzhelskaya, E.; Giniatullina, R.; Gafurov, O.; Malm, T.; Karjalainen, T.; Gröhn, O.; Giniatullin, R. Mechanosensitive meningeal nociception via Piezo channels: Implications for pulsatile pain in migraine? Neuropharmacology 2019, 149, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, C.; Guo, R.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shu, X.; Jiang, M. Examination of the mechanism of Piezo ion channel in 5-HT synthesis in the enterochromaffin cell and its association with gut motility. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1193556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ranade, S.S.; Woo, S.H.; Dubin, A.E.; Moshourab, R.A.; Wetzel, C.; Petrus, M.; Mathur, J.; Bégay, V.; Coste, B.; Mainquist, J.; et al. Piezo2 is the major transducer of mechanical forces for touch sensation in mice. Nature 2014, 516, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, X.; Wanggou, S.; Bodalia, A.; Zhu, M.; Dong, W.; Fan, J.J.; Yin, W.C.; Min, H.-K.; Hu, M.; Draghici, D. A feedforward mechanism mediated by mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO1 and tissue mechanics promotes glioma aggression. Neuron 2018, 100, 799–815.e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Chai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Astrocyte-mediated inflammatory responses in traumatic brain injury: Mechanisms and potential interventions. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1584577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trotier, A.; Bagnoli, E.; Walski, T.; Evers, J.; Pugliese, E.; Lowery, M.; Kilcoyne, M.; Fitzgerald, U.; Biggs, M. Micromotion Derived Fluid Shear Stress Mediates Peri-Electrode Gliosis through Mechanosensitive Ion Channels. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, J.; Fang, B.; Shan, S.; Li, Q. Mechanical stiffness promotes skin fibrosis through Piezo1-mediated arginine and proline metabolism. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rashidi, N.; Harasymowicz, N.S.; Savadipour, A.; Steward, N.; Tang, R.; Oswald, S.; Guilak, F. PIEZO1-mediated mechanotransduction regulates collagen synthesis on nanostructured 2D and 3D models of fibrosis. Acta Biomater. 2025, 193, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Yan, X.; Bi, Y. Mechanosensitive Piezo1 channels promote neurogenic bladder fibrosis via regulating TGF-β1/smad and Hippo/YAP1 pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Deng, P.; Yao, Z.; Sun, Q. The Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Promotes Obliterative Bronchiolitis through YAP-Dependent Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Curr. Mol. Med. 2025, ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zou, H.; Wei, J.; Dong, L.; Hou, W. Piezo1: The Potential Novel Target for Radiation-induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating FAP + fibroblasts. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2025, ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migulina, N.; Kelley, B.; Zhang, E.Y.; Pabelick, C.M.; Prakash, Y.S.; Vogel, E.R. Mechanosensitive Channels in Lung Health and Disease. Compr. Physiol. 2023, 13, 5157–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, J.; Deng, B.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.; et al. Piezo1 specific deletion in macrophage protects the progression of liver fibrosis in mice. Theranostics 2023, 13, 5418–5434, Erratum in Theranostics 2025, 15, 1156–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Drobnik, M.; Smólski, J.; Grądalski, Ł.; Niemirka, S.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Mechanosensitive Cation Channel Piezo1 Is Involved in Renal Fibrosis Induction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Steinecker-Frohnwieser, B.; Lohberger, B.; Toegel, S.; Windhager, R.; Glanz, V.; Kratschmann, C.; Leithner, A.; Weigl, L. Activation of the Mechanosensitive Ion Channels Piezo1 and TRPV4 in Primary Human Healthy and Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes Exhibits Ion Channel Crosstalk and Modulates Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brylka, L.J.; Alimy, A.R.; Tschaffon-Müller, M.E.A.; Jiang, S.; Ballhause, T.M.; Baranowsky, A.; von Kroge, S.; Delsmann, J.; Pawlus, E.; Eghbalian, K.; et al. Piezo1 expression in chondrocytes controls endochondral ossification and osteoarthritis development. Bone Res. 2024, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, Q.; Tang, L.; Cao, Y.; Nourse, J.L.; Pathak, M.M.; Lu, X.; Yang, Q. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Regulates Diet-Induced Adipose Inflammation and Systemic Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Della Pietra, A.; Mikhailov, N.; Giniatullin, R. The Emerging Role of Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels in Migraine Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gomes, L.; Pardo-Pastor, C.; Rosenblatt, J.; Pouliopoulos, A.N. Mechanotransduction as a therapeutic target for brain tumours. EBioMedicine 2025, 117, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scarpellino, G.; Munaron, L.; Cantelmo, A.R.; Fiorio Pla, A. Calcium-Permeable Channels in Tumor Vascularization: Peculiar Sensors of Microenvironmental Chemical and Physical Cues. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 182, 111–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Guo, T. Visceral pain from colon and rectum: The mechanotransduction and biomechanics. J. Neural. Transm. 2020, 127, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gudin, J.; Sakr, M.; Fason, J.; Hurwitz, P. Piezo Ion Channels and Their Association with Haptic Technology Use: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e77433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Allerkamp, H.H.; Bondarenko, A.I.; Tawfik, I.; Kamali-Simsek, N.; Horvat Mercnik, M.; Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.T.; Wadsack, C. In vitro examination of Piezo1-TRPV4 dynamics: Implications for placental endothelial function in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2025, 328, C227–C244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
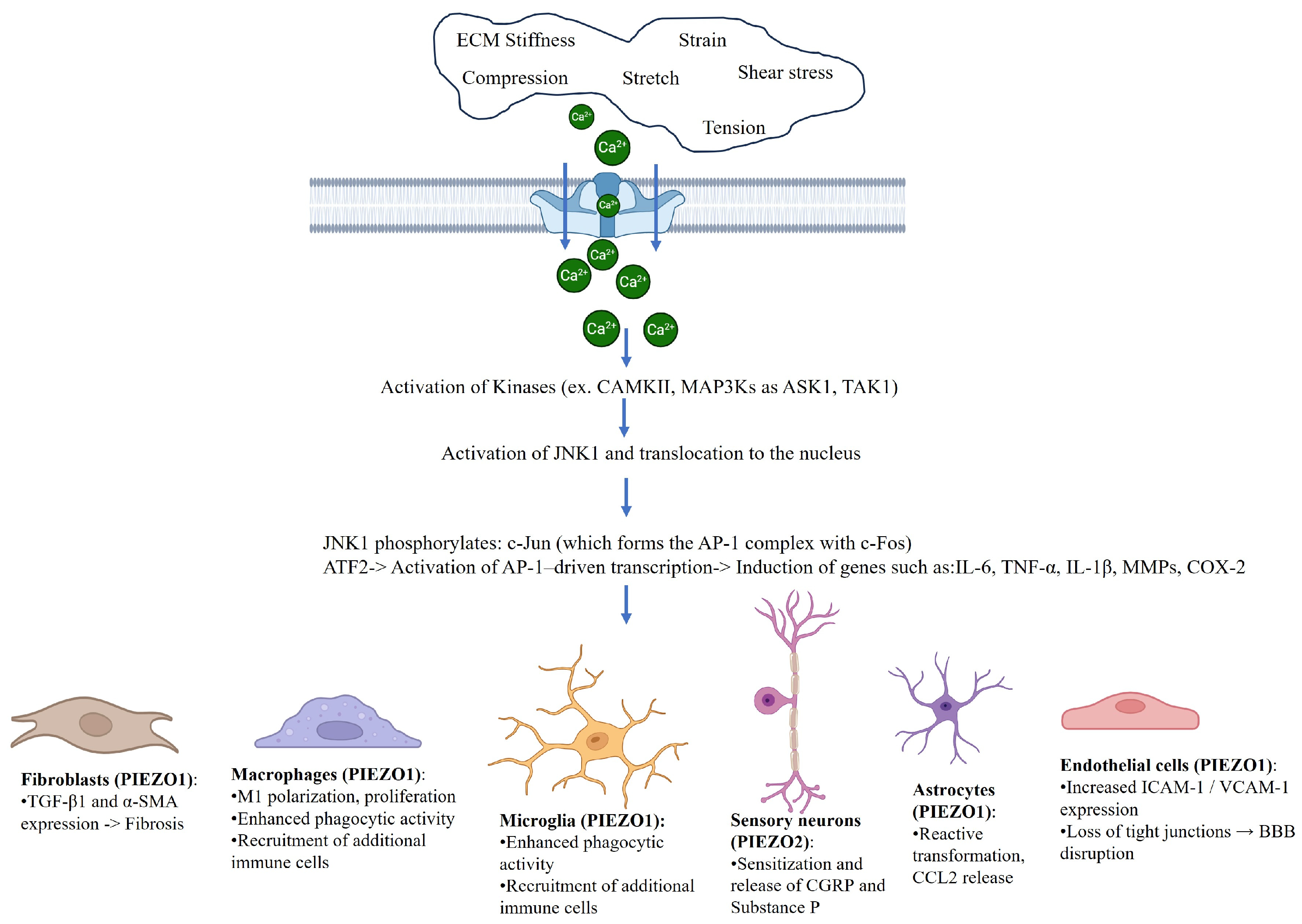
| Cell Type | PIEZO Isoform | Mechanical Stimulus | Functional Outcome | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macrophages | PIEZO1 | Matrix stiffness and stretch | M1 polarization and IL-6/TNF-α release | [12,19,20] |
| Microglia | PIEZO1 | Hyperglycemia and substrate stiffness | NF-kB activation and IL-1β production | [21,22] |
| Astrocytes | PIEZO1 | Mechanical strain | Polarity, migration, and CCL2/IL-1β expression | [23] |
| Fibroblasts | PIEZO1 | Tension and compression | Myofibroblast transition and TGF-β expression | [24,25,26,27,28] |
| Sensory neurons | PIEZO2 | Tactile/mechanical load | Mechanical allodynia and neuropeptide release | [17,29,30,31] |
| Endothelial cells | PIEZO1 | Shear stress and inflammation | ICAM/VCAM expression barrier breakdown | [10,32] |
| Disease Model | PIEZO Isoform | Tissue/Cell Target | Pathological Role | Possible Modulation Strategy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | PIEZO1 | Chondrocytes | Promotes IL-6 and MMP13 expression under mechanical stretch + IL-1β; induces apoptosis | GsMTx4 antagonist protects cartilage integrity | [51,52] |
| Pulmonary fibrosis/VILI | PIEZO1 | Lung macrophages and fibroblasts | Enhances HIF1α, endothelin-1, and fibrotic remodeling under cyclic stretch | Genetic silencing or pharmacological inhibition | [44,46] |
| Metabolic syndrome | PIEZO1 | Adipocytes | Increases IL-6 and leptin secretion under obesogenic stress, promoting insulin resistance | Targeted inhibition reduces low-grade inflammation | [53] |
| Migraine and pain syndromes | PIEZO1 + PIEZO2 | Trigeminal afferents and dural vasculature | PIEZO2 contributes to tactile hypersensitivity; PIEZO1 regulates endothelial permeability and inflammation | PIEZO2 inhibition reduces pain; PIEZO1 inhibition modulates BBB | [10,31,39] |
| Chronic neuroinflammation | PIEZO1 | Microglia, astrocytes, and endothelial cells | Triggers JNK/mTOR and NF-kB signaling; promotes cytokine production, leucocyte recruitment, and BBB breakdown | siRNA or GsMTx4 inhibition dampens inflammatory signaling | [1,10,18,30,37] |
| Systemic sclerosis/fibrosis | PIEZO1 | Fibroblast and myofibroblasts | Induces TGF-β1 and α-SMA expression; drives myofibroblast differentiation and collagen deposition | Inhibition reduces ECM gene expression and contractility | [4,46] |
| Tendinopathy/enthesitis | PIEZO1 | Fibroblasts from enthesis | Promotes neutrophil recruitment via LIF under stretch; contributes to local inflammation | Mechanical unloading or PIEZO inhibition | [4,13,19,33] |
| Irritable bowel syndrome/bladder pain | PIEZO2 | Visceral afferents | Mediates visceral hypersensitivity, CGRP, and substance P release under stretch | PIEZO2 antagonists reduce afferent firing and nociception | [31,39,40] |
| Glioblastoma/CNS tumors | PIEZO1 | Glioma cells and CNS endothelium | Promotes VEGF, MMPs, and immune evasion; supports vascular mimicry and tumor progression | Pharmacological blockade reduces invasion and vascular remodeling | [10,24,40,41,42] |
| Vascular cognitive impairment/aging | PIEZO1 | Cerebral endothelium | Alters neurovascular coupling and increases ROS and BBB permeability under chronic stress | Long-term PIEZO modulation under investigation | [25,26,27,28] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirri, C. PIEZO Channels in Mechano-Inflammation: Gatekeepers of Neuroimmune Crosstalk. Diseases 2025, 13, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13080263
Pirri C. PIEZO Channels in Mechano-Inflammation: Gatekeepers of Neuroimmune Crosstalk. Diseases. 2025; 13(8):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13080263
Chicago/Turabian StylePirri, Carmelo. 2025. "PIEZO Channels in Mechano-Inflammation: Gatekeepers of Neuroimmune Crosstalk" Diseases 13, no. 8: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13080263
APA StylePirri, C. (2025). PIEZO Channels in Mechano-Inflammation: Gatekeepers of Neuroimmune Crosstalk. Diseases, 13(8), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13080263






