1. Table Legend
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in the legend for Table 2. Table 2 did not include the data source in the table footer. The correct legend appears below.
Major features include enhancing “capsule”, non-peripheral “washout”, and threshold growth. * If enhancing “capsule” (LR-4), non-peripheral “washout”, or threshold growth (LR-5). Table 2 was created using data from the AASLD 2023 guidelines [63].
2. Error in Figures 2–4
In the original publication, there was a mistake in Figures 2–4 as published. Figures 2–4 lacked scale bars and corresponding descriptions in their legends. The corrected versions of Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 appear below.
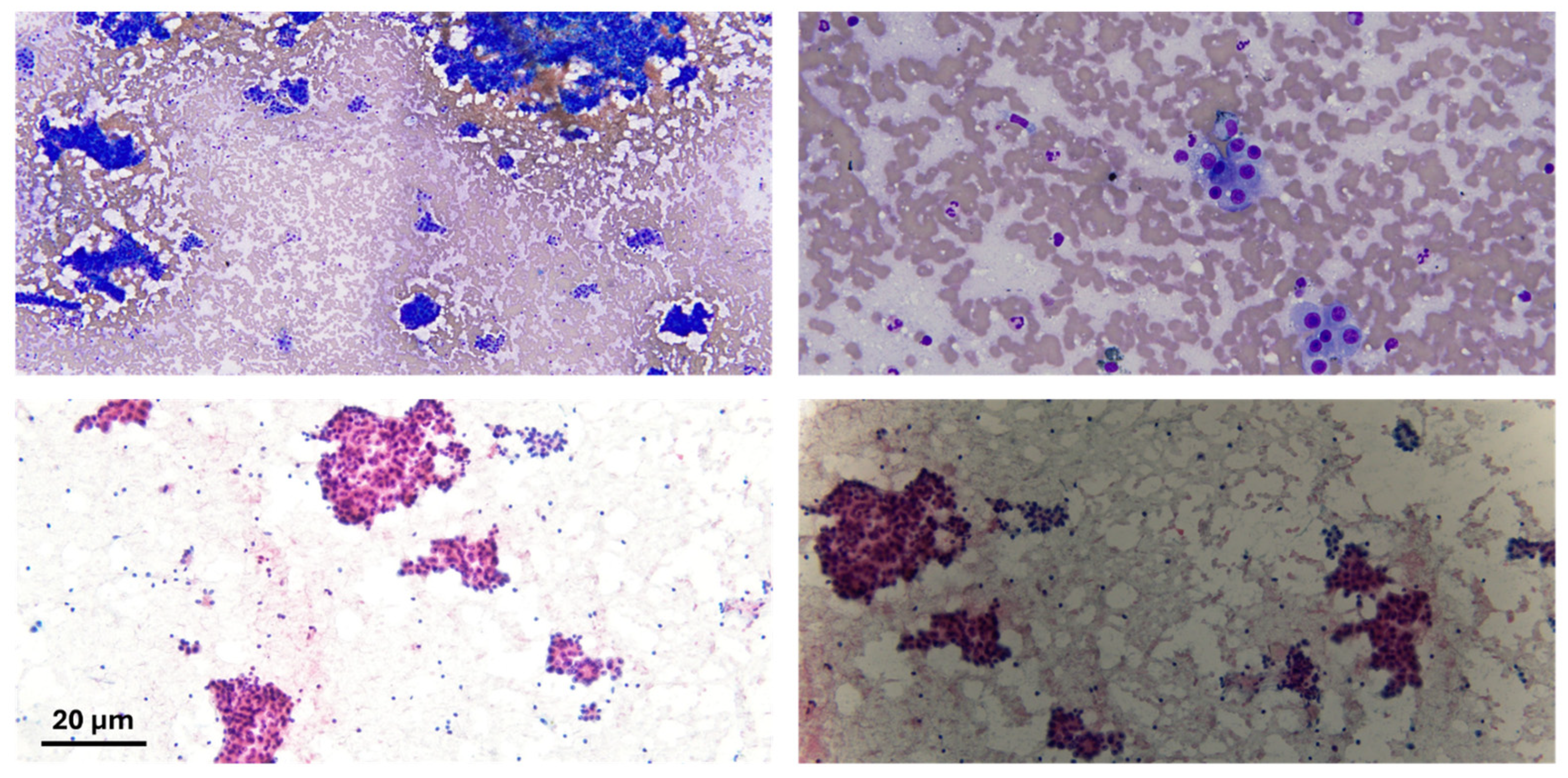
Figure 2.
Cytological preparation of lesional material; the lesional material shows atypical sheets of cells in both diff-quick (bright blue) and pap stain (pink cytoplasm). Scale bar: 20 µm.
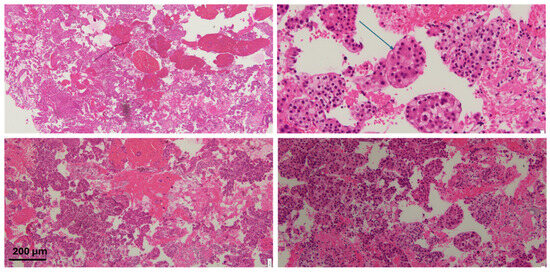
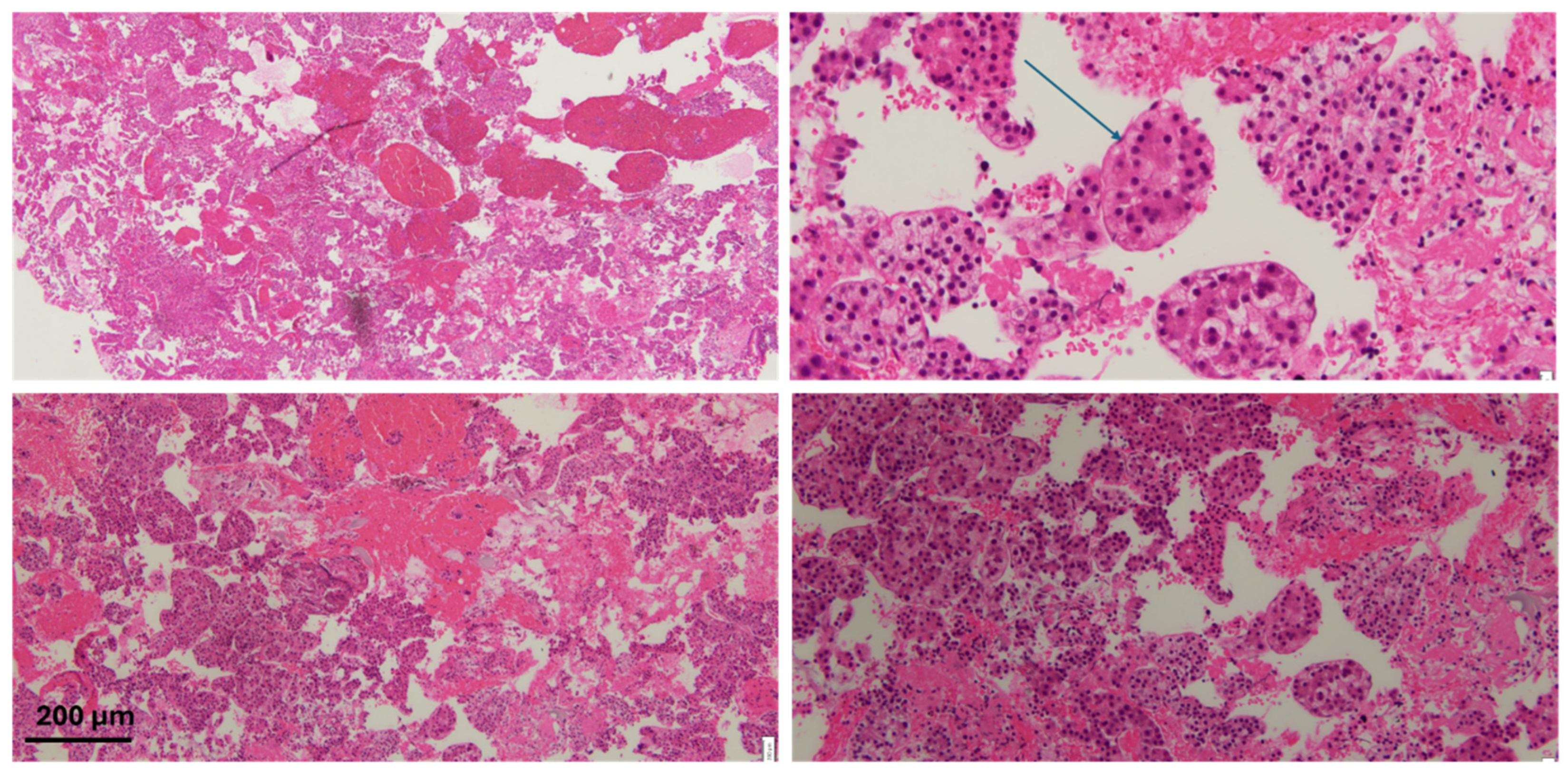
Figure 3.
H&E staining of the specimen with atypical cells with some areas of clear/vacuolated cytoplasm. The arrow highlights endothelial wrapping, a feature suggestive of hepatocellular carcinoma. Scale bar: 200 µm.
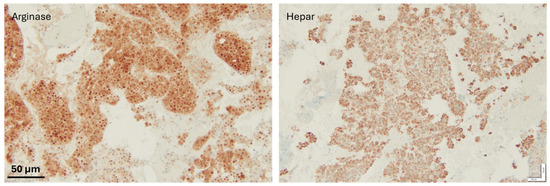
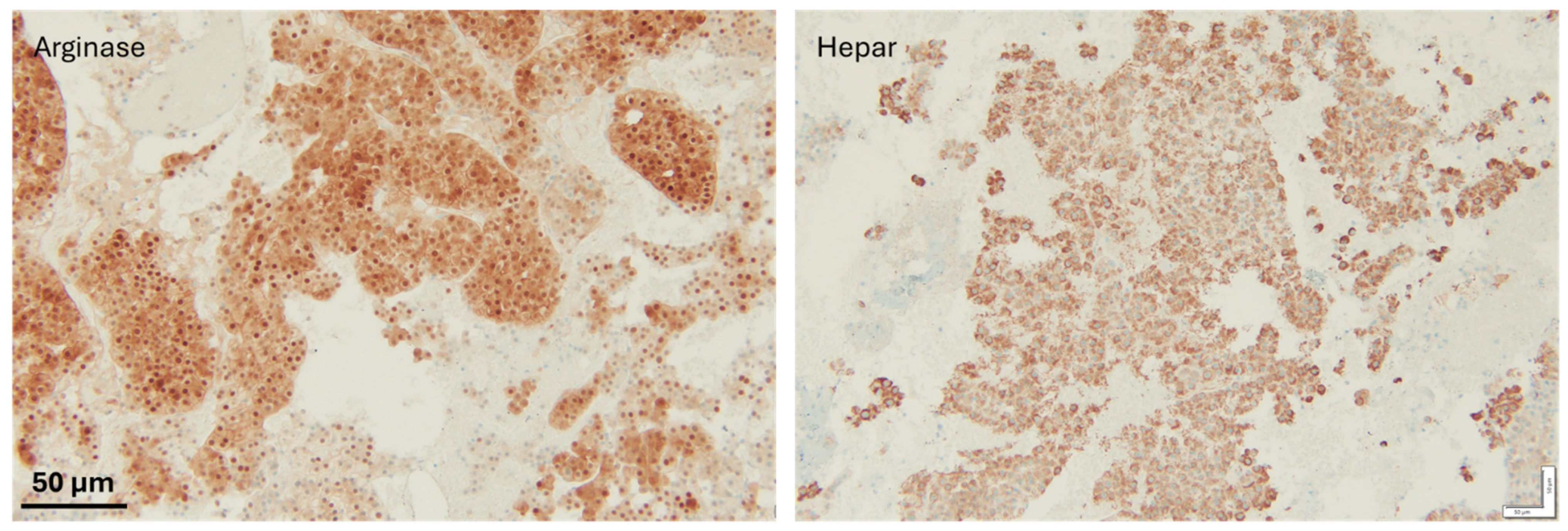
Figure 4.
IHC staining to confirm metastasis; both hepatocyte markers were positive, therefore supporting the diagnosis of a metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Scale bar: 50 µm.
3. Missing Institutional Review Board and Informed Consent Statement
In the original publication, the Institutional Review Board and Informed Consent Statement were not included.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The histological images (Figures 2–4) were obtained from de-identified human tissue samples. As no identifiable patient information is included, this study was exempt from IRB review in accordance with institutional guidelines.
Informed Consent Statement: Histologic images were used in accordance with institutional regulations. Per institutional policy, informed consent was not required for the use of de-identified pathology images.
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Amin, N.; Anwar, J.; Sulaiman, A.; Naumova, N.N.; Anwar, N. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Diseases 2025, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).