Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke (IS), a major cerebrovascular disease, is associated with high disability and mortality rates. Acute kidney injury (AKI) often complicates IS and increases in-hospital mortality. While antiplatelet agents are commonly used for IS treatment, their effectiveness in IS patients with AKI is unclear. Methods: This study, using data from the MIMIC-IV database, divided patients into non-combination (clopidogrel or ticagrelor alone) and combination (with aspirin) groups. The primary outcome was 28-day mortality, with secondary outcomes including 90-day, 1-year, and in-hospital mortality. Multivariable Cox and logistic regression models were used to analyze the relationship between antiplatelet regimens and mortality. Subgroup analyses and interaction tests were conducted. Results: Results showed the combination group had lower 28-day, 90-day, 1-year, and in-hospital mortality risks than the non-combination group (all p < 0.001). Subgroup analysis revealed an interaction effect by AKI stage, with combination therapy not significantly reducing mortality in severe AKI (stages 2 and 3, p = 0.743, p = 0.244). Conclusions: This study demonstrates that combination antiplatelet therapy significantly reduces 28-day, 90-day, 1-year, and in-hospital mortality risks of IS patients with AKI, suggesting its potential benefits in improving both short- and long-term clinical outcomes. However, this does not apply to patients with severe AKI, indicating heterogeneous survival benefits of combination therapy across AKI severity. Clinical decision-making should incorporate AKI stage stratification to evaluate the applicability of combination antiplatelet therapy. Further research is needed to explore the impact of AKI staging on antiplatelet therapy in IS patients.
1. Introduction
As the second leading cause of death globally, stroke is linked to high rates of disability and mortality1 [1,2,3]. Ischemic stroke (IS) accounts for 70% of all strokes [1], primarily manifested as cerebral infarction due to insufficient blood supply to brain tissue. Patients with IS often suffer from acute kidney injury (AKI), which is associated with a significant increase in in-hospital mortality [4]. AKI is defined as an acute deterioration of kidney function, characterized by abnormal elevation of serum creatinine and reduced urine output within a short period. AKI is frequently observed in patients with acute stroke and other critically ill patients with various diseases. Medications, fluid intake, sepsis, and contrast agents used in diagnostic processes can all lead to the occurrence of AKI [5].
Antiplatelet agents have been widely used in the therapy of individuals with IS to prevent the recurrence of ischemic events. Antiplatelet agents mainly include aspirin and P2Y12 receptor antagonists (clopidogrel and ticagrelor) [6,7]. In clinical practice, antiplatelet therapy often involves the combined or separate use of antiplatelet agents with different mechanisms of action. Multiple clinical trials based on different racial populations [7,8,9] have shown that the combined use of aspirin and P2Y12 receptor antagonists significantly reduces the risk of recurrent ischemic events. However, in specific populations of patients with IS (for example, patients carrying the CYP2C19 loss-of-function (LoF) allele [10], the clinical efficacy of the combined use of aspirin and clopidogrel is not significant. The differences in clinical efficacy of combined antiplatelet drug regimens among different populations limit the generalizability of the conclusions from previous clinical trials. Although several current studies have shown the protective effects of antiplatelet agents in AKI [11,12], there is no evidence to indicate the superiority or inferiority of combined antiplatelet drug regimens among patients suffering from IS along with AKI.
Therefore, this study analyzed patient records from the MIMIC-IV database related to intensive care to evaluate the clinical efficacy of combined antiplatelet therapy regimens in patients experiencing both IS and AKI. Our study comprehensively assessed the effects of antiplatelet therapy regimens upon short-term and long-term mortality outcomes, aiming to assist in the selection of antiplatelet therapy regimens for special patient populations in clinical practice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
The dataset for this study was gathered from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV (version 2.2). This dataset encompasses de-identified clinical details of patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston, Massachusetts, from 2008 to 2019. The information includes demographic characteristics, vital signs, laboratory test results, treatments, and prescription data. The author (Qiangqiang Zhou) was given permission to access the database (certificate number: 43904630). Approval for using this database was granted by the Institutional Review Boards of MIT and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, with informed consent being waived.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
A total of 4195 patients with IS were initially recruited according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9/10 guidelines. Among these, 3018 individuals with a concurrent diagnosis of AKI were selected for further study. According to the KDIGO criteria, AKI was diagnosed if any of the following conditions were met: an increase in serum creatinine (Scr) of more than 26.5 μmol/L (0.3 mg/dl) within 48 h; an increase in Scr to more than 1.5 times the baseline level, confirmed or presumed to have occurred within 7 days; or urine output less than 0.5 mL/(kg·h) for more than 6 h. The AKI stage was determined based on the changes in Scr and urine output.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Individuals admitted who are below the age of 18;
- Individuals with an ICU duration of under 3 h;
- Only the data from the first ICU admission were included for subjects with multiple admissions;
- Patients who did not receive antiplatelet therapy during hospitalization;
- Individuals diagnosed with severe liver disease, malignant tumors, or other serious illnesses.
2.3. Data Collection
Navicat Premium Lite 17 was deployed to retrieve patient data using Structured Query Language (SQL). The extracted patient information primarily encompassed five aspects:
- Demographic Data: Age, sex, racial background, and body mass index (BMI).
- Physiological Parameters within 24 h of ICU Admission: Mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), body temperature, and oxygen saturation (SpO2) measured by pulse oximetry.
- Laboratory Parameters within 24 h of ICU Admission: Red blood cell count (RBC), platelet count (PLT), white blood cell count (WBC), blood glucose (BG), sodium and potassium levels, serum creatinine (Scr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urine output.
- Severity of Illness Scores and Comorbidities at Admission: Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA), Logistic Organ Dysfunction System (LODS), Oxford Acute Severity of Illness Score (OASIS), Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III (APACHE III), Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II), Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), bleeding, heart failure (HF), chronic lung disease (CLD), diabetes, hypertension, dementia, smoking, alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation (AF), coronary atherosclerotic heart disease (CHD; carotid atherosclerosis (CAS) myocardial infarction (MI), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and history of antiplatelet drug use.
According to the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) definition criteria, bleeding includes, but is not limited to the following: intracranial bleeding, intraocular bleeding with visual impairment, pericardial tamponade, and other life-threatening bleeding events. Additionally, clinically significant declines in hemoglobin levels (requiring laboratory confirmation) or cases necessitating substantial blood transfusion within a short timeframe (per clinical transfusion guidelines) are also encompassed within this definition.
- 5.
- Prescription Information during ICU Stay: Medication usage and therapeutic interventions, including antiplatelet drugs (aspirin, clopidogrel, ticagrelor), warfarin, new oral anticoagulants (NOAC), vasoactive drugs, mechanical ventilation (MV), thrombolysis, and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT).
2.4. Primary Outcome and Secondary Outcomes
The primary outcome of this study was the 28-day mortality rate, with 90-day mortality, 1-year mortality, and in-hospital mortality serving as secondary outcomes.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
For all participants, descriptive analysis was performed. Continuous variables with normal distribution were presented as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD), while those with skewed distribution were represented by median and interquartile range [M (Q1, Q3)]. Independent samples t-tests and Mann–Whitney U tests were used to compare differences between groups. Categorical data were expressed as counts and proportions [n (%)], and analyzed using χ2 tests or Fisher’s exact test. Multiple imputation was employed to handle missing data in the study. VIFs were used to assess multicollinearity among variables, with variables having a VIF exceeding 5 being excluded. To mitigate baseline imbalances, propensity score matching (PSM) was utilized to adjust for confounding factors between groups. A caliper value of 0.1 was set, and the nearest neighbor matching method was applied at a 1:1 ratio. Standardized mean differences (SMD) were used to compare differences between groups, with SMD < 0.10 indicating acceptable balance between groups. Kaplan–Meier methods were employed for survival analysis, with log-rank tests used for comparisons. Cox proportional hazards regression models were applied to assess the risk ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for mortality outcomes (28-day, 90-day, and 1-year mortality). Logistic regression models were constructed to examine the impact of treatment regimens on in-hospital mortality. Four models were built with adjustments for confounding factors: Model 1 was the baseline model without adjustments; Model 2 adjusted for age, race, gender, BMI, and ICU admission details; Model 3 further adjusted for admission laboratory tests and disease severity scores, including HR, MBP, SpO2, RR, WBC, PLT, RBC, BG, blood potassium, blood sodium, urine volume, Scr, BUN, SOFA, LODS, OASIS, APS III, SIRS, and admission GCS; and Model 4 adjusted for comorbidities and prescription usage, including HF, CLD, diabetes, hypertension, dementia, smoking, alcohol consumption, AF, CHD, MI, CKD, history of antiplatelet drugs, statins, warfarin, NOAC, vasoactive drugs, MV, thrombolysis, and CRRT. All statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.2.2, two-tailed tests, and p < 0.05 was statistically significant.
2.6. Subgroup Analysis
Subgroup analysis was conducted according to age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, anticoagulants, atherosclerosis, AKI stage, atrial fibrillation, and bleeding. For each subgroup, Cox proportional hazards regression analysis or logistic regression was performed, and the results were visually presented using forest plots. Likelihood ratio tests were employed to detect interactions between the intervention effects and subgroup factors. A p-value for interaction < 0.05 indicated a significant subgroup effect, suggesting that the subgroup factor modified the effect of the intervention.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
Data from 4195 IS patients were extracted from the MIMIC-IV database. After applying exclusion criteria (patients with hospitalization duration < 3 h and comorbid malignant diseases were excluded), 1878 patients with IS complicated by AKI were included in the study finally (Figure 1).
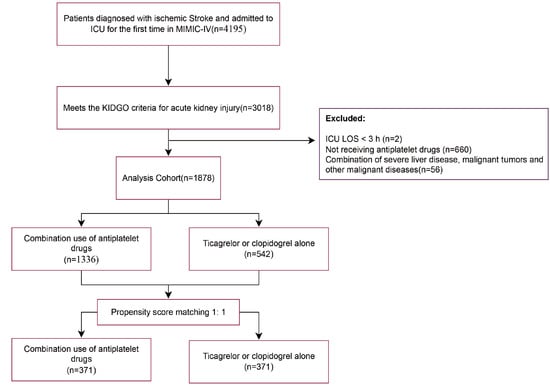
Figure 1.
Research flowchart.
Table S1 presents the variance inflation factors (VIF) for the study variables, with variables having a VIF greater than 5 indicating significant collinearity and thus being excluded from the study. Table S2 displays baseline characteristics of patients. A total of 1336 patients (71.2%) were on a combination therapy of ticagrelor or clopidogrel along with aspirin during their hospital stay (combination group), while the remaining 542 patients (28.8%) did not receive aspirin (non-combination group). Table 1 demonstrates that a substantial proportion of IS patients had high-risk predisposing conditions. Notably, over 20% of patients exhibited concomitant carotid and coronary atherosclerosis. Additionally, the prevalence of atrial fibrillation reached 42.3% in the combination group and 46.8% in the non-combination group. Compared to the non-combination group, the combination group had a relatively lower mean age. Regarding routine admission examination indicators, the two groups showed different distribution patterns. The combination group had higher levels of mean arterial pressure (MBP), heart rate (HR), and respiratory rate (RR), whereas the non-combination group had higher levels of blood potassium and blood sodium. In terms of disease severity scores, the combination group had a relatively higher average OASIS. However, the combination group had a lower proportion of patients with chronic complications such as heart failure (19.7%), chronic lung disease (14.0%), myocardial infarction (10.3%), diabetes (31.9%), hypertension (75.1%), CHD (12.0%), and other conditions. To reduce confounding bias, propensity score matching was applied to the covariates, resulting in 371 matched pairs after 1:1 matching. The probability density curves of the propensity scores before and after the matching process are shown in Figure 2A. The baseline characteristics of the patients in both groups were similar, with the standardized mean differences (SMD) of the variables before and after matching reflecting the balance of the baseline data between groups (Figure 2B).

Table 1.
Multi-model regression analysis of primary outcomes.
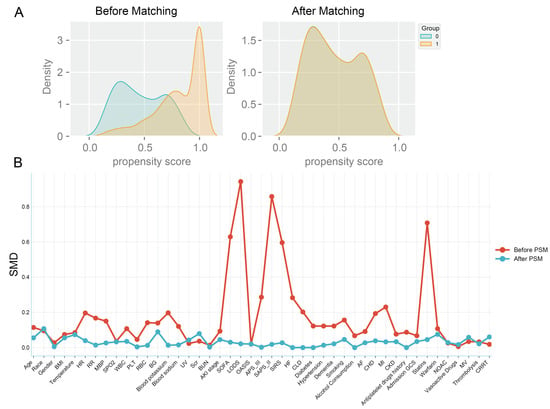
Figure 2.
Balance of baseline characteristics between groups before and after propensity score matching, (A). Probability density curves before and after matching: the probability density curves of the propensity scores of the two groups intersect before matching (left panel), indicating that the propensity scores can be matched. The higher the degree of concordance of the probability density curves after matching, the better the matching effect, (B). Standardized Mean Difference SMD of the variables before and after the PSM, SMD < 0.1 indicates a good balance.
3.2. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
The Kaplan–Meier curves demonstrated that compared to the patients in the non-combination group, the combination group had significantly lower 28-day, 90-day, and 1-year mortality rates. (log-rank test, p < 0.0001, Figure 3).
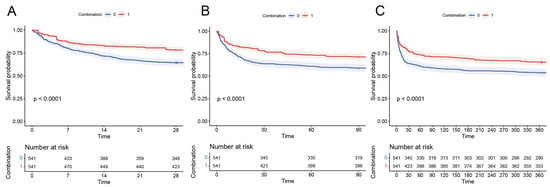
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves of combination group and non-combination group: (A) 28-day mortality, (B) 90-day mortality, and (C) 1-year mortality.
The development of four multivariable Cox regression models was undertaken to assess the independent impact of two treatment regimens on mortality outcomes, with respective hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) presented in Table 1 and Table S3. The unadjusted Model 1 Cox regression results indicated that individuals in the combination group had a significantly reduced 28-day mortality rate (HR 0.56, 95% CI 0.44–0.70, p < 0.001). For secondary outcomes, the combination group also showed significantly lower risks for 90-day and 1-year mortality, as well as in-hospital mortality (HR 0.56, 95% CI 0.44–0.70, p < 0.001; HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.51–0.77, p < 0.001; HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.55–0.80, p < 0.001; HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.39–0.60, p < 0.001). In the extended multivariable Cox regression models, the combination group consistently exhibited a lower risk of death, emphasizing the potential benefits of combined antiplatelet therapy in reducing the mortality risk among patients with IS complicated by AKI.
Given that atrial fibrillation (AF) is an independent risk factor for stroke prognosis, adjustment for its confounding effects on the therapeutic outcomes of antiplatelet therapy was required. A separate survival analysis conducted in AF patients (n = 1605) demonstrated through Kaplan–Meier curves that combination antiplatelet therapy significantly improved survival outcomes even in this population (Figure S1, log-rank test, p < 0.001).
3.3. Subgroup Analysis and Interaction Analysis
Patients were stratified into different subgroups based on age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, anticoagulants, atherosclerosis, AKI stage, atrial fibrillation, and bleeding to explore the impact of exposure on mortality outcomes across these subgroups. The results of the subgroup analysis for the 28-day mortality outcome are presented in a forest plot (Figure 4).
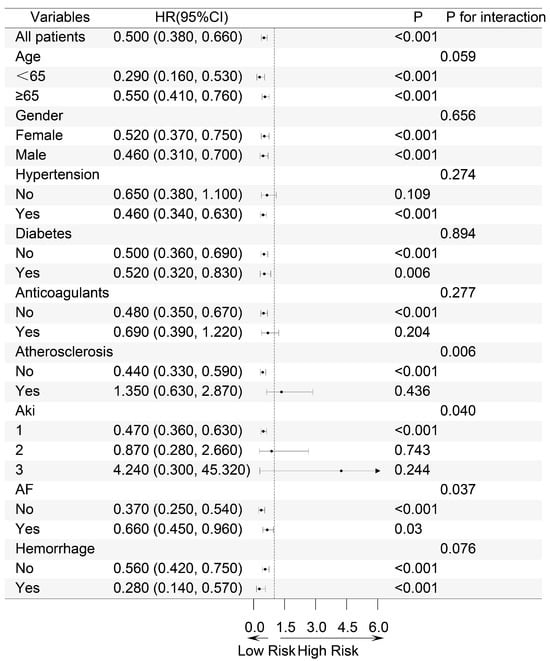
Figure 4.
Subgroup Forest Map of 28-day all-cause mortality. Based on age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, anticoagulants, atherosclerosis, AKI stage, atrial fibrillation and bleeding. HR: Hazard Ratio, CI: Confidence Interval.
Significant interactions were observed in the subgroups of atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, and AKI stage. Notably, in the AKI stage subgroup, a significant difference in the 28-day mortality risk was observed across different stages of AKI (p for interaction 0.04). For patients diagnosed with AKI stage 1, the implementation of combination therapy resulted in a 47% reduction in mortality risk. (HR 0.53, 95% CI 0.36–0.63, p < 0.001), whereas this benefit was not evident in patients with stages of AKI 2 and 3. Consistent results were also observed in the subgroup analyses for secondary mortality outcomes (Figures S2–S4). This suggests that for IS patients with more severe stages of AKI, the combined use of antiplatelet drugs does not improve the mortality risk compared to the use of clopidogrel or ticagrelor alone.
3.4. Outcomes in Mild and Severe AKI Subgroups
Subsequently, the patients were divided into two groups according to the stage of AKI they were experiencing. Patients with AKI stage 1 were defined as having mild AKI (MAKI), while those with stages 2 and 3 were categorized as having severe AKI (SAKI). Kaplan–Meier (KM) curves were used to display the 28-day, 90-day, and 1-year mortality rates for patients with mild and severe AKI, respectively (Figure 5).
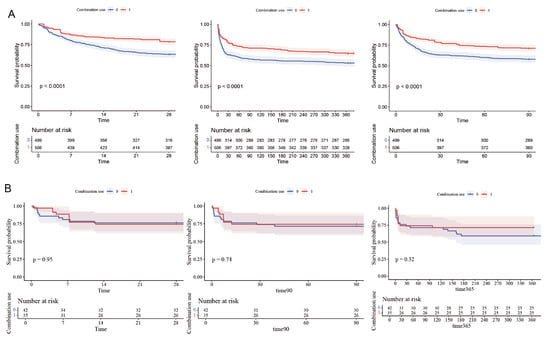
Figure 5.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for 28-day, 90-day and 1-year mortality in MAKI and SAKI groups. (A) MAKI group. (B) SAKI group.
The results of the multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis, as presented in Table 2, indicated that patients in the mild AKI (MAKI) group had a significantly reduced 28-day mortality rate (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.46–0.76, p < 0.001). Consistent findings were observed in the Cox regression models for secondary outcomes in the MAKI group. In contrast, for patients with severe AKI (SAKI), no significant differences in the impact of the two treatment regimens on primary and secondary mortality outcomes were observed. These findings align with the results depicted in the Kaplan–Meier (KM) curves. This suggests that for IS patients with more severe stages of AKI, the combined use of antiplatelet drugs does not confer a survival benefit over the use of clopidogrel or ticagrelor alone.

Table 2.
Regression Analysis of Outcomes in Mild and Severe AKI Subgroups.
For patients with AKI complicated by IS, we conducted mediation analysis (Table S4) considering potential bleeding events influenced by antiplatelet therapy that might mediate clinical outcomes. Bootstrap testing revealed no significant indirect mediation effects of bleeding events across all primary and secondary outcomes (p = 0.570, p = 0.496, p = 0.305, p = 0.840).
Furthermore, in addition to the AKI-complicated IS cohort, we analyzed outcomes in IS patients without AKI. Propensity score matching-adjusted survival analysis (Figure S5) demonstrated that combination antiplatelet therapy significantly prolonged 28-day, 90-day, and 1-year survival durations (all p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
In the treatment of IS, combination antiplatelet therapy (P2Y12 receptor antagonists combined with aspirin) has been widely used. Previous trials such as CHANCE [8], POINT [7], and THALES [9] have demonstrated that combination antiplatelet therapy reduces the risk of new ischemic vascular events compared to monotherapy with antiplatelet drugs and can prevent myocardial infarction and ischemic events. However, the efficacy of combination antiplatelet therapy varies in certain populations; for instance, clopidogrel is less effective in patients carrying the CYP2C19 LOF alleles [10].
In this study, the clinical efficacy of antiplatelet combination therapy versus monotherapy in patients with IS who also experienced AKI was investigated. After propensity score matching and adjustment for confounding factors using multiple models, we determined that combination antiplatelet therapy significantly reduced the 28-day, 90-day, 1-year, and in-hospital mortality risks.
Baseline characteristics revealed a high prevalence of atherosclerotic disease and atrial fibrillation (>40%) as comorbid conditions among ischemic stroke patients with concurrent acute kidney injury. Both atherosclerosis severity and atrial fibrillation are established risk factors for cerebral infarction. Clinical evidence confirms that stroke patients with comorbid atrial fibrillation typically exhibit poorer clinical outcomes. Therefore, a separate analysis was conducted to evaluate the prognostic impact of antiplatelet regimens specifically in this high-risk subgroup. The results demonstrated that combination antiplatelet therapy significantly reduced mortality risk even when restricted to the atrial fibrillation cohort (p < 0.001).
However, subsequent subgroup analyses revealed that the severity of AKI may influence the clinical benefits of this therapeutic regimen. The Cox proportional hazards model revealed that in patients with mild renal impairment, combination antiplatelet therapy was associated with a significantly lower risk of mortality. Similarly, in ischemic stroke patients without renal impairment, this therapy was linked to better prognosis. But in severe renal impairment cases, no statistically significant difference was found between the two treatment regimens. The survival analyses for patients with mild and severe AKI, along with multivariable Cox proportional hazards analyses and Kaplan–Meier survival curves, corroborated the subgroup analysis results. That is, in stroke patients, combination antiplatelet therapy improved the prognosis of those with mild AKI compared to single antiplatelet drug use but offered no benefits for severe AKI patients.
Antiplatelet therapy has been shown to improve AKI in animal models and some clinical studies, indicating that platelets are an important target in the pathophysiology of AKI. Two mouse studies reported the protective effects of clopidogrel on AKI. Clopidogrel increases the total antioxidant capacity of the kidneys to eliminate renal tubular cell apoptosis and reduces renal NET formation to prevent kidney ischemia–reperfusion injury (I/R)-induced AKI [13,14]. Regarding the clinical effects of aspirin in AKI patients, there are conflicting results. Several studies have shown that the use of aspirin significantly reduces the risk of postoperative AKI. However, the POISE-2 trial results indicated that preoperative ASA administration did not reduce the risk of AKI in patients undergoing major non-cardiac surgery but was instead associated with an increased incidence of major bleeding [15]. This may be due to bleeding as an independent risk factor for AKI affecting the protective effect of aspirin on AKI [16,17].
In AKI patients, activated platelets contribute to the pathologic process of AKI by affecting renal hemodynamics and renal inflammation. Activated platelets release mediators that increase endothelial permeability, such as platelet-activating factor (PAF) [18] and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) [19]. Platelets promote thrombus formation and the release of coagulation mediators, further leading to the deterioration of renal microcirculation [20]. Moreover, platelets cause renal tubular epithelial cell injury by stimulating endothelial cells and recruiting and activating white blood cells during inflammatory responses [21], ultimately leading to renal functional impairment.
Based on the protective effects of antiplatelet therapy in IS and AKI patients, the benefits of combination antiplatelet therapy in patients with both conditions could be anticipated. However, in our study, the benefits of combination antiplatelet therapy did not surpass those of P2Y12 antagonist monotherapy. This may be attributed to the heterogeneity of platelet reactivity and the increased bleeding risk associated with combination antiplatelet drugs.
The severity of renal impairment was found to significantly influence clinical outcomes following antiplatelet therapy, potentially attributable to differential therapeutic responsiveness in severe renal impairment patients, which may contribute to elevated mortality risk.
We postulate that hemorrhagic events may act as a mediator between antiplatelet therapy and mortality in ischemic stroke patients with severe renal impairment, whereas in those with mild renal impairment, mortality reduction appears primarily driven by antithrombotic efficacy, with hemorrhagic complications demonstrating minimal mediating effects. Mediation analysis employing the Bootstrap method revealed no significant mediating role of hemorrhagic events in mortality risk across both primary and secondary endpoints in severe renal impairment stroke cohorts (p = 0.570, p = 0.496, p = 0.305, p = 0.840). These results suggest that the prognostic impact of renal impairment severity on antiplatelet therapy efficacy may be mediated through mechanisms independent of hemorrhagic complications.
In clinical practice, it is acknowledged that certain populations exhibit variability in the effectiveness of antiplatelet therapy, known as variable platelet reactivity (VPR) [22]. High on-treatment platelet reactivity (HPR) after antiplatelet therapy indicates a higher risk of thrombotic events [23], while low on-treatment platelet reactivity (LPR) corresponds to a higher risk of bleeding events [24].
Factors influencing the mechanism of action of antiplatelet drugs can lead to the heterogeneity of platelet reactivity.
Firstly, the severity of renal impairment correlates with abnormal metabolism of antiplatelet drugs, particularly in patients with advanced renal disease. In addition, in patients with severe renal impairment, alterations in platelet pharmacological targets occur, leading to diverse platelet reactions. Changes in renal function can affect drug pharmacokinetics, including both renally cleared and non-renally cleared drugs [25]. Numerous studies indicate that chronic kidney disease reduces renal drug excretion. Moreover, accumulated uremic toxins may affect the activity and/or expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters. Research in rodent models of renal failure shows that the mRNA and protein expression of many members of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) gene family, as well as the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) and solute carrier (SLC) gene families of drug transporters, is reduced. In uremic patients, the impaired excretion of renal toxins leads to the accumulation of substances that interfere with transcriptional activation. This results in down-regulation of gene expression mediated by pro-inflammatory cytokines and directly inhibits the activity of cytochrome P450 and drug transporters [26].
Aspirin irreversibly inhibits platelet cyclooxygenase (COX-1), reducing the production of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. Thienopyridine drugs such as clopidogrel and ticagrelor [27] act on the P2Y12 receptor to inhibit platelet aggregation, with irreversible and reversible binding to the P2Y12 receptor, respectively, blocking the activation of GPⅡb/Ⅲa by ADP. External and internal factors acting on these pharmacological targets lead to the VPR phenomenon. External factors include patient race [28], sex, age [29], drug interactions [30], disease severity [31], and comorbidities [32]. Internal factors include genes related to drug absorption and metabolism [33] and polymorphisms of platelet receptor genes [34]. Taking clopidogrel as an example, genetic loci involved in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics all affect platelet reactivity, including the ABCB1 gene related to drug absorption, the CYP2C19 gene for drug metabolism, and the platelet action targets P2Y12 and ITGB3 genes. As the genetic basis for aspirin’s variable platelet reactivity, genetic variations in COX-1-dependent and -independent platelet activation pathways have been proposed to explain the differences in aspirin reactivity among individuals [35]. Many studies have reported specific gene variations in COX-1, with Halushka reporting that two SNPs (A-842G and C50T) in a cohort of healthy individuals were in linkage disequilibrium, and individuals with the G/T haplotype showed greater inhibition of prostaglandin H formation and arachidonic acid-induced aggregation [36].
It is noteworthy that the presence and severity of renal impairment may also affect platelet reactivity, which may partly explain the different effects of combination antiplatelet therapy in patients with different degrees of renal injury in this study. In the case of renal impairment, the efficacy of clopidogrel and aspirin is affected, increasing mortality and the incidence of cardiovascular events [37].
Moreover, in cases of renal impairment, platelet activity and responsiveness to drugs are compromised, potentially increasing cardiovascular event and mortality rates [38]. Uremic patients show altered platelet activity and structure. During dialysis, blood–film contact in uremia causes PF4 and β-thromboglobulin release from platelets due to granule–membrane defects, activating platelets [39].
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have a higher prevalence of HPR [40], impaired P2Y12 inhibition [41], and reduced bioavailability of clopidogrel’s active metabolite [42]. Similarly, impaired aspirin reactivity has been observed in CKD patients [43]. A. Polzin et al. further demonstrated that the degree of renal impairment in CKD is associated with impaired antiplatelet effects of aspirin [44]. Possible reasons include the concentration of von Willebrand factor in platelets of CKD patients, the expression of activated glycoprotein IIb/IIIa, and the increase in platelet-derived microparticles46 [45].
Given the significant heterogeneity in P2Y12 receptor reactivity among individuals, optimization strategies for antiplatelet therapy combining P2Y12 receptor inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel) with aspirin have garnered considerable attention. Although combination antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel demonstrates consistent efficacy across diverse clinical settings, patients receiving this regimen continue to exhibit a high residual risk of ischemic events. To reduce the incidence of high platelet reactivity (HPR) during treatment, multiple approaches have been proposed, including the use of more potent P2Y12 receptor inhibitors. Studies have shown that compared to clopidogrel, ticagrelor administered as a loading dose followed by a standard maintenance dose is associated with a significant reduction in long-term ischemic events in patients with acute coronary syndrome [46]. Furthermore, low-dose ticagrelor regimens appear to offer superior safety and efficacy profiles while maintaining equivalent ischemic protection [47]. Notably, in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis, low-dose ticagrelor exerts a more pronounced platelet inhibitory effect compared to clopidogrel [48]. Additionally, precision antiplatelet therapy guided by CYP2C19 genotyping has enhanced antiplatelet treatment efficacy in clinical practice [49]. Patients carrying CYP2C19 LoF alleles exhibit reduced clopidogrel metabolism, which is associated with diminished platelet inhibition and an elevated risk of thrombotic events [50]. Clinical trials have demonstrated that ticagrelor provides greater anti-ischemic benefits in patients harboring CYP2C19 LoF alleles [51].
The CHANCE-2 trial results demonstrated that among Chinese patients with minor ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) carrying CYP2C19 LoF alleles, ticagrelor was associated with a modestly reduced risk of stroke at 90 days compared to clopidogrel. And ticagrelor was linked to a higher incidence of total bleeding events [52].
As a retrospective study, our results have some limitations. First, the possibility of selection bias cannot be overlooked. The patient population in this study comes from the MIMIC database, which records patients from intensive care units. The study group may not fully represent a broader patient population, which may limit the generalizability of the study results. Future studies should expand the scope to include patient populations from different sources. Second, although multiple measures were used to reduce the impact of confounding factors, the presence of unmeasured confounding variables may still affect the study conclusions. Third, as a retrospective study, it is not possible to determine the exact causal relationship between the differences in treatment regimens and mortality. Finally, due to the particularity of database data recording, there are some missing data, including new adverse events during hospitalization, such as hypersensitivity reactions, which limits the comprehensiveness of the clinical efficacy of different antiplatelet drug regimens in our study.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study demonstrates that combination antiplatelet therapy significantly reduces 28-day, 90-day, 1-year, and in-hospital mortality risks of IS patients with AKI, suggesting its potential benefits in improving both short- and long-term clinical outcomes. However, this does not apply to patients with severe AKI, indicating heterogeneous survival benefits of combination therapy across AKI severity. Clinical decision-making should incorporate AKI stage stratification to evaluate the applicability of combination antiplatelet therapy. Further research is needed to explore the impact of AKI staging on antiplatelet therapy in IS patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/diseases13050141/s1, Figure S1: Kaplan Meier survival curves of combination group and non-combination group in patients with atrial fibrillation; Figure S2: Subgroup forest map of 90-day mortality; Figure S3: Subgroup forest map of 1-year mortality; Figure S4: Subgroup forest map of in-hospital mortality.; Figure S5: Kaplan Meier survival curves of combination group and non-combination group in patients without acute kidney injury. Table S1: The respective factors of variance inflation for the variables studied; Table S2: Patient demographics and baseline characteristics; Table S3: Multi-model regression analysis of secondary outcomes; Table S4: Mediating effect analysis of Bleeding in MAKI combined with IS patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z. and H.X.; methodology, Q.Z. and S.L.; software, Q.Z. and S.L.; validation, Q.Z., W.W. and X.L.; formal analysis, Q.Z.; investigation, Q.Z.; resources, Q.Z.; data curation, Q.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, W.W., X.L; visualization, Q.Z.; supervision, W.W. and X.L.; project administration, W.W. and X.L.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project has received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (number: 82001421).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Accountability Act (HIPAA) Safe Harbor provision, no additional IRB approval or ethical review was required for this secondary analysis. The MIMIC database access protocol adheres to ethical guidelines, and our usage complies with the database’s data use agreement.
Informed Consent Statement
This research involves the analysis of publicly available databases. Consequently, this manuscript does not require ethical approval and informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
All data analyzed in this study can be obtained through the MIMIC database.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all members who contributed to this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IS | Ischemic stroke |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| SMD | Standardized Mean Difference |
| LOS | Length of Stay |
| VIF | variance inflation factor |
| BG | Blood glucose |
| UV | Urine volume |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| LODS | Logistic Organ Dysfunction System |
| OASIS | Oxford Acute Severity of Illness Score |
| APS III | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation III |
| SAPS II | Simplified Acute Physiology Score II |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| CLD | Chronic Lung Disease |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| MV | Mechanical Ventilation |
| CRRT | Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy |
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2014, 383, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Ng, K.P.; Sims, D.; Gill, P.; Cockwell, P.; Ferro, C. Incidence and impact on outcomes of acute kidney injury after a stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, M.; Himmelfarb, J.; Adams, D.; Becker, K.; Longstreth, W.T.; Tirschwell, D.L. Acute kidney injury is associated with increased hospital mortality after stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2014, 23, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Aslam, H.; Zafar, W.; Huang, W.M.; Lobanova, I.; Naqvi, S.H.; Malhotra, K.; Arora, N.; Chandrasekaran, P.N.; Siddiq, F.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients in Clinical Trials. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, S.; Emanuelsson, H.; Heptinstall, S.; Sandset, P.M.; Wickens, M.; Peters, G. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and safety of the oral reversible P2Y12 antagonist AZD6140 with aspirin in patients with atherosclerosis: A double-blind comparison to clopidogrel with aspirin. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Johnston, S.C.; Liu, L.; Meng, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; et al. Clopidogrel with aspirin in acute minor stroke or transient ischemic attack. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkos, S.K.; Tsolakis, I.A. Clopidogrel with Aspirin in Minor Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.C.; Amarenco, P.; Denison, H.; Evans, S.R.; Himmelmann, A.; James, S.; Knutsson, M.; Ladenvall, P.; Molina, C.A.; Wang, Y. Ticagrelor and Aspirin or Aspirin Alone in Acute Ischemic Stroke or TIA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, C.M.; Murray, S.S.; Teirstein, P.S.; Kandzari, D.E.; Topol, E.J.; Price, M.J. Pilot Study of the Antiplatelet Effect of Increased Clopidogrel Maintenance Dosing and Its Relationship to CYP2C19 Genotype in Patients With High On-Treatment Reactivity. JACC-Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Xu, E.; Ge, R.; Hu, M.; Jin, S.; Mu, J.; Liu, Y. Aspirin alleviates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through the AMPK-PGC-1α signaling pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 380, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.H.; Xu, Q.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Ling, Y.; Fu, C. Ticagrelor Protects against Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury through an Adenosine Receptor-Dependent Pathway. Curr. Med. Sci. 2022, 42, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Batteux, F.; Chéreau, C.; Kavian, N.; Marut, W.; Gobeaux, C.; Borderie, D.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Weill, B.; Nicco, C. Clopidogrel protects from cell apoptosis and oxidative damage in a mouse model of renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J. Pathol. 2011, 225, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.P.; Emal, D.; Teske, G.J.; Dessing, M.C.; Florquin, S.; Roelofs, J.J. Release of extracellular DNA influences renal ischemia reperfusion injury by platelet activation and formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.X.; Kurz, A.; Sessler, D.I.; Cuerden, M.; Robinson, A.; Mrkobrada, M.; Parikh, C.R.; Mizera, R.; Jones, P.M.; Tiboni, M.; et al. Perioperative aspirin and clonidine and risk of acute kidney injury: A randomized clinical trial. Jama 2014, 312, 2254–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karrowni, W.; Vora, A.N.; Dai, D.; Wojdyla, D.; Dakik, H.; Rao, S.V. Blood Transfusion and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury Among Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, e003279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkouti, K. Transfusion and risk of acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109 (Suppl. 1), i29–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, I.I.; Predescu, S.A.; Neamu, R.F.; Gorovoy, M.S.; Knezevic, N.M.; Easington, C.; Malik, A.B.; Predescu, D.N. Tiam1 and Rac1 are required for platelet-activating factor-induced endothelial junctional disassembly and increase in vascular permeability. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5381–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, N.; Paré, A.; Farndale, R.W.; Schumacher, H.R.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Lacroix, S.; Boilard, E. Platelets can enhance vascular permeability. Blood 2012, 120, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenberg, E.C.; Meijers, J.C.; Levi, M. Platelet-vessel wall interaction in health and disease. Neth. J. Med. 2010, 68, 242–251. [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Yang, L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, J.P.; Drouet, L. The individual variability of response to antiplatelet therapy must be taken into account. Sang. Thromb. Vaisseaux. 2009, 21, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Würtz, M.; Grove, E.L. Interindividual Variability in the Efficacy of Oral Antiplatelet Drugs: Definitions, Mechanisms and Clinical Importance. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 5344–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello, L.; Tantry, U.S.; Marcucci, R.; Blindt, R.; Angiolillo, D.J.; Becker, R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Cattaneo, M.; Collet, J.P.; Cuisset, T.; et al. Consensus and future directions on the definition of high on-treatment platelet reactivity to adenosine diphosphate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudeva, K.; Chaurasia, P.; Singh, S.; Munshi, A. Genetic Signatures in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Aspirin Resistance. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, P.; Labouret, C.; Delesque, N.; Guette, F.; Lupker, J.; Herbert, J.M. P2Y12, a new platelet ADP receptor, target of clopidogrel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, S.; van Giezen, J.J.J. Ticagrelor: The First Reversibly Binding Oral P2Y12 Receptor Antagonist. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2009, 27, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, L.O.; Giordano, S.; Franchi, F.; Rollini, F.; Been, L.; Al Saleh, T.; Uzunoglu, E.C.; Maldonado, A.M.P.; Suryadevara, S.; Soffer, D.; et al. Impact of race on platelet reactivity profiles in patients on clopidogrel treatment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, G.J.A.; Janssen, P.W.; Bergmeijer, T.O.; Jhagroe, D.; Godschalk, T.C.; Gimbel, M.E.; Willemsen, L.M.; Hackeng, C.M.; Ten Berg, J.M. Platelet reactivity is gender and age related. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1159. [Google Scholar]
- Pelliccia, F.; Rollini, F.; Marazzi, G.; Greco, C.; Gaudio, C.; Angiolillo, D.J. Drug-drug interactions between clopidogrel and novel cardiovascular drugs. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 765, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobs, K.; Reinshagen, L.; Puccini, M.; Friebel, J.; Wilde, A.-C.B.; Alsheik, A.; Rroku, A.; Landmesser, U.; Haghikia, A.; Kränkel, N.; et al. Disease Severity in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Is Associated With Platelet Hyperreactivity and Innate Immune Activation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 844701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiadi, B.M.; Hartono, B.; Prakoso, A.B.; Lubis, A.C.; Munandar, R.M.; Munawar, M. Antiplatelet for Coronary Artery Disease in Specific Condition “No Size Fits All”. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, P.L.; Becker, R.C. Pharmacogenetics of Antiplatelet Therapy. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veninga, A.; Handtke, S.; Aurich, K.; Tullemans, B.M.E.; Brouns, S.L.N.; Schwarz, S.L.; Heubel-Moenen, F.C.J.I.; Greinacher, A.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; van der Meijden, P.E.J.; et al. GPVI expression is linked to platelet size, age, and reactivity. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4162–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrör, K. Aspirin and platelets: The antiplatelet action of aspirin and its role in thrombosis treatment and prophylaxis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1997, 23, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halushka, M.K.; Walker, L.P.; Halushka, P.V. Genetic variation in cyclooxygenase 1: Effects on response to aspirin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, W.; Park, C.S.; Kang, W.Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, W. A comparison of clopidogrel responsiveness in patients with versus without chronic renal failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 104, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.S.N.R.; Zafar, H.; Fatima, S. Effects of lipid based Multiple Micronutrients Supplement on the birth outcome of underweight pre-eclamptic women: A randomized clinical trial. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yeung, C.K.; Shen, D.D.; Thummel, K.E.; Himmelfarb, J. Effects of chronic kidney disease and uremia on hepatic drug metabolism and transport. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, M.; Iwata, A.; Ozeki, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Akiba, T.; Nihei, H. Circulating platelet-derived microparticles with procoagulant activity may be a potential cause of thrombosis in uremic patients. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodanno, D.; Angiolillo, D.J. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease. Circulation 2012, 125, 2649–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, O.; Muller, C.; Jesel, L.; Moulin, B.; Hannedouche, T. Impaired platelet P2Y12 inhibition by thienopyridines in chronic kidney disease: Mechanisms, clinical relevance and pharmacological options. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2013, 28, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraday, N.; Yanek, L.R.; Mathias, R.; Herrera-Galeano, J.E.; Vaidya, D.; Moy, T.F.; Fallin, M.D.; Wilson, A.F.; Bray, P.F.; Becker, L.C.; et al. Heritability of platelet responsiveness to aspirin in activation pathways directly and indirectly related to cyclooxygenase-1. Circulation 2007, 115, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polzin, A.; Dannenberg, L.; Sansone, R.; Levkau, B.; Kelm, M.; Hohlfeld, T.; Zeus, T. Antiplatelet effects of aspirin in chronic kidney disease patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J. Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Drug Metabolism in Renal Failure. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamaa, M.F.; Elghoroury, E.A.; Helmy, A. Intradialytic and postdialytic platelet activation, increased platelet phosphatidylserine exposure and ultrastructural changes in platelets in children with chronic uremia. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis An. Int. J. Haemost. Thromb. 2009, 20, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollini, F.; Franchi, F. Standard- and Low-Dose Ticagrelor After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Finding the Balance for Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2018, 138, 1301–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, W.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, S.; Hao, G. Safety and feasibility of low-dose ticagrelor in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Woo, J.S.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, T.W.; Kim, K.S.; Ihm, C.G.; Kim, W.; Jeong, K.H. The pharmacodynamics of low and standard doses of ticagrelor in patients with end stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 238, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, N. Genotyping genetic variants of CYP2C19 for precision antiplatelet dosing: State of the art and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rouby, N.; Lima, J.J.; Johnson, J.A. Proton pump inhibitors: From CYP2C19 pharmacogenetics to precision medicine. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantry, U.S.; Singh, S.; Raghavakurup, L.N.; Bliden, K.P.; Gurbel, P.A. Can CYP2C19 genotyping improve antiplatelet therapy efficacy in real-life practice? Recent advances. Pol. Heart J. 2024, 82, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).