Surgical Treatment of Enchondromas of the Hand: Our Experience in Curettage Only and Early Mobilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.4. Post-Operative Care
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sassoon, A.A.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.D.; Harmsen, W.S.; Moran, S.L. Enchondromas of the Hand: Factors Affecting Recurrence, Healing, Motion, and Malignant Transformation. J. Hand Surg. 2012, 37, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milgram, J.W. The Origins of Osteochondromas and Enchondromas: A Histopathologic Study. Clin. Orthop. 1983, 174, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachoura, A.; Rice, I.S.; Lubahn, A.R.; Lubahn, J.D. The Surgical Management of Hand Enchondroma without Postcurettage Void Augmentation: Authors’ Experience and a Systematic Review. Hand 2015, 10, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figl, M.; Leixnering, M. Retrospective review of outcome after surgical treatment of enchondromas in the hand. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2009, 129, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey, M.D.; Flemming, D.J.; Boyea, S.R.; Bojescul, J.A.; Sweet, D.E.; Temple, H.T. Enchondroma versus chondrosarcoma in the appendicular skeleton: Differentiating features. Radiographics 1998, 18, 1213–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Chan, M.; Fok, M.; Fung, B. Current management of hand enchondroma: A review. Hand Surg. 2015, 20, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulke, R. The Distribution of Solitary Enchondromata at the Hand. J. Hand Surg. 2002, 27, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riester, S.; Ramaesch, R.; Wenger, D.; Van Wijnen, A.; Kakar, S. Predicting Fracture Risk for Enchondroma of the Hand. Hand 2016, 11, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, H.; Herget, G.W.; Füllgraf, H.; Sutter, R.; Benndorf, M.; Bamberg, F.; Jungmann, P.M. Chondrogenic Bone Tumors: The Importance of Imaging Characteristics. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der bildgebenden Verfahren; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart-Feuerbach, Germany, 2021; Volume 193, pp. 262–275. [Google Scholar]
- Vanel, D.; Kreshak, J.; Larousserie, F.; Alberghini, M.; Mirra, J.; De Paolis, M.; Picci, P. Enchondroma Vs. Chondrosarcoma: A Simple, Easy-To-Use, New Magnetic Resonance Sign. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeys, L.M.; Thorkildsen, J.; Kurisunkal, V.; Puri, A.; Ruggieri, P.; Houdek, M.T.; Boyle, R.A.; Ebeid, W.; Botello, E.; Morris, G.V.; et al. Controversies in orthopaedic oncology. Bone Jt. J. 2024, 106, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, C.; Man, K.; Prashanth, N.; Kubba, F.; Shaerf, D. Case Report of a Distal Phalanx Interosseous Epidermoid Inclusion Cyst Presenting as an Enchondroma. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2022, 12, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini-Araujo, E.; Kalil, R.K.; Bertoni, F.; Park, Y.K. (Eds.) Tumors and TumorLike Lesions of Bone: For Surgical Pathologists, Orthopedic Surgeons and Radiologists; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Bickels, J.; Wittig, J.C.; Kollender, Y.; Kellar-Graney, K.; Mansour, K.L.; Meller, I.; Malawer, M.M. Enchondromas of the hand: Treatment with curettage and cemented internal fixation. J. Hand Surg. 2002, 2, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, P.E.; Durr, H.R.; Wegener, B.; Pellengahr, C.; Maier, M.; Jansson, V. Solitary enchondromas: Is radiographic follow-up sufficient in patients with asymptomatic lesions? Acta Orthop. Belg. 2003, 69, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselgren, G.; Forssblad, P.; Törnvall, A. Bone grafting unnecessary in the treatment of enchondromas in the hand. J. Hand Surg. 1991, 16, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tordai, P.; Hoglund, M.; Lugnegård, H. Is the Treatment of Enchondroma in the Hand by Simple Curettage a Rewarding Method? J. Hand Surg. 1990, 15, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuur, E.; Hansen, S.L.; Lindequist, S. Treatment of solitary enchondromas in fingers. J. Hand Surg. 1989, 14, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, F.; Fanfani, F.; Taccardo, G. Lésions tumorales et pseudo-tumoralescartilagineuses des parties molles de la main [Tumorous and pseudotumorous cartilaginous lesions of the soft tissues of the hand]. Ann. Chir. Main 1988, 7, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollaci, C.; Araújo, G.C.S. Enchondromas of the hand: A 20-year experience. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2019, 54, 714–720. [Google Scholar]
- Myeroff, C.; Archdeacon, M. Autogenous bone graft: Donor sites and techniques. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2011, 93, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Onga, T.; Marui, T.; Mizuno, K. Use of hydroxyapatite to fill cavities after excision of benign bone tumours. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2000, 82B, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, N.K. Curettage and calcium phosphate bone cement injection for the treatment of enchondroma of the finger. Hand Surg. 2012, 17, 6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morii, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Tajima, T.; Satomi, K. Treatment outcome of enchondroma by simple curettage without augmentation. J. Orthop. Sci. 2010, 15, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, P.; Baer, W. Operative treatment of enchondromas of the hand: Is cancellous bone grafting necessary? Scand. J. PlastReconstr. Surg. Hand Surg. 2009, 43, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablove, R.H.; Moy, O.J.; Peimer, C.A.; Wheeler, D.R. Early versus delayed treatment of enchondroma. Am. J. Orthop. 2000, 29, 771–772. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, R.D.; Lewis, M.M.; Posner, M.A. Treatment of enchondromas of the hand with allograft bone. J. Hand Surg. 1988, 13, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
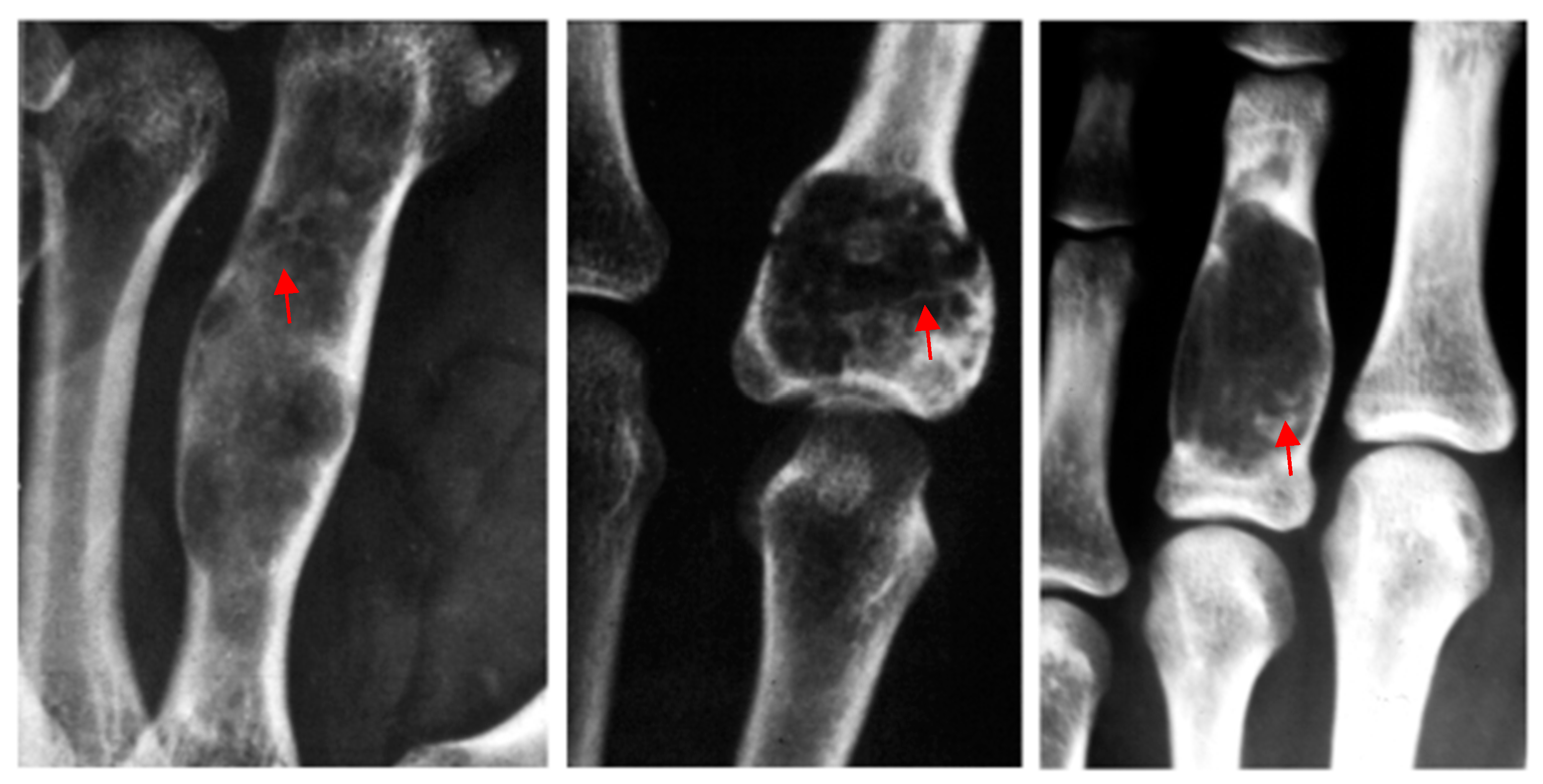


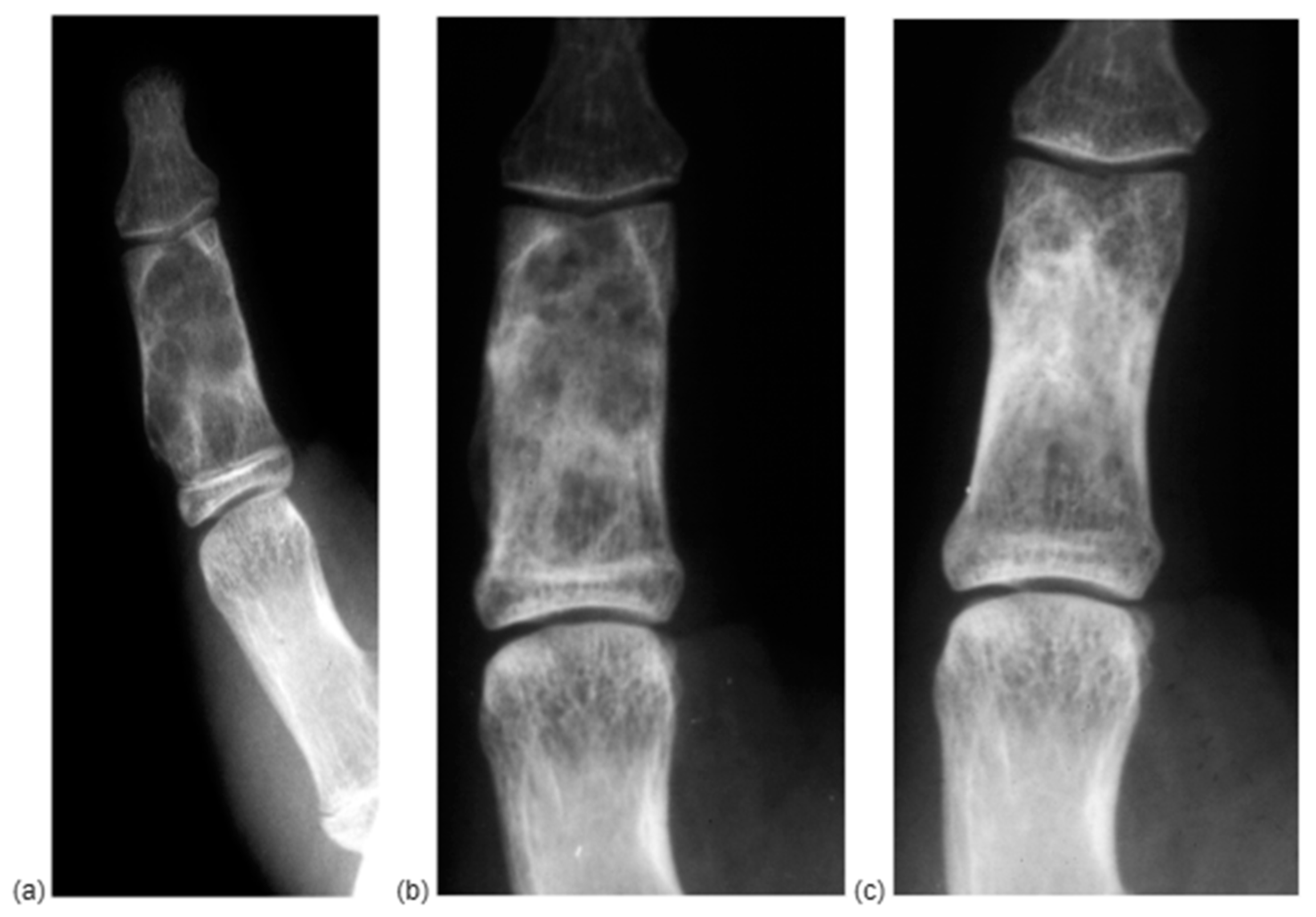
| ID | Gender | Age | Location | Symptoms | Imaging | Fracture | Immobilization | FUP | RTW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 27 | P1D4 | Pain/deformity | X-RAY | yes | no | 12 | 30 |
| 2 | F | 32 | P2D4 | Pain | X-RAY | no | no | 12 | 20 |
| 3 | F | 51 | P2D2 | Pain/deformity | X-RAY/MRI | no | no | 12 | 20 |
| 4 | M | 67 | 5MC | Pain, stiffness | X-RAY/CT | yes | no | 12 | / |
| 5 | M | 25 | PF1D2 | Stiff PIP flexion | X-RAY | no | no | 20 | 20 |
| 6 | F | 72 | PF1D4 | Stiff PIP | X-RAY | yes | no | 22 | / |
| 7 | F | 56 | 3MC | No | X-RAY | no | no | 36 | 20 |
| 8 | M | 34 | 4MC | No | X-RAY | yes | no | 36 | 40 |
| 9 | F | 60 | P2D2 | No | X-RAY | no | yes | 38 | 20 |
| 10 | F | 49 | P1D4 | No | X-RAY | yes | no | 40 | 20 |
| 11 | F | 10 | P2D2 | Swelling | X-RAY | no | no | 24 | / |
| 12 | M | 87 | P1D2 | Swelling | X-RAY/CT | yes | no | 30 | / |
| 13 | F | 45 | P2D3 | No | X-RAY | no | no | 25 | 20 |
| 14 | F | 48 | 3MC | Swelling | X-RAY | yes | no | 30 | 25 |
| 15 | F | 26 | P1D5 | No | X-RAY | no | no | 12 | 20 |
| 16 | M | 45 | P1D4 | Pain/deformity | X-RAY | no | no | 18 | 23 |
| 17 | M | 56 | P2D4 | Pain, stiffness | X-RAY | yes | no | 22 | 15 |
| 18 | F | 28 | P2D2 | Stiff PIP flexion | X-RAY | yes | no | 31 | 30 |
| 19 | F | 42 | 5MC | No | X-RAY | no | no | 36 | 20 |
| 20 | F | 54 | P1D4 | No | X-RAY/CT | yes | no | 40 | 18 |
| 21 | M | 61 | P2D4 | Swelling | X-RAY | yes | no | 12 | 15 |
| 22 | M | 19 | P1D2 | Swelling | X-RAY | yes | no | 24 | / |
| 23 | M | 23 | P2D3 | No | X-RAY/CT | yes | no | 28 | 20 |
| 24 | F | 21 | P1D2 | Swelling | X-RAY | no | no | 24 | 25 |
| 25 | M | 42 | P1D5 | No | X-RAY | no | no | 24 | 20 |
| 26 | F | 27 | P1D4 | Pain/deformity | X-RAY | yes | no | 12 | 30 |
| 27 | F | 32 | P2D4 | Pain | X-RAY | no | no | 12 | 20 |
| 28 | F | 51 | P2D2 | Pain/deformity | X-RAY/MRI | no | no | 12 | 20 |
| 29 | M | 67 | 5MC | Pain, stiffness | X-RAY/CT | yes | no | 12 | / |
| 30 | M | 25 | PF1D2 | Stiff PIP flexion | X-RAY | no | no | 20 | 20 |
| 31 | F | 72 | PF1D4 | Stiff PIP | X-RAY | yes | no | 22 | / |
| 32 | F | 56 | 3MC | No | X-RAY | no | no | 36 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pietramala, S.; Rovere, G.; Ravaioli, C.; Mignano, C.; Smakaj, A.; Fidanza, A.; Farsetti, P.; Rocchi, L.; Fulchignoni, C. Surgical Treatment of Enchondromas of the Hand: Our Experience in Curettage Only and Early Mobilization. Diseases 2025, 13, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13030084
Pietramala S, Rovere G, Ravaioli C, Mignano C, Smakaj A, Fidanza A, Farsetti P, Rocchi L, Fulchignoni C. Surgical Treatment of Enchondromas of the Hand: Our Experience in Curettage Only and Early Mobilization. Diseases. 2025; 13(3):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13030084
Chicago/Turabian StylePietramala, Silvia, Giuseppe Rovere, Camilla Ravaioli, Ciro Mignano, Amarildo Smakaj, Andrea Fidanza, Pasquale Farsetti, Lorenzo Rocchi, and Camillo Fulchignoni. 2025. "Surgical Treatment of Enchondromas of the Hand: Our Experience in Curettage Only and Early Mobilization" Diseases 13, no. 3: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13030084
APA StylePietramala, S., Rovere, G., Ravaioli, C., Mignano, C., Smakaj, A., Fidanza, A., Farsetti, P., Rocchi, L., & Fulchignoni, C. (2025). Surgical Treatment of Enchondromas of the Hand: Our Experience in Curettage Only and Early Mobilization. Diseases, 13(3), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13030084







