Impact of Red Pack Cell Transfusion Before or After Endoscopy on Mortality in Patients with Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Factors Affecting Mortality
3.3. Timing to Transfusion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UGIB | Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding |
| RBC | Red Blood Cell |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| PSM | Propensity Score Matching |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| ESGE | European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy |
| ACG | American College of Gastroenterology |
| ASGE | American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy |
| NICE | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence |
| BSG | British Society of Gastroenterology |
| ATE | Average Treatment Effect |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| GBS | Glasgow–Blatchford Score |
| AIMS65 | Albumin, INR, Mental Status, Systolic BP < 90 mmHg, Age > 65 |
| ABC | Age, Blood tests, Comorbidities |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Laine, L.; Barkun, A.N.; Saltzman, J.R.; Martel, M.; Leontiadis, G.I. ACG Clinical Guideline: Upper Gastrointestinal and Ulcer Bleeding. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gralnek, I.M.; Stanley, A.J.; Morris, A.J.; Camus, M.; Lau, J.; Lanas, A.; Laursen, S.B.; Radaelli, F.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Cúrdia Gonça, T.; et al. Endoscopic diagnosis and management of nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage (NVUGIH): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline—Update 2021. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 300–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.Y.W.; Yu, Y.; Tang, R.S.Y.; Chan, H.C.; Yip, H.C.; Chan, S.M.; Luk, S.W.; Wong, S.H.; Lau, L.H.; Lui, R.N.; et al. Timing of Endoscopy for Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Koo, Y.K.; Kim, S.; Chung, H.S.; Park, I.; Kwon, S.S.; Myung, J. Association of time to red blood cell transfusion with outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal bleeding. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Lui, R.N.S.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Tang, R.S.Y.; Yip, T.C.F.; Wu, W.K.K.; Wong, G.L.H.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Timing of endoscopy for acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Gut 2022, 71, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, C.; Colomo, A.; Bosch, A.; Concepción, M.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Aracil, C.; Graupera, I.; Poca, M.; Alvarez-Urturi, C.; Gordillo, J.; et al. Transfusion strategies for acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 11–21, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jairath, V.; Kahan, B.C.; Gray, A.; Doré, C.J.; Mora, A.; James, M.W.; Stanley, A.J.; Everett, S.M.; Bailey, A.A.; Dallal, H.; et al. Restrictive versus liberal blood transfusion for acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding (TRIGGER): A pragmatic, open-label, cluster randomised feasibility trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadeer, M.A.; Lopez, A.R.; Dumot, J.A.; Vargo, J.J. Hypoxemia during Moderate Sedation for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Causes and Associations. Digestion 2011, 84, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Welte, M.; Welte, C.; Albert, J.; Meckbach, Y.; Herrmann, E.; Kannengiesser, M.; Trojan, J.; Filmann, N.; Schroeter, H.; et al. Capnographic monitoring during colonoscopy. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.; Kaeley, N.; Prasad, H.; Patnaik, I.; Bahurupi, Y.; Joshi, S.; Shukla, K.; Galagali, S.; Patel, S. Prospective observational study on clinical and epidemiological profile of adult patients presenting to the emergency department with suspected upper gastrointestinal bleed. BMC Emerg Med. 2023, 23, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daabiss, M. ASA physical status classification. Indian. J. Anaesth. 2011, 55, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltzman, J.R.; Tabak, Y.P.; Hyett, B.H.; Sun, X.; Travis, A.C.; Johannes, R.S. A simple risk score accurately predicts in-hospital mortality, length of stay, and cost in acute upper GI bleeding. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatchford, O.; Murray, W.R.; Blatchford, M. A risk score to predict need for treatment for upper-gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Lancet 2000, 356, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, S.B.; Oakland, K.; Laine, L.; Bieber, V.; Marmo, R.; Redondo-Cerezo, E.; Dalton, H.R.; Ngu, J.; Schultz, M.; Soncini, M.; et al. ABC score: A new risk score that accurately predicts mortality in acute upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding: An international multicentre study. Gut 2021, 70, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C.; Abraldes, J.G.; Albillos, A.; Baiges, A.; Bajaj, J.; Bañares, R.; et al. Baveno VII Faculty. Baveno VII-Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutsch, B.; Veres, D.S.; Pálinkás, D.; Simon, O.A.; Hegyi, P.; Erőss, B. Potential benefits of restrictive transfusion in upper gastrointestinal bleeding: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Siau, K.; Hearnshaw, S.; Stanley, A.J.; Estcourt, L.; Rasheed, A.; Walden, A.; Thoufeeq, M.; Donnelly, M.; Drummond, R.; Veitch, A.M.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology-led multisociety consensus care bundle for the early clinical management of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.J.; Chiu, P.W.; Chan, F.K.L.; Lau, J.Y.; Goh, K.-L.; Ho, L.H.; Jung, H.-Y.; Sollano, J.D.; Gotoda, T.; Reddy, N.; et al. Asia-Pacific working group consensus on non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding: An update 2018. Gut 2018, 67, 1757–1768, Erratum in Gut 2019, 68, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmo, R.; Soncini, M.; de Franchis, R. GISED–Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio dell’Emorragia Digestiva Patient’s performance status should dictate transfusion strategy in nonvariceal acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding (NV-AUGIB): Aprospective multicentre cohort study: Transfusion strategy in, N.V.-A.U.G.I.B. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | After Endoscopy (N = 1317) | Before Endoscopy (N = 700) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years mean (SD) | 69.1 (±15.1) | 70.8 (±14.6) | 0.015 |
| Male | 900 (68.3%) | 467 (66.7%) | 0.46 |
| Inpatients’ bleeding | 229 (17.4%) | 147 (21.0%) | 0.048 |
| ASA Score 1 | 324 (24.6%) | 122 (17.4%) | <0.001 |
| ASA Score 2 | 460 (34.9%) | 222 (31.7%) | – |
| ASA Score 3 | 450 (34.2%) | 285 (40.7%) | – |
| ASA Score 4 | 83 (6.3%) | 71 (10.1%) | – |
| Chronic Renal Failure | 173 (13.1%) | 132 (18.9%) | <0.001 |
| Stroke | 40 (3.0%) | 27 (3.9%) | 0.33 |
| Cerebrovascular Disease | 120 (9.1%) | 80 (11.4%) | 0.097 |
| Chronic ischemic heart disease | 281 (21.3%) | 175 (25.0%) | 0.056 |
| Chronic Pulmonary Disease | 151 (11.5%) | 99 (14.1%) | 0.082 |
| Neoplasia | 221 (16.8%) | 131 (18.7%) | 0.28 |
| Cirrhosis | 309 (23.5%) | 130 (18.6%) | 0.010 |
| ABC score, mean (SD) | 5.1 (2.5) | 5.2 (2.4) | 0.17 |
| AIMS65 score, mean (SD) | 1.6 (1.0) | 1.9 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| Hematemesis | 576 (43.7%) | 273 (39.0%) | 0.040 |
| Melena | 869 (66.0%) | 514 (73.4%) | <0.001 |
| Pulse rate, mean (SD) | 90.0 (16.5) | 91.9 (17.9) | 0.022 |
| Blood pressure, mean (SD) | 114.5 (22.5) | 110.7 (22.9) | <0.001 |
| Shock index | 109 (8.3%) | 89 (12.7%) | 0.002 |
| Variable | After Endoscopy | Before Endoscopy | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin at admission (g/dL), mean (SD) | 8.3 (1.9) | 7.3 (1.9) | <0.001 |
| <7 g/dL | 322 (24.5%) | 313 (44.7%) | <0.001 |
| 7–8 g/dL | 301 (22.9%) | 182 (26.0%) | – |
| 8–10 g/dL | 474 (36.1%) | 157 (22.4%) | – |
| >10 g/dL | 217 (16.5%) | 48 (6.9%) | – |
| Creatinine, mean (SD) | 1.4 (1.2) | 1.5 (1.3) | 0.024 |
| INR, mean (SD) | 1.4 (0.9) | 1.6 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| Albumin, mean (SD) | 3.1 (0.7) | 3.1 (0.7) | 0.14 |
| Bilirubin, mean (SD) | 1.5 (4.7) | 1.3 (2.7) | 0.21 |
| BUN, mean (SD) | 136.4 (260.9) | 98.1 (148.7) | 0.018 |
| Variable | After Endoscopy | Before Endoscopy | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 h | 905 (68.7%) | 383 (54.7%) | <0.001 |
| 6–12 h | 196 (14.9%) | 133 (19.0%) | |
| 12–24 h | 146 (11.1%) | 133 (19.0%) | |
| >24 h | 70 (5.3%) | 52 (7.4%) | |
| Normal working hours | 662 (50.3%) | 383 (54.7%) | 0.16 |
| Night shift | 225 (17.1%) | 105 (15.0%) | |
| On-call shift | 428 (32.5%) | 211 (30.2%) | |
| Weekdays | 998 (75.8%) | 519 (74.1%) | 0.063 |
| Weekend | 125 (9.5%) | 89 (12.7%) | |
| Preholiday | 196 (14.9%) | 92 (13.1%) | |
| Non-variceal bleeding | 1051 (79.8%) | 582 (83.1%) | 0.069 |
| Variceal bleeding | 266 (20.2%) | 118 (16.9%) | |
| Transfusions, mean (SD) | 2.8 (1.9) | 3.6 (2.8) | <0.001 |
| No endoscopic therapy | 425 (32.3%) | 259 (37.0%) | 0.056 |
| Therapy in non-variceal | 626 (47.5%) | 323 (46.1%) | |
| Therapy in variceal | 266 (20.2%) | 118 (16.9%) |
| Variable | After Endoscopy | Before Endoscopy | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of stay, days (mean ± SD) | 11.3 (±10.1) | 11.1 (±9.2) | 0.59 |
| Rebleeding | 121 (9.2%) | 69 (9.9%) | 0.62 |
| Interventional radiology | 17 (1.3%) | 16 (2.3%) | 0.094 |
| Surgery | 54 (4.1%) | 38 (5.4%) | 0.17 |
| Overall mortality | 109 (8.3%) | 69 (9.9%) | 0.23 |
| Factor | Odds Ratio | Std. Err. | z | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASA Score 1 (Ref) | – | – | – | – | – |
| ASA Score 2 | 3.07 | 1.39 | 2.47 | 0.013 | 1.26 |
| ASA Score 3 | 3.82 | 1.72 | 2.98 | 0.003 | 1.58 |
| ASA Score 4 | 14.48 | 6.86 | 5.64 | 0.000 | 5.72 |
| Hemodynamic shock | 1.26 | 0.35 | 0.82 | 0.413 | 0.73 |
| Timing 0–6 h (Ref) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Timing 6–12 h | 0.77 | 0.21 | 0.94 | 0.346 | 0.45 |
| Timing 12–24 h | 0.86 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.604 | 0.48 |
| Timing > 24 h | 1.04 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.911 | 0.50 |
| In-hospital bleeding | 2.34 | 0.49 | 4.10 | 0.000 | 1.56 |
| Chronic renal failure | 1.44 | 0.33 | 1.60 | 0.109 | 0.92 |
| Neoplasia | 1.88 | 0.38 | 3.14 | 0.002 | 1.27 |
| Cirrhosis | 1.31 | 0.28 | 1.25 | 0.213 | 0.86 |
| Hematemesis | 1.92 | 0.40 | 3.14 | 0.002 | 1.28 |
| Transfusion number | 1.11 | 0.03 | 3.62 | 0.000 | 1.05 |
| Admission Hb < 7 g/dL (Ref) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hb 7–8 g/dL | 1.18 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0.511 | 0.73 |
| Hb 8–10 g/dL | 1.02 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.922 | 0.64 |
| Hb > 10 g/dL | 0.84 | 0.27 | 0.55 | 0.586 | 0.45 |
| Transfusion Before vs. After | 0.94 | 0.18 | 0.33 | 0.742 | 0.64 |
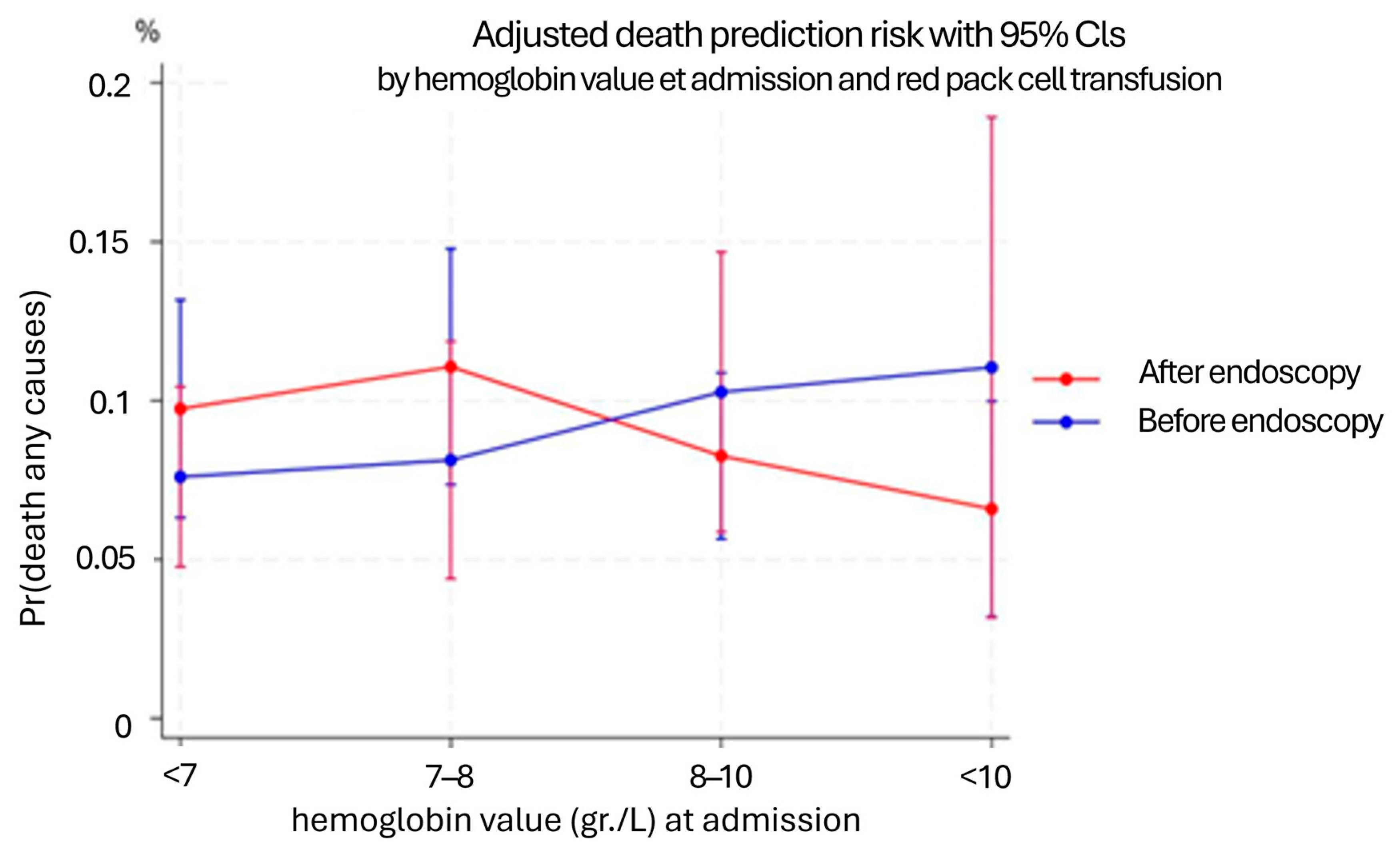
| Group | Odds Ratio | Std. Err. | z | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <7 g/dL—Before | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.96 | 0.338 | 0.38 |
| 7–8 g/dL—After | 1.18 | 0.38 | 0.51 | 0.610 | 0.62 |
| 7–8 g/dL—Before | 0.79 | 0.30 | 0.62 | 0.538 | 0.38 |
| 8–10 g/dL—After | 0.81 | 0.25 | 0.68 | 0.497 | 0.44 |
| 8–10 g/dL—Before | 1.07 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.853 | 0.52 |
| >10 g/dL—After | 0.61 | 0.24 | 1.23 | 0.219 | 0.28 |
| >10 g/dL—Before | 1.18 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 0.760 | 0.41 |
| Hb Admission (g/dL) | Coefficient | Std. Err. | z | p > |z| | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤7 g/dL | −0.06 | 0.03 | −1.86 | 0.063 | −0.11 to 0.00 |
| 7–8 g/dL | −0.03 | 0.04 | −0.95 | 0.342 | −0.10 to 0.04 |
| 8–10 g/dL | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.605 | −0.05 to 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marmo, C.; Bucci, C.; Soncini, M.; Riccioni, M.E.; Marmo, R., on behalf of the GISED Study Group. Impact of Red Pack Cell Transfusion Before or After Endoscopy on Mortality in Patients with Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Diseases 2025, 13, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100329
Marmo C, Bucci C, Soncini M, Riccioni ME, Marmo R on behalf of the GISED Study Group. Impact of Red Pack Cell Transfusion Before or After Endoscopy on Mortality in Patients with Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Diseases. 2025; 13(10):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100329
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarmo, Clelia, Cristina Bucci, Marco Soncini, Maria Elena Riccioni, and Riccardo Marmo on behalf of the GISED Study Group. 2025. "Impact of Red Pack Cell Transfusion Before or After Endoscopy on Mortality in Patients with Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Multicenter Cohort Study" Diseases 13, no. 10: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100329
APA StyleMarmo, C., Bucci, C., Soncini, M., Riccioni, M. E., & Marmo, R., on behalf of the GISED Study Group. (2025). Impact of Red Pack Cell Transfusion Before or After Endoscopy on Mortality in Patients with Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Diseases, 13(10), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100329





