Efficacy and Safety of Different Treatments for Melasma: Network Meta-Analysis of Updated Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment of the Included Studies
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Data Synthesis
2.5. Inconsistencies and Sensitivity
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included RCTs
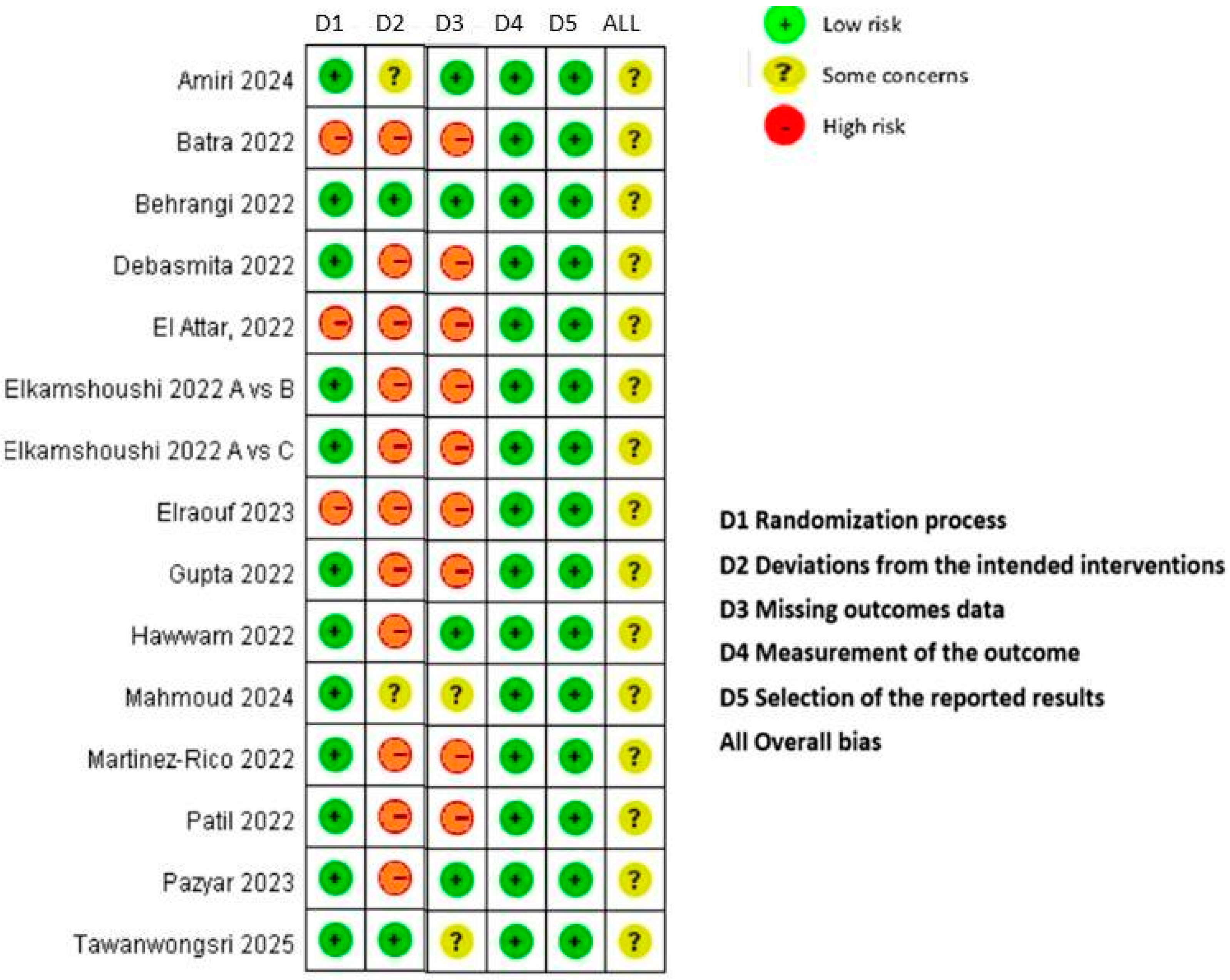
3.2. Quality of Included Studies
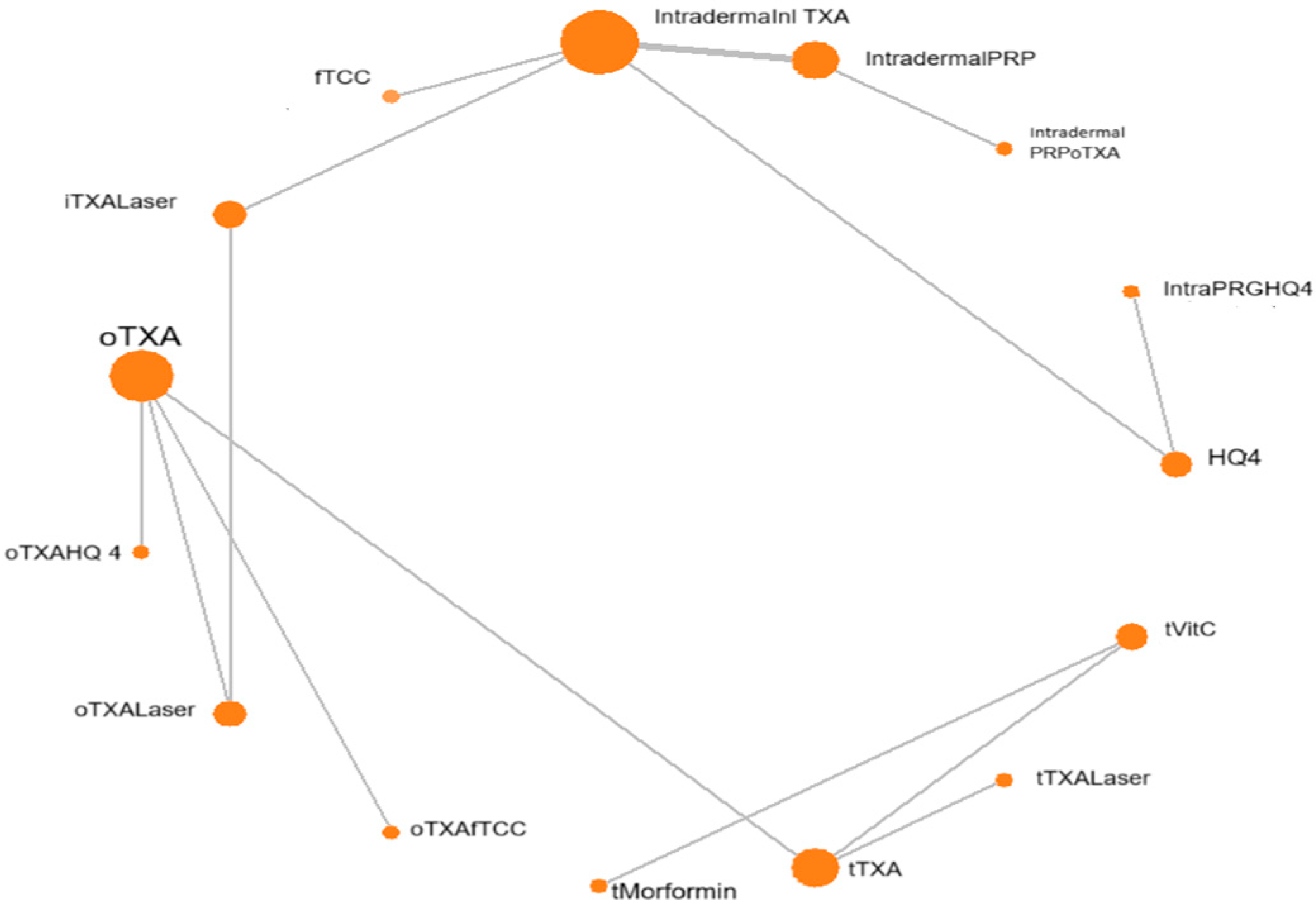
3.3. Network Meta-Analysis Results
3.3.1. Direct Pairwise Meta-Analysis
3.3.2. Bayesian NMA
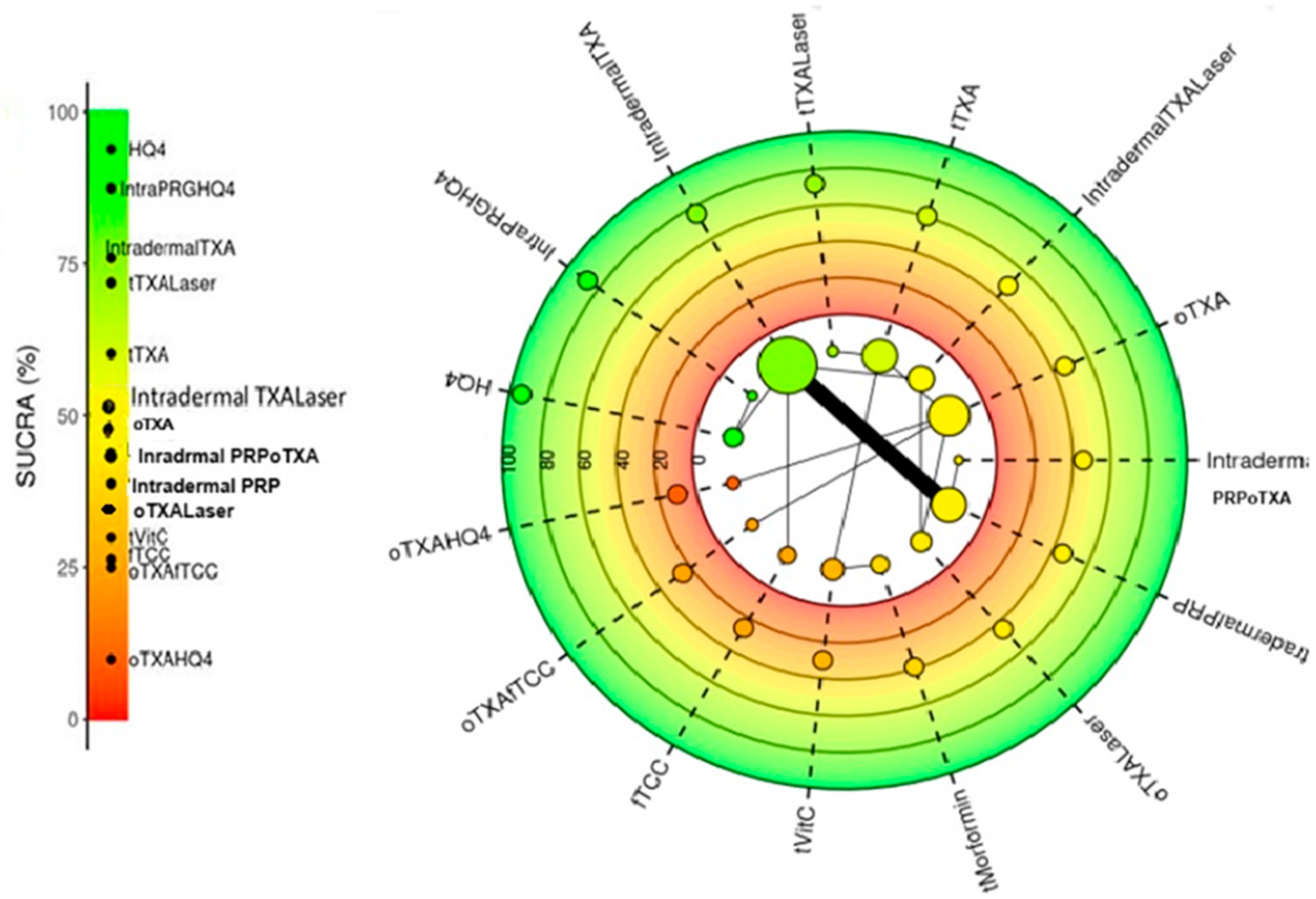
3.3.3. SUCRA Ranking of All Treatments Included
3.3.4. Inconsistency and Sensitivity Analysis
3.4. Adverse Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogbechie-Godec, O.A.; Elbuluk, N. Melasma: An Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Q.A.; Abdi, P.; Farkouh, C.; Anthony, M.R.; Chundru, A.; Amatul, F.; Parimi, K.; Santiago, N.; Farkouh, M.; Iram, S.; et al. Effectiveness of laser and topical tranexamic acid combination therapy in melasma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lasers Med. Sci. 2023, 38, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, H.; Godse, K.V.; Al Aboud, A.M. StatPearls. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459271/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Liu, W.; Chen, Q.; Xia, Y. New Mechanistic Insights of Melasma. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espósito, A.C.C.; Cassiano, D.P.; da Silva, C.N.; Lima, P.B.; Dias, J.A.F.; Hassun, K.; Bagatin, E.; Miot, L.D.B.; Miot, H.A. Update on Melasma-Part I: Pathogenesis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1967–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.; Elghblawi, E.; Aung, S.T. Melasma management in primary care. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2024, 53 (Suppl. S12), S56–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.V.; Jhawar, N.; Saedi, N. Tranexamic acid for melasma: Evaluating the various formulations. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2019, 12, E73–E74. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Tian, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Xu, W.; Li, K.; Wu, L. Effectiveness of combination therapy of broadband light and intradermal injection of tranexamic acid in the treatment of chloasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Luo, H.; Pan, W.; Yang, S.; Peng, X.; Kuang, B.; Huang, H.; Liu, C. Comparative efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid for melasma by different administration methods: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 1150–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiryis, B.; Toledano, O.; Avitan-Hersh, E.; Khamaysi, Z. Management of Melasma: Laser and Other Therapies-Review Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.G.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan) Computer Program; Version 7.2.0; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2024; Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/system/files/uploads/protected_file/RevMan5.4_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Owen, R.K.; Bradbury, N.; Xin, Y.; Cooper, N.; Sutton, A. MetaInsight: An interactive web-based tool for analyzing, interrogating, and visualizing network meta-analyses using R-shiny and netmeta. Res. Synth. Methods 2019, 10, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamshoushi, A.M.; Romisy, D.; Omar, S.S. Oral tranexamic acid, hydroquinone 4% and low-fluence 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for mixed melasma: Clinical and dermoscopic evaluation. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangi, E.; Shemshadi, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Goodarzi, A.; Dilmaghani, S. Comparison of efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid mesotherapy versus oral tranexamic acid in patients with melasma undergoing Q-switched fractional 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser: A blinded RCT and follow-up. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Attar, Y.; Doghaim, N.; El Far, N.; El Hedody, S.; Hawwam, S.A. Efficacy and Safety of tranexamic acid versus vitamin c after microneedling in treatment of melasma: Clinical and Dermoscopic study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Poojary, S.; Dubey, L. A Randomized Comparative Study of Intralesional Tranexemic Acid and Kligman’s Regimen in Indian Patients with Melasma. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2022, 15, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hawwam, S.A.; Ismail, M.; El-Attar, Y.A. Split-face comparative study between intradermal tranexamic acid injection alone versus intradermal tranexamic acid injection combined with Q-switched Nd:YAG laser in melasma treatment: Dermoscopic and clinical evaluation. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Rico, J.C.; Chavez-Alvarez, S.; Herz-Ruelas, M.E.; Sosa-Colunga, S.A.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Suro-Santos, Y.; Martinez, O.V. Oral tranexamic acid with a triple combination cream versus oral tranexamic acid monotherapy in the treatment of severe melasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elraouf, I.G.; Obaid, Z.M.; Fouda, I. Intradermal injection of tranexamic acid versus platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of melasma: A split-face comparative study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.K.; Bubna, A.K. A comparative evaluation of the efficacy of intralesional tranexamic acid versus platelet rich plasma in the treatment of melasma. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawanwongsri, W.; Siri-Archawawat, D.; Sindhusen, S.; Eden, C. Therapeutic efficiency and safety assessment of intradermal platelet-rich plasma combined with oral tranexamic acid in patients with facial melasma. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 34, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazyar, N.; Dezfuly, M.B.; Hadibarhaghtalab, M.; Parvar, S.Y.; Molavi, S.N.; Mapar, M.A.; Zeinali, M. Intradermal Injection of 100mg Tranexamic Acid Versus Topical 4% Hydroquinone for the Treatment of Melasma: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.M.Y.; Kamel, A.M.; Galal, S.A. Evaluation the efficacy of microneedling with topical metformin solution compared with microneedling with topical vitamin C solution in treatment of melasma. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Karimi Maskooni, M.; Farsinejad, A.; Karvar, M.; Khalili, M.; Aflatoonian, M. Combination of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors With Topical 4% Hydroquinone Compared With Topical 4% Hydroquinone Alone in the Treatment of Dermal Type of Melasma: A Single-Blinded Randomized Split-Face Study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2024, 15, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, J.; Brar, B.K.; Kumar, S.; Arora, H. Tranexamic Acid in Melasma: Comparative Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Oral Tranexamic Acid versus Its Transepidermal Administration. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2022, 15, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debasmita, B.; Raj, C.; Ishan, A.; Ipsita, D. A prospective randomized controlled trial of Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with topical 3% tranexamic acid (TA) versus microneedling with topical 3% tranexamic acid (TA) in treatment of melasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 2801–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp-Dormston, W.G. Melasma: A Step-by-Step Approach Towards a Multimodal Combination Therapy. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Nasrollahi, S.; Sabet Nematzadeh, M.; Samadi, A.; Ayatollahi, A.; Yadangi, S.; Abels, C.; Firooz, A. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of a triple combination cream (hydroquinone, tretinoin, and fluocinolone) for treatment of melasma in Middle Eastern skin. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 12, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konisky, H.; Balazic, E.; Jaller, J.A.; Khanna, U.; Kobets, K. Tranexamic acid in melasma: A focused review on drug administration routes. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Cheng, F.; Guo, S.; Cheng, H.; Wu, J. Application of PRP in Chloasma: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7487452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuknayat, A.; Bhalla, M.; Thami, G.P. Platelet-rich plasma is a promising therapy for melasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, R.; Gupta, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Melasma—A Systematic Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, N.M.; Almustafa, Z.Z.; AlBaqshi, H.N.; Abu Jawhar, Z. Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Melasma: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e63746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, K.S.; Tuqan, S.; Hilal, R.F. Q-Switched Nd:YAG (532 nm) Laser Versus Intra-Dermal Tranexamic Acid for Treatment of Facial Ephelides: A Split Face, Randomized, Comparative Trial. Lasers Surg. Med. 2021, 53, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Treatment of Melasma with Q-Switched Laser in Combination with Tranexamic Acid. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2025, 2025, 1883760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladulescu, D.; Scurtu, L.G.; Simionescu, A.A.; Scurtu, F.; Popescu, M.I.; Simionescu, O. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicines 2023, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.C.; Lana, G.L.; Santos, G.S.; Visoni, S.B.C.; Brigagão, R.J.; Santos, N.; Sobreiro, R.; da Cruz Silva Reis, A.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Ferrari, S. The Biological Role of Platelet Derivatives in Regenerative Aesthetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Ge, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, T. Metformin inhibits melanin synthesis and melanosome transfer through the cAMP pathway. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongkhon, P.; Ruengorn, C.; Awiphan, R.; Phosuya, C.; Ruanta, Y.; Thavorn, K.; Jamjanya, S.; Chuamanochan, M.; Nochaiwong, S. Efficacy and safety of metformin for melasma treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1281050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| fTCC | ||||||||||||||
| −3.49 | HQ4 | |||||||||||||
| (−6.18, 0.79) | ||||||||||||||
| −1.01 | 2.47 | Intradermal PRP | ||||||||||||
| (−3.23, 1.23) | (0.72, 4.23) | |||||||||||||
| −1.01 | 2.46 | 0 | Intradermal PRPoTXA | |||||||||||
| (−3.25, 1.25) | (0.7, 4.24) | (−0.25, 0.25) | ||||||||||||
| −2.19 | 1.29 | −1.18 | −1.18 | Intradermal TXA | ||||||||||
| (−4.32, −0.05) | (−0.33, 2.92) | (−1.85, −0.5) | (−1.89, −0.45) | |||||||||||
| −1.08 | 2.4 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 1.1 | Intradermal TXALaser | |||||||||
| (−3.43, 1.26) | (0.5, 4.28) | (−1.25, 1.11) | (−1.27, 1.14) | (0.14, 2.07) | ||||||||||
| −3.28 | 0.21 | −2.25 | −2.25 | −1.08 | −2.19 | Intra PRGFHQ4 | ||||||||
| (−5.99, −0.55) | (−0.18, 0.6) | (−4.06, −0.46) | (−4.08, −0.45) | (−2.76, 0.58) | (−4.11, −0.25) | |||||||||
| −0.92 | 2.57 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 1.3 | 0.17 | 2.37 | oTXA | |||||||
| (−4.83, 2.97) | (−1.07, 6.22) | (−3.23, 3.43) | (−3.24, 3.44) | (−1.95, 4.56) | (−2.92, 3.27) | (−1.29, 6.02) | ||||||||
| −0.03 | 3.46 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 2.19 | 1.05 | 3.25 | 0.89 | oTXAfTCC | ||||||
| (−4.02, 3.94) | (−0.28, 7.19) | (−2.43, 4.43) | (−2.44, 4.43) | (−1.14, 5.56) | (−2.14, 4.28) | (−0.51, 7.01) | (0.05, 1.73) | |||||||
| 1.31 | 4.79 | 2.32 | 2.32 | 3.53 | 2.4 | 4.58 | 2.22 | 1.33 | oTXAHQ4 | |||||
| (−3.2, 5.82) | (0.48, 9.09) | (−1.71, 6.36) | (−1.71, 6.38) | (−0.44, 7.52) | (−1.46, 6.25) | (0.25, 8.9) | (−0.09, 4.54) | (−1.13, 3.81) | ||||||
| −0.98 | 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.23 | 0.1 | 2.28 | −0.07 | −0.96 | −2.3 | oTXALaser | ||||
| (−3.39, 1.43) | (0.54, 4.46) | (−1.27, 1.33) | (−1.29, 1.35) | (0.13, 2.34) | (−0.45, 0.65) | (0.28, 4.28) | (−3.13, 2.98) | (−4.14, 2.2) | (−6.11, 1.52) | |||||
| −0.37 | 3.11 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 1.85 | 0.71 | 2.9 | 0.54 | −0.35 | −1.68 | 0.61 | tMorformin | |||
| (−4.93, 4.18) | (−1.24, 7.45) | (−3.45, 4.72) | (−3.45, 4.73) | (−2.17, 5.88) | (−3.19, 4.63) | (−1.47, 7.26) | (−1.83, 2.9) | (−2.86, 2.14) | (−4.99, 1.6) | (−3.26, 4.47) | ||||
| −1.46 | 2.03 | −0.45 | −0.45 | 0.76 | −0.37 | 1.82 | −0.54 | −1.43 | −2.76 | −0.47 | −1.08 | tTXA | ||
| (−5.49, 2.59) | (−1.76, 5.82) | (−3.92, 3.06) | (−3.94, 3.06) | (−2.66, 4.19) | (−3.65, 2.93) | (−1.99, 5.63) | (−1.59, 0.51) | (−2.78, −0.08) | (−5.32, −0.23) | (−3.7, 2.78) | (−3.21, 1.05) | |||
| −1.9 | 1.57 | −0.89 | −0.89 | 0.31 | −0.82 | 1.36 | −0.99 | −1.89 | −3.22 | −0.92 | −1.54 | −0.45 | tTXALaser | |
| (−6.02, 2.2) | (−2.31, 5.45) | (−4.46, 2.69) | (−4.47, 2.71) | (−3.2, 3.84) | (−4.18, 2.56) | (−2.53, 5.25) | (−2.32, 0.32) | (−3.44, −0.33) | (−5.89, −0.55) | (−4.24, 2.42) | (−3.78, 0.74) | (−1.24, 0.34) | ||
| −0.26 | 3.22 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 1.96 | 0.82 | 3.01 | 0.65 | −0.24 | −1.57 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 1.19 | 1.65 | MNVitC |
| (−4.81, 4.29) | (−1.13, 7.56) | (−3.34, 4.83) | (−3.34, 4.85) | (−2.05, 5.99) | (−3.08, 4.74) | (−1.35, 7.37) | (−1.72, 3.02) | (−2.74, 2.25) | (−4.88, 1.72) | (−3.15, 4.58) | (0.02, 0.2) | (−0.94, 3.31) | (−0.63, 3.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leung, J.H.; Leung, H.W.C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Jang, Y.-C.; Chan, A.L.F. Efficacy and Safety of Different Treatments for Melasma: Network Meta-Analysis of Updated Data. Diseases 2025, 13, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100316
Leung JH, Leung HWC, Wang S-Y, Jang Y-C, Chan ALF. Efficacy and Safety of Different Treatments for Melasma: Network Meta-Analysis of Updated Data. Diseases. 2025; 13(10):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeung, John Hang, Henry W. C. Leung, Shyh-Yau Wang, Yeu-Chai Jang, and Agnes L. F. Chan. 2025. "Efficacy and Safety of Different Treatments for Melasma: Network Meta-Analysis of Updated Data" Diseases 13, no. 10: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100316
APA StyleLeung, J. H., Leung, H. W. C., Wang, S.-Y., Jang, Y.-C., & Chan, A. L. F. (2025). Efficacy and Safety of Different Treatments for Melasma: Network Meta-Analysis of Updated Data. Diseases, 13(10), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100316






