AI-Driven Patient Education in Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluating Chatbot Responses against Clinical Guidelines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
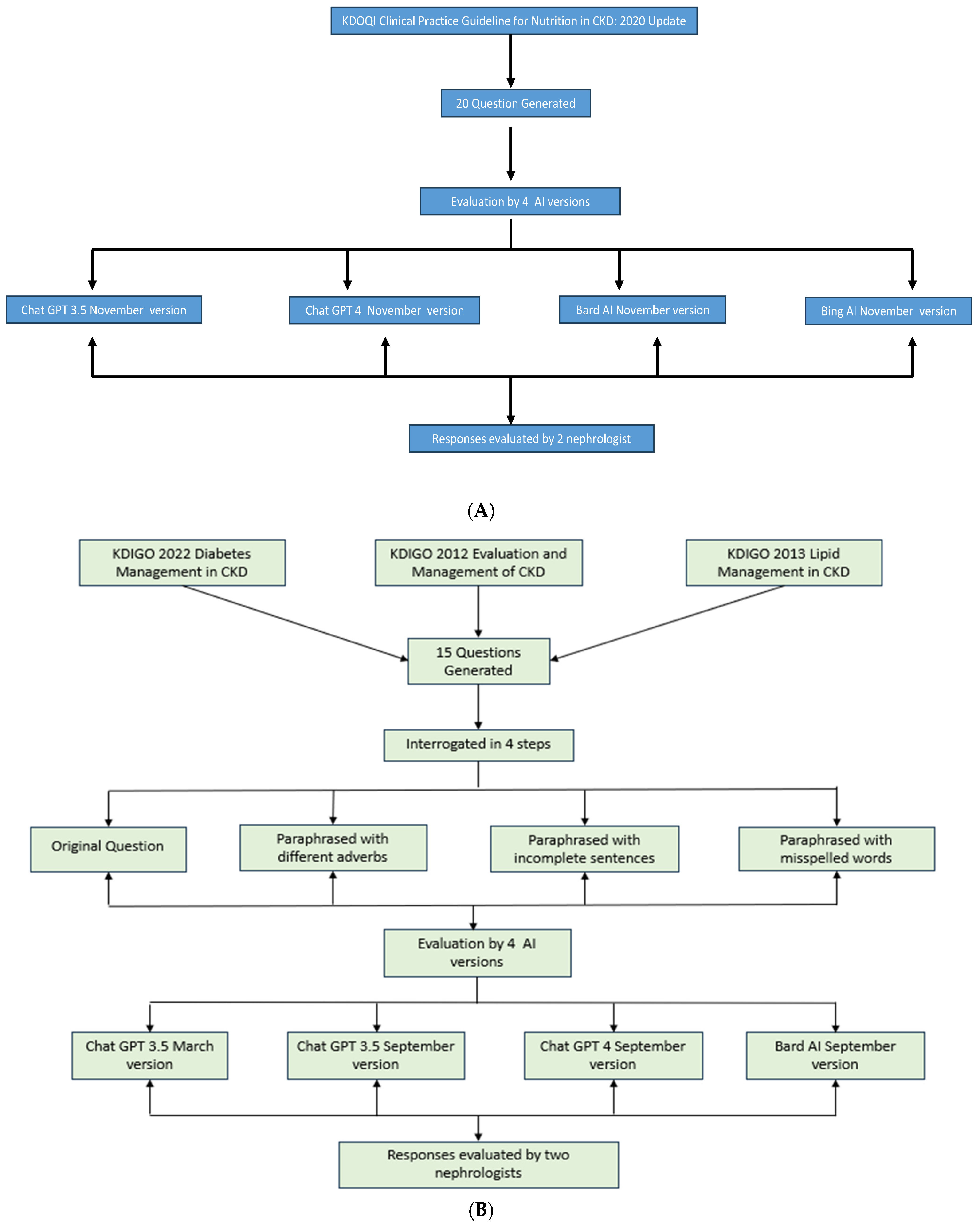
2.1. Question Generation from KDIGO Guidelines
- “KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease” [18].
- “KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease” [19].
- “KDIGO 2013 Clinical Practice Guideline for Lipid Management in Chronic Kidney Disease” [20].
2.2. Question Generation from NKF KDOQI Guidelines
2.3. Question Interrogation Process for KDIGO Guideline Questions
- The original question formulation as per the guideline’s recommendations.
- Paraphrasing each question while employing different interrogative adverbs.
- Crafting paraphrased questions with incomplete sentences.
- Formulating paraphrased questions with deliberate misspellings.
- ChatGPT 3.5.
- ChatGPT 4.0.
- Bard AI.
- Bing AI.
2.4. Evaluative Review by Nephrologist
- (a)
- Clinical accuracy: Assessing whether the information aligns with current medical knowledge and practice.
- (b)
- Potential for patient harm: Identifying any advice that could lead to adverse outcomes if followed.
- (c)
- Clarity and relevance: Evaluating whether the response directly addresses the question in a clear manner.
- (d)
- Consistency with guidelines: While not the sole criterion, responses were checked against relevant guidelines when significant discrepancies were noted.
2.5. Readability Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ChatGPT 3.5 (March 2023 Version) for KDIGO Guideline Questions
3.2. Chat GPT 3.5 (September 2023 Version) for KDIGO Guideline Questions
3.3. Chat GPT 4 (September 2023 Version) for KDIGO Guideline Questions
3.4. Bard AI (September 2023 Version) for KDIGO Guideline Questions
3.5. ChatGPT 3.5 (November 2023 Version) for KDOQI Guideline Questions
3.6. ChatGPT 4 (November 2023 Version) for KDOQI Guideline Questions
3.7. Bard AI (November 2023 Version) for KDOQI Guideline Questions
3.8. Bing AI (November 2023 Version) for KDOQI Guideline Questions
4. Readability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francis, A.; Harhay, M.N.; Ong, A.; Tummalapalli, S.L.; Ortiz, A.; Fogo, A.B.; Fliser, D.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Fontana, M.; Nangaku, M.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: An international consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Li, Y. Mendelian randomization analysis revealed that albuminuria is the key factor affecting socioeconomic status in CKD patients. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2367705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, B.-H.; Sumida, K.; Scholes-Robertson, N.; Chan, M.; Lambert, K.; Kramer, H.; Lui, S.-F.; Wang, A.Y.-M. Nutrition education models for patients with chronic kidney disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2023, 43, 151404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narva, A.S.; Norton, J.M.; Boulware, L.E. Educating patients about CKD: The path to self-management and patient-centered care. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladin, K.; Rossi, A. Person-centered kidney education: The path forward. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Leaman, R.; Lu, Z. Retrieve, summarize, and verify: How will ChatGPT affect information seeking from the medical literature? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 34, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, T.H.; Cheatham, M.; Medenilla, A.; Sillos, C.; De Leon, L.; Elepaño, C.; Madriaga, M.; Aggabao, R.; Diaz-Candido, G.; Maningo, J.; et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, G.N. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Nephrology. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introducing ChatGPT. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Yuan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Tang, S.; Yuan, X.; Tang, W.; Xie, Y.; Ge, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Role of Artificial Intelligence in Kidney Disease. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naber, T.; Purohit, S. Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Diet for a Reduction in the Severity of the Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, H. Diet and Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S367–S379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Jung, J.Y. Nutritional management in patients with chronic kidney disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Shi, Y. Association of the dietary inflammation index DII with the prevalence of chronic kidney disease in patients with hypertension. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2373279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikumoro, A.O.; Jawad, M.S. Assessing intelligence conversation agent trends-chatbots-ai technology application for personalized marketing. TEST Eng. Manag. 2019, 81, 4779–4785. [Google Scholar]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eknoyan, G.; Lameire, N.; Eckardt, K.; Kasiske, B.; Wheeler, D.; Levin, A.; Stevens, P.; Bilous, R.; Lamb, E.; Coresh, J. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 3, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wanner, C.; Tonelli, M. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Lipid Management in CKD: Summary of recommendation statements and clinical approach to the patient. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPT-4. Available online: https://openai.com/gpt-4 (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Bard AI Chat. Available online: https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/bard-ai-chat/pkgciiiancapdlpcbppfkmeaieppikkk (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Gemini. Available online: https://gemini.google.com/app (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Suppadungsuk, S.; Thongprayoon, C.; Krisanapan, P.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Garcia Valencia, O.; Miao, J.; Mekraksakit, P.; Kashani, K.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Examining the Validity of ChatGPT in Identifying Relevant Nephrology Literature: Findings and Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Heart Association Recommendations for Physical Activity in Adults and Kids. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/fitness/fitness-basics/aha-recs-for-physical-activity-in-adults (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Qarajeh, A.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Thongprayoon, C.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Krisanapan, P.; Aiumtrakul, N.; Garcia Valencia, O.A.; Miao, J.; Qureshi, F.; Cheungpasitporn, W. AI-Powered Renal Diet Support: Performance of ChatGPT, Bard AI, and Bing Chat. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Valencia, O.A.; Thongprayoon, C.; Miao, J.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Krisanapan, P.; Craici, I.M.; Jadlowiec, C.C.; Mao, S.A.; Mao, M.A.; Leeaphorn, N.; et al. Empowering inclusivity: Improving readability of living kidney donation information with ChatGPT. Front. Digit. Health 2024, 6, 1366967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, H.A.; Mai, M.; Abdel-Megid, H.; Liew, S.Q.R.; Kidanemariam, S.; Omar, A.S.; Tiwari, U.; Hamze, J.; Ahn, S.H.; Maxwell, A.W.P. Using ChatGPT to Improve Readability of Interventional Radiology Procedure Descriptions. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2024, 47, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acharya, P.C.; Alba, R.; Krisanapan, P.; Acharya, C.M.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Csongradi, E.; Mao, M.A.; Craici, I.M.; Miao, J.; Thongprayoon, C.; et al. AI-Driven Patient Education in Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluating Chatbot Responses against Clinical Guidelines. Diseases 2024, 12, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12080185
Acharya PC, Alba R, Krisanapan P, Acharya CM, Suppadungsuk S, Csongradi E, Mao MA, Craici IM, Miao J, Thongprayoon C, et al. AI-Driven Patient Education in Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluating Chatbot Responses against Clinical Guidelines. Diseases. 2024; 12(8):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12080185
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcharya, Prakrati C., Raul Alba, Pajaree Krisanapan, Chirag M. Acharya, Supawadee Suppadungsuk, Eva Csongradi, Michael A. Mao, Iasmina M. Craici, Jing Miao, Charat Thongprayoon, and et al. 2024. "AI-Driven Patient Education in Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluating Chatbot Responses against Clinical Guidelines" Diseases 12, no. 8: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12080185
APA StyleAcharya, P. C., Alba, R., Krisanapan, P., Acharya, C. M., Suppadungsuk, S., Csongradi, E., Mao, M. A., Craici, I. M., Miao, J., Thongprayoon, C., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2024). AI-Driven Patient Education in Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluating Chatbot Responses against Clinical Guidelines. Diseases, 12(8), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12080185







