Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Pazopanib Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
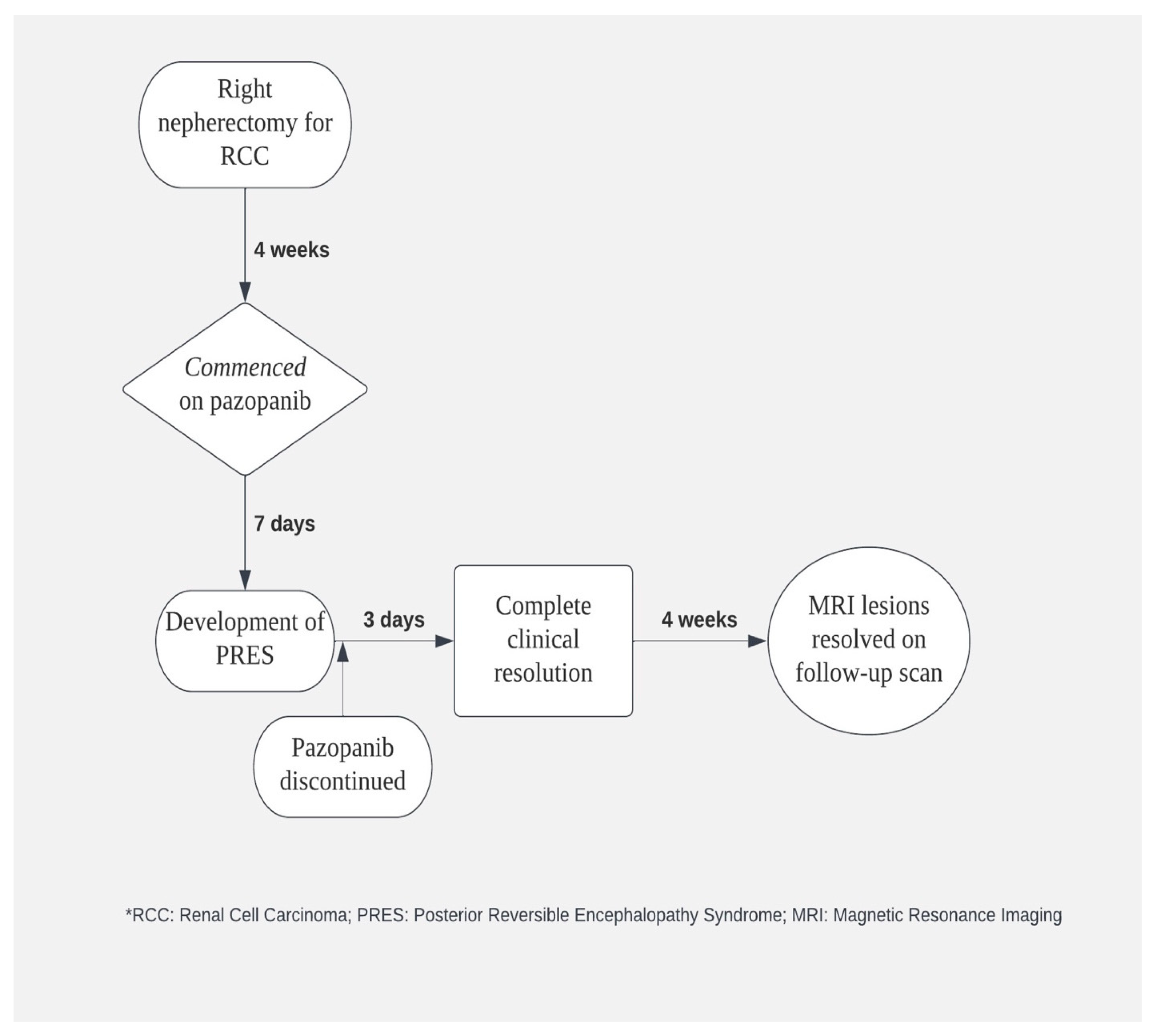
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Thandra, K.C.; Saginala, K.; Mohammed, A.; Vakiti, A.; Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. World. J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Alekseev, B.; Soulières, D.; Melichar, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Royle, K.L.; Gregory, W.; Ralph, C.; Maraveyas, A.; Din, O.; Eisen, T.; Nathan, P.; Powles, T.; Griffiths, R.; et al. Temporary treatment cessation versus continuation of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (STAR): An open-label, non-inferiority, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelis, L.; Souftas, V.; Amarantidis, K.; Xenidis, N.; Chamalidou, E.; Dimopoulos, P.; Michailidis, P.; Christakidis, E.; Prassopoulos, P.; Kakolyris, S. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome induced by pazopanib. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, C.; Oppenheim, C.; Méder, J.F.; Mas, J.L. Neuroimaging in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J. Neuroimaging 2004, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias, D.J.; Luetmer, P.H.; Campeau, N.G. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R.R. Anti-Angiogenic Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome: Could Hypomagnesaemia Be the Trigger? Drug Saf. 2017, 40, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchhanolla, P.; Bir, S.; Angelette, A.; Lewis, A.; Kandregula, S.; Guthikonda, B.; Javalkar, V.; Chernyshev, O.; Kelley, R. Determination of Prevalence of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) and Its Association with Cerebral Infarction, and Outcome in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 2016–2018 (P16-10.002). Neurology 2022, 98, 3555. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Davis, I.D.; Mardiak, J.; Szczylik, C.; Lee, E.; Wagstaff, J.; Barrios, C.H.; Salman, P.; Gladkov, O.A.; Kavina, A.; et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Morales, J.M.; Swierkowski, M.; Wells, J.C.; Fraccon, A.P.; Pasini, F.; Donskov, F.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Lee, J.L.; Sim, H.W.; Sliwczynsk, A.; et al. First-line sunitinib versus pazopanib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results from the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 65, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.B.; Oudard, S. Antiangiogenic therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Management of treatment-related toxicities. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudulagunta, S.R.; Sodalagunta, M.B.; Kumbhat, M.; Settikere Nataraju, A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 2017, omx011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeau, B.; Le Tilly, O.; Sautenet, B.; Salmon Gandonnière, C.; Barin-Le Guellec, C.; Ehrmann, S. Arginine Vasopressin and Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Pathophysiology: The Missing Link? Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6792–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, S.; Finocchi, V.; Borgia, M.L.; Nania, C.; Della Vella, B.; Pierallini, A.; Bozzao, A. Intracranial hypotension and PRES: Case report. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Schmutzhard, E. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Petäjä, K.M.; McGeoch, A.; Yang, L.L.; Hubsch, A.; McEniery, C.M.; Meyer, P.A.R.; Mir, F.; Gajendragadkar, P.; Ramenatte, N.; Anandappa, G.; et al. Mechanisms Underlying Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition–Induced Hypertension: The HYPAZ Trial. Hypertension 2021, 77, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, M.L.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Chen, H.X.; Durand, J.B.; Elliott, W.J.; Ivy, S.P.; Leier, C.V.; Lindenfeld, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Initial assessment, surveillance, and management of blood pressure in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servillo, G.; Bifulco, F.; De Robertis, E.; Piazza, O.; Striano, P.; Tortora, F.; Striano, S.; Tufano, R. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, J.D.; Kutlubaev, M.A.; Kermode, A.G.; Hardy, T. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): Diagnosis and management. Pract. Neurol. 2022, 22, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinduja, A. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: Clinical Features and Outcome. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, R.; Welzel, T.; Debus, J.; Gruellich, C.; Jaeger, D.; Potthoff, K. Posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome associated with pazopanib. Case Rep. Oncol. 2013, 6, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaithambi, G.; Peters, B.R.; Hurliman, E.; Moran, B.P.; Khan, A.S.; Taylor, R.A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome induced by pazopanib for renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller-Patterson, C.; Fehnel, C.R. Pazopanib-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with intracerebral haemorrhage. BMJ Case. Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, B.M.; Bajrami, A.; Demir, E.; Cabalar, M.; Yayla, V. Pazopanib induced unilateral posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Ideggyogy. Szle. 2017, 70, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaris, N.; Maltezou, M.; Papaxoinis, G.; Visvikis, A.; Samantas, E. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome with Concurrent Nephrotic Syndrome in a Patient Treated with Pazopanib for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2017, 15, e99–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, S.; Mitsuya, K.; Nakasu, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Katagiri, H.; Murata, H.; Wasa, J.; Takahashi, M.; Endo, M. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) induced by pazopanib, a multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in a patient with soft-tissue sarcoma: Case report and review of the literature. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.T.; Yen, C.T.; Cheng, H.L.; Lee, C.H. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Induced by Pazopanib in a Patient with Soft-Tissue Sarcoma: A Case Report. Case Rep. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleszar, J.; Dasgupta, R.; Sidda, A.; Rich, M. A case of late-onset pazopanib-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tatsumichi, T.; Okazaki, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kawakita, K.; Kaji, M.; Kosaka, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Houchi, H. A case of uterine sarcoma with pazopanib-induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Aust. Crit. Care 2020, 33, S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong So, J.; Largeau, B.; Beau-Salinas, F.; Ehrmann, S.; Magni, C.; Meunier, J. Pazopanib-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with possible syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone: An incidental or pathophysiological association? Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumichi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Okazaki, T.; Takahashi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kawakita, K.; Houchi, H.; Kuroda, Y.; Kosaka, S. Uterine sarcoma with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with pazopanib. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time Interval between Discontinuation of Pazopanib and Resolution of PRES Symptoms | Time Interval between Initiation of Pazopanib and PRES | Dose | Primary Cancer | Age/Gender | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | 21 days | Not specified | RCC | 40/F | Chelis et al. [4] |
| 6 days | 8 weeks | 800 mg/day | RCC | 63/F | Foerster et al. [22] |
| 2 days | 4 weeks | Not specified | RCC | 76/M | Asaithambi et al. [23] |
| Not specified | 3 weeks | Not specified | RCC | 69/F | Miller-Patterson et al. [24] |
| 60 h | 16–20 weeks | 400 mg/day | Testicular tumour | 32/M | Arslan et al. [25] |
| 3 days | 9 days | 800 mg/day | RCC | 56/F | Miaris et al. [26] |
| 5 days | 5–6 weeks | 800 mg/day | Retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma | 49/F | Deguchi et al. [27] |
| 5 days | 4 days | 800 mg/day | HCC | 76/F | Wu et al. [28] |
| 5 days | 20 months | Not specified | Hurthel cell thyroid carcinoma | 56/F | Koleszar et al. [29] |
| 9 days | 4 days | Not specified | Uterine sarcoma | 64/F | Takahashi et al. [30] |
| 6 days | 12 days | 600 mg/day | RCC | 73/F | Wong So et al. [31] |
| 7 days | 3 days | 800 mg/day | Uterine sarcoma | 64/F | Tatsumichi et al. [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savaliya, M.; Surati, D.; Surati, R.; Padmani, S.; Boussios, S. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Pazopanib Therapy. Diseases 2023, 11, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11020076
Savaliya M, Surati D, Surati R, Padmani S, Boussios S. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Pazopanib Therapy. Diseases. 2023; 11(2):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11020076
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavaliya, Madhavkumar, Drishty Surati, Ramesh Surati, Shailesh Padmani, and Stergios Boussios. 2023. "Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Pazopanib Therapy" Diseases 11, no. 2: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11020076
APA StyleSavaliya, M., Surati, D., Surati, R., Padmani, S., & Boussios, S. (2023). Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Pazopanib Therapy. Diseases, 11(2), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11020076







