Electromagnetic Noise Suppression of Magnetic Resonance Sounding Combined with Data Acquisition and Multi-Frame Spectral Subtraction in the Frequency Domain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
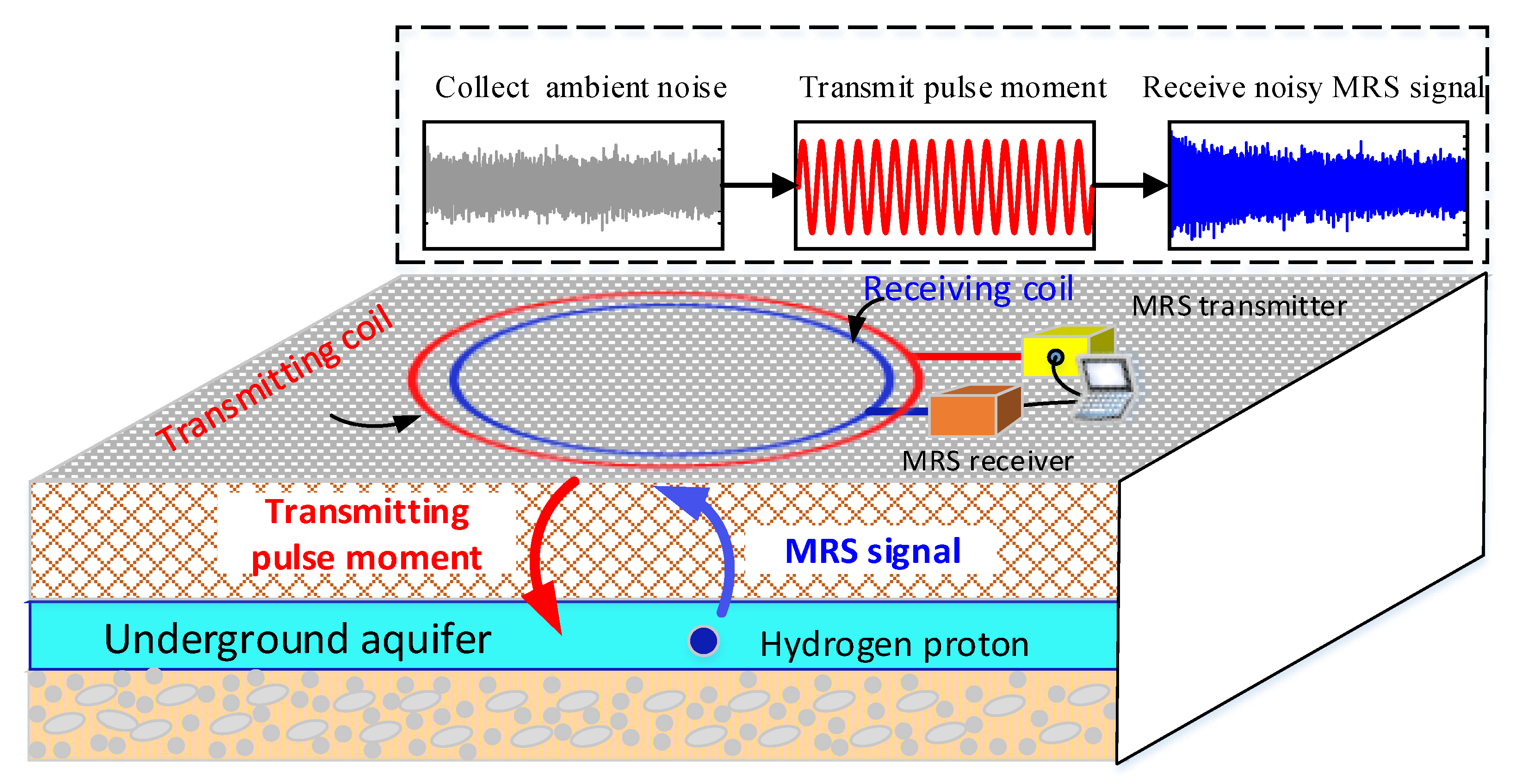
2.1. Noise and Signal in MRS Measurement
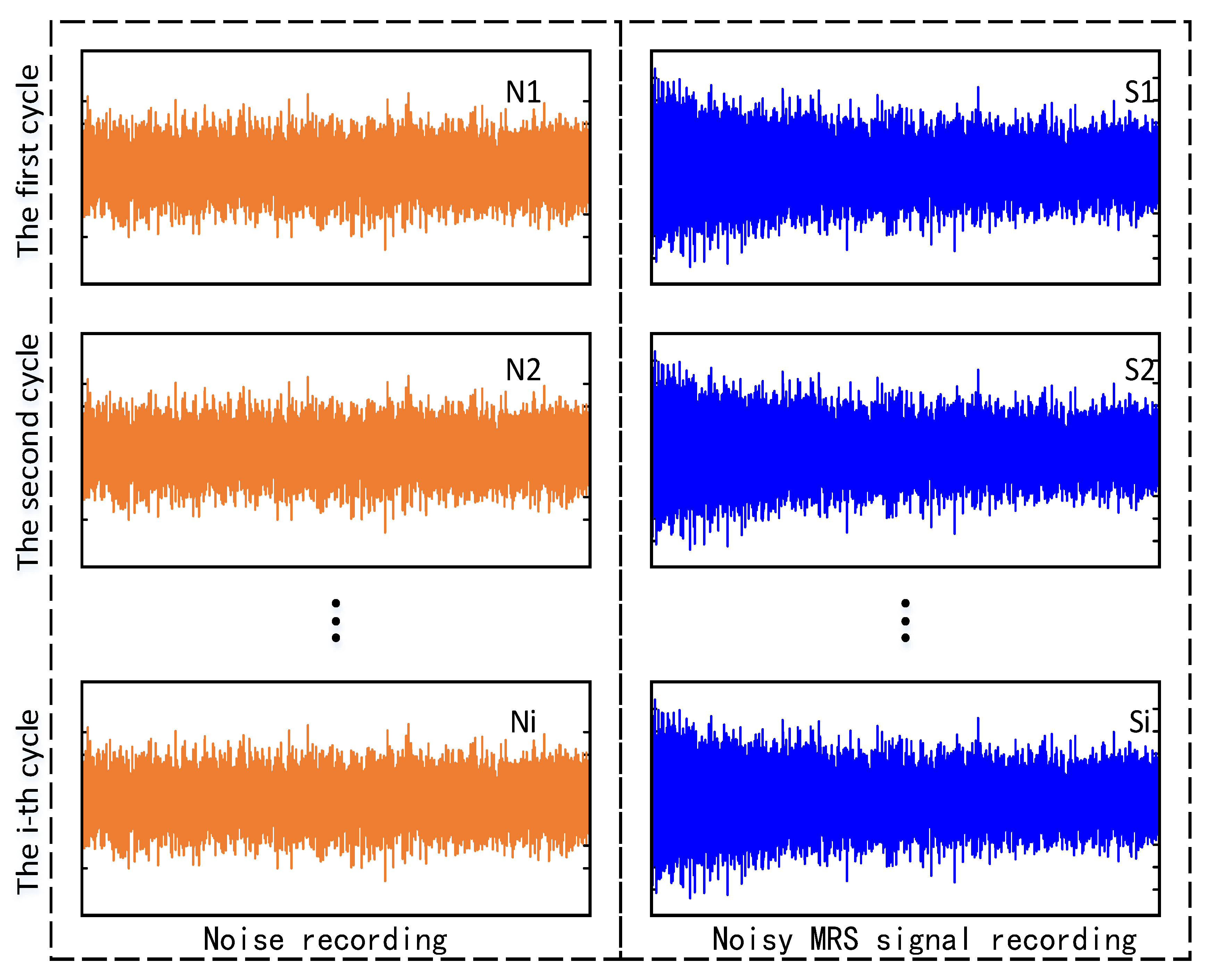
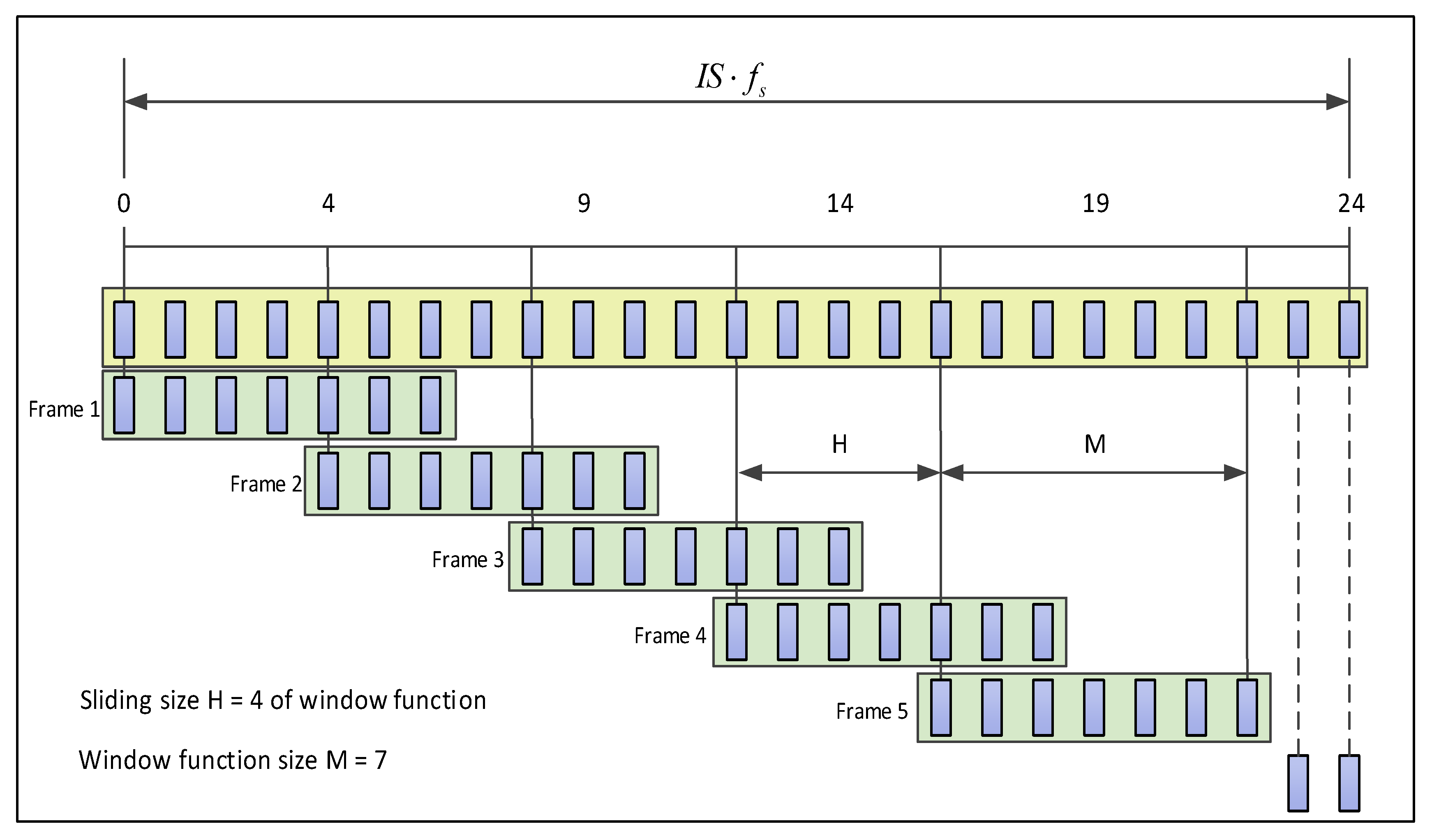
2.2. MRS Data Acquisition for DA-MFSS
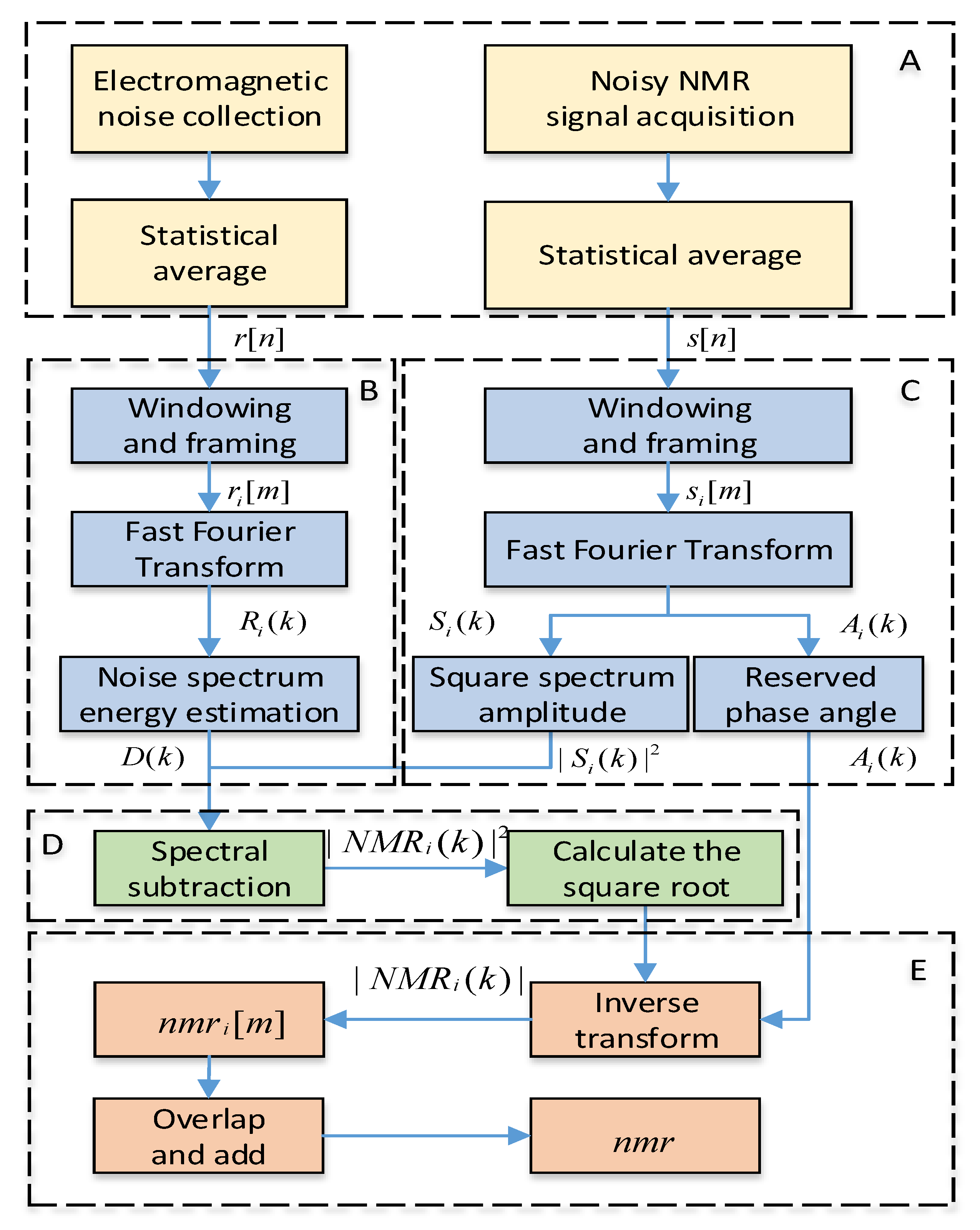
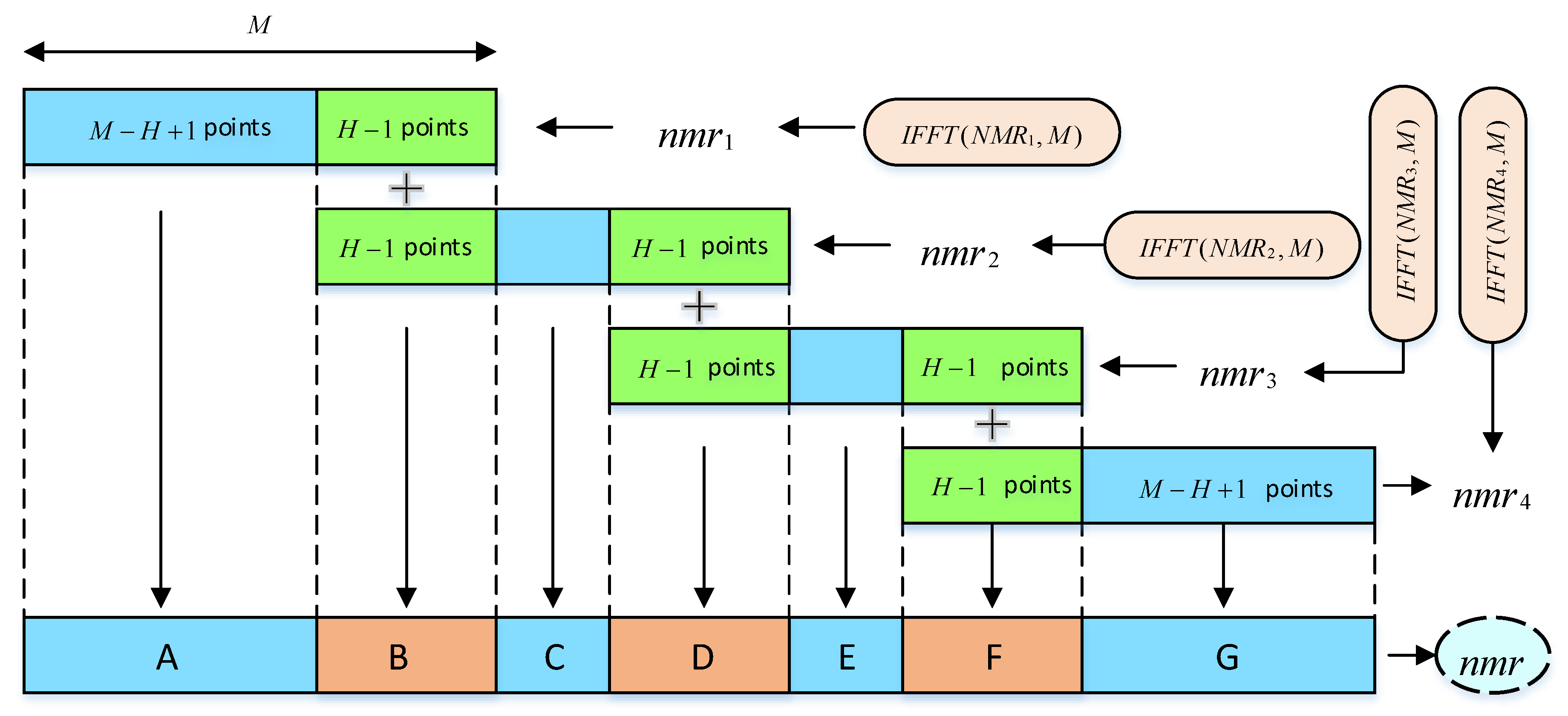
2.3. Noise Suppression Procedure for DA-MFSS
- Stage 1, the pure noise and the noisy MRS signals are calculated by statistical average, as shown in part A of Figure 3.
- Stage 2, the stacked noise is used to calculate the spectrum value at each frequency, as shown in part B of Figure 3.
- Stage 3, the stacked noisy MRS signal is applied to calculate the spectrum value at each frequency, as shown in part C of Figure 3.
- Stage 4, according to the MFSS theory, the above two spectral values are brought into the calculation of the energy value at different frequencies, as shown in part D of Figure 3.
- Stage 5, based on inverse transformation formula and the overlap-add method, the MRS signal in the time domain after spectral subtraction is obtained, as shown in part E of Figure 3.
3. Noise Suppression Implementation of MFSS
3.1. Discrete Fourier Transform of the Segmented Noisy MRS Signal
3.2. Energy Calculation of Each Frame Noise Data in the Frequency Domain
3.3. MRS Signal Estimation by MFSS
4. Noise Suppression Experiments of DA-MFSS
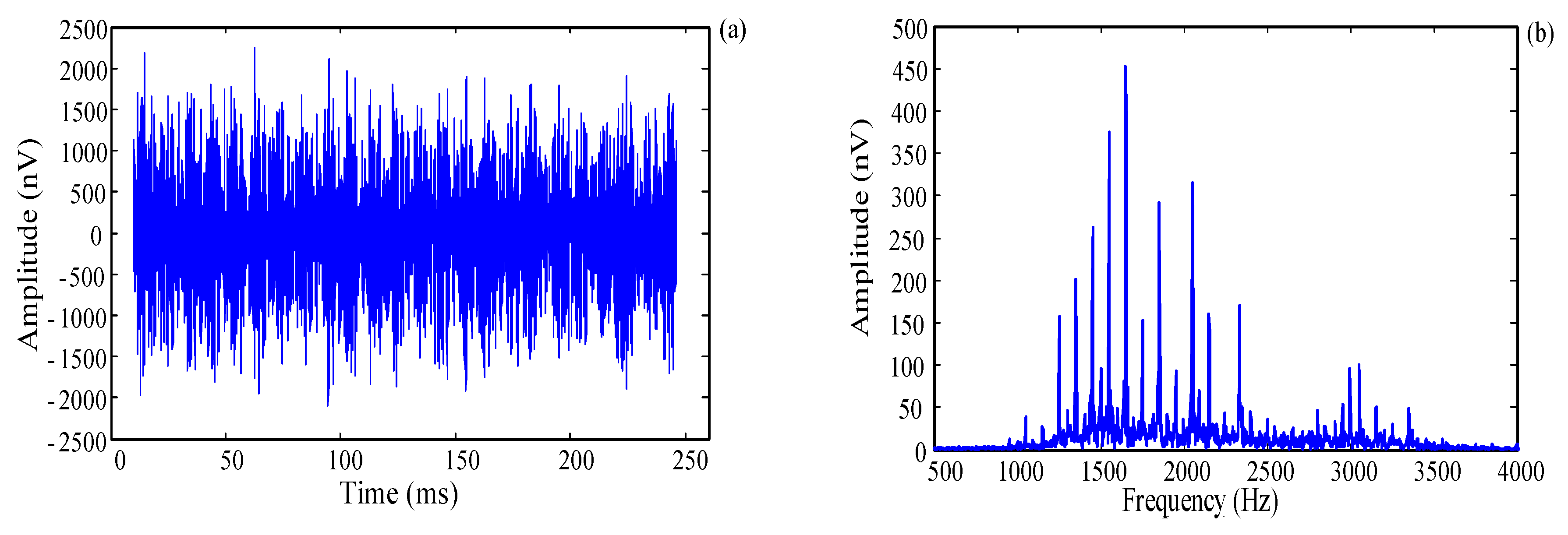
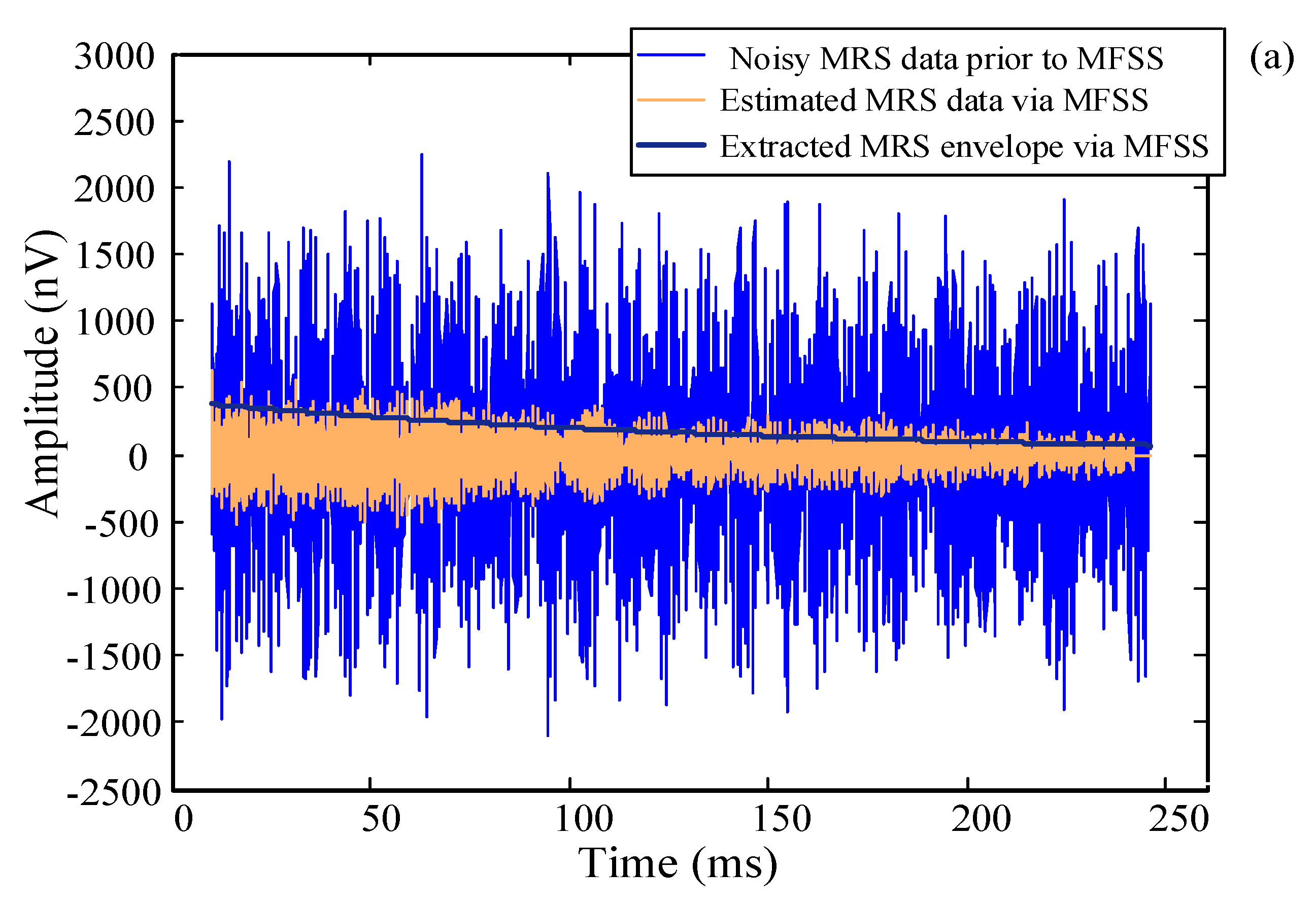
4.1. Simulation Experiment
4.2. Field Data Processing
4.2.1. Select Short Frame Length and Small Frame Sliding Distance
4.2.2. Select Long Frame Length and Large Frame Sliding Distance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hertrich, M.; Braun, M.; Gunther, T.; Green, A.G.; Yaramanci, U. Surface nuclear magnetic resonance tomography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legchenko, A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Groundwater; ISTE Ltd.: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Legchenko, A.; Valla, P. A review of the basic principles for proton magnetic resonance sounding measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 50, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Yi, X.; Jiang, C. Study on shortening the dead time of surface nuclear magnetic resonance instrument using bipolar phase pulses. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legchenko, A.; Valla, P. Removal of power-line harmonics from proton magnetic resonance measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 10–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yang, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Wan, L.; Teng, F. Exploiting adiabatic pulses with prepolarization in detection of underground nuclear magnetic resonant signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, X.; Fan, T.; Wan, L. Time–frequency peak filtering for random noise attenuation of magnetic resonance sounding signal. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 213, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.O. Multi-channel surface NMR instrumentation and software for 1D/2D groundwater investigations. J. Appl. Geophys. 2008, 66, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, E.; Grombacher, D.; Walsh, D. Adiabatic pulses enhance surface nuclear magnetic resonance measurement and survey speed for groundwater investigations. Geophysics 2016, 81, WB85–WB96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Petke, M.; Braun, M.; Hertrich, M.; Costabel, S.; Walbrecker, J. MRSmatlab—a software tool for processing, modeling, and inversion of magnetic resonance sounding data. Geophysics 2016, 81, WB9–WB21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, S.; Keating, K. Algorithms for removing surface water signals from surface nuclear magnetic resonance infiltration surveys. Geophysics 2016, 81, WB97–WB107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Petke, M.; Yaramanci, U. QT inversion—Comprehensive use of the complete surface NMR data set. Geophysics 2010, 75, WA199–WA209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lin, J.; Duan, Q.; Sun, S.; Tian, B. Statistical stacking and adaptive notch filter to remove high-level electromagnetic noise from MRS measurements. Near Surf. Geophys. 2011, 9, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgaard, E.; Auken, E.; Larsen, J.J. Adaptive noise cancelling of multichannel magnetic resonance sounding signals. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Dalgaard, E.; Auken, E. Noise cancelling of MRS signals combining model-based removal of powerline harmonics and multichannel Wiener filtering. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 196, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.J. Model-based subtraction of spikes from surface nuclear magnetic resonance data. Geophysics 2016, 81, WB1–WB8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabel, S.; Müller-Petke, M. Despiking of magnetic resonance signals in time and wavelet domains. Near Surf. Geophys. 2014, 12, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Müller-Petke, M. Random noise suppression of magnetic resonance sounding oscillating signal by combining empirical mode decomposition and time-frequency peak filtering. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 79917–79926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Y. Random noise suppression of magnetic resonance sounding data with intensive sampling sparse reconstruction and kernel regression estimation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, S. Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1979, 27, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruden, S.; Zajc, B. Using spectral subtraction for suppression of noise in speech signals with analog integrated circuits. Analog Integr. Circuits Process. 1999, 18, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Shimamura, T. Non-stationary noise estimation using low-frequency regions for spectral subtraction. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2005, 12, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Yin, F. Speech dereverberation method based on spectral subtraction and spectral line enhancement. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 112, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemeh, A.; Antoine, T.; Marc, T. Tool condition monitoring using spectral subtraction and convolutional neural networks in milling process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 3217–3227. [Google Scholar]
- Mohindru, P.; Khanna, R.; Bhatia, S.S. New tuning model for rectangular windowed FIR filter using fractional Fourier transform. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.H.; Pearce, J.A. A new window and comparison to standard windows. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Singh, S.P.; Pandey, V.K. Spectrum shaping analysis using tunable parameter of fractional based on Bartlett window. In Proceeding of the 3rd IEEE International Advance Computing Conference, Ghaziabad, India, 22–23 February 2013; pp. 1625–1630. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C. An Iterative Hybrid Harmonics Detection Method Based on Discrete Wavelet Transform and Bartlett–Hann Window. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkovic, Z.S.; Bakmaz, B.M.; Bakmaz, M.R. Hamming Window to the Digital World. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Qureshi, I.M.; Khan, W.; ur Rehman, S.; Khan, M.M. Beam Pattern Synthesis for an FDA Radar with Hamming Window-Based Nonuniform Frequency Offset. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2283–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.H.; Yang, S.M. An approach for electrical harmonic FFT analysis based on Hanning self-multiply window. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2016, 19, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.F.; Mei, S.L. Composite Interpolated Fast Fourier Transform with the Hanning Window. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.J.; Kim, N.K.; Ryu, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S.H.; Huh, S.R.; Kim, G.H. Determination of electron energy probability function in low-temperature plasmas from current-Voltage characteristics of two Langmuir probes filtered by Savitzky-Golay and Blackman window methods. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2015, 15, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R.K.; Jain, A.; Saxena, R. An improved and simplified design of pseudo-transmultiplexer using Blackman window family. Digit. Signal Prog. 2010, 20, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, R.; Huang, X. ISAR imaging of maneuvering target based on the estimation of time varying amplitude with Gaussian window. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 11180–11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.; Singh, J. Analysis of Kaiser and Gaussian Window Functions in the Fractional Fourier Transform Domain and Its Application. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2019, 43, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
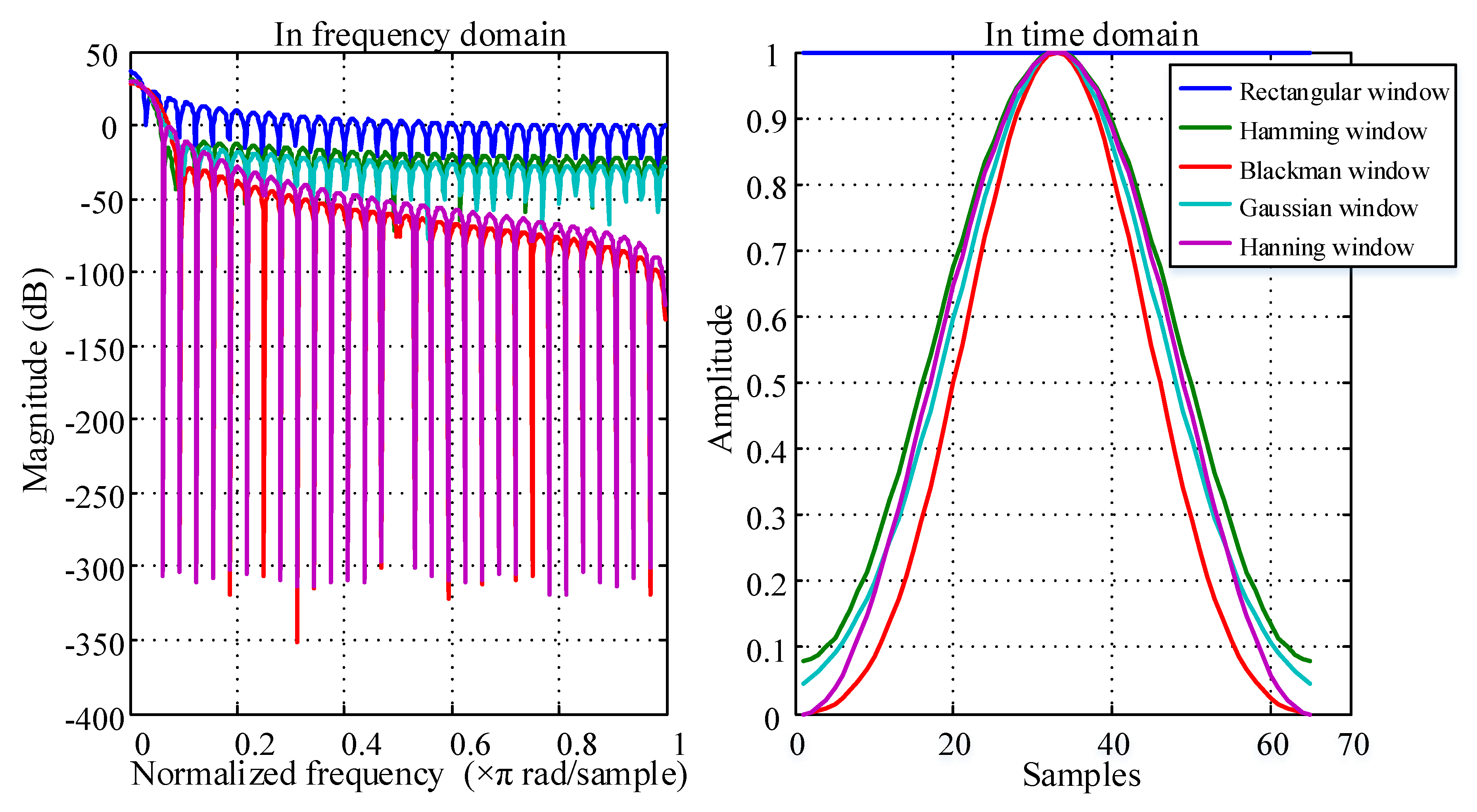





| Window Function | Time Domain Expression | Window Type |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangular window [25,26] | Power function type | |
| Bartlett window [26,27,28] | Power function type | |
| Hamming window [29,30] | Trigonometric function type | |
| Hanning window [31,32] | Trigonometric function type | |
| Blackman window [33,34] | Trigonometric function type | |
| Gaussian window [35,36] | Exponential function type |
| Parameter Name | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 130 | 150 | 2335 | 0 |
| Parameter name | Mean Value [nV] | Standard Deviation [nV] | Noise Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | −0.19 | 61.45 | Gaussian noise |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, T.; Yao, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y. Electromagnetic Noise Suppression of Magnetic Resonance Sounding Combined with Data Acquisition and Multi-Frame Spectral Subtraction in the Frequency Domain. Electronics 2020, 9, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081254
Lin T, Yao X, Yu S, Zhang Y. Electromagnetic Noise Suppression of Magnetic Resonance Sounding Combined with Data Acquisition and Multi-Frame Spectral Subtraction in the Frequency Domain. Electronics. 2020; 9(8):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081254
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Tingting, Xiaokang Yao, Sijia Yu, and Yang Zhang. 2020. "Electromagnetic Noise Suppression of Magnetic Resonance Sounding Combined with Data Acquisition and Multi-Frame Spectral Subtraction in the Frequency Domain" Electronics 9, no. 8: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081254
APA StyleLin, T., Yao, X., Yu, S., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Electromagnetic Noise Suppression of Magnetic Resonance Sounding Combined with Data Acquisition and Multi-Frame Spectral Subtraction in the Frequency Domain. Electronics, 9(8), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081254





