3D Multiple Sound Source Localization by Proposed Cuboids Nested Microphone Array in Combination with Adaptive Wavelet-Based Subband GEVD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State of the Art-Sound Source Localization
3. Microphone Signal Model and Cuboids Nested Microphone Array
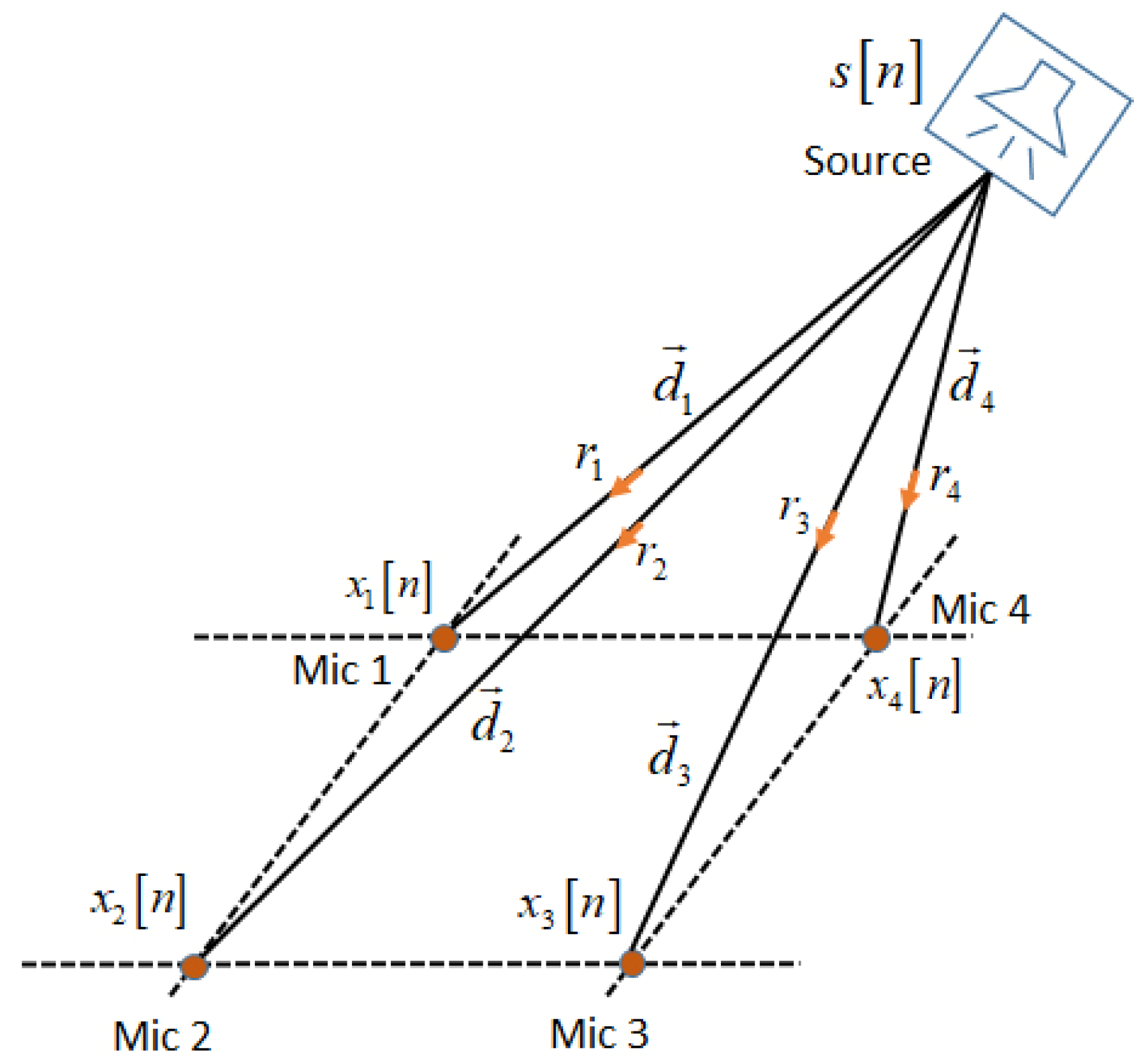
3.1. Microphone Signal Model in Localization Algorithms
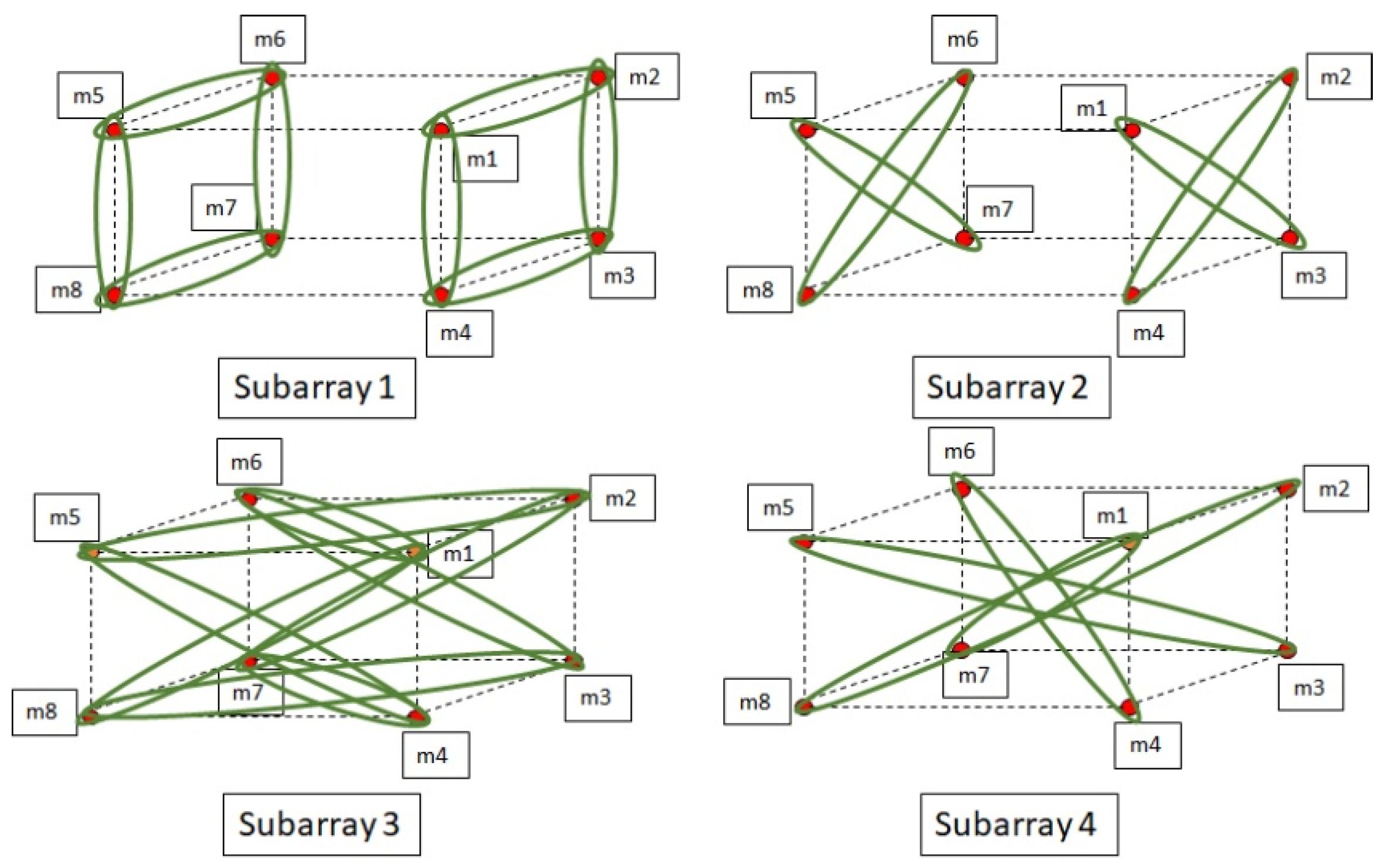
3.2. The Proposed Cuboids Nested Microphone Array for SSL
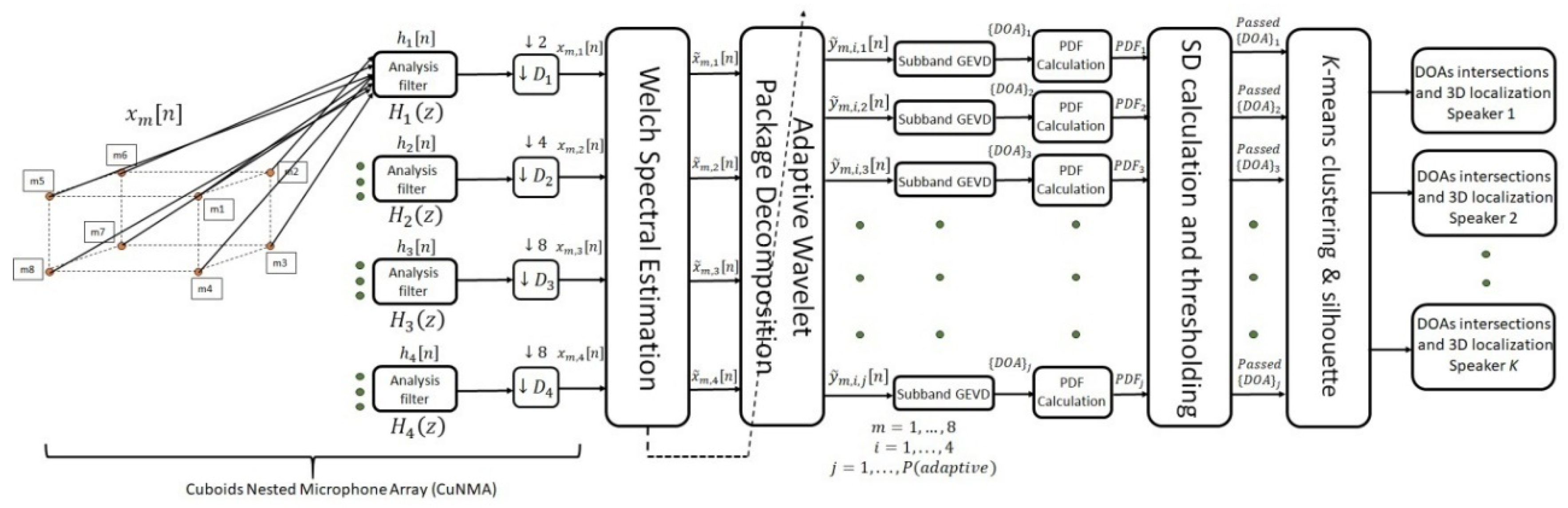
4. The Proposed Algorithm for Multiple SSL Based on SBGEVD
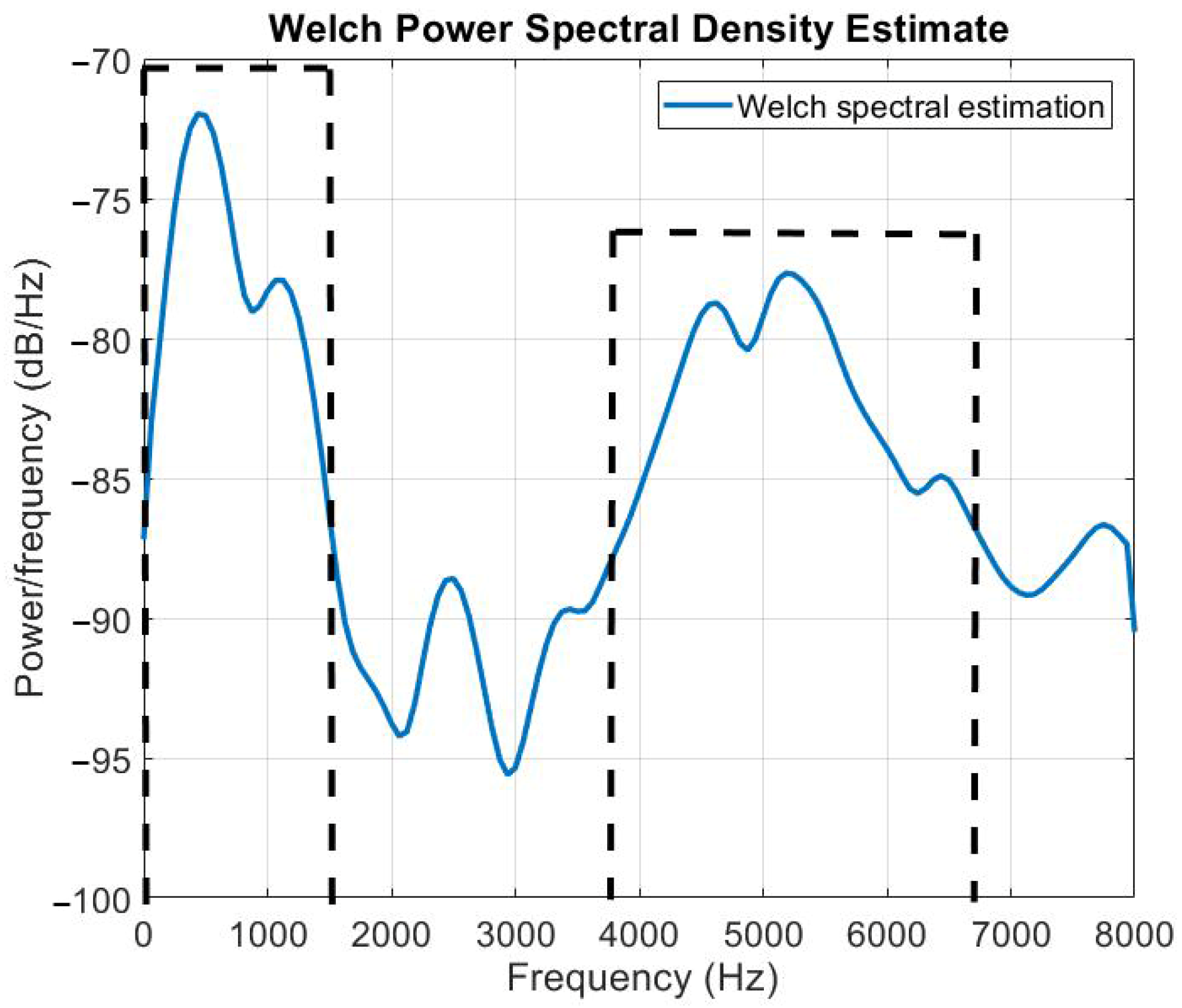
4.1. Spectral Estimation for Noise Reduction
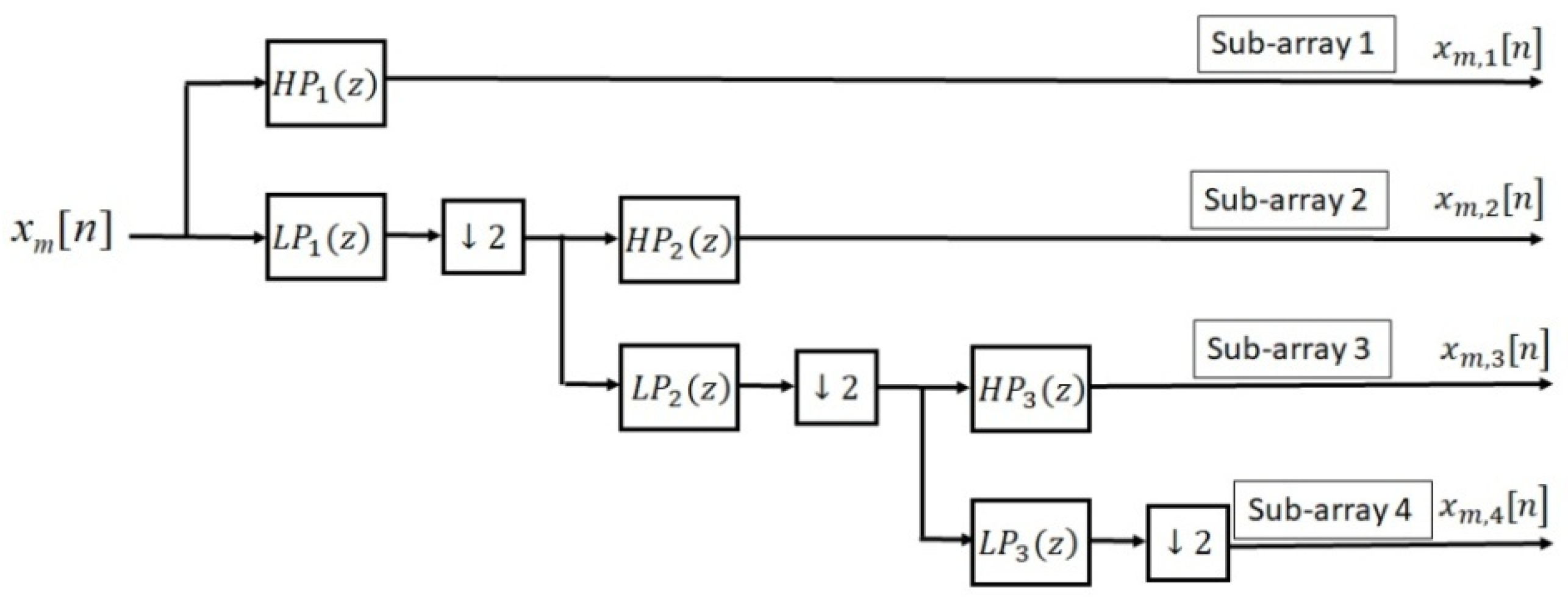
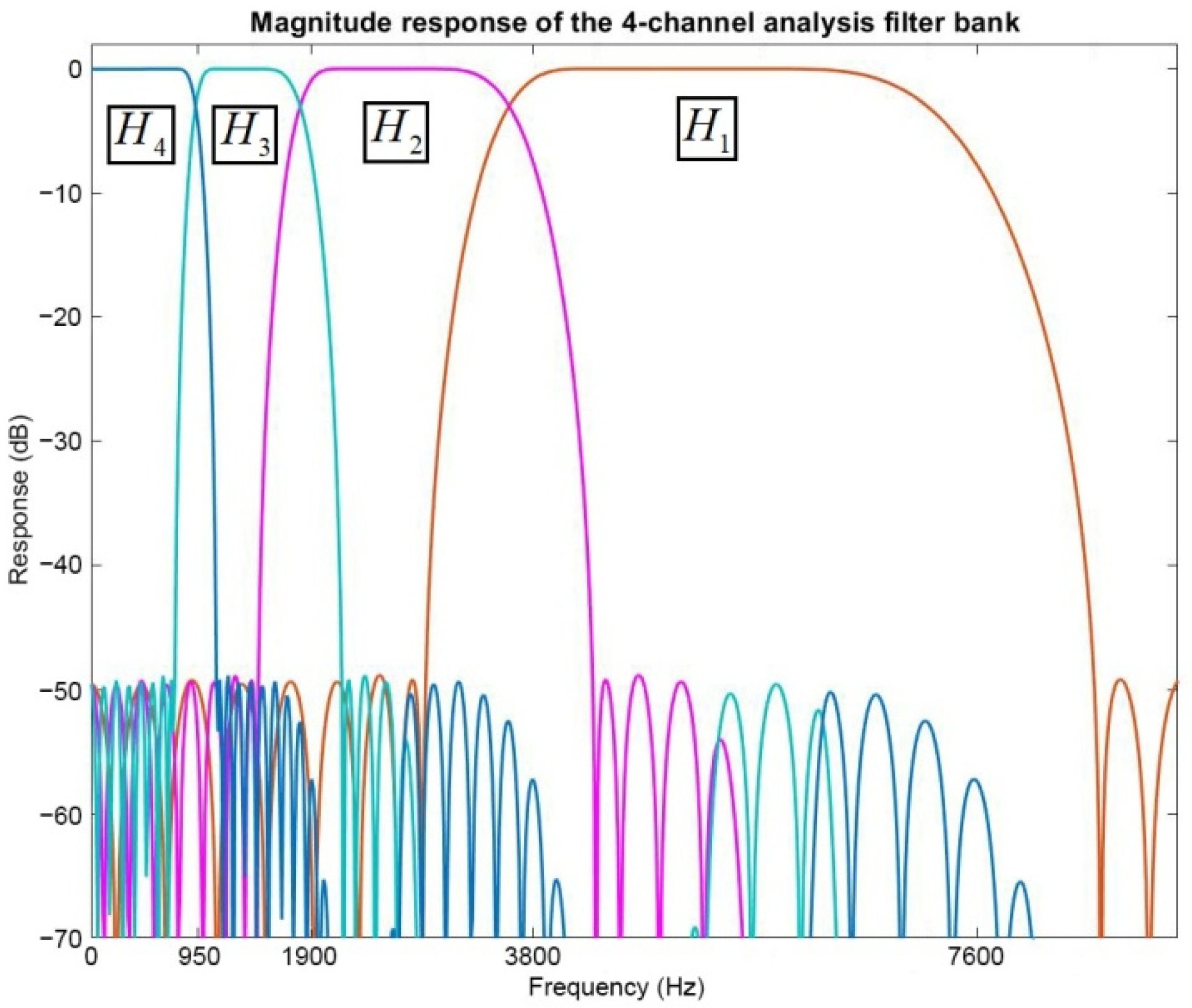
4.2. Adaptive Wavelet Transform
4.3. The Subband GEVD Algorithm for DOA Estimation
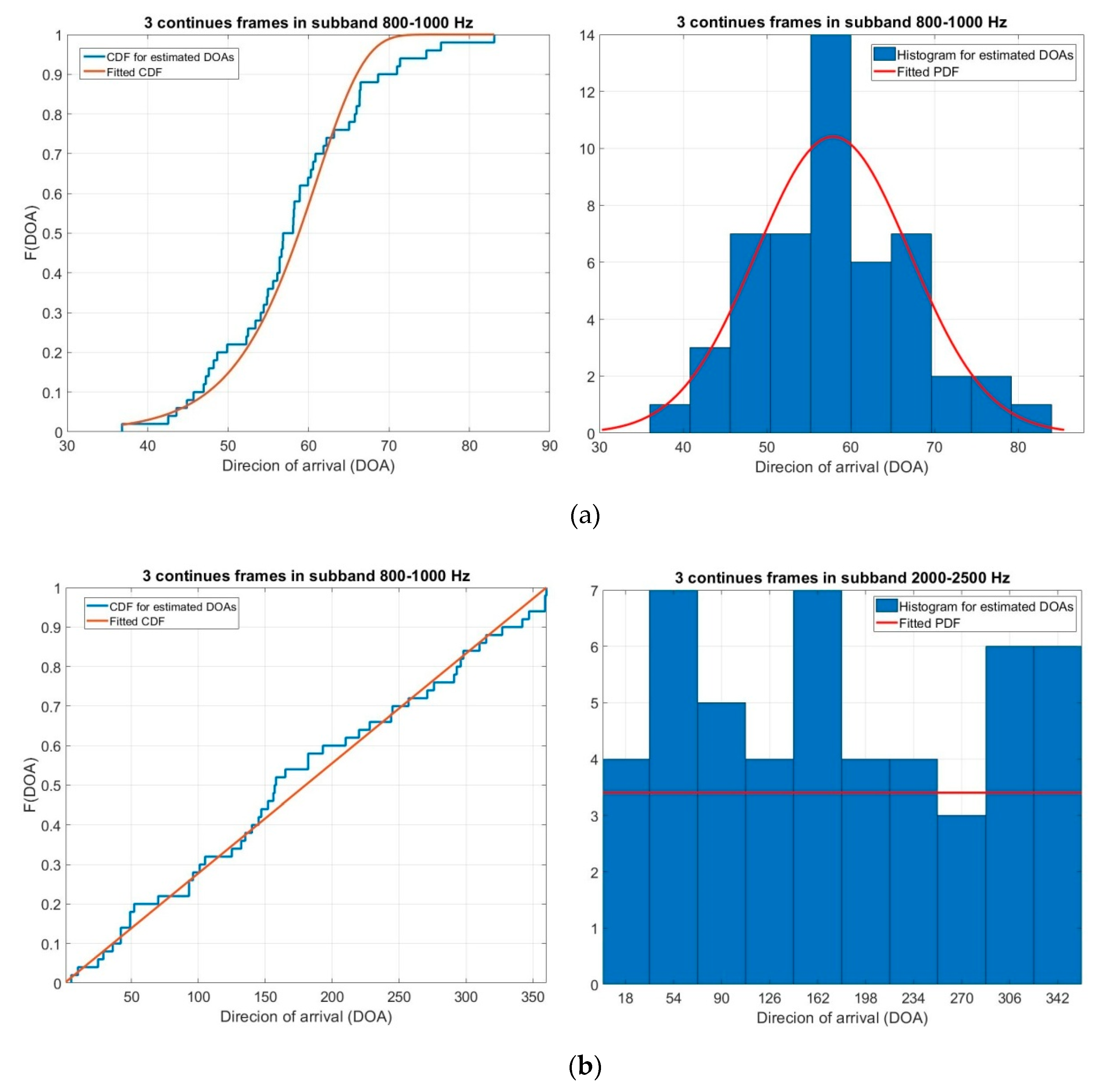
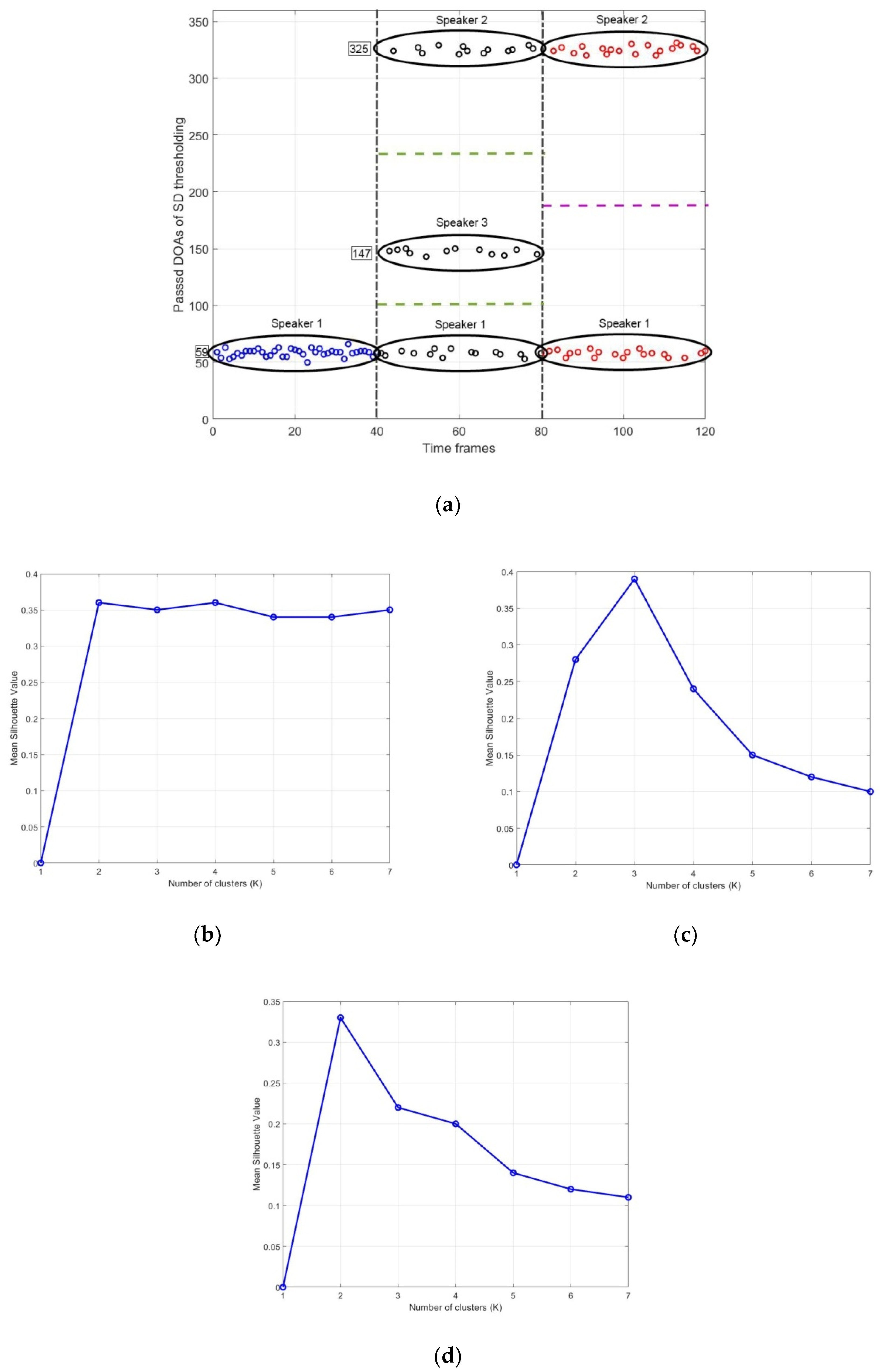
4.4. Clustering and 3D Sound Source Localization
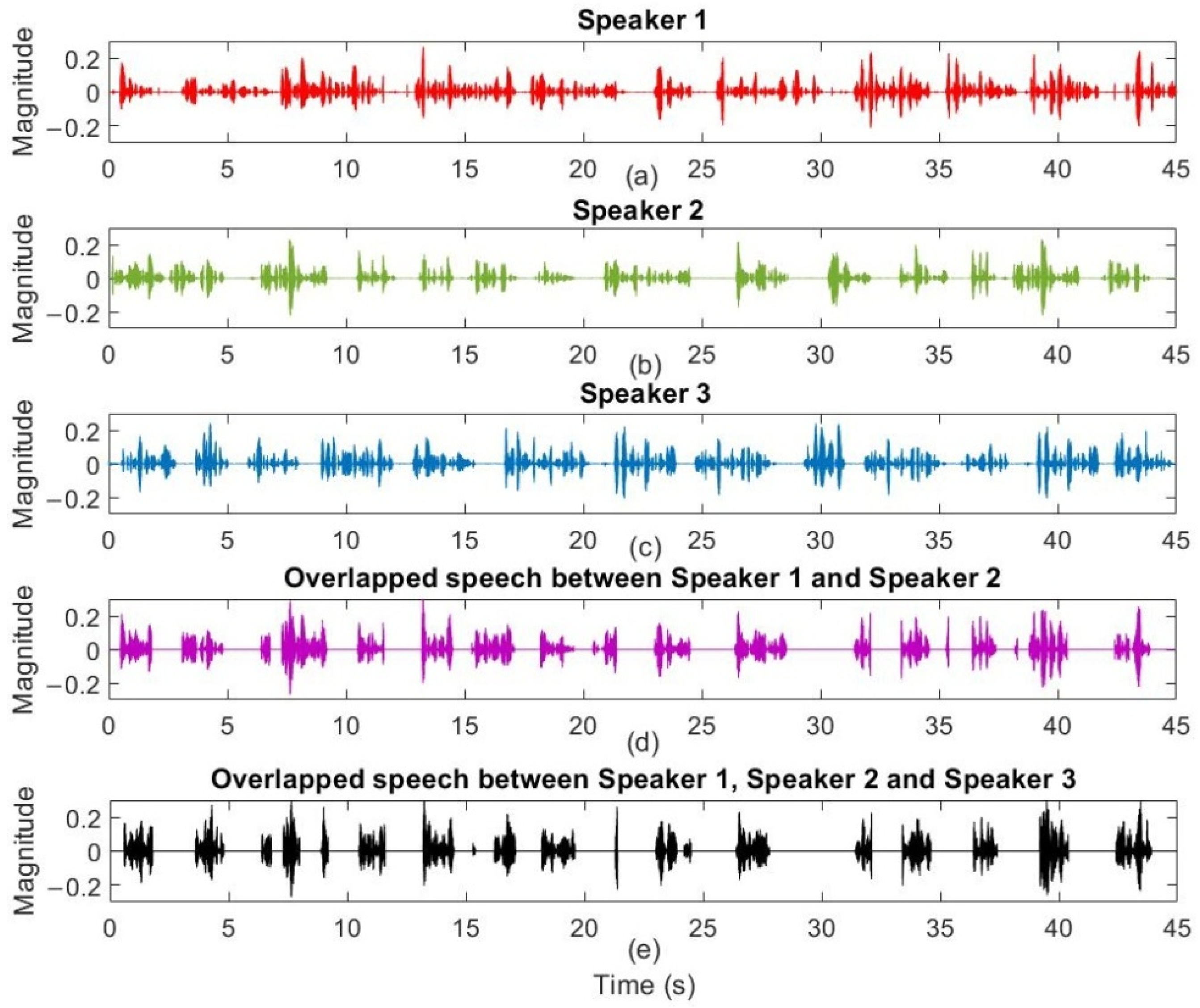
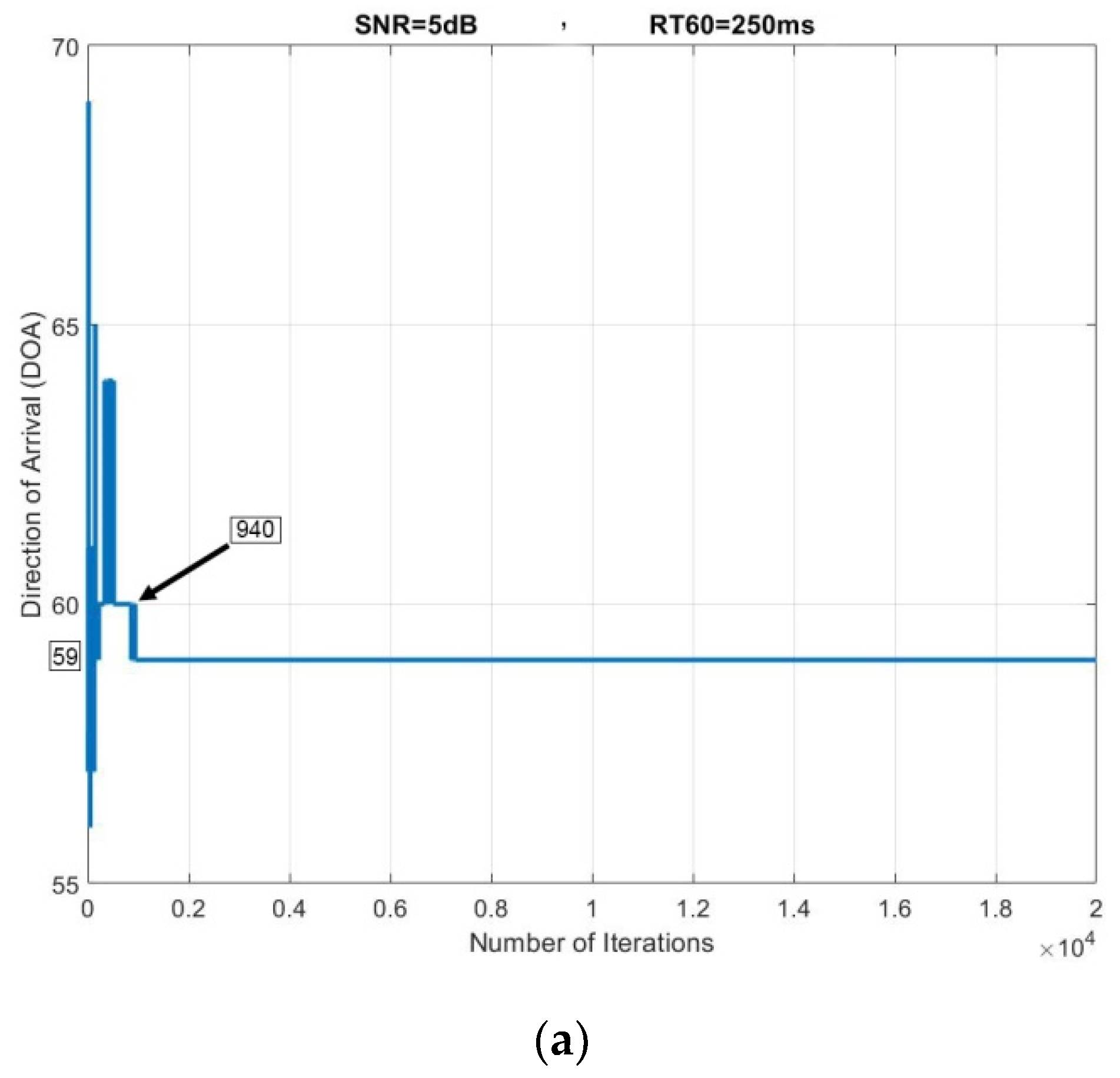
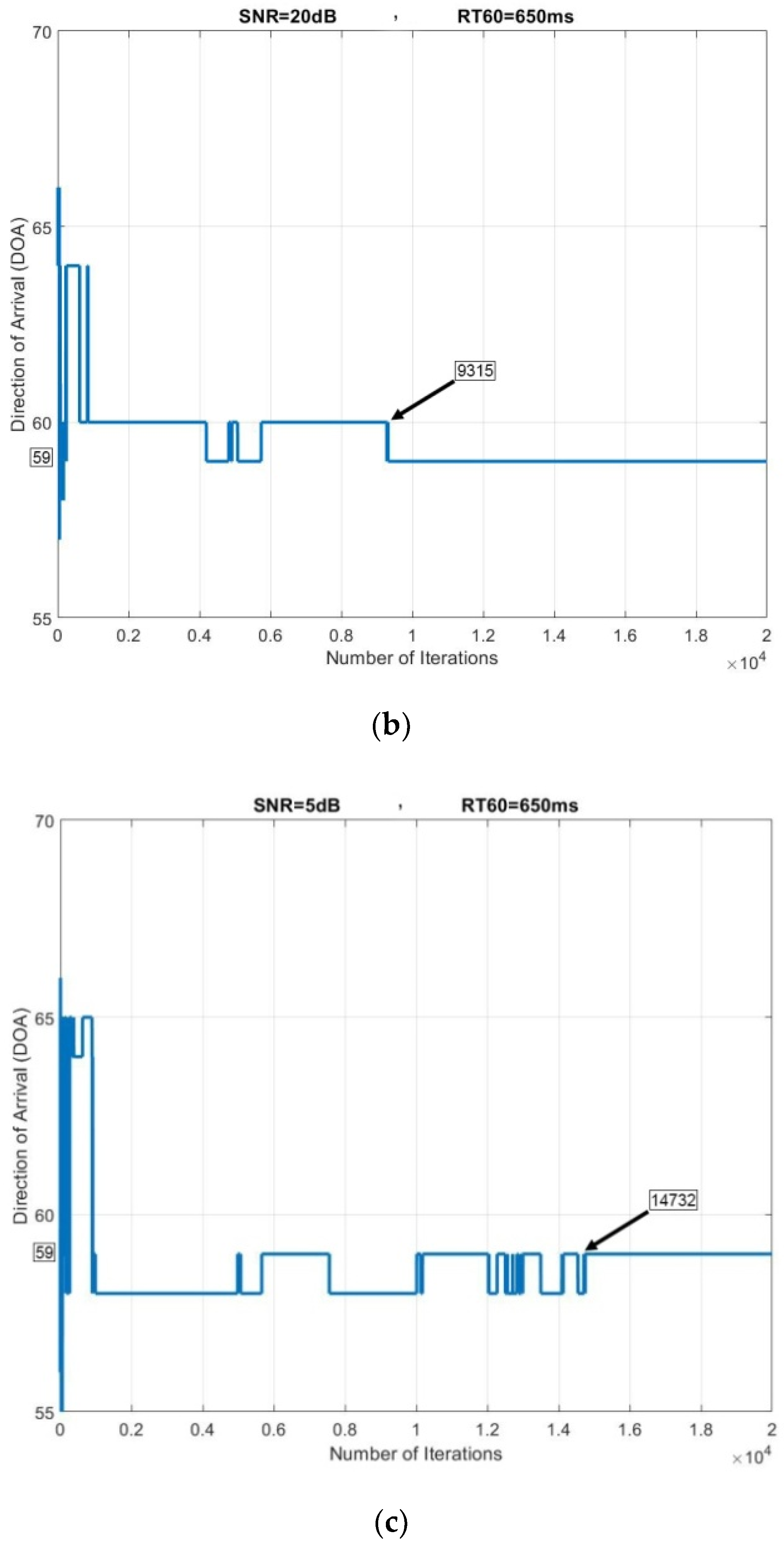
5. Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Autoregressive |
| ARMA | Autoregressive–moving-average |
| AWPD | Adaptive wavelet packet decomposition |
| CC | Cross-correlation |
| CPSP | Cross-power spectrum phase analysis |
| CuNMA | Cuboids nested microphone array |
| CuNMA-SBGEVD | Cuboids nested microphone array-sub-band generalized eigenvalue decomposition |
| CWT | Continues wavelet transform |
| DOA | Direction of arrival |
| DWT | Discrete wavelet transform |
| EM | Expectation-maximization |
| ESPRIT | Estimating signal parameters via rotational invariance technique |
| FIR | Finite impulse response |
| GEVD | Generalized eigenvalue decomposition |
| HAS | Hearing aids system |
| HiGRID | Hierarchical grid |
| HPF | High-pass filter |
| IDFT | Inverse discrete Fourier transform |
| LPF | Low-pass filter |
| MA | Moving average |
| MAEE | Mean absolute estimation error |
| ML | Maximum likelihood |
| MSV | Means silhouette value |
| MUSIC | Multiple signal classification |
| PCSF | Perpendicular cross-spectra fusion |
| Probability density function | |
| RTF | Relative transfer function |
| SBGEVD | Sub-band generalized eigenvalue decomposition |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SRP | Steered response power |
| SRPD | Steered response power density |
| SSL | Sound source localization |
| SSM-DNN | Spectral source model-deep neural network |
| TDOA | Time difference of arrival |
| TF-wise SSC | Time-frequency wise spatial spectrum clustering |
| W-DO | Windowed-disjoint orthogonality |
References
- Brandstein, M.; Ward, D. Microphone Arrays: Signal Processing Techniques and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y. Microphone Array Signal Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chu, P. Voice source localization for automatic camera pointing system in videoconferencing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 1997), Munich, Germany, 21–24 April 1997; pp. 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann, W. Beamforming for speech and audio signals. In Handbook of Signal Processing in Acoustics; Havelock, D., Kuwano, S., Vorländer, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 691–702. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, T.; Whitmire, E.; Novak, T.; Bozkurt, A. Sound localization sensors for search and rescue biobots. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 3444–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Waterschoot, T.V.; Moonen, M. Integration of a Priori and Estimated Constraints into an MVDR Beamformer for Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 2288–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Brutti, A.; Lanz, O.; Omologo, M.; Cavallaro, A. Multi-Speaker Tracking From an Audio–Visual Sensing Device. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 2576–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trees, H.L.V. Optimum Array Processing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, S.; Liu, W.; Mo, Y. Indoor localization based on curve fitting and location search using received signal strength. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzilla, M.A.; Harun, A.; Shahriman, A.B. Localization Assessment for Asset Tracking Deployment by Comparing an Indoor Localization System with a Possible Outdoor Localization System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Approach in Smart Systems Design and Applications (ICASSDA), Kuching, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vashist, A.; Bhanushali, D.R.; Relyea, R.; Hochgraf, C.; Ganguly, A.; Manoj, P.D.S.; Ptucha, R.; Kwasinski, A.; Kuhl, M.E. Indoor Wireless Localization Using Consumer-Grade 60 GHz Equipment with Machine Learning for Intelligent Material Handling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–6 January 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinni, G.; Avitabile, G.; Coviello, G. Narrowband distance evaluation technique for indoor positioning systems based on Zadoff-Chu sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE 13th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), Rome, Italy, 9–11 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Honma, N.; Sato, J.; Murakami, T.; Murata, K. Accuracy Comparison of Wireless Indoor Positioning Using Single Anchor: TOF only Versus TOF-DOA Hybrid Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Singapore, 10–13 December 2019; pp. 1679–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinni, G.; Avitabile, G.; Coviello, G.; Talarico, C. Analysis and Modeling of a Novel SDR-Based High-Precision Positioning System. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods and Applications to Circuit Design (SMACD), Prague, Czech Republic, 2–5 July 2018; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Low, K.S.; Nguyen, H.A. Optimizing the localization of a wireless sensor network in real time based on a low-cost microcontroller. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, S.; Moradi, H.; Shahabadi, M.; Mehdi Dehghan, S.M. RF source localization using reflection model in NLOS condition. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICROM), Tehran, Iran, 26–28 October 2016; pp. 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ji, B.; Song, R. Low-cost and High-accuracy LIDAR SLAM for Large Outdoor Scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Irkutsk, Russia, 4–9 August 2019; pp. 868–873. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, A.K.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Yu, K.; Sato, T. Detour Path Angular Information based Range Free Localization with Last Hop RSSI Measurement based Distance Calculation. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Mobile Computing and Ubiquitous Network (ICMU), Kathmandu, Nepal, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Guan, S.; Yue, X.; Gu, X.; Chen, J.; Lv, J.; Li, J. Energy-based sound source localization with low power consumption in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4894–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaely, B. Fundamentals of Spherical Array Processing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett, D.P.; Habets, E.A.P.; Naylor, P.A. Theory and Applications of Spherical Microphone Array Processing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, A.; Zheng, Y.; Buchner, H.; Kellermann, W. TDOA Estimation for Multiple Sound Sources in Noisy and Reverberant Environments Using Broadband Independent Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.O.; Martins, W.A.; Lima, M.V.S.; Biscainho, L.W.P.; Costa, M.V.M.; Gonçalves, F.N.; Said, A.; Lee, B. A Steered-Response Power Algorithm Employing Hierarchical Search for Acoustic Source Localization Using Microphone Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 5171–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krim, H.; Viberg, M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Moses, R. Introduction to Spectral Analysis; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple Emitter Location and Signal Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, AP-34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, K. ESPRIT-Estimation of Signal Parameters via Rotational Invariance Techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewfik, A.; Hong, W. On the application of uniform linear array bearing estimation techniques to uniform circular arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Morf, M. Signal subspace approach for multiple wide-band emitter location. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1983, 31, 1502–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiura, T.; Yamada, T.; Nakamura, S.; Shikano, K. Localization of multiple sound sources based on a CSP analysis with a microphone array. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2000), Istanbul, Turkey, 5–9 June 2000; pp. 1053–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.D.; Komatani, K.; Ogata, T.; Okuno, H.G. Evaluation of Two-Channel-Based Sound Source Localization using 3D Moving Sound Creation Tool. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Informatics Education and Research for Knowledge Circulating Society, Kyoto, Japan, 17 January 2008; pp. 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H. Reverberation Robust Feature Extraction for Sound Source Localization Using a Small-Sized Microphone Array. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 6331–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çöteli, M.B.; Olgun, O.; Hacıhabiboğlu, H. Multiple Sound Source Localization with Steered Response Power Density and Hierarchical Grid Refinement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 2215–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmani, M.; Pedersen, M.S.; Tan, Z.; Jensen, J. Informed Sound Source Localization Using Relative Transfer Functions for Hearing Aid Applications. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanakis, N.; Pavlidi, D.; Mouchtaris, A. Perpendicular Cross-Spectra Fusion for Sound Source Localization with a Planar Microphone Array. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Brown, G.J. Robust Binaural Localization of a Target Sound Source by Combining Spectral Source Models and Deep Neural Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 2122–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Pang, C.; Li, X. Multiple Sound Source Counting and Localization Based on TF-Wise Spatial Spectrum Clustering. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.; Rickard, S. Blind separation of speech mixtures via time-frequency masking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 52, 1830–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBiase, J.H. A High-Accuracy, Low-Latency Technique for Talker Localization in Reverberant Environments Using Microphone Arrays. Ph.D. Thesis, Brown University, Providence, RI, USA, May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.R.; Goubran, R.A.; El-Tanany, M. Experimental evaluation of a nested microphone array with adaptive noise cancellers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2004, 53, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santen, V.; Sproat, J. High-accuracy automatic segmentation. In Proceedings of the EUROSPEECH, Budapest, Hungary, 5–9 September 1999; pp. 2809–2812. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.M. Modern Spectral Estimation: Theory and Application; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Firoozabadi, A.D.; Abutalebi, H.R. Extension and Improvement of the Methods for the Localization of Multiple Simultaneous Speech Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, Yazd University, Yazd, Iran, 2015; pp. 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Mamatha, I.; Tripathi, S.; Sudarshan, T.S.B. Convolution based efficient architecture for 1-D DWT. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation, Greater Noida, India, 5–6 May 2017; pp. 1436–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Ghodrati Amiri, G.; Asadi, A. Comparison of Different Methods of Wavelet and Wavelet Packet Transform in Processing Ground Motion Records. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 7, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Doclo, S.; Moonen, M. Robust Adaptive Time Delay Estimation for Speaker Localization in Noisy and Reverberant Acoustic Environments. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. 2003, 11, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.R. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Garofolo, J.S.; Lamel, L.F.; Fisher, W.M.; Fiscus, J.G.; Pallett, D.S.; Dahlgren, N.L.; Zue, V. TIMIT Acoustic-Phonetic Continuous Speech Corpus LDC93S1. Web Download. Philadelphia: Linguistic Data Consortium. 1993. Available online: https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC93S1 (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Cetin, O.; Shriberg, E. Analysis of overlaps in meetings by dialog factors, hot spots, speakers, and collection site: Insights for automatic speech recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Pittsburg, PA, USA, 17–21 September 2006; pp. 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.; Berkley, D. Image method for efficiently simulating small-room acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 65, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

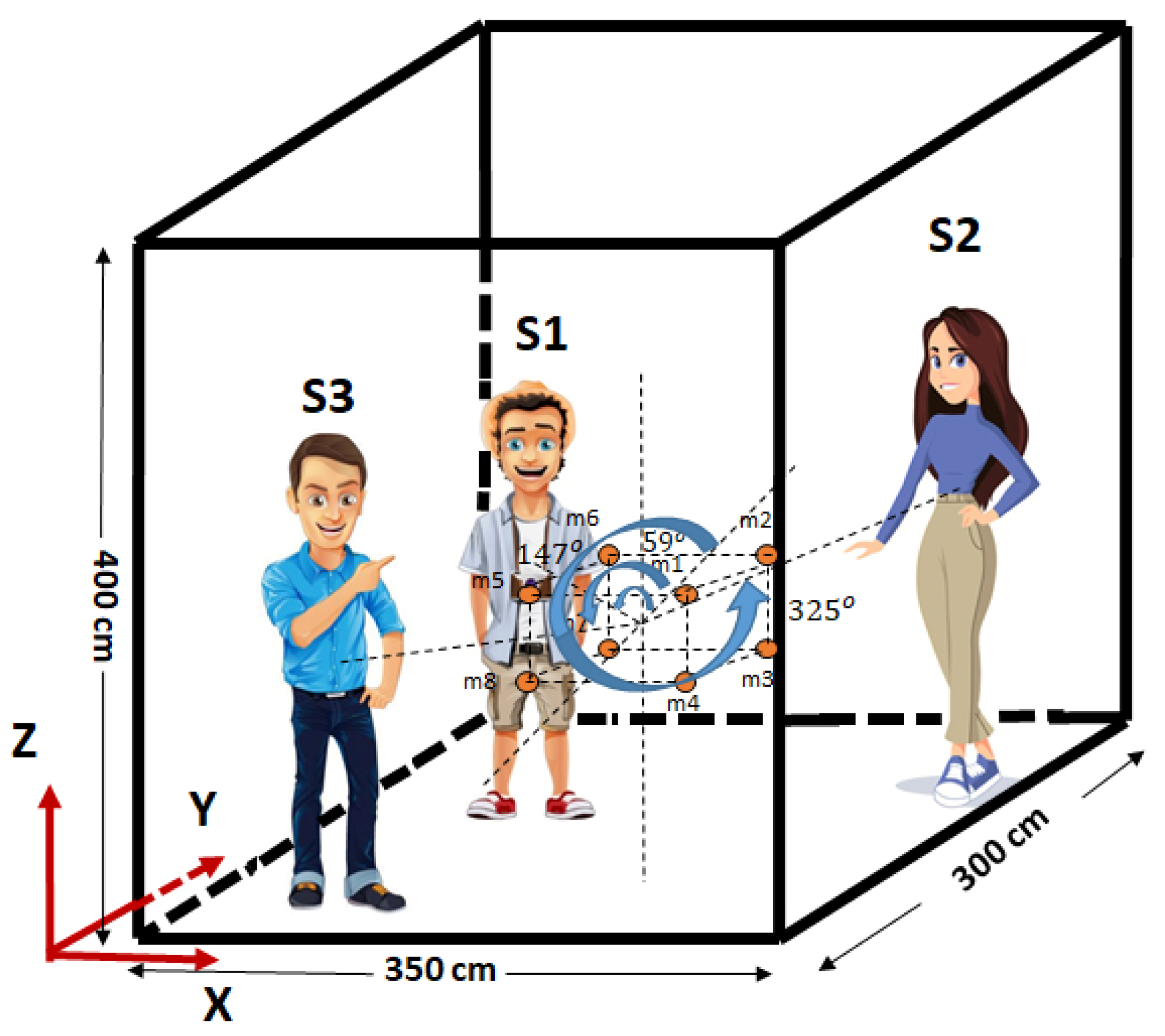
| Positions | X, cm | Y, cm | Z, cm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microphone 1 (m1) | 179.5 | 148.8 | 121.2 |
| Microphone 2 (m2) | 179.5 | 151.1 | 121.2 |
| Microphone 3 (m3) | 179.5 | 151.1 | 118.9 |
| Microphone 4 (m4) | 179.5 | 148.8 | 118.9 |
| Microphone 5 (m5) | 170.5 | 148.8 | 121.2 |
| Microphone 6 (m6) | 170.5 | 151.1 | 121.2 |
| Microphone 7 (m7) | 170.5 | 151.1 | 118.9 |
| Microphone 8 (m8) | 170.5 | 148.8 | 118.9 |
| Speaker 1 | 60 | 220 | 170 |
| Speaker 2 | 310 | 245 | 175 |
| Speaker 3 | 95 | 75 | 180 |
| Room Dimension | 350 | 300 | 400 |
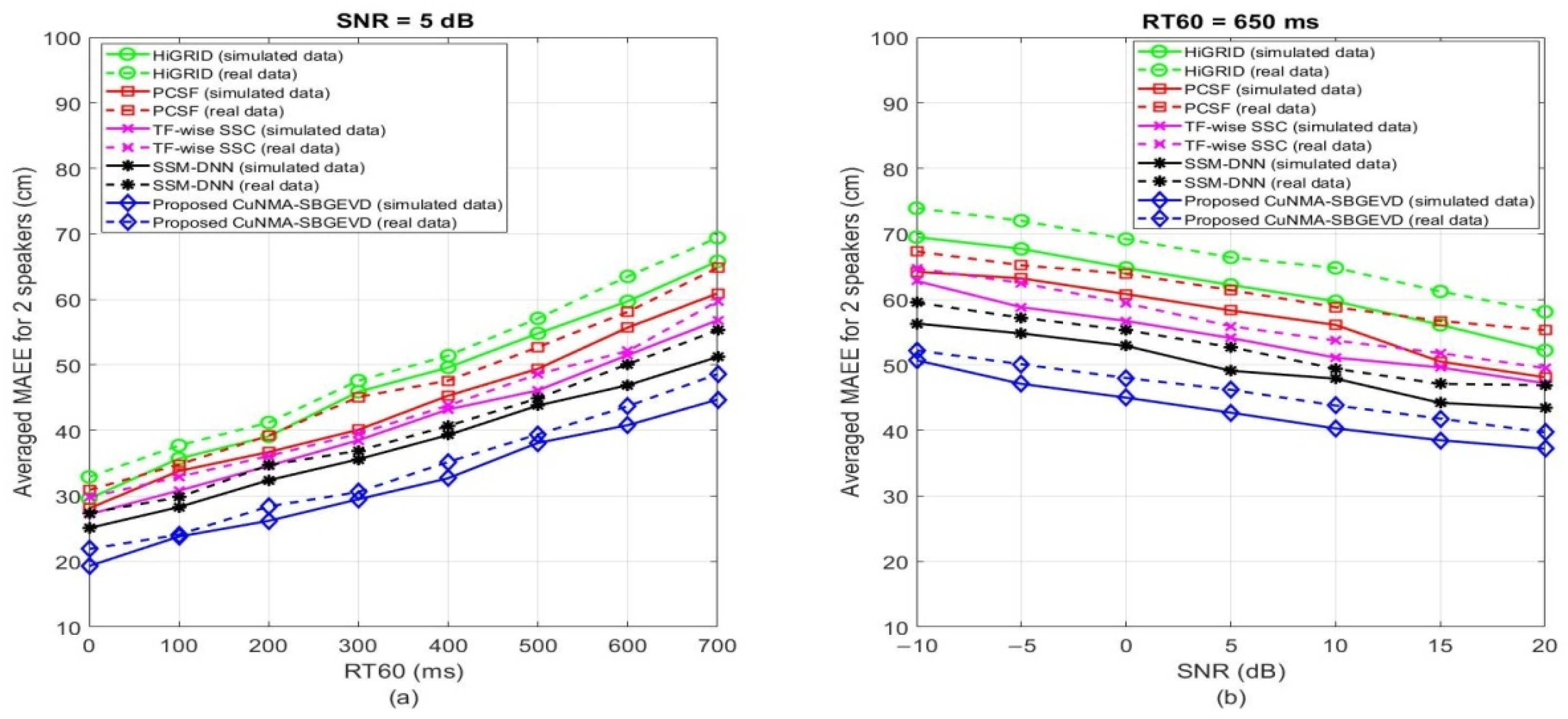
| MAEE (cm) | HiGRID [33] | PCSF [35] | TF-Wise SSC [37] | SSM-DNN [36] | Proposed CuNMA-SBGEVD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated Data | ||||||||||
| Speaker | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 |
| Scenario 1 | 51 | 53 | 46 | 50 | 45 | 49 | 43 | 44 | 36 | 38 |
| Scenario 2 | 40 | 44 | 37 | 39 | 34 | 38 | 32 | 36 | 25 | 29 |
| Scenario 3 | 59 | 65 | 55 | 61 | 54 | 55 | 48 | 51 | 41 | 43 |
| Real Data | ||||||||||
| Speaker | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 | S1 | S2 |
| Scenario 1 | 55 | 62 | 55 | 54 | 46 | 52 | 45 | 47 | 37 | 41 |
| Scenario 2 | 43 | 46 | 41 | 44 | 36 | 39 | 36 | 33 | 26 | 30 |
| Scenario 3 | 64 | 68 | 61 | 63 | 53 | 61 | 44 | 54 | 45 | 46 |
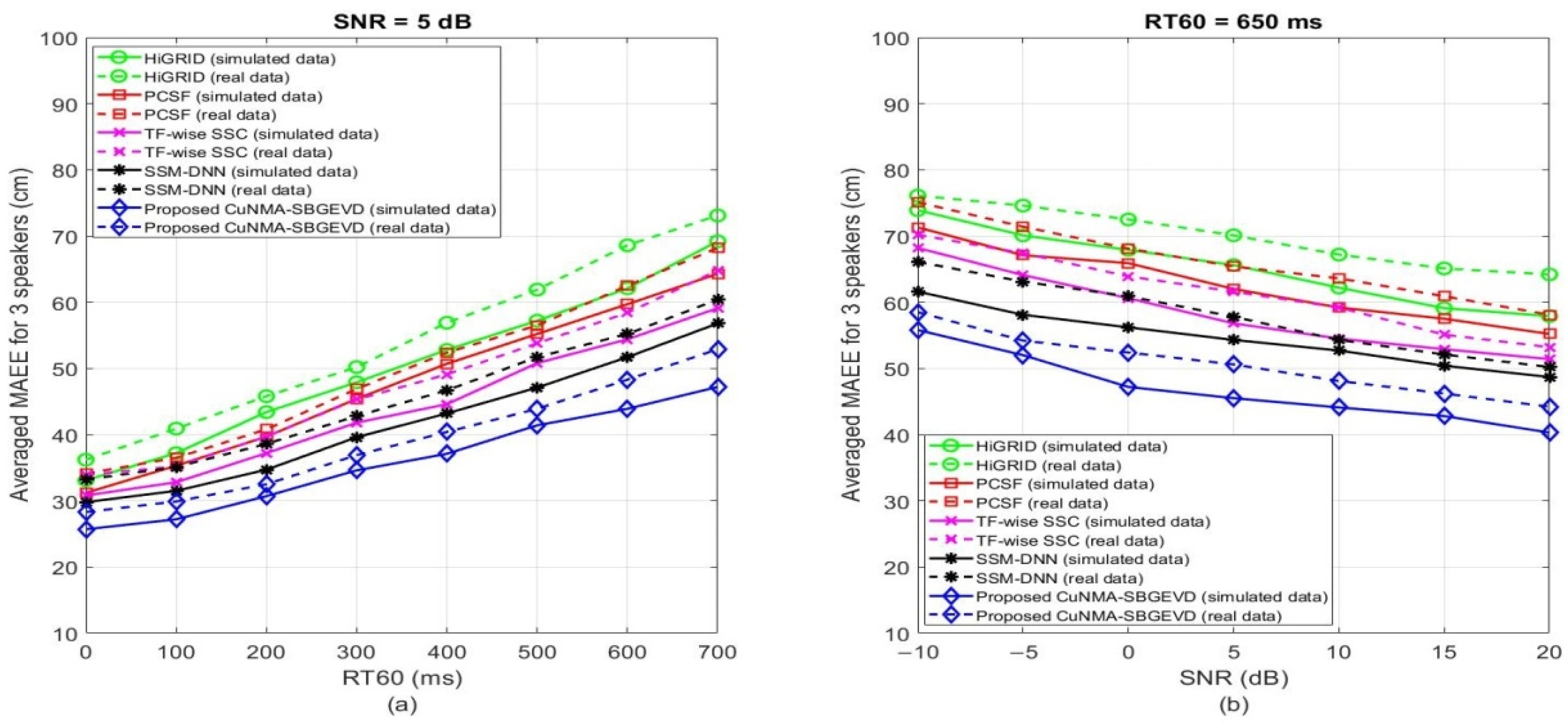
| MAEE (cm) | HiGRID [33] | PCSF [35] | TF-wise SSC [37] | SSM-DNN [36] | Proposed CuNMA-SBGEVD | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated Data | |||||||||||||||
| Speaker | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| Scenario 1 | 55 | 54 | 59 | 53 | 56 | 58 | 48 | 50 | 54 | 43 | 48 | 47 | 41 | 39 | 44 |
| Scenario 2 | 43 | 46 | 47 | 39 | 43 | 44 | 39 | 42 | 40 | 34 | 37 | 39 | 28 | 29 | 32 |
| Scenario 3 | 65 | 67 | 64 | 58 | 63 | 61 | 57 | 56 | 59 | 54 | 56 | 54 | 39 | 42 | 49 |
| Real Data | |||||||||||||||
| Speaker | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
| Scenario 1 | 65 | 63 | 69 | 59 | 55 | 61 | 53 | 51 | 56 | 45 | 53 | 50 | 38 | 45 | 43 |
| Scenario 2 | 45 | 47 | 51 | 43 | 44 | 46 | 38 | 42 | 44 | 35 | 42 | 43 | 29 | 34 | 35 |
| Scenario 3 | 68 | 71 | 72 | 59 | 65 | 68 | 59 | 65 | 61 | 53 | 57 | 59 | 42 | 51 | 50 |
| Run-time (s) | HiGRID [33] | PCSF [35] | TF-wise SSC [37] | SSM-DNN [36] | Proposed CuNMA-SBGEVD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Simultaneous Speakers | |||||
| Scenario 1 | 641 | 548 | 446 | 589 | 453 |
| Scenario 2 | 592 | 529 | 419 | 557 | 438 |
| Scenario 3 | 668 | 570 | 474 | 612 | 462 |
| 3 Simultaneous Speakers | |||||
| Scenario 1 | 693 | 596 | 466 | 607 | 459 |
| Scenario 2 | 659 | 572 | 437 | 582 | 448 |
| Scenario 3 | 724 | 634 | 495 | 637 | 483 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dehghan Firoozabadi, A.; Irarrazaval, P.; Adasme, P.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Palacios-Játiva, P.; Azurdia-Meza, C. 3D Multiple Sound Source Localization by Proposed Cuboids Nested Microphone Array in Combination with Adaptive Wavelet-Based Subband GEVD. Electronics 2020, 9, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050867
Dehghan Firoozabadi A, Irarrazaval P, Adasme P, Zabala-Blanco D, Palacios-Játiva P, Azurdia-Meza C. 3D Multiple Sound Source Localization by Proposed Cuboids Nested Microphone Array in Combination with Adaptive Wavelet-Based Subband GEVD. Electronics. 2020; 9(5):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050867
Chicago/Turabian StyleDehghan Firoozabadi, Ali, Pablo Irarrazaval, Pablo Adasme, David Zabala-Blanco, Pablo Palacios-Játiva, and Cesar Azurdia-Meza. 2020. "3D Multiple Sound Source Localization by Proposed Cuboids Nested Microphone Array in Combination with Adaptive Wavelet-Based Subband GEVD" Electronics 9, no. 5: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050867
APA StyleDehghan Firoozabadi, A., Irarrazaval, P., Adasme, P., Zabala-Blanco, D., Palacios-Játiva, P., & Azurdia-Meza, C. (2020). 3D Multiple Sound Source Localization by Proposed Cuboids Nested Microphone Array in Combination with Adaptive Wavelet-Based Subband GEVD. Electronics, 9(5), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050867








