Touch-Based Dual-Band System Combined Human Body Communication and Wireless LAN for Wearable Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Network Protocol of Dual-Band Application System
2.1. Touch-Based Dual-Band Communication
2.2. Physical Signaling
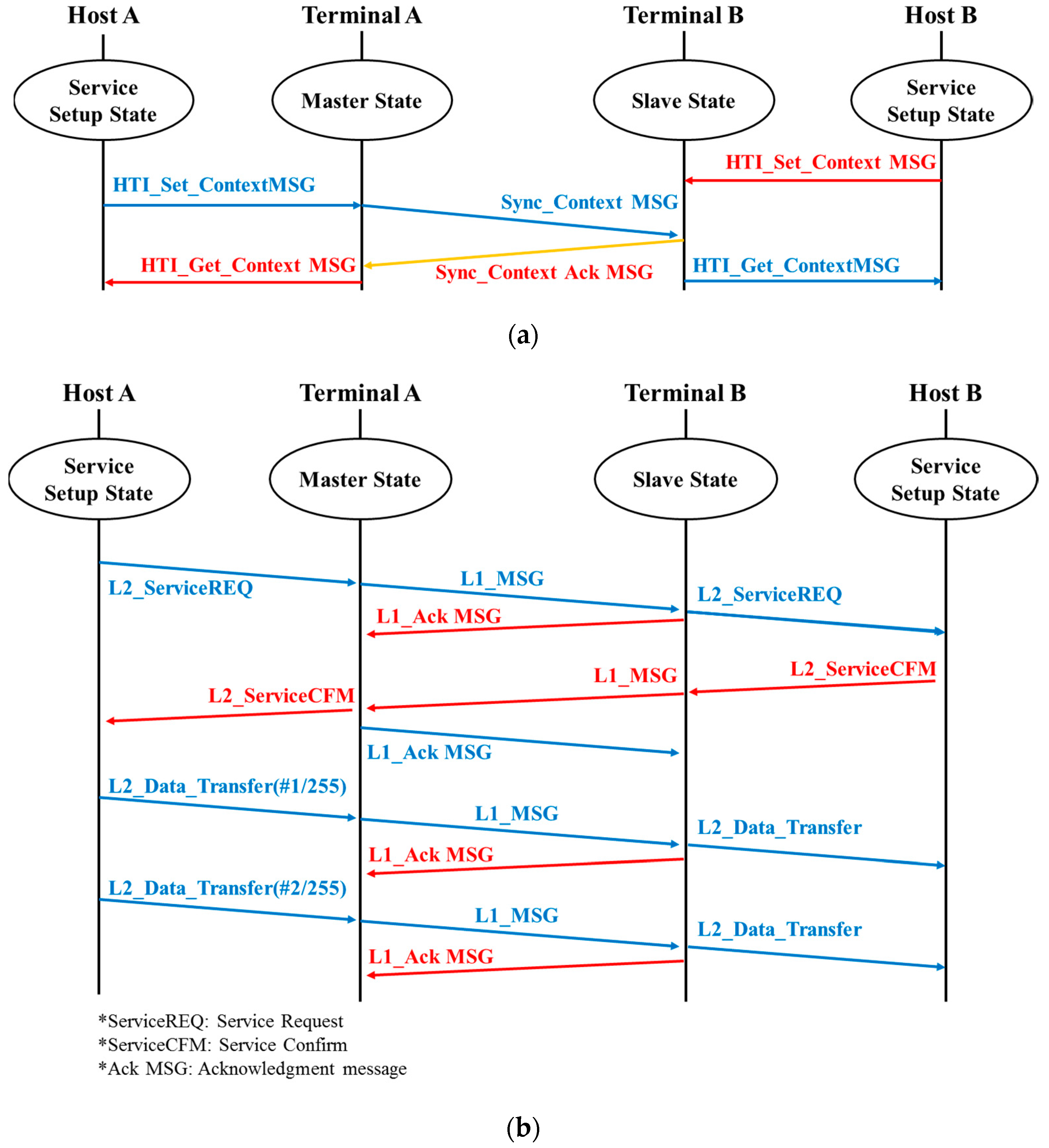
2.3. Nework Setup
2.4. Data Transfer
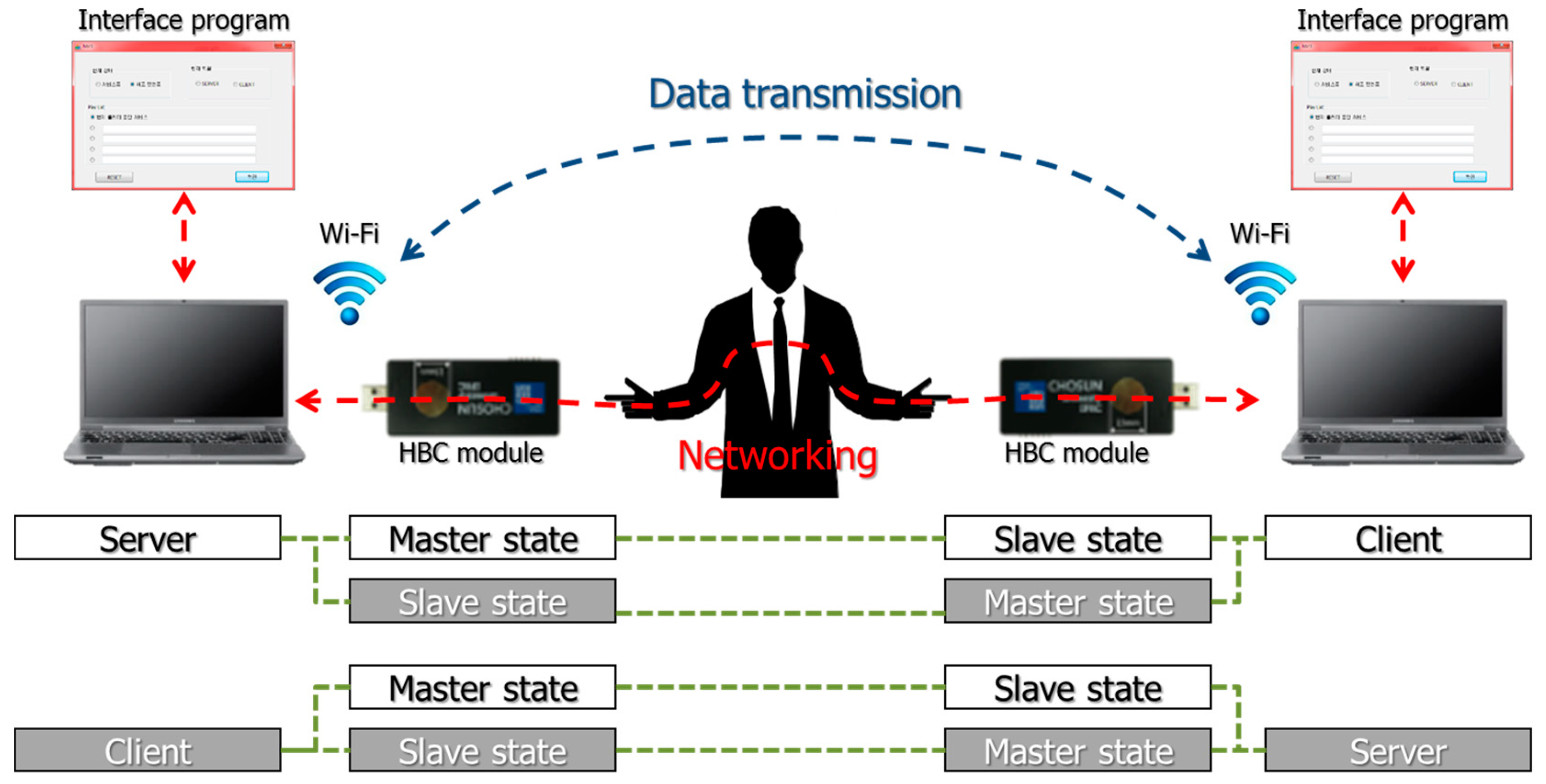
2.5. System Configuration
3. Demonstration of Dual-Band Application System
3.1. Dual-Band Service
3.2. Service Scenario and Demonstration
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinstein, R. RFID: A technical overview and its application to the enterprise. IT Prof. 2005, 7, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, V.; Ozdenizci, B.; Ok, K. A survey on near field communication (NFC) technology. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2013, 71, 2259–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluetooth Special Interest Group Bluetooth Core Specification Version 4.2; Bluetooth Core Specif. Version 4.2. 2014, p. 2684. Available online: https://www.bluetooth.org/en-us/specification/adopted-specifications (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- IEEE 802.11. IEEE Std 802.11-2012 (Revision IEEE Std 802.11-2007) 2012. 2012, p. 2793. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/standard/802_11-2012.html (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Camps-Mur, D.; Garcia-Saavedra, A.; Serrano, P. Device-to-device communications with WiFi Direct: Overview and experimentation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2013, 20, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, T.G. Personal area networks: Near-field intrabody communication. IBM Syst. J. 1996, 35, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.G.; Kim, T.K.; Bong, S.T.; Hwang, J.H.; Hyung, C.H.; Kang, S.W. Context aware service using intra-body communication. In Proceedings of the Fourth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Pisa, Italy, 13–17 March 2006; pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.G.; Kim, J.K.; Sung, J.B.; Hwang, J.H.; Hyung, C.H.; Kang, S.W. TAP: Touch-and-play. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 22–27 April 2006; pp. 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- La Polla, M.; Martinelli, F.; Sgandurra, D. A Survey on Security for Mobile Devices. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 446–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negra, R.; Jemili, I.; Belghith, A. Wireless Body Area Networks: Applications and Technologies. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 83, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Wang, J. Applications, challenges, and prospective in emerging body area networking technologies. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2010, 17, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Leung, V.; Chow, C.; Chan, H. Enabling technologies for wireless body area networks: A survey and outlook. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Standards Association IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks—Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE Stand. Inf. Technol. 2012, 802, 1–271.
- Chung, C.C.; Chang, C.T.; Lin, C.Y. A 1 Mb/s-40 Mb/s human body channel communication transceiver. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test, VLSI-DAT, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 27–29 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, N.; Yan, L.; Bae, J.; Yoo, H.-J. A 60 kb/s--10 Mb/s adaptive frequency hopping transceiver for interference-resilient body channel communication. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 2009, 44, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Jang, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, K.J.; Bae, J.; Yoo, H.J. A 79 pJ/b 80 Mb/s full-duplex transceiver and a 42.5μW 100 kb/s super-regenerative transceiver for body channel communication. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 2016, 51, 310–317. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, J.; Song, K.; Lee, H.; Cho, H.; Yoo, H.J. A 0.24-nJ/b wireless body-area-network transceiver with scalable double-FSK modulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 2012, 47, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand Gopalan, S. Energy-efficient MAC protocols for wireless body area networks: Survey. Int. Congr. Ultra Mod. Telecommun. Control Syst. 2010, 739–744. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.I.; Lim, I.G.; Kang, S.; Kim, W.W. Human body communication system with FSBT. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Consumer Electronics, Braunschweig, Germany, 7–10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Ito, K. Evaluation of the Received Signal Level in Relation to the Size and Carrier Frequencies of the Wearable Device Using Human Body as a Transmission Channel. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2004; Volume 1, pp. 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.; Qiao, M.; Carpenter, A. Security of the Near Field Communication Protocol: An Overview. J. Comput. Sci. Coll. 2013, 29, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Vipul, C.; Dong, S.H. An overview of passive RFID. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2007, 45, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, C.; Lee, D.G.; Han, J. A Proposal of Security Framework for Wireless Body Area Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security Technology, Hainan Island, China, 13–15 December 2008; pp. 202–205. [Google Scholar]





| Characteristics | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Modulation | Frequency Selective Digital Transmission |
| Duplexing | Time Division Duplexing |
| Frequency | 8–22 MHz |
| Power supply | 3.3 V |
| Power consumption | 194.7 mW |
| Size | 34 mm × 87 mm |
| Electrode type | Metal electrode, Transparent electrode |
| Characteristics | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Size | 22 mm × 48 mm × 0.7 mm |
| Conductivity (S/m) | 0.12 × 106 |
| Resistance (Ω/sq) | 8.6 |
| Dielectric constant (εr) | 5.7 |
| Transmittance in visible spectrum | 69% < T < 86% |
| Characteristics | NFC | RFID | HBC | Wi-Fi | Proposed Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data rate | Poor (424 kbps) | Poor (40 kbps) | Fair (10 Mbps) | Good (54 Mbps) | Good (54 Mbps) |
| Service area | Poor (10 cm) | Fair (7 to 15 cm) | Poor (touch) | Good (90 m) | Good (touch + 90 m) |
| Connection frequency | 13.56 MHz | 13.56 MHz | 8–22 MHz | 2.4 GHz | 8–22 MHz |
| Set-up time | Good (0.1 s) | Good (0.1 s) | Fair (1 s) | Poor (3–5 s) | Fair (1 s) |
| Power consumption | Good (42 dBµA/m @ 10 m) | Good (42 dBµA/m @ 10 m) | Fair (194.7 mW) | Poor (975 mW) | Poor (194.7 + 975 mW) |
| Security | Fair | Poor | Good | Fair | Good |
| Accessibility | Good | Good | Good | Fair | Good |
| Feature | Full duplexing | Half duplexing | Need contact | Need access point | Easy networking |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.; Baek, J.J.; Kim, S.W.; Jeong, M.J.; Kim, Y.T. Touch-Based Dual-Band System Combined Human Body Communication and Wireless LAN for Wearable Devices. Electronics 2019, 8, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030335
Park K, Baek JJ, Kim SW, Jeong MJ, Kim YT. Touch-Based Dual-Band System Combined Human Body Communication and Wireless LAN for Wearable Devices. Electronics. 2019; 8(3):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030335
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kunho, Jong Jin Baek, Se Woong Kim, Min Joo Jeong, and Youn Tae Kim. 2019. "Touch-Based Dual-Band System Combined Human Body Communication and Wireless LAN for Wearable Devices" Electronics 8, no. 3: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030335
APA StylePark, K., Baek, J. J., Kim, S. W., Jeong, M. J., & Kim, Y. T. (2019). Touch-Based Dual-Band System Combined Human Body Communication and Wireless LAN for Wearable Devices. Electronics, 8(3), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030335






