A Hierarchical Vision-Based UAV Localization for an Open Landing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Previous Work
3. Feature Recognition and Pose Recovery
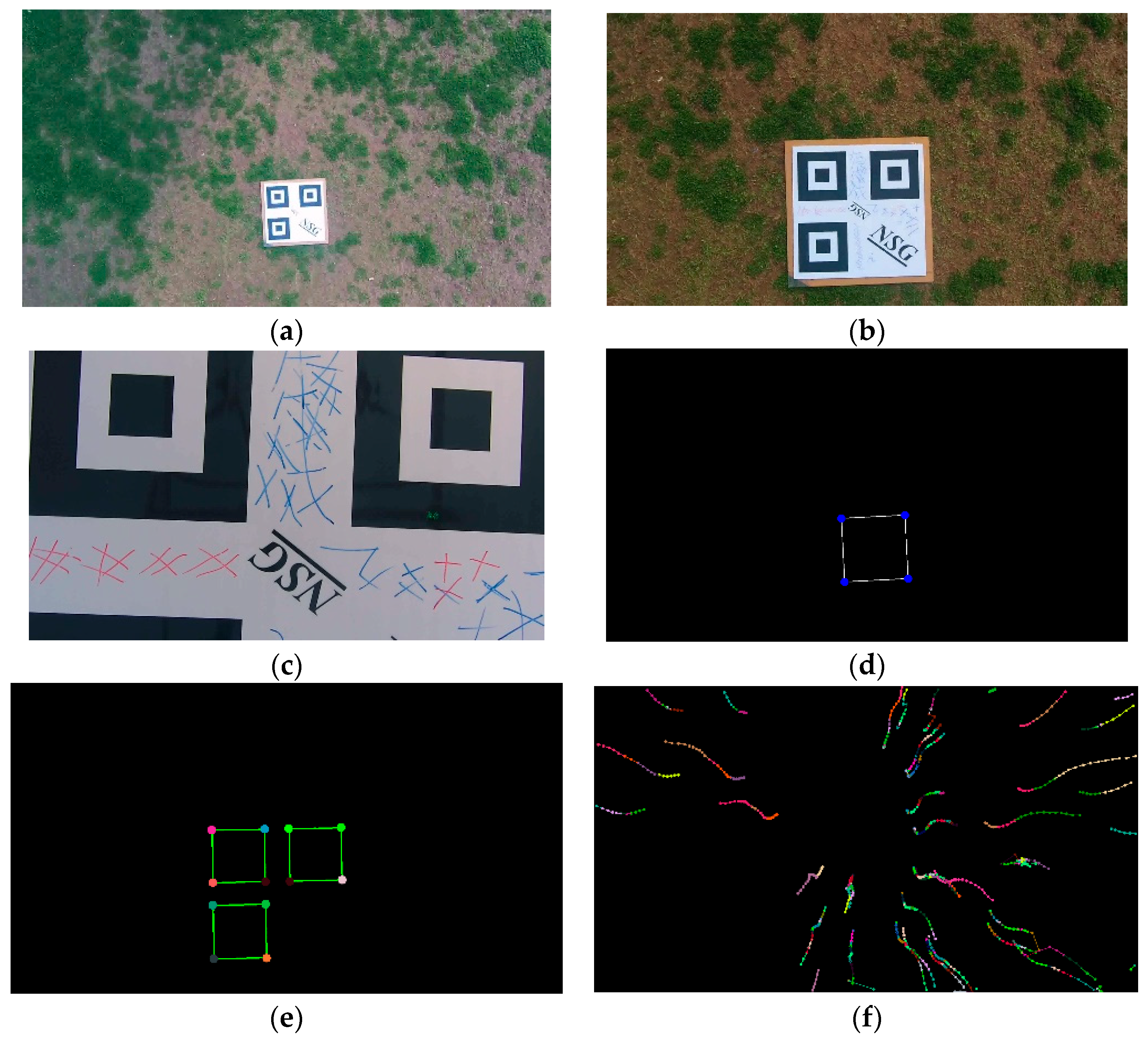
3.1. The RQRLP as Landing Object
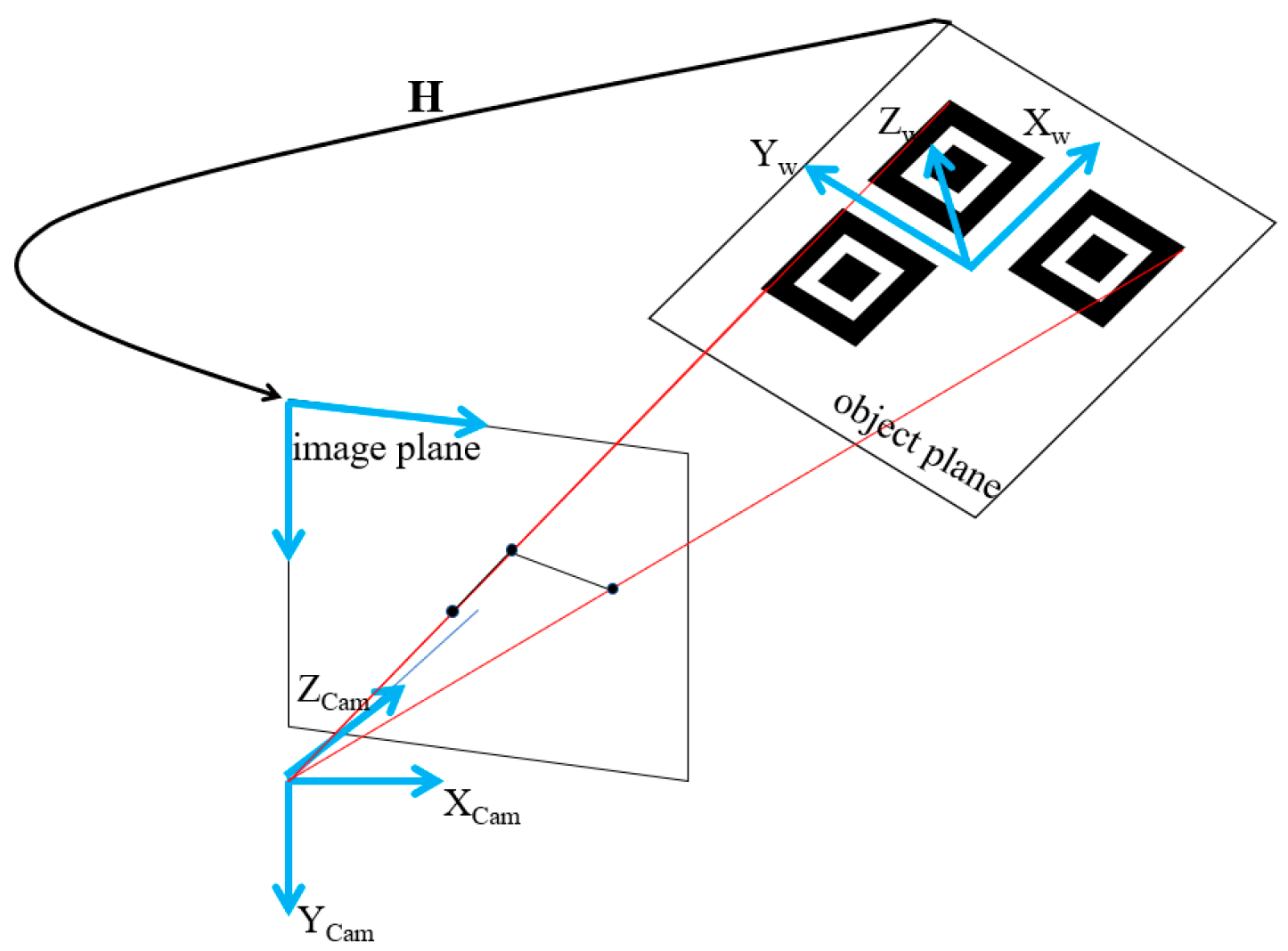
3.2. Pose Recovery Based on Image Homography
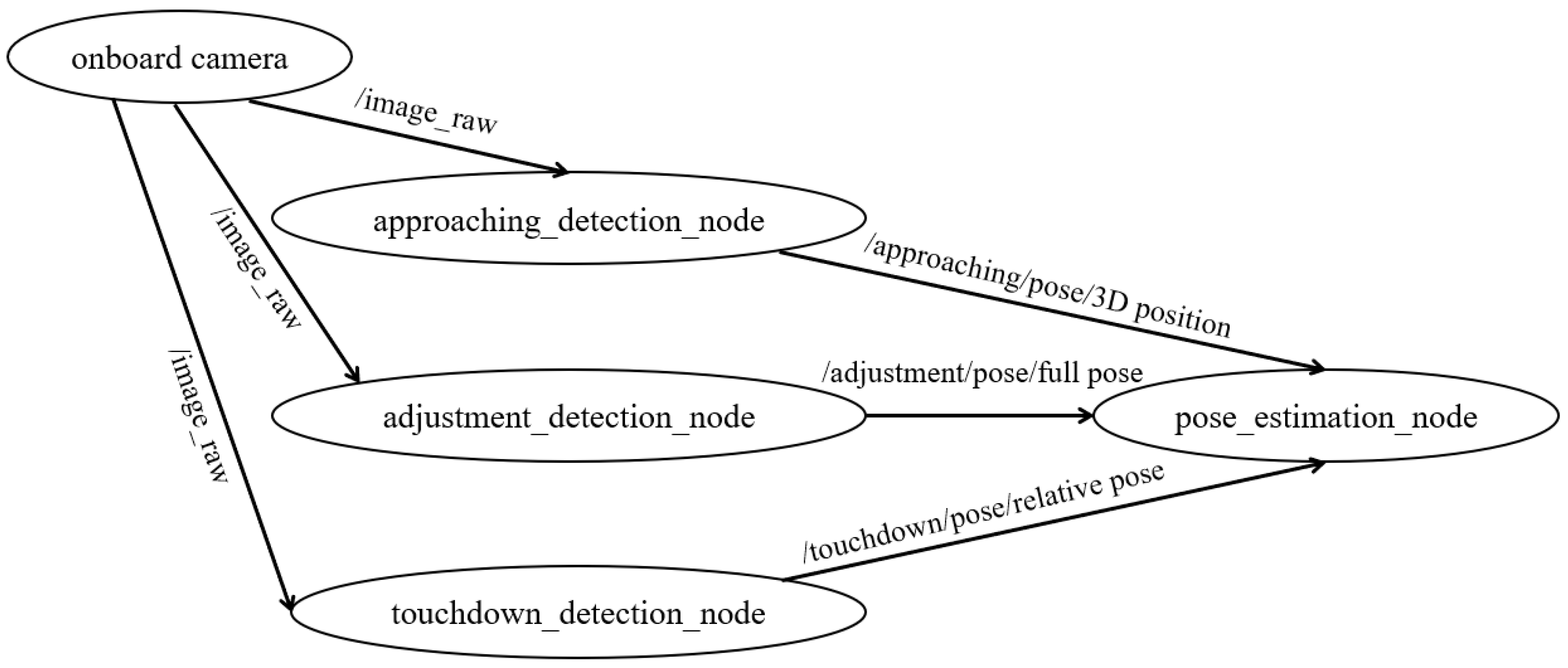
4. A Hierarchical Vision-Based Localization Framework
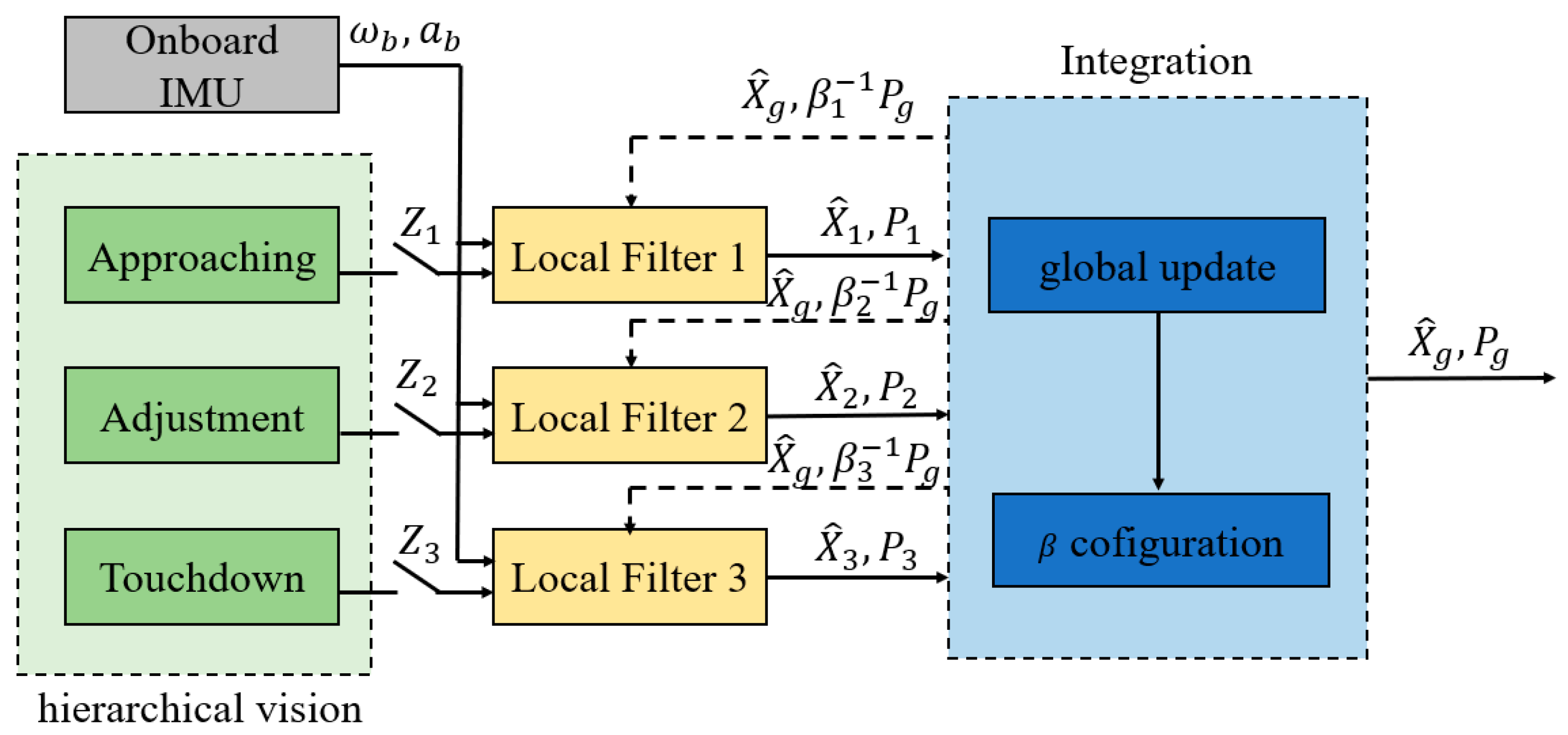
4.1. Hierarchical Localization
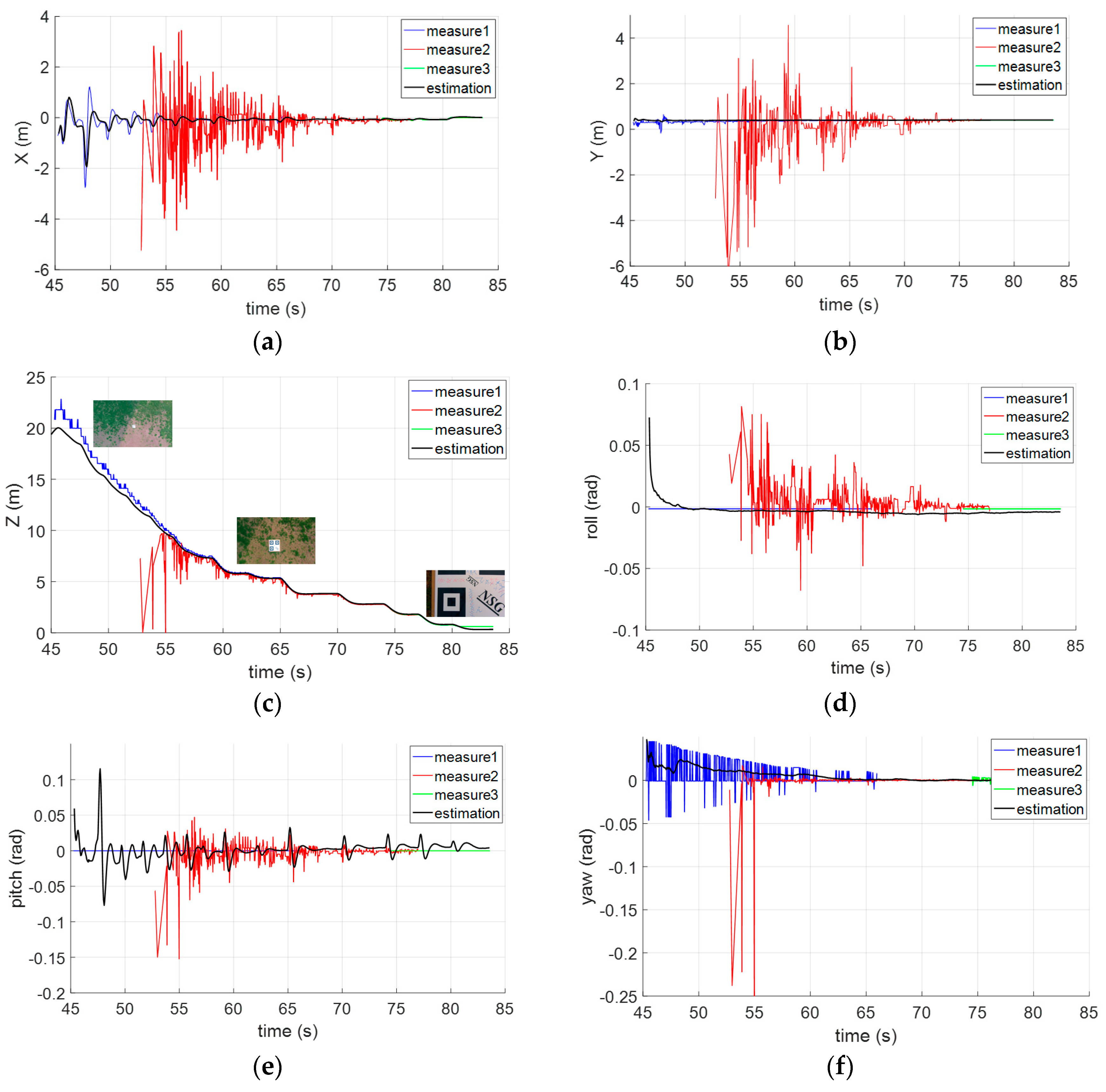
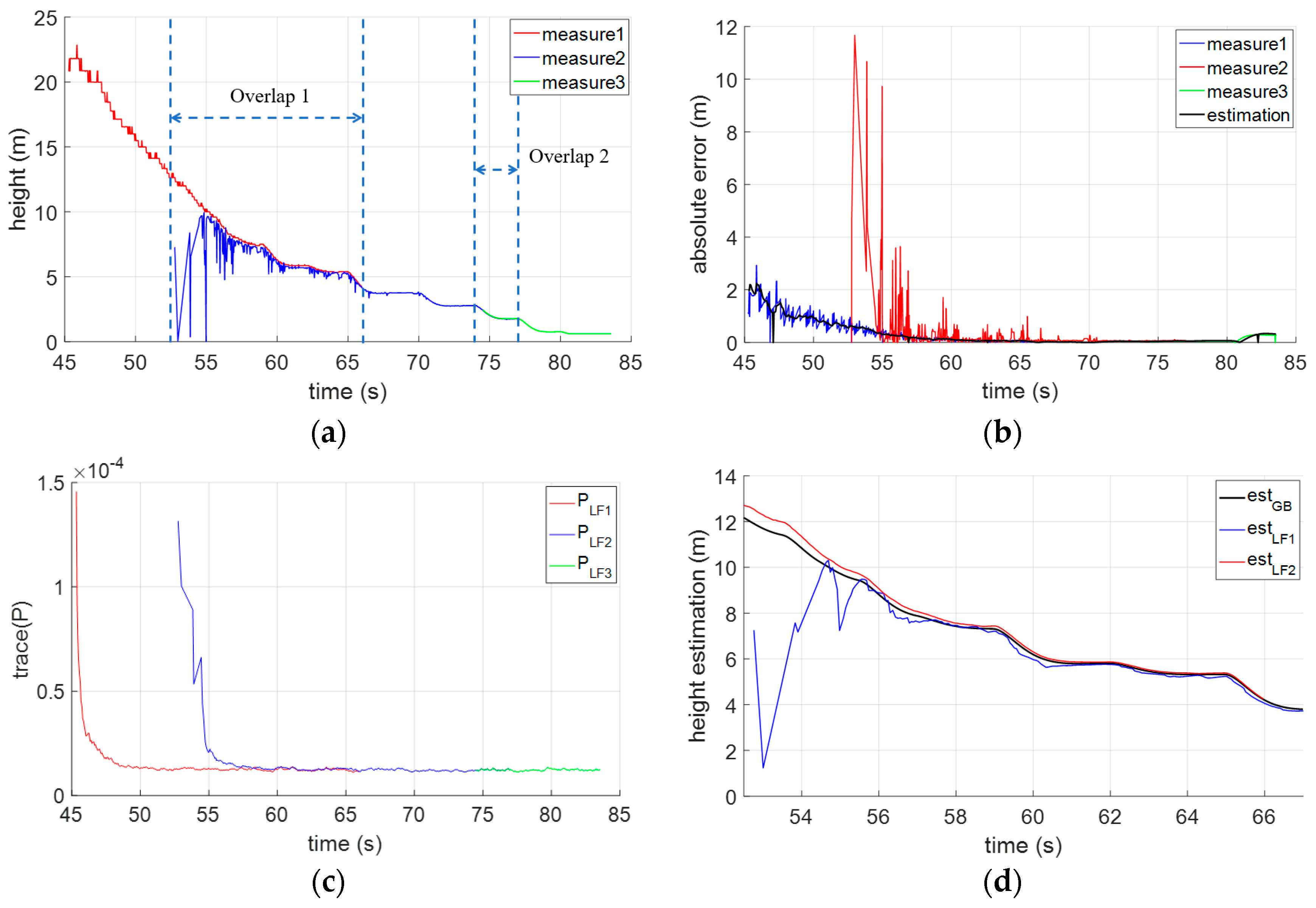
4.2. Pose Integration
5. Field Experiments and Results
5.1. RQRLP-Based Localization
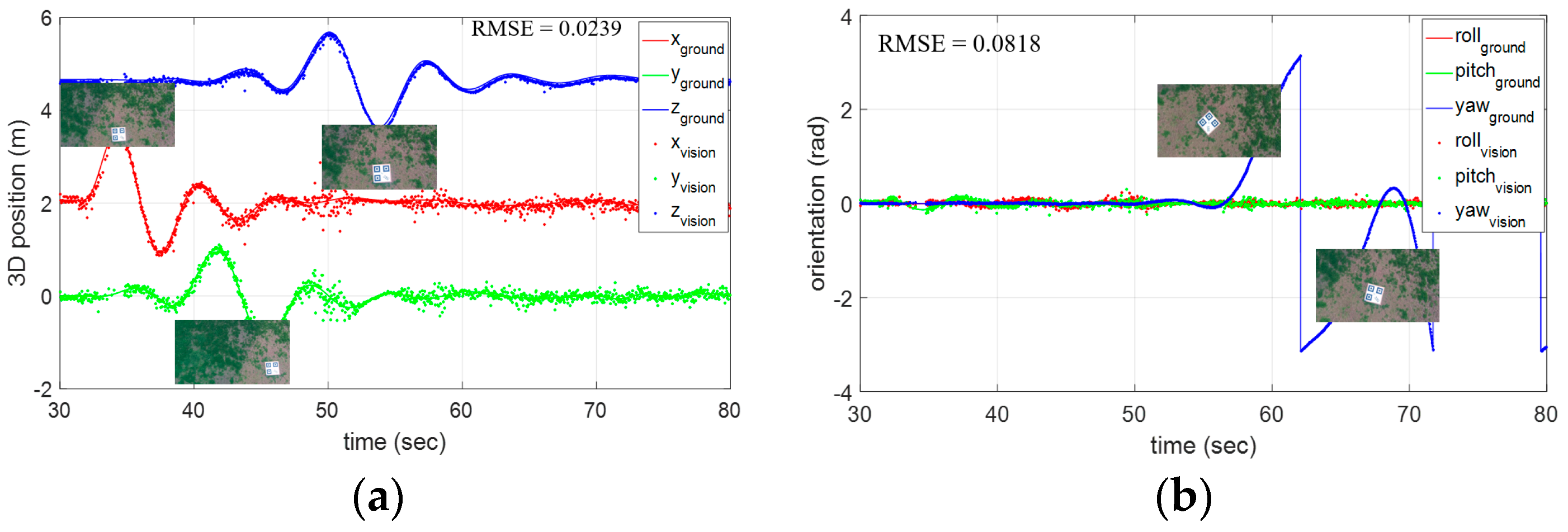
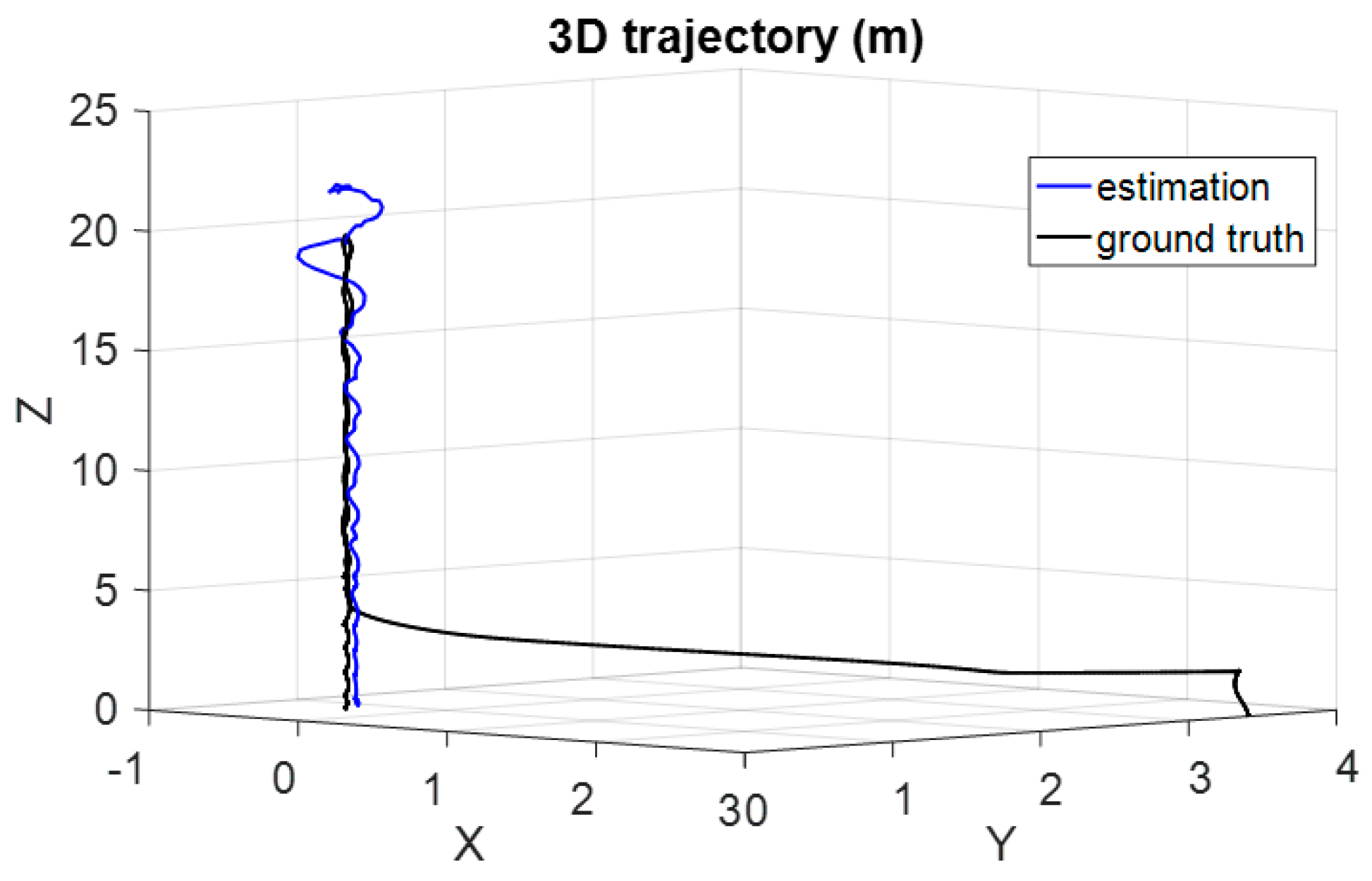
5.2. Hierarchical Localization for an Open Landing
5.3. Performance Analysis and Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kendoul, F. A survey of advances in guidance, navigation and control of unmanned rotorcraft systems. J. Field Robot. 2012, 29, 315–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saripalli, S.; Montgomery, J.F.; Sukhatme, G.S. Visually Guided Landing of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Robot Auton. 2003, 19, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Sunderhauf, N.; Protzel, P. A Vision Based Onboard Approach for Landing and Position Control of an Autonomous Multirotor UAV in GPS-Denied Environments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Munich, Germany, 22–26 June 2009; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zeng, X.; Tian, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, B. Use of Land’s Cooperative Object to Estimate UAV’s Pose for Autonomous Landing. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Scherer, S.A.; Schauwecker, K.; Zell, A. Autonomous Landing of MAVs on an Arbitrarily Textured Landing Site Using Onboard Monocular Vision. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2014, 74, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragon, I.F.; Campoy, P.; Martinez, C.; Olivares-Méndez, M.A. 3D pose estimation based on planar object tracking for UAVs control. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, C.; Mondragon, I.F.; Olivares-Mendez, M.A.; Campoy, P. On-board and Ground Visual Pose Estimation Techniques for UAV Control. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2011, 61, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockers, R.; Bouffard, P.; Ma, J.; Matthies, L.; Tomlin, C. Autonomous landing and ingress of micro-air-vehicles in urban environments based on monocular vision. In Proceedings of the Micro- and Nanotechnology Sensors, Systems, and Applications III, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–29 April 2011; p. 803111. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lopez, J.L.; Pestana, J.; Saripalli, S.; Campoy, P. An Approach Toward Visual Autonomous Ship Board Landing of a VTOL UAV. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2014, 74, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Garratt, M.A.; Lambert, A.J. Monocular vision-based real-time target recognition and tracking for autonomously landing an UAV in a cluttered shipboard environment. Auton. Robots 2016, 41, 881–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Q.; Coskun, A.; Doherty, S.M.; Ghasemlou, S.; Jagtap, A.S.; Modasshir, M.; Rahman, S.; Singh, A.; Xanthidis, M.; O’Kane, J.M.; et al. Experimental Comparison of open source Vision based State Estimation Algorithms. Int. Symp. Exp. Robot. 2016, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.V. Honeybees as a model for the study of visually guided flight navigation and biologically inspired robotics. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 413–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahl, J.S.; Srinivasan, M.V.; Zhang, S.W. Landing strategies in honey bees and applications to uninhabited airborne vehicles. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2004, 23, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, R.; Thurrowgood, S.; Srinivasan, M.V. Visual Odometry: Autonomous UAV Navigation using Optic Flow and Stereo. In Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Melbourne, Australia, 2–4 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Mulgaonkar, Y.; Michael, N.; Kumar, V. Vision-based state estimation for autonomous rotorcraft mavs in complex environments. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 1758–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, C.; Pizzoli, M.; Scaramuzza, D. SVO: Fast semi-direct monocular visual odometry. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Thurrowgood, S.; Moore, R.J.D.; Soccol, D.; Knight, M.; Srinivasan, M.V. A Biologically Inspired, Vision-based Guidance System for Automatic Landing of a Fixed-wing Aircraft. J. Field Robot. 2014, 31, 699–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denuelle, A.; Thurrowgood, S.; Strydom, R.; Kendoul, F.; Srinivasan, M.V. Biologically-inspired visual stabilization of a rotorcraft UAV in unknown outdoor environments. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Denver, CO, USA, 9–12 June 2015; pp. 1084–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Kendoul, F.; Fantoni, I.; Nonami, K. Optic flow-based vision system for autonomous 3D localization and control of small aerial vehicles. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herisse, B.; Hamel, T.; Mahony, R.; Russotto, F.X. Landing a VTOL Unmanned Aerial Vehicle on a Moving Platform Using Optical Flow. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, K.E.; Rosset, P.; Zell, A. Low-Cost Visual Tracking of a Landing Place and Hovering Flight Control with a Microcontroller. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2010, 57, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Garratt, M.; Lambert, A. Monocular Snapshot-based Sensing and Control of Hover Takeoff and Landing for a Low-cost Quadrotor: Monocular Snapshot-based Sensing and Control. J. Field Robot. 2015, 32, 984–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Hu, T.; Zhang, D.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J. Localization Framework for Real-Time UAV Autonomous Landing: An On-Ground Deployed Visual Approach. Sensor 2017, 17, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, T.; Shen, L. Stereo vision guiding for the autonomous landing of fixed-wing UAVs: A saliency-inspired approach. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xiao, C.; Xiu, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, Q. A new combined vision technique for micro aerial vehicle pose estimation. Robotics 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargani, H.; Bilaniuk, O.; Laganière, R. A fast and robust homography scheme for real-time planar target detection. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 2015, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XSENS MTi-G-700. Available online: https://www.xsens.com/products/mti-g-700/ (accessed on 30 March 2018).
- Breitenmoser, A.; Kneip, L.; Siegwart, R. A Monocular Vision based System for 6D Relative Robot Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, C.S.; Shakernia, O.; Sastry, S.S. A vision system for landing an unmanned aerial vehicle. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.01CH37164), Seoul, Korea, 21–26 May 2001; pp. 1720–1727. [Google Scholar]


| Device | Specification |
|---|---|
| UAV frame | six rotors, arm length 1.6 m, total weight 3.2 kg |
| GOPRO camera | 1080 p, 50 fps, focal length 1280 pixels, principal point: (948.9, 543.2), distortion factor (−0.00908, −0.03128, 0.00109, −0.00198, 0) |
| Xsens IMU | 100~400 Hz, Gyroscope: full range 450 deg/s, noise density 0.01 ; Acceleration: full range 50 m/s2, noise density 80 . |
| Methods | Ref [6] | Ref [29] | Ref [5] | Ref [30] | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position RMSE (m) | 0.2467 | 0.015 | 0.0392 | <0.05 | 0.0639 |
| Orientation RMSE () | 0.0653 | 0.0209 | 0.0436 | <0.0872 | 0.0818 |
| Range (m) | 3~10 | 0.677~1.741 | 1 | 1~1.1 | 0~20 |
| Pose (DOF) | 4-DOF | 6-DOF | 6-DOF | 6-DOF | 6-DOF |
| Object size (m) | 0.91 × 1.19 | 0.01 (diameter) | 0.18 (diameter) | unknown | 0.85 × 0.85 |
| Vision Resolution (pixels) | 640 × 480 | 752 × 480 | 640 × 480 | 320 × 240 | 1920 × 1080 |
| field of view () | unknown | 90 | 90 | unknown | 90 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Xiao, C.; Xiu, S.; Zhan, W.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, C.; Wen, Y.; Li, Q. A Hierarchical Vision-Based UAV Localization for an Open Landing. Electronics 2018, 7, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7050068
Yuan H, Xiao C, Xiu S, Zhan W, Ye Z, Zhang F, Zhou C, Wen Y, Li Q. A Hierarchical Vision-Based UAV Localization for an Open Landing. Electronics. 2018; 7(5):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7050068
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Haiwen, Changshi Xiao, Supu Xiu, Wenqiang Zhan, Zhenyi Ye, Fan Zhang, Chunhui Zhou, Yuanqiao Wen, and Qiliang Li. 2018. "A Hierarchical Vision-Based UAV Localization for an Open Landing" Electronics 7, no. 5: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7050068
APA StyleYuan, H., Xiao, C., Xiu, S., Zhan, W., Ye, Z., Zhang, F., Zhou, C., Wen, Y., & Li, Q. (2018). A Hierarchical Vision-Based UAV Localization for an Open Landing. Electronics, 7(5), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7050068







