DoA and DoD Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Radar-Aided mmWave MIMO Vehicular Communication Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The MIMO radar subsystem is only involved in the transmitter, the positions and velocities of vehicles are estimated. With the assistance of the radar, it is much easier to detect and track the moving vehicles. Moreover, radar can also be used to distinguish the shape of different vehicles in civil transportations in the city, e.g., identifying the bus from cars and trucks.
- In the mmWave MIMO communication subsystem, based on the parameters including positions and velocities obtained from the MIMO radar system, the efficiency as well as the performance of channel estimation, sector and beam selection, hybrid beamforming, cell discover and inter-cell handover can all be improved.
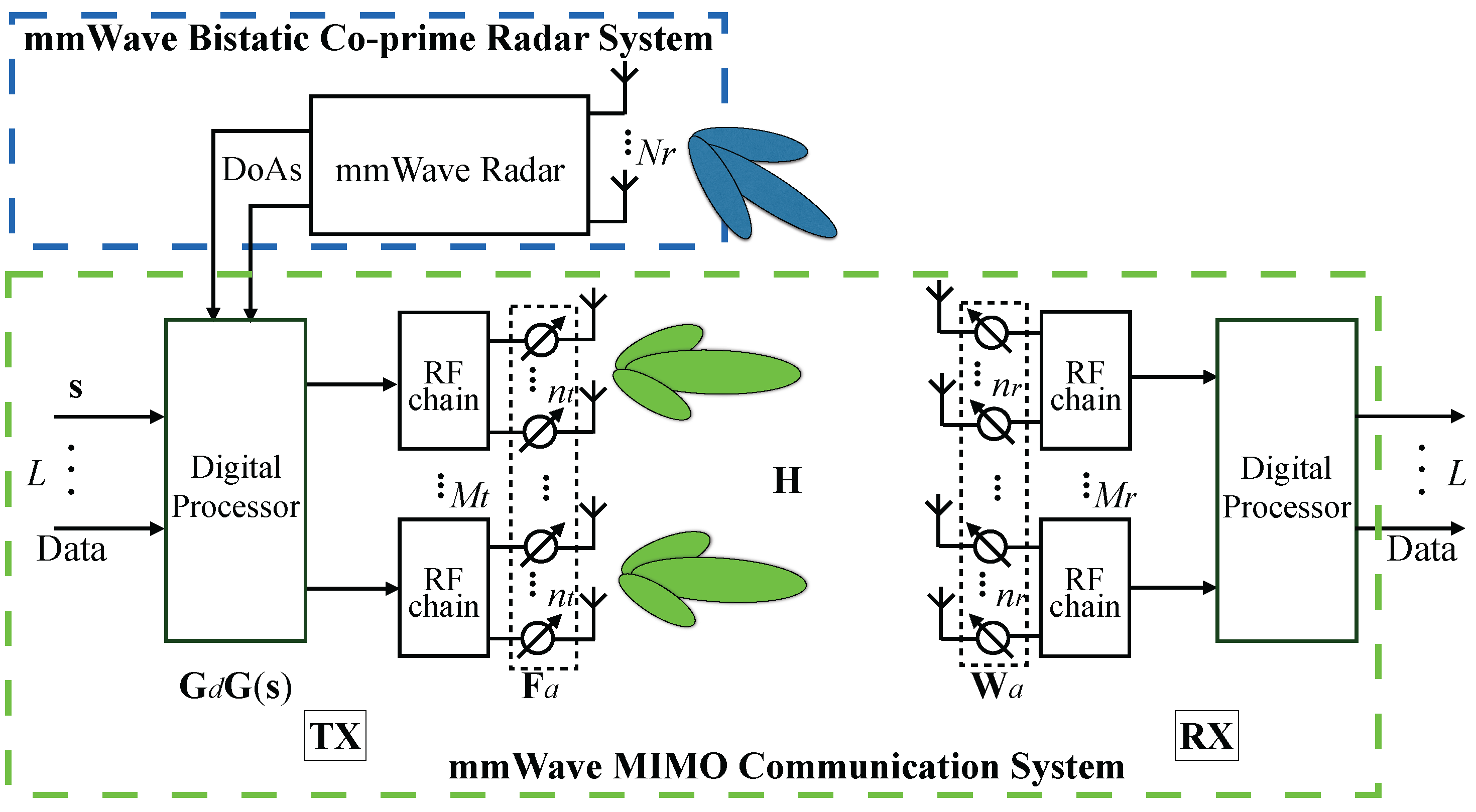
2. System Descriptions
2.1. System Model for Radar Subsystem
Compressed Sensing-Based DoA and DoD Estimation Method
| Algorithm 1 OMP algorithm for DoA and DoD estimation |
|
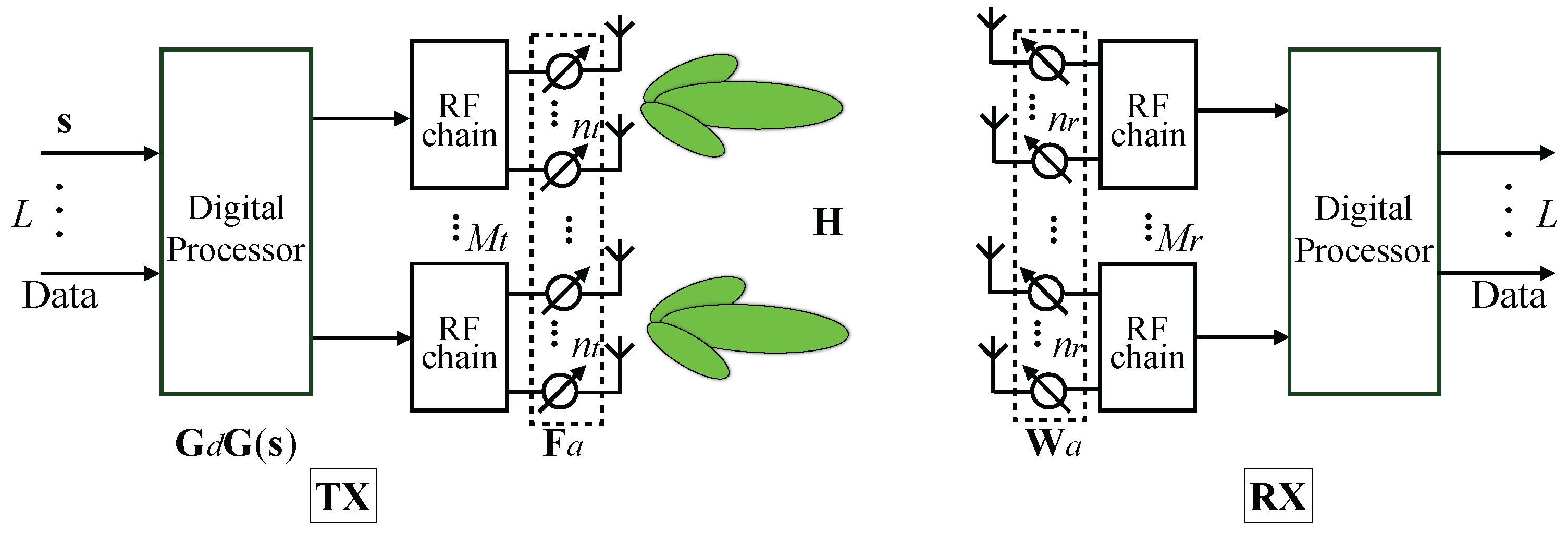
2.2. System Model for mmWave Communication Subsystem
3. The Hybrid Beamforming
3.1. Analog Beamformer Design for the Receiver
The Hybrid Beamformer Design of the Transmitter
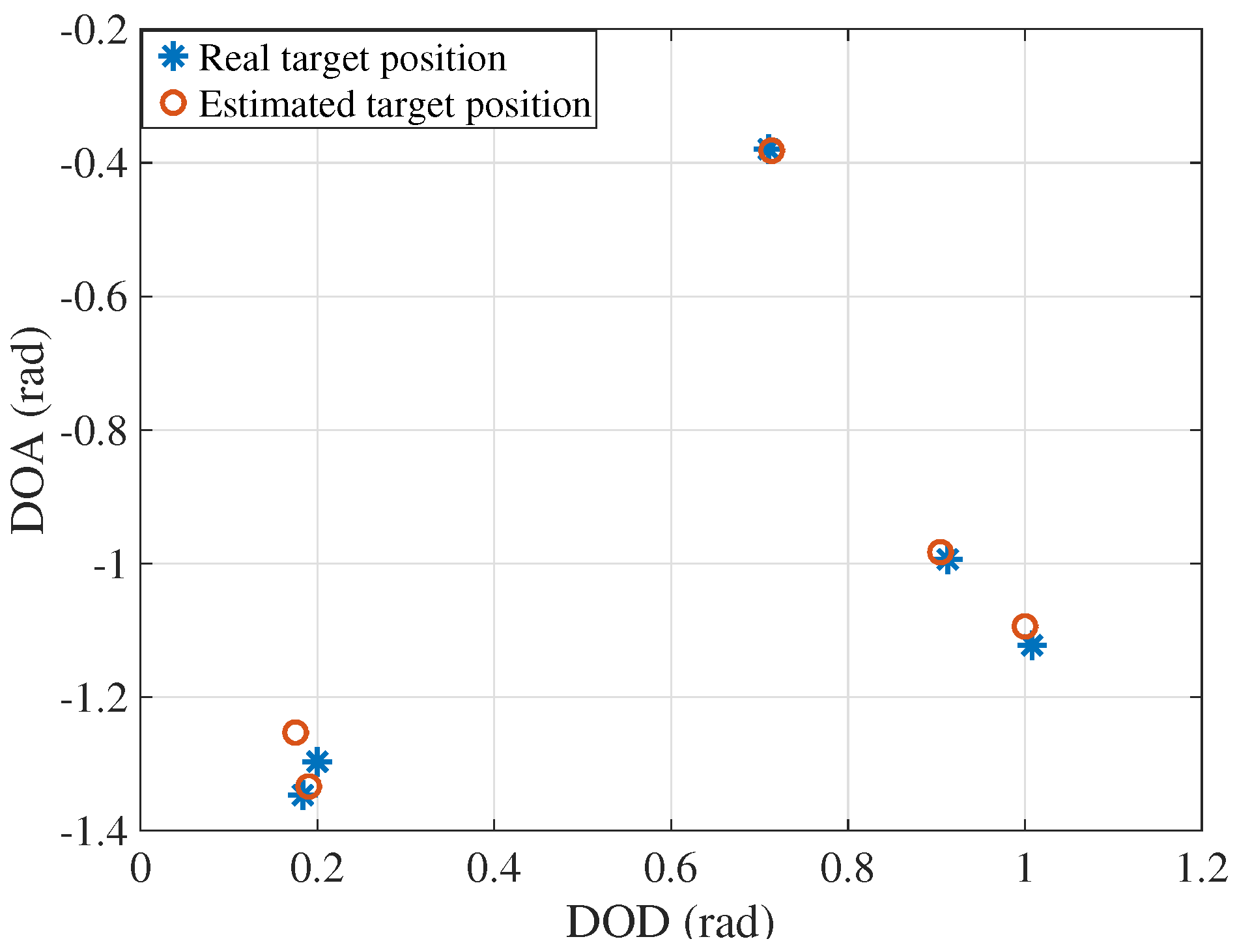
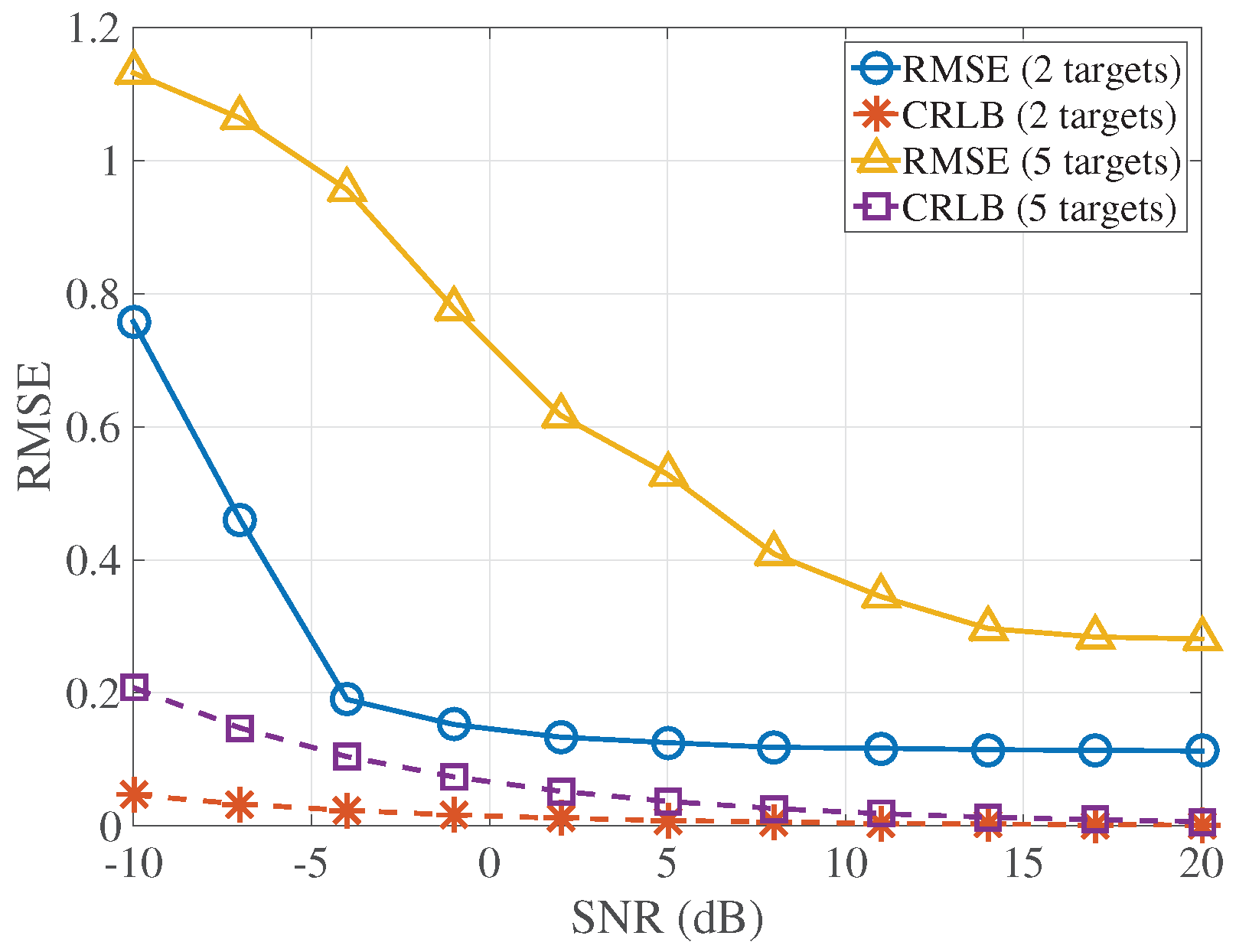
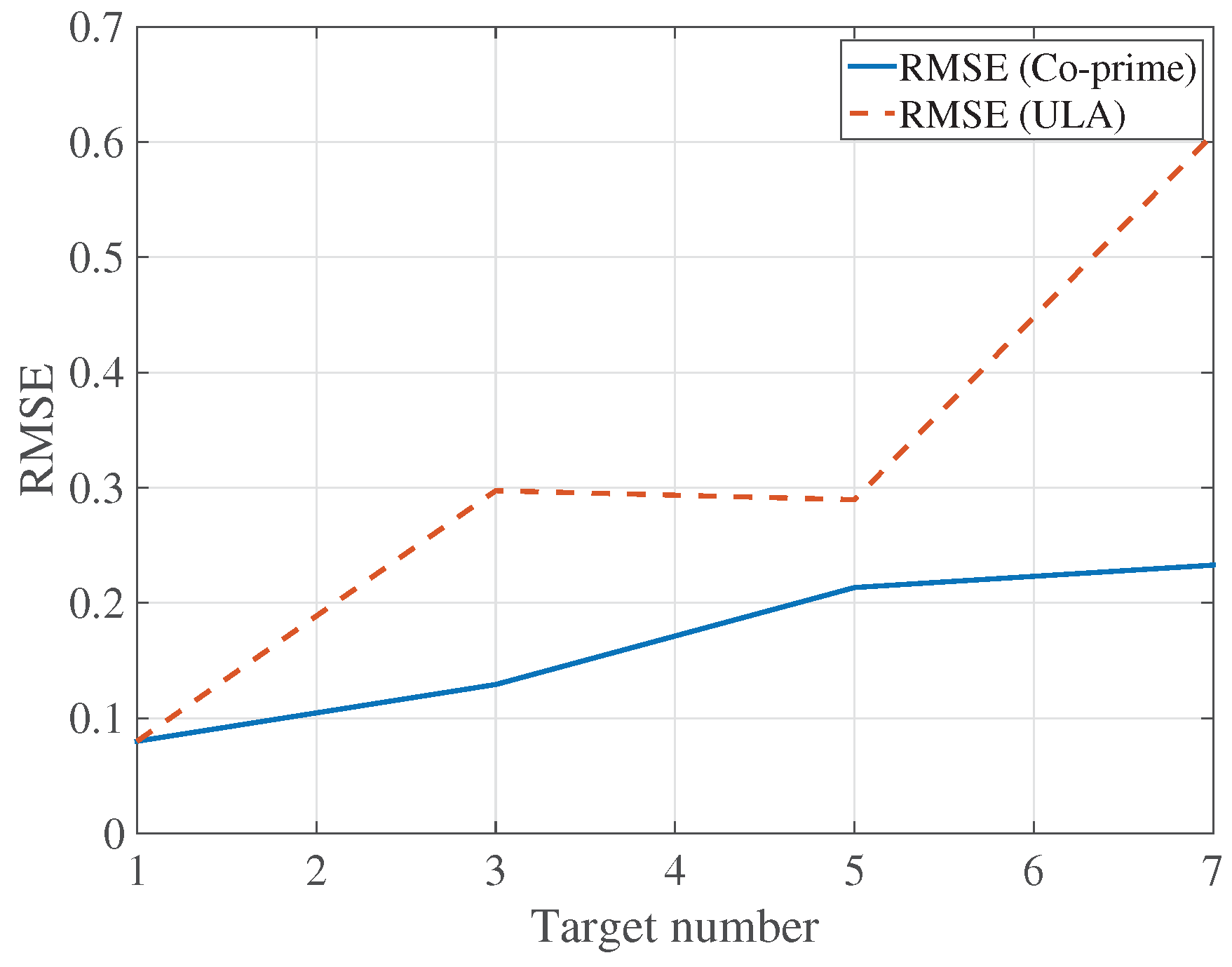
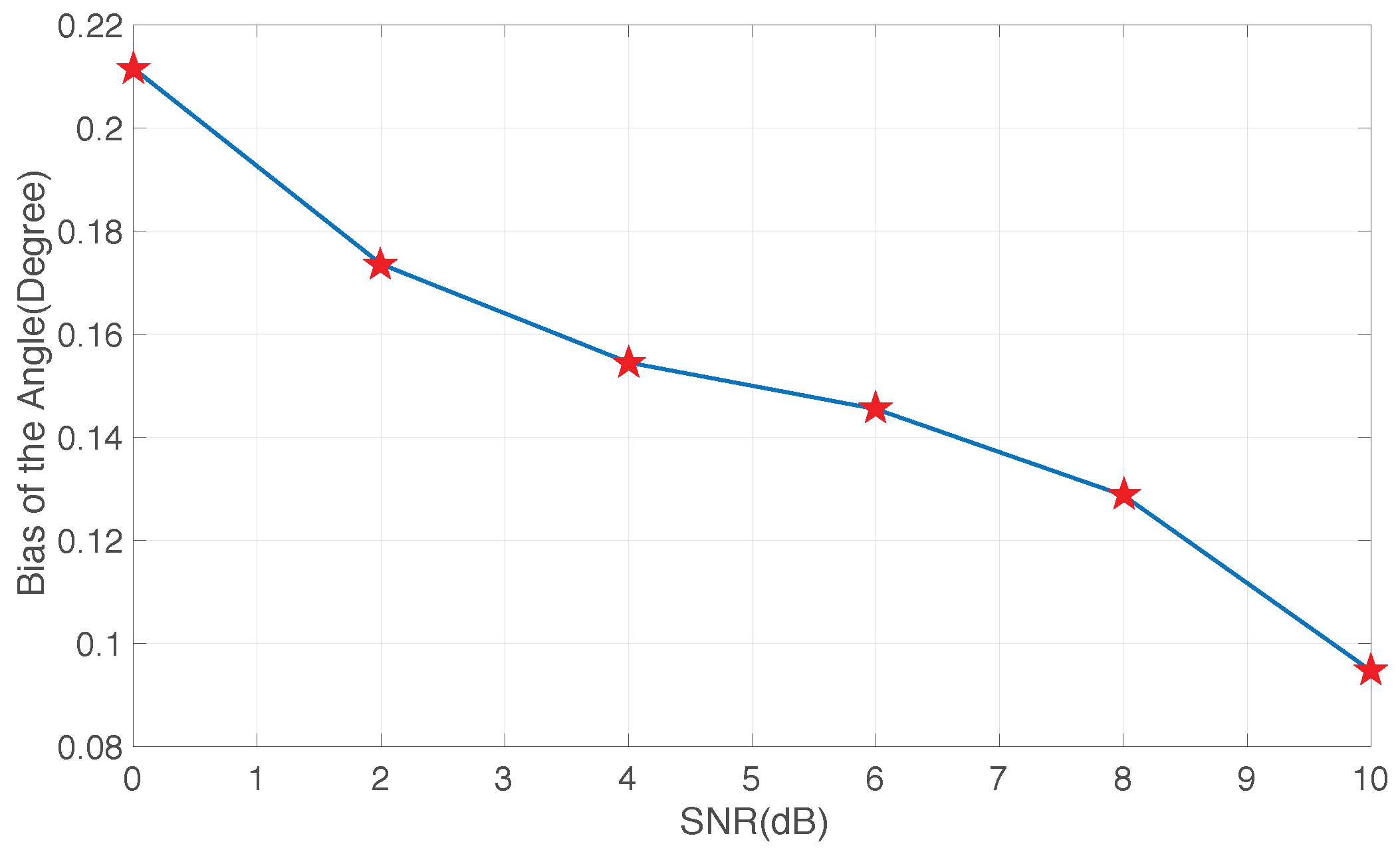
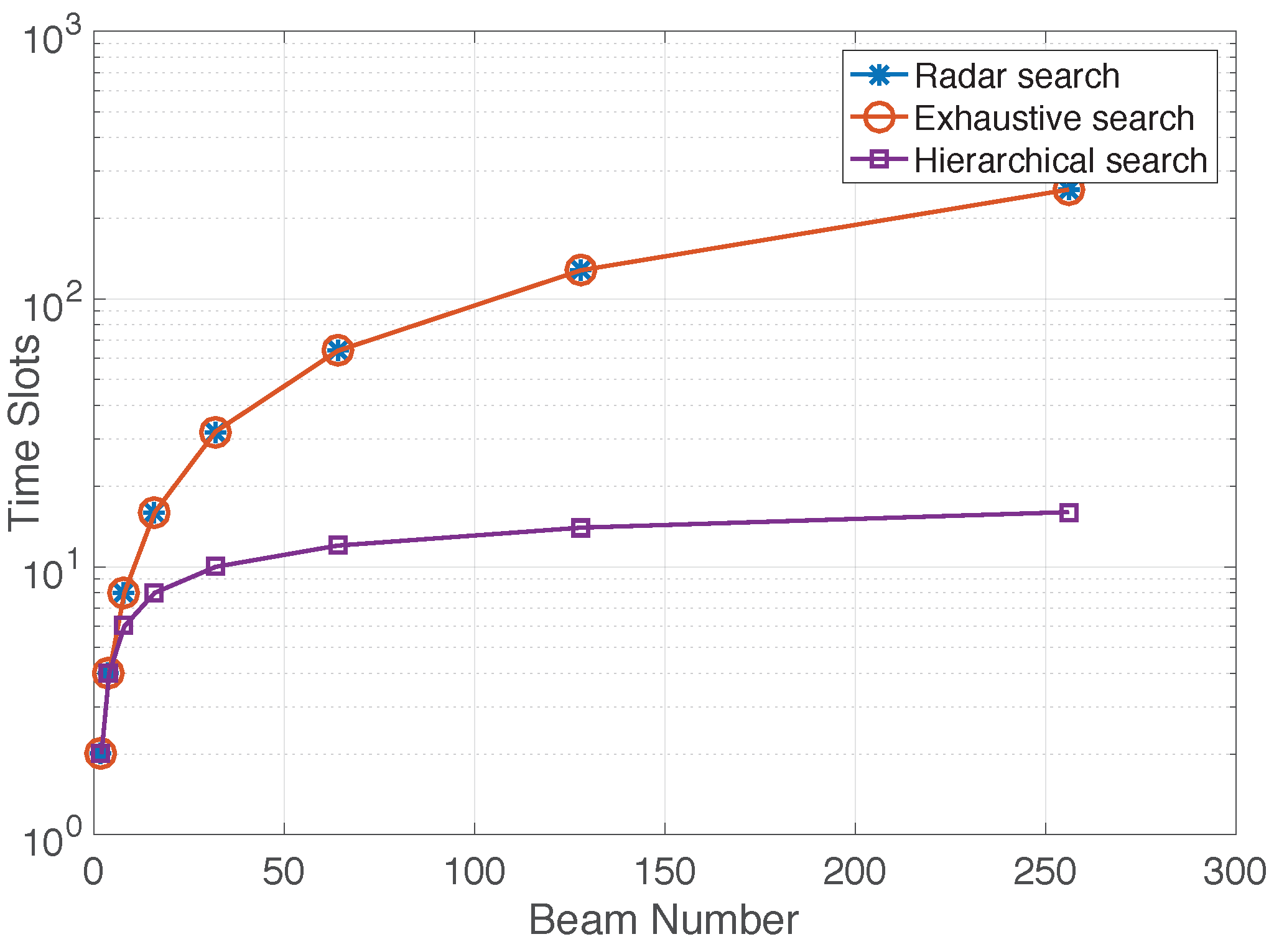
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rangan, S.; Rappaport, T.S.; Erkip, E. Millimeter wave cellular wireless networks: potentials and challenges. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.W.; González-Prelcic, N.; Rangan, S.; Roh, W.; Sayeed, A.M. An Overview of Signal Processing Techniques for Millimeter Wave MIMO Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 10, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCartney, G.R.; Rappaport, T.S. 73 GHz millimeter wave propagation measurements for outdoor urban mobile and backhaul communications in New York City. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, Australia, 10–14 June 2014; pp. 4862–4867. [Google Scholar]
- Akoum, S.; Ayach, O.E.; Heath, R.W. Coverage and capacity in mmWave cellular systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 4–7 November 2012; pp. 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Oh, J.; Kweon, C.; Qin, X.; Shao, H.R.; Ngo, C. A 60 GHz wireless network for enabling uncompressed video communication. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2008, 46, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.; Leus, G.; Heath, R.W. Limited Feedback Hybrid Precoding for Multi-User Millimeter Wave Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2015, 14, 6481–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, R.Q.; Qian, Y.; Wu, G. Key elements to enable millimeter wave communications for 5G wireless systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Mag. 2014, 21, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, W.; Seol, J.Y.; Park, J.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J.; Cheun, K.; Aryanfar, F. Millimeter-wave beamforming as an enabling technology for 5G cellular communications: Theoretical feasibility and prototype results. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xu, W.; Dong, X. Low-Complexity Hybrid Precoding in Massive Multiuser MIMO Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2014, 3, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S.; MacCartney, G.R.; Samimi, M.K.; Sun, S. Wideband Millimeter-Wave Propagation Measurements and Channel Models for Future Wireless Communication System Design. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 3029–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.; Mo, J.; Gonzalez-Prelcic, N.; Heath, R.W. MIMO Precoding and Combining Solutions for Millimeter-Wave Systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Cordeiro, C.; Perahia, E.; Yang, L.L. Millimeter-wave multi-Gigabit WLAN: Challenges and feasibility. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Cannes, France, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanien, A.; Vorobyov, S.A. Transmit energy focusing for DOA estimation in MIMO radar with colocated antennas. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 2669–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Behnia, F.; Zamani, H. Asymptotically efficient target localization from bistatic range measurements in distributed MIMO radars. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Prelcic, N.; Méndez-Rial, R.; Heath, R.W. Radar aided beam alignment in MmWave V2I communications supporting antenna diversity. In Proceedings of the 2016 Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), La Jolla, CA, USA, 31 January–5 February 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wu, L. Moving target detection using colocated MIMO radar on multiple distributed moving platforms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 4670–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhan, P.; Wu, L. Clutter estimation based on compressed sensing in bistatic MIMO radar. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Communication, Control, Computing and Electronics Engineering (ICCCCEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 16–18 January 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Blum, R. MIMO radar waveform design based on mutual information and minimum mean-square error estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qi, H.; Yao, S. Direction finding of multiple targets using coprime array in MIMO radar. IEICE Commun. Express 2016, 6, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X. DOA estimation based on combined Uunitary ESPRIT for coprime MIMO radar. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhong, X.; Guo, Y.; Huo, W. DOA and DOD estimation based on bistatic MIMO radar with co-prime array. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 394–397. [Google Scholar]
- BouDaher, E.; Jia, Y.; Ahmad, F.; Amin, M.G. Multi-frequency co-prime arrays for high-resolution direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 3797–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, X. Super-Resolution Delay-Doppler Estimation for OFDM Passive Radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Qi, C.; Wu, L. Antenna placement optimisation for compressed sensing-based distributed MIMO radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wu, L.; Qi, C. Waveform optimization for target scattering coefficients estimation under detection and peak-to-average power ratio constraints in cognitive radar. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropp, J.A.; Gilbert, A.C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropulu, A.P.; Poor, H.V. Measurement matrix design for compressive sensing—Based MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 5338–5352. [Google Scholar]
- Akdeniz, M.R.; Liu, Y.S. Millimeter wave channel modeling and cellular capacity evaluation. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateeb, A.; Omar El Ayach, G.; Robert, W.; Heath, J. Channel Estimation and Hybrid Precoding for Millimeter Wave Cellular Systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 8, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, L.; Chen, P. Efficient modulation and demodulation methods for multi-carrier communication. IET Commun. 2016, 10, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayach, O.E.; Rajagopal, S.; Abu-Surra, S.; Pi, Z.; Heath, R.W. Spatially Sparse Precoding in Millimeter Wave MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 13, 1499–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chih-Lin, I.; Xu, Z.; Rowell, C. Large-scale antenna systems with hybrid analog and digital beamforming for millimeter wave 5G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, J.; Ali, B.; Naqvi, S.S.; Saleem, S. Hybrid Precoding via Successive Refinement for Millimeter Wave MIMO Communication Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, K.; Alkhateeb, A.; Prelcic, N.G.; Heath, R.W. Channel Estimation for Hybrid Architecture Based Wideband Millimeter Wave Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Cao, Z.; He, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, P. DoA and DoD Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Radar-Aided mmWave MIMO Vehicular Communication Systems. Electronics 2018, 7, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7030040
Chen Z, Cao Z, He X, Jin Y, Li J, Chen P. DoA and DoD Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Radar-Aided mmWave MIMO Vehicular Communication Systems. Electronics. 2018; 7(3):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhimin, Zhenxin Cao, Xinyi He, Yi Jin, Jingchao Li, and Peng Chen. 2018. "DoA and DoD Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Radar-Aided mmWave MIMO Vehicular Communication Systems" Electronics 7, no. 3: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7030040
APA StyleChen, Z., Cao, Z., He, X., Jin, Y., Li, J., & Chen, P. (2018). DoA and DoD Estimation and Hybrid Beamforming for Radar-Aided mmWave MIMO Vehicular Communication Systems. Electronics, 7(3), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7030040






