An Advanced Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for Photovoltaic Systems by Using Variable Universe Fuzzy Logic Control Considering Temperature Variability
Abstract
1. Introduction
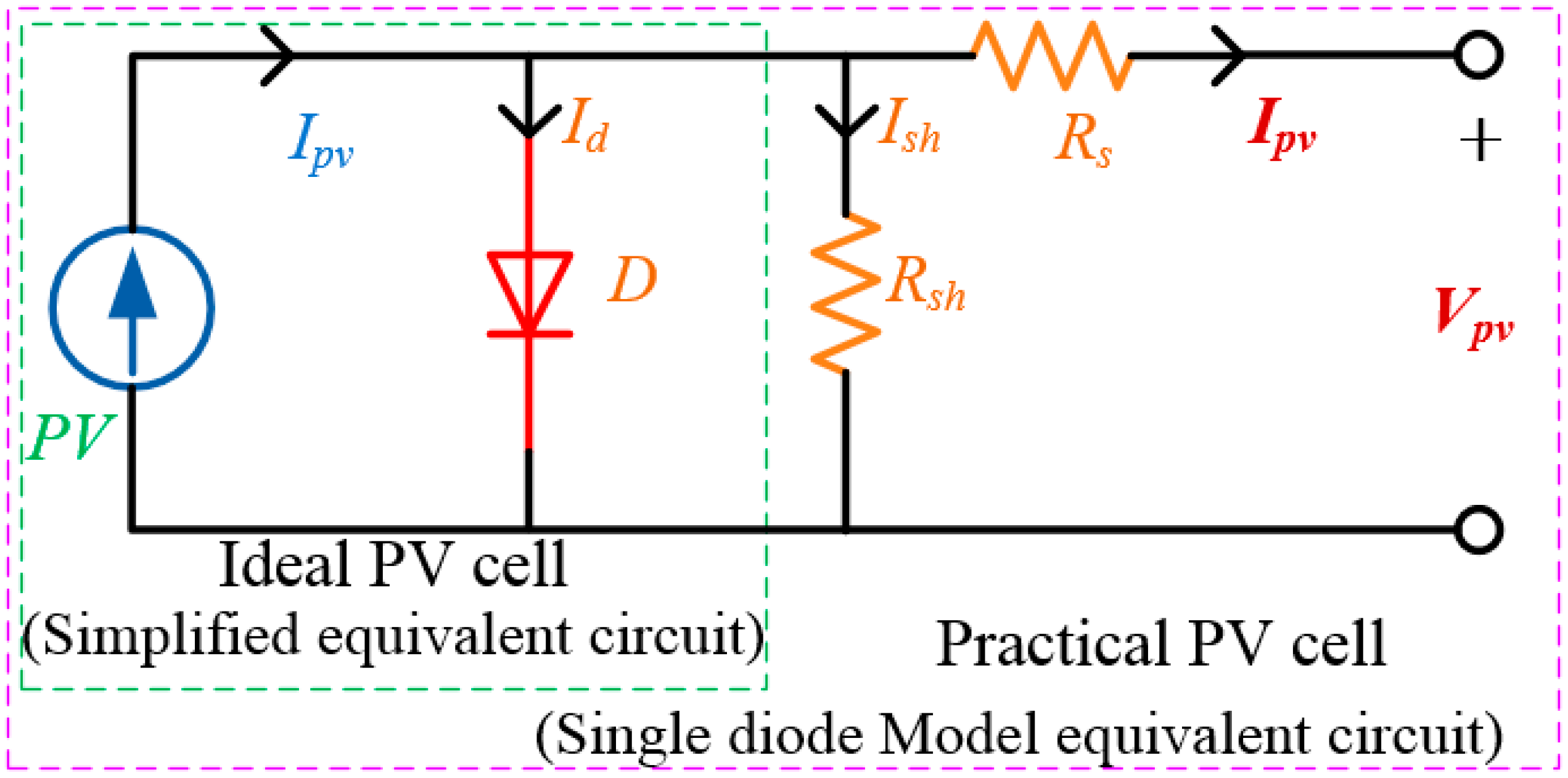
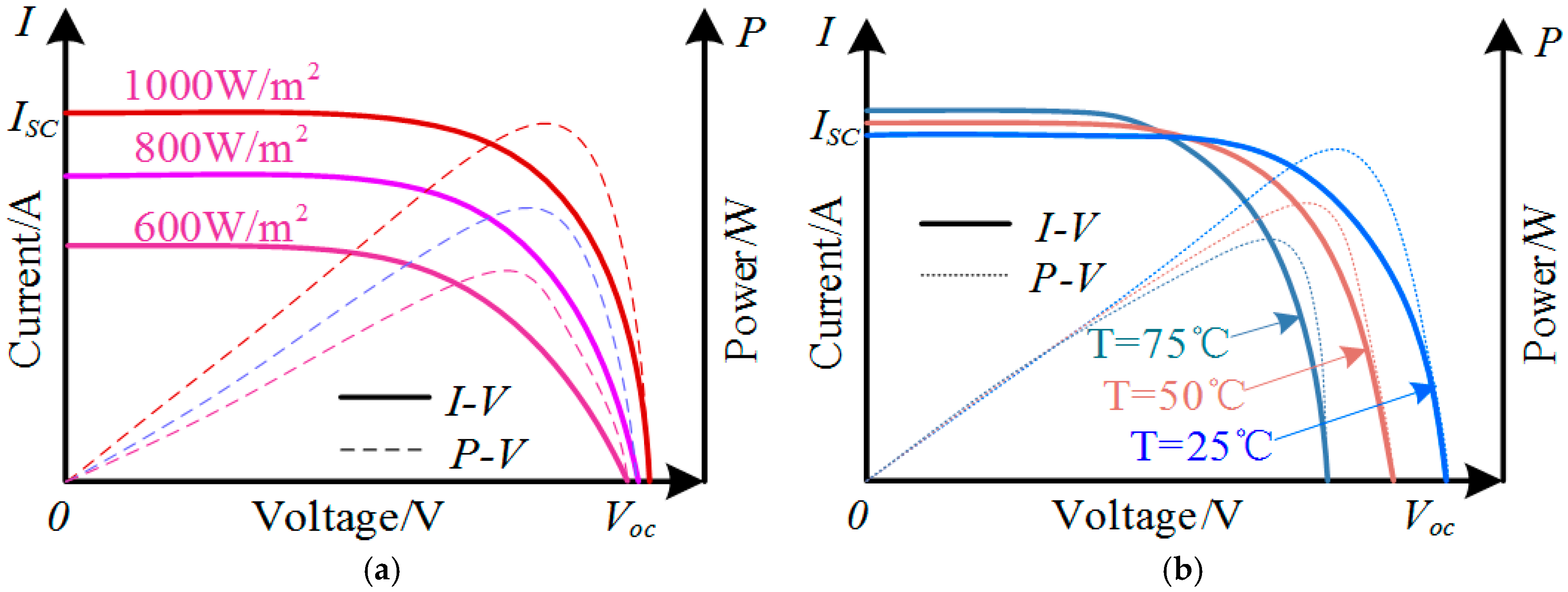
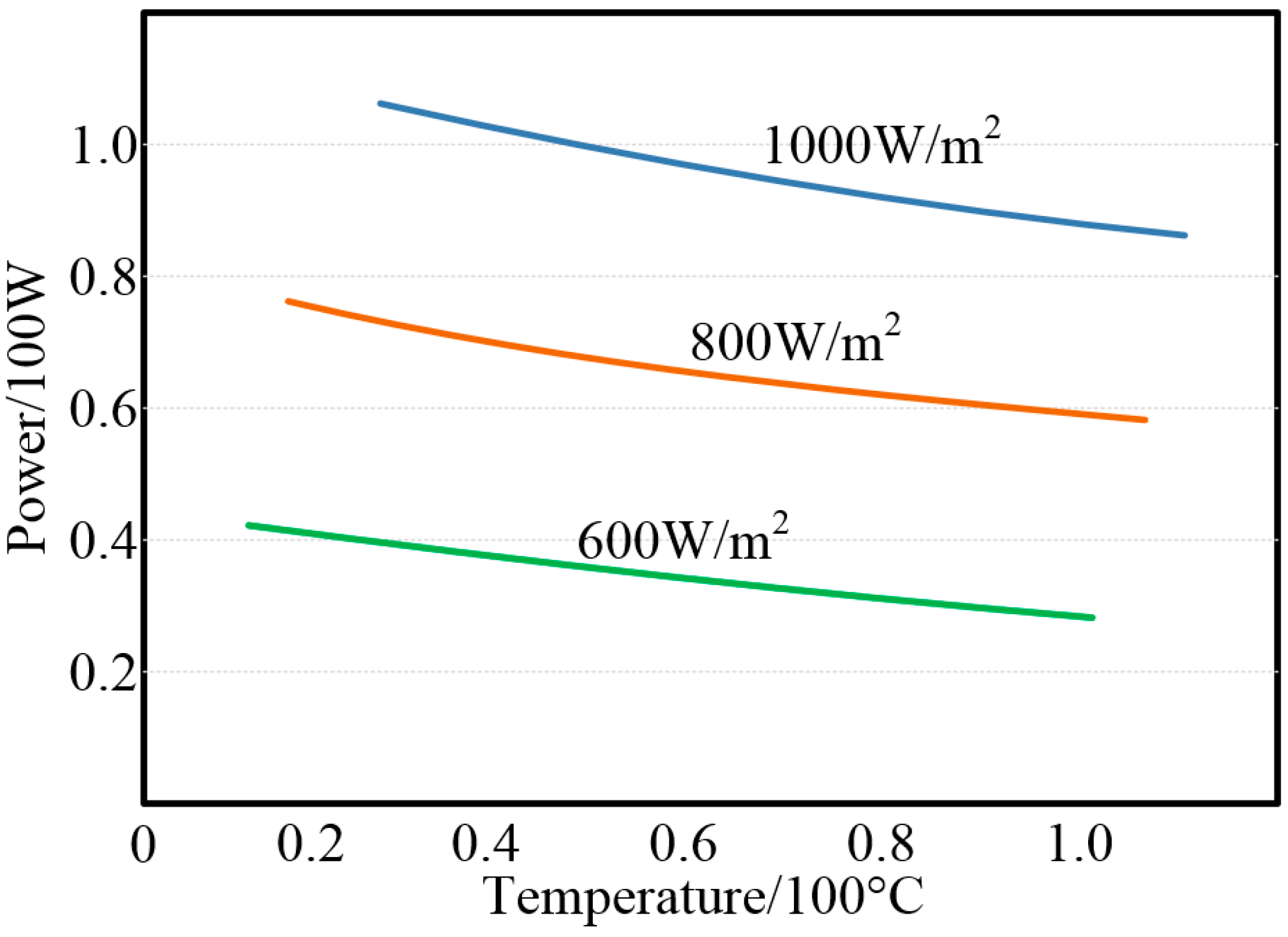
2. Model and Characteristics of a PV System
3. MPPT Control System and Proposed Control Method
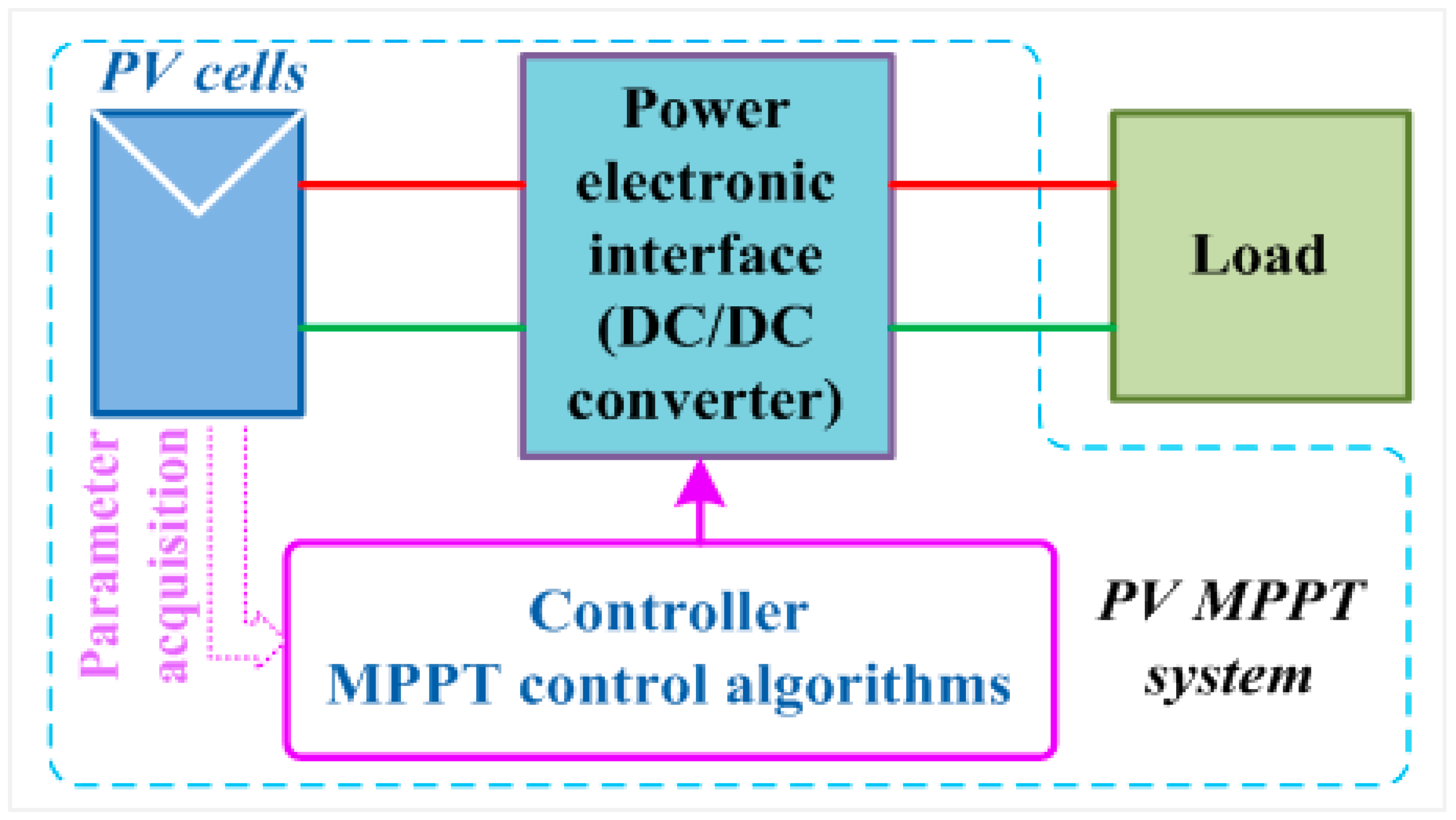
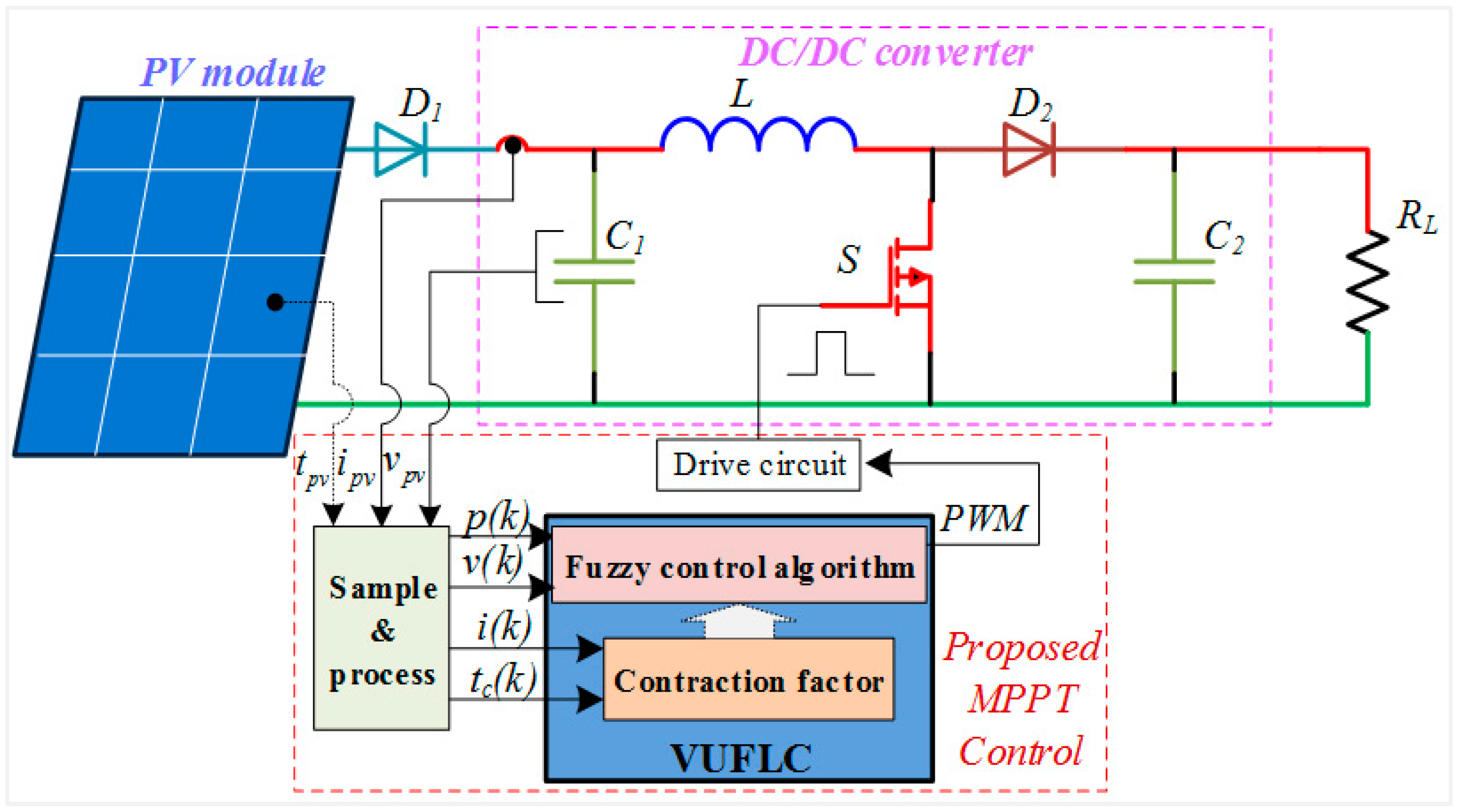
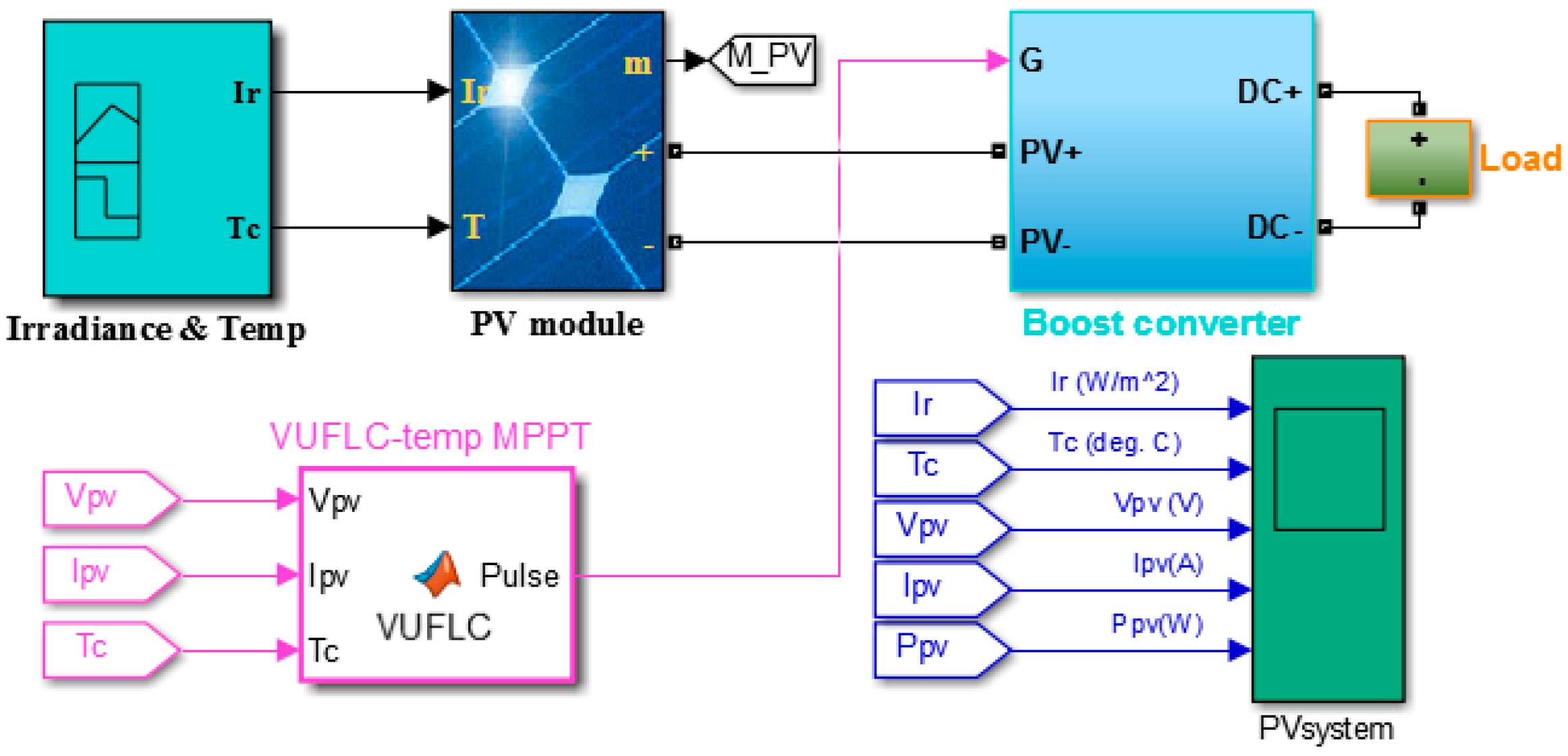
3.1. MPPT Control System
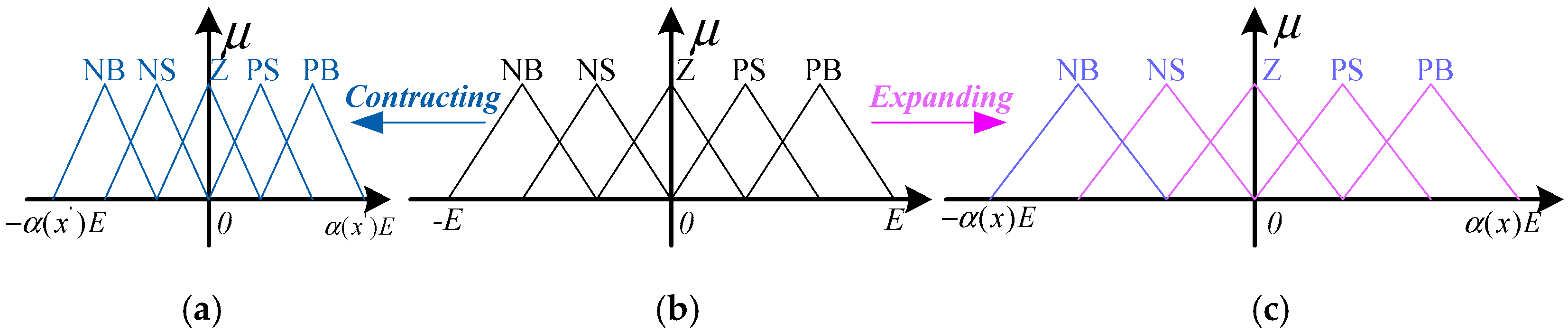
3.2. Variable Universe Fuzzy Logic Control (VUFLC)
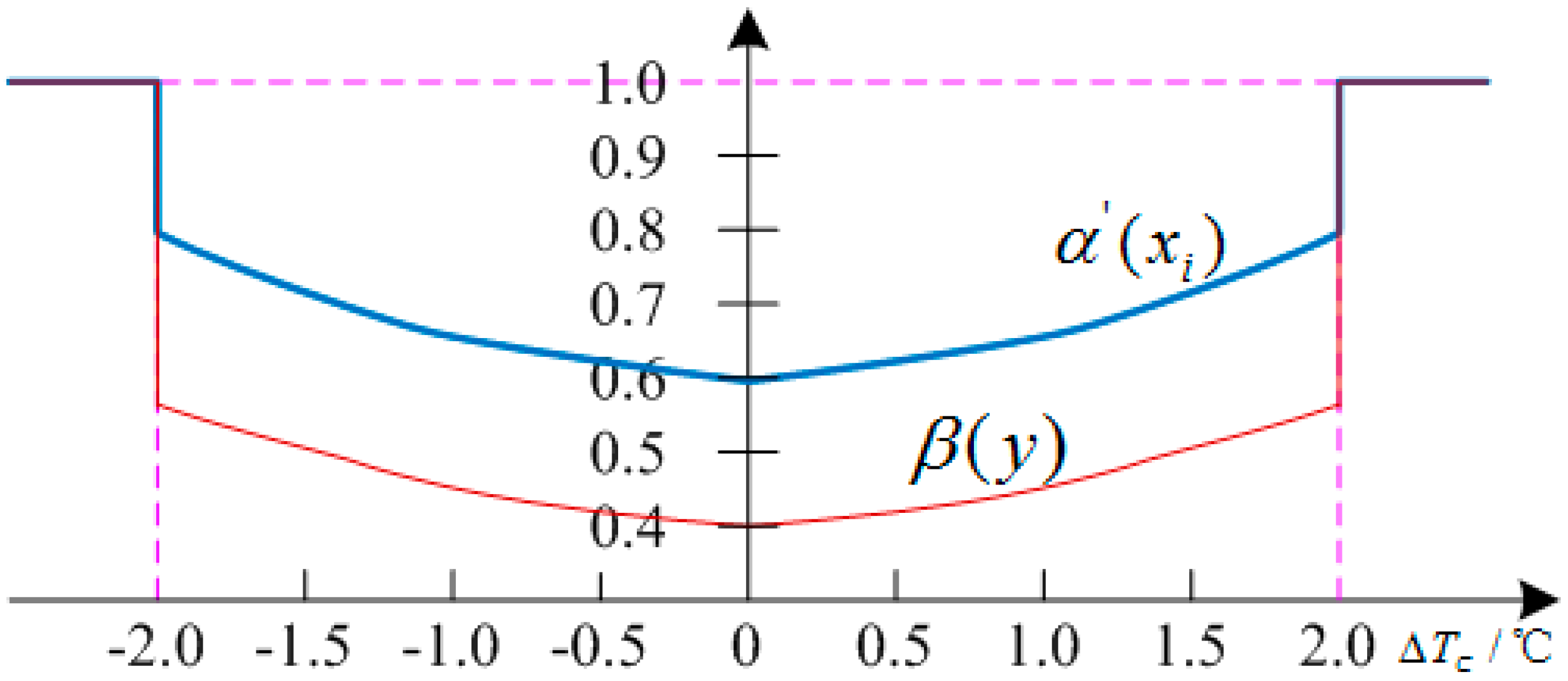
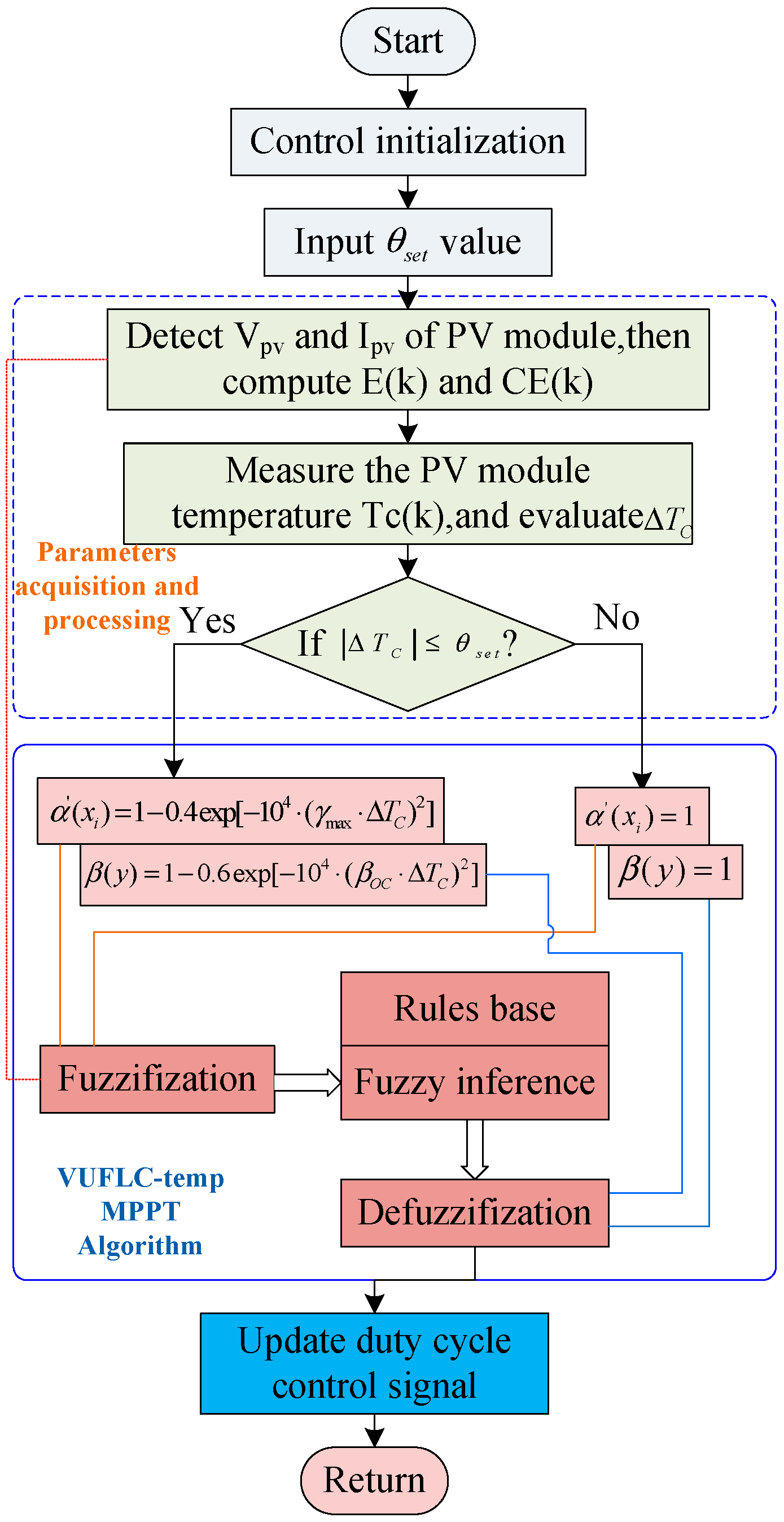
3.3. Proposed Control Method
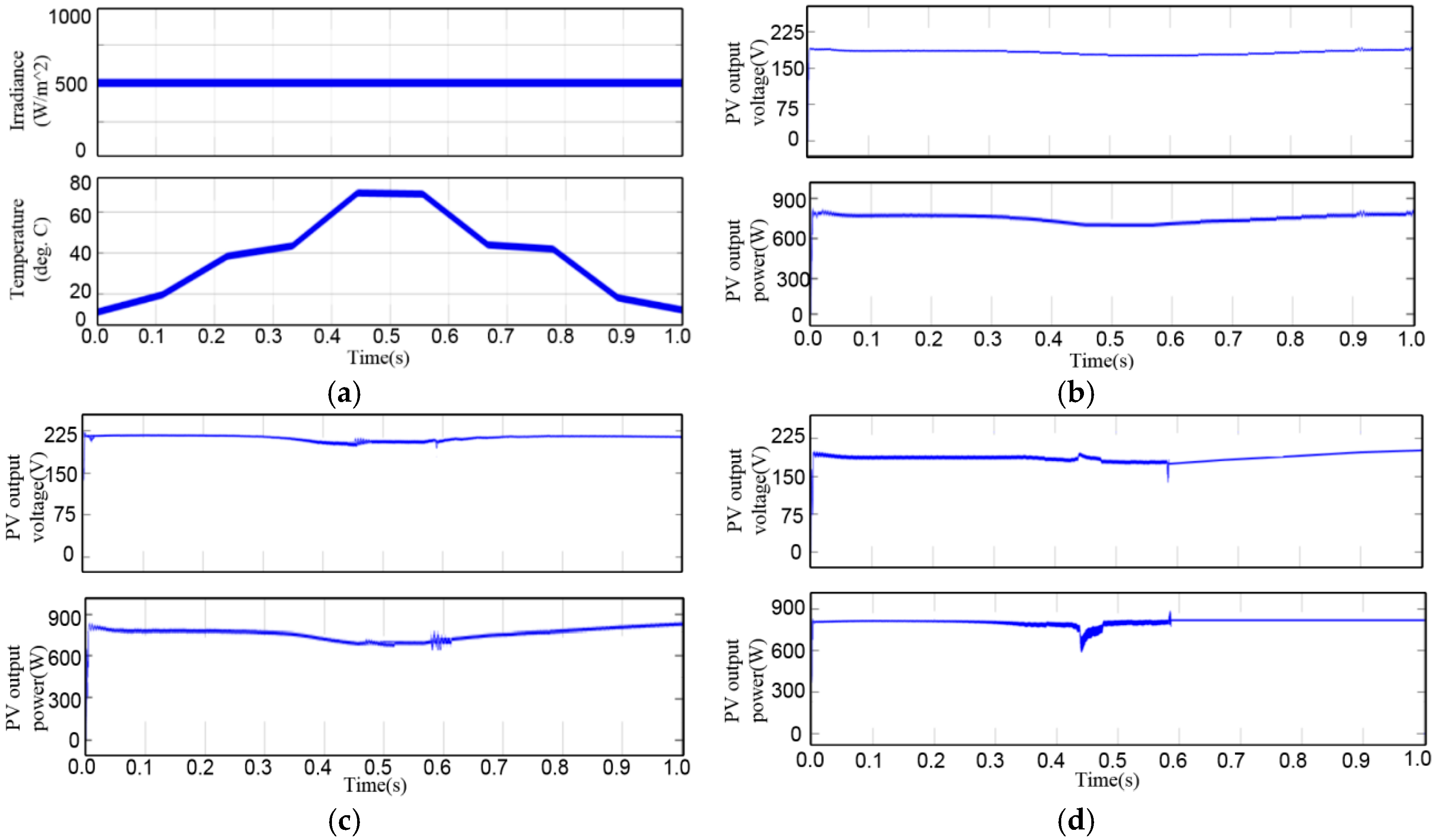
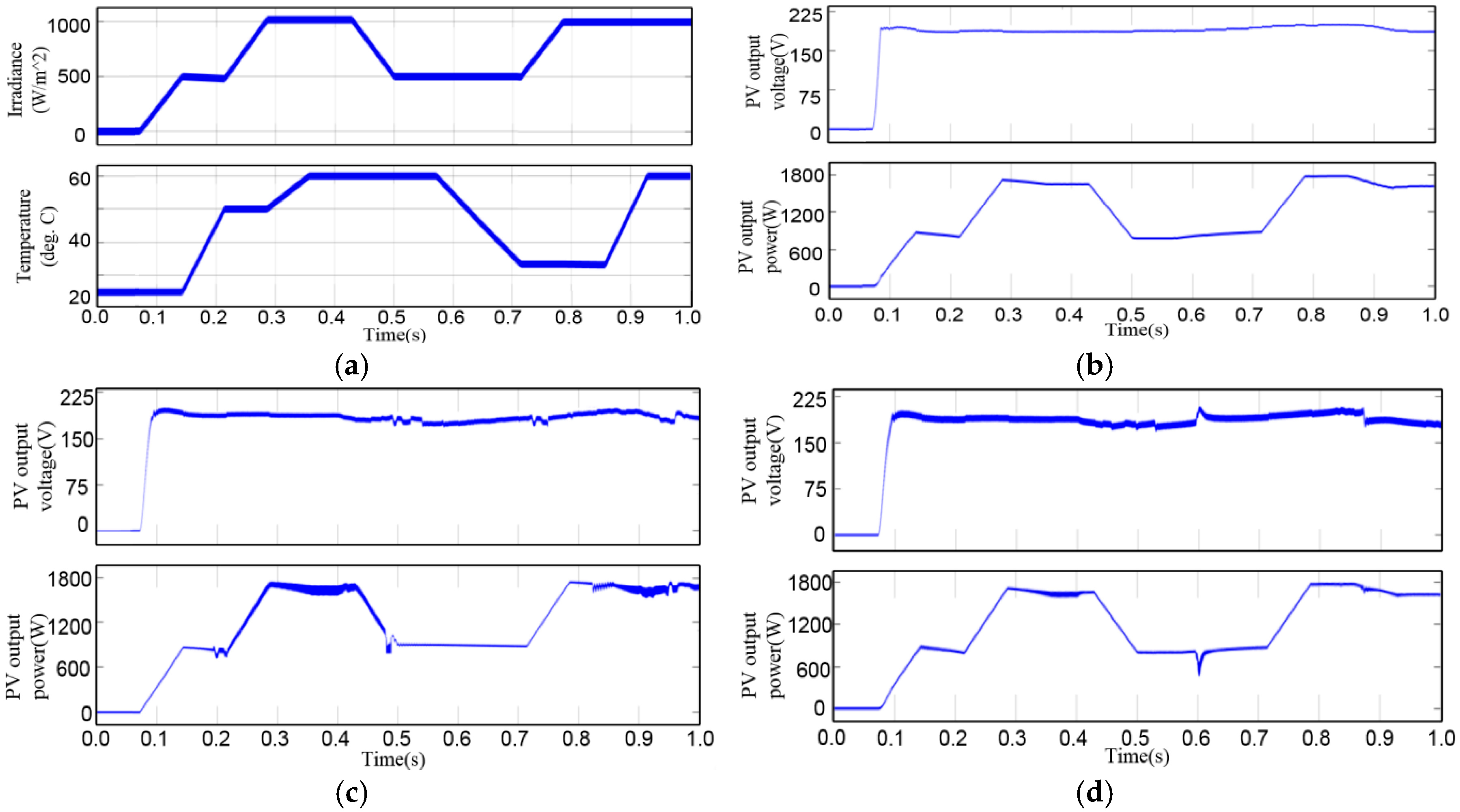
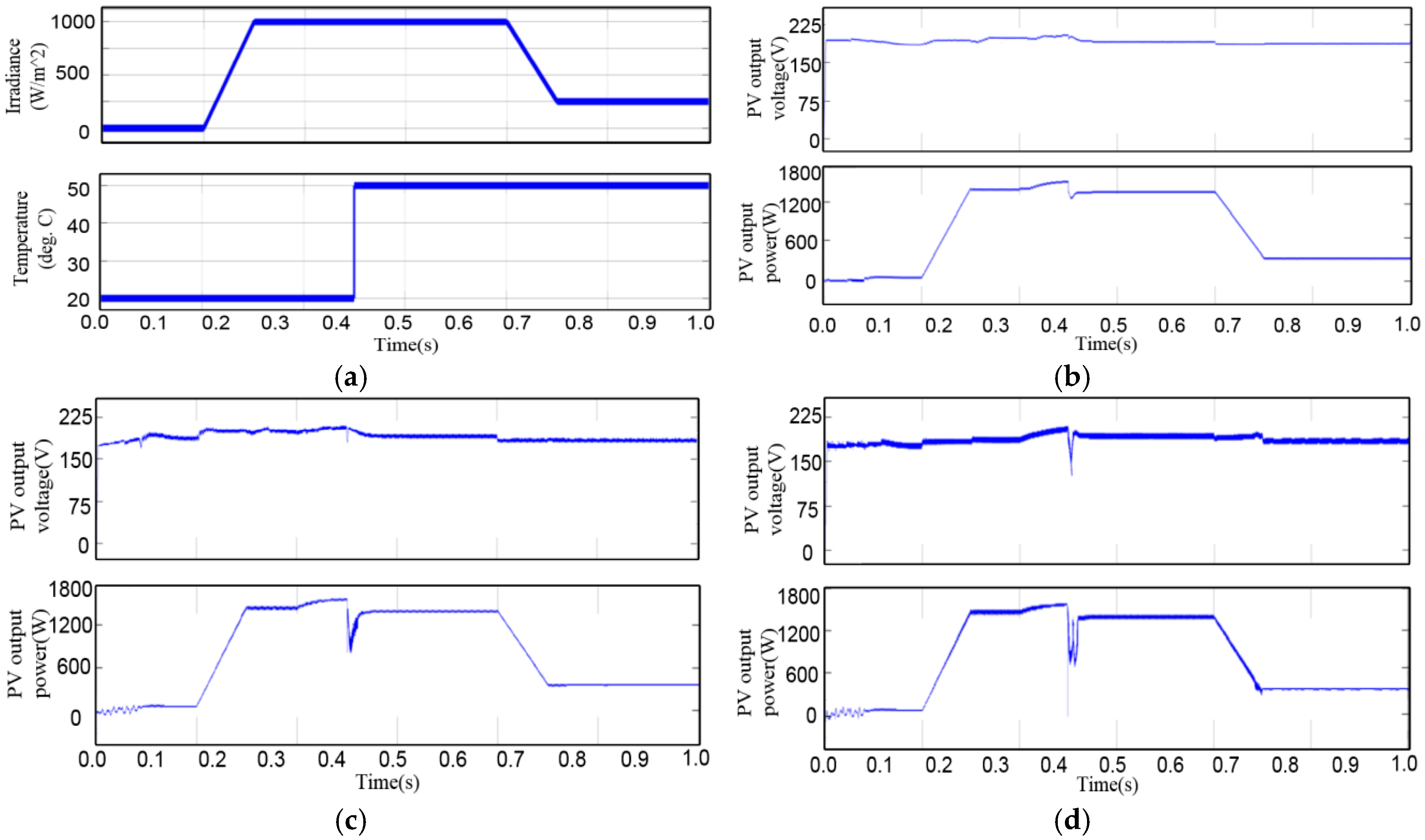
4. Simulation Results
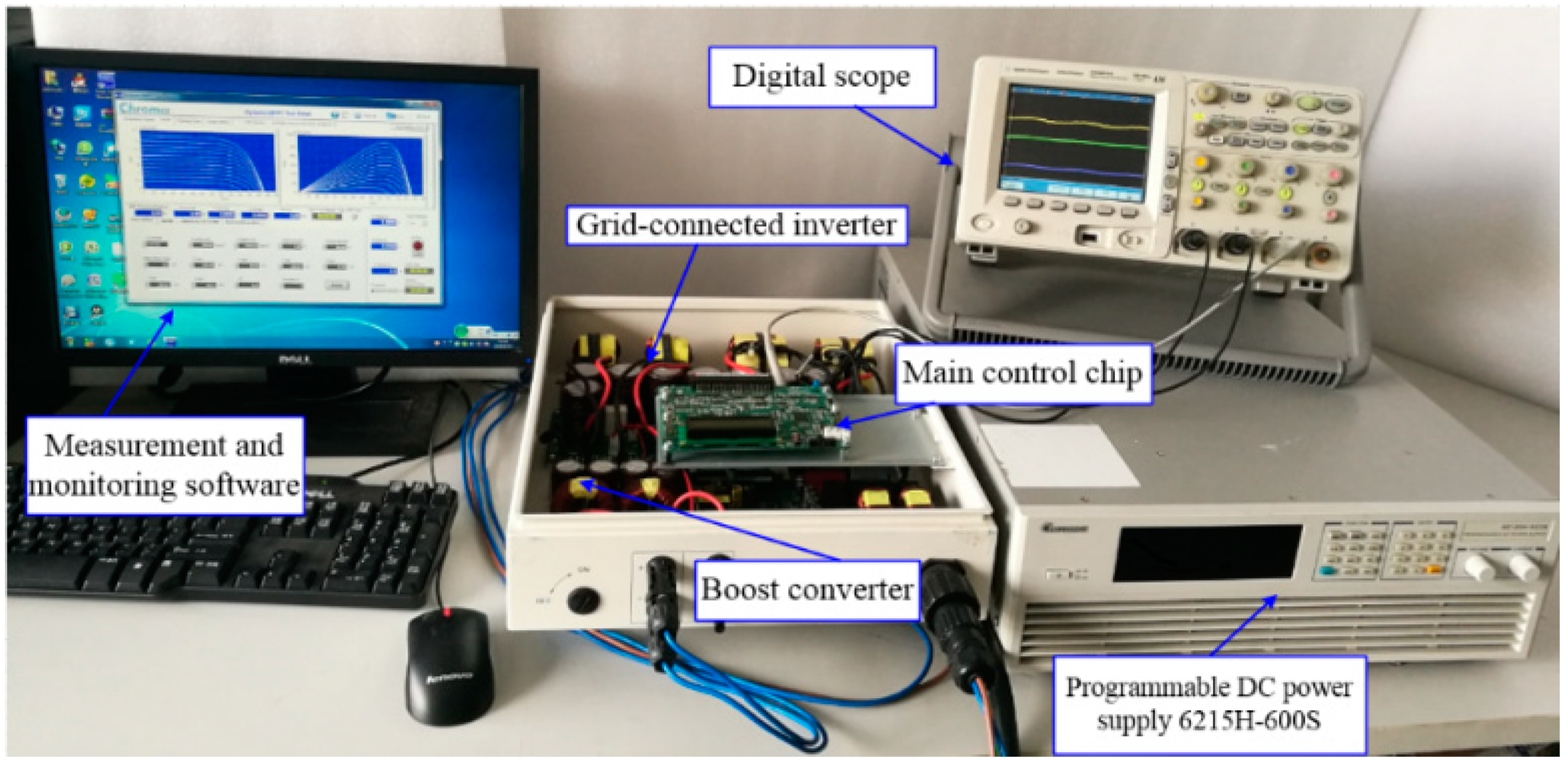
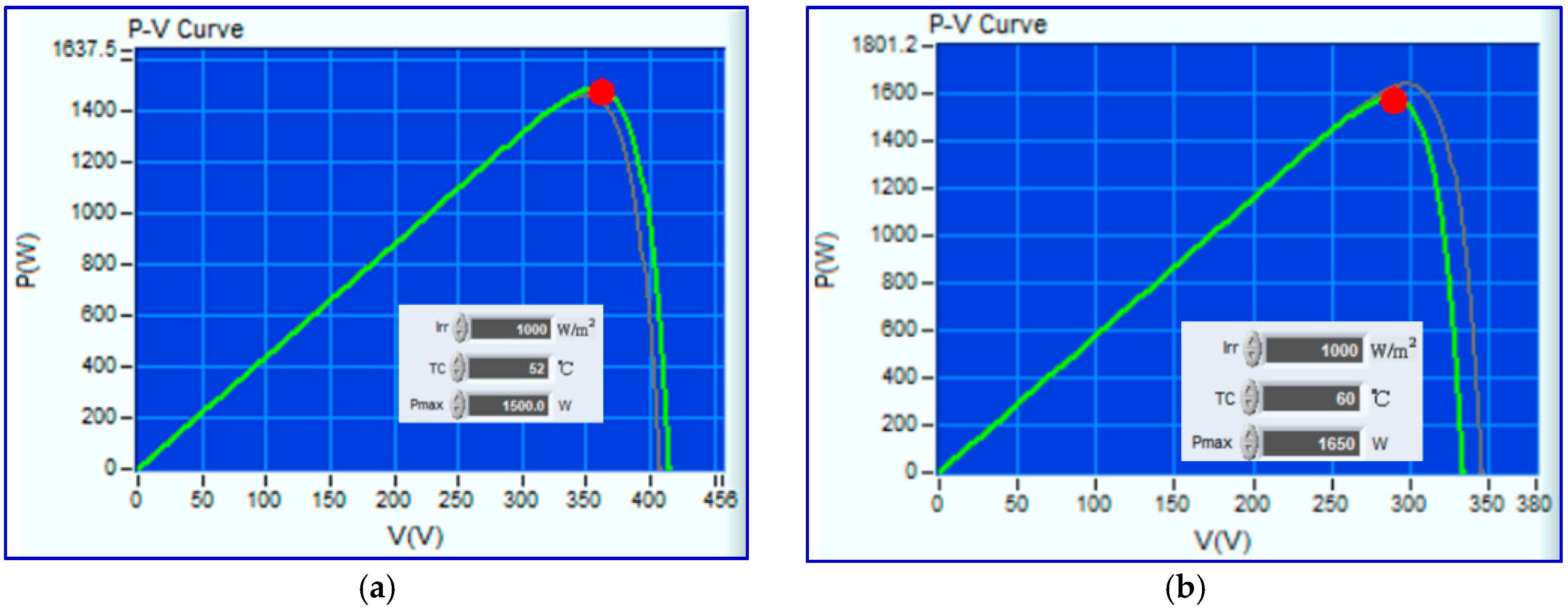
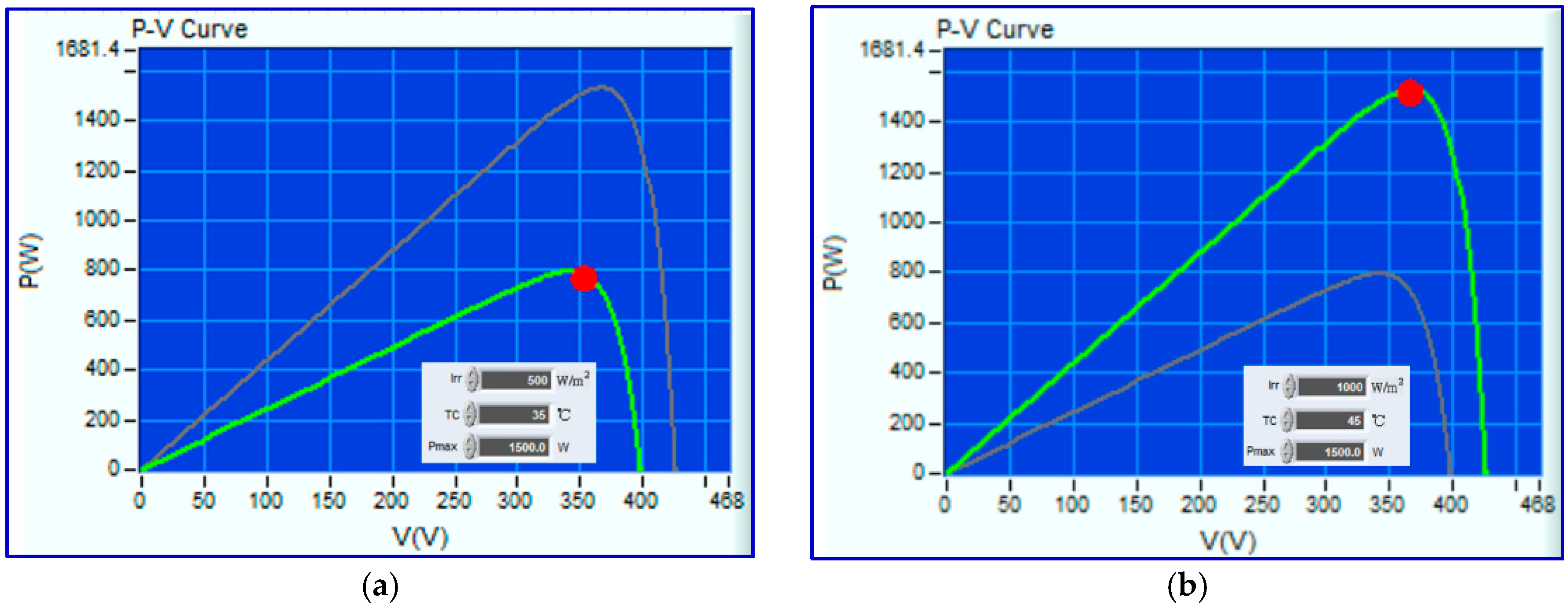
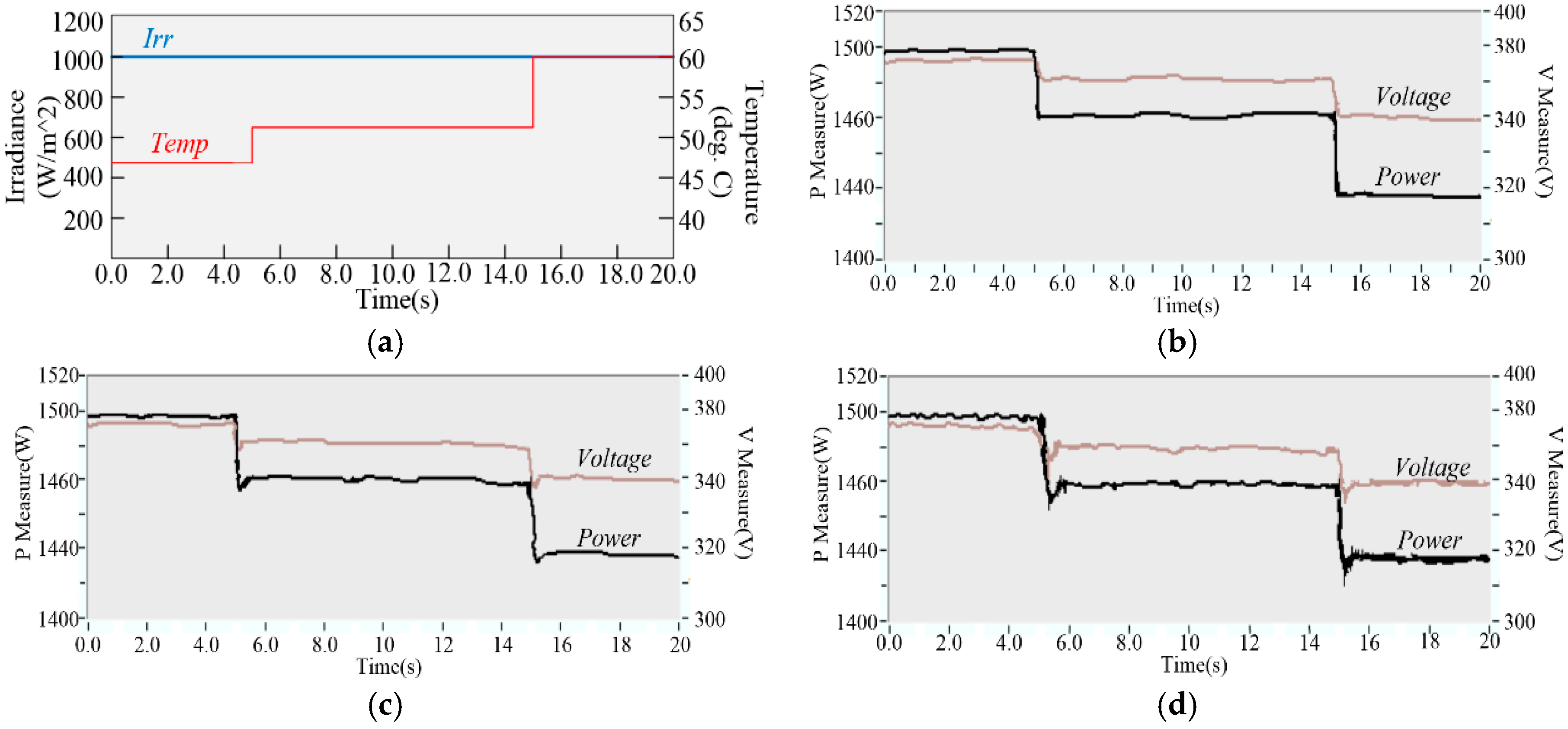
5. Experimental Validation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metry, M.; Shadmand, M.B.; Balog, R.S.; Abu-Rub, H. MPPT of Photovoltaic Systems Using Sensorless Current-Based Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. 2017, 53, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreeumporn, W.; Ngamroo, I. Optimal Superconducting Coil Integrated Into PV Generators for Smoothing Power and Regulating Voltage in Distribution System With PHEVs. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5402805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisi, A.R.; Moradi, M.H.; Jamasb, S. Classification and comparison of maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic system: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, J.P.; Babu, T.S.; Rajasekar, N. A comprehensive review on solar PV maximum power point tracking techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 826–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Seem, J.E.; Lei, P. Detection of Internal Resistance Change for Photovoltaic Arrays Using Extremum-Seeking Control MPPT Signals. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles Algarín, C.; Sevilla Hernández, D.; Restrepo Leal, D. A Low-Cost Maximum Power Point Tracking System Based on Neural Network Inverse Model Controller. Electronics 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebani, M.M.; Iqbal, T.; Quaicoe, J.E. Comparing bisection numerical algorithm with fractional short circuit current and open circuit voltage methods for MPPT photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 12–14 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Masoum, M.A.S.; Dehbonei, H.; Fuchs, E.F. Theoretical and experimental analyses of photovoltaic systems with voltageand current-based maximum power-point tracking. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2002, 7, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deopare, H.; Deshpande, A. Modeling and simulation of Incremental conductance Maximum Power Point tracking. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Energy Systems and Applications, Pune, India, 30 October–1 November 2015; pp. 501–505. [Google Scholar]
- Amri, B.; Ashari, M. The comparative study of Buck-boost, Cuk, Sepic and Zeta converters for maximum power point tracking photovoltaic using P&O method. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Information Technology, Computer, and Electrical Engineering (ICITACEE), Semarang, Indonesia, 16–18 October 2015; pp. 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.-M.; Hong, C.-M.; Chen, C.-H. Neural-Network-Based MPPT Control of a Stand-Alone Hybrid Power Generation System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3571–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatepe, E.; Hiyama, T. Artificial neural network-polar coordinated fuzzy controller based maximum power point tracking control under partially shaded conditions. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2009, 3, 239–253. [Google Scholar]
- Modani, D.; Shrivastava, V. Improvement in efficiency of PV module using soft computing based MPPT. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 16–18 March 2016; pp. 2273–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Narendiran, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Das, R.; Sahoo, A.K. Fuzzy logic controller based maximum power point tracking for PV system. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fourth International Conference on Computing, Communications and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Tiruchengode, India, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Da Rocha, N.M.M.; Martins, D.C.; Passos, J.C. MPPT method based on temperature control of the photovoltaic cells. In Proceedings of the 2016 12th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON), Curitiba, Brazil, 20–23 November 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, R.; Cruz, D. An Optimized Maximum Power Point Tracking Method Based on PV Surface Temperature Measurement. In Sustainable Energy—Recent Studies; Gebremedhin, A., Ed.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R.F.; Concerand, F.M.; Martins, D.C. A MPPT approach based on temperature measurements applied in PV systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies (ICSET), Kandy, Sri Lanka, 6–9 December 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Yu, I.A. Study on the optimal voltage for MPPT obtained by surface temperature of solar cell. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Busan, South Korea, 2–6 Novemver 2004; Volume 30, pp. 2040–2045. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.M.; Mustafa, S.S.; Mutlag, A.H. Design optimization of solar power system with respect to temperature and sun tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 Al-Sadeq International Conference on Multidisciplinary in IT and Communication Science and Applications (AIC-MITCSA), Baghdad, Iraq, 9–10 May 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. MPPT-based artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic systems and its implementation into field programmable gate array chips: Review of current status and future perspectives. Energy 2014, 70, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellita, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. Artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic applications: A review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 574–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, B.; Pradhan, R. A Comparative Study on Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques for Photovoltaic Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2013, 4, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algazar, M.M.; AL-monier, H.; EL-halim, H.A.; El Kotb Salem, M.E. Maximum power point tracking using fuzzy logic control. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 39, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.S.; Neelakantan, P.; Yoong, H.P.; Teo, K.T.K. Fuzzy Logic Based MPPT for Photovoltaic Modules Influenced by Solar Irradiation and Cell Temperature. In Proceedings of the 2011 UkSim 13th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation, Cambridge, UK, 30 March–1 April 2011; pp. 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Rezk, H.; Eltamaly, A.M. A comprehensive comparison of different MPPT techniques for photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy 2015, 112, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-X. Variable universe stable adaptive fuzzy control of a nonlinear system. Comput. Math. Appl. 2002, 44, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Chen, W. Fuzzy Logic Controllers for Specialty Vehicles Using a Combination of Phase Plane Analysis and Variable Universe Approach. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Ma, Y.; Newcomb, R.W.; Jin, D. Analog Circuit Implementation of a Variable Universe Adaptive Fuzzy Logic Controller. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 2008, 10, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Szeto, W. An Enhanced MPPT Method Combining Fractional-Order and Fuzzy Logic Control. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2017, 7, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekioua, D.; Matagne, E. Optimization of Photovoltaic Power Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, M.; Senjyu, T. Fuzzy Control of Distributed PV Inverters/Energy Storage Systems/Electric Vehicles for Frequency Regulation in a Large Power System. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Bian, X.G.; Liu, H.H.; Peng, T. A MATLAB-Simulink-Based PV Module Model and Its Application Under Conditions of Nonuniform radiation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2012, 27, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qahouq, J.A.A.; Batarseh, I. Improved solar PV cell Matlab simulation model and comparison. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Paris, France, 30 May–2 June 2010; pp. 2770–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Villalva, M.G.; Gazol, J.R.; Filho, E.R. Modeling and circuit-based simulation of photovoltaic arrays. In Proceedings of the 2009 Brazilian Power Electronics Conference, Bonito-Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, 27 September–1 October 2009; pp. 1244–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.T.; Kirschen, D.S.; Jenkins, N. A Model of PV Generation Suitable for Stability Analysis. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J. Variable Universe Adaptive Fuzzy Control for Liquid Lever. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, Wuhan, China, 17–18 October 2008; Volume 1, pp. 58–161. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.-Y.; Zeng, S.-P.; Li, J.-H. Variable universe fuzzy expert system for aluminum electrolysis. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messai, A.; Mellit, A.; Guessoum, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. Maximum power point tracking using GA optimized fuzzy logic controller and its FPGA implementation. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousi, S.M.R.; Moradi, M.H.; Basir, N.S.; Nemati, M. A functionbased maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Type | Linguistic | Universe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I/O | Min | Max | ||
| Power error/Volt error (x1) | Input | NB NS ZE PS PB | −40 | +40 |
| Error change (x2) | Input | NB NS ZE PS PB | −80 | +80 |
| Duty change (y) | Output | NB NM NS ZE PS PM PB | −0.09 | +0.09 |
| CE(x2) U(y) E(x1) | NB | NS | ZE | PS | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB | NB | NS | PS | PM | PB |
| NS | NS | PS | PM | PM | PB |
| ZE | NM | NS | ZE | PS | PM |
| PS | NS | ZE | PS | PM | PB |
| PB | NB | NM | NS | PS | PB |
| Electrical(STC) | Temperature Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Data | Specification | Data |
| Maximum Power (Pmax) | 330 W | Temperature Coefficient of Pmax | −0.41%/°C |
| Optimum Operating Voltage (Vmp) | 37.5 V | Temperature Coefficient of VOC | −0.38%/°C |
| Temperature Coefficient of ISC | 0.05%/°C | ||
| Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) | 46.2 V | Nominal Operating Cell Temperature | 45±2 °C |
| Operational Temperature | −40~+85 °C | ||
| Items | MPPT Methods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P&O | INC | ANN | FLC | Proposed VUFLC | |
| Dynamic response | Poor | Medium | High | Medium | High |
| Transient fluction | Bad | Bad | Good | Good | Good |
| Steady oscillation | Large | Moderate | Zero | Small | Zero |
| Static error | High | High | Low | Low | Low |
| Control accurcy | Low | Accurate | Accurate | Accurate | Excellect |
| Tracking speed | Slow | Slow | Moderate | Fast | Very fast |
| Overall efficiency | Medium | Medium | High | High | High |
| System complexity | Simple | Simple | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Temperature characteristics | Poor | Poor | Good | Good | Excellect |
| Condition (1000 W/m2) | The Experimental Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INC | FLC | Proposed VUFLC | ||
47 °C | Maximum power (W) | 1481.2 | 1485.3 | 1488.9 |
| Tracking efficiency (%) | 98.23 | 98.92 | 99.93 | |
52 °C | Maximum power (W) | 1452.1 | 1455.8 | 1460.0 |
| Tracking efficiency (%) | 98.01 | 98.74 | 99.90 | |
| 60 °C | Maximum power (W) | 1403.9 | 1407.7 | 1411.9 |
| Tracking efficiency (%) | 97.87 | 98.21 | 99.87 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fang, G.; Zhang, B.; Wen, H.; Tang, H.; Fu, L.; Chen, X. An Advanced Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for Photovoltaic Systems by Using Variable Universe Fuzzy Logic Control Considering Temperature Variability. Electronics 2018, 7, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120355
Wang Y, Yang Y, Fang G, Zhang B, Wen H, Tang H, Fu L, Chen X. An Advanced Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for Photovoltaic Systems by Using Variable Universe Fuzzy Logic Control Considering Temperature Variability. Electronics. 2018; 7(12):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120355
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yiwang, Yong Yang, Gang Fang, Bo Zhang, Huiqing Wen, Houjun Tang, Li Fu, and Xiaogao Chen. 2018. "An Advanced Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for Photovoltaic Systems by Using Variable Universe Fuzzy Logic Control Considering Temperature Variability" Electronics 7, no. 12: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120355
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, Y., Fang, G., Zhang, B., Wen, H., Tang, H., Fu, L., & Chen, X. (2018). An Advanced Maximum Power Point Tracking Method for Photovoltaic Systems by Using Variable Universe Fuzzy Logic Control Considering Temperature Variability. Electronics, 7(12), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120355






