Abstract
In the IoT/wearable devices, the antenna is shared with the receiver and transmitter of the transceiver. This requires the control of the switch between the antenna and the control circuitry to achieve both low insertion loss and high isolation. This paper presents a low insertion loss and high isolation switch based on Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch for 2.4 GHz Bluetooth low power (BLE) transceiver. The body-floating technique is used to improve the insertion loss’s performance. An ultra-small on-chip matching network with high Q-factor is proposed. The shunt transistors are used as active shunt capacitors that create the active matching network to improve isolation characteristics. The proposed SDPT switch was designed using 55 nm CMOS process with the total area of 110 μm × 210 μm. The insertion loss and isolation characteristics of the proposed SPDT switch observed at 2.4 GHz are 1.85 dB and 40 dB, respectively.
1. Introduction
Recently, IoT and wearable devices are constantly expanding their functionalities and applications. Some sensors are integrated into the devices to collect information from the environment. Each device has the role of monitoring and processing some parameters by its sensors and sharing information within the IoT system. To maintain the communication between these devices, some communication standards can be used such as Wi-Fi, ZigBee or Bluetooth. ZigBee is known as one of the most popular communication standards used in smart houses. However, ZigBee requires a special smart hub to control the communication of components within the system [1,2]. Wi-Fi is also a powerful communication standard that allows many features in the IoT field. Users can control and access the information of the remote sensing system via the internet connection provided by the Wi-Fi standard. However, Wi-Fi consumes more power, which has limited its application in wearable devices [3,4]. More prominent than the standard mentioned earlier, Bluetooth is known as a cheap solution for communication. Bluetooth is designed for the short distance communication with extremely low power consumption and simple communication protocol [5,6]. Therefore, Bluetooth is the standard communication idea for the sensor system [7,8,9,10]. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) plays an important role in achieving lower cost, lower power, and compact size.
The transmitter/receiver (Tx/Rx) of BLE requires antennas for communication. One antenna is shared between the Tx and Rx for reducing the size of the system, as shown in Figure 1. The key component that realizes this system is the radio frequency (RF) switch called the Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch [5,6,7,8,9]. The SPDT switch connects the transmit path or the receive path to the antenna in the Tx or Rx mode, respectively, while disconnecting the other path. This approach requires low insertion loss and high isolation to be achieved at the same time. The BLE applied to IoT/wearable devices is also required to have a compact size. Thus, integrating the full transceiver including the SPDT switch and its matching network into a single die is the best solution. Fully on-chip integration also improves the impedance discontinuity problem [11] when combining on-chip and off-chip components in the communication system. In another aspect, the Bluetooth standard is known as a cost-effective solution for communication. Therefore, the implement of the BLE should be based on the standard Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) process, which is commonly used for a low-cost solution.
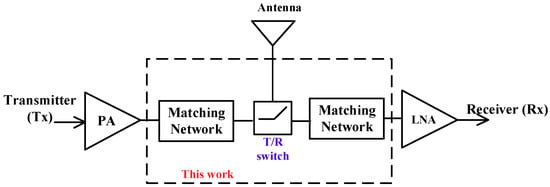
Figure 1.
Transceiver system diagram.
Several approaches have been proposed and the implemented SPDT switch has high performance for the transceiver system [12,13,14,15,16]. Most radio-frequency (RF) SPDT switches use the Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) process to implement the circuit because of the high on-state resistance and low off-state capacitance of the GaAs transistor. The work presented in [17] implemented SPDT switch by adopting High-Electron-Mobility Transistors (HEMTs) and thick anodized aluminum (Al2O3) layers that directly were mounted on an aluminum substrate for high electrical isolation. The SPDT switch presented in this article obtains the good insertion loss and return loss at 1.3 dB and 23 dB, respectively. However, this approach targets the low-noise and high-power system because this process requires a high power supply to maintain the performance of the transistors. Therefore, this approach cannot be used for the BLE. Another technology commonly used for implementing the SPDT switch is the RF micro-electromechanical system (MEMS). The approach presented in [18] constructed SPDT switch using the power splitter and two pairs of capacitive MEMS shunt switches. This structure is implemented on a quartz substrate. The performance of insertion, isolation, and return loss at 20 GHz are 0.32, 31.2, and 25.3 dB, respectively, which is impressive. However, the size of the SPDT switch is relatively big (21 mm × 8 mm). The size of this techniques is expected to be bigger if it is scaled up to operate at 2.4 GHz resonant frequency of BLE. These two processes mentioned above are suitable for the off-chip level application because they are hard to be integrated in IoT/wearable devices and they require expensive techniques for implementation.
The approach presented in [19] is proposed for the on-chip level. The SPDT switch presented in this article is implemented using silicon-germanium (SiGe) BiCMOS process technology. The shunt-shunt topology is used in the structure of the SPDT switch in [19]. The performance of this SPDT switch is obtained based on the layout optimization and highly depends on the process’ performance itself. However, the final insertion loss and isolation are 2.3 dB and 32 dB, respectively, which is under the expectation because the SiGe is a high-cost process. This is also difficult to integrate with traditional CMOS processes as the target of this research mentioned above.
When the transistor of the standard CMOS process is used as a main switch in the SPDT switch, the transistor input impedance drops when the input power increases. This is a major disadvantage of the standard CMOS. To solve this problem, the study presented in [20] proposes the floating body technique by connecting a 5 kΩ resistor to the body terminal of the transistor to maintain the minimum impedance when the input power increases. The technique provides an impressive result of insertion loss of 0.7 dB and isolation of 35 dB at 8 GHz. However, it requires the off-chip matching network. The matching network takes an important role in the structure of SPDT. It not only matches the impedance between two terminals for maximizing the power transferred but the power loss in the matching network also decides the efficiency of the transceiver system. The off-chip matching network will cause the impedance discontinuity problem and large size occupation, and requires long connection line to the SPDT switch core. Therefore, the off-chip matching network reduces the overall effectiveness of the SPDT switch dramatically.
This paper proposes a fully on-chip SPDT switch design using a standard CMOS process for a low-cost BLE. The fully on-chip active matching network that connects two terminals of the SPDT switch to the receiver and transmitter circuits is proposed. The on-chip solenoid inductor structure is used to implement the matching network for reducing the total size of SPDT switch and eliminating the effect of magnetic flux generated from the on-chip inductor to the surrounding circuits. The body resistors of the main switch transistors have a great effect on the loss when power is transferred through the transistor channel. Therefore, in this study, the effects of the parasitic resistors at the body of the switch transistor are discussed and the body floating technique is used to improve the insertion loss performance. This SPDT switch structure is proposed to be adopted in the 55 nm CMOS process devices.
2. Circuits Implementation
2.1. SPDT Switch Circuit Design
The proposed SPDT switch structure is shown in Figure 2. The two main switches are the most important components that decide the insertion loss characteristic of the SPDT. The two main switches consist of two serial transistors M1 and M3. Typically, the body of the transistor is connected to the source or the drain directly. When the power level is increased, the parasitic diode formed between the drain and the body is of the transistor is turned on. As a result, the power is transferred to the source as well as to the body through the parasitic diode, increasing the insertion-loss of the transistor [20]. To reduce the power loss through the parasitic body diode, a large resistor is connected to the body terminal of the two main-switch-transistor. When the switch is turned on, it works as a resistor and dissipates power. By increasing the size of the transistor, the turn-on resistance is reduced, creating an increment of the parasitic capacitance that commonly causes several side effects. Therefore, the sizes of the transistors should be optimized to achieve the trade-off between the turn-on resistor and the parasitic capacitance that affect the power loss and isolation characteristics of the SPDT switch. The detailed size of the main switch transistors is specified in Table 1.
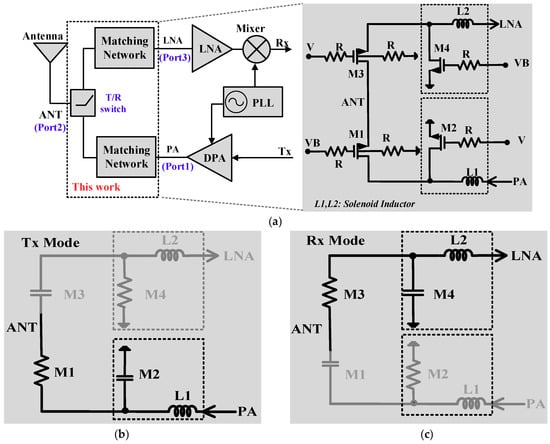
Figure 2.
(a) RF Transceiver system with the proposed SPDT based switch; (b) equivalent model in Tx mode; and (c) equivalent model in Rx mode.

Table 1.
Components size information.
In the RF system, the impedance mismatch is a critical problem, especially in the SPDT switch design. A matching network not only improves the power transfer through the SPDT switch when it is enabled but also limits the power through SPDT switch when it is disabled. Therefore, this research proposes the concept of an active matching network. The two types of components that are mostly used in a matching network are capacitor and inductor. To implement the concept of an active matching network, the value of the components of the matching network need to be controllable. The inductor is always a big component in all systems, thus making controllability costly and area consuming. On the other hand, the capacitor is always cheaper. The value controllable capacitor is easily obtained using a passive capacitor or an active MOSFET device capacitor. Therefore, in the proposed SPDT switch, the active matching network is implemented using the shunt transistors M2 and M4 as a shunt capacitor when they are turned off. When the transceiver operates in Tx mode, the transistor M1 is turned on and acts as a resistor while the transistor M2 is turned off and plays the role of a capacitor to increase isolation. In Tx mode, the input impedance of M1 side must be matched with the output impedance of the Power Amplifier (PA). The inductor L1 is used to form the matching network for the Tx path. A similar concept is applied for M4 and L2 in the Rx path. In Rx mode, the input impedance of M4 side is matched with input impedance of the Low-Noise Amplifier (LNA) by the inductor L2. Based on this concept, the active matching network can be obtained with a cheap and compact size solution. For the on-chip integration purpose, the matching network must be extremely small. Solenoid structure inductor, explained in next section, is used to create L1 and L2. To match the terminals’ impedance of the SPDT switch with the input impedance of the LNA and output impedance of the PA, the value of L1 and L2 are designed to be 1.1 nH and 9.9 nH, respectively.
2.2. Solenoid Inductor Design
The traditional on-chip inductance has the spiral structure formed by the on-chip metal in a signal layer. The magnetic flux of the spiral has the vertical direction. The magnetic flux line points to the silicon substrate of the chip or other metal layers in the area wherein the spiral inductor is located. It is very difficult to isolate and protect the other components from the effect of the magnetic flux. Therefore, other components of the circuit are not allowed to be placed around the conventional spiral inductor. The size of the spiral inductor is fixed for a wide range inductance value. To increase the inductance value of the inductor within a specific range, the number of metal wire turns is increased into the internal of spiral inductor. That is the reason for large area consumption when using spiral structure. This research proposes to use the solenoid inductor structure formed by two stacked metal layers on the chip, as shown in Figure 3. The magnetic flux is formed in the concentric rectangle of the solenoid structure. The magnetic flux line of the solenoid has horizontal direction, thus can be isolated by the via barrier cover around the solenoid inductance structure. The size of solenoid structure depends on the inductance value, thus is flexible for design size optimization.
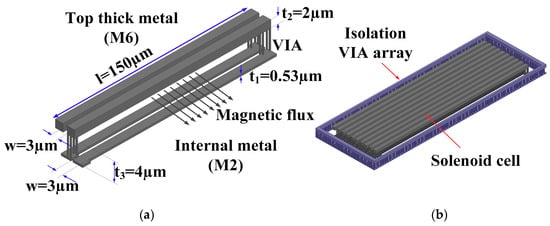
Figure 3.
(a) Solenoid unit cell; and (b) 3D model of proposed solenoid inductor.
There are two ways to increase the inductance value of the solenoid: increasing the number of turns (N) of the solenoid or increasing the magnetic flux through each turn by increasing the cross-section area of the solenoid. By increasing the number of turns, parasitic resistance of the solenoid is increased, thus qualify factor (Q-factor) of the inductor is reduced. In this study, the cross-section area is increased using metal 2 and metal 6 to form the solenoid inductor. Hence, the inductance value is increased while the Q-factor is maintained. The proposed solenoid inductor structure is created and extracted using 3D field solver, HFSS. The detailed size of the metal layers of the solenoid are specified in Figure 3. The top metal layer is a thick aluminum metal layer and the bottom is the copper in the 55 nm CMOS process. The dielectric material is stacked by four internal back-end-of-line (BEOL) dielectric layers with the sizes and material characteristics specified in the process design kit (PDK). At 2.4 GHz, the extracted Q-factor of L1 and L2 are 10.5 and 7.5, respectively, as shown in Figure 4. The s-parameter of the proposed solenoid is extracted from the 3D field electromagnetic (EM) simulation and imported to Cadence Spectre to simulate the full SPDT switch.
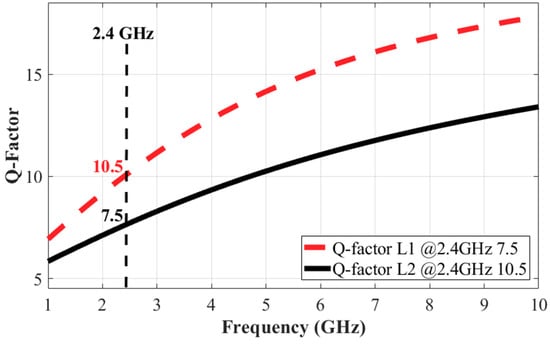
Figure 4.
Simulated quality factors of solenoid inductors.
To validate the magnetic flux distribution of the solenoid inductor structure, the 3D field simulation is also used to extract the radiation field. Two structures with and without the via array ring are simulated in ANSYS HFSS. The H-field simulation results are shown in Figure 5. The magnetic fields are plotted at the operating frequency of the SPDT switch at 2.4 GHz. To examine the effectiveness of the via array to the solenoid inductor, the internal magnetic fields of these two versions are shown at the cross view in Figure 5c. The internal magnetic fields are mostly the same in the two versions, thus the inductance of the solenoid is not affected by adding the via array ring. In the structure without via array ring, the magnetic field widely expands in the horizontal direction, as shown in Figure 5b. By using the via array ring to cover the boundary of the solenoid inductor, the magnetic field surrounds the solenoid is isolated inside the via array ring, as shown in Figure 5a. Outside of the via array ring, the magnetic field is significantly reduced. The strength of the H-field is examined at the points that have the same distance from the solenoid; the field strength is 0.2 A/m and 50 A/m for the simulation case with and without the via array ring, respectively. The magnetic H-field is well known as the main reason causing electromagnetic interference (EMI) in the electronic devices [21]. Reducing the H-field at the area surrounding the solenoid improves the EMI characteristic of the SPDT switch and the overall transceiver system. This allows other components in the system to be placed closer to the solenoid without suffering from the EMI effect, thus reducing the total size of the SPDT switch and improving the overall performance of the transceiver system.
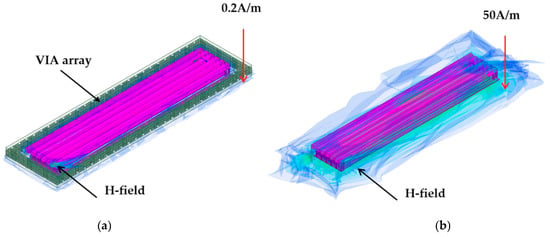
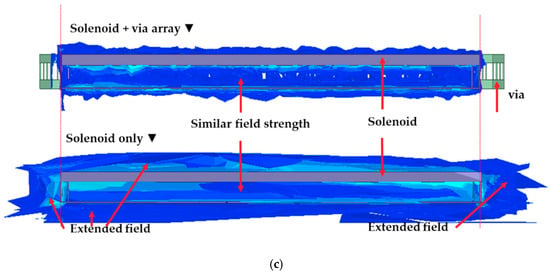
Figure 5.
Solenoid inductor magnetic field 3D simulation results: (a) Solenoid and via array H-field; (b) Solenoid without via array H-field; and (c) internal of solenoid H-field.
3. Results and Discussion
The dimensional parameter of the solenoid is optimized in HFSS to get the exact value before implemented in the circuit layout. The material and process information of the CMOS 55 nm process are considered when designing the solenoid inductor. Figure 6 shows the layout of the proposed SPDT switch. Four solenoid unit cells are combined to create an eight-turn inductor (L1 = 1.1 nH) for the matching network of the Tx side. Eighteen solenoid unit cells are combined to create the 36-turn inductor (L2 = 9.9 nH) for the matching network of the Rx side. The metal rings formed by metal 2 to metal 6 are combined with VIAs to create the barrier for isolating the electromagnetic flux. The area of the SPDT switch is 110 µm × 210 µm. By considering only inductances, layout size is reduced by six times compared to that of the traditional on-chip spiral inductor with the same value [22]. The rectangular shape of the solenoid inductor is easier to place with another component than the octagon shape of the traditional spiral inductor.
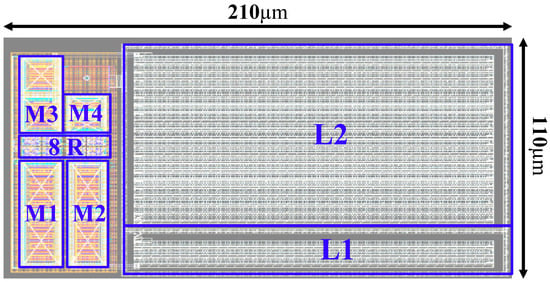
Figure 6.
Layout pattern of proposed SPDT switch.
The S-parameter of the two solenoid inductor structures (L1 and L2) are extracted by the 3D-field solver HFSS (frequency range up to 5 GHz; resolution step 1 MHz) and applied to the simulation of the SPDT switch. All the layout parasitics are extracted and applied to post-layout simulation process. The Monte Carlo analysis is applied to validate the process variation and temperature variation during the post-layout simulation. The temperature deviation is from −35 to 80 °C. Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 show the insertion losses, reflection losses, and isolations of the Tx and Rx modes, respectively. The definition of ports is specified in Figure 2a where port 1 is the Tx side, port 2 is the antenna termination, and port 3 is the Rx side. In typical simulation condition, the proposed SPDT switch achieves the insertion loss of −0.9 dB and −1.85 dB at the Tx and Rx modes, respectively. The simulation results already included the insertion loss in the parasitic resistor of the main switch, on-chip interconnect, and pad parasitic. By using Monte Carlo in the post-layout simulation, with a consideration of the process and temperature variations, the deviations of insertion losses are 0.4 dB for Rx mode and 0.2 dB for Tx mode, as shown in Figure 8. In the worst case, insertion losses of the Rx and Tx mode are −1.95 dB and −1.09 dB, respectively. The process variation has small effect on the deviation of the insertion loss of the proposed SPDT switch. Similar for the reflection loss of both the operating mode Rx and Tx, the process and temperature variations create the deviation on the reflection loss of the proposed SPDT switch by 1.9 dB in the Rx mode and 0.4 dB in the Tx mode. The worst case of the reflection loss performance is −11.3 dB for the Rx mode and −13.4 dB for the Tx mode, as shown in Figure 8.
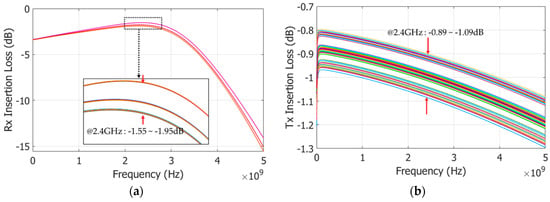
Figure 7.
Insertion losses—Monte Carlo simulation results: (a) Rx mode; and (b) Tx mode.
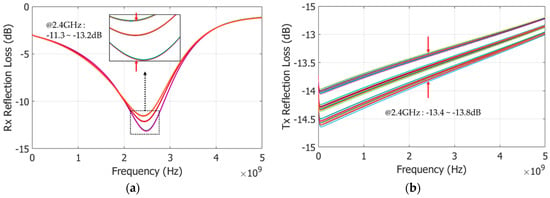
Figure 8.
Reflection loss—Monte Carlo simulation results: (a) Rx mode; and (b) Tx mode.
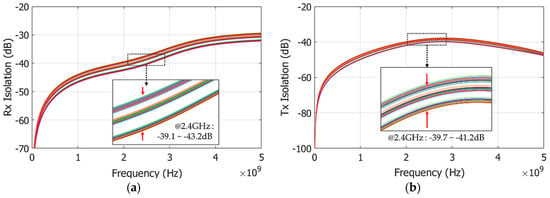
Figure 9.
Isolation—Monte Carlo simulation results: (a) Rx mode; and (b) Tx mode.
In typical simulation condition, the isolations of Rx and Tx modes are −42.4 dB −40.56 dB, respectively. The deviations when considering the process and temperature variations are 4.1 dB and 1.5 dB for Rx and Tx mode, respectively. The isolation characteristic of the Rx mode of the proposed SPDT switch is significantly affected by the process and temperature variations. However, in the worst case, the isolation of the Rx mode maintains a good value at −39.1 dB, as shown in Figure 9. With this isolation property, the Tx and Rx signals are isolated completely. This significantly improves the noise figure performance of the overall transceiver system. The isolation is achieved by adopting the active matching network implemented by two shunt transistors M2 and M4. When these transistors are turned off, it matches the SPDT switch terminal to the driver. When they are turned on, the matching network changes their impedance so that the SPDT switch terminal is not matched to driver making the isolation increase.
There is a trade-off between the die size and the performance of the switch. Compared to the SPDT switch with the spiral inductor, performance is slightly degraded but can be negligible when considering the benefit of the ultra-small area of the switch. Besides the insertion loss and isolation, the reflection loss (S22) also maintains below −11 dB over the wide frequency range for both the Rx and Tx mode.
The overall performance of the proposed SPDT switch is compared with the previous works in Table 2. Among the SPDT switch designs compared in Table 1, only two works implemented the SPDT switch using a normal CMOS process which is the SPDT switch proposed in this paper and the structure presented in [20]. Compared to [20], the insertion loss of the proposed SPDT switch is slightly higher but the isolation characteristic is significantly better compared to the approach presented in [19]. The SPDT switch proposed in this paper has better performance and a smaller size while it only requires normal CMOS process to implement the circuit. As mentioned above, the matching network plays a very important role in the performance of SPDT switch. The solenoid inductor used in the matching network slightly reduces the insertion loss performance by 0.75 dB as compared to [20]. In return, the die space is reduced by six times when compared to using the traditional spiral inductor. The isolation performance is also improved significantly. When compared with all others previous work, the proposed SPDT switch has the highest isolation factor at 40.56 dB.

Table 2.
Performance comparison with prior works.
4. Conclusions
This paper presents a low insertion loss, high isolation and extreme compact SPDT switch design for an on-chip 2.4 GHz Bluetooth Low-Energy transceiver. At the operating frequency of 2.4 GHz, in typical simulation condition, the switch achieved −0.96 dB and −1.85 dB insertion loss, and −40.56 dB and −44.4 dB isolation of the Tx and Rx modes, respectively. By considering the process and temperature variations on the post-layout simulation, in the worst case, the insertion loss is maintained at −1.95 dB and isolation is maintained at −39.1 dB. The isolation factor is achieved by adopting the proposed active matching network. The low insertion loss is obtained by using the body floating techniques and switch transistor dimension optimization.
By using the on-chip solenoid inductor, the total size of the proposed SPDT switch including the matching network is much lower than in previous works while good performance is maintained. The isolation characteristic of this SPDT switch is even better than those of the previous works. The performance of the SPDT switch presented in this research article is obtained by the post-layout simulation with the consideration of the process and temperature variations by Monte Carlo method. The s-parameter of solenoid inductor design is extracted by the 3D field simulation and imported to cadence to do the post-layout simulation. The total size of this SPDT switch is 0.21 × 0.11 mm2. This SPDT switch is suitable for the transceiver system of IoT/wearable devices which require compact size and high-performance components. In the future, this proposed SDPT switch structure can be optimized to operate at different frequency ranges and applied to another transceiver system such as ZigBee and Wi-Fi to reduce the size and cost of these systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T.K.N.; Investigation, T.T.K.N.; Methodology, D.L. and S.K.; Supervision, M.L., K.H., Y.Y. and K.-Y.L.; Writing—original draft, T.T.K.N.; Writing—review & editing, T.T.K.N.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the MOTIE (Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy) (10080622) and KSRC (Korea Semiconductor Research Consortium) support program for the development of the future semiconductor device.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Peng, C.; Qian, K.; Wang, C. Design and Application of a VOC-Monitoring System Based on a ZigBee Wireless Sensor Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2255–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Choi, C.; Lee, I. More efficient home energy management system based on ZigBee communication and infrared remote controls. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2011, 57, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Savolainen, P.; Siekkinen, M.; Wang, A.; Yang, L.; Ylä-Jääski, A.; Tarkoma, S. Modeling Energy Consumption of Data Transmission over Wi-Fi. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2014, 13, 1760–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Cheung, H.M.; Huang, L.; Huang, J. Power-Delay Tradeoff with Predictive Scheduling in Integrated Cellular and Wi-Fi Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensworth, J.F.; Reynolds, M.S. BLE-Backscatter: Ultralow-Power IoT Nodes Compatible with Bluetooth 4.0 Low Energy (BLE) Smartphones and Tablets. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, W.S.; Dwijaksara, M.H.; Jeong, D.G. Performance Analysis of Neighbor Discovery Process in Bluetooth Low-Energy Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, B.; Huang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, H.; Xu, K.; Deng, F. A Low Cost BLE Transceiver with RX Matching Network Reusing PA Load Inductor for WSNs Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Mo, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, F.; Wang, W. A 11 mW 2.4 GHz 0.18 µm CMOS Transceivers for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2017, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-R.; Beak, D. 25–34 GHz Single-Pole, Double-Throw CMOS Switches for a Ka-Band Phased-Array Transceiver. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papotto, G.; Carrara, F.; Finocchiaro, A.; Palmisano, G. A 90-nm CMOS 5-Mbps Crystal-Less RF-Powered Transceiver for Wireless Sensor Network Nodes. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Goto, K.; Ishihara, T. Asymptotic solution with higher-order terms for scattered fields by an impedance discontinuity of a planar impedance surface. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; pp. 2503–2506. [Google Scholar]
- Cetindogan, B.; Ustundag, B.; Turkmen, E.; Wietstruck, M.; Kaynak, M.; Gurbuz, Y. A D-Band SPDT Switch Utilizing Reverse-Saturated SiGe HBTs for Dicke-Radiometers. In Proceedings of the German Microwave Conference (GeMiC), Freiburg, Germany, 12–14 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Song, C.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, H.; Yoo, S.-S.; Hong, S.; et al. Low Power FSK Transceiver using ADPLL with direct modulation and integrated SPDT for BLE Application. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), Toyama, Japan, 7–9 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Thome, F.; Ture, E.; Brückner, P.; Quay, R.; Ambacher, O. W-band SPDT switches in planar and tri-gate 100-nm gate-length GaN-HEMT technology. In Proceedings of the German Microwave Conference (GeMiC), Freiburg, Germany, 12–14 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ulusoy, A.Ç.; Song, P.; Schmid, R.L.; Khan, W.T.; Kaynak, M.; Tillack, B.; Papapolymerou, J.; Cressler, J.D. A Low-Loss and High Isolation D-Band SPDT Switch Utilizing Deep-Saturated SiGe HBTs. IEEE Microwave Wireless Compon. Lett. 2014, 24, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, P. Analysis of parasitic effects in triple-well CMOS SPDT switch. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.K.; Won, Y.S. X-band high-power HEMT SPDT switch with selectively anodised aluminum substrate. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Rantakari, P.; Malmqvist, R.; Samuelsson, C.; Vaha-Heikkila, T.; Rydberg, A.; Varis, J. Switched Beam Antenna Based on RF MEMS SPDT Switch on Quartz Substrate. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2009, 8, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davulcu, M.; Özeren, E.; Kaynak, M.; Gurbuz, Y. A New 5–13 GHz Slow-Wave SPDT Switch with Reverse-Saturated SiGe HBTs. IEEE Microwave Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 27, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.C.; Tsai, Z.M.; Liu, R.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Huei, W. Design and Analysis for a Miniature CMOS SPDT Switch Using Body-Floating Technique to Improve Power Performance. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 2006, 54, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Beinart, R.; Nazarian, S. Effects of External Electrical and Magnetic Fields on Pacemakers and Defibrillators: From Engineering Principles to Clinical Practice. Circulation 2013, 128, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, T.K.N.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, K.Y. A Low Insertion Loss, High Isolation Switch Based on Single Pole Double Throw for 2.4GHz BLE Applications. IEIE Trans. Smart Process. Comput. 2016, 5, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).