A Multi-Slope Sliding-Mode Control Approach for Single-Phase Inverters under Different Loads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
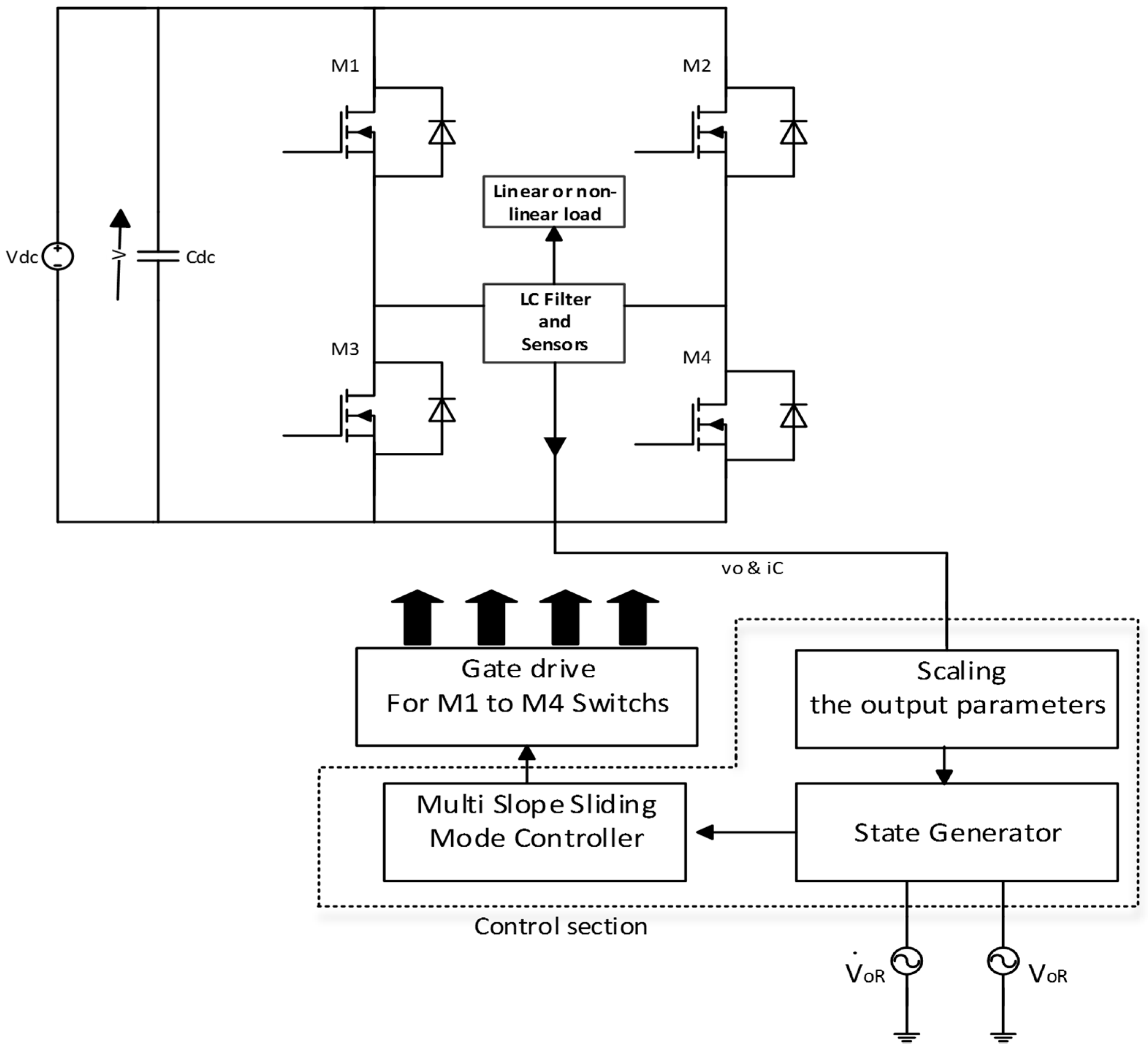
2. System Description
3. Suggested Control Structure
3.1. Conventional SMC Drawbacks
3.2. SMC Using Non-Linear Function
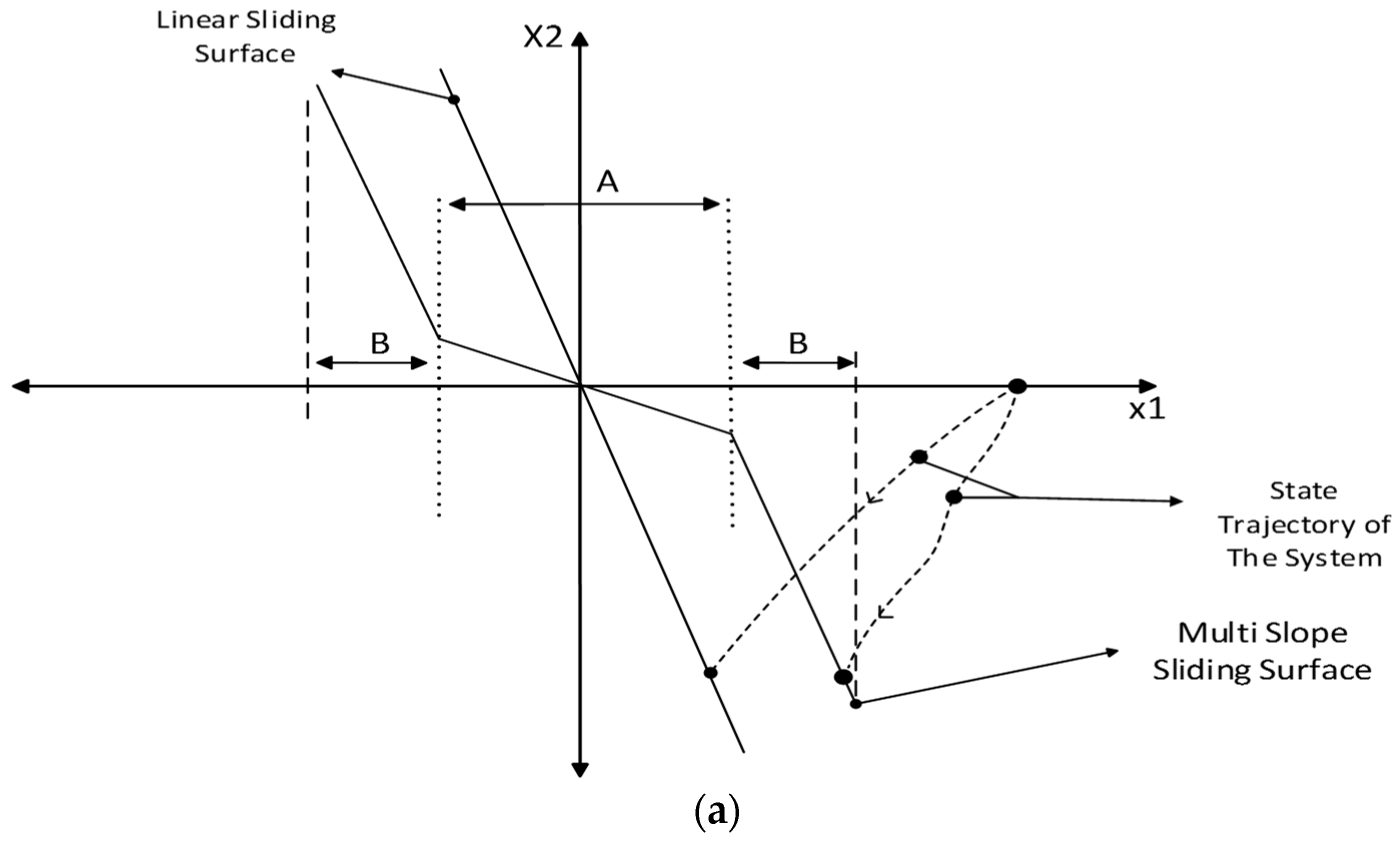
3.3. Multi-Slope (MS) Function
3.4. MS Function Coefficients Setting
- (1)
- δ coefficient: This coefficient adjusts the slope of Part A and should be positive (δ > 0). On the other hand, by changing this coefficient, the gain of the function will be changed for small error values.
- (2)
- α1 coefficient: This coefficient is utilized in MS function to adjust the slope of Part B and its effect on slope of Part A is negligible. In principle, this coefficient is utilized to adjust the gain of the MS function for large values of the error.
- (3)
- α2 coefficient: This coefficient adjusts the height of Part A. Therefore, by increasing this coefficient, the height of Part A will increase. It is worth mentioning that by increasing the value of this coefficient, low values of error in the input of the function creates more effect in the output of the function.
3.5. Sliding Surface and Stability Considerations
4. Simulation Results
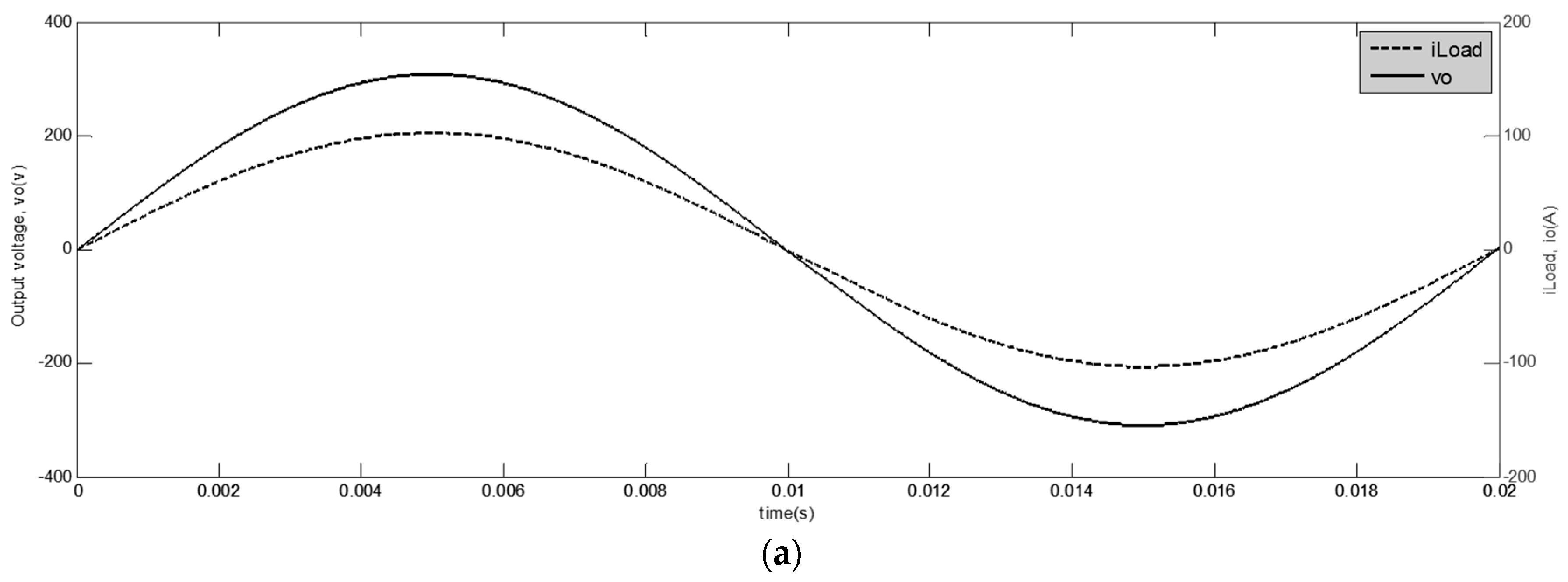
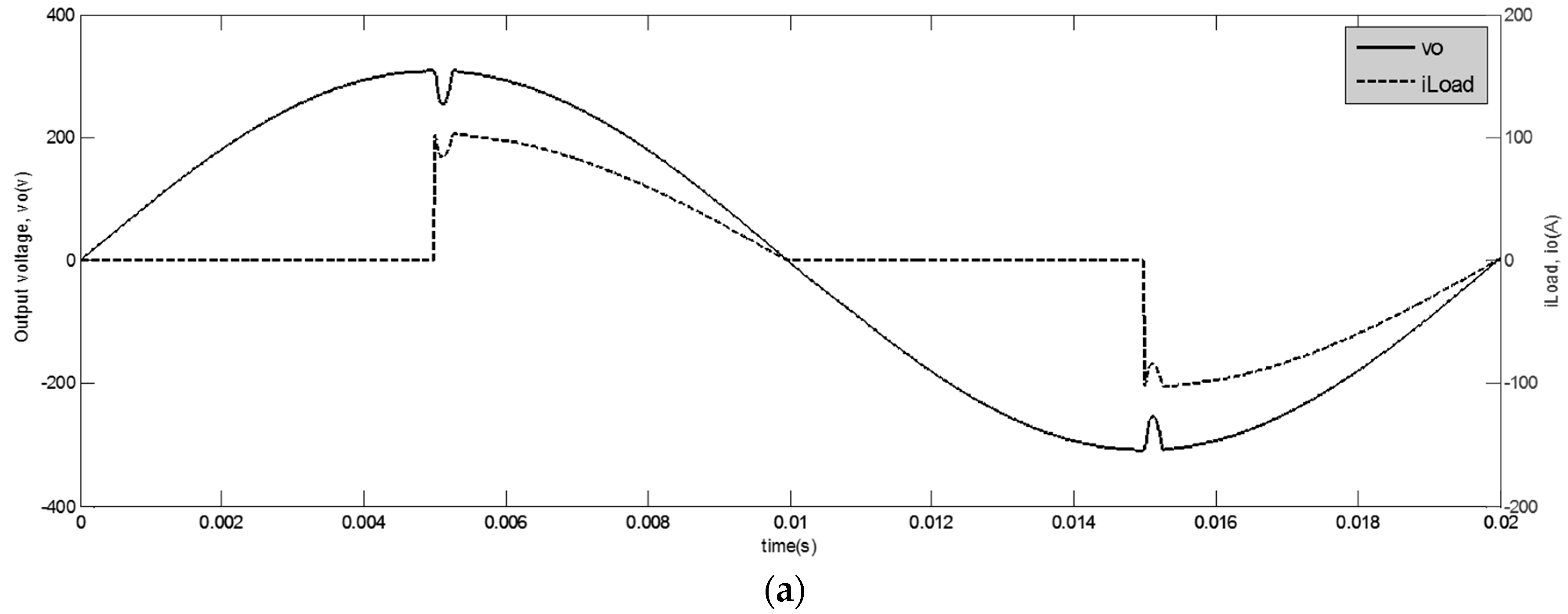
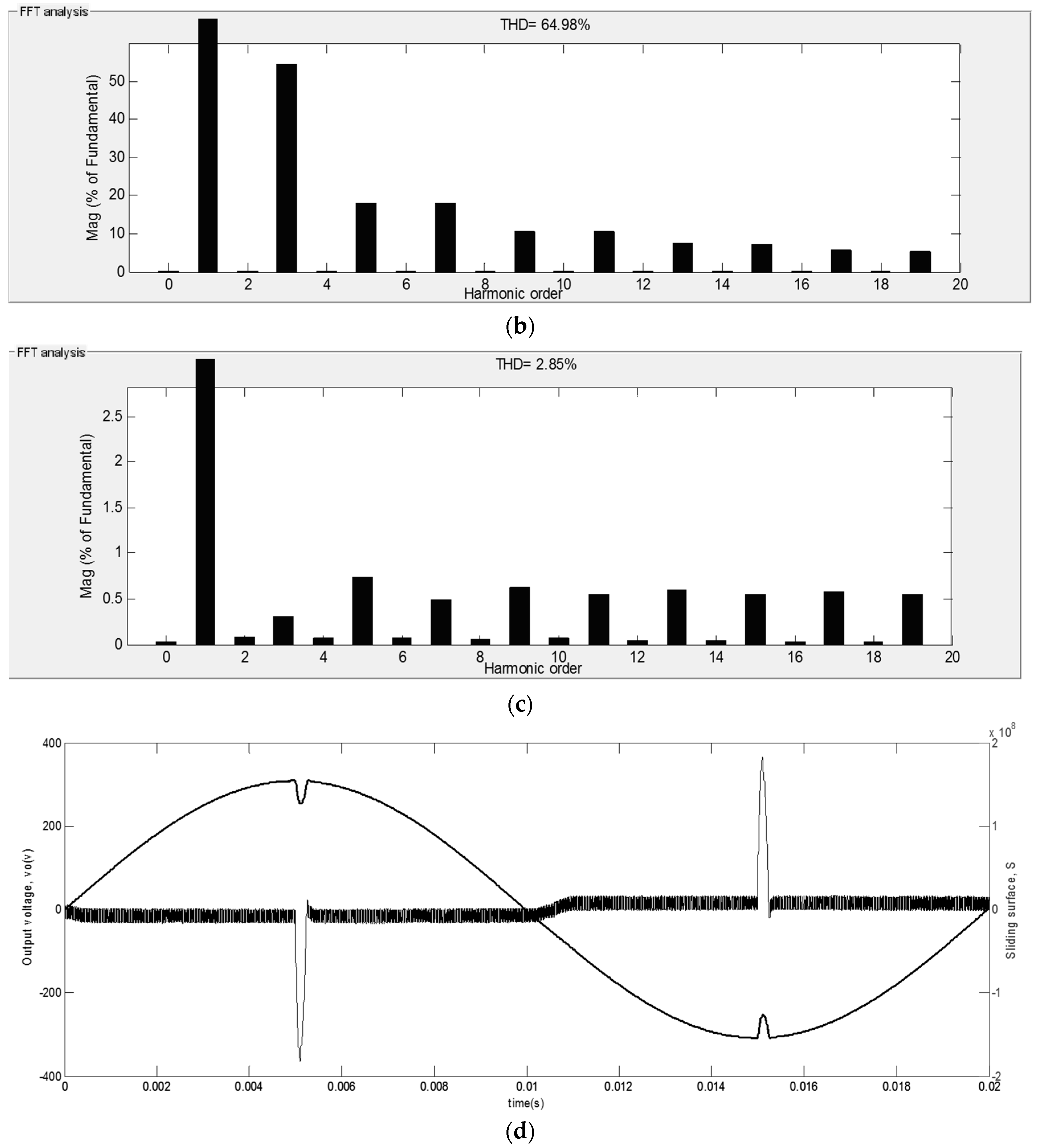
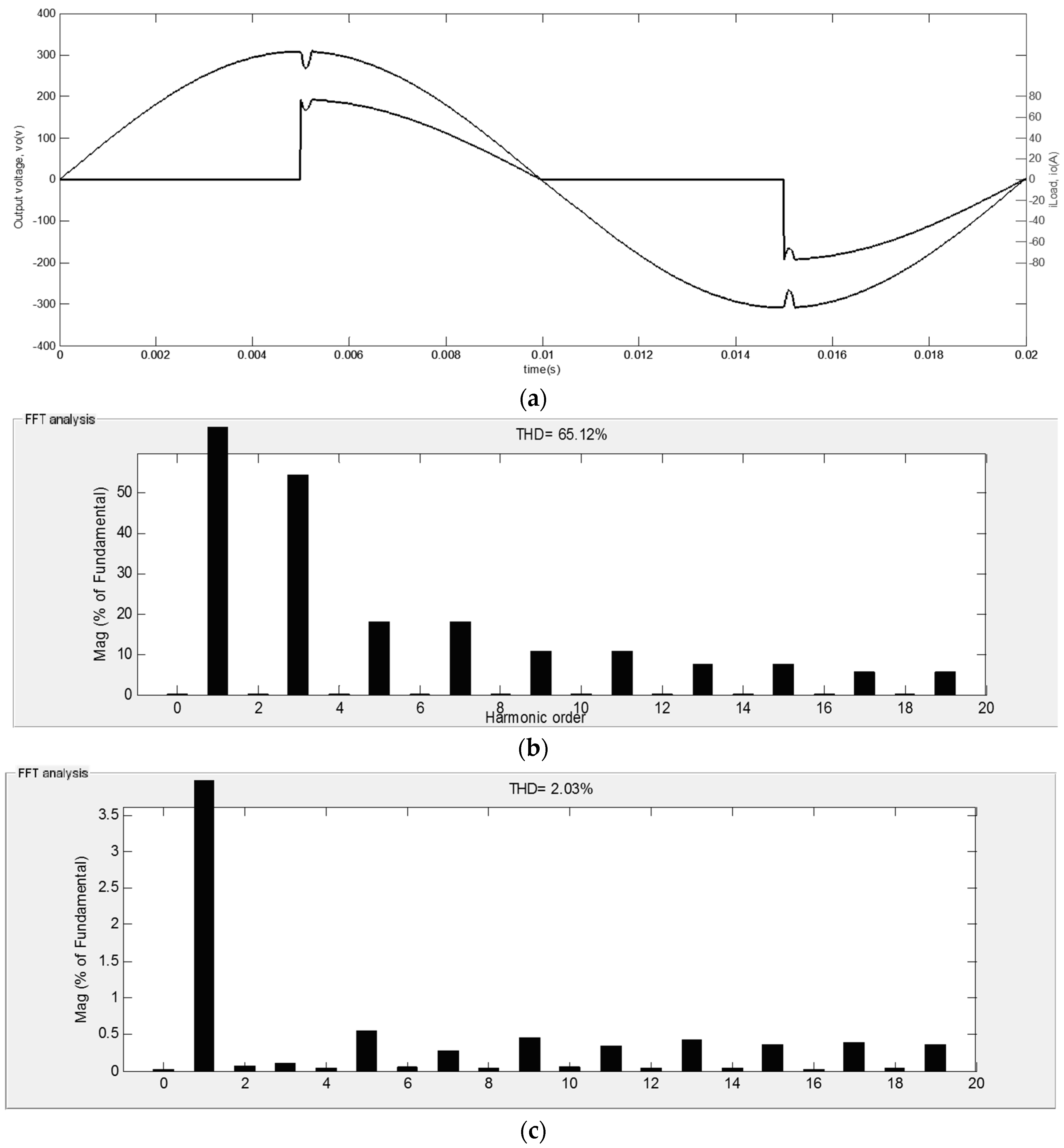
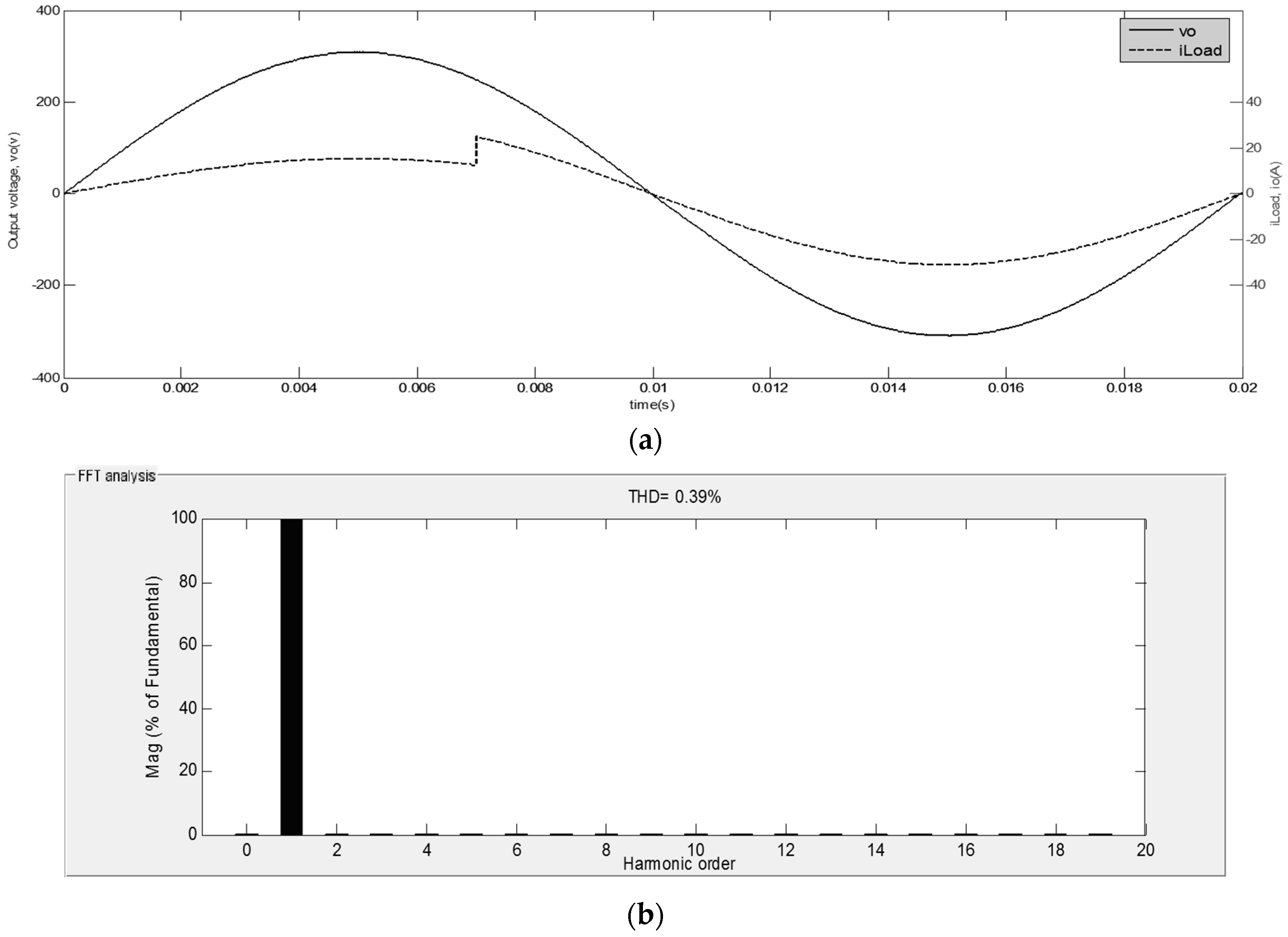
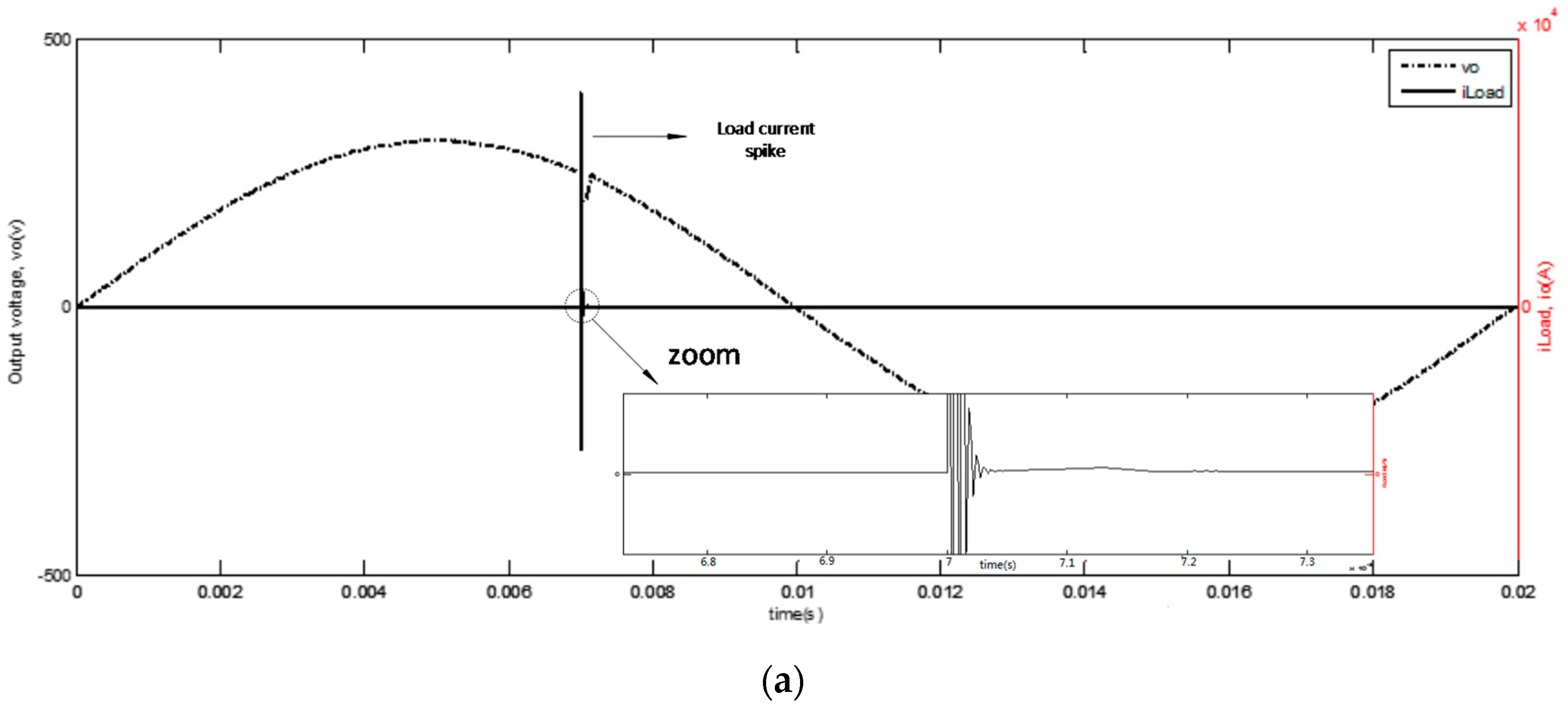
4.1. Resistive Load (R = 3 Ω)
4.2. Non-Linear TRIAC-Controlled Resistive Load (R = 3 Ω)
4.3. Non-Linear TRIAC-Controlled Resistive Load (R = 4 Ω)
4.4. Dynamic Change in the Load Resistance
4.5. Load Type Change
4.6. Rectifier Load
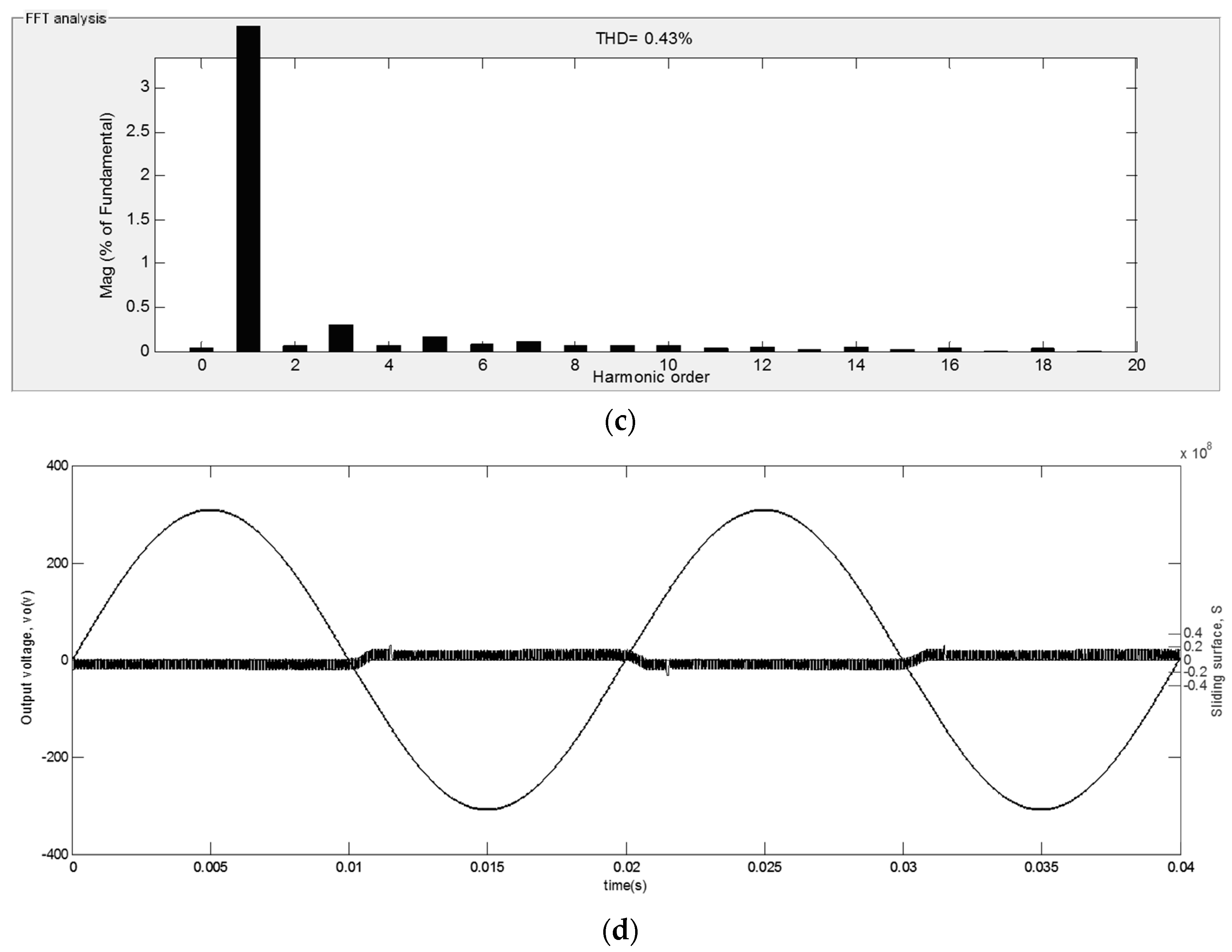
4.7. State Trajectories
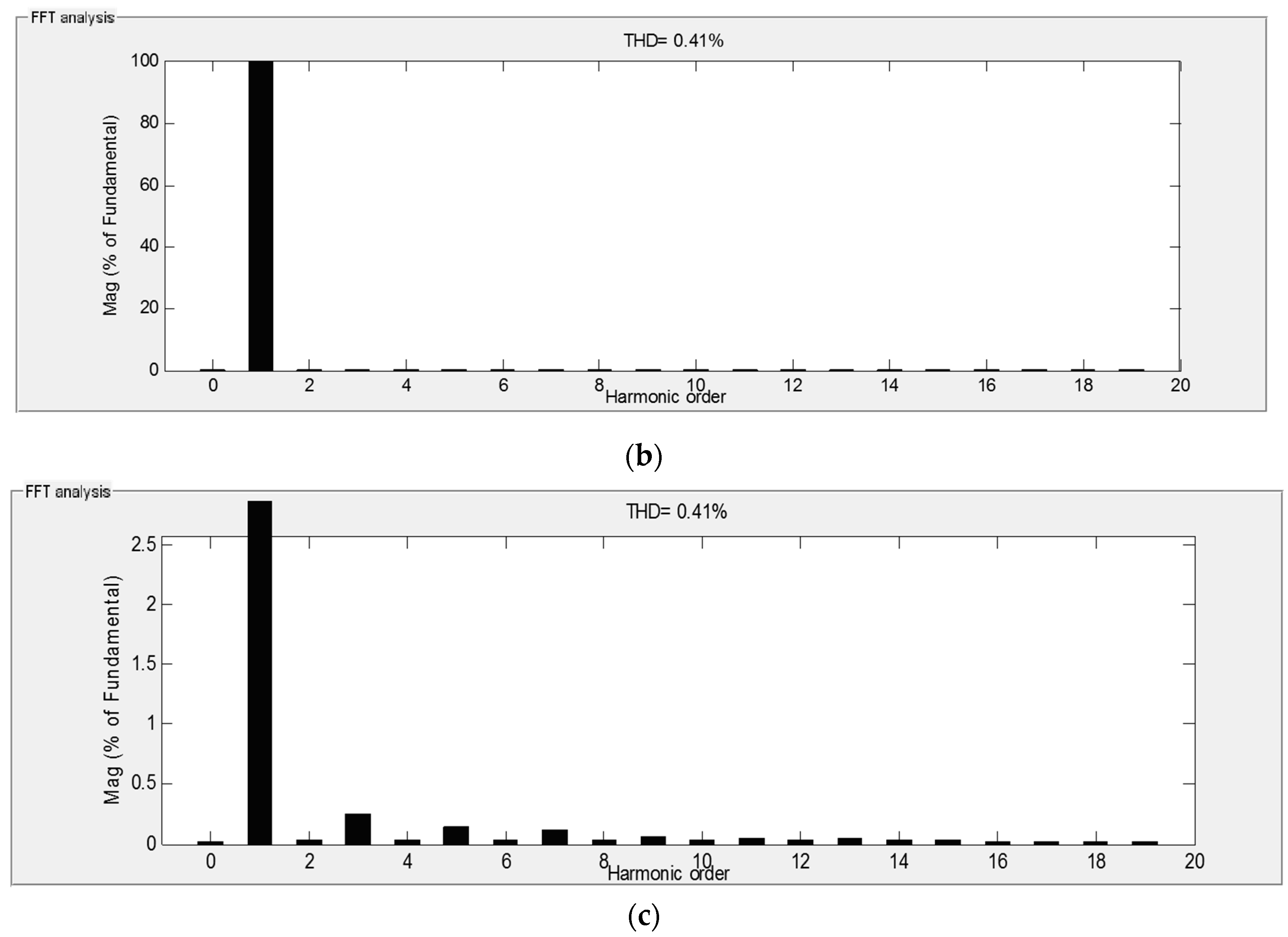
4.8. Comparative THD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geisa, J.M.; Rajaram, M. Selective elimination of harmonic contents in an uninterruptible power supply: An enhanced adaptive hybrid technique. IET Power Electron. 2012, 5, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Umanand, L. Magnetic arm-switch-based three-phase series-shunt compensated quality ac power supply. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 6, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Shahgholian, G.; Mahdavian, M. Analysis and simulation of a three-phase UPS inverter with output multiple-filter. Armen. J. Phys. 2009, 2, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Chen, Q.; Xie, B. Series hybrid active power filter based on controllable harmonic impedance. IET Power Electron. 2012, 5, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, A.M.; Finney, S.J.; Cruden, A.; Williams, B.W. Mapped phase-shifted space vector modulation for multi-level voltage-source inverters. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2007, 1, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, K.R.; Srinivas, S. Discontinuous decoupled PWMs for reduced current ripple in a dual two-level inverter fed open-end winding induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.H.; Cuong, N.M. Implementation of sensorless DC-link capacitorless inverter-based interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drive via measuring switching-state current ripples. IET Electric Power Appl. 2016, 10, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.R.; Dong, J.Y. New zero-voltage switching DC-DC converter for renewable energy conversion systems. IET Power Electron. 2012, 5, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahgholian, G.; Khani, K.; Moazzami, M. Frequency control in autanamous microgrid in the presence of DFIG based wind turbine. J. Intell. Proced. Electr. Technol. 2015, 6, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shahgholian, G.; Izadpanahi, N. Improving the performance of wind turbine equipped with DFIG using STATCOM based on input-output feedback linearization controller. Energy Equip. Syst. 2016, 4, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Pouresmaeil, E.; Montesinos-Miracle, D.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O. Control scheme of three-level NPC inverter for integration of renewable energy resources into AC grid. IEEE Syst. J. 2012, 6, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Shahgholian, G.; Ehsan, M. Stability analysis and simulation of a single-phase voltage source UPS inverter with two-stage cascade output filter. Eur. Trans. Electr. Power 2008, 18, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Shahgholian, G.; Ehsan, M. Modeling and simulation of the single phase voltage source UPS inverter with fourth order output filter. J. Intell. Proced. Electr. Technol. 2011, 1, 63–58. [Google Scholar]
- Shahgholian, G.; Faiz, J.; Jabbari, M. Voltage control techniques in uninterruptible power supply inverters: A review. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2011, 6, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Faiz, J.; Shahgholian, G. Modeling and simulation of a three-phase inverter with rectifier-type non-linear loads. Armen. J. Phys. 2009, 2, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar, G.; Valdez, A.A.; Leyva-Ramos, J.; Mattavelli, P. Repetitive rased controller for a UPS inverter to compensate unbalance and harmonic distortion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, D.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y. Linear phase lead compensation repetitive control of a CVCF PWM inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ooi, B.-T. Incorporating deadbeat and low-frequency harmonic elimination in modular multilevel converters. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2015, 9, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattavelli, P. An improved deadbeat control for UPS using disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.C.; Newman, M.J.; Zmood, D.N.; Holmes, D.G. A comparative analysis of multi-loop voltage regulation strategies for single and three-phase UPS systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2003, 18, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Chow, M.H.L.; Leung, F.H.F.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lee, Y.S. Analogue implementation of a neural network controller for UPS inverter applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Shahgholian, G.; Faiz, J.; Arezoomand, M. Dynamic analysis and control design of a single-phase UPS inverter with novel topology and experimental verification. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2009, 4, 513–523. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.W.E.; Wang, H.Y.; Sutanto, D. Adaptive directive neural network control for three-phase AC/DC PWM converter. Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2001, 148, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Oruganti, R.; Srinivasan, D. Analysis and design of iterative learning control strategies for UPS inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, G.; Mattavelli, P.; Stankovic, A.M.; Valdez, A.A.; Ramos, J.M. An adaptive control for UPS to compensate unbalance and harmonic distortion using a combined capacitor/load current sensing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Shahgholian, G. Uninterruptible power supply—A review. J. Electomotion 2006, 13, 276–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Ting, Y.H.; Hung, S.W. Robust current control-based sliding-mode control with simple uncertainties estimation in permanent magnet synchronous motor drive systems. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2010, 4, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H.; Ozdemir, S.; Sefa, I.; Altin, N.; Kukrer, O. Sliding-mode control for single-phase grid connected LCL-filtered VSI with double band hysteresis control scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H. Nonsingular terminal sliding-mode control of DC-DC buck converters. Control Eng. Pract. 2013, 21, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Huang, L.; Chen, W. A sliding-mode controller with multiresonant sliding surface for single-phase grid-connected VSI with an LCL filter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susperregui, A.; Martinez, M.I.; Zubia, I.; Tapia, G. Design and tuning of fixed-switching-frequency second-order sliding-mode controller for doubly fed induction generator power control. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2012, 6, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, T.L.; Chen, J.S. UPS inverter design using discrete-time sliding-mode control scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Komurcugil, H.; Altin, N.; Ozdemir, S.; Sefa, I. An extended Lyapunov-function-based control strategy for single-phase UPS inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3976–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.J.; Tie, T.L.; Lee, T.S. Variable structure control of UPS inverters. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 1998, 145, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Lu, D.D.; Li, C. Adaptive sliding-mode control method for DC–DC converters. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, H.; Zheng, X.; Khan, S.; Ali, H.; Wu, X. Hysteresis modulation-based sliding-mode current control of z-source DC-DC converter. Int. Power Electron. Motion Control Conf. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levron, Y.; Shmilovitz, D. Maximum power point tracking employing sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2013, 60, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Pastor, A.; Martinez-Salamero, L.; Alonso, C.; Estibal, B.; Alzieu, J.; Schweitz, G.; Shmilovitz, D. Analysis and design of power gyrators in sliding-mode operation. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2005, 152, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, I.; Kuperman, A.; Shmilovitz, D. Analysis of dual-carrier modulator for bidirectional noninverting buck–boost converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestan, S.; Monfared, M.; Guerrero, J.M.; Joorabian, M. A D-Q synchronous frame controller for single-phase inverters. In Proceeding of the IEEE/PEDSTC, Tehran, Iran, 16–17 February 2011; pp. 317–323.
- Komurcugil, H. Rotating-sliding-line-based sliding-mode control for single-phase UPS inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3719–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, M.; Golestan, S.; Guerrero, J.M. Analysis, design, and experimental verification of a synchronous reference frame voltage control for single-phase inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Fundamental Frequency, ω | 2π50 |
| Output Filter Inductance, L | 250 µH |
| Output Filter Capacitance, C | 100 µF |
| ESR of the filter Inductance and Capacitor, rL, rC | ≈0 |
| Dc-link voltage | 460 V |
| Comparison Category | Proposed Method in [42] kp = 25, ki = 60, k = 30 | Proposed MSSMC | Single Slope SMC (s = λx1 + x2), λ = 75,000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| THD (%) for non-linear load case | 3 | 2.85 | 3.22 |
| Output Voltage Fundamental (v) | 308.4 | 306.2 | 308.6 |
| 2nd harmonic (% of fundamental) | 0.036 | 0.08 | 0.005 |
| 3rd harmonic (% of fundamental) | 0.63 | 0.3 | 0.69 |
| 4th harmonic (% of fundamental) | 0.042 | 0.078 | 0.001 |
| 5th harmonic (% of fundamental) | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.71 |
| Robustness | Good | Very good | Very good |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khajeh-Shalaly, B.; Shahgholian, G. A Multi-Slope Sliding-Mode Control Approach for Single-Phase Inverters under Different Loads. Electronics 2016, 5, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5040068
Khajeh-Shalaly B, Shahgholian G. A Multi-Slope Sliding-Mode Control Approach for Single-Phase Inverters under Different Loads. Electronics. 2016; 5(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhajeh-Shalaly, Babak, and Ghazanfar Shahgholian. 2016. "A Multi-Slope Sliding-Mode Control Approach for Single-Phase Inverters under Different Loads" Electronics 5, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5040068
APA StyleKhajeh-Shalaly, B., & Shahgholian, G. (2016). A Multi-Slope Sliding-Mode Control Approach for Single-Phase Inverters under Different Loads. Electronics, 5(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5040068






