Multibattery Charger System Based on a Multilevel Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter
Abstract
1. Introduction
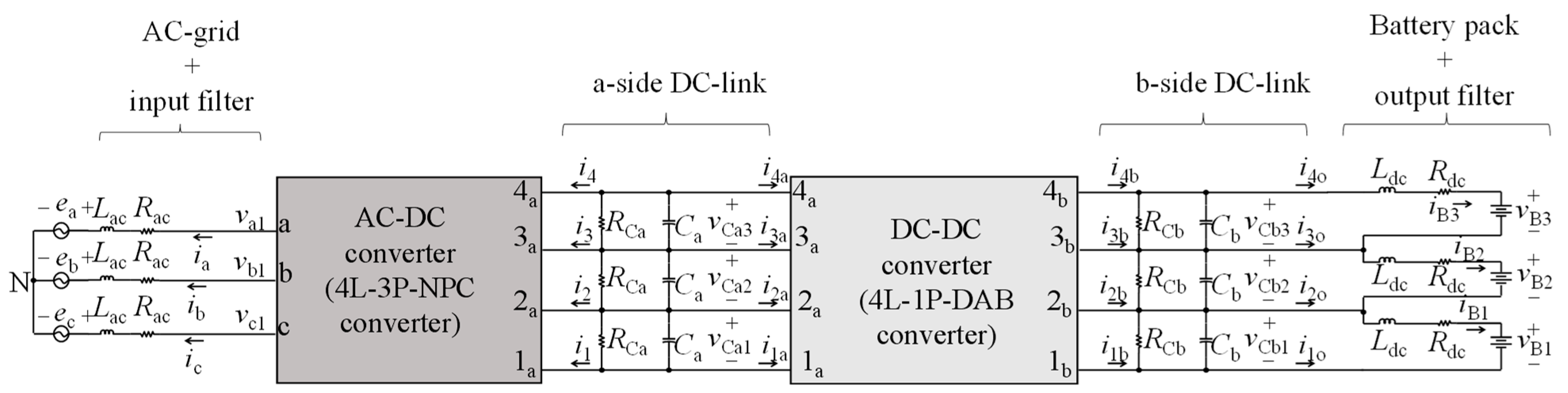
2. Battery Charger Topology
3. Battery Charger Switching Model
3.1. 4L-3P-NPC Converter Switching Model
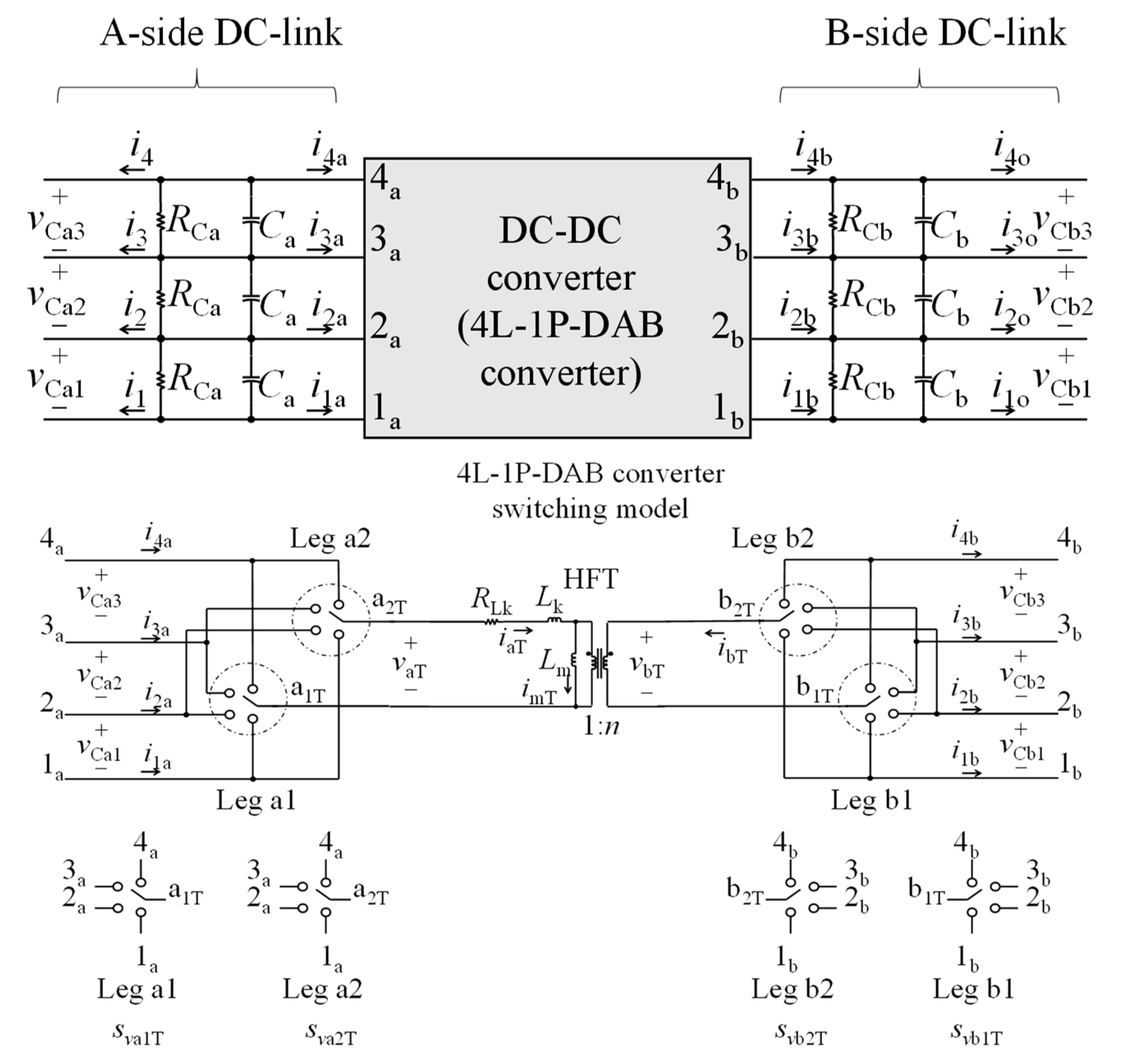
3.2. 4L-1P-DAB Converter Switching Model
3.3. Battery Bank Model
4. Large-Signal Averaged Model
4.1. 4L-3P-NPC Converter Large-Signal Averaged Model
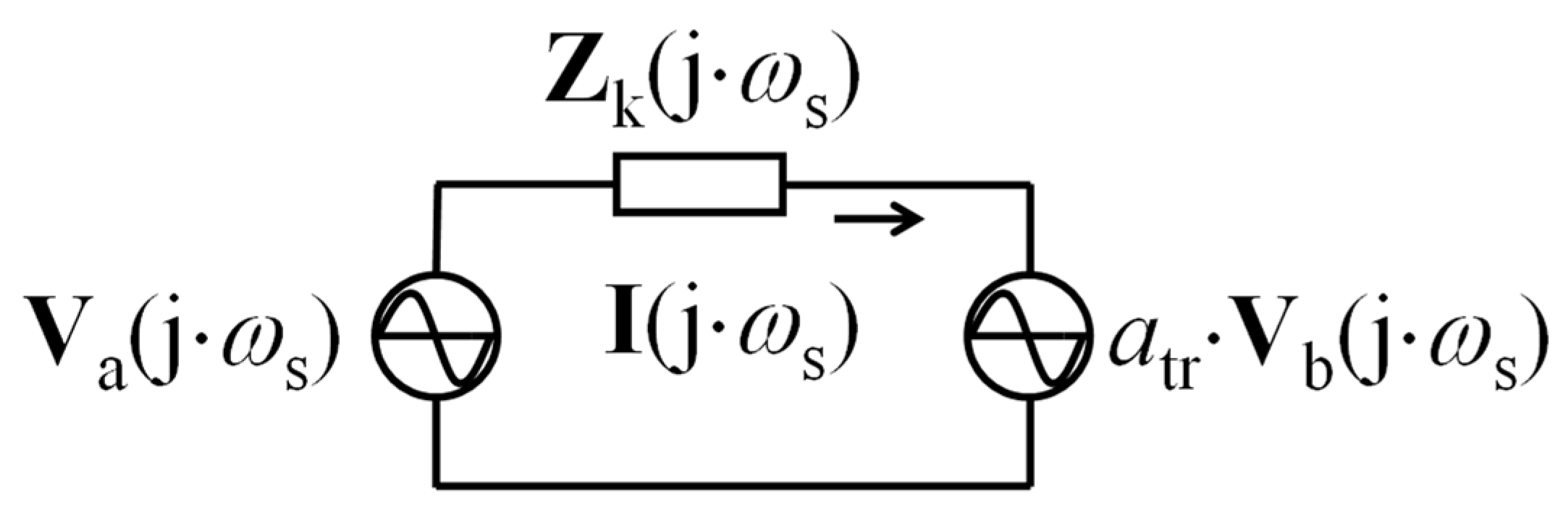
4.2. 4L-3P-DAB Converter Large-Signal Averaged Model
5. Small-Signal Model
6. Control System and Modulation Algorithms
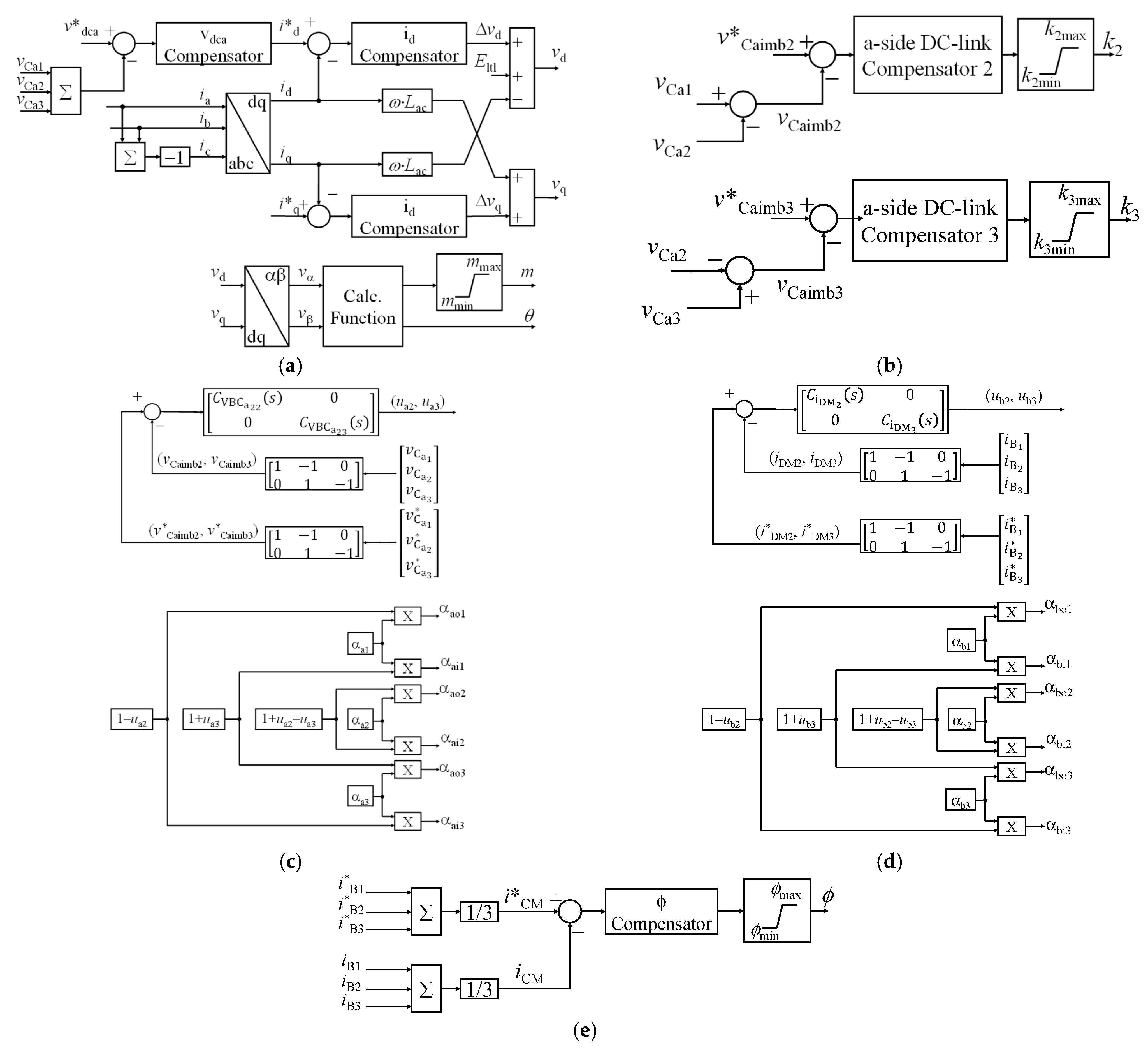
6.1. 4L-3P-NPC Converter Control Description
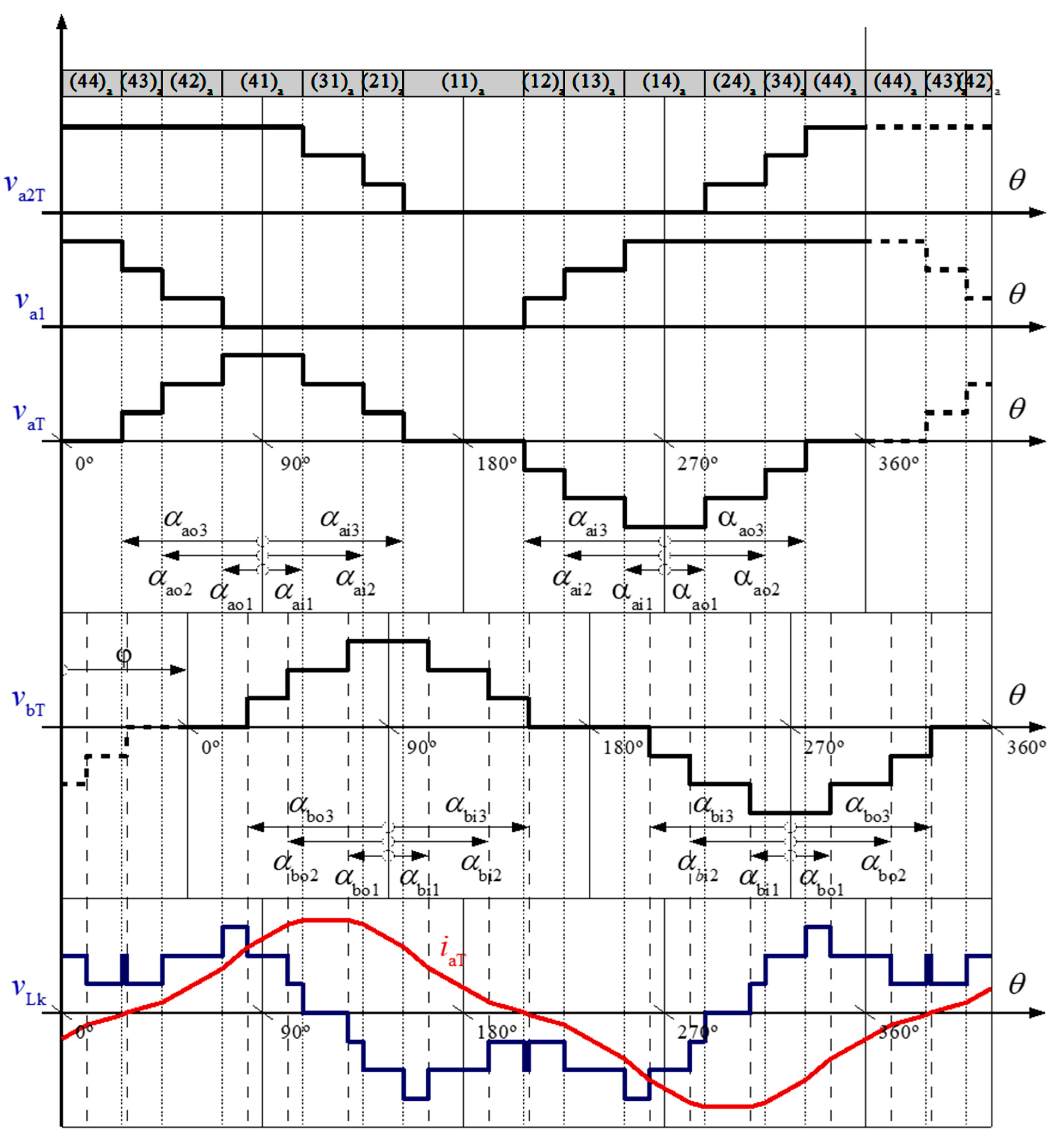
6.2. 4L-3P-NPC Converter Modulation
6.3. 4L-1P-DAB Converter Control Description
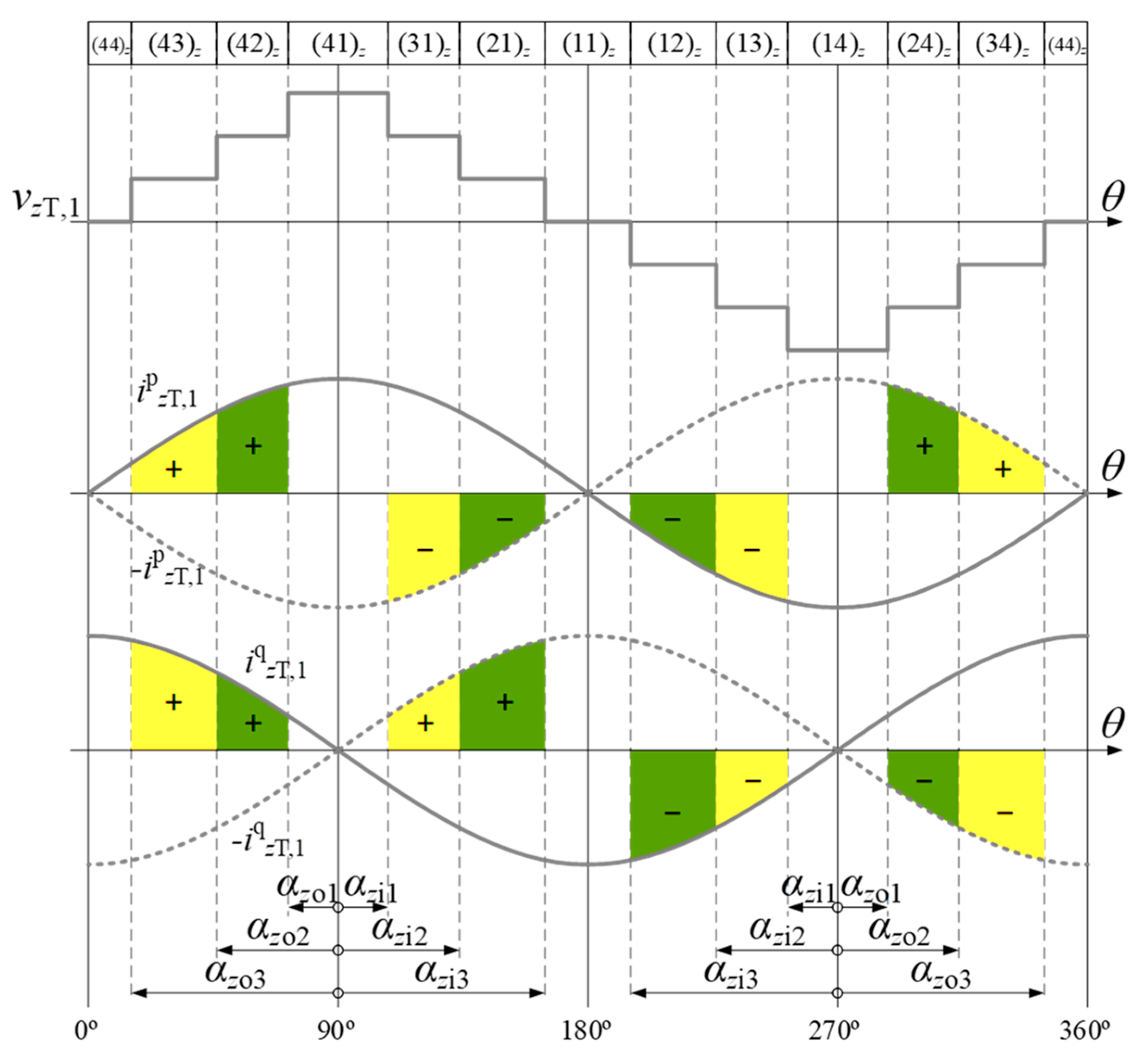
6.4. 4L-1P-DAB Converter Modulation
6.5. Control System Transfer Function
6.5.1. Voltage Regulation Loop—4L-3P-NPC
6.5.2. DQ-Frame Current Regulation Loops
6.5.3. A-Side DC-Link Voltage Balancing
6.5.4. Differential-Mode Current Control—4L-1P-DAB
6.5.5. Common-Mode Current Control and Power Transfer
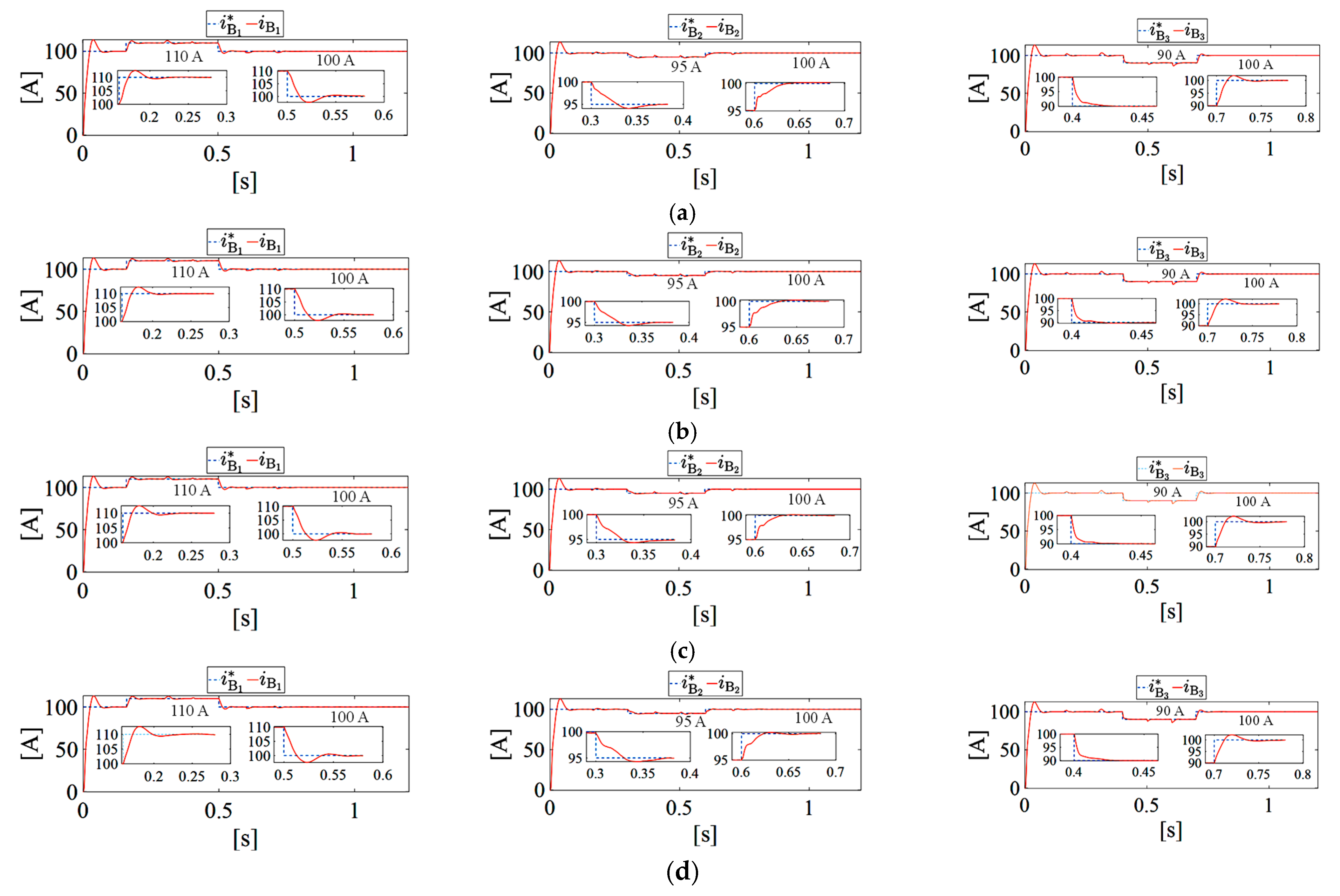
7. Simulation Results
7.1. Specifications, Scenarios, and Cases Definition
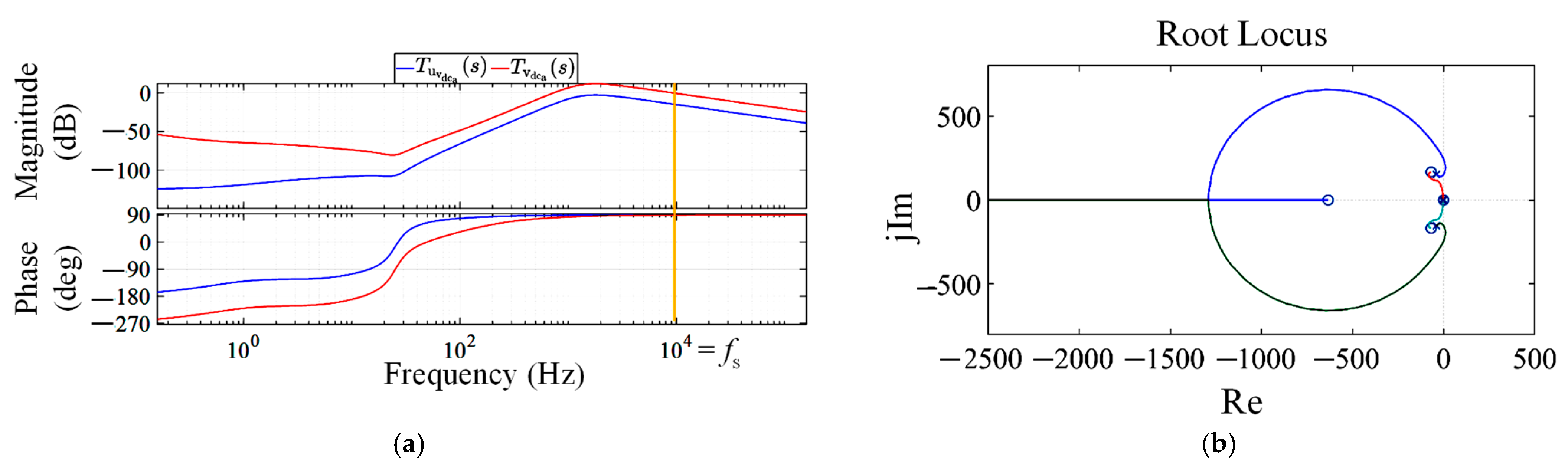
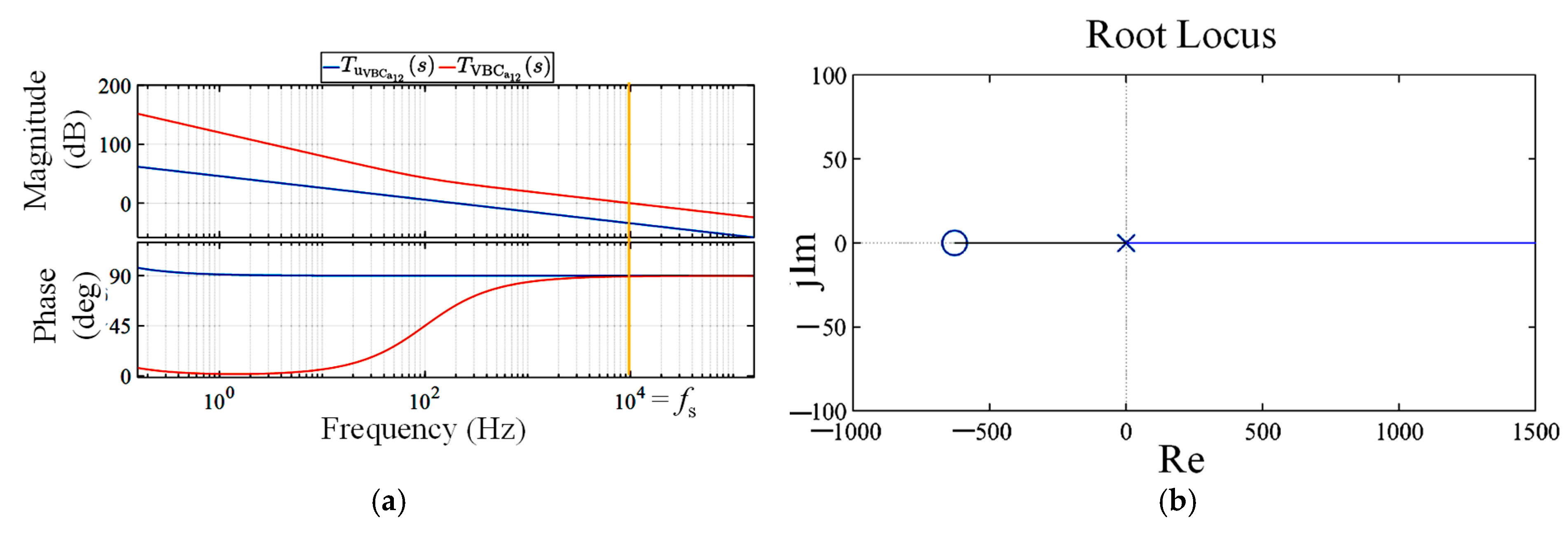
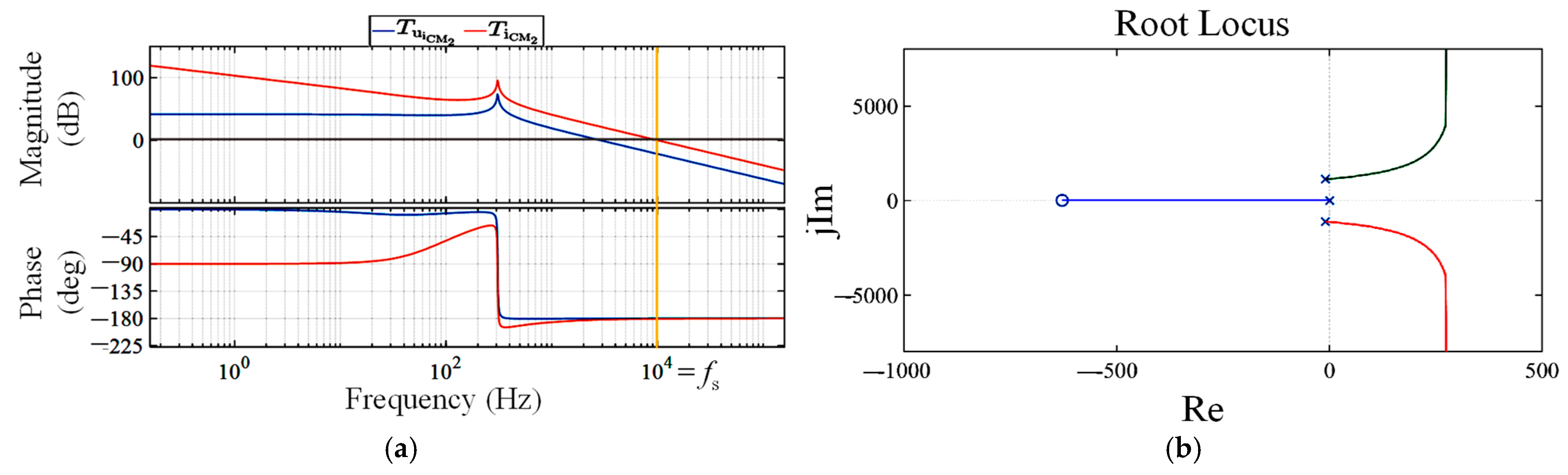
7.2. System Stability Analysis
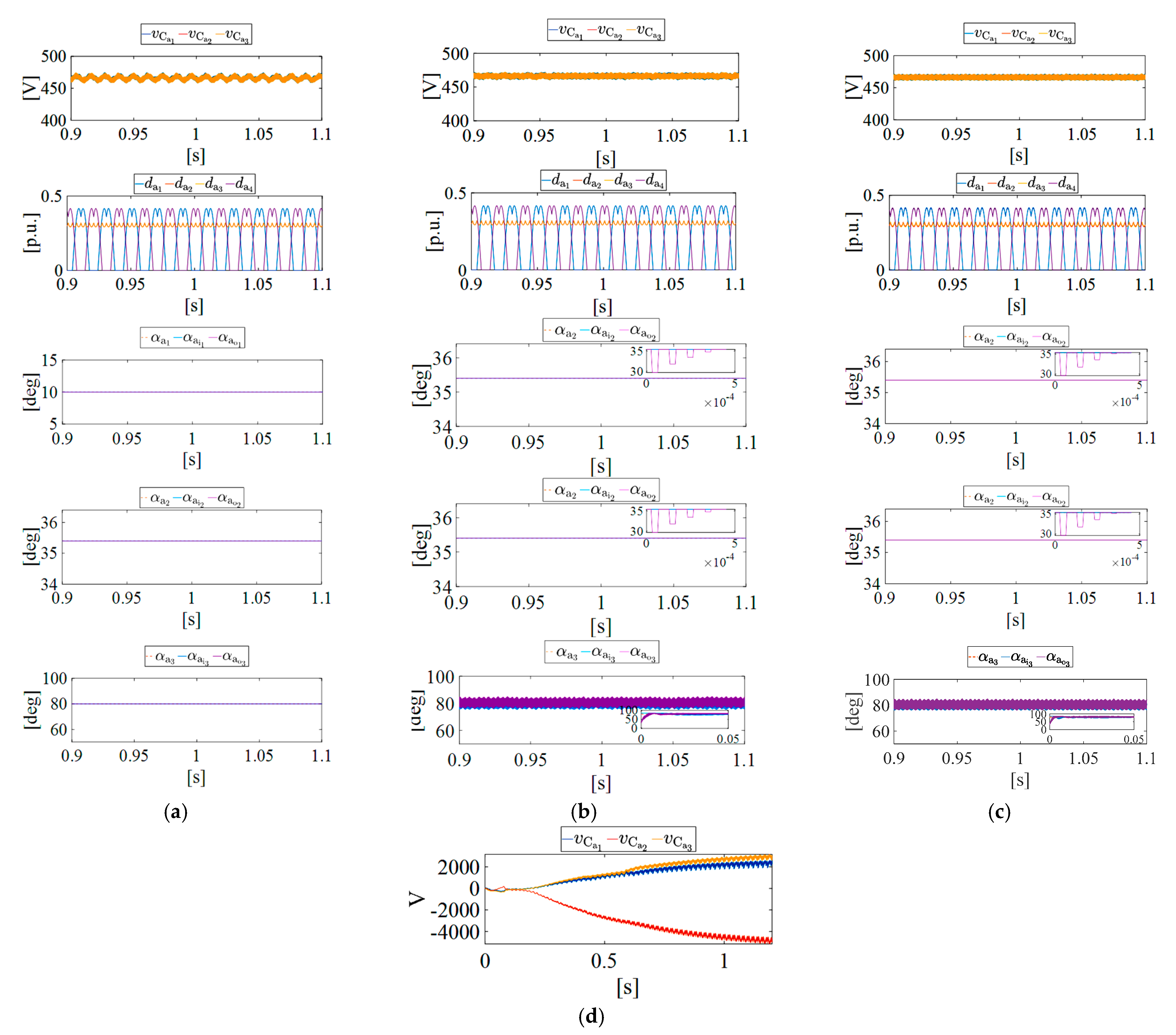
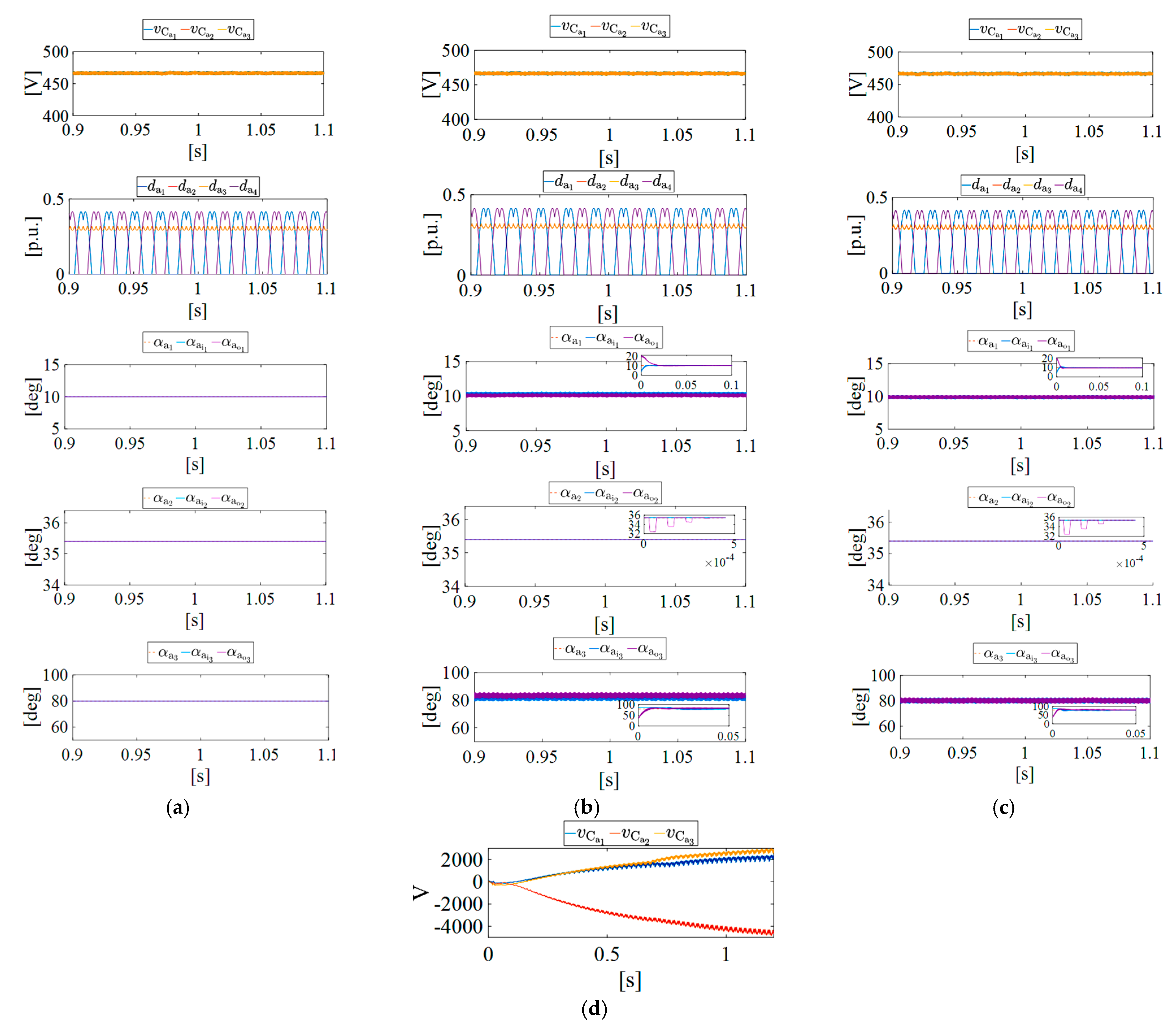
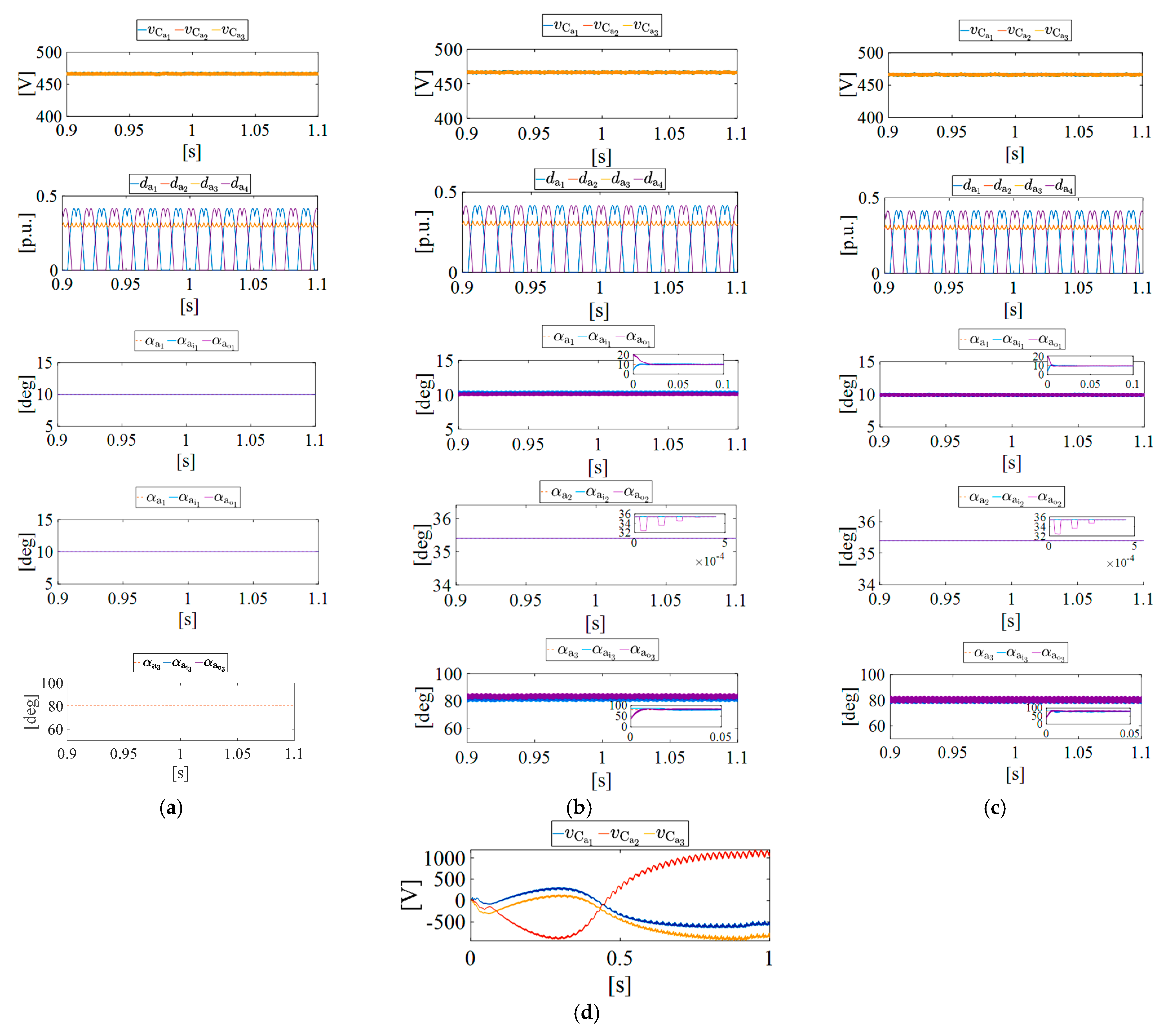
7.3. Time-Domain Simulation Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Razmjoo, A.; Ghazanfari, A.; Jahangiri, M.; Franklin, E.; Denai, M.; Marzband, M.; Astiaso Garcia, D.; Maheri, A. A Comprehensive Study on the Expansion of Electric Vehicles in Europe. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharige, S.S.G.; Haque, M.E.; Arif, M.T.; Hosseinzadeh, N.; Hasan, K.N.; Oo, A.M.T. Review of Electric Vehicle Charging Technologies, Standards, Architectures, and Converter Configurations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 41218–41255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.R.; Haque, A.; Khan, M.A.; Kurukuru, V.S.B.; Mehfuz, S. On-Board Chargers for Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Performance and Efficiency Review. Energies 2024, 17, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadi, S.; Bayindir, R.; Colak, A.M.; Hossain, E. A Review on Communication Standards and Charging Topologies of V2G and V2H Operation Strategies. Energies 2019, 12, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyhart, J. Electric Vehicles and Energy Communities: Vehicle-to-Grid Opportunities and a Sustainable Future. Energies 2025, 18, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.A.; Numan, M.; Tahir, H.; Rahman, U.; Khan, M.W.; Iftikhar, M.Z. A Comprehensive Overview of Vehicle to Everything (V2X) Technology for Sustainable EV Adoption. J. Energy Storage 2023, 74, 109304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwendtner, C.; Sinsel, S.R.; Stephan, A. Vehicle-to-X (V2X) Implementation: An Overview of Predominate Trial Configurations and Technical, Social and Regulatory Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumder, M.R.H.; Ahmed Antara, F.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Alamri, B.; Alsharef, M. Electric Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technologies: Impact on the Power Grid and Battery. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Tao, Y.; Lai, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z. Powering Future Advancements and Applications of Battery Energy Storage Systems Across Different Scales. Energy Storage Appl. 2025, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavhan, S.; Mohale, V.; Kumbhar, M. A Review of Recent Advancements and Challenges in Battery Energy Storage System (BESS). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Sustainable Technologies for Energy, Mechatronics and Smart Systems (ISTEMS), Dehradun, India, 26–27 April 2024; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Mao, H.; Tian, Y.; Xu, B.; Huang, J. A Novel Cooperative Control for SMES/Battery Hybrid Energy Storage in PV Grid-Connected System. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaligh, A.; Dantonio, M. Global Trends in High-Power On-Board Chargers for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3306–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Feng, H.; Srdic, S.; Lukic, S. Extreme Fast Charging of Electric Vehicles: A Technology Overview. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 861–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Kouro, S.; Vazquez, S.; Goetz, S.M.; Lizana, R.; Romero-Cadaval, E. Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: From Grid to Battery. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2021, 15, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Goetz, S.M.; Kouro, S.; Lehn, P.W.; Pathmanathan, M.; Bauer, P.; Mastromauro, R.A. Charging Infrastructure and Grid Integration for Electromobility. Proc. IEEE 2022, 111, 371–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, N.; Sadarnac, D.; Gascher, A. A Review of On-Board Integrated Chargers for Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, EPE-ECCE Europe, Lappeenranta, Finland, 26–28 August 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwly, M.Y.; Abdel-Majeed, M.S.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Hamdy, R.A.; Hamad, M.S.; Ahmed, S. A Review of Integrated On-Board EV Battery Chargers: Advanced Topologies, Recent Developments and Optimal Selection of FSCW Slot/Pole Combination. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85216–85242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.R.; Vishnuram, P.; Alagarsamy, S.; Bajaj, M.; Blazek, V.; Damaj, I.; Rathore, R.S.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Othman, K.M. Electric Vehicle Charging Technologies, Infrastructure Expansion, Grid Integration Strategies, and Their Role in Promoting Sustainable e-Mobility. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 105, 300–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, H.; Martinez, W. Bidirectional Onboard Chargers for Electric Vehicles: State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 693–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Doncker, R.W.A.A.; Divan, D.M.; Kheraluwala, M.H. A Three-Phase Soft-Switched High-Power-Density DC/DC Converter for High-Power Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.R.; Sebastian, J.; Lamar, D.G.; Hernando, M.M.; Vazquez, A. An Overall Study of a Dual Active Bridge for Bidirectional DC/DC Conversion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress & Exposition (ECCE), Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filba-Martinez, A.; Busquets-Monge, S.; Nicolas-Apruzzese, J.; Bordonau, J. Operating Principle and Performance Optimization of a Three-Level NPC Dual-Active-Bridge DC-DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Salazar, J.M.; Busquets-Monge, S.; Filba-Martinez, A.; Alepuz, S. Multibattery Charger System Based on a Three-Level Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter. In Proceedings of the IECON 2021—47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–16 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Salazar, J.M.; Busquets-Monge, S.; Filba-Martinez, A.; Alepuz, S. Comparison of Modulations and Dc-Link Balance Control Strategies for a Multibattery Charger System Based on a Three-Level Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 31st International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Anchorage, AK, USA, 1–3 June 2022; pp. 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbà Martínez, À. Contributions to the Modulation and Closed-Loop Control of Multilevel Dual-Active-Bridge Dc-Dc Converters. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leon, J.I.; Vazquez, S.; Franquelo, L.G. Multilevel Converters: Control and Modulation Techniques for Their Operation and Industrial Applications. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Monge, S.; Filba-Martinez, A.; Alepuz, S.; Nicolas-Apruzzese, J.; Luque, A.; Conesa-Roca, A.; Bordonau, J. Multibattery-Fed Neutral-Point-Clamped DC-AC Converter with SoC Balancing Control to Maximize Capacity Utilization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Monge, S.; Maheshwari, R.; Nicolas-Apruzzese, J.; Lupon, E.; Munk-Nielsen, S.; Bordonau, J. Enhanced DC-Link Capacitor Voltage Balancing Control of DC-AC Multilevel Multileg Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2663–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghossein, N.; Salameh, J.P.; Karami, N.; El Hassan, M.; Najjar, M.B. Survey on Electrical Modeling Methods Applied on Different Battery Types. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Technological Advances in Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (TAEECE), Beirut, Lebanon, 29 April–1 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Rincón-Mora, G.A. Accurate Electrical Battery Model Capable of Predicting Runtime and I–V Performance. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzl, H. BATTERIES|Capacity. In Encyclopedia of Electrochemical Power Sources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 395–400. ISBN 978-0-444-52745-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bacha, S.; Munteanu, I.; Bratcu, A.I. Power Electronic Converters Modeling and Control; Advanced Textbooks in Control and Signal Processing; Springer: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4471-5477-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.H. Power Electronics Handbook; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2024; ISBN 9780323993432. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, K. Modern Control Engineering; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, B.C. Automatic Control Systems; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1991; ISBN 978-0-13-051046-4. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, W.S. The Control Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781420073676. [Google Scholar]
- Skogestad, S.; Postlethwaite, I. Multivariable Feedback Control: Analysis and Design, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0-470-01167-6. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Salazar, J.M. Design and Analysis of Battery Chargers for Electric Vehicles Based on Multilevel Neutral-Point-Clamped Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Busquets-Monge, S.; Bordonau, J.; Boroyevich, D.; Somavilla, S. The Nearest Three Virtual Space Vector PWM—A Modulation for the Comprehensive Neutral-Point Balancing in the Three-Level NPC Inverter. IEEE Power Electron. Lett. 2004, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayt, W.H.; Kemmerly, J.E.; Phillips, J.D.; Durbin, S.M. Engineering Circuit Analysis, 10th ed.; McGraw Hill, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 1264149913. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, R.W.; Maksimović, D. Fundamentals of Power Electronics, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-43879-1. [Google Scholar]







| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Rac | 10 [mΩ] |
| Lac | 1 [mH] |
| RCa = RCb | 10 [kΩ] |
| Cb | 800 [μF] |
| Lk | 25 [μH] |
| Lm | 10 [H] |
| RLk | 50 [mΩ] |
| atr | 1 |
| Rdc | 20 [mΩ] |
| Ldc | 1 [mH] |
| f | 50 [Hz] |
| fs | 10 [kHz] |
| Parameter | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | Scenario 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 300 [μF] | 600 [μF] | 800 [μF] | 1100 [μF] |
| Case | Converter |
|---|---|
| 1 | only 4L-3P-NPC |
| 2 | only 4L-1P-DAB |
| 3 | both 4L-3P-NPC and 4L-1P-DAB |
| Scenarios | rrvCa1, rrvCa2, and rrvCa3 in [%] | Cases | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 1 | rrvCa1 | 3.77 | 1.90 | 3.89 |
| rrvCa2 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.83 | |
| rrvCa3 | 3.36 | 1.97 | 3.30 | |
| 2 | rrvCa1 | 1.87 | 1.65 | 1.65 |
| rrvCa2 | 0.47 | 0.24 | 0.30 | |
| rrvCa3 | 1.70 | 1.58 | 1.67 | |
| 3 | rrvCa1 | 1.43 | 1.37 | 1.28 |
| rrvCa2 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.26 | |
| rrvCa3 | 1.28 | 1.45 | 1.48 | |
| 4 | rrvCa1 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.03 |
| rrvCa2 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | |
| rrvCa3 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.90 | |
| Step Change Time [ms] | Step Change Current | FoM | Scenarios | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| 160 | i*B1 | Overshoot [%] | 3.46 | 3.33 | 3.02 |
| Settling time [ms] | 91.50 | 97.74 | 97.82 | ||
| 300 | i*B2 | Overshoot [%] | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.78 |
| Settling time [ms] | 85.12 | 85.25 | 85.32 | ||
| 400 | i*B3 | Overshoot [%] | 1.28 | 1.11 | 0.95 |
| Settling time [ms] | 81.35 | 81.32 | 81.57 | ||
| 500 | i*B1 | Overshoot [%] | 0.69 | 0.72 | 0.76 |
| Settling time [ms] | 52.71 | 52.63 | 55.66 | ||
| 600 | i*B2 | Overshoot [%] | 1.75 | 1.65 | 1.23 |
| Settling time [ms] | 60.75 | 60.83 | 60.81 | ||
| 700 | i*B3 | Overshoot [%] | 1.69 | 1.61 | 1.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos-Salazar, J.M.; Busquets-Monge, S.; Filba-Martinez, A.; Alepuz, S. Multibattery Charger System Based on a Multilevel Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter. Electronics 2025, 14, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081659
Campos-Salazar JM, Busquets-Monge S, Filba-Martinez A, Alepuz S. Multibattery Charger System Based on a Multilevel Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter. Electronics. 2025; 14(8):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081659
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos-Salazar, José M., Sergio Busquets-Monge, Alber Filba-Martinez, and Salvador Alepuz. 2025. "Multibattery Charger System Based on a Multilevel Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter" Electronics 14, no. 8: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081659
APA StyleCampos-Salazar, J. M., Busquets-Monge, S., Filba-Martinez, A., & Alepuz, S. (2025). Multibattery Charger System Based on a Multilevel Dual-Active-Bridge Power Converter. Electronics, 14(8), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081659









