Abstract
Human activity recognition (HAR) is vital for applications in fields such as smart homes, health monitoring, and navigation, particularly in GNSS-denied environments where satellite signals are obstructed. Wi-Fi channel state information (CSI) has emerged as a key technology for HAR due to its wide coverage, low cost, and non-reliance on wearable devices. However, existing methods face challenges including significant data fluctuations, limited feature extraction capabilities, and difficulties in recognizing complex movements. This study presents a novel solution by integrating a multi-sensor array of Wi-Fi CSI with deep learning techniques to overcome these challenges. We propose a 2 × 2 array of Wi-Fi CSI sensors, which collects synchronized data from all channels within the CSI receivable range, improving data stability and providing reliable positioning in GNSS-denied environments. Using the CNN-LSTM-attention (C-L-A) framework, this method combines short- and long-term motion features, enhancing recognition accuracy. Experimental results show 98.2% accuracy, demonstrating superior recognition performance compared to single Wi-Fi receivers and traditional deep learning models. Our multi-sensor Wi-Fi CSI and deep learning approach significantly improve HAR accuracy, generalization, and adaptability, making it an ideal solution for GNSS-denied environments in applications such as autonomous navigation and smart cities.
1. Introduction
Human activity recognition (HAR) is crucial in applications such as navigation, smart healthcare, and health monitoring. Early stages of HAR research relied primarily on grayscale or RGB videos, but the field has since expanded over time to include a variety of other sensing modalities [1,2]. Traditional methods rely on wearable sensors to capture acceleration data or physiological signals like ECG and PPG for activity identification [3,4]. However, wearable systems often limit user mobility and face challenges in accurately monitoring diverse motion features in real time. Vision-based methods also encounter issues such as blind spots and high energy consumption. In addition, the use of the visible spectrum can be intrusive and raise privacy concerns [5,6].
Wi-Fi CSI (channel state information) provides detailed, real-time data about the wireless communication channel, including both amplitude and phase information of each subcarrier. This allows for a finer understanding of the channel conditions compared to standard signal strength measurements like the RSSI [7]. CSI is particularly useful in applications such as indoor localization, MIMO optimization, interference management, and activity recognition. It can resolve multipath effects, enabling more accurate tracking and network performance improvements, making it valuable for advanced wireless technologies and sensing applications. Wi-Fi CSI offers a promising solution, providing broad coverage, low cost, and real-time data acquisition without the need for wearables [8,9,10].
However, Wi-Fi CSI-based HAR faces several challenges: (1) single Wi-Fi receiver data often fluctuates with noise, reducing recognition accuracy [11,12]; (2) traditional machine learning models struggle to capture both short- and long-term features or spatiotemporal information effectively [13,14]; and (3) Wi-Fi CSI data may suffer from phase and frequency shifts, affecting accuracy [15,16].
To address these limitations, we propose a multi-sensor array Wi-Fi CSI-based HAR method utilizing a CNN-LSTM-attention framework. A 2 × 2 Wi-Fi CSI array is developed to record and merge data from all channels within the coverage area of the Wi-Fi signal, improving data stability. The CNN-LSTM-attention deep learning model captures both short- and long-term motion features, enhancing recognition accuracy. This method performs well in daily environments.
Key contributions of this paper include the following:
- (1)
- A 2 × 2 array Wi-Fi CSI receiver that merges all channel data within the coverage area of the Wi-Fi signal, improving data stability over single Wi-Fi receivers.
- (2)
- A hybrid HAR framework combining CNN, LSTM, and attention, offering superior generalization, data focusing, and precision, achieving recognition accuracy near 98%.
2. Related Work
Human activity recognition (HAR) aims to record and analyze daily activities to better understand human behavior [17]. As a crucial technology in fields like smart homes, healthcare, and virtual reality (VR), HAR has garnered substantial attention. HAR methods vary across application scenarios [18,19], with visual models and dynamic recognition networks being the dominant approaches. However, these visual methods struggle in low-light conditions, prompting increased interest in alternative signal-based recognition techniques.
Early developments in dynamic recognition, particularly through Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), have been pivotal. IMUs, which do not rely on external information, can sense acceleration and angular velocity, allowing for the extraction of motion features and body posture recognition [20]. While IMUs are practical and simple, the reliance on wearable sensors introduces user inconvenience, leading to Wi-Fi wireless sensing as a promising alternative, especially in non-IMU-based scenarios.
Wi-Fi wireless sensing technology leverages the received signal strength indicator (RSSI) or channel state information (CSI) to detect human motion. While the RSSI estimates signal strength for basic distance measurement, CSI provides more detailed information on signal propagation, offering higher precision and richer data [21].
2.1. Models Existing Human Motion Detection Methods
Advancements in electronics have improved the portability, accuracy, and availability of sensors, enabling enhanced human behavior and health monitoring. Wearable sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, ECG, and PPG generate large volumes of data, widely applied in activity recognition and personalized healthcare. Methods combining ECG and inertial sensors have improved recognition accuracy [22] but remain complex and energy-intensive. Innovations like ultra-wideband (UWB) and thermal imaging have also contributed to HAR but face their own challenges [23].
Wi-Fi CSI provides fine-grained, real-time channel information, capturing both amplitude and phase, which enables more accurate activity detection. Unlike wearable sensors or cameras, Wi-Fi CSI is non-intrusive, preserves privacy, and does not require additional hardware. It can also penetrate walls and obstacles, allowing for activity recognition across multiple rooms. Wi-Fi CSI handles multipath propagation well, making it reliable in dynamic environments. Additionally, it avoids issues like device loss, battery limitations, and user discomfort, offering a seamless and scalable solution for activity monitoring.
Wi-Fi-based recognition, leveraging ubiquitous indoor signals, has gained traction. Initially, the received signal strength information (RSSI) was used, but it provided limited information, achieving only 72.47% accuracy. In contrast, channel state information (CSI), which captures multipath signal propagation, offers richer data and improved recognition accuracy.
William Taylor et al. [24] applied the Universal Software Radio Peripheral (USRP) and CNN, achieving 88.13% accuracy in activity recognition and 95.68% in indoor localization. However, these methods mainly rely on direct-path Wi-Fi signals, complicating universal signal collection.
2.2. Models of HAR in Wi-Fi CSI Technique
Wi-Fi CSI signals are often influenced by interference from multiple reflections and transmissions. Zhang et al. [25] modeled Wi-Fi propagation using the Fresnel zone for sub-carrier CSI, while Dahou et al. [26] estimated the Angle of Arrival (AoA) of Wi-Fi subcarriers. In wall-penetrating scenarios, the Time of Flight (ToF) can be estimated by referencing relative errors between channels.
Pedestrian motion pattern recognition using Wi-Fi CSI has employed various statistical models, data processing techniques, and machine learning approaches. Early methods used Gradient Boosting Decision Trees (GBDTs) for denoising Wi-Fi signals [27]. Xia et al. [28] applied CNN-LSTM models to combine time and spatial features from Intel Wi-Fi 5300 cards. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) have been used for multi-room human presence detection, though they are primarily limited to detecting presence rather than behavior patterns [29].
Despite advancements, Wi-Fi CSI-based applications still face challenges, particularly in detecting wall-penetrating signals. Additionally, open-source Wi-Fi CSI datasets often fail to accurately represent real-world scenarios. To address these issues, this study utilizes an ESP32-based Wi-Fi CSI module with an array configuration to prevent data loss and proposes a real-time multi-sensor array Wi-Fi CSI human motion recognition method based on a CNN-LSTM-attention framework, enhancing motion recognition in real-world environments.
3. Materials and Methods
This paper presents a multi-sensor array Wi-Fi CSI data acquisition and human motion recognition system, comprising three key components: data acquisition, data processing, and motion recognition.
The overall architecture of the system is depicted in Figure 1.
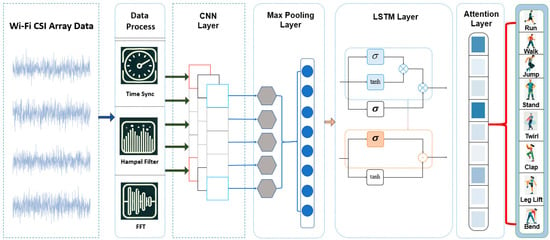
Figure 1.
A framework for human activity recognition using array-based Wi-Fi CSI sensors and deep learning.
3.1. Data Reception and Processing of Wi-Fi Array Sensors
During the acquisition of Wi-Fi CSI signals, the implementation of an array-based collection system necessitates precise time synchronization and noise mitigation across multiple channels to maintain data accuracy and consistency. To achieve this, a time synchronization algorithm is first applied to align signals from different channels, minimizing distortions and errors induced by temporal misalignment. Subsequently, the Hampel filter algorithm is utilized to enhance signal quality by effectively suppressing high-frequency noise and removing outliers. These preprocessing steps enable the extraction of clean and reliable signals, forming a robust foundation for downstream data analysis and activity recognition. Finally, the processed data from all channels are integrated into a high-dimensional dataset, ensuring high-quality input for deep learning models.
Wi-Fi CSI reflects attenuation factors along each transmission path, such as signal scattering and decay. Initially, the displacement or movement state of a person or object was estimated based on variations in the received signal strength indicator (RSSI) measurements. The Wi-Fi RSSI signal quantifies the instantaneous signal strength of a Wi-Fi transmission and is mathematically expressed as follows:
where and represent the received signal power in and , respectively, denotes the logarithmic operation, and is the reference power, typically 1 . Given the relatively weak nature of the signal, the Wi-Fi RSSI is typically expressed in dBm. is the signal strength at the transmission end and is a constant in this formula. is the path loss exponent (typically in free space, and in indoor environments) and is the distance between the transmitter and receiver (in meters). is a random variation in the signal strength that occurs due to obstacles (e.g., buildings, trees, or other large structures) between the transmitter and receiver. In practical scenarios, an RSSI value ranging from 0 to −50 dBm generally signifies a strong and stable connection to the access point, whereas values below −70 dBm are more susceptible to interference and signal degradation.
Despite having good hardware and configuration, the received CSI data remain susceptible to noise and cannot be directly used in its raw form. Specifically, CSI data can be affected by factors such as Carrier Frequency Offset (CFO), Sampling Frequency Offset (SFO), and errors in the Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC) process.
where represents the raw Wi-Fi CSI input data, represents the fitted variable, which likely refers to the processed or adjusted CSI data. is the th polynomial function obtained by interpolating and fitting the data. The coefficients , , , and are determined by solving the given conditions, and represents the total number of CSI data samples and also indicates the number of polynomials to be fitted. and represent the first and the second derivative of the polynomial represented by the CSI.
Since these noises primarily originate from environmental or interference sources and are approximately Gaussian-distributed, they can be filtered using the mean of the four Wi-Fi CSI receivers. Additionally, to achieve time synchronization across the four ESP32 Wi-Fi CSI receivers, we calibrated the local clocks with the clock obtained during Wi-Fi communication, ensuring data synchronization for subsequent interpolation or sorting.
Figure 2 presents a comparison between the original and processed data. The CSI data from channels 0 to 10 are shown in distinct colors for clarity. The processed data exhibit more distinct characteristics than the raw data, making them more suitable for model training.
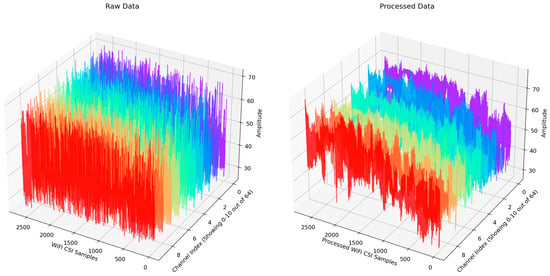
Figure 2.
Comparison of original and processed data.
Wi-Fi CSI infers the user’s activity status by analyzing the propagation characteristics of wireless signals, and does not rely on wearable devices, thus reducing direct privacy infringement at the physical layer. However, data collection and analysis may still pose privacy risks, especially without user consent. To mitigate the risk of privacy breaches, we plan to implement the following strategies in the future:
- (1)
- Data Anonymization and De-identification: We will anonymize the collected Wi-Fi CSI data to ensure they cannot be directly linked to an individual’s identity. Even if the data are leaked, they will not pose a threat to user privacy.
- (2)
- Data Encryption: We will encrypt all Wi-Fi CSI data to ensure security during transmission and storage, preventing malicious interception.
- (3)
- Edge Computing and Local Processing: We will use edge computing technologies to analyze and process data locally, avoiding the transmission of data to the cloud, which will further reduce the risk of privacy leakage.
These measures will help reduce privacy risks while ensuring the security of the system.
3.2. Feature Extraction from Raw Data
The Wi-Fi CSI data received through the ESP32 module contain time-domain state information across 64 different channels, including both real and imaginary parts. Each data frame comprises 2 × 64 data points, with a transmission frequency of 20 Hz. Due to the high dimensionality of the data, directly using the data for recognition tasks would result in substantial computational complexity.
Therefore, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [30] was applied for dimensionality reduction to extract key channel information:
Here, the variable represents the CSI reception sequence, is the mean of each feature, and is the standard deviation of each feature. is the covariance matrix of size , represents the variance explained by each principal component, and is the corresponding eigenvector, representing the direction of each principal component. is the transformed dataset in the lower-dimensional space .
The experiment was designed to capture CSI data under line-of-sight conditions, with actions including running, walking, jumping, standing still, spinning, clapping, bending, and leg lifting. After noise filtering and dimensionality reduction, the CSI data require further analysis. However, a single time-domain data point cannot clearly differentiate between activities, as actions at different times may produce similar or indistinguishable effects on the Wi-Fi CSI signal. For instance, walking and running may generate similar signal variations at the same location. Therefore, a frequency-domain transformation of the raw data is considered.
The wavelet transform is a versatile and powerful tool for signal analysis and image processing, enabling the simultaneous decomposition of signals in both the time and frequency domains. This dual-domain representation facilitates the extraction of specific signal characteristics with high precision. In this study, the Haar wavelet transform was employed to decompose the signal, offering a computationally efficient approach while preserving essential transformation features and ensuring high-quality signal representation.
where represents the wavelet coefficient at scale and translation ; is the scale parameter, determining the resolution of the wavelet; is the translation parameter, shifting the wavelet in time; is a normalization factor to maintain energy consistency across scales; is the scaling function, used in wavelet decomposition; and is the conjugate value of the .
Experimental results confirm that the wavelet transform [31] effectively reveals the characteristic patterns of different actions in the frequency domain (detailed experimental results and conclusions will be presented in Section 4).
To capture temporal dependencies between the current state and past moments, we initially incorporated the previous ten data points during network training. However, in practical tests, the high dimensionality of the data led to feature ambiguity. To mitigate this issue, we applied dimensionality reduction by computing the mean and variance of the data, preserving essential statistical characteristics while enhancing feature clarity.
3.3. The CNN-LSTM-Attention Network for Human Motion Recognition
For multivariate data prediction, this paper utilizes a model based on the CNN-LSTM-attention framework, which assigns different labels to various motion phases for precise action recognition and prediction. The CNN-LSTM-attention framework designed is illustrated in Figure 3. First, the data are preprocessed through a normalization layer. The purpose of normalization is to eliminate interference from different magnitudes, facilitating subsequent calculations. Then, the input data are flattened into a 64 × 2 vector and passed through a dropout layer with a 20% rate to prevent overfitting. After that, the data enter the convolutional layer, where each convolution kernel has a size of 5 × 1.
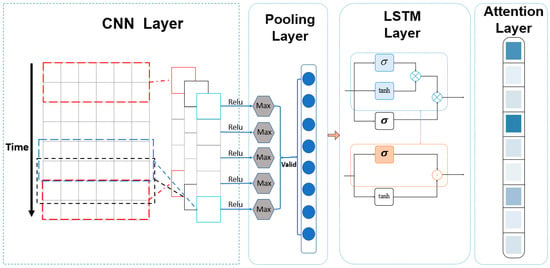
Figure 3.
CNN-LSTM-attention network for human activity recognition.
The output from the convolutional layer is subsequently passed into the LSTM model. The LSTM, a type of recurrent neural network (RNN), has a time-memory effect, utilizing historical input data to predict the current output. This feature is ideal for the memory requirements in action recognition tasks, thereby enhancing model performance.
Convolutional Layer Operation:
where is the output feature map at layer , is the convolution kernel (filter), is the input from the previous layer, is the bias term, and is the kernel size.
LSTM Unit:
where : input at time step t, : hidden state at time step t, : cell state at time step t, : input gate, : forget gate, : output gate, : candidate cell state; , and : weights and bias terms; : sigmoid activation function, which in our paper is replaced by the ReLU function: , tanh: hyperbolic tangent function, : element-wise multiplication [32,33].
Attention Mechanism:
Where , , , and : learnable parameters in the attention mechanism, : attention weight at time step , : context vector (the weighted sum of hidden states), : the previous hidden state of the decoder [24].
Final Output:
where : output category distribution, : weight matrix for the fully connected layer, : bias term for the fully connected layer, and : softmax function, used to compute the probability distribution over the categories.
In the LSTM, an attention layer is interspersed, applying the attention strategy to determine which parts of the input data are crucial, allowing the model to focus on these key pieces of information [34]. In Wi-Fi CSI prediction, the attention model plays a crucial role by allowing our approach to focus on the most relevant parts of the input data. Given that CSI data are highly temporal and some time steps are more critical for activity recognition or signal prediction than others, the attention mechanism enables our model to dynamically prioritize the most important features. This approach improves our model’s ability to capture key signal patterns, enhancing the overall prediction accuracy and robustness.
In this paper, when processing multi-channel Wi-Fi CSI data, we apply the attention mechanism to compute attention weights for each time step, directing the model’s focus on important time windows or signal features instead of using the entire sequence. This allows our method to effectively handle data fluctuations and noise, while also improving the capture of critical spatial and temporal features. As demonstrated in our experiments, this significantly enhances the accuracy of human activity recognition (HAR) and signal strength prediction, particularly in challenging environments.
In future research, we will take a series of measures to optimize the model, enabling it to run efficiently on devices with limited computational resources. First, we plan to apply model compression techniques, such as weight pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation, to reduce computational complexity and lower power consumption. At the same time, by optimizing the structure of the convolutional neural network, such as reducing the number of convolutional layers or adjusting the kernel size, we aim to reduce the computational load.
Next, we will explore the use of hardware accelerators, such as GPUs, NPUs, or TPUs, on the device side (e.g., smartphones, edge devices) to perform inference tasks, significantly improving computational efficiency and reducing power consumption. Finally, we will investigate how to further optimize power consumption through the collaborative design of hardware and algorithms, ensuring that the device can efficiently use battery power during real-time operation.
Through these optimization measures, we expect to make the method run efficiently in resource-constrained real-time systems as well.
4. Experiments and Results
This section presents experimental validation of the model and methods proposed in this paper using real-world data. Section 4.1 provides a detailed description of the experimental setup, including equipment, environment, and content. In Section 4.2, the model is validated with the collected data, and basic feature analysis is performed, demonstrating improvements in robustness and stability after data fusion processing. Section 4.3 showcases the effects of wavelet transformation and the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on the data, further confirming the effectiveness of the data processing. Finally, Section 4.4 compares the performance parameters of different models during the training process, highlighting the superiority of the proposed model.
4.1. Experimental Setup
To ensure real-world applicability, a methodology was developed for collecting Wi-Fi CSI data under a range of action scenarios. Figure 4 illustrates the experimental equipment, setup, and the various human actions performed during the experiment.

Figure 4.
Instruments, experimental setup, and human activities in the experiment.
In this experiment, the Wi-Fi signal transmission device used is a TP-LINK 5400 router, which supports the Wi-Fi 6 protocol and provides stable signals on both the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz bands. The Wi-Fi CSI collection chip is the ESP32-WROOM series from Espressif, which gathers data from nearby routers’ Beacon frames and CSI information. The detailed device information is listed in the Table 1.

Table 1.
Devices used in the experiment.
To ensure data stability and integrity, a 2 × 2 array receiver was developed based on the ESP32 and placed between the test subject and the Wi-Fi router. A serial output program was written to decode the Wi-Fi CSI information from the ESP32. The 2 × 2 Wi-Fi receiver array compensates for data loss and errors, effectively reducing environmental noise interference that might affect a single device. The experiment took place in 105, in the East Building of the Library at Beihang University. The Wi-Fi router and the Wi-Fi CSI receiver arrays were placed in room 105. Room 105 is a typical everyday environment with a Wi-Fi router, desks, chairs, and standard furnishings. The test subject performed various actions in room 105, including walking, running, standing still, jumping, turning, clapping, bending, and leg lifting. Each action was sampled for approximately 90 s. The Wi-Fi CSI receiver array had a data rate of 20 Hz, effectively capturing the time intervals between different human actions.
4.2. Array Wi-Fi Data Feature Analysis
To address limitations in serial communication and noise interference, this paper introduces a Wi-Fi CSI receiver array, exploiting the complementary nature of the array data to mitigate noise and prevent signal loss. We perform a comprehensive analysis of four sets of data collected through direct Wi-Fi signal transmission, processing each set to extract its amplitude and phase information.
By fusing, interpolating, and averaging data from four receiver channels, the array receiver mitigates most interference, with minimal data gaps. As shown in Figure 5, compared to a single Wi-Fi CSI signal, the fused data provide richer information, clearer transitions, and improved feature distinguishability.
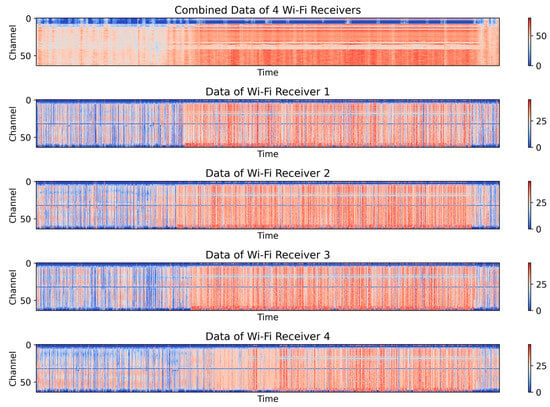
Figure 5.
Data processed and raw data of 4 Wi-Fi receivers.
4.3. Data Synchronization and Filtering
As observed in the previous section, fused data provide richer information and better capture behavioral characteristics. However, directly inputting raw data into a neural network may not be efficient, as it could lead to prolonged feature search processes and extended training times. Therefore, we introduce a feature extraction step to address this issue.
First, we applied PCA and the wavelet transform to preprocess the raw data. PCA was used to reduce the dimensionality of the data, helping to eliminate redundancies and noise, while the wavelet transform was employed to decompose the signal into multiple frequency components. By combining these methods, we were able to capture both low-frequency and high-frequency features, resulting in a clearer representation of the data, as illustrated in Figure 6.
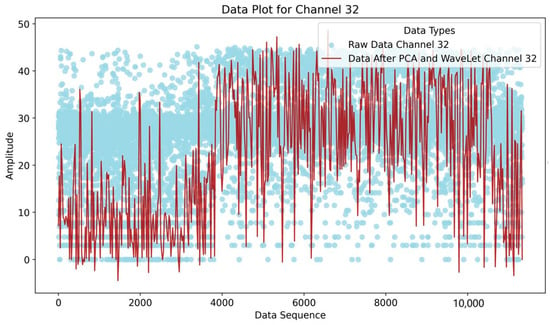
Figure 6.
Data after PCA and wavelet, showing channel 32.
Through these preprocessing steps, we achieved the effective cleaning of the Wi-Fi CSI data, removing unnecessary noise and improving the signal quality. This data cleaning process ensured that the model could focus on the most relevant information, enhancing the performance and accuracy of subsequent analysis, such as activity recognition or signal strength prediction.
The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), a fast algorithm for discrete Fourier transform (DFT), is employed to convert time-domain data into frequency-domain data. Since FFT is optimized in many chips and industrial products, we utilize it to extract frequency-domain characteristics. Actions often exhibit distinct features in the frequency domain, making it ideal for action recognition. We apply FFT to 1 s sampled data (20 time-domain points), with the processed result shown in Figure 7.
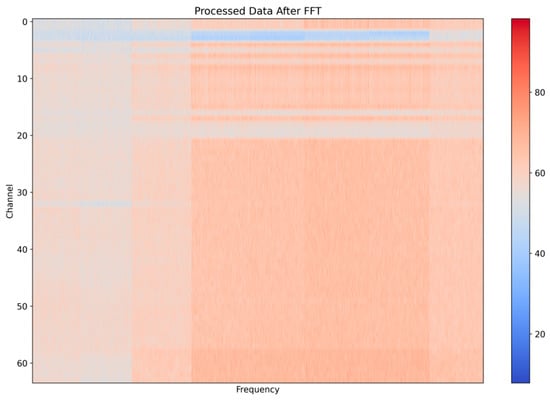
Figure 7.
Combined data processed by FFT.
By PCA and wavelet transformation, the tangled data that may be caused by the multipath effect can be figured out. Also, as seen, the initially chaotic time-domain data become more distinct in the frequency domain, with each action showing a clearer frequency characteristic. The features developed by the PCA, wavelet transform, and FFT can represent the main influencing factors of the activity, with different harmonic components reflecting the frequency characteristics of the action. These techniques help to capture key aspects of the signal that are essential for accurate action recognition.
4.4. Performance Analysis of Action Detection Experiments
After the preceding three sections, this study has completed the data cleaning and feature extraction processes. While evaluating the data, we choose recognition accuracy and latency as the performance metrics. The recognition accuracy directly reflects the system’s ability to correctly identify human activities, which is crucial for the reliability of the detection system. Latency, on the other hand, was chosen because it measures the responsiveness of the system, which is critical for real-time applications where quick reaction times are required. These two metrics are fundamental in evaluating the overall performance of the system, especially in scenarios that demand high accuracy and low latency for practical use, such as human activity detection.
In the experimental phase, we first compared the performance of a single Wi-Fi receiver with that of the 2 × 2 array receiver we designed. The following results from Table 2 validate the significant advantages of employing a Wi-Fi receiver array over a single receiver in human activity detection, demonstrating improved robustness and recognition accuracy.

Table 2.
Evaluation metrics.
The processed data perform better than the single receivers in both recognition accuracy and latency/response time. The processed data has a recognition accuracy of 98%, which is significantly higher than the 86% to 81% range of the single receivers, and the latency is only 12 ms, lower than the 17 ms to 21 ms of the single receivers. Therefore, the processed data offer better performance, making these data more suitable for applications that require high accuracy and low latency.
We evaluate the models using accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score, where TP (true positive) refers to correctly predicted positive samples, TN (true negative) refers to correctly predicted negative samples, FP (false positive) refers to samples incorrectly predicted as positive, and FN (false negative) refers to samples incorrectly predicted as negative.
Compared with the conventional models like CNN, LSTM, BP, SVM, and the recently introduced P-A Network [35], in the real-world scenario, the C-L-A model outperforms others in all metrics according to Figure 8 and Table 3. The C-L-A model outperforms all others across all metrics, making it ideal for tasks requiring high accuracy and low latency. The LSTM follows closely behind, performing excellently in most metrics, though slightly behind C-L-A in some areas like accuracy and specificity. BP (backpropagation) and SVM models perform poorly, especially in terms of accuracy and precision, making them less suitable for high-performance applications. CNN and P-A models also perform well, with P-A showing balanced performance across metrics and being suitable for applications requiring both high precision and high recall.
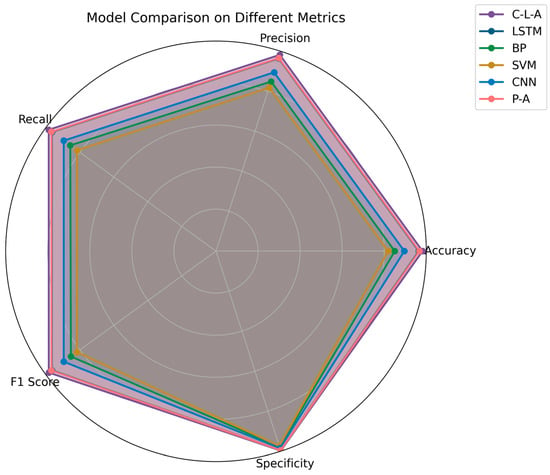
Figure 8.
Comparison of model metrics.

Table 3.
Detailed number for each model and metric.
When using data from four sensor types, the multi-source sensor fusion model consistently outperforms others across all metrics. The chest sensor model ranks second, followed by the foot sensor, with the wrist sensor model performing the weakest. These results confirm the superiority of the multi-source fusion approach for motion recognition using wearable sensors on the wrist, foot, and chest.
From the discussion of the Wi-Fi array and the analysis of the models above, it is evident that the Wi-Fi array provides reliable data support for model training. The CNN-LSTM-attention (C-L-A) model designed in this paper maintains good performance in LOS environments. When both datasets are labeled and trained simultaneously, as shown in Figure 9, the training results still achieve an average accuracy of approximately 98%.
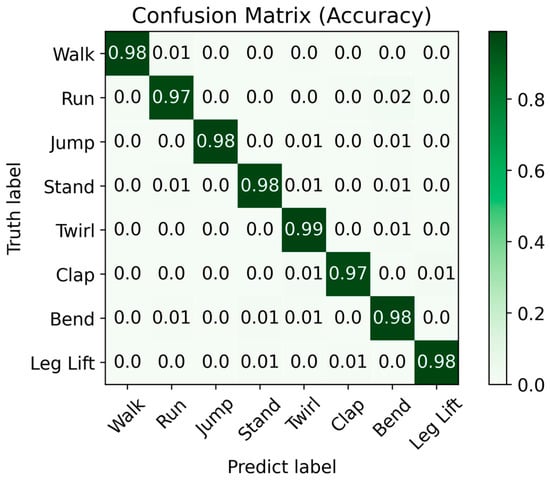
Figure 9.
The confusion matrix generated by the C-L-A model in accuracy.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Human activity recognition plays a crucial role in health monitoring and smart healthcare [36]. Wi-Fi CSI-based motion recognition has emerged as a promising solution, but common challenges in Wi-Fi CSI-based human activity recognition include signal fluctuations, difficulty in extracting meaningful features, and high computational complexity. This paper introduces key innovations to address these challenges.
We developed a 2 × 2 array Wi-Fi CSI acquisition system based on the ESP32 microcontroller, improving data stability compared to a single receiver. By using the FFT and wavelet transform for feature extraction, we reduced the model training time and complexity. Additionally, we proposed a hybrid CNN-LSTM-attention model that achieves nearly 98% accuracy even in complex environments.
This paper presents a complete Wi-Fi CSI-based motion recognition framework, covering data acquisition, feature extraction, and activity recognition. Future work will focus on recognizing more activities, integrating visual sensors or IMU data, and conducting recognition with a more lightweight model to enhance the model’s robustness and expand its applicability.
Author Contributions
Software, T.L.; Investigation, S.Q.; Writing—original draft, N.L.; Writing—review & editing, M.X.; Supervision, Q.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Project of State Grid Corporation of China (Research and Application of Key Technologies for Autonomous and Controllable Power Beidou High Reliable Space-Time Service, No. 5700-202441237A-1-1-ZN).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hossen, M.A.; Abas, P.E. Machine Learning for Human Activity Recognition: State-of-the-Art Techniques and Emerging Trends. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.E.; Kim, S.; Sul, J.H.; Kim, S.M. Data Reconstruction Methods in Multi-Feature Fusion CNN Model for Enhanced Human Activity Recognition. Sensors 2025, 25, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; He, D.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y. sEMG Signals Characterization and Identification of Hand Movements by Machine Learning Considering Sex Differences. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexan, A.R.; Alexan, A.I.; Oniga, S. Multi-User Activity Recognition Using Plot Images Based on Ambiental Sensors. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kim, D.; Toh, K.-A. Human Activity Recognition Through Augmented WiFi CSI Signals by Lightweight Attention-GRU. Sensors 2025, 25, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Deng, W. Human Similar Activity Recognition Using Millimeter-Wave Radar Based on CNN-BiLSTM and Class Activation Mapping. Eng 2025, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikas, C.M.; Rajendran, S.; Pattar, A.; Jamadagni, H.S.; Budihal, R. WiFi RSSI and inertial sensor based indoor localisation system: A simplified hybrid approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (IConSIP), Nanded, Maharashtra, 6–8 October 2016; 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, W. A Deep Learning Based Lightweight Human Activity Recognition System Using Reconstructed WiFi CSI. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2024, 54, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, D. Critical Analysis of Data Leakage in WiFi CSI-Based Human Action Recognition Using CNNs. Sensors 2024, 24, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahverdi, H.; Nabati, M.; Fard Moshiri, P.; Asvadi, R.; Ghorashi, S.A. Enhancing CSI-Based Human Activity Recognition by Edge Detection Techniques. Information 2023, 14, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Solimene, R. A Framework for Human Activity Recognition Based on WiFi CSI Signal Enhancement. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2021, 6654752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard Moshiri, P.; Shahbazian, R.; Nabati, M.; Ghorashi, S.A. A CSI-Based Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, J.A.; Yi Da Xu, R. Environment-Robust WiFi-Based Human Activity Recognition Using Enhanced CSI and Deep Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 24643–24654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiqul, I.M.; Jannat, M.K.A.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, S.-W.; Yang, S.-H. HHI-AttentionNet: An Enhanced Human-Human Interaction Recognition Method Based on a Lightweight Deep Learning Model with Attention Network from CSI. Sensors 2022, 22, 6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y.; Topuz, E.K. Human activity recognition from multiple sensors data using deep CNNs. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 10815–10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, H.E.; Mourad-Chehade, F.; Amoud, H. CSI-Based Human Activity Recognition via Lightweight CNN Model and Data Augmentation. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 25060–25069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobanputra, C.; Bavishi, J.; Doshi, N. Human Activity Recognition: A Survey. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 155, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Hua, C.; Zhao, X. Two-Path Spatial-Temporal Feature Fusion and View Embedding for Gait Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, J.K.; Xia, L. Human activity recognition from 3D data: A review. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 48, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lama, B.; Joo, S.; Kwon, J. Enhancing Human Key Point Identification: A Comparative Study of the High-Resolution VICON Dataset and COCO Dataset Using BPNET. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C.; Cao, Z.; Cui, W. WiFi CSI Based Passive Human Activity Recognition Using Attention Based BLSTM. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 18, 2714–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, S.; Dargie, W.; Poellabauer, C. Human Activity Recognition Based on Wireless Electrocardiogram and Inertial Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 6490–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia ur Rehman, M.; Gilani, S.O.; Waris, A.; Niazi, I.K.; Slabaugh, G.; Farina, D.; Kamavuako, E.N. Stacked Sparse Autoencoders for EMG-Based Classification of Hand Motions: A Comparative Multi Day Analyses between Surface and Intramuscular EMG. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.; Shah, S.A.; Dashtipour, K.; Le Kernec, J.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Assaleh, K.; Arshad, K.; Imran, M.A. Wireless Sensing for Human Activity Recognition Using USRP. In Proceedings of the 16th EAI International Conference on Body Area Networks (EAI BODYNETS 2021), Glasgow, UK, 25–26 October 2021; pp. 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Human Activity Recognition Across Scenes and Categories Based on CSI. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 21, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahou, A.; Al-qaness, M.A.A.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Helmi, A. Human activity recognition in IoHT applications using Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm and deep learning. Measurement 2022, 199, 111445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Ye, L.; Zhang, Y. A Human Activity Recognition Algorithm Based on Stacking Denoising Autoencoder and LightGBM. Sensors 2019, 19, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Huang, J.; Wang, H. LSTM-CNN Architecture for Human Activity Recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 56855–56866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.H.; Hsiao, A.H.; Chu, F.Y.; Feng, K.T. Time-Selective RNN for Device-Free Multiroom Human Presence Detection Using WiFi CSI. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekruksavanich, S.; Phaphan, W.; Hnoohom, N.; Jitpattanakul, A. Attention-Based Hybrid Deep Learning Network for Human Activity Recognition Using WiFi Channel State Information. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, K.; Sun, H. Indoor Localization System Based on WiFi RSSI using Wavelet-CNN Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2023 China Automation Congress (CAC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 November 2023; pp. 2305–2309. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Xie, W.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Human Action Recognition Based on Hierarchical Multi-Scale Adaptive Conv-Long Short-Term Memory Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhu, A.; Tu, Y.; Huang, H.; Arif, M.A.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cao, G. Effects of Different Feature Parameters of sEMG on Human Motion Pattern Recognition Using Multilayer Perceptrons and LSTM Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, R. A Combination of RNN and CNN for Attention-based Relation Classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 131, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Xian, H. P-A Scheme: A Robust and Lightweight Wi-Fi Device Identification Approach for Enhancing Industrial Security. Electronics 2025, 14, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madokoro, H.; Nix, S.; Woo, H.; Sato, K. A Mini-Survey and Feasibility Study of Deep-Learning-Based Human Activity Recognition from Slight Feature Signals Obtained Using Privacy-Aware Environmental Sensors. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).