Abstract
To address the limitations in the efficiency of modality feature fusion in existing RGB-T semantic segmentation methods, which restrict segmentation performance, this paper proposes an edge-supervised attention-aware algorithm to enhance segmentation capabilities. Firstly, we design a feature fusion module incorporating channel and spatial attention mechanisms to achieve effective complementation and enhancement of RGB-T features. Secondly, we introduce an edge-aware refinement module that processes low-level modality features using global and local attention mechanisms, obtaining fine-grained feature information through element-wise multiplication. Building on this, we design a parallel structure of dilated convolutions to extract multi-scale detail information. Additionally, an EdgeHead is introduced after the edge-aware refinement module, with edge supervision applied to further enhance edge detail capture. Finally, the optimized fused features are fed into a decoder to complete the RGB-T semantic segmentation task. Experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm achieves mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) scores of 58.52% and 85.38% on the MFNet and PST900 datasets, respectively, significantly improving the accuracy of RGB-T semantic segmentation.
1. Introduction
Semantic segmentation, as a core research topic in computer vision, aims to achieve the classification and understanding of each pixel within an image. This technology plays an irreplaceable role in various cutting-edge fields such as security monitoring [1], autonomous driving [2], and robot navigation [3]. Traditional semantic segmentation methods primarily rely on processing RGB images, distinguishing different objects by analyzing visual elements such as color features, geometric structures, and texture characteristics. However, these unimodal approaches often face challenges in real-world applications due to factors like changes in ambient lighting, occlusions, and complex scenes, making it difficult to ensure stable and reliable segmentation results. With the rapid advancement of multimodal sensing technologies, RGB-T semantic segmentation has emerged as a research hotspot [4,5,6]. By leveraging the complementary advantages of fusing RGB visible light images with thermal images, this approach significantly enhances segmentation system performance. Thermal imaging possesses the unique advantage of being independent of ambient lighting, allowing for accurate capture of an object’s thermal distribution even in low-light conditions or adverse weather such as fog, effectively compensating for the limitations of RGB images in these scenarios. Despite the promising potential of RGB-T semantic segmentation, numerous technical challenges remain. The primary challenge lies in the differences in modality characteristics; RGB images reflect the object’s appearance features, while thermal images record temperature information. This fundamental disparity leads to significant inconsistencies between the two modalities at the pixel level. Additionally, designing an efficient multimodal feature fusion mechanism is another critical challenge. Inappropriate information interaction strategies may reduce segmentation accuracy, necessitating the development of advanced algorithmic frameworks to achieve the seamless integration of the two modalities, thereby maximizing their respective strengths.
The current research on RGB-T image semantic segmentation primarily focuses on two core directions: multimodal feature enhancement and multimodal feature fusion. In the realm of feature enhancement, Deng et al. [7] introduced a methodology leveraging channel and spatial attention mechanisms. The channel attention mechanism targets the foreground object regions, while the spatial attention mechanism concentrates on global small targets, thereby extracting more discriminative feature information. Li et al. [8] concentrated on multiscale feature processing, proposing an edge-sharpening module to enhance low-level texture features, an auxiliary activation module to optimize mid-level features, and a collaborative localization module to process high-level semantic features, achieving a multilevel optimization of feature representation. Wu et al. [9] employed a gating mechanism to filter and integrate intra-modal effective information, using symmetric gating to acquire complementary information within the modality, and effectively reduced modality differences through weighted aggregation. Zhang et al. [10] innovatively proposed generating cross-modal pseudo-images using multilayer unimodal features, reducing modality differences by enforcing similarity constraints between real and pseudo-image features. However, in practical scenarios where the proportion of foreground region pixels is small, this global processing approach may struggle to adequately reduce modality differences in the foreground regions.
In the domain of multimodal feature fusion, Sun et al. [11] utilized a fusion strategy based on ResNet feature extraction and simple element-wise summation. However, this straightforward fusion method may not fully exploit the complementary information between modalities. To address this issue, Frigo et al. [12] proposed a confidence-based adaptive weighted fusion method that dynamically adjusts the contribution weights based on the reliability of different modal features, and introduced a matching layer mechanism to improve the consistency of feature fusion. Zhou et al. [13] captured shared semantic and spatial information by computing inter-channel and inter-pixel relationship matrices, effectively reducing the interference of modality-specific information and enhancing segmentation performance. Although these studies have made significant progress in the field of RGB-T semantic segmentation, challenges remain in feature enhancement and fusion in complex scenes. Particularly, in scenarios where the foreground regions occupy a small proportion, further exploration is needed to more precisely extract and fuse effective feature information.
Considering the differences in feature properties resulting from the imaging mechanisms of RGB and thermal images, this paper proposes an Edge-Aware Attention Fusion Network (EAAFNet). The feature fusion module of EAAFNet employs global max pooling and average pooling strategies to integrate features with different statistical properties, mitigating the adverse effects of noise. Additionally, the dual attention mechanism in both channel and spatial domains effectively leverages complementary feature information between RGB and thermal images, allowing unique feature information from one modality to supplement the other. In retaining more low-level features, an edge-aware refinement module is designed, enabling the network to learn the edge correspondence between different modalities, thereby aiding the model in better aligning and fusing the features of the two modalities.
The primary contributions of this study are as follows:
- We propose an edge-supervised attention-aware fusion network that effectively leverages complementary information across modalities, mitigates the adverse effects of interfering noise, and achieves superior performance through the efficient integration of multimodal feature information.
- We introduce a feature fusion module that employs Channel Attention and Spatial Attention mechanisms, enabling it to capture richer complementary feature information across both channel and spatial dimensions, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the fusion process.
- We design an edge-aware refinement module that learns the edge correspondence between different modalities, enhancing the accuracy and clarity of segmentation boundaries.
2. Proposed Method
This paper employs the classical encoder–decoder network framework to perform segmentation tasks. The proposed RGB-T semantic segmentation algorithm is depicted in Figure 1. First, the RGB and thermal modalities are separately input into two parallel ResNet-152 encoder branches, each consisting of five feature extraction stages. To accommodate the encoder’s input requirements, the single-channel thermal modality is replicated and expanded to three channels before input. In the first feature extraction stage, an Edge-Aware Refinement Module (ERM), is designed to preserve fine structural details of the target objects, enhancing the accuracy and clarity of segmentation boundaries. Subsequently, the Feature Fusion Module (FFM) utilizes channel and spatial attention mechanisms to complement the features between the RGB and thermal modalities, forming an adaptive fused feature representation. Finally, the decoder processes the fused multi-scale features to produce the desired segmentation result.
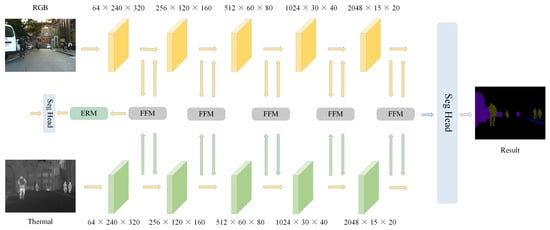
Figure 1.
Architecture of proposd EAAFNet.
2.1. Feature Fusion Module
In multimodal semantic segmentation, different modalities exhibit distinct feature representations, each contributing unique advantages. For instance, the RGB modality provides rich color information, crucial for discerning object details and textures. However, RGB cameras are susceptible to performance degradation in low-light or low-contrast environments and are vulnerable to noise. Conversely, the thermal modality, unaffected by lighting conditions, captures thermal radiation emitted by objects, proving invaluable in scenarios with limited visibility, such as nighttime. Therefore, integrating the strengths of both modalities effectively mitigates their individual limitations, achieving robust performance under complex environmental conditions.
This paper introduces a novel feature fusion module, illustrated in Figure 2, designed to embed salient features from one modality into its complementary counterpart while simultaneously reducing the impact of modality-specific noise. This module leverages both Channel Attention (CA) and Spatial Attention (SA) mechanisms, enabling the capture of richer feature information across both channel and spatial dimensions. This facilitates a deeper understanding of the unique attributes and complementary nature of RGB and thermal images. By independently analyzing the features of each modality and subsequently employing a cross-multiplication approach, the module not only effectively suppresses background noise but also significantly enhances the model’s adaptability to diverse environmental conditions by integrating the strengths of both modalities.
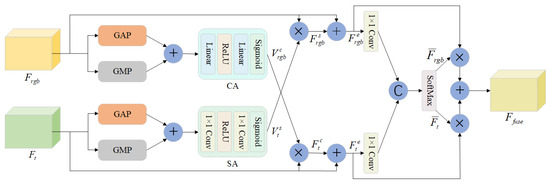
Figure 2.
Illustration of our FFM module.
To comprehensively extract and leverage features and from the two modalities, both are initially subjected to Global Average Pooling (GAP) and Global Max Pooling (GMP) along the spatial axis. These pooling operations effectively capture global statistical information of the background while preserving crucial local details, thereby mitigating the influence of interfering noise. GAP focuses on extracting holistic background features, whereas GMP emphasizes the most salient foreground features. The outputs of these two pooling strategies are summed to integrate features with distinct statistical properties. This integration enhances the model’s sensitivity to key signals and effectively reduces noise interference.
To precisely modulate inter-modal features, the combined RGB modality features are fed into a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP). This MLP includes a linear transformation followed by a non-linear ReLU activation function, further refining the feature representation. Subsequently, a Sigmoid function is applied to generate the channel attention weight vector, , for the RGB modality. Concurrently, the combined thermal (T) modality features are concatenated along the spatial axis. This concatenated output is then processed through a structure comprising two convolutional layers and a ReLU activation function for further feature refinement. Finally, a Sigmoid function is applied to generate the spatial attention weight vector, . The method employs the cross-multiplication of two attention weight vectors to generate complementary feature information and . This approach enhances the contrast between the foreground and background within each modality, effectively leveraging the complementary information from both modalities. The formula is as follows:
where ⊛ denotes channel multiplication, and represents the Sigmoid function.
Upon identifying the complementary characteristics of channel and spatial attention, we add the enhanced features to the original features element-wise, specifically denoted as and . The relationship can be expressed as follows:
This integration results in a more enriched and detailed feature representation. Subsequently, these enhanced modal features are fed into the feature fusion module. The ultimate goal of this process is to achieve optimal feature fusion, thereby enhancing the segmentation performance. To achieve the final modality fusion, the two modalities are merged using a convolution and then separated after applying the SoftMax activation function to obtain an adaptive fused feature representation. This approach integrates the feature maps from the two branches into a single feature map, enhancing the model’s ability to capture detailed information and improving the accuracy and efficiency of semantic segmentation. This phenomenon can be mathematically represented as:
2.2. Edge-Aware Refinement Module
Due to the often ambiguous or unclear boundaries of targets in RGB-T images, the edge-aware refinement module plays a crucial role in enhancing the model’s ability to accurately identify and localize target boundaries, thereby improving the precision of segmentation results. The first layer of stage features retains a significant amount of detailed information, enabling the edge-aware refinement module to learn the correspondence of edges between different modalities. This facilitates better alignment and fusion of features from the two modalities. The fused features are then input into the edge-aware refinement module, as illustrated in Figure 3. To achieve fine-grained feature representation, this module is designed with two branches. The first branch incorporates a global attention mechanism that employs global average pooling and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to preserve global channel context information. The second branch utilizes a local attention mechanism that leverages max pooling (MP) and an MLP to capture critical detail information. Through this method, we obtain two feature vectors R and T, which can be expressed as:
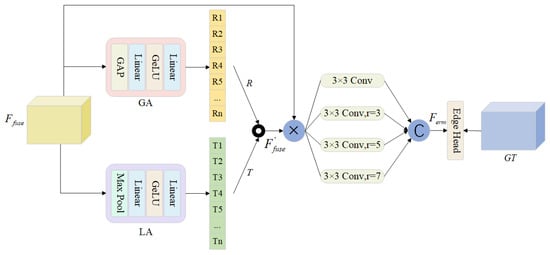
Figure 3.
Illustration of our ERM module.
To generate a weight vector rich in multimodal information, we perform element-wise multiplication of the two processed feature vectors. Subsequently, we apply channel-wise multiplication to further refine these multimodal feature representations:
Subsequently, we design a parallel structure of dilated convolutions to extract multi-scale detail information. Finally, we concatenate and aggregate these multi-scale features to generate the output features. Following the edge-aware refinement module, we attach an EdgeHead and apply edge supervision to obtain more accurate edge information. The aforementioned process can be succinctly summarized as follows:
2.3. Loss Function
Our network incorporates two types of supervision: edge supervision and final semantic segmentation supervision . Specifically, for edge supervision, we employ Dice Loss. For the final semantic segmentation results, we utilize both Dice Loss and Soft Cross Entropy, with the coefficient weights set to 0.5. Let denote final semantic segmentation results, denote edge-aware refinement module results, and the overall loss function can be expressed as follows:
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm in this study, we conducted an in-depth analysis using the MFNet and PST900 datasets. We implemented the proposed EAAFNet using the PyTorch 1.9.0, CUDA 11.1, and Python 3.8.17 libraries. Our model was trained on two A100 GPUs, each with 40GB of memory, utilizing the SGD optimizer. The initial learning rate was set to 0.02, with momentum decay and weight decay parameters set to 0.9 and 0.0005, respectively. We trained the model for 300 epochs with a batch size of 5. In order to enhance the generalization ability of the model, we also apply a variety of data augmentation techniques, including random image resizing and random horizontal flipping, to further improve the robustness and performance of the model.
3.1. Datasets and Experimental Metrics
The MFNet dataset, as the first publicly available large-scale RGB-Thermal (RGB-T) image semantic segmentation dataset, holds significant research value and practical implications in the field of urban scene understanding. This dataset comprises a total of 1569 precisely aligned RGB-T image pairs, each with a resolution of 640 × 480 pixels, including 820 daytime scenes and 749 nighttime scenes. Notably, the MFNet dataset provides detailed annotations for nine common target categories in urban street scenes, such as background, traffic cones, pedestrians, and car blockers. These comprehensive annotations offer crucial support for model training and evaluation in the autonomous driving domain. Currently, MFNet has become one of the most representative benchmark datasets in the field of RGB-T image semantic segmentation research. To maintain consistency in our study, we adopted the same data partitioning strategy as MFNet [14].
The PST900 dataset contains 894 precisely aligned RGB-T image pairs, providing pixel-level annotations for five target categories, including background, hand drills, backpacks, fire extinguishers, and survivors. It serves as a vital data resource for image analysis and understanding in challenging environments. In this study, we followed the original partitioning method of PST900 [15], dividing the dataset into training and testing sets.
It is important to note that current multimodal image semantic segmentation datasets commonly suffer from class imbalance issues, which may lead to the Class Average Accuracy metric inadequately reflecting the true performance of models. Therefore, the mIoU has emerged as a more representative evaluation metric and has become a key objective standard for assessing semantic segmentation model performance. In this research, we primarily employ the mIoU metric for model performance evaluation and optimization to ensure the reliability and scientific validity of our findings.
3.2. Comparison of MFNet Dataset
This paper conducts a comparative analysis of the EAAFNet method against several state-of-the-art approaches on the MFNet dataset, including PSTNet [15], RTFNet [11], FuseSeg [16], MFFENet [17], GMNet [18], DHFNet [19], MFTNet [20], DooDLeNet [12], EGFNet [21], DBCNet [22], FDCNet [23], MMDRNet [24], SGFNet [25], CCFFNet [9]. The comparative results of these methods are detailed in Table 1. The findings demonstrate that the proposed FFM, in conjunction with ERM, significantly enhances the fusion efficacy of RGB-T modalities, with EAAFNet achieving a leading mIoU of 58.5%. Furthermore, the paper contrasts the performance of these methods under both daytime and nighttime conditions, with quantitative results indicating the superiority of the proposed method across various scenarios. To further elucidate the advantages of our approach, Figure 4 presents visual comparisons under different lighting conditions. According to the visualization results, our method can effectively capture the boundary segmentation of small targets even in the presence of occlusion. For instance, in the first column of Figure 4, where a person is interacting with a vehicle and is partially obscured by other objects, our method still successfully segments the category of ’person,’ thereby validating the effectiveness of our approach. However, in the long-range images presented in the third and fourth columns, there may be instances of minor missegmentation. Therefore, it is necessary to enhance the reliability of segmentation predictions in distant scenes and reduce uncertainty.

Table 1.
Comparison with SOTA methods on the testing sets of MFNet dataset.
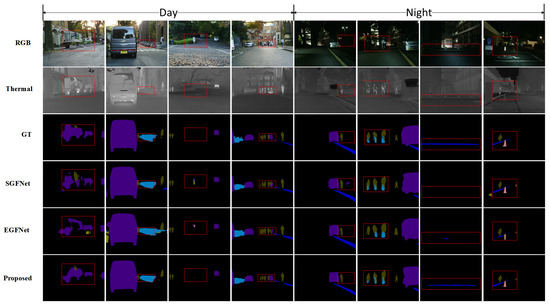
Figure 4.
Visual comparisons of our method and other SOTA methods on the MFNet dataset.
3.3. Comparison of PST900 Datasets
In this study, we conducted a comprehensive comparison of the EAAFNet method against several state-of-the-art techniques on the PST900 dataset, including RTFNet [11], CCNet [26], PSTNet [15], ABMDRNet [10], FDCNet [23], ACNet [27], DHFNet [19], DBCNet [22], MMDRNet [24], SGFNet [25], CCFFNet [9], GCNet [28], GCGLNet [29] and GMNet [18]. The comparative results of these methods are meticulously detailed in Table 2. The findings reveal that EAAFNet achieved the highest mIoU of 85.38%, which robustly demonstrates the superior performance and practical efficacy of our proposed method.

Table 2.
Comparison with SOTA methods on the testing sets of PST900 dataset.
3.4. Comparison of NYUDv2 Datasets
To evaluate the generalization ability of EAAFNet, we use the NYUD V2 dataset for training and testing. We use RGB and depth images as input, and the comparison results are shown in Table 3. Benefiting from EAAFNet’s proposed FFM and REM modules, we obtained 53.8% mIoU on the NYUDv2 test set, confirming its competitiveness and showing generalization to RGB-D data.

Table 3.
Comparison with other methods on the testing sets of NYUDv2 dataset.
3.5. Computational Complexity Analysis
To evaluate the computational performance and efficiency of the proposed model, we further conducted experiments. As shown in Table 4, the results show that the model proposed in this paper demonstrates good efficiency in terms of FLOPs, significantly outperforming CCFFNet [9] and slightly surpassing GEBNet [34]. Our model has a parameter size of 147.35 M, suggesting that alongside its high performance, it requires certain storage and memory resources.

Table 4.
Results of computational complexity analysis.
3.6. Ablation Experiment
This study conducts ablation experiments to evaluate the performance of key modules in the proposed EAAFNet. Under consistent experimental conditions, we obtained the results as shown in Table 5. When only the RGB modality was used for semantic segmentation, the model achieved an mIoU of 53.43%. Upon incorporating the FFM module, the mIoU of the algorithm increased to 57.82%. When only the ERM module was retained, the mIoU of the algorithm rose to 55.37%. The simultaneous utilization of both the FFM and ERM modules significantly enhanced the discriminability of the fused features, leading to a notable improvement in semantic segmentation performance, with the mIoU increasing by 5.09%.

Table 5.
Results of ablation experiment on the MFNet dataset.
4. Conclusions
This study proposes an innovative algorithm to address the limitations of existing RGB-T semantic segmentation methods in feature fusion efficiency. The proposed algorithm enhances inter-modal feature complementarity through a dedicated feature fusion module, which effectively captures and amplifies critical information from each modality by leveraging channel attention and spatial attention mechanisms, thereby significantly reducing noise interference. Furthermore, an edge-aware refinement module is incorporated to enhance the accuracy and clarity of segmentation boundaries by learning edge correspondence relationships across different modalities. Extensive experimental evaluations on MFNet and PST900 datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our algorithm, with the mIoU metric significantly outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods. These results substantiate the effectiveness of our feature complementarity enhancement and cross-modal fusion strategy in improving the accuracy of RGB-T semantic segmentation tasks. This research represents a significant advancement in the field of RGB-T semantic segmentation, offering substantial value for performance enhancement in applications such as autonomous driving and robotic navigation. Future work will focus on exploring optimization strategies for diverse scenarios to improve the algorithm’s generalizability and robustness, thereby contributing to the continuous development of this field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.W. and Z.Z.; methodology, M.W. and R.T.; validation, M.W. and Y.W.; resources, Z.Z.; data curation, M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W.; writing—review and editing, M.W., Z.Z., R.T., J.W. and X.Y.; visualization, M.W.; supervision, Z.Z., Y.W. and R.T.; project administration, Z.Z.; funding acquisition, Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the Ningbo Municipal Major Project of Science and Technology Innovation 2025 (2022Z076); the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LZ24F010004); the Yongjiang Sci-Tech Innovation 2035 (2024Z023, 2024Z122, 2024Z125, 2024Z295); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61671412).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions of this study are presented within the article. Further inquiries can be directed to acwarming@stu.ouc.edu.cn (accessed on 11 June 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jiuxing Weng was employed by the company Ningbo Sunny Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. Author Xianchao Yu was employed by the company Ningbo Anglin Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Deng, L.; Yang, M.; Hu, B.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Wang, C. Semantic segmentation-based lane-level localization using around view monitoring system. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10077–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Haase-Schütz, C.; Rosenbaum, L.; Hertlein, H.; Glaeser, C.; Timm, F.; Wiesbeck, W.; Dietmayer, K. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S.K.; Lee, Y.; Jawed, M.K. Agronav: Autonomous Navigation Framework for Agricultural Robots and Vehicles using Semantic Segmentation and Semantic Line Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6271–6280. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Wan, B.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Cae-net: Cross-modal attention enhancement network for rgb-t salient object detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, X. Real-Time RGBT Target Tracking Based on Attention Mechanism. Electronics 2024, 13, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Lu, J.; Sun, X. DuSiamIE: A Lightweight Multidimensional Infrared-Enhanced RGBT Tracking Algorithm for Edge Device Deployment. Electronics 2024, 13, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Feng, H.; Liang, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Guo, X.; Lam, T.L. FEANet: Feature-enhanced attention network for RGB-thermal real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 4467–4473. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, D. RGB-T semantic segmentation with location, activation, and sharpening. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chu, T.; Liu, Q. Complementarity-aware cross-modal feature fusion network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 131, 108881. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, N.; Han, J. ABMDRNet: Adaptive-weighted bi-directional modality difference reduction network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2633–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Liu, M. RTFNet: RGB-thermal fusion network for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigo, O.; Martin-Gaffe, L.; Wacongne, C. DooDLeNet: Double DeepLab enhanced feature fusion for thermal-color semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3021–3029. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H.; He, Z. Channel and Spatial Relation-Propagation Network for RGB-Thermal Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12534. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar, S.S.; Rodrigues, N.; Zhou, A.; Miller, I.D.; Kumar, V.; Taylor, C.J. Pst900: Rgb-thermal calibration, dataset and segmentation network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 9441–9447. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Yun, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, M. FuseSeg: Semantic segmentation of urban scenes based on RGB and thermal data fusion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Lin, X.; Lei, J.; Yu, L.; Hwang, J.N. MFFENet: Multiscale feature fusion and enhancement network for RGB–Thermal urban road scene parsing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 2526–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Lei, J.; Yu, L.; Hwang, J.N. GMNet: Graded-feature multilabel-learning network for RGB-thermal urban scene semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7790–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Luo, T. DHFNet: Dual-decoding hierarchical fusion network for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation. Vis. Comput. 2023, 40, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huo, Q.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z. Multispectral fusion transformer network for RGB-thermal urban scene semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhou, W.; Xu, C.; Yan, W. EGFNet: Edge-aware guidance fusion network for RGB–thermal urban scene parsing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gong, T.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. DBCNet: Dynamic bilateral cross-fusion network for RGB-T urban scene understanding in intelligent vehicles. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 7631–7641. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q. A Feature Divide-and-Conquer Network for RGB-T Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 33, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Long, X.; Shan, C. Mask-guided modality difference reduction network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 2023, 523, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Z. SGFNet: Semantic-Guided Fusion Network for RGB-Thermal Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 7737–7748. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Yang, K.; Fei, L.; Wang, K. Acnet: Attention based network to exploit complementary features for rgbd semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1440–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; Cui, Y.; Yu, L.; Luo, T. GCNet: Grid-like context-aware network for RGB-thermal semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, T.; Zhou, W.; Qian, X.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. Global contextually guided lightweight network for RGB-thermal urban scene understanding. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105510. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, Y.; Lei, J.; Yu, L. Embedded control gate fusion and attention residual learning for RGB–thermal urban scene parsing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 4794–4803. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Context-aware interaction network for rgb-t semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 6348–6360. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Bai, L.; Sun, Y.; Tian, C.; Mao, M.; Wang, G. Pixel difference convolutional network for RGB-D semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Zhou, W.; Qian, X.; Yu, L. GEBNet: Graph-enhancement branch network for RGB-T scene parsing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).